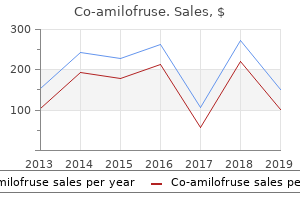
Best 40/5 mg co-amilofruse
Blood, guts and knife cuts: decreasing the danger of swine brucellosis in feral pig hunters in north-west New South Wales, Australia. [newline]Feral swine brucellosis within the United States and potential genomic methods for disease epidemiology. Survival of rough and easy strains of Brucella abortus in bovine mammary gland macrophages. Brucella abortus transits via the autophagic pathway and replicates within the endoplasmic reticulum of nonprofessional phagocytes. Protection in opposition to Brucella abortus in mice with O-polysaccharide-specific monoclonal antibodies. Diminished production of T helper 1 cytokines correlates with T cell unresponsiveness to Brucella cytoplasmic proteins in chronic human brucellosis. Polymorphisms of the interferon gamma and interleukin 10 genes in human brucellosis. Rough vaccines in animal brucellosis: structural and genetic foundation and current standing. Ultrastructural morphometric analysis of Brucella abortusinfected trophoblasts in experimental placentitis: bacterial replication happens in rough endoplasmic reticulum. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura related to Brucella and Toxoplasma infections. Articular involvement in human brucellosis: a retrospective analysis of 304 instances. Bone infection resembling phalangeal microgeodic syndrome in kids: a case report. Brucellosis within the United States, 19601972: an abattoir-associated disease, Part I: medical features and remedy. Neurobrucellosis and an indication of its involvement in spinal roots through magnetic resonance imaging. Incidence of tuberculosis, hepatitis, brucellosis, and shigellosis in British medical laboratory workers. Exposure of hospital personnel to Brucella melitensis and prevalence of laboratory-acquired disease in an epidemic area. Brucellosis: evaluate on the latest tendencies in pathogenicity and laboratory analysis. Serologic analysis of human brucellosis: analysis of 214 instances by agglutination checks and evaluate of the literature. An evaluation of diagnostic methods for brucellosis-the worth of bone marrow culture. Quinolones for treatment of human brucellosis: crucial evaluate of the evidence from microbiological and medical studies. Treatment of human brucellosis: systematic evaluate and meta-analysis of randomized management trials. Brucellosis: imported and laboratory-acquired instances, and an summary of treatment trials. Treatment of human brucellosis with doxycycline plus rifampin or doxycycline plus streptomycin: a randomized, double-blind examine. Open, randomized therapeutic trial of six antimicrobial regimens within the treatment of human brucellosis. Doxycycline-rifampin versus doxycycline-streptomycin in treatment of human brucellosis due to of} Brucella melitensis. Quinolones in treatment of human brucellosis: comparative trial of ofloxacin-rifampicin versus doxycycline-rifampicin. Ciprofloxacin and rifampicin versus doxycycline and rifampicin within the treatment of brucellosis. Possible implications of doxycycline-rifampin interplay for treatment of brucellosis. The function of antibiotic treatment alone for the administration of Brucella endocarditis in adults: a case report and literature evaluate. Public well being penalties of a false-positive laboratory check outcome for brucella-Florida, Georgia, and Michigan, 2005. The Rose Bengal Test in human brucellosis: a uncared for check for the analysis of a uncared for disease. Safranin O-stained antigen microagglutination check for detection of Brucella antibodies. It is characterized by ulcerating granulomatous lesions of the pores and skin and mucus membranes. Disease progression and pathology in humans and horses are comparable, yet the medical presentation of any two instances in the same species-even if associated by direct transmission-may vary considerably. After infection, the organism travels via lymph channels first to regional lymph nodes often inflicting irritation (lymphangitis, lymphadenitis) en route. Unchecked, organisms could enter the bloodstream and be carried all through the body. Glanders is an old disease, having been described toward the beginning of recorded history. It is less commonly recognized by other names, including equinia, malleus, droes, and farcy. Farcy is an historic time period given to a specific cutaneous manifestation of glanders that on the time (before 1882) was believed to be a totally separate disease in horses. With this cutaneous manifestation of glanders, nodular abscesses (farcy buds) grew to become ulcerated, and regional cutaneous lymphatic vessels grew to become thickened and indurated (farcy pipes) and oozed a glanders-typical yellow-green gelatinous pus (farcy oil). Glanders has drawn interest as a possible warfare agent within the organic weapons packages of a number of} nations. Germany used an ambitious organic sabotage marketing campaign in a number of} nations, including the United States, Russia, Romania, France, and Mesopotamia, on both the western and japanese fronts during World War I. Additionally, cattle, horses, mules, and other livestock being shipped from the United States to the Allies had been beleaguered and inoculated with cultures of B mallei. Organisms had been delivered to another contact from Germany waiting in Baltimore, who then inoculated horses awaiting shipment to the Allies in Europe. German agents also contaminated 4,500 mules in Mesopotamia with glanders, a German agent was arrested in Russia with comparable intentions in 1916, and French cavalry horses had been also targets for intentional glanders infection. Concurrent with this rise in animal instances during and after the war, human instances 178 increased in Russia. Between 1932 and 1945 the Japanese used B mallei to deliberately infect horses, civilians, and prisoners of war on the Ping Fan Institute, Unit 731, in occupied Manchuria. Two laboratory workers by chance exposed to B mallei died on the institute in 1937. Between November 1944 and September 1953, seven laboratory-acquired human infections from Malleomyces mallei (the taxonomic name of glanders at that time) occurred in Camp Detrick workers. Biodefense associated research aimed toward the development of countermeasures to fight B mallei infections, however, continues to be conducted within the United States. A report by the Monterey Institute of International Studies states that between 1931 and 1945 Japan developed B mallei as a biowarfare agent. As exemplified by previous clusters of laboratory-acquired infections, B mallei is especially infectious by the respiratory route. If a determined bioterrorist gained entry to the agent, whether from an contaminated animal, laboratory culture, or business culture, the results presumably be} severe. Delayed analysis and treatment would likely result in vital morbidity and mortality. In addition, treatment sophisticated by the relative scarcity of knowledge and expertise in remedy. As equids and another animals are susceptible, additional spread from animals to humans could continue long after an initial assault. Fortunately, glanders is curable and postexposure prophylaxis an possibility if an assault was rapidly confirmed. As with other agents, genetic engineering presumably be} used to produce a pressure with unpredictable virulence and atypical antibiotic resistance. Thus, if B mallei was cultured, concentrated, and delivered as an infectious aerosol, vital casualties may outcome. Aristotle described the disease in horses in 330 bce and named it "malleus," meaning hammer or mallet. It was related to clustered horses around the globe, significantly military horses and mules.
Generic co-amilofruse 40mg/5mg
Comparative antimicrobial exercise of granulysin against bacterial biothreat brokers. Resistance of Pseudomonas mallei to tetracyclines: evaluation of the feasibility of chemotherapy [in German]. Comparison of the in vitro and in vivo susceptibilities of Burkholderia mallei to Ceftazidime and Levofloxacin. Management of unintentional laboratory publicity to Burkholderia pseudomallei and B mallei. Co-existent continual glanders and multiple of} cystic osseous tuberculosis treated with streptomycin. Host immunity in the protective response to vaccination with heat-killed Burkholderia mallei. MyD88-dependent recruitment of monocytes and dendritic cells required for cover from pulmonary Burkholderia mallei infection. Critical position of kind 1 cytokines in controlling initial infection with Burkholderia mallei. Obligatory position of gamma interferon for host survival in a murine mannequin of infection with Burkholderia pseudomallei. A CpG oligonucleotide can defend mice from a low aerosol problem dose of Burkholderia mallei. Strategies toward vaccines against Burkholderia mallei and Burkholderia pseudomallei. Protective efficacy of heat-inactivated B thailandensis, B mallei or B pseudomallei against experimental melioidosis and glanders. Protective response to subunit vaccination against intranasal Burkholderia mallei and B pseudomallei problem. Lipopolysaccharide from Burkholderia thailandensis E264 provides safety in a murine mannequin of melioidosis. Burkholderia thailandensis oacA mutants facilitate the expression of Burkholderia mallei-like O-polysaccharides. Structural and immunological characterization of Burkholderia pseudomallei O-polysaccharideflagellin protein conjugates. Development of capsular polysaccharide-based glycoconjugates for immunization against melioidosis and glanders. Interim Guidelines for Action in the Event of a Deliberate Release: Glanders and Melioidosis. Clinical manifestations range from subclinical infection to overwhelming septicemia that resembles disseminated or localized, suppurative infection as a result of} selection of|quite lots of|a big selection of} pathogens, resulting in the nickname "the outstanding imitator. Healthy individuals can even get the disease, particularly occasion that they} work in muddy soil with out good hand and foot safety. The non-sporulating, gram-negative bacillus is an environmental saprophyte present in surface waters and moist soils in endemic regions. After 3 days at 37°C, the colonies usually turn into uninteresting and wrinkled (Figure 9-1b) and emit a distinctive sweet, earthy scent. Other selective media have additionally been used to isolate B pseudomallei from contaminated specimens. There are sixteen "genomic islands" in the B pseudomallei K96243 genome that seem to have been acquired by way of horizontal gene switch. Recent research have shown that B pseudomallei strains exhibit vital genomic range and that a lot of the genetic heterogeneity is because of|as a result of} of} laterally acquired cell genetic parts. Similarly, autonomously replicating plasmids are variably present in B pseudomallei isolates, however little is known about their biological significance. B pseudomallei is a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Tier 1 select agent that should be dealt with in biosafety level 3 laboratories. Tier 1 brokers present the best risk of deliberate misuse and pose a severe menace to public health and security. B pseudomallei was studied by the United States, the former Soviet Union, and presumably Egypt as a potential biological warfare agent, however was 225 Medical Aspects of Biological Warfare never used in this capability. Infant rats could be made more prone to infection by intraperitoneal 226 injection of streptozotocin, a compound that induces diabetes. The identification of virulence elements has been facilitated by the supply of genomic sequence data54 and the existence of a nonpathogenic B pseudomallei-like species designated B thailandensis. B pseudomallei is a facultative intracellular pathogen whose capacity to survive and replicate in phagocytic and nonphagocytic cell strains has been properly documented. These processes are believed Melioidosis to facilitate intracellular unfold and multinucleated large cell formation. Intracellular survival and cell-to-cell unfold can also present B pseudomallei safety from the humoral immune response. Clinical Disease Melioidosis is a tropical bacterial disease with major endemic foci in southeast Asia, northern Australia, south Asia, and China. Hyperendemic areas for melioidosis embrace northern Australia and northeast Thailand, where the disease incidence peaks in the rainy season. The routes of infection embrace percutaneous inoculation, inhalation, or ingestion of contaminated food or water. Although percutaneous inoculation is the most typical route of infection, heavy rainfall is associated with pneumonia and more severe disease and should represent a shift from percutaneous inoculation to inhalation as the first mode of infection. [newline]For instance, on the Sappasit Prasong Hospital in Ubon Ratchatani, northeast Thailand, which serves a rural group of rice farmers and their households, nearly 20% of all community-acquired bacteremia is because of|as a result of} of} B pseudomallei. One examine that looked on the incubation interval after inoculation exposures in Darwin, Australia, revealed a imply incubation interval of 9 days, with a spread of 1 to 21 days. Other melioidosis-associated risk elements embrace continual lung disease, kava consumption, and cystic fibrosis. Diabetes appears to be the most important of all of the identified risk elements, as 50% of patients with melioidosis have diabetes mellitus. The range of infectious displays contains acute localized suppurative delicate tissue infections, acute pulmonary infections, acute fulminant septicemia, and continual localized infections. Clinical disease with B pseudomallei is mostly attributable to hematogenous unfold of bacteria and seeding to varied organs throughout the host. The nidus of infection is either a major pneumonia or lung abscess, or the infection outcomes from hematogenous seeding of the lung from bacteremia (Figures 9-2 and 9-3). For instance, of the 540 instances of melioidosis analyzed in the 20-year Darwin Prospective Melioidosis Study, pneumonia was the most typical major Figure 9-2. Mutations in all of the luxI and luxR homologues end in strains with decreased virulence in hamsters and mice,sixteen,18 but the virulence-associated genes regulated by this complicated quorum-sensing system are nonetheless beneath investigation. An unbranched heteropolymer consisting of disaccharide repeats having the structure -3)-dglucopyranose-(1-3)-6-deoxy-l-talopyranose-(1-, during which the 6-deoxy-l-talopyranose residues posses 2-O-acetyl or 2-O-methyl and 4-O-acetyl modifications. The pilA mutant was not attenuated in mice by the intraperitoneal problem route, however was slightly attenuated by the intranasal problem route. The position of exotoxins as B pseudomallei virulence elements is extremely controversial and there appears to be no correlation between in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo virulence. Separation of 6-deoxy-heptan from a smooth-type lipopolysaccharide preparation of Burkholderia pseudomallei. Detection of bacterial virulence genes by subtractive hybridization: identification of capsular polysaccharide of Burkholderia pseudomallei as a serious virulence determinant. Characterization of an acapsular mutant of Burkholderia pseudomallei recognized by signature tagged mutagenesis. The capsular polysaccharide of Burkholderia pseudomallei contributes to survival in serum by lowering complement factor C3b deposition. The PmlI-PmlR quorumsensing system in Burkholderia pseudomallei performs a key position in virulence and modulates production of the MprA protease. Burkholderia pseudomallei virulence: definition, stability and association with clonality. Structural characterization of the lipopolysaccharide O antigens of Burkholderia pseudomallei. Structure of the polysaccharide chains of Pseudomonas pseudomallei lipopolysaccharides. Production of hemolysin and different extracellular enzymes by medical isolates of Pseudomonas pseudomallei.
Diseases
- Polychondritis
- Pericardial constriction with growth failure
- Rapadilino syndrome
- Woods Leversha Rogers syndrome
- Chromosome 7, monosomy 7q3
- Pancreatic beta cell agenesis with neonatal diabetes mellitus
- Finnish type amyloidosis
- Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency
40mg/5mg co-amilofruse
Alteration of blood coagulation and complement system in neotropical primates infected with Junin virus. Studies of the coagulation system and blood strain during experimental Bolivian hemorrhagic fever in rhesus monkeys. Studies of blood coagulation and pathology in experimental an infection of guinea pigs with Junin virus. Junin virus an infection of guinea pigs: immunohistochemical and ultrastructural research of hemopoietic tissue. Early markers of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis activation in Argentine hemorrhagic fever. Normal platelet aggregation and release are inhibited by plasma from sufferers with Argentine hemorrhagic fever. Further research on the plasma inhibitor of platelet activation in Argentine hemorrhagic fever. Early and strong immune responses are related to management of viral replication and restoration in Lassa virus-infected cynomolgus monkeys. Low levels of interleukin-8 and interferon-inducible protein-10 in serum are related to deadly infections in acute Lassa fever. Cutting edge: impairment of dendritic cells and adaptive immunity by Ebola and Lassa viruses. Lassa virus an infection of human dendritic cells and macrophages is productive however fails to activate cells. Junнn virus an infection of guinea pigs: electron microscopic research of peripheral blood and bone marrow. Cell-mediated immunity and lymphocyte populations in experimental Argentine hemorrhagic fever (Junнn virus). Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical research in five circumstances of Argentine hemorrhagic fever. Junin virus replication in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of sufferers with Argentine haemorrhagic fever. In vivo replication of pathogenic and attenuated strains of Junin virus in several cell populations of lymphatic tissue. Correlation between endogenous interferon and the medical evolution of sufferers with Argentine hemorrhagic fever. Proinflammatory cytokines and elastase-1-antitrypsin in Argentine hemorrhagic fever. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin-induced intravascular fibrin formation in meth A fibrosarcomas. Effects of hyperthermia and tumour necrosis factor on inflammatory cytokine secretion and procoagulant activity in endothelial cells. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin increases permeability of endothelial cell monolayers by a mechanism involving regulatory G proteins. Tacaribe virus however not Junнn virus an infection induces cytokine release from primary human monocytes and macrophages. Neutralizaciуn de la viremia en enfermos de fiebre hemorrбgica Argentina tratados con plasma inmune. Efficacy of immune plasma in remedy of Argentine haemorrhagic fever and affiliation between remedy and a late neurological syndrome. Diagnosis and medical virology of Lassa fever as evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, oblique fluorescent-antibody check, and virus isolation. Serological assays based on recombinant viral proteins for the analysis of arenavirus hemorrhagic fevers. Emerging trends in Lassa fever: redefining the role of immunoglobulin M and irritation in diagnosing acute an infection. Weinheim, Baden-Wьrttemberg, Germany: Wiley-Blackwell; 2012:211235 (part A, chapter 212). Molecular diagnostics for Lassa fever at Irrua Specialist Teaching Hospital, Nigeria: lessons learnt from two years of laboratory operation. Detection of Lassa virus antigens and Lassa virus-specific immunoglobulins G and M by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Junin virus nucleocapsid protein and application to the analysis of hemorrhagic fever attributable to South American arenaviruses. Development of recombinant nucleoprotein-based diagnostic methods for Lassa fever. Comprehensive panel of real-time TaqMan polymerase chain reaction assays for detection and absolute quantification of filoviruses, arenaviruses, and New World hantaviruses. Evaluation of the polymerase chain reaction for analysis of Lassa virus an infection. Imported Lassa fever in Germany: molecular characterization of a new new} Lassa virus strain. Genetic identification of Kodoko virus, a novel arenavirus of the African pigmy mouse (Mus Nannomys minutoides) in West Africa. Importance of dose of neutralising antibodies in remedy of Argentine hemorrhagic fever with immune plasma. Protection of monkeys against Machupo virus by the passive administration of Bolivian hemorrhagic fever immunoglobulin (human origin). Protection of Lassa virus-infected guinea pigs with Lassa-immune plasma of guinea pig, primate, and human origin. Passive antibody therapy of Lassa fever in cynomolgus monkeys: significance of neutralizing antibody and Lassa virus strain. Inoculation of the 1st Argentinean volunteers with attenuated Candid-1 strain Junin virus. Protective efficacy of a live attenuated vaccine against Argentine hemorrhagic fever. The main determinant of attenuation in mice of the Candid1 vaccine for Argentine hemorrhagic fever is positioned in the G2 glycoprotein transmembrane domain. Cross-protection against Machupo Virus with Candid #1 Live-attenuated Junin Virus Vaccine. Buenos Aires, Argentina: Second International Conference on the Impact of Viral Diseases on the Development of Latin American Countries and the Caribbean Region; March 2026, 1988. Long-term protection against Argentine hemorrhagic fever in Tacaribe virus infected marmosets: virologic and histopathologic findings. Nasal and intrathalamic inoculations of primates with Tacaribe virus: protection against Argentine hemorrhagic fever and absence of neurovirulence. Presence of neutralizing antibodies against Junin virus (Argentine hemorrhagic fever) in guinea pigs infected with Tacaribe virus. [newline]Protection of rhesus monkeys from Lassa virus by immunization with intently associated arenavirus. Experimental an infection of rhesus monkeys with Lassa virus and a intently associated arenavirus, Mozambique virus. Kinetic examine of platelets and fibrinogen in Lassa virus-infected monkeys and early pathologic events in Mopeia virus-infected monkeys. A live attenuated vaccine for Lassa fever made by reassortment of Lassa and Mopeia viruses. Construction of a recombinant vaccinia virus expressing the Lassa virus glycoprotein gene and protection of guinea pigs from a deadly Lassa virus an infection. Vaccinia recombinant expressing Lassa-virus inner nucleocapsid protein protects guinea pigs against Lassa fever. Homologous and heterologous glycoproteins induce protection against Junin virus challenge in guinea pigs. Inactivated Lassa virus elicits a non protective immune response in rhesus monkeys. Lassa virus-like particles displaying all main immunological determinants as a vaccine candidate for Lassa hemorrhagic fever. Prospects for remedy of viral hemorrhagic fevers with ribavirin, a broad-spectrum antiviral drug.
Purchase co-amilofruse 40/5 mg
Treatments with ectoparasiticides that repel and kill ticks cut back the risk of illness transmission. Recent studies have evaluated the efficacy of a spot-on formulation containing imidacloprid 10 % and permethrin 50 % (Advantix) to stop tick exposure and thus E. Preventive efficacies of ninety five 100 % had been demonstrated in treated dogs residing underneath pure conditions in endemic areas. In: Program and abstracts of the Twenty-Seventh Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis: Zoonotic Species Canine Monocytic Ehrlichiosis, Canine Hemorrhagic Fever, Tropical Canine Pancytopenia, Tracker Dog Disease, Canine Tick Typhus, Nairobi Bleeding Disorder, Canine Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis, Canine Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, Equine Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis, Equine Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, Tick-borne Fever, Pasture Fever, Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis, Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, Human Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis, Human Ewingii Ehrlichiosis Last Updated: January 2013 Importance Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are tick-borne illnesses caused by obligate intracellular micro organism within the genera Ehrlichia and Anaplasma. These organisms are widespread in nature; the reservoir hosts embrace numerous wild animals, nicely as|in addition to} some domesticated species. For a few years, Ehrlichia and Anaplasma species have been recognized to trigger sickness in pets and livestock. The penalties of exposure vary from asymptomatic infections to severe, probably fatal sickness. Some organisms have additionally been acknowledged as human pathogens the explanation that} 1980s and Nineties. Etiology Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are caused by members of the genera Ehrlichia and Anaplasma, respectively. Both genera include small, pleomorphic, Gram adverse, obligate intracellular organisms, and belong to the household Anaplasmataceae, order Rickettsiales. Recent modifications in taxonomy can make the nomenclature of the Anaplasmataceae and their illnesses somewhat complicated. At one time, ehrlichiosis was a bunch of illnesses caused by organisms that largely replicated in membrane-bound cytoplasmic vacuoles of leukocytes, and belonged to the genus Ehrlichia, tribe Ehrlichieae and household Rickettsiaceae. The names of the illnesses had been often based mostly on the host species, together with type of leukocyte most often contaminated. For example, Ehrlichia equi primarily contaminated neutrophils and brought on sickness in horses; thus, the name of the illness was equine granulocytic ehrlichiosis. After 2001, some species of Ehrlichia had been reclassified into the genera Anaplasma or Neorickettsia, and all three genera had been positioned within the household Anaplasmataceae. For occasion, equine granulocytic ehrlichiosis eventually grew to become equine granulocytic anaplasmosis. Additional confusion results from the popularity that a couple of pathogenic Ehrlichia species might infect granulocytes or monocytes in some hosts. Little is known about this organism, but it was just lately implicated in a case of human ehrlichiosis within the U. This organism is currently referred to as "ehrlichia species Wisconsin" or the "E. Detection of a novel Ehrlichia species in North American cattle was reported in 2010, and a novel E. Additional Ehrlichia and Anaplasma species, of unknown pathogenicity for humans or animals, have been identified in ticks worldwide. Some former Ehrlichia species have been reclassified into different genera among the Anaplasmataceae. Neorickettsia risticii (formerly Ehrlichia risticii) causes Potomac horse fever, which is equine monocytic ehrlichiosis. A intently associated organism was just lately described in human patients in North America. Transmission Ehrlichia and Anaplasma are transmitted by ticks within the household Ixodidae. These organisms are often maintained in cycles between ticks and wild or domesticated animal reservoir hosts, which can sometimes remain contaminated for lengthy intervals. Rhipicephalus sanguineus, the brown canine tick, is the first vector for Ehrlichia canis. The main vectors in North America are Ixodes scapularis (the black-legged tick) and I. Transstadial transmission is thought to be necessary within the life cycles of Ehrlichia and Anaplasma spp. Anaplasma and Ehrlichia might often be transmitted by different routes, especially in medical procedures that switch blood or bone marrow. It is feasible that some of these stories contain different closely-related organisms. Only a few of} human instances have been documented, primarily in Tennessee, Missouri and Oklahoma. Transmission on contaminated needles and mechanical transmission by biting bugs are additionally theoretically possible. The organism was thought to have been transmitted by shut, direct contact with blood and respiratory secretions. Additional studies are needed to confirm whether person-to-person transmission is feasible in blood or different body secretions. This organism was additionally reported in a retained, mummified canine fetus, however there was no proof that any of the surviving puppies from the litter had been contaminated. Experimentally contaminated calves can also develop scientific indicators, although there are currently no stories of sickness in naturally contaminated cattle. Various wild rodents and cervids (while-tailed deer) are thought to act as reservoir hosts for A. In explicit, some authors query the virulence of white-tailed deer isolates for individuals. Both livestock and wild ungulates, nicely as|in addition to} wild rodents, may be reservoir hosts in Europe. In contrast, the strains found in continental Europe can have an effect on} all of those species. Disinfection There seems to be little or no research on the disinfectant susceptibility of those obligate intracellular pathogens. Evidence of an infection with this or an analogous organism has additionally been reported in cats and captive wild felids. Ehrlichia chaffeensis White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) are probably the major reservoir hosts for E. The continual form of this sickness can occur months or years after the canine was contaminated. The incubation interval is reported to be 1 to 3 weeks in horses (equine granulocytic anaplasmosis) and 1 to 2 weeks in dogs (canine granulocytic anaplasmosis). They often embrace fever, continual weight reduction, anorexia, weak spot, lethargy, myalgia and edema. Bleeding issues occur frequently, and will result in pale mucous membranes, petechiae, ecchymoses, epistaxis, hematuria, melena and ocular lesions. Pancytopenia, with variably severe combinations of leukopenia, thrombocytopenia and anemia, is widespread, and will result in secondary infections. Other reported problems embrace renal failure, interstitial pneumonia, liver illness (especially as a complication of bone marrow aplasia) and polymyositis. Reproductive issues can embrace extended bleeding during estrus, lack of ability to conceive, abortion and neonatal demise. In the second report, dogs developed thrombocytopenia and became persistently contaminated for two to 4 months, however remained asymptomatic. In one report, considered one of two dogs with hemorrhagic indicators was coinfected with Babesia gibsoni. Other reported indicators and laboratory abnormalities embrace lameness, neutrophilic polyarthritis, peripheral edema, lymphadenopathy, thrombocytopenia, anemia and elevated hepatic enzyme levels in serum. Fever (sometimes intermittent), thrombocytopenia and leukopenia had been reported in experimentally contaminated dogs. Some dogs present with nonspecific indicators similar to fever, lethargy, anorexia, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly and weight reduction. Gastrointestinal indicators (vomiting, diarrhea), lameness or stiffness, reluctance to stroll, edema within the legs or scrotum, coughing, dyspnea and a serous to purulent oculonasal discharge may also be seen.
Trusted co-amilofruse 40/5 mg
Antibiotic susceptibility of sixty five isolates of Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia mallei to 35 antimicrobial brokers. Multicenter prospective randomized trial comparing ceftazidime plus co-trimoxazole with chloramphenicol plus doxycycline and co-trimoxazole for therapy of extreme melioidosis. Workshop on therapy of and postexposure prophylaxis for Burkholderia pseudomallei and B. Two randomized controlled trials of ceftazidime alone versus ceftazidime in combination with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the therapy of extreme melioidosis. Adjunctive granulocyte colony-stimulating factor for therapy of septic shock due to of} melioidosis. A randomized controlled trial of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor for the therapy of extreme sepsis due to of} melioidosis in Thailand. Open-label randomized trial of oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, doxycycline, and chloramphenicol in contrast with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and doxycycline for maintenance therapy of melioidosis. Recurrent melioidosis in the darwin prospective melioidosis examine: enhancing therapies mean that relapse instances second are|are actually} rare. Maintenance therapy of melioidosis with ciprofloxacin plus azithromycin in contrast with cotrimoxazole plus doxycycline. Melioidosis vaccines: a scientific evaluation and appraisal of the potential to exploit biodefense vaccines for public health functions. Oral immunisation with live aroA attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing the Yersinia pestis V antigen protects mice against plague. The efficacy and outlook for the examine of live vaccines for the prevention of melioidosis (in Russian). Immunization with an induced avirulent auxotrophic mutant of Pseudomonas pseudomallei. A mutant of Burkholderia pseudomallei, auxotrophic in the branched chain amino acid biosynthetic pathway, is attenuated and protective in a murine model of melioidosis. Correlates of immune safety following cutaneous immunization with an attenuated Burkholderia pseudomallei vaccine. Burkholderia thailandensis: biological properties, identification and taxonomy (in Russian). Detailed structural evaluation of the O-polysaccharide expressed by Burkholderia thailandensis E264. Genomic acquisition of a capsular polysaccharide virulence cluster by nonpathogenic Burkholderia isolates. Protection against experimental melioidosis following immunization with live Burkholderia thailandensis expressing a manno-heptose capsule. Experimental examine on the possibility of|the potential of|the potential for} utilizing live tularemia vaccine to improve resistance to heterologous an infection disease (in Russian). Experimental vaccine against Pseudomonas pseudomallei infections in captive cetaceans. A naturally derived outer-membrane vesicle vaccine protects against lethal pulmonary Burkholderia pseudomallei an infection. Identification of a LolC homologue in Burkholderia pseudomallei, a novel protective antigen for melioidosis. Protective response to subunit vaccination against intranasal Burkholderia mallei and B. Evaluation of lipopolysaccharide and capsular polysaccharide as subunit vaccines against experimental melioidosis. Humoral and cell-mediated adaptive immune responses are required for protection against Burkholderia pseudomallei problem and bacterial clearance postinfection. Passive safety of diabetic rats with antisera specific for the polysaccharide portion of the lipopolysaccharide isolated from Pseudomonas pseudomallei. Development of novel O-polysaccharide primarily based glycoconjugates for immunization against glanders. It is foremost a disease of rodents; greater than 200 species of mammals have been reported to be contaminated with Y pestis, but maintenance of plague in nature depends virtually exclusively on a smaller number of rodent species and their fleas. Pneumonic plague is of particular concern to the military outcome of|as a result of} it can also be|may also be|can be} acquired from artificially generated aerosols. In the sixth, 14th, and 20th centuries Y pestis was the cause of|the reason for} three nice pandemics of human disease. The bubonic form of the disease in humans is characterised by the abrupt onset of excessive fever, painful local lymphadenopathy draining the publicity web site (ie, a bubo, the inflammatory swelling of a number of} lymph nodes, normally in the groin, axillary, or cervical regions; the confluent mass of nodes, if untreated, may suppurate), and bacteremia. Septicemic plague can ensue from untreated bubonic plague or by passage of bacteria instantly into the bloodstream bypassing the local lymph nodes. Patients with the bubonic and septicemic types of the disease may develop secondary pneumonic plague, which may result in human-to-human spread by the respiratory route. Cervical lymphadenitis has been famous in several of} human plague instances, together with many fatal instances, and is usually associated with the septicemic form of the disease. Mortality from endemic plague continues at low rates all through the world despite the availability of effective antibiotics. No vaccine is on the market for plague in the United States, though candidates are present process medical trials. A higher understanding of the preventive drugs features of the disease will assist in the immediate prognosis and effective therapy essential to survive an enemy assault of plague and protect military and civilian personnel in plague endemic areas where military operations are underway. Enzootic refers to when plague is current in a small number of animals; the host, vector, and bacterium live in an obvious equilibrium in which mortality among rodent hosts is tough to detect and never clearly resulting from plague. The dying of a rodent causes the residing fleas to go away that host and seek other mammals, and when those other mammals die in giant numbers, they might seek humans. Knowledge of these two ideas of enzootic and epizootic will help to clarify how and when humans contaminated, in endemic or biological warfare scenarios. When bales of these furs were opened in Astrakhan and Saray, hungry fleas jumped from the fur seeking the first out there blood meal, often a human leg. During the 15th through the 18th centuries, 30% to 60% of the populations of main cities, such as Genoa, Milan, Padua, Lyons, and Venice, died of plague. Some believed that a viral hemorrhagic fever or unknown agent brought on the Black Death as an alternative of Y pestis. Physicians at the University of Paris theorized that a conjunction of the planets Saturn, Mars, and Jupiter at 1:00 pm on March 20, 1345, corrupted the surrounding ambiance, which led to the plague. They grew to the size of a small apple or an egg, kind of, and were vulgarly known as tumours. In a brief area of time these tumours spread from the two parts named all over the the} physique. Soon after this, the signs modified and black or purple spots appeared on the arms or thighs or any other part of of} the physique, sometimes a couple of of} giant ones, sometimes many little ones. Such was the terror this brought on that seeing it take maintain in a household, as quickly as it started, nobody remained: everybody abandoned the dwelling in fear, and fled to one other; some fled into the city and others into the countryside. The disease subsequently appeared in New York City and Washington state the same year. Among these quite a few occasions, only the outbreaks in California appear to have spread inland, resulting in the institution of everlasting plague foci in native rodent and flea populations in the interior of the western United States. After common rat control and hygiene measures were instituted in numerous port cities, city plague vanished-only to spread into rural areas, where nearly all instances in the United States have been acquired since 1925. Some writers described bizarre neurological issues (which led to the term "dance of dying"), adopted by anxiety and terror, resignation, blackening of the skin, and dying. The sick emitted a horrible stench: "Their sweat, excrement, spittle, breath, [were] so foetid as to be overpowering" [in addition, their urine was] "turbid, thick, black, or pink. The theories are all flawed to some extent, and the disappearance of plague from Europe remains one of many nice epidemiological mysteries. Based on an evaluation of Y pestis genomes from Black Death victims, no vital differences existed between 14th century and twenty first century strains of the bacterium. Medical officers must distinguish instances doubtless acquired from pure sources in a plague-endemic area from those occurring following publicity to a biological warfare agent. French military operations in Egypt were considerably impeded by plague in 1798, which brought on them to abandon their assault on Alexandria. The trendy pandemic 251 Medical Aspects of Biological Warfare started in China when its troops were deployed in an epidemic plague area to suppress a Muslim insurrection.
Best 40mg/5mg co-amilofruse
All of those assays had been developed to use the identical solid phase, buffers and different reagents, with comparable incubation periods, incubation temperatures, and basic procedures (Table 26-8). The small size of Ru (1,057 kDa) makes it easily conjugated to any protein ligand (antigen or antibody) utilizing commonplace chemistries with out affecting immunoreactivity or solubility of the protein. A magnet positioned just below the electrode captures the magnetic bead-Ru-tagged immune complicated and holds it in opposition to the electrode. Application of an electric area ends in a speedy electron switch response between the substrate (tripropylamine) and the Ru. The response does not undergo surface steric and diffusion limitations encountered in solid-phase immunoassays; as a substitute it happens in a turbulent bead suspension, thus permitting for speedy response kinetics and short incubation time. Detection limits as low as 200 fmol/L are attainable with a linear dynamic vary that can span six orders of magnitude. For antigen detection assays, the beads are coated with capture antibody, whereas for antibody detection assays the beads are coated with antigen or capture antibody. The coated paramagnetic beads, in the presence of organic agent (target), kind immune complexes that are be} detected by the Ru-conjugated detector antibody. After a short 15-minute incubation period the analyzer attracts the sample into the flow cell, captures and washes the magnetic beads, and measures the electrochemiluminescent sign (up to 1 minute per sample cleansing and studying time). The platform stays in use, however Roche is now not producing reagents and the system might be pressured into obsolescence when supplies are now not out there. In multiwell microplates, capture antibodies are sure to carbon electrodes built-in into the bottom of the plate. The plates can have up to as} 10 electrodes per nicely, with each electrode coated with a unique capture antibody. As in the M1M system, electrochemical stimulation ends in the Ru label emitting mild at the surface of the electrodes, from which the concentration of goal related to the particular electrode can be decided. For environmental testing, the Model 1500 is designed for automated aerosol sample testing. This multiplexed immunoassay platform has more than 400 assays commercially out there to be used in scientific, environmental, and research purposes, with kits that are be} specifically designed for biodefense. Dependence on any single firm for each instrument and assays will increase the chance to the DoD diagnostic and detection applications, which is again to|paying homage to} the BioVeris experience. The approach works by placing organic samples (ie, cells or different particles) right into a liquid suspension. A fluorescent dye, the choice of which is based on its capacity to bind to the particles of interest, is added to the solution. Light is scattered, and the distribution and depth of scattered mild is characteristic of the sample passing via. The wavelength of mild is chosen such that it causes the dye-bound to the particle of interest-to fluoresce. A pc counts and/or analyzes the fluorescent sample because it passes via the laser beam. Using the identical excitation source, fluorescence may be be} break up into totally different shade elements so that a number of} totally different fluorophores can be measured simultaneously and indicators interpreted by specialised software program. Multiplexed flow cytometry assays have been demonstrated for selection of|quite lots of|a wide selection of} cytokine targets. Interrogation of the beads by two lasers identifies the spectral property of the bead (address) and hence the related analyte, along with the phycoerythrin labeled secondary antibody in opposition to the specific analyte. They incorporate three familiar technologies: (1) bioassays, (2) microspheres, and (3) fluorescence. Assays happen in answer; thus, response kinetics are speedy and incubation instances are shorter. Capture antibodies or ligands are sure to Laboratory Identification of Threats microspheres labeled with two spectrally distinct fluorochromes. By adjusting the ratio of each fluorochrome, microspheres can be distinguished primarily based on their spectral address. Detector antibodies are labeled with any of quantity of|numerous|a variety of} totally different green fluorescent dyes. The instruments use two lasers: one for detection of the microsphere itself, and the opposite for the detector. Microspheres are analyzed individually as they move by two separate laser beams, are categorized primarily based on their spectral address, and are measured in actual time. Thousands (20,000) of microspheres are processed per second resulting in an assay system theoretically capable of analyzing up to as} a hundred totally different reactions on a single sample in simply seconds. The manufacturer reports assay sensitivities in the femtomole degree, dynamic vary of 3 to four orders of magnitude, and claims results are highly consistent and reproducible. The system, which might use tubes 96- and 384-well plates, can be automated. In addition to the Luminex instrument, a plate shaker and liquid handling gadgets are required to complete assays. Many multiplexed assay kits are commercially out there from totally different manufacturers for various cytokines, phosphoproteins, and hormones. No fieldready versions of the Luminex 100/200 are out there, which limits the sensible use of this instrument in deployment situations. No business or DoD sources for organic menace agent assays are available for this platform. The instrument, which eliminates a few of the the} shortcomings of the flow cytometry-based instruments, has large potential for forward laboratory purposes in such resource-limited environments. Three photographs, each taken with a unique filter, are used to discriminate bead sets and decide assay indicators. Two photographs are used to establish the unique bead address and the third picture measures the presence of tracer fluorophore, indicating the presence of goal analyte. The system is fully suitable with all magnetic bead-based assays at present carried out on the Luminex flow cytometers; all assay, sample, and reagent preparation protocols for each systems are analogous. Per instrument cost has also been significantly decreased, which can also make it more reasonably priced for widespread deployment in forward services. A capture antibody (for antigen detection) or antigen (for antibody detection) is sure to the membrane and a second 733 Medical Aspects of Biological Warfare antibody labeled with some visible marker factor is placed on a sample utility pad. As sample flows across the membrane, antigen or antibody current in the sample binds to labeled antibody and is captured because the complicated passes the sure antibody or antigen (Figure 26-6). Colloidal gold, carbon, paramagnetic, or coloured latex beads are commonly used particles that create a visual line in the capture zone of the assay membrane. To reply to this deficiency, a number of} technologies are available to make these assays more quantitative and have extra advantage|the additional benefit} of accelerating their sensitivity. The DoD Medical Countermeasure Systems, Critical Reagent Program, a repository for DoD diagnostic reagents, presents lateral flow assays for this purpose. In addition, a number of} business companies have begun to market selection of|quite lots of|a wide selection of} menace agent checks to be used by first responders. However, unbiased analysis of those assays has not typically been carried out, so information acquired from the use of of} these assays must be interpreted fastidiously. Future Perspectives Traditionally, assays for detecting proteins and different nonnucleic acid targets, including antigens, antibodies, carbohydrates, and different organic molecules had been conducted utilizing antibodies produced in applicable host animals. As a outcome, these assays had been generically referred to as immunodiagnostic or immunodetection strategies. In actuality, numerous nonantibody molecules, including aptamers, peptides, and engineered antibody fragments, second are|are actually} being used in affinity-based detection technologies. Naturally occurring single domain antibodies (sdAbs) derived from camelids and sharks possess unique properties that would enhance current day immunodiagnostics. Through convergent evolutionary processes, each camelid and shark immune systems naturally possess nonconventional antibody subsets composed solely of heavy chain homodimers and a single variable domain. Unique structural traits provide them a excessive temperature (>6090°C), proteolytic and pH stability,8693 excessive solubility,94 and environment friendly and economical expression in selection of|quite lots of|a wide selection of} microorganisms (including Escherichia coli). Antibody-based biosensors provide probably the most reliable detection capability across the broadest vary of biowarfare brokers. However, the fragility of the antibody molecule along with the short shelf life (typically 2 weeks or less) of antibodybased biosensors severely complicates their use exterior of a scientific laboratory surroundings. In addition, the variability in affinity across various antibody systems has precluded the event of multiplexing anti- body arrays for biosensor purposes.
Love Parsley (Lovage). Co-amilofruse.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Lovage?
- Dosing considerations for Lovage.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Lovage work?
- Indigestion, heartburn, intestinal gas, irregular menstrual periods, sore throat, boils, jaundice, gout, migraines, use as "irrigation therapy" for urinary tract inflammation and kidney stones, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96709
Generic 40/5 mg co-amilofruse
Warren Skippon) for endorsement, and for allowing distribution through its web-site. Jan Sargeant) for endorsement, and for allowing distribution through its web-site. Gluck Equine Research Center, University of Kentucky Cathy Egan, Network Coordinator, Wellington Infection Control Network WaterlooDr. Jim Hutchinson, Canadian Committee on Antibiotic Resistance, Health Sciences Centre, St. Scott McEwen, Professor, Department Population Medicine, University of Guelph of Dr. Craig Stephen, Professor, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Calgary Dr. Its use must be versatile to accommodate specific challenges and dangers in different services and regions while ensuring finest practices in an infection prevention and control. The instructed format is indicated beneath: Canadian Committee on Antibiotic Resistance (2008) Infection Prevention and Control Best Practices for Small Animal Veterinary Clinics First Printing, November 2008. The Committee offers outreach to the well being care and agricultural communities through a variety of|quite lots of|a big selection of} actions, including skilled seminars, a series of reviews and informational documents for specific target audiences, and managing one of the most comprehensive websites on antimicrobial resistance in Canada ( The Public Health Agency of Canada offers appreciable financial assist through a three-year contract for companies which expires in March of 2008. Elizabeth Henderson, Linda Kingsbury, Marg McKenzie, Judy Morrison, Patsy Rawding, Liz Van Horne, and Rick Wray, beneath the auspices of the Canadian Committee on Antibiotic Resistance. The fundamental contents and key messages are summarized beneath, and a extra detailed abstract is out there in Appendix I. Infection prevention and control strategies are designed to protect patients, owners, veterinary personnel and the neighborhood. All veterinary personnel ought to play an lively function in defending every particular person and animal related to the veterinary clinic. Routine Practices may be} crucial to infectious disease prevention and control: a. Proper wound care is crucial to preventing transmission of micro organism, notably multidrug-resistant pathogens, between animals, personnel and the surroundings. Animals from shelters and comparable services must be considered high risk from an infectious disease standpoint and managed appropriately to prevent transmission of disease. Personnel ought to take all necessary precautions to prevent animal-related injuries. Proper sharps dealing with practices must be emphasized to reduce the danger of needle-stick injuries. Education of personnel and clients about zoonotic and infectious disease dangers and prevention is essential. Veterinary services face lots of the similar challenges that human healthcare services encounter. Veterinary clinics can act as reservoirs of human and animal pathogens and play a task in dissemination of infectious agents including antimicrobial-resistant micro organism into the final inhabitants, with potential results on people and animals. Veterinary personnel also face an inherent risk of zoonotic disease from contact with each wholesome and sick animals. All these issues clearly indicate why an infection control is an important facet of veterinary apply. However, the sphere of veterinary an infection control is poorly developed compared to with} that of an infection control in human healthcare, and few sources are at present obtainable to assist veterinarians design and implement sufficient an infection control packages. This document offers the basic data wanted to develop an an infection control program and set up fundamental an infection control practices for such a clinic, with specific emphasis on crucial elements corresponding to hand hygiene, and cleaning and disinfection. This consists of non-clinical staff, as in lots of} conditions these people should have periodic direct or indirect contact with patients and pathogens within a clinic. A systematic strategy to an infection prevention and control requires all veterinary personnel to play an lively function in defending every particular person and animal related to the veterinary clinic, patients or veterinary personnel. Veterinary personnel must comply with an infection prevention and control protocols always and use crucial pondering and problem fixing in managing scientific conditions. This might vary from merely a written assortment of fundamental an infection control practices, to a proper an infection control handbook with specific training, monitoring, surveillance and compliance packages. Lack of a clearly defined an infection control program might result in unnecessary patient morbidity and mortality, and publicity of veterinarians, staff and owners to zoonotic pathogens. There are also extra animals at higher risk for an infection normally because of extra invasive and immunosuppressive therapies. In addition to the desire to obtain "finest apply" requirements each time attainable, the more and more litigious nature of society one of many driving forces towards improved an infection control in veterinary clinics. While the potential liability related to morbidity and mortality in individual pets is limited, the potential penalties of zoonotic illnesses in owners and staff are significant and warrant cautious consideration. Infection prevention and control measures could be broadly divided into three major classes: those who decrease host publicity, decrease host susceptibility and enhance host resistance to infectious pathogens. Decreasing publicity is an important facet of disease control in most conditions. The variety of organisms to which a host is exposed an necessary factor in figuring out whether or not or not colonization or an infection (disease) will ensue. Depending on the pathogen, lowering or preventing publicity easy, troublesome or impossible. There are many elements that work together to determine whether or not or not infectious disease will develop in a specific host. The susceptibility of the person to a specific variety of an infectious agent plays an necessary function. Although troublesome to quantify, certain conditions might result in elevated susceptibility to an infection and disease. Factors to consider include judicious use of antimicrobials and other medication, provision of proper diet, sufficient pain control, and acceptable administration of underlying disease. Measures to actively enhance resistance of a host are generally utilized in veterinary medication, however these must be considered only the third line of protection, after those meant to decrease publicity and susceptibility. Vaccination is at present the primary approach used to enhance resistance of animals or people to an infection. Therefore, while vaccination is an important half of} an infection prevention and control, it must not be the only element of an an infection control program if the program is to be successful. Prevention of an infection in animal well being care settings must be directed primarily at interrupting the transmission of microorganisms from supply to host, outcome of|as a end result of} agent and host elements are typically tougher to control. People could be an necessary supply of zoonotic pathogens, and like animals they might be colonized or infected. Inanimate objects, including medical equipment, supplies and medicines, animal bedding, environmental surfaces and waste which were contaminated necessary sources. In some cases, vectors corresponding to lice, mosquitoes, flies, ticks, fleas, rodents and other vermin can transmit certain pathogens. Regarding patients, the judicious use of antimicrobials, minimizing the use of of} immunosuppressive agents, avoidance of dietary adjustments each time attainable, ensuring sufficient dietary intake, sufficient pain control, and limiting the use of of} invasive devices must be considered, as these can all have an impact on host immune function. For hospital personnel, it may not be not|will not be} attainable to directly decrease their own susceptibility to an infection, however be aware of|concentrate on|pay consideration to} those people who might have elevated susceptibility. Good communication between veterinary personnel, their physicians and clinic administration is necessary to reduce the danger of zoonotic an infection. Increasing host resistance Vaccination is at present the primary approach used to enhance resistance of animals and people to an infection. As noted, no vaccine is one hundred pc efficient and tons of|there are numerous} infections for which vaccines are unavailable. Factors to consider when growing vaccination suggestions or necessities include the prevalence of a specific disease within the space, risk to wholesome and compromised patients, transmissibility of the disease, risk to veterinary personnel, capacity to deal with the disease, efficacy of vaccination and safety of vaccination. This typically includes body floor contact with an inanimate object, environmental floor or the integument of one other animal or person that has been transiently contaminated by the original animal (or human) supply. However, the mechanism of switch of the pathogen from host to host type of|is type of} distinct from both direct or indirect contact transmission. Droplets are generated from the supply animal primarily throughout coughing or sneezing, and during the efficiency of certain procedures corresponding to suctioning. Droplets also can contaminate the encompassing surroundings and result in indirect contact transmission.
Buy co-amilofruse 40mg/5mg
The importance of socio-economic standing and particular person traits on the prevalence of head lice in schoolchildren. Faulde Summary the commonest vector-borne ailments in each Europe and North America are transmitted by ticks. Ticks dwell predominantly in woodlands and meadows, and in association with animal hosts, with solely restricted colonization of human dwellings by a few of} species. Therefore, suburbanization has contributed considerably to the rise in tick-borne illness transmission in North America by fostering elevated publicity of people to tick habitat. The present pattern towards suburbanization in Europe could doubtlessly lead to similar increases in transmission of tick-borne ailments. Incidence of tick-borne ailments can be lowered by energetic public education campaigns, focused on the occasions and locations of best potential for encounter between people and infected ticks. Consultation with vector-borne illness experts through the planning levels of latest human developments can reduce the potential for residents to encounter infected ticks. Furthermore, analysis on tick vectors, pathogens, transmission ecology, and on geographic distribution, unfold, and management of tick-borne ailments can lead to progressive and improved methods to decrease the incidence of those ailments. Surveillance applications to monitor the distribution and unfold of ticks, related pathogens, and their reservoirs, can enable better-targeted management efforts, and supply data to assess effectiveness and to enhance management applications. Introduction Ticks transmit extra instances of human illness than another arthropod vector in Europe and North America. They are additionally necessary worldwide as illness vectors to folks and domestic animals, and so they cause substantial economic losses, each by transmitting illness and by direct adverse results on cattle (Jongejan & Uilenberg, 2004). In addition to their importance as illness vectors, some exhausting tick species can directly cause antagonistic results, similar to tick paralysis, a toxicosis (systemic poisoning) as a result of} toxic salivary proteins. Similarly, gentle ticks can provoke extreme allergenic chunk reactions in folks (IgE-mediated type-I allergy). States with a high incidence of illness have quite a few public education programmes, and a number of|various|a variety of} other|and quantity of} other} novel methods of tick and illness management have been developed (Stafford & Kitron, 2002). However, coordination and analysis of programmes is spotty, and the incidence of illness remains high in many of} locales and has elevated nationwide (Piesman & Gern, 2004). Ecological variations in transmission dynamics from website to website imply that the method to management must be tailored to circumstances at every locale. The scenario in Europe is totally different in that nationwide reporting strategies differ amongst international locations (Table 10. Ticks of Europe and North America Ticks are arachnids (the class Arachnida includes spiders, scorpions, ticks and mites) in the subclass Acari, which includes mites and ticks. There are three households of ticks (Barker & Murrell, 2004): the exhausting ticks, Ixodidae (713 species), which includes most ticks of medical importance to folks; the gentle ticks, Argasidae (185 species), which includes a few species that transmit ailments to people; and Nuttalliellidae, which includes just one species from Africa with no identified medical importance. Tick vectors of medical importance would possibly be} endemic in Europe Species Geographical distribution North-western Europe (westwards to Baltic states) Habitat Host a Remarks Castor-bean tick (Ixodes ricinus) Humid microhabitats in woodlands, rough grasslands and moorlands Many totally different varieties of untamed and domestic animals; readily feeds on man; threehost tick Many totally different varieties of untamed and domestic animals; readily feeds on man; threehost tick Larvae and nymphs feed on rabbits and small mammals, additionally on birds; adults feed on large mammals, similar to deer, cattle and sheep; readily feeds on man; three-host tick Larvae and nymphs feed on small mammals, often on birds; adults feed on wild and domestic mammals, similar to deer, canine, foxes, cattle and sheep; often feeds on man; three-host tick Larvae, nymphs and adults primarily feed on canine (90%), however are additionally found on cattle, cats, foxes and human beings; three-host tick Larvae and nymphs feed on one fowl host for 1226 days; adults actively seek for mammal hosts, similar to cows, donkeys, canine, foxes and human beings; twohost tick Larvae and nymphs feed on small mammals and barely birds; adults primarily feed on sheep and cattle, often on human beings, three-host tick Most widespread tick species in north-west Europe Taiga tick (Ixodes persulcatus) North-eastern Europe (eastwards to Baltic states) Humid microhabitat in taiga woodlands, rough grasslands and moorlands Most widespread tick species in north-east Europe and northern Asia Endemic tick species in Europe can be peridomestic or can be related to pets and livestock (Table 10. European ticks that may infest buildings in city environments embody: the ixodid brown canine tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus, as far north as southern Germany; and the argasids: the European pigeon tick, Argas reflexus (associated with pigeons), and the fowl tick, Argas persicus (associated with poultry in south-eastern Europe). Long-term infestations with brown canine ticks can happen in human dwellings, if control efforts are uncared for (Gothe, 1999). The solely survey thus far for European pigeon ticks was carried out in the metropolis of Berlin, where greater than 200 infested buildings were found between 1989 and 1998 (Dautel, Scheurer & Kahl, 1999). Recent studies in Germany have shown increases in city and periurban collections of castor-bean ticks, Ixodes ricinus (Mehnert, 2004). Other ticks, such because the gentle tick Ornithodoros erraticus, and the exhausting ticks Dermacentor spp. The brown canine tick attaches to canine and can be found in the house, however not often attaches to folks. These ticks are found primarily in natural areas and are often encountered by recreational users of parks and woodlands (Ginsberg & Ewing, 1989). However, increasing suburbanization round major city centres has resulted in substantial contact between folks and ixodid ticks, and most illness transmission from ticks to folks occurs in the peridomestic environment (Maupin et al. Ornate sheep tick (Dermacentor marginatus) Southern Europe, southwards to 50th parallel Scrub steppes, temperate forests, grasslands and sheep pastures As many as 200 grownup ticks can be found on one sheep Marsh tick (also called the ornate cow tick; Dermacentor reticulatus) Generally southern Europe southwards to 50th parallel; localized populations happen in north-western Europe in Belgium, south-west England and Wales Grasslands, pastures and woodlands Spreading geographically in Germany Brown canine tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) Mediterranean Europe and Africa, with focal populations in Belgium, United Kingdom, France, Germany, Denmark, Norway Arid microhabitat in scrub steppes, buildings and kennels Local populations could survive in kennels and different sheltered locations with canine in central and northern Europe; transported over longer distances by canine Transported over longer distances by migrating birds and should sporadically appear in northern Europe (such as Denmark and Norway) Bont-legged tick (Hyalomma marginatum) Southern Europe (southwards to fortieth parallel), southern Asia and most of Africa Scrub steppes, temperate forests, grasslands and sheep pastures, and migrating birds Coastal pink tick (Haemaphysalis punctata) Throughout Europe, besides Ireland Wide selection: from relatively cold and humid coasts (such as United Kingdom) to semi-desert zones of central Asia Bite could cause tick paralysis a Some ticks, called one-host ticks, feed on just one host all through all three levels of life (larval, nymphal and adult). In Europe, 31 viral, 14 bacterial, and 5 Babesia species are identified endemic tick-borne pathogens of individuals (Table 10. Among 307 called two-host ticks, feed and remain on the first host through the larval and nymphal levels of life, after which drop off and attach to a special host as an grownup. Finally, three-host ticks feed, drop off and reattach to progressively bigger hosts subsequently to every moulting. In the Czech Republic, castor-bean tick populations unfold a median of 161 meters into greater altitude sites (from about 780m to 960m above sea level) over the last 30 years. Data from the Baltic states show that landscape-level ecological modifications (resulting from agricultural practices) have led to increases in ecotopes (the smallest ecologically distinct options in a panorama mapping and classification system) appropriate for tick infestation. Q fever, attributable to Coxiella burnetii, is primarily a livestock illness (McQuiston & Childs, 2002). Important vectors embody Ornithodoros hermsi (which transmits the spirochete Borrelia hermsii), Ornithodoros parkeri (which transmits Borrelia parkerii), and Ornithodoros turicata (which transmits Borrelia turicatae) (Barbour, 2005). Tularaemia, attributable to the bacterium Francisella tularensis, is often acquired by rabbit hunters that handle infected rabbits (especially in japanese North America), however is typically transmitted by ticks (especially in western states). Western North America Rodent nests Can chunk human beings who utilize rustic cabins with rodent nests a Some ticks, called one-host ticks, feed on just one host all through all three levels of life (larval, nymphal and adult). Other ticks, called two- host ticks, feed and remain on the first host through the larval and nymphal levels of life, after which drop off and attach to a special host as an grownup. Yearly charges of incidence in hyperendemic foci (sites where illness organisms exist in host populations at very high rates) can exceed 300 instances per a hundred 000 population, with average occupational seroprevalence charges of up to as} 48% in forest employees. Symptoms apparently depend upon the Borrelia genospecies involved, the tissues affected, the period of infection and particular person human host elements, together with genetic predisposition. Generally, medical presentations can be divided into three levels (Gern & Falco, 2000; Steere, Coburn & Glickstein, 2005). The rash can be faint and difficult to notice and resolves even with out therapy. Late stage central nervous system involvement can be extreme and difficult to deal with. A specific vaccine for folks, based on outer surface protein A (OspA), was briefly out there in the United States, however was withdrawn by the manufacturer in 2002. In Germany, for example, the average incidence in the Oder-Spree area in the federal state of Brandenburg was estimated to be 89. Cases observe the geographic distribution of the Ixodes vectors (the black-legged tick and the western black-legged tick). This focal sample is illustrated by the distribution of instances in 1999, when the nationwide incidence was 6. The number of instances in particular person states various dramatically, with a maximal incidence of 98. An economic burden of quantity of} a hundred million up to as} 1 billion a 12 months is plausible for Europe. Assuming 83% of instances with efficient early therapy, and 17% with disseminated illness (12% with 313 Ticks Public Health Significance of Urban Pests. [newline]Expenses related to household accommodations for sufferers, misplaced work time and the like would greatly increase these estimates. Again, unreported instances (probably the vast majority of precise cases) would greatly inflate this estimate. For instance, some present approaches to city planning can provide further ecotopes appropriate for castor-bean tick and taiga tick, Ixodes persulcatus, infestations (Kriz et al. In North America, suburbanization has produced in depth suburban and periurban areas that provide an interface between city and sylvan environments a so-called border impact. Property sizes in these areas probably to|are inclined to} be bigger than in city areas and therefore enable prepared entry to tick habitats that border infested natural ecosystems. Moreover, some studies counsel that climate modifications in Europe have resulted in a northern shift in the distributional restrict of castor-bean ticks, an increase of their population density in Sweden and a shift into greater altitudes in mountainous areas in the Czech Republic (Lindgren, Talleklint & Polfeldt, 2000; Danielova, 2006). Scattered foci additionally exist in the Great Lakes area in southern Ontario and possibly different components of Canada (Barker & Lindsay, 2000). Ticks would possibly be} typically related to temperate deciduous woodlands that embody patches of dense vegetation with little air motion and high humidity carry the infective agent. In open habitats in Europe, similar to meadows and moorland, the main supply of blood-meals is often livestock, similar to sheep and cows.
Generic co-amilofruse 40/5 mg
Through increasingly accessible molecular biology methods, utterly new organisms-or significant modification of present ones-can now be made in the laboratory (ie, artificial biology). The use of those strategies is helpful and necessary for contemporary biomedical analysis to proceed. However, the identical strategies and methods can be used for nefarious purposes and, along with naturally occurring emerging infections, represent significant future threats to both military and civilian populations. More than 20 years after the Institute of Medicine Report, a lot progress on emerging infectious diseases has been made, including a higher consciousness; use of next-generation sequencing for the characterization of pathogens, vectors, and their hosts and for enhanced diagnostics; and increased laboratory infrastructure including extra biocontainment laboratories (ie, biosafety level three laboratories and biosafety level 4 laboratories) to safely work with these pathogens. This continuous emergence of new infectious diseases poses a seamless challenge, requiring constant surveillance, the power to promptly reply with new diagnostics and new vaccines and medicine, and ongoing analysis into the essential biology of novel pathogens. From 2007 to 2008, forty eight disease outbreaks related to contaminated consuming water have been reported in the United States, leading to 4,128 unwell folks and 3 deaths. Bacterial pathogens related to consuming water disease outbreaks included Legionella (12 outbreaks), Campylobacter (4 outbreaks), Salmonella (3 outbreaks), Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Providencia (1 outbreak each). Diseases related to exposure to recreational water are extra numerous than those related to consuming water and embrace acute gastrointestinal illness, acute respiratory illness, and dermatologic illness. Accordingly, the record of bacterial pathogens accountable is extra numerous and consists of E coli O157:H7, Shigella sonnei, Legionella, Plesiomonas shigelloides, and Vibrio vulnificus. Dermatitis outbreaks have been most frequently attributed to Pseudomonas, primarily P aeruginosa. Cholera and Vibrio cholerae Cholera considered one of the|is amongst the|is likely one of the} most quickly fatal diseases recognized, capable of killing inside 12 to 24 hours after onset of diarrhea. Cholera occurs through fecal-oral transmission brought about by deterioration of sanitary situations. Epidemics are strongly linked to the consumption of unsafe water, poor hygiene, poor sanitation, and crowded residing situations (Figure 25-1). Water or meals contaminated by human waste is the main automobile for disease transmission. Cholera transmission is believed to require 103 organisms to exert an effect in the gut, with 1011 organisms as a minimum infective dose needed to survive stomach acid. Large outbreaks in 1992 resulted from transmission of a previously unknown serogroup, V cholerae O139, which has since unfold from India and Bangladesh to nations throughout Asia, including Pakistan, Nepal, China, Thailand, Kazakhstan, Afghanistan, and Malaysia. In severe instances, profuse watery diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting can lead to rapid dehydration, acidosis, circulatory collapse, and renal failure. Successful therapy of cholera sufferers decided by} rapid fluid and electrolyte alternative. Historically, stay attenuated vaccines have been simpler than killed whole-cell vaccines. This photograph was taken in 1974 during a cholera analysis and vitamin survey amidst floodwaters in Bangladesh. Photograph: Courtesy of Dr Jack Weissman, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Public Health Image Library. By mid-November, cholera had unfold to each part of of} the country and to neighboring Dominican Republic, and by mid-December a complete of 121,518 instances of cholera, leading to 63,711 hospitalizations and 2 of|and a pair of},591 deaths, had been reported from Haiti. These findings led to considerable political unrest and have eternally changed the global response to natural disasters. In late 2013, survivors and relations of the almost 700,000 Haitians who contracted cholera sued the United Nations, accusing them of covering up its role in beginning the cholera outbreak in Haiti. Nine months later, in October, a cholera outbreak was confirmed in Haiti,22 indicating the primary occurrence of cholera in Haiti in a minimum of|no much less than} one hundred years. In lower than 24 hours after the onset of symptoms, he died at residence without seeking medical attention. The first hospitalized case of cholera in Haiti occurred at the Mirebalais Government Hospital on October 17, 2010. It varieties part of of} the worldwide border between Haiti and the Dominican Republic and empties into the Gulf of Gonвve. It is believed that the 2010 cholera outbreak began in the upstream region of this river. Other Vibrioses In latest years, some noncholera vibrios have acquired increasing importance due to their association with human disease. More than 70 members are in the family Vibrionaceae, 12 of which have been isolated from human clinical specimens and apparently are pathogenic for humans. V parahemolyticus and V vulnificus are halophilic vibrios generally related to consumption of undercooked seafood. Diarrhea, cramping, nausea, vomiting, fever, and headache are generally related to V parahemolyticus infections. Cases of diarrhea associated to seafood consumption increased worldwide with the emergence of pandemic strain O3:K6, which was initially noticed in Southeast Asia. In most instances the disease begins several of} days after the patient has eaten raw oysters. Other human pathogenic species embrace V mimicus, V metschnikovii, V cincinnatiensis, V hollisae, V damsela, V fluvialis, V furnissii, V alginolyticus, and V harveyi; most of those have been related to sporadic diarrhea, septicemia, and wound infections. A total of 182 folks, all members of the Pennsylvania American Legion, developed an acute respiratory illness, and 29 individuals died from the disease. Retrospective evaluation, however, confirmed that outbreaks of acute respiratory disease from as far back as|way again to} 1957 have now been attributed to L pneumophia. Water is the main reservoir for legionellae, and the micro organism are found in freshwater environments worldwide. One Legionella species, L longbeachae, has been related to disease transmission from potting soil. Temperatures generally reach 102°F to 105°F and are associated with nonproductive cough, belly pain, and diarrhea. The disease might ultimately progress to respiratory failure and has a case-fatality fee as high as 39% in hospitalized instances. Nonpneumonic legionellosis, or Pontiac fever, occurs after exposure to aerosols of water colonized with Legionella species. After a typical asymptomatic interval of 12 to forty eight hours after exposure, sufferers notice the abrupt onset of fever, chills, headache, malaise, and myalgias. Pneumonia is absent are affected recuperate in 2 to 7 days without receiving specific therapy. Although 90% of Legionella infections in humans are attributable to L pneumophila, there are 50 named species of Legionella, with roughly 20 649 Medical Aspects of Biological Warfare recognized to trigger human infections. In the United States, the burden of foodborne illness is estimated at roughly 76 million diseases, 325,000 hospitalizations, and 5,000 deaths each year. The majority of gastrointestinal diseases are attributable to foodborne brokers not but identified. It is estimated that 62 million foodborne-related diseases and 3,200 deaths occur in the United States each year from unknown pathogens. Even in areas of the world where gastrointestinal anthrax is extra widespread, the oropharyngeal form is underreported end result of|as a outcome of} physicians are unfamiliar with it. Gastrointestinal Anthrax Bacillus anthracis is the causative agent of anthrax, a naturally occurring zoonotic disease. The biggest bioweapons risk from anthrax is thru aerosol dispersion and subsequent inhalation of concentrated spores (for extra details, see Chapter 6, Anthrax). Gas650 trointestinal anthrax, however, is contracted through the ingestion of B anthracis spores in contaminated meals or water. Of these, 91% had gastrointestinal complaints and 9% oropharyngeal edema; nine of them-all children- died inside forty eight hours of illness onset. Misdiagnosis of gastrointestinal anthrax might lead to a higher mortality than other forms of anthrax; thus consciousness of this disease remains important in anthrax-endemic areas and in the setting of attainable bioterrorism. Disease Caused by Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter was first identified in 1909 (then referred to as Vibrio fetus) from the placentas and aborted fetuses of cattle. The organism was not isolated from humans till almost 40 years later when it was found in the blood of a pregnant woman who had an infectious abortion in 1947. Scanning electron microscope image of Campylobacter jejuni illustrating its corkscrew appearance. Photograph: Courtesy of Janice Carr, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Public Health Image Library.
Quality 40mg/5mg co-amilofruse
Relationship between transpiration price and temperature within the mite Dermatophagoides farinae. Kinetics of water energetic and passive components of water change between the air and a mite, Dermatophagoides farinae. Predicting the population dynamics of the house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Acari: Pyroglyphidae) in response to a relentless hygrothermal surroundings utilizing a mannequin of the mite life cycle. Distribution of pyroglyphid mites in Birmingham with explicit reference to Euroglyphus maynei. Individual and area-based indicators of socioeconomic status and childhood bronchial asthma. Effects of temperature and relative humidity on growth occasions and mortality of eggs from laboratory and wild populations of the European house-dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Acari: Pyroglyphidae). Population research on the house dust mite, Euroglyphus maynei (Cooreman, 1950) (Pyroglyphidae). Practical and theoretical features of the ecology of home dust mites in relation to the study of mite mediated allergy. A pilot study of the impact of mechanical ventilation and warmth change on house-dust mites and Der p 1 in New Zealand properties. A easy mannequin for predicting the impact of hygrothermal situations on populations of home dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Acari: Pyroglyphidae). Controlling dust mites psychrometrically a review for building scientists and engineers. Quantitative measurement of airborne allergens from dust mites, canines, and cats utilizing and ion-charging gadget. Effect of warmth remedies on the house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and D. Explaining home dust mite infestations on the basis of temperature and air humidity measurements. Wellington, New Zealand, November 1997, Wellington Asthma Research Group, Wellington School of Medicine, Otago University:1319. House dust mites (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus) in mattresses: vertical distribution. Water steadiness of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Acari: Pyroglyphidae) maintained at temporary day by day spells of elevated air humidity. House dust mite (Pyroglyphidae) populations in mattresses, and their control by electric blankets. The decay of home dust mite allergens, Der p 1 and Der p 2, beneath natural situations. Vitamin requirements of the European home dust mite, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Acari: Pyroglyphidae), in relation to its fungal association. Optimal efficacy of a fungicide preparation, Natamycin, within the control of the house dust mite, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Residential traits influence Der p 1 ranges in properties in Melbourne, Australia. The significance of the fungus Aspergillus penicilloides to the house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Mechanical ventilation protects one-storey single-dwelling home in opposition to increased air humidity, home mite allergens and indoor pollutants in a chilly local weather region. Morphology, systematics and geographical distribution of mites responsible for allergic illness in man. Reduction in humidity as a way of controlling mites and mite allergens: using of} mechanical ventilation in British home dwellings. Tackling condensation: a guide to the causes of, and remedies for, surface condensation and mold in conventional housing. A new method for isolation of mites exploiting the difference in density between ethanol and saturated NaCl: qualitative and quantitative research. In vitro analysis of acaricidal and fungicidal activity of the house dust mite acaricide, Allerbiocid. Reproduction and growth of laboratory and wild home dust mites (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Acari: Pyroglyphidae)) and their relation to the natural dust ecosystem. House dust mite exposure reduction in specially designed, mechanically ventilated "wholesome" properties. An in situ coring method for estimating the population dimension of home dust mites in their natural habitat. A case study of chew reactions in man and home dust samples that implicate the house dust mite predator Cheyletus malaccensis Oudemans (Acari: Cheyletidae). Benzyl benzoate moist powder; investigation of acaricidal activity in cultures and reduction of dust mite allergens in carpets. Thermal demise point of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Trouessart 1897) (Astigmata, Pyroglyphidae), the house dust mite. American Academy of Allergy and Immunology 45th Meeting, San Antonio, 24 February 1 March, 1989. Husstшvmider (Pyroglyphidae, Acari) i danske boliger [House dust mites (Pyroglyphidae, Acari) in Danish homes]. Natural variation in mite antigen density in home dust and relationship to residential components. The important equilibrium activity of adult females of the house dust mite Dermatophagoides farinae Hughes [PhD thesis]. The effects of season, local weather and air-conditioning on the prevalence of Dermatophagoides allergens in family dust. Evaluation of changes in indoor air quality occurring over the previous a number of} many years. The function of water temperature and laundry procedures in lowering home dust mite populations and allergen content material of bedding. The effectiveness of benzyl benzoate and some essential plant oils as laundry components for killing home dust mites. Redefinition of the capabilities of a window to achieve improved air quality and vitality efficiency in European housing. Some home dust control measures and abundance of Dermatophagoides mites in Southern California (Acari: Pyroglyphidae). Mite sensitization within the Scandinavian international locations and components influencing exposure ranges. Preventive impact of bedding encasement with microfine fibers on mite sensitization. Attempting to control mite allergens with mechanical ventilation and dehumidification in British homes. Development of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Acari: Pyroglyphidae) at constant and simultaneously fluctuating temperature and humidity situations. Report of an International Workshop, Bad Kreuznach, Federal Republic of Germany, September 1987. Seasonal variation in dust mite and grass pollen allergens in dust from the houses of sufferers with bronchial asthma. Changing ideas of allergic illness: the try and sustain with actual changes in lifestyles. A mixed transient hygrothermal and population mannequin of home dust mites in beds. A steady-state mannequin for predicting hygrothermal situations in beds in relation to home dust mite requirements. A comparison of mite populations in mattress dust from hospital and from personal homes in Cardiff, Wales. Asthma, dust mites, ventilation and air quality: a subject study of an environmental method to lowering bronchial asthma. Seasonal dynamics of home dust mite populations in bed/mattress dust from two dwellings in Sosnoweic (Upper Silesia, Poland): an try and assess exposure. The impact of a mixed acaricide/cleaning agent on home dust mite allergen load in carpet and mattress. Dermatophagoides farinae allergen ranges from two different sources throughout the similar residence: analysis of two different collection strategies. Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Trouessart, 1897) in mattress and floor dust in a temperate local weather (Acari: Pyroglyphidae). On the abundance of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Trouessart, 1897) (Pyroglyphidae: Acarina) in home dust.
References:
- https://www.carcinoid.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/Neuroendocrine-Tumors-4th-Edition.pdf
- http://www.columbia.edu/~nvg1/Wickelgren/papers/1974dWAW.pdf
- https://cdn.vortala.com/childsites/uploads/41/files/spondylolisthesis.pdf
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/021660s045lbl.pdf
.png)