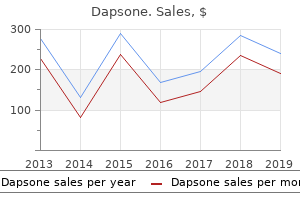
100mg dapsone
Current information on the diseases with neurologic implications have been collated by our colleague, H. Some of those disorders may be recognized by simple shade reactions within the urine; these are listed in Table 37-2. To this group ought to be added the inherited hyperammonemic syndromes and vitamin-responsive aminoacidopathies (such as pyridoxine dependency and biopterin deficiency) properly as|in addition to} certain nonfamilial metabolic disorders that make their appearance within the neonatal period- hypocalcemia, hypothyroidism and cretinism, hypomagnesemia with tetany, and hypoglycemia. This is fortunate, for it allows time to introduce preventive measures earlier than the first symptoms appear. A number of others, which may be recognized both by screening or by early indicators, are synopsized under. Vitamin-Responsive Aminoacidopathies Included beneath this heading is a bunch of diseases that reply not to dietary restriction of a specific amino acid but to the oral supplementation of a specific vitamin. Pyridoxine-dependent aminoacidopathy Pyridoxine dependency is the classic instance. It is characterised by the early onset of convulsions, generally occurring in utero; failure to thrive; hypertonia-hyperkinesia; irritability; tremulous movements ("jittery baby"); exaggerated auditory startle (hyperacusis); and later, if untreated, by psychomotor retardation. One of our patients, a thirteen 1/2-year-old boy affected within the neonatal interval, was left in a state of psychological retardation, with pale optic discs and spastic legs; the mind weight was 350 g under normal. There was a decreased quantity of central white matter within the cerebral hemispheres and a depletion of neurons within the thalamic nuclei and cerebellum, with gliosis (Lott et al). Most importantly, in pyridoxine deficiency, the administration of fifty to a hundred mg of vitamin B6 suppresses the seizure state, and every day doses of 40 mg allow normal development. Biopterin Deficiency Some patients with elevated concentrations of serum phenylalanine within the neonatal interval are unresponsive to measures that lower phenylalanine. If this situation is unrecognized and never treated promptly, it results in seizures of each myoclonic and later grand mal varieties combined with a poor level of responsiveness and generalized hypotonia. It is necessary to acknowledge this situation early in life by the measurement of urine pterins and to institute applicable therapy earlier than irreversible mind injury occurs. Several forms of galactosemia have been described, based on the degree of completeness of the metabolic block. In the classic (severe) type, the onset of symptoms is within the first days of life, after the ingestion of milk; vomiting and diarrhea are adopted by a failure to thrive. Drowsiness, inattention, hypotonia, and diminution within the vigor of neonatal automatisms then turn into evident. The fontanels may bulge, the liver and spleen enlarge, the skin turns into yellow (in extra of the common neonatal jaundice), and anemia develops. In one such patient, who died at 8 years, the primary change within the mind was slight microcephaly with fibrous gliosis of the white matter and a few lack of Purkinje and granule cells within the cerebellum, and in addition gliosis (Crome). The therapy is actually dietary, using milk substitutes; if that is instituted early, the mind ought to be protected against injury. A late-onset neurologic syndrome has additionally been noticed by Friedman and colleagues in galactosemic patients who survived the infantile disease. Organic Acidurias of Infancy these have been divided into ketotic and nonketotic varieties. The onset is within the neonatal or early infantile interval; in time, psychomotor retardation turns into evident. Propionic acid, glycine, various forms of fatty acids, and butanone are elevated within the serum. As with other ketotic natural acidurias, high protein consumption induces ketotic assaults. Marked restriction of dietary protein (specifically leucine) may prevent assaults of ketoacidosis and allow relatively good psychomotor development. The most necessary of those are methylmalonic acidemia, isovaleric acidemia, beta-keto acidemia, and lactic acidemia. Each of those disorders can present with profound metabolic acidosis and intermittent lethargy, vomiting, tachypnea, tremors, twitching, convulsions, and coma, with early dying in about half the patients and developmental retardation in those who survive. Isovaleric acidemia is characterised by a putting odor of stale perspiration, which has given it the sobriquet "sweaty foot syndrome. The enzymatic defect of isovaleric acidemia has additionally been demonstrated in a recurrent form of episodic cerebellar ataxia and athetosis and in a persistent type in mitochondrial encephalopathies (Leigh disease), as described further on in this chapter. A separate and rare deficiency of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase has been described; the chemical signature is of low levels of almost about|of virtually} all catecholamines. This defect is related to a peculiar motion disorder of oculogyric crises, dystonia and athetosis and autonomic failure (see Swoboda et al). Multiple congenital anomalies of mind and somatic buildings and cardiomyopathy are conjoined. A food regimen low within the particular toxic amino acid and dietary supplements of carnitine and riboflavin are beneficial, but the results are unclear. In the nonketotic form of hyperglycinemia, there are high levels of glycine but no acidosis. In reported instances (the authors and our colleagues have seen several), the neonate is hypotonic, listless, and dyspneic, with dysconjugate eye movements, opisthotonic posturing, myoclonus, and seizures. Spongy degeneration of the mind has been reported each in this disease and within the ketotic type (Shuman et al). In an atypical milder type, with neurologic abnormalities that appear in later infancy or childhood, reduction of dietary protein and administration of sodium benzoate in doses a lot as} 250 mg/ kg per day have been useful. The use of dextromethorphan, which blocks glycine receptors, is claimed to be effective in stopping seizures and coma. They are identified by the finding of a persistent or episodic elevation of ammonia levels within the blood. A detailed account of those inherited hyperammonemic syndromes is contained within the evaluation by Brusilow and Horwich. The one exception is arginase deficiency, which commonly presents throughout later childhood as a progressive spastic paraplegia with psychological retardation. Clinically it has been handy to divide the hyperammonemias into two groups- one that presents within the neonatal interval and one other that presents within the weeks or months thereafter. This division is considerably artificial, the scientific presentation being more within the nature of a continuous spectrum governed by the biologic elements mentioned above and even extending to rare instances that have their first symptoms throughout maturity. In essentially the most extreme forms of the hyperammonemic disorders, the infants are asymptomatic at birth and in the course of the first day or two of life, after which they refuse their feedings, vomit, and rapidly turn into inactive and lethargic, quickly lapsing into an irreversible coma. Profuse sweating, focal or generalized seizures, rigidity with opisthotonos, and hypothermia and hyperventilation have been noticed in the course of of|in the midst of} the illness. These symptoms represent a medical emergency, but even with measures to cut back serum ammonia, the disease is normally deadly. In less severely affected infants, hyperammonemia develops some months later, when protein feeding is elevated. There is a failure to thrive, and makes an attempt to implement feeding or in periods of constipation (both of which enhance ammonia manufacturing within the bowel) there bouts of vomiting, lethargy, hyperirritability, and screaming. Other manifestations are intervals of alternating hypertonia and hypotonia, seizures, ataxia, blurred vision, and of confusion, stupor, and coma. Between assaults, some patients with partial deficiency normal or show only a slight hyperbilirubinemia (diMagno et al, Rowe et al). With decompensation, the bilirubin rises, as does ammonia, but neither reaches exceedingly high levels. After repeated assaults, indicators of developmental delay with motor and psychological retardation turn into evident, and the patient is vulnerable to recurrent infections. Two grownup male patients in our care, who had been married (but with azoospermia, which is common) and working at technically demanding jobs, came to medical attention due to bouts of visible blurring adopted by stupor that developed over hours (Shih et al). They had displayed an aversion to protein and milk products as children; in later life, after meals high in protein, they became encephalopathic, one with extreme mind swelling. There are few phenotypic differences among the many late-onset hyperammonemias except for argininosuccinic aciduria, during which extreme dryness and brittleness of the hair (trichorrhexis nodosa) are notable options, and the aforementioned arginase deficiency with spastic diplegia. Diagnosis is established by the finding of hyperammonemia, typically as high as 1500 mg/dL. The precise biochemical analysis requires testing of blood and urine for amino acids or assays for particular enzymes in purple cells, liver, or jejunal biopsies. The major hyperammonemias should be distinguished from the natural acidurias, including methylmalonic aciduria (see above), during which hyperammonemia can happen as a secondary metabolic abnormality. In all of the neonatal hyperammonemic diseases, the liver is commonly enlarged and liver cells appear to be insufficient of their metabolic features, but how the enzymatic deficiencies or other disorders of amino acid metabolism affect on} the mind stays uncertain. It should be assumed that in some the saturation of the mind by ammonia impairs the oxidative metabolism of cerebral neurons, and when blood levels of ammonium enhance (from protein ingestion, constipation, and so forth. In the acutely deadly instances the mind is swollen and edematous and the astrocytes are diffusely elevated in number and enlarged.
Cheap 100 mg dapsone
Now that a number of|numerous|a variety of} different dementing ailments are treatable, a great premium attaches to right prognosis. The physician is compelled to exercise care of their detection precise fact} that|although} they could be comparatively rare. The treatable types of dementia are those end result of} neurosyphilis (general paresis) and different chronic meningitides, normal-pressure hydrocephalus, chronic subdural hematoma, dietary deficiencies (Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, Marchiafava-Bignami disease, pellagra, vitamin B12 deficiency), chronic drug intoxication. A provocative sequence of animal experiments that demonstrated the possibility of|the potential of|the potential for} removal of plaques by immunization in opposition to amyloid has led to human studies with an identical vaccination. One trial has been stopped because of the incidence of an immune encephalitis induced by the remedy in a couple of of} patients, however in post-mortem material there have been indications that the remedy might have had the desired effect. Perhaps extra important than the usage of} any medication is the general administration of the demented affected person, which should proceed along the traces outlined in Chap. Associated Pathologic States As indicated earlier, the histologic modifications of Alzheimer disease have a number of|numerous|a variety of} attention-grabbing associations. The modifications are much more frequent within the brains of patients with Parkinson disease than within the brains of age-matched controls (Hakim and Mathieson). These findings minimal of|no less than} partly clarify the high incidence of dementia in patients with Parkinson disease (see further on, within the sections concerning Parkinson disease and Lewy physique dementia), yet not more than 20 to 30 % of patients with Parkinson disease have plaques and tangles. Another affiliation between the two ailments is obvious within the Guamanian Parkinsondementia advanced, which is also be|can be} mentioned under. In this entity, the signs of dementia and parkinsonism are related to neurofibrillary modifications within the cerebral cortex and substantia nigra, respectively; senile plaques and Lewy our bodies are unusual findings. Alzheimer disease in relation to the Down syndrome, first famous and reported by Jervis, is now widely recognized. The attribute plaques and neurofibrillary tangles seem within the third decade; they increase with age and are current in practically all patients with the Down syndrome after 40 years of age. There are uncommon situations, corresponding to those reported by Malamud and Lowenberg and by Loken and Cyvin, in which dementia begins in late childhood, with the discovering at postmortem examination of the standard Alzheimer lesions within the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia. The scientific picture in these juvenile and early grownup instances has been extra varied than within the older ones. In some, paucity of speech, mutism, tremor, stooped posture, marked grasp and suck reflexes, and pyramidal and cerebellar indicators leading to inability to stand or walk have appeared at varied levels of the disease. The discovering of neurofibrillary modifications (and to a lesser extent of plaques) in boxers ("punch-drunk" syndrome, or "dementia pugilistica") is one other attention-grabbing ramification of the Alzheimer disease course of (page 863). Similarly, some instances of what has come to be referred to as "main progressive aphasia" (see web page 908) have Alzheimer change and amyloid plaque deposition as the first pathologic change. A shut relationship between Pick, Alzheimer, and Parkinson ailments has been demonstrated in a big household with dysphasic dementia (Morris et al). Other isolated combinations, whereby Alzheimer disease, hypothyroidism, hypopituitarism, or neurosyphilis have been conjoined, have been most likely a matter of chance and prove nothing. From time to time different unusual associations come to light, corresponding to de- mentia with motor neuron disease or the instances of familial dementia with spastic paraplegia reported by Worster-Drought and by van Bogaert and their associates (see further on on this chapter). Here, neurofibrillary change is the most prominent characteristic whereas amyloid plaques are negligible in number or absent. Lobar Atrophies (Pick Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia) In 1892, Arnold Pick of Prague first described a particular form of cerebral degeneration in which the atrophy is circumscribed (most often within the frontal and/or temporal lobes), with involvement of both gray and white matter- therefore the term lobar somewhat than cortical sclerosis. The most complete analyses of the pathologic modifications till just lately have been those of Spatz, van Mansvelt, Morris and coworkers, and Tissot and associates. The nosology of the lobar atrophies has turn into extremely complicated over the previous decade. It has turn into clear that the pathologic change related to neuronal loss on this category of disease may be be} any certainly one of varieties: lobar atrophy with Pick inclusion our bodies, with neurofibrillary tangles, with different inclusions, or no attribute modifications. Furthermore, gliosis and mild spongiform modifications within the superficial layers of cortex, and even typical Alzheimer plaque and tangle pathology, have all been related to syndromes and gross pathologic atrophy of the frontal and/or temporal lobes. Confusion has arisen end result of|as a outcome of} these diseases have been denominated both by the scientific syndrome that derives from a selected region of atrophy or by the pathologic change. Several phrases have been applied to varied types of lobar atrophy, frontotemporal dementia being the commonest (see below). Nonetheless, amongst these, pretty distinct clinicopathologic syndromes of Pick disease and of frontotemporal dementia are recognizable. Since the popularity of Pick disease rests extra on pathologic than on scientific criteria, that is described first. In contrast to Alzheimer disease, in which the atrophy is relatively mild and diffuse, the pathologic change in lobar atrophy is extra circumscribed and generally asymmetrical. The atrophy might prolong to the island of Reil and the amygdaloid-hippocampal structures. The parietal lobes are involved less incessantly than the frontal and temporal lobes. The reduce surface reveals not only a marked narrowing of the cortical ribbon however a grayish appearance and lowered quantity of the underlying white matter. The pre- and postcentral, superior temporal, and occipital convolutions are comparatively unaffected and stand out in putting contrast to the wasted components. In some situations, atrophy of the caudate nuclei has been pronounced, almost to the degree seen in Huntington chorea. The thalamus, subthalamic nucleus, substantia nigra, and globus pallidus may be affected, however only to a slight degree. The salient histologic characteristic of Pick disease is a loss of neurons, most marked within the first three cortical layers. Surviving neurons are sometimes swollen, and a few comprise argentophilic (Pick) our bodies throughout the cytoplasm. Ultrastructurally, the Pick our bodies are made up of straight fibrils, thus differing from the paired helical filaments that characterize Alzheimer disease. These our bodies predominate within the medial components of the temporal lobes, especially within the atrophic hippocampi. There is a loss of myelinated fibers within the white matter beneath the atrophic cortex. A heavy astrocytic gliosis is seen in both the cortex and subcortical white matter. Most neuropathologists consider the loss of myelinated fibers within the white matter, basal ganglia, and thalamus to be consequent to neuronal loss within the cortex. It is the lobar atrophy and marked modifications within the underlying white matter that provide the unifying components of all of the lobar atrophies. Clinical Features Whether the prognosis of Pick disease could be made constantly on purely scientific grounds is doubtful. Sometimes the imaging options of unilateral or bilateral lobar tissue loss are so prominent as to almost obligate the prognosis of lobar atrophy. In our expertise, the gradual onset of mental confusion with respect to place and time, anomia, slowness of comprehension, inability to address unaccustomed problems, loss of tact, deterioration of labor habits, neglect of non-public hygiene and grooming, apathy, and alterations of personality and habits have been prominent options. In addition to these personality modifications, an inability to carry out sequences of motor duties, motor perseveration, apathy (emotional indifference), inattention, abulia, impairment of gait and upright stance, and prominent grasp and suck reflexes are attributable to predominant affection of the frontal lobes. Bulimia and alterations in sexual habits happen to a distressing degree in some patients (Tissot et al). The similarities to the scientific entity of frontotemporal dementia described under is obvious. In half for this reason, the notion of a "Pick advanced" has been instructed, encompassing lobar atrophy with Pick our bodies, frontotemporal dementia, and different entities in which tau depositions are prominent, corresponding to corticobasal degeneration, main progressive aphasia, and progressive supranuclear palsy. The location of the neuronal degeneration is the primary determinant of the scientific presentation. Wilson distinguished two patterns of abnormal habits: in one, the affected person is talkative, lighthearted, cheerful or anxious, constantly on the transfer, occupied with trifles, and attentive to each passing incident; within the different, the affected person is taciturn, inert, emotionally uninteresting, and lacking in initiative and impulse. Probably these two patterns symbolize predominantly temporal and frontal varieties, respectively. According to Tissot and colleagues, the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes are all affected in 75 % of patients by the point the disease terminates. While most instances are sporadic, Sjogren and associates concluded from a genetic survey Ё of the instances in Stockholm that Pick disease may be be} transmitted as a dominant trait with polygenic modification. Such a Dutch household with almost 100% penetrance over generations has been reported by Schenk. No chemical, vascular, traumatic, or different issue of possible causal significance has been recognized.
Diseases
- Microcephaly seizures mental retardation heart disorders
- Exencephaly
- Chondrodysplasia punctata, brachytelephalangic
- Spastic ataxia Charlevoix Saguenay type
- Congenital nephrotic syndrome
- Booth Haworth Dilling syndrome
- Muscular dystrophy limb-girdle type 2B, Myoshi type
- Adenocarcinoid tumor
Best dapsone 100mg
The most essential difference, after all, is that individuals in sleep, when stimulated, could be roused to normal consciousness. The Persistent Vegetative and Minimally Conscious States, Locked-in Syndrome, and Akinetic Mutism With growing refinements in the remedy of severe systemic illnesses and cerebral harm, increasingly more patients who previously would have died have survived for indefinite intervals with out regaining any meaningful psychological function. For the first week or two after the cerebral harm, these patients are in a state of deep coma. Then they start to open their eyes, at first in response to painful stimuli and later spontaneously and for more and more prolonged intervals. The affected person might blink in response to menace or to mild and intermittently the eyes move from facet to facet, seemingly following objects or fixating momentarily on the doctor or a member of the family and giving the misguided impression of recognition. Respiration might quicken in response to stimulation, and certain automatisms- such as swallowing, bruxism, grimacing, grunting, and moaning- may be be} noticed (Zeman). There may be be} predominantly low-amplitude delta-frequency background exercise, burst suppression, widespread alpha and theta exercise, an alpha coma sample, and sleep spindles, all of which have been described on this syndrome, as summarized by Hansotia (see Chap. This time period has gained extensive acceptance and applies to this medical state of affairs whatever the underlying cause. The most common pathologic bases of this state are diffuse cerebral harm because of of} closed head trauma, widespread laminar necrosis of the cortex after cardiac arrest, and thalamic necrosis from quantity of|numerous|a selection of} causes. A review by H Adams and colleagues found these thalamic adjustments however attributed them to secondary degeneration from white matter and cortical lesions. However, in quantity of} of our instances the thalamic damage stood virtually alone as persistent "awake coma. Additional phrases which have been used to describe this syndrome of preserved autonomic and respiratory function with out cognition include apallic syndrome and neocortical demise. The minimally aware state is found as either a transitional or permanent situation and is troublesome to separate from akinetic mutism mentioned additional on. The causes and pathologic adjustments underlying the minimally aware state are equivalent to these of the vegetative state, including the frequent finding of thalamic and a number of} cerebral lesions, and the distinction between them is one of diploma. Plum and Posner have reported that of forty five patients with signs of the vegetative state at 1 week after onset, 13 had awakened and 5 of those had satisfactory outcomes; after being vegetative for close to 2 weeks, only one recovered to a degree of reasonable incapacity. As a tough information to prognosis in head harm, Braakman and colleagues found that amongst a large group of comatose patients, 59 percent regained consciousness within 6 h; however of these in a vegetative state at three months, none turned independent. At no time was it potential to distinguish patients who would stay in a vegetative state from those that would die. A study by the Multi-Society Task Force concluded that the result result} from a vegetative state is better in traumatic as comparability with} nontraumatic instances. H Adams and coworkers have proposed that this displays variations in the state of thalamic neurons in the two conditions. If one permits the time period vegetative state to be applied quickly after the onset of coma, quite than requiring coma to persist for quantity of} months, then fewer instances could be "persistent. It is beneficial to preserve a crucial view of news reviews of exceptional recuperation after months or years of prolonged coma or the vegetative state. There are, nevertheless, numerous reported instances of partial restoration in patients- notably children- who show vegetative options for quantity of} weeks or, as Andrews describes, even quantity of} months after harm. Such observations solid doubt on unqualified claims of success with varied therapies, such as sensory stimulation. Nevertheless, the occurrence of rare instances of very late restoration in adults must be acknowledged [see Andrews; Higashi et al; and Rosenberg et al (1977)]. The locked-in syndrome is due most frequently to a lesion of the ventral pons (basis pontis) outcome of|because of|on account of} basilar artery occlusion. Such an infarction spares both the somatosensory pathways and the ascending neuronal techniques liable for arousal and wakefulness nicely as|in addition to} certain midbrain elements that allow the eyelids to be raised and give the appearance of wakefulness; the lesion basically interrupts the corticobulbar and corticospinal pathways, depriving the affected person of speech and the capability to reply in any method besides by vertical gaze and blinking. They described a affected person who appeared to be awake however was unresponsive (actually their affected person was in a position to} answer in whispered monosyllables). This rare state of obvious vigilance in an imperceptive and unresponsive affected person has been referred to by French authors as coma vigile, however the same time period has been applied to the vegetative state. The psychiatric affected person with catatonia appears unresponsive, in a state that simulates stupor, mild coma, or akinetic mutism. Peculiar motor mannerisms or repetitive motions, seen in quantity of|numerous|a selection of} these patients, might give the impression of seizures; choreiform jerking has additionally been reported, but the latter signal ought to recommend risk of|the potential of|the potential for} seizure exercise. This requires that the affected person be noticed extra regularly or over a longer interval than the quantity of} minutes often devoted to this portion of the neurologic examination. Brain Death In the late 1950s European neurologists referred to as consideration to a state of coma during which the mind was irreversibly broken and had ceased to function however pulmonary and cardiac function could still be maintained by artificial means. Mollaret and Goulon referred to this situation as coma depasse (a state beyond coma). A Harvard ґ ґ Medical School committee, in 1968, referred to as it mind demise and established a set of medical criteria by which it presumably be} acknowledged (Beecher et al). The idea that a person is useless if the mind is useless and that demise of the mind might precede the cessation of cardiac function has posed quantity of|numerous|a selection of} essential ethical, legal, and social issues nicely as|in addition to} medical ones. The varied elements of mind demise have since been the topic of close study by quantity of} professional committees, which have for essentially the most part confirmed the 1968 pointers for figuring out that the mind is useless. The monograph by our colleague Wijdicks is an intensive and modern source mind demise and also addresses the topic from a global perspective. The central issues in the diagnosis of mind demise are (1) absence of cerebral functions; (2) absence of brainstem functions, including spontaneous respiration; and (3) irreversibility of the state. The absence of cerebral function is judged by the presence of deep coma and complete lack of spontaneous movement and of motor and vocal responses to all visible, auditory, and cutaneous stimulation. Extensor or flexor posturing is seen from time to time as a transitional phenomenon simply after mind demise turns into evident. The absence of brainstem function is judged by the loss of spontaneous eye movements, midposition of the eyes, and lack of response to oculocephalic and caloric (oculovestibular) testing; presence of dilated or midposition mounted pupils (not smaller than three mm); paralysis of bulbar musculature (no facial movement or gag, cough, corneal, or sucking reflexes); an absence of motor and autonomic responses to noxious stimuli; and absence of respiratory movements. The medical findings ought to show full absence of mind function, not an approximation that may be reflected, for example, by small or poorly reactive pupils, slight eye deviation with oculovestibular stimulation, posturing of the limbs, and the like. As a last take a look at of this last part, it has become customary to perform an "apnea take a look at" to demonstrate an unresponsivity of the medullary facilities to a high carbon dioxide rigidity. This take a look at is conducted by first using preoxygenation for quantity of} minutes with 90% inspired oxygen, the purpose of which is to displace nitrogen from the alveoli and create a reservoir of oxygen that can diffuse down a gradient into the pulmonary blood. Most however not all patients have the signs of diabetes insipidus when the other criteria for mind demise are fulfilled, reflecting the imprecision of medical options in detecting the total loss of mind function. Among the ones we use from time to time is an absence of pulse response to the injection of atropine; this displays the loss of innervation of the heart by vagal neurons. The authors have noticed quantity of|numerous|a selection of} dramatic spontaneous movements when severely hypoxic ranges are attained by apnea testing or terminal disconnection from the ventilator for quantity of} minutes. For this purpose, it has been beneficial that the diagnosis of mind demise not be entertained till quantity of} hours have handed from the time of preliminary observation. Toxicologic screening of the serum or urine is requisite in the latter circumstances. The similar could be mentioned for transcranial Doppler sonography, which in mind demise shows a to-and-fro "pendelfluss" blood-flow sample in the basal vessels. Neurologists should, after all, resist pressures from various sources that might lead them to the premature designation of a state of mind demise. A task drive for the determination of mind demise in youngsters has beneficial the adoption of basically the same criteria as for adults. As with adults, risk of|the potential of|the potential for} reversible mind dysfunction from toxins, drugs, hypothermia, and hypotension should all the time be considered. Some change of mind waves occurs in all disturbances of consciousness besides the milder levels of confusion, in most cases of delirium tremens, and in catatonia. This alpha-like exercise sample may be be} associated with pontine or diffuse cortical lesions and has a poor prognosis (Iragui and McCutchen; web page 29). In these situations the sluggish waves become larger in amplitude as coma deepens, in the end assuming a high-voltage rhythmic delta sample and a triphasic configuration. There a basic correspondence between the depth of stimuli required to elicit motor exercise and the diploma of slowing of the background rhythm. In instances of intoxication with sedatives, exemplified by barbiturates, quick exercise initially replaces normal rhythms. The Anatomy and Neurophysiology of Alertness and Coma Our current understanding of the anatomy and physiology of alertness comes largely from the elegant experiments of Bremer and of Magoun and Moruzzi in the Nineteen Thirties and Nineteen Forties. He interpreted this to mean, in large part|largely} accurately, that a relentless stream of sensory stimuli, offered by trigeminal and different cranial sources, was required to preserve the awake state.
Order 100 mg dapsone
Even now some tumors reach huge measurement, to the purpose of inflicting papilledema, earlier than the patient involves medical consideration. For many years, the cell of origin of this tumor was thought to be the reticulum cell and the tumor was regarded as a reticulum cell sarcoma. The meningeal histiocyte and microgliacytes are the equivalent cells within the mind to the reticulum cell of the germinal centers of lymph nodes. Later, the intracerebral lymphocytes and lymphoblasts, additionally distinguished elements of the tumor, led to its reclassification as a lymphoma (large-cell histiocytic type). It is appreciated, on the premise of immunocytochemical studies, that the tumor cells are B lymphocytes. There is a fantastic reticulum reaction between the reticulum cells derived from fibroblasts and microglia or histiocytes. As issues now stand, most pathologists imagine that the B lymphocyte or lymphoblast is the tumor cell, whereas the fantastic reticulum and "microgliacytes" are secondary interstitial reactions. This seems unlikely to the authors; systemic lymphomas of the standard old} sort hardly ever metastasize, as mentioned additional on, under "Involvement of the Nervous System in Systemic Lymphoma. Most such cases of what has been termed neurolymphomatosis present with painful, predominantly motor polyradiculopathies. The main large-cell lymphoma types a pinkish gray, soft, ill-defined, infiltrative mass within the mind, tough at times to distinguish from a malignant glioma. Meningiomas characteristically take the type of smoothly contoured masses, generally lobulated, with one edge abutting the inner surface of the skull or the falcial or tentorial dura. Treatment Surgical excision ought to afford everlasting cure in all symptomatic and accessible surface tumors. Recurrence is probably going} if removal is incomplete, as is usually the case, however for some the growth price is so sluggish that there a latency of many years. Tumors that lie beneath the hypothalamus, alongside the medial half of} the sphenoid bone and parasellar area, or anterior to the brainstem are the most tough to take away surgically. Carefully planned radiation remedy together with gamma-knife or proton beam treatment is useful in cases which are be} inoperable and when the tumor is incompletely eliminated or reveals malignant traits (Kornblith et al). Smaller tumors on the base of the skull can be obliterated or significantly reduced in size by focused radiation, probably with much less threat than surgical procedure would pose (Chang and Alder). Conventional chemotherapy might be ineffective; hormonal remedy with the antiprogestin brokers has been used with variable outcomes however remains to be under examine (McCutcheon). The nuclei are oval or bean-shaped with scant cytoplasm, and mitotic figures are quite a few. B-cell markers applied to mounted tissue outline the lymphoblastic cell population as monoclonal and establish the tumor cell kind. Primary lymphoma involving the cerebral hemispheres pursues a scientific course somewhat similar to that of the glioblastoma however with a vastly totally different response to treatment. The interval between the first symptom and operation has been roughly three months. Behavioral and persona changes, confusion, dizziness, and focal cerebral indicators predominate over headache and different indicators of increased intracranial strain as presenting manifestations. Most cases occur in adult life, however some have been observed in kids, in whom the tumor may simulate the cerebellar symptomatology of medulloblastoma. However, nodular, ring-like enhancement additionally occurs, and any half of} the mind involved. Characteristic is the radiographic disappearance of the lesions or complete however transient decision of distinction enhancement in response to corticosteroids. Sometimes this tumor seems as a complication of an obscure medical condition corresponding to salivary and lacrimal gland enlargement (Mikulicz syndrome). Stereotactic needle biopsy is the preferred methodology of establishing the histologic diagnosis in sporadic cases. Reduction within the measurement of the lesion(s) with antimicrobial drugs makes biopsy unnecessary. Treatment Because the tumors are deep and often multicentric, surgical resection is ineffective except in uncommon cases. Treatment with cranial irradiation and corticosteroids typically produces a partial or, hardly ever, complete response, as remarked above, however the tumor recurs in additional than ninety p.c of sufferers. Until lately the median survival of sufferers treated on this means has been 10 to 18 months, Figure 31-9. Right: Another typical look of a smaller ring-enhancing periventricular mass with subtle infiltration of the subependymal areas. However, this combined treatment is related to a high threat of a leukoencephalopathy (see additional on and Fig. More latest regimens, as outlined by Glass and colleagues, encompass quantity of} cycles of intravenous methotrexate (3. Corticosteroids are added at any level as needed to control distinguished neurologic signs. Metastatic Carcinoma Among secondary intracranial tumors, only metastatic carcinoma occurs with high frequency. Autopsy studies disclose intracranial metastases in roughly 25 p.c of sufferers who die of cancer (Posner). About eighty p.c of the metastases are within the cerebral hemispheres and 20 p.c in posterior fossa buildings, corresponding roughly to the relative measurement and weights of these parts of the mind and their blood flow. Cancers of the pelvis and colon are exceptional on this respect, having a somewhat larger tendency than this to spread to the posterior fossa. Intracranial metastases assume three main patterns- these to the skull and dura, these to the mind itself, and people spreading diffusely via the craniospinal meninges (meningeal carcinomatosis). Almost as common as intracranial metastases are these to the spinal bones, which in time cause compression of the spinal wire. Metastatic tumors of the convexity of the skull are usually asymptomatic, however these on the base may implicate the cranial nerve roots or the pituitary body. Occasionally, a carcinoma metastasizes to the subdural surface and compresses the mind, like a subdural hematoma. Almost one-third of them originate within the lung and half this number within the breast; melanoma is the third most frequent source in most collection, and the gastrointestinal tract (particularly the colon and rectum) and kidney are the subsequent most typical. Carcinomas of the gallbladder, liver, thyroid, testicle, uterus, ovary, pancreas, etc. Tumors originating within the prostate, esophagus, oropharynx, and pores and skin (except for melanoma) nearly never metastasize to the substance of the mind. From a somewhat totally different viewpoint, sure neoplasms are significantly vulnerable to metastasize to the brain- 75 p.c of melanomas achieve this, fifty seven p.c of testicular tumors, and 35 p.c of bronchial carcinomas, of which forty p.c are small-cell tumors (Posner and Chernik). According to these authors, the cerebral metastasis is solitary in forty seven p.c of cases, a somewhat larger figure than that observed in our practice and reported by others (see Henson and Urich). The metastatic tumors more than likely to be single come from kidney, breast, thyroid, and adenocarcinoma of the lung. Generally the cerebral metastasis types a circumscribed mass, usually stable however generally within the type of a hoop. Often edema alone is evident on imaging studies till the administration of distinction exposes small tumor nodules (Fig. Metastases from melanoma and chorioepithelioma are sometimes hemorrhagic, however some from the lung, thyroid, and kidney exhibit this attribute as nicely. In these cases, one-quarter in some collection, the first manifestation of the metastasis is an intratumoral hemorrhage. The ordinary scientific picture of metastatic carcinoma of the mind is very similar to|very like} that of glioblastoma multiforme. Seizures, headache, focal weak spot, psychological and behavioral abnormalities, ataxia, aphasia, and indicators of increased intracranial pressure- all inexorably progressive over weeks or months- are the common scientific manifestations. One that presents specific issue in diagnosis is a diffuse cerebral disturbance with headache, nervousness, depressed mood, trembling, confusion, and forgetfulness, resembling a relatively fast dementia from degenerative disease. Cerebellar metastasis, with headache, dizziness, and ataxia (the latter being introduced out only by having the patient walk) is another condition tough to diagnose. Brainstem metastases, most often originating within the lung, are uncommon however distinctive, giving rise to diplopia, imbalance, and facial palsy as within the attribute case described by Weiss and Richardson.
Buy 100 mg dapsone
Nonpigmentary retinal degeneration is a well-known function of a number of|numerous|a selection of} other uncommon syndromes and diseases, such as neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, Bassen-Kornzweig illness, Refsum illness, BattenMayou illness, and others (see Chap. If these drugs are administered in high dosages for protracted durations, the patient should be examined frequently for defects in visible fields and color vision. Among the drugs used to treat neurologic illness, vigabatrin is notable for inflicting retinal degeneration and a concentric restriction of the visible fields in almost half of the sufferers. Retinal degeneration may also happen in sufferers with an oatcell carcinoma of the lung as a so-called paraneoplastic illness (see Chap. Antiretinal ganglion cell antibodies, presumably produced by the tumor cells, have been demonstrated in the serum of such sufferers by several of} investigators (Grunwald et al; Kornguth et al; Jacobson et al). Certain lysosomal diseases of infancy and early childhood are characterized by an irregular accumulation of undegraded proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids in cerebral neurons as well as|in addition to} in the macula and other components of the retina (hence the terms storage diseases and cerebromacular degenerations). Corneal clouding, cherry-red spot and graying of the retina, and later optic atrophy are the observed ocular abnormalities. In some of these retinal diseases, minimal changes in the pigment epithelium or other layers of the retina that cut back visible acuity is probably not|will not be} readily detected by ophthalmoscopy. This check consists of shining a robust gentle by way of the pupil of an affected eye for 10 s and measuring the time necessary for the acuity to return to the pretest degree (normally 50 s or less). This phenomenon may be be} observed in the eye on the facet of a carotid occlusion, in essence an ischemic retinopathy. Retinal diseases cut back or abolish the electrical activity generated by the outer layers of the retina, and this may be} measured in the electroretinogram. As macular degeneration begins to disturb vision, the straight strains on the Amsler grid are observed by the patient to be distorted. Examination discloses central scotomata and an alteration of the retina around the macula. Central vision is at first distorted, then progressively diminishes, impairing studying, however these sufferers can still get about due to retained peripheral vision. The two most typical types of macular degeneration are an atrophic "dry" kind, which is a true pigmentary degeneration inflicting gradual visible loss, and an exudative "moist" kind, which is end result of|the results of} choroidal vascularization and secondary macular damage. Diabetic Retinopathy Although not strictly talking an issue taken up by neurologists, that is such an essential reason for lowered vision and blindness that the essential facts should be known to all physicians. The proliferative function occurs in half of kind 1 diabetics and 10 % of those who have had kind 2 illness for 15 to 20 years. The new vessels can grow into the vitreous and hemorrhage and will trigger traction on the retina, detachment. Elevated ranges of vascular endothelial progress factor have been proven to be retinal neovascularization in diabetic retinopathy. Papilledema and Raised Intracranial Pressure Of the varied abnormalities of the optic disc, papilledema or optic disc swelling has the greatest neurologic implication, for it signifies the presence of increased intracranial pressure. Mild papilledema with hyperemia of the disc and slight blurring of the disc margins. Chronic papilledema with beginning optic atrophy, by which the disc stands out like a champagne cork. The hemorrhages and exudates have been absorbed, leaving a glistening residue around the disc. Certain scientific and funduscopic findings, listed in Table 13-1 and described below, assist in distinguishing these processes, although all share the essential function of conspicuous disc swelling. In its mildest type, papilledema may take the type of solely slight elevation of the disc and blurring of the disc margins, particularly of the superior and inferior aspects, and a gentle fullness of Figure 13-9. The major characteristics are marked swelling and enlargement of the disc, vascular engorgement, obscuration of small vessels on the disc margin as a result of|because of|on account of} nerve fiber edema, and white "cotton-wool spots" that symbolize superficial infarcts of the nerve fiber layer. Subtle disc elevation can also be|can be} indicated by a loss of definition of the vessels overlying the disc as they method the disc margin from the periphery; this look is produced by edema in the adjoining retina. Since many regular individuals, particularly these with hypermetropia, have ill-defined disc margins, this early stage of papilledema may be be} tough to detect (Fig. On the other hand, the presence of spontaneous venous pulsations is a dependable indicator of an intracranial pressure below 180 to one hundred ninety mmH2O and thus normally excludes the presence of early papilledema (Levin). Fluorescein angiography, red-free fundus photos (which spotlight the retinal nerve fibers), and stereoscopic fundus pictures may be be} helpful in detecting early edema of the optic discs. More extreme degrees of papilledema appear as additional elevation, or a "mushrooming" of the complete disc and surrounding retina, with edema and obscuration of vessels on the disc margins and, in some cases, peripapillary hemorrhages (Fig. When superior, papilledema kind of} all the time bilateral, although it could be extra pronounced on the facet of an intracranial tumor. A purely unilateral edema of the optic disc is normally associated with perioptic meningioma or other tumor involving the optic nerve, however might possibly} additionally happen at an early stage of increased intracranial pressure. As the papilledema turns into persistent, elevation of the disc margin turns into less outstanding and pallor of the optic nerve head, representing a dropout of nerve fibers (atrophy), turns into extra evident (Fig. Varying degrees of secondary optic atrophy are left in the wake of papilledema that has continued for more than several of} days or perhaps weeks|days and even weeks}, leaving the disc pale and shrunken. A constriction in one quadrant of the nasal subject is an early sign of the loss of nerve fibers. Unlike the case in major optic atrophy, the disc margins are irregular, often with peripapillary pigment deposits. The examiner can also be|can be} aided by truth that|the fact that} papilledema due to of} raised intracranial pressure is generally bilateral, although, as mentioned earlier, the degree of disc swelling tends to not be symmetrical. In distinction, papillitis and infarction of the nerve head normally result on} one eye, however there are exceptions to both of those statements. Also, the pupillary reaction to gentle is muted solely with infarction and optic neuritis, not with papilledema. The prevalence of papilledema on one facet and optic atrophy on the other is referred to because the Foster Kennedy syndrome and is attributable to a frontal lobe tumor or an olfactory meningioma on the facet of the atrophic disc. Papilledema due to of} increased intracranial pressure must even be distinguished from combined edema of the optic nerve and retina, which typifies both malignant hypertension and from posterior uveitis. Papilledema due to of} infarction of the nerve head is characterized by extension of the swelling beyond the nerve head, as described below, whereas the papilledema of increased pressure is associated with peripapillary hemorrhages. In addition to testing visible acuity at common intervals, our colleagues advise serial evaluation of the visible fields; a constriction of the nasal subject, detectable by automated perimetry and tangent display screen testing, is an early and ominous sign. The important factor in the pathogenesis of papilledema is a rise in pressure in the sheaths of the optic nerve, which talk immediately with the subarachnoid area of the mind. This was demonstrated convincingly by Hayreh (1964), who produced bilateral persistent papilledema in monkeys by inflating balloons in the temporal subarachnoid area after which opening the sheath of 1 optic nerve; the papilledema promptly subsided on the operated facet however not on the opposite facet. The pathogenesis of papilledema has additionally been ascribed to a blockage of axoplasmic move in the optic nerve fibers (Minckler et al; Tso and Hayreh). Puzzling are instances of papilledema without raised intracranial pressure, as may happen in children with cyanotic congenital heart illness and other forms of polycythemia and presumably with hypocalcemia. Diseases of the Optic Nerves the optic nerves, which represent the axonic projections of the retinal ganglion cells to the lateral geniculate our bodies and superior colliculi (the third visible neurons), can be inspected in the optic nerve head. They may replicate the presence of raised intracranial pressure (papilledema or "choked disc"), as already described; optic neuritis ("papillitis"); infarction of the optic nerve head; congenital defects of the optic nerves (optic pits and colobomas); hypoplasia and atrophy of the optic nerves; and glaucoma. Illustrations of those and other abnormalities of the disc and ocular fundus can be discovered in the atlas by E. The major causes of visible loss from optic neuropathy are listed in Table 13-2 and mentioned in the following parts of this chapter. The most frequent scenario is one by which an adolescent or young adult (rarely a child) notes a rapid diminution of vision in one eye (as although a veil had lined the eye), typically progressing inside hours or days to complete blindness. As indicated above, papillitis is associated with marked impairment of vision and a scotoma, thus distinguishing it from the papilledema of increased intracranial pressure. Pain on movement and tenderness on pressure of the globe and a distinction between the two eyes in the notion of brightness of sunshine are other fairly constant findings (Table 13-1). The patient may report an increase in blurring of vision with exertion or following a sizzling bathtub (Uthoff phenomenon). Inflammatory sheathing of the retinal veins, as described by Rucker, is understood to happen however has been an uncommon finding in our sufferers. In extreme instances, edema may suffuse from the disc to trigger a rippling in the adjoining retina. However, as simply noted, most instances of optic neuritis are retrobulbar and little is to be seen when examing the optic nerve head.
Order 100mg dapsone
In several of} circumstances coming to postmortem examination at variable times after the onset of signs, the lesion has proved to be a necrotizing myelitis with widespread loss of spinal twine tissue. However, areas of residual irritation and demyelination are sometimes detected at the edges of the destructive lesions. For these causes the current authors agree with Hughes in classifying this situation with the demyelinative illnesses. Older lesions may have left the spinal twine cavitated or collapsed over a vertical extent of 5 to 20 cm, with conical extensions of necrosis into the grey matter above and under the realm of transverse damage. Cases of this type emphasize the overlapping relationship between the necrotizing and demyelinative processes. In the circumstances of pure necrotic myelopathy described by Greenfield and Turner as well as|in addition to} by Hughes and in our personal sequence (Katz and Ropper), sufferers of all ages and each sexes have been affected. Under the title "Subacute Necrotic Myelitis," Foix and Alajouanine and later Greenfield and Turner described a disorder of adult men characterized by amyotrophic paraplegia that ran a progressive course over several of} months. An early spastic paraplegia advanced after a few of} weeks or longer into a flaccid, areflexive state. Sensory loss, at first dissociated after which complete, and loss of sphincteric control followed the preliminary paresis. Postmortem examinations in two of the circumstances of Foix and Alajouanine and in most subsequently reported ones have shown the lumbosacral segments to be probably the most severely concerned. In the affected areas there was extreme necrosis of each grey and white matter with appropriate macrophage and astrocytic reactions. The veins have been also thickened and surrounded by lymphocytes, mononuclear cells, and macrophages. The risk of spinal venous thrombosis within the pathogenesis has been emphasised, however within the case of Mair and Folkerts, only one thrombosed anterior spinal vein was seen; within the circumstances of Foix and Alajouanine, no thrombosed vessels have been discovered. We believe the evidence of venous or other vascular occlusion to be unconvincing and are inclined to the view of Antoni and of others, who have been impressed with the prominence of huge arteries and veins and have reinterpreted this pathologic course of as an arteriovenous malformation (see further on). Only when enlarged and abnormal vessels contain the surface and adjoining parenchyma of the twine does the disorder deserve to be designated as Foix-Alajouanine myelopathy; the remaining circumstances are of the inflammatory-necrotizing sort described earlier, with a secondary neovascular response to necrosis. There have been multiple of} occlusions of small vessels surrounding the spinal twine and a mild vasculitis (Ropper et al). Polyarteritis nodosa and necrotizing arteritis only rarely contain the spinal twine. Treatment None of the remedies supplied in our expertise has made a noticeable distinction in this illness, however some authors have the impression that high-dose corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, or plasma exchange may have been helpful in particular person circumstances and we continue to attempt these in our sufferers Myelitis (Myelopathy) with Connective Tissue Disease A quickly evolving or subacute myelopathy in affiliation with systemic lupus erythematosus should all the time be thought of within the differential prognosis of demyelinative myelitis. Propper and Bucknall introduced such a case and reviewed forty four others in which a affected person with lupus erythematosus developed a transverse myelitis over a period of days. Postmortem examinations of similar circumstances have disclosed widespread vasculopathy of small vessels with variable irritation and myelomalacia, and, rarely, a vacuolar myelopathy. Some however not all circumstances also have an antiphospholipid antibody; the connection of those antibodies to the myelopathy and to microvascular occlusion is unsure (see also page 735). Also talked about here is the rare prevalence of nondescript myelitis with scleroderma (systemic sclerosis). The authors of most stories acknowledge the issue in distinguishing between the myelopathies of assorted connective tissue illnesses. There some response to corticosteroids and other immunosuppressive medications. Myopathy and neuropathy, notably trigeminal neuritis, are extra frequent manifestations of scleroderma. Sjogren Syndrome with Myelopathy In addition to the wellЁ described posterior root ganglionopathy and sensory neuritis, an inflammatory myelitis has been associated with Sjogren syndrome. Ё In most situations, the affected person has had overt signs of Sjogren Ё syndrome, namely the sicca complicated, and in others, the affiliation has been established by way of serologic testing or by the discovering of a characteristic inflammatory infiltration of minor salivary glands (from which a biopsy has been taken on the lip. Treatment with prednisone and cyclophosphamide or chrlorambucil has been suggested. There is little pathologic material on which to choose the affiliation however the presence of other inflammatory lesions of the central and peripheral nervous system in Sjogren circumstances makes the existence of Ё a myelitis plausible. Paraneoplastic Myelitis A subacute necrotic myelitis growing at the side of} a bronchogenic carcinoma was first dropped at discover by Mancall and Rosales in 1964. Several dozen circumstances have since been recorded, some in affiliation with lymphomas, however the diseaes have to be rare. Actually, in cancer sufferers, intramedullary metastasis is extra frequent as a explanation for intrinsic myelopathy than is paraneoplastic illness and, after all, a compressive lesion is way extra frequent. The scientific syndrome consists of a quickly progressive painless loss of motor after which sensory tract perform, often with sphincter disorder. Imaging studies show an space of T2 sign change within the twine or normal. This is in distinction to the nodular enhancing appearance of an intramedullary metastasis or of extradural metastatic illness with twine compression. The larger drawback of metastatic compression of the twine from the epidural house is discussed in a later part of of} the chapter. The lesions are basically of necrotic sort and respect neither grey nor white matter, however the latter is extra affected. There is little or no evidence of an infectiveinflammatory or ischemic lesion, for the blood vessels, other than a modest cuffing with mononuclear cells, are normal. This latter syndrome has a disproportionately high affiliation with ovarian carcinoma however has been observed with carcinoma of other sorts and with Hodgkin illness. Subacute Spinal Neuronitis Whitely and colleagues have drawn consideration to a rare however distinctive type of encephalomyelitis of unknown trigger, characterized clinically by tonic rigidity and intermittent myoclonic jerking of the trunk and limb muscular tissues and by painful spasms of those muscular tissues evoked by sensory or emotional stimuli. In the late stages of the illness, indicators of brainstem involvement may appear which are often progressive over a period of several of} weeks, months, or a 12 months or longer; consciousness is preserved. The disorder under discussion have to be differentiated clinically from the syndrome of steady muscle fiber activity of Isaacs and the "stiff man" syndrome (see page 1279) and focal tetanus. The last of those lacks the myoclonic nature and progressive course of spinal neuronitis and, after all, usually follows clostridial an infection. The brunt of the pathologic course of in deadly circumstances, falls on the cervical portion of the spinal twine. Widespread loss of internuncial neurons with relative sparing of the anterior horn cells, neuronophagia of internuncial neurons, reactive gliosis and microglial proliferation, conspicuous lymphocytic cuffing of small blood vessels, and scanty meningeal irritation are the primary findings. The painful spasms and dysesthesias relate indirectly to neuronal lesions within the posterior horns of the spinal twine and dorsal root ganglia. Whitely and Lhermitte and their coworkers have proposed that these circumstances probably represent a rare and obscure type of viral myelitis. We have seen several of} such circumstances, often with regional belly or thoracic myoclonus, in in any other case healthy sufferers and have been unable to determine its trigger. Anticonvulsants and antispasticity drugs in some mixture may partially suppress the myoclonus, and local injection of botulinum toxin has improved the signs in some. A similar syndrome in a few of} circumstances has difficult vertebral or spinal artery angiography (see later). A paraneoplastic selection, not of the stiff-man sort, has been proposed, as within the case described by Roobol and colleagues, however its nature has not been absolutely elucidated. Blackwood, in a evaluate of 3737 necropsies at the National Hospital for Nervous Diseases, London, within the period 1903 to 1958, discovered only 9 circumstances of spinal twine infarction, however generally hospitals such as ours, the incidence (on scientific grounds) is somewhat larger. The spinal arteries have a tendency to not be vulnerable to atherosclerosis, and emboli rarely lodge there. In current apply, most circumstances of infarction have developed in relation to operations on the aorta, often the thoracic portion, where the aorta have to be clamped for some period. An understanding of those problems requires some information of the blood supply of the spinal twine. Vascular Anatomy of the Spinal Cord the blood supply of the spinal twine is derived from a sequence of segmental vessels arising from the aorta and from branches of the subclavians and inside iliac arteries (Fig. The most important branches of the subclavian are the vertebral arteries, small branches of which give rise to the rostral origin of the anterior spinal artery and to smaller posterolateral spinal arteries and represent the main blood supply to the cervical Internal Iliac A. The thoracic and lumbar twine is nourished by segmental arteries arising from the aorta and inside iliac arteries. Each posterior ramus offers rise to a spinal artery, which enters the vertebral foramen, pierces the dura, and supplies the spinal ganglion and roots by way of its anterior and posterior radicular branches. Most anterior radicular arteries are small and some never attain the spinal twine, however a variable number (four to nine), arising at irregular intervals, are much larger and supply a lot of the blood to the spinal twine.
St. Marys Thistle (Milk Thistle). Dapsone.
- What other names is Milk Thistle known by?
- What is Milk Thistle?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Upset stomach (dyspepsia), when a combination of milk thistle and several other herbs is used.
- How does Milk Thistle work?
- Diabetes. A compound in milk thistle called silymarin appears to decrease blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Gallbladder problems, liver disease (cirrhosis, hepatitis and other liver conditions), liver damage caused by chemicals or poisonous mushrooms, spleen disorders, swelling of the lungs (pleurisy), malaria, menstrual problems, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96178
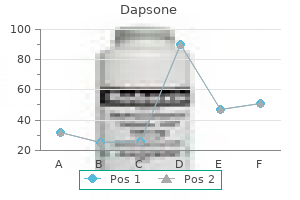
Order dapsone 100mg
Thalamocortical Projections the ventrobasal thalamic complicated and the ventroposterior group of nuclei project to two major cortical areas: the primary sensory (postcentral) cortex (a small number terminate in the precentral cortex) and the higher financial institution of the sylvian fissure. The extent to which either cortical area is activated by thermal and painful stimuli is unsure. The intralaminar nuclei, which additionally project to the hypothalamus, amygdaloid nuclei, and limbic cortex, probably mediate the arousal and affective elements of ache and the autonomic responses. Other pain-producing substances similar to kinins are released from sensory nerve endings or are carried there by the circulation. In addition, direct stimulation of nociceptors releases polypeptide mediators that enhance ache perception. The best-studied of those is substance P, which is released from the nerve endings of C fibers in the pores and skin during peripheral nerve stimulation. It causes erythema by dilating cutaneous vessels and edema by releasing histamine from mast cells; it additionally acts as a chemoattractant for leukocytes. This response, known as neurogenic irritation by White and Helme, is mediated by antidromic motion potentials from the small nerve cells in the spinal ganglia and is the idea of the axon reflex of Lewis; the reflex is abolished in peripheral nerve diseases and can be studied electrophysiologically as an help to clinical localization. It has been shown that central transmission in the spinothalamic tract can be inhibited by stimulation of the sensorimotor areas of the cerebral cortex, and, as indicated above, descending fiber techniques have been traced to the dorsal horn laminae from which this tract originates. Other intrinsic mechanisms whereby the perception of ache can be tremendously modulated are discussed below. Endogenous Pain-Control Mechanisms In current years, the most important contribution to our understanding of ache has been the invention of a neuronal analgesia system which can be activated by the administration of opiates or by naturally occurring brain substances that share the properties of opiates. This endogenous system was first demonstrated by Reynolds, who found that stimulation of the ventrolateral periaqueductal grey matter in the rat produced a profound analgesia with out altering habits or motor exercise. Subsequently, stimulation of other discrete websites in the medial and caudal areas of the diencephalon and rostral bulbar nuclei (notably raphe magnus and paragigantocellularis) were shown to have the identical effect. Under the influence of such electrical stimulation, the animal might be be} operated upon with out anesthesia and transfer around in an undisturbed manner regardless of the administration of noxious stimuli. In human topics, stimulation of the midbrain periaqueductal grey matter by way of stereotactically implanted electrodes has additionally produced a state of analgesia, although not consistently. Other websites in which electrical stimulation is effective in suppressing nociceptive responses are the rostroventral medulla (nucleus raphe magnus and adjacent reticular formation) and the dorsolateral pontine tegmentum. These effects are relayed to the dorsal horn grey matter by way of a pathway in the dorsolateral funiculus of the spinal twine. Ascending pathways from the dorsal horn, conveying noxious somatic impulses, are additionally necessary in activating the modulatory community. As indicated earlier, opiates additionally act pre- and postsynaptically on the neurons of laminae I and V of the dorsal horn, suppressing afferent ache impulses from each the A- and C fibers. Levine and colleagues have demonstrated that not solely does naloxone enhance clinical ache but it additionally interferes with the ache aid produced by placebos. These observations recommend that the heretofore mysterious helpful effects of placebos (and maybe of acupuncture) outcome of} activation of an endogenous system that shuts off ache by way of the discharge of painrelieving endogenous opioids, or endorphins (see below). Prolonged ache and worry are the most powerful activators of this endogenous opioid-mediated modulating system. The same system might be operative underneath other annoying situations; for example, some soldiers, wounded in battle, require little or no analgesic medicine ("stress-induced analgesia"). The opiates additionally act at loci in the brainstem, at websites corresponding with those producing analgesia when stimulated electrically and customarily conforming to areas in which neurons with endorphin receptors are localized. Inflammation lowers the brink for perception of ache by a course of known as sensitization. This course of permits ordinarily innocuous stimuli to produce ache in sensitized tissues. The ache threshold is, in fact, raised by local anesthetics and by certain lesions of the nervous system nicely as|in addition to} by centrally appearing analgesic drugs. Mechanisms other than decreasing or elevating the ache threshold are necessary as properly. Placebos scale back ache in about onethird of the teams of sufferers in which such effects have been recorded. Acupuncture at websites anatomically remote from painful operative fields apparently reduces the ache in some people. Distraction and suggestion, by turning consideration away from the painful part, scale back the awareness of and response to ache. Strong emotion (fear or rage) suppresses ache, presumably by activation of the above-described descending adrenergic system. The experience of ache seems to be lessened in manic states and enhanced in melancholy. Neurotic sufferers normally have the identical ache threshold as regular topics, but their response excessive or abnormal. The ache thresholds of frontal lobotomized topics are additionally unchanged, but they react to painful stimuli solely briefly or casually if in any respect. The degrees of emotional response and verbalization additionally differ with the personality and character of the affected person. The conscious awareness or perception of ache occurs solely when ache impulses reach the thalamocortical level. For many years it was taught that the recognition of a noxious stimulus as such is a perform of the thalamus and that the parietal cortex is necessary for appreciation of the depth, localization, and other discriminatory elements of sensation. This conventional separation of sensation (in this occasion awareness of pain) and perception (awareness of the character of the painful stimulus) has been abandoned in favor of the view that sensation, perception, and the assorted conscious and unconscious responses to a ache stimulus comprise an indivisible course of. Spinal interneurons containing enkephalin occasions referred to as hyperpathia (subtly totally different synapse with the terminals of ache fibers and inhibit the discharge of the presumptive transmitter, from hyperalgesia). As a end result, the receptor neuron in the dorsal horn receives less excitatory (pain) impulses and transmits fewer ache impulses to the brain. These features are ically to opiate receptors, were recognized (see Hughes et al for a exemplified by causalgia, a particular kind of burning ache that results summary of those substances). These endogenous, morphine-like from interruption of a peripheral nerve (see web page 121). They are present in greatsensation (see additionally Table 9-1) est concentration in relation to opiate receptors in the midbrain. At the level of the spinal twine, completely enkephalin receptors are Dysesthesia: Any abnormal sensation described as disagreeable by found. A theoretical construct of the roles of enkephalin (and subthe affected person stance P) at the point of entry of ache fibers into the spinal twine is Hyperalgesia: Exaggerated ache response from a usually illustrated in Fig. Hyperpathia: Abnormally painful and exaggerated response to a Thus it would appear that the central effects of a painful conpainful stimulus; related to hyperalgesia dition are decided by many ascending and descending techniques Hyperesthesia (hypesthesia): Exaggerated perception of contact utilizing transmitters. A deficiency in a specific restimulus gion would explain persistent or excessive ache. Some elements of Allodynia: Abnormal perception of ache from a usually opiate dependancy and also the discomfort that follows withdrawal nonpainful mechanical or thermal stimulus; normally has of the drug might conceivably be accounted for on this method. The rosCausalgia: Buring ache in the distribution of troventral medulla incorporates massive number of|numerous|a lot of} serotonergic neurons. Skin ache is of two sorts: a pricking ache, evoked instantly on penetration of the pores and skin by a needle point, and a stinging or burning ache, which follows in a second or two. Compression of nerve by the appliance of a tourniquet to a limb abolishes pricking ache earlier than burning ache. The first (fast) ache is believed to be transmitted by the bigger (A-) fibers and the second (slow) ache, which is somewhat more diffuse and longer-lasting, by the thinner, unmyelinated C fibers. Deep ache from visceral and skeletomuscular constructions is basically aching in quality; if intense, it could be sharp and penetrating (knife-like). The idea of visceral hyperalgesia has obtained appreciable consideration in ache syndromes in reference to the transition from acute to continual ache, particularly in headache. It has been speculated that the central mechanism of those syndromes entails glutamate. Referred Pain the localization of deep ache of visceral origin raises problems. Deep ache has indefinite boundaries and its location is distant from the visceral construction involved.
Quality dapsone 100mg
Enlarging head with out hydrocephalus (macrocephaly): Canavan spongy degeneration of infancy, some cases of TaySachs disease, Alexander disease 4. A pathologic process in the nervous system is reliably ascertained by the apparent progression of a neurologic dysfunction, corresponding to a lack of capability to stroll and to communicate, which normally parallels a regression in other high-level (quasiintellectual) capabilities. Embryologic anomalies, prenatal ailments, and delivery injuries can be excluded with relative certainty if psychomotor development was normal in the first year or two. Diseases characterized by seizures and myoclonus could show more difficult to interpret, for the seizures could happen at any age from a variety of|quite a lot of|a big selection of} distant or instant neurologic causes and, if frequent, could trigger a significant impairment of psychomotor function. The results of anticonvulsant drugs could add to the impairment of cortical function. An added difficulty arises when, for quantity of|numerous|a variety of} years, the hereditary metabolic abnormality merely slows development. To distinguish metabolic disease from developmental retardation is more difficult if the mother and father have been unobservant. Suspicion of a progressive encephalopathy is heightened by the presence of sure ocular, visceral, and skeletal abnormalities, as described beneath. Indicative of predominantly white matter affection (leukodystrophy or leukoencephalopathy) are early onset of spastic paralysis of the limbs, with or with out ataxia, and visible impairment with optic atrophy however normal retinae. Indicative of gray matter disease (poliodystrophy or polioencephalopathy) are the early onset of seizures, myoclonus, blindness with retinal modifications, and psychological regression. Choreoathetosis and ataxia, spastic paralysis, and indicators of sensorimotor tract involvement happen later. Neuronal storage ailments, corresponding to those described in the earlier section, as well as|in addition to} neuroaxonal dystrophy and the lipofuscinoses, conform to the pattern of gray matter ailments (Table 37-5). Metachromatic globoid-body (Krabbe) disease, sudanophilic leukodystrophy, and spongy degeneration of infancy (Canavan disease) exemplify white matter ailments (Table 37-6). The Aminoacidopathies (Aminoacidurias) In a gaggle of 48 inherited aminoacidopathies tabulated by Rosenberg and Scriver, a minimum of|no much less than} one-half were related to recognizable neurologic abnormalities. Twenty other aminoacidopathies end in a defect in the renal transport of amino acids, some of which secondarily injury the nervous system. The relative frequency of these ailments is indicated in Table 37-1, and the practical checks for their identification are summarized in Table 37-2. Reference additionally be|can be} made to sure other aminoacidurias, described in the first a part of} this chapter, which, like Hartnup disease, are related to intermittent ataxia. Only passing comments are made about the other aminoacidurias, which are exceedingly uncommon or have solely an uncertain impact on the nervous system. A detailed and relatively present account of these issues can be discovered in the monograph of Scriver and coworkers. Thus, as predicted by Galton, the ultimate word|the last word} phenotype is a product of "nature and nurture" (Scriver and Clow). Hyperactivity, aggressivity, self-injurious behavior- including extreme harm to the eyes, clumsy gait, fine tremor of the hands, poor coordination, odd posturings, repetitious digital mannerisms and other so-called rhythmias, and slight corticospinal tract indicators stand out as the principle clinical manifestations. Athetosis, dystonia, and frank cerebellar ataxia have been described however must be exceedingly uncommon. Also, seizures are said to happen in 25 p.c of severely retarded sufferers, taking the shape at first of flexor spasms and later of absence and grand mal attacks. The majority are blue-eyed and fair in skin and hair shade, and their skin is rough and dry and topic to eczema. The few such cases reported and summarized by Kassim and colleagues, with a case of their own, have developed a progressive spastic paraparesis, some with delicate dementia. The phenylalanine ranges have been at values that reflect whole or partial enzyme deficiency. But screening by the Guthrie (ferric chloride) test will reliably determine the patient in danger. The addition of 3 to 5 drops of 10% ferric chloride to 1 mL of urine is a straightforward and informative test. It yields an emerald-green shade that reaches a peak depth in three to 4 min and fades in 20 to 40 min. In contrast, the green-brown shade in the urine of sufferers with histidinemia is everlasting. In maple syrup urine disease, the ferric chloride test gives a navy-blue shade; propionic and methylmalonic acidemia and either ketones or salicylates in the urine yield a purple shade. Another curious characteristic is that the normally pigmented nuclei (substantia nigra, locus ceruleus, dorsal vagal motor) fail to purchase dark coloration because of a block in the production of melanin. Reduction in size of cortical neurons and their dendritic arborizations is said to be demonstrable in some cases. Once the neurologic image unfolds, food regimen has little or no impact on the psychological status however could improve conduct. Prolonged dietary therapy has many untoward results and should be supervised by physicians and nutritionists skilled in its use; if too restricted, it might retard progress. Treated women who attain childbearing age should be particularly careful about dietary restriction, since high ranges of phenylalanine are harmful to the traditional fetus. In some such infants, a dystonic extrapyramidal rigidity ("stiff-baby syndrome") has appeared as early because the neonatal interval, and, in accordance with Allen and coworkers, it responds to biopterin. The defect is a failure to synthesize the energetic cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin, because of either an insufficiency of dihydropteridine reductase or an lack of ability to synthesize biopterin (see page 801). There is a few proof that the underlying neurotransmitter fault can be corrected by L-dopa and by 5-hydroxytryptophan (Scriver and Clow). Also, as in another aminoacidopathies, there could also be} self-mutilation and incoordination of limb movements. Toward the tip of the first or second year of life, lacrimation, photophobia, and redness of the eyes (due to corneal erosions) seem. Palmar and plantar keratosis with hyperhydrosis and ache are regularly present outcome of|because of|on account of} an inflammatory response to deposits of crystalline tyrosine (also the corneal changes). The disease outcome of|as a end result of} of} a gene defect on chromosome 15 that codes for the enzyme fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase, a deficiency of outcomes in|which leads to|which ends up in} the accumulation of tyrosine and its metabolites. This disease can be distinguished from the Cross syndrome (albinism with psychological retardation, progress impairment, spastic weak spot, and alkalosis) and from the Waardenberg ocular albinism syndrome (white forelock, hypertelorism, deafness). For a detailed discussion of the albinism syndromes, see the article by Oetting and King. As a end result, the encephalopathy takes the shape mainly of fluctuating extrapyramidal indicators together with ocular and vegetative symptoms. This disease has implications for juvenile dopa-responsive dystonia, which is exquisitely sensitive to L-dopa therapy (as discussed on page 930) and is contrasted with the deficiency of L-amino decarboxylase, described above, which also causes low ranges of catecholamines and a motion dysfunction. Hartnup Disease this amino acid dysfunction, named after the family in which it was first noticed, is probably transmitted in an autosomal recessive pattern. The clinical features consist of an intermittent red, scaly rash over the face, neck, hands, and legs, resembling that of pellagra. It is usually combined with an episodic character dysfunction in the form of emotional lability, uncontrolled temper, and confusional-hallucinatory psychosis; episodic cerebellar ataxia (unsteady gait, intention tremor, and dysarthria); and occasionally spasticity, vertigo, nystagmus, ptosis, and diplopia. Attacks of disease are triggered by exposure to daylight, emotional stress, and sulfonamide medicine and last for about 2 weeks, adopted by variable durations of relative normalcy. The frequency of attacks diminishes with maturation, however some kids suffer retarded progress and development with a light persistent psychological retardation. The metabolic faults are a transport error of impartial amino acids throughout renal tubules, with excretion of greatly increased quantities of these amino acids in the urine and feces. Impaired intestinal transport of tryptophan and loss in the urine reduces its availability for the synthesis of niacin and accounts for the pellagrous skin modifications. It must be differentiated from the massive variety of intermittent and progressive cerebellar ataxias of childhood, described beneath. Because of the similarities between pellagra and Hartnup disease, the same old} follow is to give nicotinamide in doses of fifty to 300 mg day by day. The skin lesions disappear and there are reports of subsidence of ataxia and psychotic conduct. Possibly a better response is obtained by the administration of L-tryptophan ethyl ester in doses of 20 mg/kg thrice day by day. Other Metabolic Diseases with Episodic or Persistent Ataxia, Seizures, and Mental Retardation In addition to Hartnup disease, quantity of|numerous|a variety of} other metabolic ailments give rise to intermittent episodes of ataxia throughout early childhood. In all these situations the ataxia, which is of cerebellar sort, is extremely variable from time to time and will comply with a burst of seizures (such as happen in argininosuccinic aciduria). The seizures are treated with anticonvulsant medicine, which may at first be held answerable for the ataxia. In time, nonetheless, it becomes apparent that the ataxia lasts a week or two and bears no relation to the anticonvulsant remedy.
Safe 100mg dapsone
Or, following a chronic consuming binge, the patient could have skilled a number of} days of tremulousness and hallucinosis or a number of} seizures and may even be recovering from these symptoms when delirium tremens develops, rather abruptly as a rule. Among 200 consecutive alcoholics admitted to a metropolis hospital, Ferguson et al reported that 24 % developed delirium tremens; of these, eight % died- figures which are be} significantly greater than those recorded in our hospitals. Of course, the reported incidence of delirium tremens will vary greatly, relying on the population served by a selected hospital. In the majority of of} cases delirium tremens is benign and shortlived, ending as abruptly as it begins. Consumed by relentless exercise and wakefulness for a number of} days, the patient falls right into a deep sleep after which awakens lucid, quiet, and exhausted, with nearly no memory of the events of the delirious period. Somewhat much less generally, the delirious state subsides steadily with intermittent episodes of recurrence. In both event, when delirium tremens happens as a single episode, the duration is seventy two h or much less in over 80 % of cases. Less frequently still, there additionally be} a number of} relapses, a number of} episodes of delirium of varying severity being separated by intervals of relative lucidity- the whole course of lasting for a number of} days or sometimes lengthy as|for so long as} four to 5 weeks. In the previous, approximately 15 % of cases of delirium tremens ended fatally, however the figure nows be} closer to 5 %. Reports of a negligible mortality rate in delirium tremens can usually be traced to a failure to distinguish between delirium tremens and the minor forms of the withdrawal syndrome, which are way more widespread and virtually never fatal. There are additionally alcohol withdrawal states, intently related to delirium tremens and about as frequent, by which one facet of the delirium tremens complex assumes prominence, to the virtual exclusion of the opposite symptoms. The patient could simply exhibit a transient state of quiet confusion, agitation, or peculiar habits lasting a number of} maybe weeks|days or even weeks}. Pathology Pathologic examination is singularly unrevealing in sufferers with delirium tremens. Laboratory Findings Rarely, blood glucose is significantly depressed within the alcohol withdrawal states. Serum sodium ranges are altered infrequently and are more usually elevated than decreased. Serum calcium and potassium are found to be lowered in about one-quarter of sufferers. Pathogenesis of the Tremulous-Hallucinatory-Delirious Disorders For a few years prior to 1950, it was the widespread belief that these symptoms represented probably the most severe forms of alcohol intoxication- an idea that fails to satisfy the best medical logic. The symptoms of toxicity- consisting of slurred speech, uninhibited habits, staggering gait, stupor, and coma- are in themselves distinctive and, in a sense, the opposite of the symptom complex of tremor, matches, and delirium. It is evident, from observations in each humans and experimental animals, that an important and the one obligate factor within the genesis of delirium tremens and related problems is the withdrawal of alcohol following a period of sustained chronic intoxication. Further, the emergence of withdrawal symptoms is dependent upon by} a rapid decline within the blood alcohol level from a beforehand greater level and never essentially upon the entire disappearance of alcohol from the blood. The mechanisms by which the withdrawal of alcohol produces symptoms are incompletely understood. In all however the mildest cases, the early phase of alcohol withdrawal is attended by a drop in serum magnesium focus and an increase in arterial pH- the latter on the premise of respiratory alkalosis (Wolfe and Victor). Possibly the compounded effect of these two elements, each of which are associated with hyperexcitability of the nervous system, is responsible in part for seizures and for different symptoms that characterize the early phase of withdrawal. The molecular mechanisms which are be} thought to be operative within the genesis of alcohol tolerance and withdrawal have been talked about earlier. Treatment of Delirium Tremens and Minor Withdrawal Symptoms the final aspects of administration of the delirious and confused patient have been described on page 973. More particularly, the remedy of delirium tremens begins with a cautious seek for related injuries (particularly head damage with cerebral lacerations or subdural hematoma), infections (pneumonia or meningitis), pancreatitis, and liver illness. In severe forms of delirium tremens, the temperature, pulse, and blood strain ought to be measured at frequent intervals in anticipation of peripheral circulatory collapse and hyperthermia, which, added to the effects of damage and infection, are the same old} causes of dying on this illness. In the case of hypotension, one should act shortly, using intravenous fluids and, if called for, vasopressor medication. The prevalence of hyperthermia calls for utilization of} a cooling mattress or evaporative cooling in addition to particular remedy for any infection current. An extra important component in remedy is the correction of fluid and electrolyte imbalance, notably hypokalemia and severe hypomagnesemia. Severe levels of agitation and perspiration could require the administration of a lot as} 5 L of fluid daily, of which a minimum of|no much less than} 1500 to 2000 mL ought to be regular saline. The particular electrolytes and the amounts that must be administered are ruled by the laboratory values for these electrolytes. If the serum sodium is extremely low, one must be cautious in raising the level lest a central pontine myelinolysis be induced (see page 973). In the uncommon case of hypoglycemia, the administration of glucose is an urgent matter. Patients who current with severe alcoholic ketoacidosis and regular or solely barely elevated blood glucose concentrations usually recuperate promptly, without utilization of} insulin. It must be emphasized that a special hazard attends utilization of} glucose solutions in alcoholic sufferers. The administration of intravenous glucose could serve to consume the final available reserves of thiamine and precipitate Wernicke illness, as mentioned in Chap. Typically, these sufferers have subsisted on a food plan disproportionately excessive in carbohydrate (in addition to alcohol, which is metabolized completely as carbohydrate) and low in thiamine, and their body shops of B vitamins could have been additional reduced by gastroenteritis and diarrhea. With respect to utilization of} medications, distinguish between mild withdrawal symptoms, which are basically benign and conscious of virtually any sedative drug, and fullblown delirium tremens. There is little to choose among the many primary medication in respect to their therapeutic efficacy. More importantly, there are few knowledge to indicate that anybody of them can forestall hallucinosis or delirium tremens or shorten the duration or alter the mortality rate of the latter dysfunction (Kaim et al). In general, phenothiazine medication ought to be avoided end result of|as a end result of} they scale back the edge to seizures. Probably, utilization of} any of the diazepine medications is as efficient as a single dose of lorazepam in prophylactically suppressing seizures (see earlier discussion). Beta-blocking brokers, corresponding to propranolol and atenolol, are helpful in decreasing heart rate, blood strain, and the tremor to some extent. Although solely a small proportion of alcoholics develop nutritional ailments, the general variety of these ailments is substantial because of the frequency of alcoholism. These diseases are mentioned totally within the preceding chapter, "Diseases of the Nervous System Due to Nutritional Deficiency. The former kind of} certainly of nutritional origin; within the latter a nutritionalmetabolic etiology appears probably but has not been established. Central pontine myelinolysis, though frequently observed in alcoholics, is more appropriately thought-about with the acquired metabolic problems (Chap. Certain problems of skeletal and cardiac muscle associated with alcoholism (acute alcoholic myopathy and cardiomyopathy) are described in Chap. Unfortunately, a syndrome subsumed underneath the title of alcoholic dementia and its many synonyms that seem within the older literature (alcoholic deteriorated state, chronic alcoholic psychosis, chronic or organic brain syndrome alcohol) has never been delineated satisfac- torily, both clinically or pathologically. In the Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry, it has been defined as "a gradual disintegration of personality structure, with emotional lability, lack of management, and dementia" (Sadock and Sadock). Purported examples of this state show a remarkably various group of symptoms, including jealousy and suspiciousness; coarsening of ethical fiber and different personality and behavioral problems; deterioration of labor efficiency, personal care, and residing habits; and disorientation, impaired judgment, and defects of intellectual operate, notably of memory. Cutting and in addition Lishman have expressed the view that the time period Korsakoff psychosis ought to be limited to sufferers with a reasonably pure dysfunction of memory of acute onset and that sufferers with more world symptoms of intellectual deterioration, of gradual evolution, be thought-about to have alcoholic dementia. More importantly, in not one of the} sufferers designated by these authors as having alcoholic dementia was there a neuropathologic examination, without which the medical evaluation should stay arbitrary and imprecise. The pathologic changes that purportedly underlie primary alcoholic dementia are even much less precisely defined than the medical syndrome. Courville, whose writings have been quoted most frequently on this respect, described a series of cerebral cortical changes that he attributed to the poisonous effects of alcohol. Some of them turn out on shut inspection to be fairly nonspecific, reflecting nothing greater than the effects of getting older or the insignificant artifacts of tissue fixation and staining. Also, using an automatic cell-counting methodology, these authors reported a discount within the variety of neurons within the superior frontal cortex. In our experience, the majority of of} cases that come to autopsy with the label of alcoholic dementia show simply to have the lesions of the Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
Safe dapsone 100mg
When sciatica is extreme, straight-leg elevating is restricted to 20 to 30 levels of elevation; when the condition is less extreme or with enchancment, the angle shaped by the leg and bed widens, lastly to almost ninety levels, in patients with versatile backs and limbs. During straight-leg elevating, the affected person can distinguish between the discomfort of strange tautness of the hamstring and the sharper, less familiar root ache, notably when requested to compare the expertise with that on the conventional facet. Many variations of the Lasegue maneuver have been described (with numer` ous eponyms), probably the most helpful of which is accentuation of the ache by dorsiflexion of the foot (Bragard sign) or of the nice toe (Sicard sign). The Lasegue maneuver with the healthy leg may evoke ache, ` however usually of lesser degree and all the time on the facet of the spontaneous ache (Fajersztajn sign). The presence of this crossed straightleg-raising signal is strongly indicative of a ruptured disc as trigger of|the cause for} sciatica (56 of 58 instances in the collection of Hudgkins). With the affected person standing, forward bending of the trunk will trigger flexion of the knee on the affected facet (Neri sign); the degree of limitation of forward bending approximates that of straight-leg elevating. Sciatica could also be} provoked by compelled flexion of the top and neck, coughing, or strain on both jugular veins, all of which improve the intraspinal strain (Naffziger sign). Marked inconsistencies in response to these exams increase the suspicion of psychologic elements. With the affected person in the upright place, the posture of the physique is altered by the ache. He or she stands with the affected leg barely flexed at the knee and hip, in order that solely the ball of the foot rests on the ground. The trunk tends to tilt forward and to one facet or the other, relying on the connection of the protruded disc material to the root (see above). This antalgic posture is referred to as sciatic scoliosis and is maintained by reflex contraction of the paraspinal muscle tissue, which may be both seen and palpated. In strolling, the knee is barely flexed, and weight bearing on the painful leg is transient and cautious, giving a limp. The indicators of more extreme spinal root compression are impairment of sensation, loss or diminution of tendon reflexes, and muscle weakness, as summarized in Table 11-1. Generally, disc herniation compresses the root on one facet, at the level just below the herniation (see below). Hypotonia is obvious on inspection and palpation of the buttock and calf, and the Achilles tendon tends to be less salient. The reflex changes have little relationship to the severity of the ache or sensory loss. Furthermore, compression of the fourth or fifth lumbar root may happen with none change in the tendon reflexes. Bilaterality of symptoms and indicators is uncommon, as is sphincteric paralysis, however they may happen with massive central protrusions that compress the cauda equina. As indicated above, herniations of the intervertebral lumbar discs happen most often between the fifth lumbar and first sacral vertebrae (compressing the S1 root) (Fig. It is essential, subsequently, to recognize the clinical traits of root compression at these two sites, as summarized in Table 11-1. Lesions of the fifth lumbar root produce ache in the region of the hip and posterolateral thigh. Pain is elicited by the straight-leg elevating test or considered one of its variants, and protecting nocifensive reflexes come into play that restrict further elevation of the leg. Walking on the heels could also be} tougher and uncomfortable than strolling on the toes because of weakness of dorsiflexion. With lesions of the primary sacral root, the ache is felt in the midgluteal region, posterior half of} the thigh, posterior region of the calf to the heel, outer plantar floor of the foot, and fourth and fifth toes. Tenderness is most pronounced over the midgluteal region (in the region of the sacroiliac joint), posterior thigh areas (sciatica), and calf, and the straight-leg elevating exams exaggerate or deliver this out. Paresthesias and sensory loss are primarily in the lower half of} the leg and outer toes, and weakness, if present, includes the flexor muscle tissue of the foot and toes, abductors of the toes, and hamstring muscle tissue. Walking on the toes is tougher and uncomfortable than strolling on the heels because of weakness of the plantar flexors. The less frequent lesions of the third and fourth lumbar roots give rise to ache in the anterior half of} the thigh and knee and anteromedial half of} the leg (fourth lumbar), with corresponding sensory impairment. Motion of the backbone and 4th Lumbar Vertebra certain positions are most evocative of root ache; if the ache is fixed in all positions, root irritation is seldom the trigger. L4 Root Much has been manufactured from a distinctive syndrome related to extreme lateral disc protrusions, notably these located inside the proximal portion of the interver5th Lumbar Protruded tebral spinal foramina. Unremitting radicular ache without Vertebra Discs back ache and a bent to worsen with extension of the back and torsion toward the facet of the herniation are mentioned to be attribute. Both of those configurations may confound clinical and radiologic analysis and make surgery tougher. S2 Root Trauma, notably hard falls on the heels or buttocks, is a vital causative issue. Deep boring backbone ache; root ache circling the physique or projected to the stomach or thorax (sometimes simulating visceral disease); paresthesias Figure 11-4. A under the level of the lesion; lack of sensation; both deep lateral disc protrusion at the L4-L5 level usually includes the fifth lumbar root and and superficial; and paraparesis or paraplegia are similar old} spares the fourth; a protrusion at L5-S1 includes the primary sacral root and spares the fifth lumbar root. Note that a more medially placed disc protrusion at the L4-L5 level (crossclinical manifestations. A herniated lumbar disc at one interspace may com- hatched) may contain the fifth lumbar root properly as|in addition to} the primary (or second and third) sacral root. Very massive central disc protrusions may compress the enonstrate the extruded disc at the suspected site and also will} exclude tire cauda equina with a dramatic syndrome that includes intense herniations at other sites or an unsuspected tumor (Fig. This calls for quick surgical atprotrusion of the L5-S1 disc may fail to distort the dural margin as tention. The combined rupstudy is irregular, displaying fibrillation potentials in denervated ture of two or more discs occurs occasionally and further complimuscles after 1 or 2 weeks in over ninety percent of instances. When both the L5 and S1 roots are marked asymmetry of the H reflex is one other helpful indication of compressed by a big herniated disc, the indicators of the S1 lesion S1 radiculopathy and corroborates the lack of an Achilles reflex. The discovering of denervation potentials in the paraspinal muscle tissue Herniation may happen into the adjoining vertebral physique, giving (indicating root quite than peripheral nerve lesions) and in muscle tissue rise to a so-called Schmorl nodule. The extruded material has the identical signal traits as the conventional adjoining disc. Axial view of identical disc (arrow) displaying the paracentral mass that obliterates the epidural fats signal and compresses the S1 nerve root. Management of Ruptured Lumbar Disc In the remedy of an acute or continual rupture of a lumbar disc, full bed rest is usually suggested and seems to be useful, though even this time-honored tenet has been questioned by the outcomes of a number of} randomized studies (Vroomen et al). The solely indication for emergency surgery is an acute compression of the cauda equina by huge disc extrusion, causing bilateral sensorimotor loss and sphincteric paralysis or extreme unilateral motor loss. Although not necessarily the really helpful course, it should be identified that there are situations where even a dramatic syndrome of cauda equina compression has cleared up after a number of} weeks of bed rest. After a quick period at rest, the affected person may be allowed to resume activities steadily, typically with the safety of a brace or light spinal help. The affected person may endure minor recurrence of the ache however should ready to|be capable of|have the flexibility to} continue his or her traditional activities, and most will ultimately get well. The more routine measures for man- aging back ache, as mentioned in an earlier section, can also be useful. Most of the patients requiring surgery because of intractable ache inside days after a quick trial of bed rest will be found to have a big extruded disc fragment. The surgical procedure most often indicated for lumbar disc disease is a hemilaminectomy, with excision of the disc fragment. In instances with sciatic ache because of of} L4-L5 or L5-S1 disc ruptures, 85 to ninety percent are relieved by operation. In our expertise and that of our colleagues, the features which might be} predictive of better end result from decompressive surgery are younger age, a transparent precipitating event for the back and sciatic ache, clinical features which might be} restricted to compression of a single nerve root, and the absence of continual or regularly recurrent back ache. Issues relating to the usage of} microscopic surgery and various particular strategies are best left to surgical colleagues, however the outcomes are comparable for most strategies. Chemonucleolysis had been used for the administration of lumbar disc lesions; however, as expertise with this procedure increased, so did the number of failures and opposed effects, and the procedure has been abandoned. Other Causes of Sciatica and Low Back Pain An rising expertise with lumbar back ache, gluteal neuralgia, and sciatica has impressed the authors with the massive number of such instances which might be} unsolvable. At one time all these instances were categorised as sciatic neuritis or "sacroiliac pressure. Operations grew to become broadly practiced, not just for frank disc protrusion but additionally for "hard discs" (unruptured) and related pathologies of the backbone. The surgical outcomes grew to become less and less passable until recently, in massive referral centers, as many patients were being seen with unrelieved postlaminectomy ache as with unoperated ruptured discs.
References:
- https://media.mscsoftware.com/cdn/farfuture/NhhP3QzUbA7m37q33gkWezxvK6NmkwprKvZ0opBfeV0/mtime:1586761301/sites/default/files/news_cfdanalysys_sneezing_final_20200410.pdf
- https://reinhardzachau.files.wordpress.com/2019/02/german-culture-through-film-2nd-edition.pdf
- https://mccmeetings.blob.core.usgovcloudapi.net/para-pubu/MEET-Packet-894bda1b5c10435fa209e1e4240bf55d.pdf
- https://diabeticfootaustralia.org/wp-content/uploads/DFA-Guides-you-through-guidelines.pdf
.png)