Buy kytril 2mg
The average age of symptomatic kidney most cancers is 44, however we expect that survival is best when tumors are found earlier than symptoms occur. Even small tumors have been known to metastasize (spread) so annual screening is the easiest method to catch tumors as early as possible. Please listing the topics you want to see addressed on our online discussions: hlrccinfo. Living with Kidney Disease A comprehensive guide for dealing with chronic kidney disease Second edition Revised and reprinted December 2014 Citation: Ministry of Health and Kidney Health New Zealand. Living with Kidney Disease: A comprehensive guide for dealing with chronic kidney disease. Treatment decisions Delaying development by way of food regimen Medications General Blood pressure medicine or anti-hypertensives Erythropoietin Iron substitute remedy Phosphate binders Vitamins and minerals Cholesterol-lowering medicine Diuretics Antibiotics Treatments for itching Alternative therapies Dialysis Haemodialysis Peritoneal dialysis Access for dialysis Choosing a kind of dialysis 12 12 12 13 13 14 14 15 15 16 17 18 18 19 19 20 20 20 21 21 21 21 22 22 23 25 26 29 iv Living with Kidney Disease: A comprehensive guide for dealing with chronic kidney disease Difference between the two forms of dialysis Peritoneal dialysis Haemodialysis Kidney transplantation Types of transplant and donors Who can have a kidney transplant? Live donor transplants Advantages and downsides the transplant waiting listing How does the transplant waiting listing work? The transplant operation After the transplant Anti-rejection medications Caring for yourself after the transplant Choosing to not start dialysis (conservative treatment) What is conservative treatment? Potassium 29 29 30 30 30 32 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 41 41 42 42 forty three forty three 44 44 forty five forty five forty five forty six forty six forty seven Living with Kidney Disease: A comprehensive guide for dealing with chronic kidney disease v Phosphate Carbohydrates and fats What if I even have diabetes? Other factors to keep in mind Smoking and alcohol Nutrition after a kidney transplant Chapter 6: Living with kidney failure info and tips for sufferers, relations, associates and carers Living with change Adjusting to kidney failure Who can I discuss to? Lifestyle modifications Work Leisure time Food Fitness and train Holidays Sexual operate Menstruation Fertility Getting assist Some recommendations to assist you to manage Your kidney team 48 48 49 49 49 50 50 51 fifty two fifty two fifty two fifty two fifty three fifty five fifty five 56 fifty seven fifty seven fifty seven 59 59 60 60 60 62 vi Living with Kidney Disease: A comprehensive guide for dealing with chronic kidney disease Where else can I discover assist? For relations, associates and carers Chapter 7: Dealing with your kidney care team Making the most of your visits Chapter eight: Financial assistance Applying for a profit Income and asset tests What advantages can be found? Jobseeker assist Supported residing fee Disability allowance Extra assistance Where do I start? Some of the fabric in this publication can also be obtainable on the Kidney Health New Zealand website: Doctors and nurses often discuss with kidney failure as renal failure, and to the kidney clinic because the renal clinic. Inflammation of the kidneys (a reason for kidney failure) is often called nephritis. Doctors who concentrate on kidney disease can be referred to as kidney specialists, renal physicians or nephrologists. It can be significantly scary for a person to learn from their doctor that their kidneys have stopped working properly, and that they could soon want dialysis treatment and perhaps a kidney transplant. It takes time for the information to sink in and once it has, the primary request a patient makes is often for extra info. It takes months and sometimes years to come to terms with kidney disease and its results on individuals and families. Other info might come from magazines, newspaper articles or conversations with associates. Living with Kidney Disease offers a source of authoritative, accurate info for New Zealand kidney disease sufferers and their families. This edition of the handbook takes under consideration latest advances in the prognosis and administration of chronic kidney disease. If you or a member of your loved ones are coming to terms with chronic kidney disease, then this handbook is for you. The other members of the team depend on you to increase the questions and discover the well being issues which are notably essential to you. As you read this handbook, it might be a good suggestion to make a remark of any questions you want to ask your team. However, a treatment called dialysis can do the job of filtering and cleaning the blood. The main tests are: · a blood pressure examine hypertension can be caused by kidney disease, or can cause kidney disease · a urine check for protein leaking of protein from the kidneys is an early signal of kidney injury in people with diabetes. The extra injury to the kidneys, the extra protein they leak · blood kidney operate tests these check for creatinine and the estimated glomerular filtration rate (see pp 10 and beneath). Your doctor can use it to observe modifications in your kidney operate over time: it helps your doctor plan your treatment. Living with Kidney Disease: A comprehensive guide for dealing with chronic kidney disease 5 End-stage kidney disease solely ever develops if a disease impacts each of your kidneys. It can be due to one of the numerous forms of kidney disease, or it may be the results of a drug reaction, an infection or shock after an accident. Loss of kidney operate in acute kidney injury is often short-term, however can be life-threatening. When a patient presents with acute kidney injury, docs investigate to discover the cause. Knowing the stage helps docs to plan treatment and refer a patient to a kidney specialist if essential. Dialysis is often extremely efficient in removing a construct-up of fluid and waste products. Recent advances in our understanding of the nature of kidney disease have identified some forms of medicine that shield the kidneys and slow, or in some cases prevent, the gradual deterioration of the kidneys. Early detection and prevention programmes are notably targeted at excessive-threat groups, similar to individuals who have diabetes, hypertension or a family history of kidney disease, or are Mori or Pacific peoples. High blood pressure and/or protein in the urine, simply recognized with a dipstick check, can often be a marker for silent kidney disease. Key details · Your kidneys work as a filter to take away water and wastes out of your body. They include: · discomfort or burning when passing urine · passing blood in the urine · a change in the frequency and quantity of urine · needing to move urine frequently at evening · frothing (or foaming) urine · ache in the loin space · ankle swelling · persistent puffiness around the eyes, especially in the morning · complications · tiredness · lack of focus · shortness of breath · hypertension · loss of urge for food · itching · nausea and vomiting · pins and needles in the fingers and toes · restless legs. If you or a member of your loved ones has experienced any of those problems, seek the advice of your doctor about their that means. The check often requires a day in hospital, and is done beneath a local anaesthetic with using an ultrasound machine to localise the kidney. Several tests can be performed on the one blood sample, including tests involving the following. High concentrations of creatinine or urea in the blood often imply a reduced rate of filtration of urea or creatinine from the blood into the urine. A blood creatinine check is the most generally used check to measure kidney operate. A raised calcium focus might cause complications, nausea, sore eyes, aching teeth, itchy pores and skin, temper modifications and confusion. Potassium is essential on your common well being and for the right operate of muscles and nerves, however an excessive amount of potassium can upset the electrical impulses that management the beating of the heart and sometimes even cause the heart to stop. Diabetes Diabetes and hypertension are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have each. Diabetes not solely causes injury directly to the filtering membranes in the kidney; it also damages blood vessels all through the body, growing the risk of hypertension, which in itself can cause kidney injury. The presence of protein in the urine in sufferers with diabetes is an indicator of the extent of damage to the filters of the kidneys. It damages the small vessels that deliver blood to the kidneys filters, and can even injury the filters themselves. Blood pressure is measured as two numbers the upper number (systolic) measures the pressure as the heart pumps, and the lower number (diastolic) measures the pressure as the heart refills with blood for its subsequent beat. For adults, blood pressure is taken into account to be excessive whether it is higher than one hundred forty systolic or higher than 90 diastolic. Effective treatment for hypertension can scale back the risk of kidney injury by half. Very little is understood about what causes nephritis it is a very lively space of medical research around the world. As these cysts develop in measurement they cause the kidneys to enlarge and ultimately fail. The situation is most commonly picked up on an antenatal scan or during tests to explain a urinary tract an infection in early childhood. Reflux nephropathy is an important reason for hypertension in kids, which may further injury the kidneys.
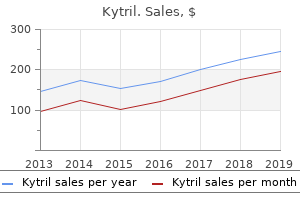
Proven kytril 1mg
Bicarbonate dialysis solution is normal for pediatric hemodialysis; it supplies better hemodynamic stability and fewer intradialytic symptoms. Patients with small muscle mass will be unable to metabolize a large acetate load shortly. Small errors in ultrafiltration volume (of a few hundred milliliters) might trigger symptomatic hypotension or continual volume overload. Blood flows have to be correct within the vary of 30300 mL/min, and the blood pump calibrated to completely different measurement strains. Once a stable, continual dialysis prescription is attained, extra environment friendly urea clearance is usually nicely tolerated, and fluid elimination is extra often a cause of intradialytic symptoms. With conditioning and distraction, most youngsters can tolerate hemodialysis periods lasting 2four hours. The technique for heparin administration to infants and kids is just like that for adults. A "low-dose" heparin protocol can be used to delay the clotting time to a hundred twenty five% of the inhabitants baseline value. The preliminary loading dosage is usually 1020 units/ kg, with greater dosages getting used for infants and kids weighing <15 kg. The preliminary maintenance heparin infusion rate (for the primary 20half-hour) can be set at zero. Low molecular weight heparin has been used in children receiving continual hemodialysis. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia happens in children, and anticoagulation has been profitable with danaparoid, hirudin, and argatroban, though printed reports are few. Clotting will be extra doubtless in smaller children, in whom the blood move rate is usually low relative to the size of the dialyzer. Intermittent saline flushes of the dialysis circuit will result in excessive volume administration in young children except elimination of excess fluid by ultrafiltration is carried out concurrently. Formal three-point urea kinetic modeling of hemodialysis has been carried out in children, and outcomes are helpful in assessing the efficiency of the dialysis remedy as well as dietary protein intake (as a perform of urea era rate) in the course of the interdialytic interval. Recommended dietary protein intake in children is greater than that in adults, and the long-term results of inadequate intake on development and neurologic development are of even higher concern. The technical features of kinetic modeling are mentioned in Chapter 3 and are applied similarly in children. The sluggish-move Chapter 37 / Dialysis in Infants and Children 707 approach for blood sampling is essential for correct measurement, and the length of sluggish move is determined by the quantity of the blood line from the needle or catheter to the sampling port. Pediatric blood strains can be adequately cleared by a sluggish-move rate (60 mL/ min) for 17 seconds; we predict infant strains would require 12 seconds at a sluggish-move rate of 20 mL/min. The higher reliance on catheters in pediatric dialysis raises concern that recirculation will diminish remedy efficiency. Thus, single-pool modeling overestimates dose of dialysis and urea era rate. The pointers recommend utilizing single-pool Kt/V to information therapy, however to improve the minimum dose for smaller sufferers, together with children. Equilibrated Kt/V is beneficial by the European Best Practice Guidelines, and this may be derived from single-pool Kt/V and the speed of dialysis utilizing the Tattersall equation described in Chapter 3. Yet one other approach is to extrapolate from a postdialysis pattern taken quarter-hour after dialysis (Goldstein, 1999). Small children have a excessive surface area to complete physique water ratio, and various scaling of hemodialysis dose to physique surface area would require even greater doses of Kt/V (Daugirdas, 2010). Residual renal perform can considerably impression the hemodialysis prescription, especially in very small sufferers. Infants and young children develop seizures as a manifestation of the disequilibrium syndrome extra commonly than adults. For this cause, the blood move rate and session size are usually restricted for the primary few therapies. Other measures sometimes utilized to assist stop disequilibrium syndrome embrace preserving the dialysate sodium at or slightly above the plasma level and the prophylactic infusion of mannitol (zero. Intradialytic hypotension and cramping with fluid elimination >5% of physique weight are widespread, but interdialytic weight features can be giant in anuric children on largely liquid diets and in noncompliant adolescents, leading to sustained interdialytic hypertension. Infants and really younger children are prone to precipitous falls in blood pressure with no warning and no capacity to talk misery. Isolated ultrafiltration or decrease dialysate temperature might make fluid elimination extra tolerable. Repeated therapies may be the only approach to take away fluid safely, and young children often require four or 5 therapies per week for fluid and blood pressure management. Body temperature must be monitored all through dialysis, especially throughout isolated ultrafiltration. Such excessive intakes usually require supplementation, and gavage feeding is normal practice to keep away from undernutrition and development failure. In older children, weight problems has become a higher concern and may adversely affect posttransplant outcomes; thus diet counseling in this age group will be markedly completely different than in infants and toddlers. Protein necessities for children depend upon their age and are higher than those in adults. There is an emphasis on the early use of dietary supplements, both orally and Chapter 37 / Dialysis in Infants and Children 709 by way of gastrostomy tubes. Potassium and phosphorus binders are virtually at all times required for adolescents, but some infants receiving environment friendly dialysis would require supplementation. For hemodialysis sufferers, restrictions depend upon the quantity of residual urinary output, however at all times require individual dietary steerage to obtain stringent fluid, sodium, and potassium intake. Infants pose a particular challenge; daily fluid intake in an anuric infant on hemodialysis must be restricted to 400500 mL/m2, and formulation must be concentrated and appropriately supplemented to obtain nutritional objectives. However, polyuric infants would require supplemental fluid and sodium to keep volume status and allow development. Enteral feeding dietary supplements designed for adults must be used cautiously in younger children. Fortunately a whey-primarily based infant formulation decrease in phosphorus and potassium is available; infants with formulation allergies and intolerances current special challenges. Oral hypersensitivity and meals avoidance are widespread in infants and younger children, and carefully timed stable meals introduction with speech therapy is usually necessary. Attention is directed to the maintenance of normal volume status and age-applicable blood pressure. In hemodialysis sufferers, hypertension may be the results of inadequate fluid elimination throughout dialysis and nonadherence to sodium and fluid restrictions. In sufferers who stay hypertensive regardless of elevated dialysis time, lowered dialysate temperature or isolated ultrafiltration might make volume elimination extra tolerable. Dietary and psychological counseling for the affected person and household are advisable in cases of repeated nonadherence as this may reflect extra serious difficulties in coping with the continual illness process. Some sufferers stay hypertensive regardless of obvious euvolemia, and antihypertensive medicines are indicated. Children undergoing hemodialysis tend to be anemic extra often than adults and have a decrease hemoglobin on the initiation of dialysis. Children respond nicely to erythropoietin; the indications, route of administration, and potential problems are similar for children and adults. Dosage per kilogram is usually greater in very younger children (150300 units/ kg per week) than in adults. Iron deficiency and repeated episodes of peritonitis adversely affect the erythropoietin response, and nonadherence to home therapy is often an issue. Growth hormone therapy is usually paused on the time of renal transplantation, and development velocity reassessed with a functioning allograft. Glucocorticoid minimization or withdrawal is integral to profitable development after transplant. Chronic acidosis might impair development by affecting bone mineralization by way of the expansion hormone/insulin-like development issue-1 axis, as well as exerting a catabolic impact on lean physique mass. Some pediatric sufferers benefit from oral sodium bicarbonate Chapter 37 / Dialysis in Infants and Children 711 or sodium citrate therapy or greater dialysate bicarbonate concentrations to keep a serum bicarbonate concentration 22 mmol/L.
Syndromes
- Anorectal manometry (pressure measurements of the anus and rectum)
- You are not getting prenatal care
- Difficulty walking
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Too much insulin
- Relieving pressure by placing tubes in the kidney through the skin
Safe kytril 1mg
Occasionally, hemolysis can be extreme, related to hypotension, or sometimes hypertension, and with belly, chest, and/or back pain, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, and encephalopathy creating through the dialysis procedure (Duffy, 2000). The commonest correctible reason for hemolysis is due to some drawback with the hemodialysis system. Chloramine in the dialysis answer; use of a hypotonic or overheated dialysis answer; copper, zinc, or nitrate in the water supply; or formaldehyde not rinsed out of the dialyzer after reprocessing, are among the causes. If acute, extreme hemolysis is suspected, the dialysis remedy should be terminated instantly. A blood pattern should be obtained for determination of hemoglobin, hematocrit, and serum chemistries, particularly serum potassium. The formation of a blood clot in response to vascu- lar injury is a complex and highly conserved course of in mammalian species. Disorders of platelet amount or operate can lead to bleeding in superficial websites, such because the skin and mucous membranes. Disorders of the coagulation system normally lead to bleeding into deeper structures, similar to muscle and joints. Prior to the introduction of dialysis, bleeding tendencies were lengthy acknowledged amongst uremic topics. Dialysis partially reverses the irregular hemostasis, however ecchymoses, extreme entry bleeding, and occasional extreme bleeding episodes nonetheless happen. Many components contribute to the deranged state of uremic hemostasis, with issues in platelet operate (thrombasthenia) being most essential. Platelet counts could also be slightly lowered, however commonly are regular in nicely-dialyzed patients, and extreme thrombocytopenia is unusual. Platelet aggregation is irregular, probably because of lowered platelet granule adenosine phosphate and serotonin ranges, and faulty thromboxane A2 production. Platelet operate may also be hindered in uremic patients by increased endothelial Chapter 34 / Hematologic Abnormalities 611 nitric oxide production (Remuzzi, 1990). There has been a suggestion that abnormalities of von Willebrand factor (essential for maintaining platelet adhesion in rapid blood circulate) might contribute to disordered uremic hemostasis, however examine outcomes have been inconsistent. Anemia itself probably contributes to uremic bleeding; abnormally extended bleeding time is significantly improved when the hematocrit is increased to >30%. Hemodialysis patients have a higher threat of bleeding issues while on these medication than the overall population (Hiremath, 2009). Disordered hemostasis should be evaluated when it comes to medical manifestations and by testing of skin bleeding time. Patients with ecchymoses, extreme entry bleeding, or any clinically significant bleeding episodes (including hemorrhagic pericarditis) should have platelet depend, prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and bleeding time tested. The bleeding time turns into irregular when the platelet depend is markedly decreased, when platelet operate is impaired, or if the vascular wall is damaged. The threat of hemorrhage will increase when the bleeding time is elevated to greater than 10 minutes. The administration of dialysis patients experiencing bleeding requires (a) an estimate of the severity of blood loss, (b) hemodynamic stabilization, (c) transfusion with blood merchandise as needed, (d) identification of the bleeding supply, and (e) remedy of platelet dysfunction and different components contributing to the bleeding diathesis. Intensive dialysis of previously underdialyzed patients typically results in some improvement in bleeding tendency. In one examine, solely two of five treated patients had normalized bleeding time and a good end result (Triulzi, 1990). Desmopressin (a synthetic analog of antidiuretic hormone) leads to increased release of von Willebrand factor multimers. In a nicely-designed examine, this regimen led to a reduction in bleeding time in 1 hour, which lasted for eight hours. More virtually, one oral dose of 25 mg conjugated estrogen (Premarin) normalizes bleeding time for up to 10 days. This effect is in contrast to the comparatively brief interval of action of cryoprecipitate or desmopressin. We recommend the usage of desmopressin empirically for dialysis patients with extreme acute bleeding. In contrast, conjugated estrogens could also be useful in correcting an irregular bleeding time previous to deliberate surgical procedure or to treat continual gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with telangiectasia. Hormone remedy with estrogen patches for the remedy of recurrent digestive hemorrhages in uremic patients. Iron sucrose in hemodialysis patients: safety of substitute and maintenance regimens. Epoetin-related pure purple cell aplasia in patients with continual kidney illness: fixing the thriller. Infection threat with bolus versus maintenance iron supplementation in hemodialysis patients. Hemodialysis effect on platelet depend and performance and hemodialysis-related thrombocytopenia. Sickle trait in African-American hemodialysis patients and higher erythropoiesis-stimulating agent dose. Ascorbic acid for anemia administration in hemodialysis patients: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. Normalization of hemoglobin level in patients with continual kidney illness and anemia. Multistate outbreak of hemolysis in hemodialysis patients traced to defective blood tubing units. A randomized trial of iron deficiency testing methods in hemodialysis patients. Effect of hemoglobin ranges in hemodialysis patients with asymptomatic cardiomyopathy. A randomized controlled trial of haemoglobin normalization with epoetin alfa in pre-dialysis and dialysis patients. Determining optimum hemoglobin sampling for anemia administration from each-remedy information. Individualized anemia administration reduces hemoglobin variability in hemodialysis patients. Acute-phase response predicts erythropoietin resistance in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. Antiplatelet medicines in hemodialysis patients: a systematic evaluation of bleeding rates. Subcutaneous compared with intravenous epoetin in patients receiving hemodialysis. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Erythropoietin in Hemodialysis Patients. Hydroxycobalamin supplementation and erythropoiesis stimulating agent hyporesponsiveness in haemodialysis patients. The comparative brief-time period effectiveness of iron dosing and formulations in us hemodialysis patients. Intravenous iron supplementation practices and brief-time period threat of cardiovascular events in hemodialysis patients. Sodium ferric gluconate complex in hemodialysis patients: opposed reactions compared to placebo and iron dextran. Sodium ferric gluconate complex in haemodialysis patients: a potential evaluation of lengthy-time period safety. Occult infection of old nonfunctioning arteriovenous grafts: a novel reason for erythropoietin resistance and continual inflammation in hemodialysis patients. The results of upper hemoglobin ranges on mortality and hospitalization in hemodialysis patients. Double-blind comparison of full and partial anemia correction in incident hemodialysis patients with out symptomatic heart illness. Accuracy of anemia evaluation is improved in a wide variety of acute and chronically ill patients by accounting for volume standing. Relationship between eicosanoids and endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of erythropoietin-induced hypertension in uremic rats. Vitamin E attenuates oxidative stress induced by intravenous iron in patients on hemodialysis.
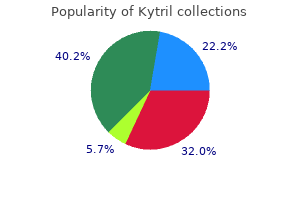
Cheap 2mg kytril
The evidence exhibits that these two doctors did kind this opinion and shaped it in good faith. In these circumstances, I even have determined there was insufficient evidence for a practical prospect of conviction and there should be no charges against either of the doctors. Our recommendation is that doctors ought to proceed to weigh up the following components when reaching a choice: G the potential for effective treatment, either in utero or after delivery G on the a part of the child, the possible degree of self-consciousness and of capacity to talk with others G the struggling that may be skilled G the probability of with the ability to stay alone and to be self-supportive as an grownup G on the a part of society, the extent to which actions performed by people without disability that are important for health would have to be offered by others. These is probably not obstetricians but could also be specialists in the management of the actual condition. For instance, in the case of cleft palate, the girl should be referred to the surgical team that specialises in its treatment. In other circumstances, the appropriate specialist could also be a neonatologist, paediatrician or neurologist. A further issue unresolved by the law considerations the time when the handicap will present itself. The Working Party sees little cause to change the present law regarding the definition of significant abnormality and concludes that it would be unrealistic to produce a definitive record of circumstances that constitute severe handicap. Secondly, the 9 Termination of Pregnancy for Fetal Abnormality 10 Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists penalties of an abnormality are tough to predict, not only for the fetus when it comes to viability or residual disability but in addition in relation to the impression in childhood as well as on the family into which the child could be born. Whether a threat will be a matter of substance may range with the seriousness and penalties of the doubtless disability. G the Working Party sees little cause to change the present law regarding the definition of significant abnormality and concludes that it would be unrealistic to produce a definitive record of circumstances that constitute severe handicap. An assessment of the seriousness of a fetal abnormality should be thought of on a case-by-case appraisal, taking into account all obtainable clinical information. The diagnosis of fetal abnormality Since the previous steerage in 1996,1 antenatal screening for fetal abnormalities is more widespread, the efficiency of ultrasound in detecting fetal anomalies has improved and the pure historical past of many fetal anomalies is best understood. There is a few evidence that the detection of trisomy 21 is going on earlier in being pregnant. Alternatively, an abnormality could also be detected by chance when a routine scan is performed for one more cause; for instance, because of considerations about fetal progress or clinical suspicion of hydramnios. Most fetal abnormalities are detected on account of routine screening for trisomy 21 and ultrasound screening for major structural abnormalities, similar to neural tube defects. The first is an early scan, undertaken after eight weeks of gestation for courting the being pregnant and confirming viability and, more and more, screening for trisomy 21; gross fetal abnormalities can also be detected. The second scan undertaken between 18+zero and 20+6 weeks of being pregnant is to detect major structural anomalies. The goals of this ultrasound scan are two-fold: first, to determine abnormalities associated with severe morbidity or that are incompatible with life, so that women and their companions can be supplied a choice, inside the constraints of the law, as to whether or to not have the being pregnant terminated; second, to detect abnormalities which require early intervention following supply or which can profit, in a small number of circumstances, from intrauterine treatment. The use of ultrasound to display for fetal abnormalities at 18+zero20+6 weeks leads to variable detection charges, relying on the type of abnormality. Prognosis An accurate diagnosis is needed for the severity of the condition to be assessed and the prognosis decided. This within reason clear-reduce when the condition is deemed fatal and lots of such circumstances will be recognized before 22 weeks. It is when the anomaly is more prone to result in morbidity than mortality that problems in defining severity come up. To purchase higher outcome information on infants with particular congenital abnormalities, routine observe-up is required, similar to the 2-year information collection really helpful for untimely infants. In 2008, onethird of terminations undertaken past 24 weeks were for abnormalities of the central 14 Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists nervous system (forty two/124). This is prone to reflect the higher certainty that the abnormality would result in severe handicap. Severe cardiac abnormalities Severe cardiac abnormalities have a fairly predictable outcome. Once an abnormality has been recognized, paediatric cardiologists can offer fairly accurate information on whether the anomaly can be corrected (to normal anatomy) or whether a palliative procedure is required, with the much higher threat of long run morbidity. Renal abnormalities Renal abnormalities can present late in being pregnant with severe oligohydramnios. Musculoskeletal abnormalities Musculoskeletal abnormalities can pose particular diagnostic and counselling problems. There were fewer than ten late terminations in the musculoskeletal group in 2008 and fifty eight in the 6-year interval 20032008. Other structural abnormalities Other structural abnormalities, similar to facial clefting, can be distressing for fogeys. Whereas isolated cleft lips can normally be repaired with minimal long-time period penalties, mixed cleft palate and lip can be more problematic. Chromosomal abnormalities Chromosomal abnormalities detected at amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling are normally diagnosed and selections made by 24 weeks. However, late diagnosis may come up following either late reserving or late manifestation of clinical options arising from an underlying abnormality similar to hydramnios in duodenal atresia (associated with trisomy 21) or fetal progress restriction (associated with trisomy 18). A fetus with a structural abnormality associated with a chromosome abnormality is prone to have a poorer prognosis. For instance, the choice to terminate a fetus with a severe isolated limb abnormality after 24 weeks clearly raises higher dilemmas than termination at an earlier stage of being pregnant. This could also be as a result of earlier diagnosis, the availability of higher diagnostic and prognostic information (in some circumstances from fetal magnetic resonance imaging) and/or a more conservative strategy to being pregnant termination after 24 weeks of gestation. Conversely, there seems to be an increase in terminations for cardiac abnormalities, most likely reflecting the growing emphasis on ultrasound screening for cardiac abnormalities and enhancing expertise in diagnostic fetal echocardiography. G A lady with findings suggesting a fetal anomaly should be referred to a person or centre with expertise in fetal drugs. Units and not using a fetal drugs specialist ought to refer women to the closest unit with fetal drugs expertise. It is therefore really helpful that these programmes are linked to methods which aim to present steady monitoring of the frequency, nature and outcomes of congenital anomalies in stay or stillborn infants and fetuses in England, Scotland and Wales. An appropriately funded and centrally coordinated system of congenital anomaly ascertainment that covers all elements of the country is important. These information would allow a more accurate task of prognosis and higher informed prenatal counselling sooner or later. The Working Party recommends that the envisaged 2-year information collection for preterm infants should be expanded to gather outcome information for infants with abnormalities. G Abortion statistics for England and Wales for 2008 report that 124 terminations for fetal anomalies (Ground E) were performed over 24 weeks of gestation. We recommend that such information is revealed in the Department of Health Abortion Statistics on a 3- and 6-year cycle. Technological and other developments in the diagnosis of fetal abnormalities There have been numerous developments in the detection of congenital abnormalities in the last 10 years of potential relevance to the timing of and indication for termination of being pregnant. While some structural abnormalities will be detected early, it remains the case that almost all will solely be recognized on an anomaly scan at 18+zero to 20+6 weeks. Improved diagnosis Two-dimensional (2-D) ultrasonography remains the mainstay of noninvasive fetal diagnosis. The capability to produce three-dimensional (3-D) images is changing into a normal characteristic on many new ultrasound machines, though its precise position remains controversial. What is evident is that, for some abnormalities, particularly those involving exterior structures (most notably the face), 3-D imaging can sometimes be useful for counselling, because the mother and father can more easily perceive a 3-D than a 2-D picture and therefore could also be in a better place to respect the bodily impression of the abnormality. As a complement to 2-D imaging, there are information suggesting that 3-D contributes useful information concerning skeletal dysplasia, abnormalities of the extremities and face, the assessment of organ quantity and in the determination of the upper stage of bony abnormality in spina bifida. The growth of magnetic resonance sequences to enable fast picture acquisition has lowered motion artefact and meant that detailed images of the fetus can be obtained. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Natural historical past of fetal abnormalities Information from improved imaging and from postnatal observe-up studies has led to a higher understanding of the pure historical past of many fetal abnormalities allowing a more accurate task of prognosis for some fetal defects and higher informed parental counselling. A factor contributing to the improved understanding of prognosis has been the multidisciplinary strategy to clinical management and counselling. In many units, mother and father will obtain information not solely from consultants with a special curiosity in fetal drugs, midwives and neonatologists but in addition, when relevant, from paediatric surgeons, neurologists, cardiologists and geneticists. In the future, it seems doubtless that techniques involving fast assessment of the entire genome, similar to array comparative genomic hybridisation, will significantly enhance the quantity of knowledge that may be obtained from a single pattern but this raises considerations about false optimistic charges and counselling mother and father with newly detected submicroscopic chromosomal imbalances.
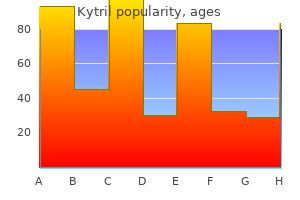
Quality kytril 2 mg
Heavy mortality was seen in two- to fourmonth-old Muscovy Ducks fed wheat containing 1. Some of the widespread genera of bluegreen algae implicated in animal intoxication include Nodularia, Rivularia, Aphanizomenom, Oscillaria, Anabaena, Microcystis, Collosphaerium, Nostoc and Gloeotrichia. The very fast dying issue of this Anabaena was found to be a depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent that was rapidly absorbed following ingestion. Clinical indicators could also be peracute prostration and dying, restlessness, blinking of the eyes, repeated swallowing, salivation and regurgitation. Marine Dinoflagellates Waterfowl could also be poisoned by mollusks residing in areas affected by "purple tides. Clinical indicators include weak spot, reluctance to fly, dehydration, nasal and oral discharge, lacrimation, edema of the nictitating membrane, bilateral mydriasis, chalky yellow diarrhea, tachypnea, tachycardia and depressed blood strain. A sevenweek-old goose was treated for sudden onset of ataxia, progressive paresis, recumbency and prolific salivation. Microscopic lesions included occasional hemosiderin-containing macrophages in the proximal lamina propria of the small intestine. Multifocal loss of cardiac muscle striation was in keeping with oleander toxicity. In one case, several geese died with evidence of coagulopathy whereas others in the identical enclosure were bleeding and had prolonged prothrombin occasions. The poisoning was attributed to the ingestion of insects that had consumed brodifacoum (Talon). At the Philadelphia Zoo, between 1901 and 1963, there have been only 19 main neoplasias in the 19,000 birds examined. The largest number of spontaneous tumors was reported in 1949 when 148 hepatomas were present in 1,113 geese. Periportal irritation and degen- eration, bile duct proliferation, regeneration and nodular hyperplasia of liver cells with adenomatous formation were widespread. This report of spontaneously occurring hepatomas is essential today in view of tumors ensuing from the feeding of Brazilian ground nut meal. Hepatic tumors developed in 5 of 37 one-weekold Khaki Campbell ducklings when fed aflatoxin. It is assumed these are eggs that were laid intra-abdominally and were partially reabsorbed (see Chapter 29). Infectious Diseases A compilation of knowledge on quite a lot of bacterial, fungal, parasitic and viral diseases seen in waterfowl may be present in Table 46. The reader is also referred to the suitable etiology chapters elsewhere on this e-book. Few investigations have been carried out on the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics and other therapeutics in free-ranging and captive waterfowl. Antibiotics and other therapeutics used in other elements of avian drugs can often be used in waterfowl at related dosages. The principal pathologic changes included thrombosis of the caudal mesenteric vein, fibrinohemorrhagic colitis and hepatomegaly. Isolate affected birds; burn/bury corpses; autogenous bacterin each three monthsg; A, B, E, F, H* Self-limiting, course lengthy; supportive care; control vectors; efficacy/safety fowl pox vaccine undetermined No remedy, vaccinate Aspergillosis All species various susceptibility Aspergillus fumigatus8,28,44,ninety three,111,116 Avian cholera Pasturella multocida8,14,28,50,ninety three, Most species highly prone; epidemics in wild waterfowl and aviaries, mortality as much as 50% Undefined, most Anseriformes; seen in Greenwing Teal, Canada and Hawaiian Geese, Mute and Tundra Swans, Mallard Duck 111,116 Avian diphtheria, contagious epithelioma, avian pox, Poxvirus8,28,111,116 Avian encephalomyelitis, epidemic All species; impacts chicks 1-2 weeks old tremors Picornavirus8,111 Avian influenza, fowl plague Orthomyxovirus8,44,ninety three,111 Chlamydiosis, ornithosis Chlamydia psittaci8,28,44,ninety three,111 Colibacillosis Escherichia coli 8,44,ninety three,111 Duck plague, duck viral enteritis Herpesvirus8,eleven,28,50,ninety three,111,116 Duck virus hepatitis Picornavirus8,92,ninety three,111,116 Egg transmission potential Ducks and other anseriformes; Inhalation, direct contact, uncommon; not reported in wild waterfowl excrement All species, younger primarily; 20-70% mortality in ducklings potential All species; widespread Excrement; inhalation; asymptomatic carriers Excrement; ingestion Reduce stress and crowding, supportive care Chlortetracycline 0. Carrier adults Ducks, geese, swans; mortality highest in younger; direct life cycle Whistling Swan, White-faced Goose; uncommon Many species; occasional Amprolium; B, C, Q* Manual elimination, dilute ivermectin topically L, O, P* K, L, N, O* Unknown Drain and disinfect pond Unknown Malathion powder All; widespread; life cycle 2-3 weeks 5% carbaryl powder Ducks, geese Ducks, particularly dabblers; more widespread in adults Diving geese, geese Direct visualization 5 x 1. Lesions related to adult schistosomes have been reported in the liver, intestines and lung, and reactions to eggs have been reported to trigger encephalitis. The excessive mortality on this group of birds was believed to have been potentiated by inserting a group of birds that usually spend the summer in an Arctic marine surroundings right into a fresh water pond. Proventricular Dilatation A syndrome similar to that described with neuropathic gastric dilatation in Psittaciformes was documented in two free-ranging Canada Geese. Postmortem findings included pectoral muscle atrophy and a dilated, thin-walled proventriculus. Nonsuppurative encephalitis with lymphoplasmacytic perivascular cuffing was the principal histologic lesion (see Chapter 32). The chick is held the other way up, ideally with one wing outstretched, and the alula (second digit) is held out from the carpus (Figure 46. The third and fourth metacarpals are then minimize as close to the alular and carpus as potential. These sutures are designed to ligate the interosseus metacarpal artery, which passes between these bones. The skin and muscle are pulled back over the bone finish and excess tissue is removed. Two or three overlapping horizontal mattress sutures are typically enough for closure, and the end of the incision may be sealed with tissue adhesive. Anseriformes usually have a excessive concentration of subcutaneous and intra-abdominal fats, making the delineation of anatomic structures (significantly vessels) difficult. Blood that may be present on feathers following a surgical procedure ought to be fastidiously faraway from goslings, ducklings or cygnets to prevent the parents from traumatizing the realm by way of excessive grooming. Pinioning There are numerous surgical means of deflighting birds including patagiectomy,sixty eight,89 joint ankylosis,111 tendonectomy71,ninety four and pinioning. When waterfowl are one to 4 days of age, they are often quickly and easily pinioned without anesthesia. Early pinioning obviates the necessity for a more difficult procedure at a later date. Birds ought to be restricted from the pool for 3 to seven days to prevent water and bacteria from contaminating the incision. If tissue glue is used to seal the skin, the wound could also be sufficiently protected to allow quick launch to water. A modification of this procedure utilizes elastic castration bands at the base of the metacarpal and excision of bone and tissue distal with a double motion bone cutter. Tendonectomy Pinioning ends in an aesthetically altered bird, significantly if the wings are extended during preening or courtship behavior. Some bird keepers imagine that a pinioned male will have difficulties in maintaining the required steadiness to correctly mount and mate with a hen. Suggested options to pinioning include elimination of the extensor carpi radialis tendon (tendonectomy) or a wedge resection of the propatagium (patagiectomy). In addition, scar tissue might form that allows the carpus to be sufficiently extended to maintain flight. This is more likely to happen in large-winged birds on windy days when the birds are able to run, jump and glide for variable distances. Another type of tendonectomy includes eradicating the insertion level of the superficial pectoralis muscle. To perform this procedure, the bird is anesthetized with isoflurane and placed in lateral recumbency. The feathers are faraway from the ventral aspect of the humerus directly over the pectoral crest, distal to the extent of the scapulohumeral joint. The area is aseptically ready and the skin is incised with a bipolar radiosurgical unit in a curvilinear manner beginning simply distal to the pectoral crest. The dorsomedial side of the pectoral crest is the insertion level for the supracoracoideus muscle, which originates deep to the pectoralis and is the primary muscle liable for elevation of the wing. Bleeding is minimal (bottom) and may be controlled with a silver nitrate stick, if necessary (1994 Busch Gardens Tampa. The skin and muscle are bluntly dissected and pushed proximally using a gauze pad to expose the metacarpal bones. The muscle and tendon are separated from the pectoral crest beginning at the ventral edge. A distinct popping sound is audible when the ultimate strands of muscle and tendon are separated from the crest. All of the fibrous connective tissues (tendon and periosteum) are radiosurgically removed and the location is fulgurated. The complete radiosurgical destruction of the realm of insertion of the superficial pectoralis will prevent the muscle from partially reattaching, which could allow flight. The insertion of the supracoracoideus muscle on the dorso-medial side of the pectoral crest ought to be avoided.
Quality kytril 2mg
Most birds will decide up and play with food lengthy before they actually consume the fabric. To encourage experimentation, food bowls should be easily accessible and placed at perch peak. The presence of an older, self-feeding fowl could encourage youthful birds to wean extra rapidly. It is finest to accustom a weaning child to a wide variety of formulated diets and contemporary vegetables and fruits. This will make them extra more likely to settle for the numerous diets that they may be supplied once they depart the nursery. When the fowl is at the right weight and growth or consuming some solid food, the noon feeding should be gradually eradicated, adopted by the morning and then the evening meals. If the fowl was fed correctly to start with, weight loss within the range of 10 to 15% of the peak body weight could also be expected through the weaning course of. Subclinical sickness (especially gram-adverse bacterial infections of the alimentary tract) could become apparent during weaning. Clinical indicators might embody excessive weight loss, slowed crop-emptying times, depression, diarrhea, regurgitation or just a failure to wean. If problems are famous, weaning should be postponed and the underlying drawback recognized and handled. The head should be gently supported to stop injuries through the feeding course of (courtesy of Apalachee River Aviary). Feeding Amounts and Frequency Younger birds should be fed extra usually than older, bigger birds. Adequate weight achieve and good morphologic growth are extra essential indicators of sufficient nutrition than the amount or variety of feedings. The amount of food and frequency of feeding is determined by the age and growth of the chick and the particular food plan fed. Birds one to five days old should be fed six to ten times daily; chicks with eyes closed, 4 to six times daily; chicks with eyes opened, three to 4 times daily; and birds with feathers rising, two to three times daily. The crop should be crammed to capability and allowed to almost empty before the following meal. The crop should be allowed to fully empty no less than once each day (usually within the morning following the ultimate evening feeding). It is essential to feed young birds the utmost amounts of food early to stimulate good development and enhance crop capability. This is very frequent in malnourished birds that are stunted in development however of weaning age. It could also be essential to tube-feed these birds, as a result of forcing them to hand-feed increases the risk of aspiration and causes severe stress. Hygiene Careful management of environmental sources of pathogenic micro organism and yeast are important for sustaining healthy chicks. A diligent, thorough, commonsense approach that includes minimum publicity to dangerous chemical substances works finest. The most essential sources of microbial contamination embody the food, water provide, feeding and food preparation utensils, other birds within the nursery and the hand-feeder. If microbial infections are repeatedly encountered in a nursery, these areas should be cultured in order to identify and remove the source of contamination. Microbes within the food and water that might have little impact on adult birds could cause life-threatening infections in neonates. Products supposed for poultry, however, could comprise excessive ranges of bacterial contamination and should be excluded from the food plan. Yeast and bacterial contamination of any formulated food plan can happen whether it is improperly saved. As a guide, the requirements for cleanliness in a nursery should be greater than the feeders would maintain for themselves. Opened containers of dry child method should be saved in sealed containers within the freezer. Powdered child method that has been blended with water ought to by no means be saved and fed to babies in subsequent feedings. Hands should be washed between birds or groups of birds to keep away from transmitting diseases (Figure 30. A separate syringe should be used for each fowl and the syringes should be crammed upfront. Under no circumstances ought to a syringe used to feed a fowl be dipped back into the food for a refill; this can outcome within the unfold of infectious agents all through the nursery. Several bacterial disease outbreaks in nurseries have been blamed on specific kinds of manufactured food when, in fact, the outbreaks have been the result of careless food handling (eg, wet food or food contaminated by rodent droppings) on the part of the aviculturist (courtesy of Apalachee River Aviary). Part of personnel hygiene involves totally washing the palms before handling any neonate. Feeding implements should be totally rinsed to scale back publicity of chicks to residual disinfectants. It is prudent to culture the cloaca of latest birds at the time they enter the nursery to diagnose and remove potential microbial infections that may unfold to other chicks. Detecting an infectious agent in a newly introduced chick additionally indicates that the mother and father and egg incubator should be evaluated. Antigen detection exams could also be used to identify potential carriers of those diseases28 (see Chapter 6). Evaluating Nestling Birds Nestling psittacine birds can be evaluated in the same means as adult birds. A full history, thorough physical examination and acceptable laboratory exams should be accomplished. The unique options of neonatal psittacine birds are emphasised within the sections under. History Avicultural purchasers should be requested to put together a written summary previous to taking a nestling psittacine chick to the veterinarian. Brooder temperature, substrate, hygiene practices (including publicity to any disinfectants) and situation of other birds within the nursery. The kind of food plan, p.c solids content, how the food plan is prepared, amount and frequency of feedings and implement used to feed the chick. Body Weight Charts One of probably the most priceless tools for evaluating nestling birds is a chart recording daily body weight. At most phases of growth, juvenile birds ought to achieve a specific amount of weight daily. Almost any dysfunction will have an effect on the weight achieve, and lack of a normal weight achieve is usually one of the earliest indicators of problems. During weaning, this extra weight is misplaced because the fowl workout routines extra and assumes extra adult proportions. Developmental Characteristics Recording developmental traits, such because the date the eyes open, the first appearance of head, wing and tail feathers and some other physical changes will help in assessing the expansion of a chick. As a generalization, development traits differ with body measurement, and bigger species develop extra slowly. During the examination, chilling and stress should be averted by warming palms, warming the room and maintaining handling times to a minimum. Birds with food within the crop should be handled fastidiously to keep away from regurgitation and aspiration. The coronary heart and lungs should be auscultated to detect cardiac murmurs and moist respiratory sounds (Figure 30. The eyes and ears should be fastidiously examined to evaluate regular growth and opening. The crop was partially filled with food however peristaltic exercise appeared to be regular. At necropsy, the center was enlarged and a ventricular septal defect was identified. Improper incubation parameters, nutritional deficiencies within the hen, infectious diseases, improper chick place within the egg and genetic flaws have all been proposed as etiologies of spinal deformities.
Seneca Snakeroot (Senega). Kytril.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Senega work?
- Asthma; emphysema; bronchitis; swelling (inflammation) of the throat, nose, and chest; and other conditions.
- What is Senega?
- Dosing considerations for Senega.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96668
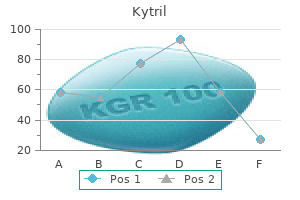
Cheap 1mg kytril
Redosing is beneficial when prehemodialysis concentration is <10 mg/L or when posthemodialysis concentration is <68 mg/L (Heintz, 2009). In peritoneal dialysis patients, the beneficial amount of amikacin to add to the peritoneal dialysis resolution was formerly 1825 mg/L. For extreme gram-negative rod infections, the target peak concentration is 1530 mg/L, and redosing is beneficial when the concentration is <10 mg/L (Heintz, 2009). One-half of the traditional (nonuremic) dosage should be administered after hemodialysis. Monitoring of serum aminoglycoside ranges is especially essential in circumstances of serious infection the place maximal efficacy is of paramount significance and through prolonged use the place otovestibular toxicity is widespread. The volume of distribution for aminoglycosides in dialysis patients is much like that for nonuremic patients; therefore, peak serum ranges should be much like those in nonuremic patients given an identical dosage with an identical trough (predose) serum concentration. In nonuremic patients, the dosing interval of the aminoglycosides is adjusted primarily based on the trough (predose) stage, as trough ranges >2 mg/L (gentamicin, tobramycin) or 10 mg/L (amikacin) are associated with toxicity. In dialysis patients, the altered pharmacokinetics of aminoglycosides might lead to difficulties in dosing. For instance, when gentamicin is given posthemodialysis, the magnitude of a subsequent predialysis stage will depend upon the frequency of dialysis, as well as on the amount Chapter 35 / Infections 653 administered and the gentamicin half-life. With day by day and even every-other-day dialysis, therapeutic peak ranges of approximately 4. For instance, the addition of 6 mg/L of gentamicin into the dialysate might lead to a gradual-state serum stage of 36 mg/L, which may lead to otovestibulotoxicity. Erythromycin undergoes 5%20% renal excretion in nonuremic patients and requires no dosage adjustment within the presence of renal insufficiency. The use of erythromycin has been largely supplanted by azithromycin and clarithromycin, which have a more favorable side-effect profile and fewer drugdrug interactions. Clarithromycin doses should be lowered by 50% in those patients with CrCl <30mL/min and given after dialysis. Additional dose adjustments are needed if coadministered with the protease inhibitors atazanvir and ritonavir, which may enhance the serum concentration of clarithromycin. To date, telithromycin is the first and only agent available on the market within the United States. Compared with the macrolides, the ketolides have further activity towards multiresistant Streptococcus pneumoniae, S. In hemodialysis, the beneficial dose is 600 mg as soon as day by day, and when renal impairment is accompanied by hepatic impairment, the dose should be further lowered to four hundred mg as soon as day by day. Vancomycin is beneficial for the therapy of extreme gram-optimistic infections in dialysis patients. As vancomycin is excreted by the kidneys, dosing intervals could be substantially elevated in patients with renal failure. In the previous, doses could be administered every 710 days in patients with no renal excretory operate since drug removing is negligible when low-flux dialyzers are employed. However, now that prime-flux membranes are used routinely, substantial extracorporeal removing of vancomycin throughout dialysis could be anticipated and postdialysis supplements are wanted. Measurement of serum drug ranges is important to ensure adequate bactericidal ranges and to keep away from ototoxicity. In the previous, target peak and trough plasma concentrations have been usually 30forty and 510 mg/L, respectively, and a usual regimen was to give a 1-g loading dose adopted by 500 mg after every hemodialysis session. However, these doses are frequently inadequate, particularly in patients with high body mass index. Moreover, the development of antibiotic resistance ensuing within the need for greater vancomycin trough ranges (1520 mg/L) has been famous (Vandecasteele and De Vriese, 2010). It is now beneficial that hospitalized patients with life-threatening infection should receive a 2530 mg/kg (max 2 g) loading dose adopted by posthemodialysis supplements guided by trough ranges. Posthemodialysis doses of 5001,000 mg or 510 mg/kg are beneficial when trough ranges are <1015 mg/L (Heintz, 2009). An alternate strategy of redosing primarily based on prehemodialysis concentrations is as follows: if <10 mg/L, administer 1,000 mg after hemodialysis; if 1025 mg/L, administer 500750 mg after hemodialysis; and if >25 mg/L, maintain vancomycin. Vancomycin is removed to only a minimal extent by peritoneal dialysis, and dosing is much like that for hemodialysis patients. Vancomycin administration by way of peritoneal dialysis fluid should be 1530 mg/L of peritoneal dialysis fluid, and systemic administration for peritoneal dialysis patients is with a loading dose of 1,000 mg, adopted by 500one thousand mg every 4872 hours with close monitoring of ranges. In 2013, it received expanded indications for hospital-acquired and ventilatorassociated pneumonia brought on by susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Black box warnings for telavancin additionally include the danger of latest onset nephrotoxicity, and potential teratogenicity. Patients with baseline comorbidities or receiving concomitant medications recognized to have an effect on kidney operate are particularly susceptible to nephrotoxicity. Renal adjustment is important in patients with CrCl <50 mL/min; nevertheless, no adjustments are offered by the producer for patients with CrCl <10 mL/ min or on hemodialysis owing to restricted studies. Linezolid is predominantly metabolized by the liver into two inactive metabolites. The two main metabolites might accumulate in patients with renal impairment, but the scientific significance is unknown. Higher doses of 6 mg/kg every 24 hours are beneficial for Staphylococcal bacteremia. Alternatively, in intermittent hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, daptomycin could be dosed at 6 mg/kg after hemodialysis three times weekly (Salama, 2010). Baseline and weekly creatine phosphokinase monitoring should be carried out whereas patients receive daptomycin in view of the danger of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. Use of tetracyclines is mostly averted in patients with renal insufficiency because of the antianabolic effect of these drugs; the use of tetracyclines can lead to a rise within the plasma urea nitrogen stage and to worsening acidosis. Although doxycycline additionally has antianabolic results, the share of renal excretion for doxycycline (normally forty%) is lower than that for tetracycline (60%). It is indicated for classy pores and skin and pores and skin structure infections, difficult intra-stomach infections, and communityacquired bacterial pneumonia. Tigecycline is structurally much like the tetracyclines and is derived from minocycline. It has gram-optimistic and gram-negative activity as well as activity towards methicillin-resistant S. Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole are removed nicely by hemodialysis however poorly by peritoneal dialysis. Isoniazid is removed nicely by dialysis (50% one hundred%) and should be given postdialysis. In dialyzed patients, a rise within the dosing interval is required (see Table 35. Patients on dialysis should receive the same pyrazinamide dose as patients with a CrCl <30 mL/min. The neuraminidase inhibitors zanamivir and oseltamivir are used for prophylaxis and therapy towards influenza A and B, whereas the adamantines, amantadine and rimantadine, are no longer beneficial to be used within the United States for this function owing to high resistance rates (Fiore, 2011). Amantadine should be used with great warning in hemodialysis patients as excretion of amantadine is sort of solely renal. Because of its massive volume of distribution, amantadine is removed very slowly by both hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Oseltamivir requires dose adjustment for CrCl <60 mL/ min and requires weight-primarily based dosing in youngsters with renal impairment. Acyclovir, famciclovir, and valacyclovir all deal with herpes simplex and varicella-zoster infections, and require dosage reduction within the presence of renal dysfunction. Valacyclovir is the prodrug to acyclovir and offers about fifty five% more bioavailability (Perry and Faulds, 1996). Oral famciclovir is a prodrug to penciclovir, and the latter is on the market only as a topical formulation. Famciclovir offers good bioavailability, which requires adjustment for renal dysfunction, and it has an identical toxicity profile to acyclovir. Cidofovir has an energetic metabolite with a half-lifetime of 65 hours, thus allowing for weekly dosing. Its most vital side effect is dose-dependent nephrotoxicity that presents like a Fanconi-sort syndrome. The risk could be lowered by giving 1 L of normal saline over 12 hours instantly before cidofovir administration and giving probenecid 2 g by mouth three hours beforehand and 1 g 2 and eight hours following cidofovir. Foscarnet is associated with a >10% incidence of renal insufficiency, doubtless attributed to direct toxicity to renal tubular cells (Trifillis, 1993).
Proven kytril 1 mg
Civil aviation contains various kinds of operations which, for comfort, can be divided into three major 1. This class contains all operations conducted with massive and complex aircraft which used to be piloted by a number of crew members. It now consists of two (or sometimes three) members, relying on the kind of aircraft. On trendy aeroplanes, computers are dealing with the systems and the pilot is changing into increasingly of a systems manager and choice maker somewhat than a control operator. Typical operations are flying instruction, crop spraying, aerial surveying, small commuter operations, air taxi and company flying. It have to be famous that helicopters now perform a significant part of these operations. During the final 20 years, a brand new dimension has been added to this class with the fast-rising popularity of the microlight aircraft. There is an actual gap between the bush pilot flying a rugged aircraft solo in a abandoned area and the pilot-in-command of a fancy aeroplane on one of the major air routes with complete ground help. This distinction, which also impacts licensed ground personnel, used to increase as technological progress turned more concerned in airline operations than in different categories, however is now decreasing somewhat as superior and complex electronics and computer-based tools have gotten out there even to the non-public pilot. The health worker, when making an evaluation, have to be familiar with the assorted working environments. This idea has remained legitimate all through the years, and the whole of Annex 1 could also be considered as an evolution of this primary thought. The personnel licensing system, as implemented in Annex 1, is now built on the next rules: · the licence is the authorization which allows the holder to perform particular actions, which otherwise can be prohibited. A licence is issued by a State when the applicant has demonstrated a suitable diploma of competency. The right to problem a licence is reserved to States either instantly or via a physique with delegated authority. The medical health required is the least restrictive of all pilot licences (Class 2). Therefore the health worker ought to be prepared to counsel the applicant against additional time and expense in pursuance of piloting ambitions if a medical condition is established which might forestall his acquisition of a more senior pilot licence, if this is his ambition. The most commonly held licence allowing the holder to fly an aeroplane aside from professionally. The holder of this licence is permitted to act as pilot-in-command of any free balloon. The senior pilot licence, allowing the holder to function any aircraft either as pilot-in-command or co-pilot. Each pilot licence have to be endorsed with a rating specifying the kind of aircraft the holder is authorized to fly. The larger aircraft (usually those with a maximum take-off mass of greater than 5 seven-hundred kg) want a particular rating. The smallest aircraft are grouped into courses (single-engine and multi-engine) and the holder of a licence endorsed with a class rating is permitted to fly all of the aircraft of the relevant class. The licence allowing the holder to perform the obligation of a flight engineer when required by aircraft certification or operational regulation. Licences for personnel aside from flight crew members Air site visitors controller licence. These are conferred with further ratings to the licence which characterizes the obligation of an air site visitors controller. Aerodrome control handles site visitors on ground and in flight at the vicinity of the runway. Approach control handles site visitors in flight throughout departure and through descent on arrival. Area control handles site visitors during the cruise, the final part of climb and the preliminary part of descent. None of the aviation licences listed above can be used for finishing up aviation duties with out evidence that the holder of the licence meets the medical necessities for health. Many Contracting States problem medical certificates, legitimate for a limited period only and designed to be kept along with the licence. The licence itself has usually an extended period of validity, sometimes lifelong or one which expires when the licence holder reaches the upper age restrict specified for the kind of licence held. Other States endorse aviation licences with the date of the medical examination and the word "handed", thus rendering the licence legitimate once more for a limited period until the next medical examination is due. When such a licence expires, a brand new one is issued, offered the holder nonetheless meets the medical necessities. To avoid confusion and errors, the time period "licence" is used solely about the document that guarantees the skilled competency of the holder, and the time period "Medical Assessment" is used about the medical certificate (in cases where such a document is issued), about endorsement of a licence to the impact that the holder meets the medical necessities, or about the aviation licence when medical health is implied in holding a valid licence (see also Note 2 to 1. A minimal stage of experience relying on the licence is required for all personnel to be licensed. The unit of measurement of experience is flight hours for flight crew, and years of obligation for ground personnel. For a number of licences, an applicant could select to take an accredited training course as an alternative of a daily course and thus be eligible for reduced experience necessities. The advent of the multi-crew pilot licence has offered a brand new methodology of coaching of individuals aspiring to function only multi-pilot aircraft. Contracting States typically use a written examination and a practical test to examine the competency of an applicant. Some different methods are also used concurrently, similar to acceptance of a army licence. Some licences (expiring sort) have a period of forex which is restricted to an outlined period. At every renewal, the holder must give evidence of his competency and his medical health. Competency is usually judged by contemplating the recent flight experience and sometimes by an examination. The holder is allowed to exercise licence privileges as long as he holds a present Medical Assessment and complies with the laws detailing the actions necessary to guarantee maintenance of competency. Other chapters of the Annex, mainly Chapter 1, comprise a number of common administrative provisions that are important for the group and conduct of the medical examination and medical certification. These are given within the following extracts from Chapter 1 of the Annex, along with explanatory remarks. Before designation, medical examiners shall demonstrate sufficient competency in aviation medicine. Such practical knowledge and experience ought to embody, every time potential, actual flight deck experience in aircraft engaged in industrial operation in addition to experience within the operational working conditions of air site visitors controllers. An accumulated complete of a minimum of ten hours per year of flight deck time may be considered fascinating. The function of the medical assessor and the evaluation of medical reports are additional outlined in Chapter 1 of Annex 1: 1. Guidance on aeromedical threat evaluation is contained within the Manual of Civil Aviation Medicine (Doc 8984). In addition to evaluating medical reports submitted to the Licensing Authority and making ultimate assessments in borderline cases, the medical assessor will usually be in control of Accredited Medical Conclusions (see 1. An important obligation of the medical assessor is the safeguarding of medical confidentiality, although pertinent medical information could also be introduced by the medical assessor to different officials of the Licensing Authority when justified by operational considerations or when an Accredited Medical Conclusion is sought. Also the audit of medical reports by designated medical examiners and refresher training of medical examiners will usually fall throughout the remit of the medical assessor. The examiner ought to be conscious that deception could also be an issue in aviation medical certification and the doubtless severe penalties of any false declaration ought to be identified by the applicant. All medical reports and information shall be securely held with accessibility restricted to approved personnel. Medical information is of a sensitive nature, and an individual who has undergone a medical examination for issuance or renewal of his licence has a right to anticipate that such information is kept confidential and disclosed only to medical officials. In many States a separate medical section is established, either throughout the authority or connected to it. Medical confidentiality is greatest assured when this medical section, where the reports from the medical examiners are acquired and evaluated, is headed by a doctor and has its personal workers, its personal channels of communication, its personal submitting system, and so forth. If the medical section is a sub-part of one other non-medical section and thus shares workplace area, workplace workers and files with that section, medical confidentiality turns into untenable. Rules concerning licences I-1-9 b) continuous re-evaluation of the medical evaluation process to think about identified areas of elevated medical threat.
Effective 2mg kytril
The biochemical substrate of artery ageing has been researched in the last few years which resulted within the discovery of elevated creation of matter corresponding to Endothelin-1 and nitric oxide- synthase (46), reactive oxygen species (forty seven), or accumulation of calcium (forty eight) within the artery partitions of aged individuals. In the first kind of changes, hyalinization and the glomerular collapse are associated to the obliteration of the afferent arteriole which is primarily the case with the glomeruli within the cortical area. The second kind is typical for the juxtamedullary glomeruli, when the above cited glomerular changes lead to the creation of shunt an anatomical continuity between the afferent and efferent arterioles. This is the explanation why a substantial a part of the blood circulate in an aged kidney is transferred from the cortex onto the medullar area. At delivery, shunts are identified in 9% of juxtamedullar glomeruli, and their number steadily increases reaching one hundred% within the ninth decade of life (49). The process of ageing leads to a substantial enhance of the interstitial tissue (2,50). The glomerular basement membrane manifests a concentration lower of sure amino acids: threonine, methionine, isoleucine, leucine, histidine, tyrosine, phenylalanine and hydroxylysine (fifty one). The most essential biochemical change induced by age consists in an elevated collagen content material. Functional Characteristics the functioning of the kidney is rather stable within the interval between early adulthood and the center years, but with additional ageing there are particular functional problems within the kidney. Fortunately, in healthy individuals these old age-associated changes develop very slowly in order that even an old kidney functionally meet the wants of the organism. An old kidney turns into weak and extra delicate to the toxicity of medicines and their metabolites, which should be taken into consideration throughout treatment of the aged (fifty three). This discount is related to a significant enhance of vascular resistance within the afferent and efferent arterioles, which may also explain agerelated enhance of filtration fraction (54). The permeability of the glomerular filtration barrier is only slightly changed with age (2). The average arterial blood strain considerably rises in the midst of ageing (57). The capability of an old kidney to preserve Na+ as a response to its inadequate intake is lowered. The aged show a lower capability of the distal tubule for the reabsorption of Na+, which is defined by interstitial fibrosis or by a lower exercise of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system. Related to that, the lower concentration of plasma renin of 30% to 50% has been noticed within the aged. The renal capability for concentration and dilution of urine decreases with age (33,fifty eight). The process of ageing can also be characterised by a reduced synthesis of renin and by its lower concentration within the plasma, regardless of the conventional concentration of its substrates (2). Age Related Renal Diseases the kidney of the aged is delicate to quite a few influences coming from the setting (excessive temperatures, inadequate intake of liquids, physical exhaustion and so forth. Because of this, sure renal diseases manifest particular etiopathogenetic characteristics within the aged. The primary cause of renal insufficiency within the aged is the atheromatose renal disease (60, sixty one). It can be manifested as the stenosis of the renal artery, a posh of intrarenal lesions with multiple stenoses, and because the cholesterol embolism. The atheromatose renal disease is responsible for renal insufficiency in 14% of the patients older than 50 within the terminal stage (62). Its most common form within the aged is a speedy progressive glomerulonephritis, with a progressive lack of renal function within the interval of some weeks up to a few months (32). At least one cyst has been postmortally present in over 50% of individuals older than 50. The prevalence of at least one cyst has been diagnosed ultrasonographically; it progressively grows from zero% in individuals between 15 and 29 years of age up to 22. Vlajkovi hypertension, persistent glomerulonephritis, hydronephrosis because of prostate hypertrophy and so forth. The number of the aged on dialysis is on the rise every year due to the longer life-span and the rising number of patients suffering from terminal renal failure (64). Their frequency is related to the functional changes of the bladder, pelvic muscle system, prostate size, impaired immune response and so forth. The reduced level of oestrogen in menopausal girls causes a higher frequency of urinary tract infections (38). V Biologija starenija Rukovodstvo po fiziologiji, Nauka, Leningrad, 1982; 370-382. The Arterial Supply of the human kidney with Special Reference to Accessory Renal Arteries. Protein restriction within the being pregnant is associated with elevated apoptosis of mesenchymal cells initially of rat metanephrogenesis. Early defect in branching morphogenesis of the ureteric bud in induced nephron deficit. Ultrasound of the conventional kidney: a sonographic, anatomic and histologic correlation. Polozaj glomerula u odnosu na krvne sudove bubrega djeteta sa aspekta uzrastne anatomije. National Kidney Foundation Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification, and Stratification. Influence of Arteriolar Hyalinization on Arterial Intimal Fibroplasia within the Renal Cortex of Subjects within the United States, Peru, and Bolivia, Applicable Also to Other Populations. In: Oxford textbook of Clinical Nephrology, Oxford college press 1998; 1445-1456. Evaluation by stable vascular casts of arterial geometric optimisation and the influence of ageing. Renal artery calcified plaque associations with subclinical renal and heart problems. Cortical Interstitial Tissue and Sclerosed Glomeruli within the Normal Human kidney, Related to Age and Sex. Age-associated changes within the amino acid composition of human glomerular basement membrane. Effects of age, intercourse, race, and body mass - the Northwick Park Hospital Database Study. Nadalje, sve do dostizanja adultnosti, bubreg karakterisu intenzivni procesi maturacije ali i evidentne involutivne promene. Prenatalni interval karakterisu intenzivni procesi nefrogeneze, koji se ostvaruju kroz tri sukcesivne razvojne forme bubrega: pronefros, mezonefros i metanefros. Funkcionisanje bubrega, iako nije neophodno u prenatalnom stadijumu, ukazuje na njihovu ekskretornu, homeostatsku i endokrinu ulogu i odraz je procesa sazrevanja. Po roenju, bubrezi se odlikuju daljim procesima strukturne i funkcionalne maturacije. Sa, na roenju, definitivnim brojem nefrona oni uveavaju svoju masu na racun rasta pojedinih struktura nefrona i intersticijuma. Do kraja seste decenije ove promene su spore; potom, sve do kraja zivota imaju pattern veoma ubrzane progresije i posledica su, pre svega, smanjene perfuzije bubrega. Uprkos tome, u normalnim uslovima i u najdubljoj starosti ne pokazuju znake funkcionalne insuficijencije. Involutivne promene na bubrezima mogu biti zasebne, a mogu se i superponirati sa odgovarajuim bubreznim bolestima, sto kod izvesnog broja osoba u poodmaklim godinama moze dovesti do progresivnog gubitka bubreznih funkcija. But for some folks, the development they really feel could also be much more restricted- often due to their severe health problems. This booklet has been written to answer some basic questions you could have in regards to the alternative to not begin dialysis. You have the proper to determine to not begin dialysis when you really feel that the burdens outweigh the advantages to you. Naming a surrogate is completed by filling out a form generally known as an advance directive, a healthcare proxy, or a sturdy healthcare energy of attorney. It is essential to make sure the person you name is willing to act in your behalf. For extra information about naming a surrogate and in regards to the legal guidelines in your state, you might want to converse with an attorney or your local or state bar affiliation. Your doctor will converse with you about what dialysis treatment includes and what deciding to not begin dialysis would imply for you. However, the final decision about starting or not starting treatment remains with you or your surrogate.
Best 1mg kytril
For this reason, none of the renal function estimating equations described above are helpful in conditions where the extent of kidney function is quickly changing. The timed urine assortment technique can be used to measure creatinine clearance, however then serum creatinine levels need to be measured at both the start and end of the collection period, and the per minute excretion rate ought to be divided by the time-averaged serum value in the calculations. Kidney harm may be manifest as pathologic changes on kidney biopsy; abnormalities in the composition of the blood or urine (proteinuria or changes in the urine sediment examination), or abnormalities in imaging exams. Urinary protein excretion and even microalbuminuria markedly enhance both the risk of progression and cardiovascular issues. Smoking is a traditional cardiovascular threat factor, and cessation of smoking is essential by way of limiting cardiovascular threat. Studies in sufferers with either kind 1 or kind 2 diabetes have demonstrated that tight glycemic management slows the development of microvascular and macrovascular disease. Data in animals recommend that high lipid levels and cholesterol loading could increase glomerular harm. Thus, these pointers have been questioned concerning their quite intensive suggestions to be used of statin therapy. Statins as a class have been associated with rhabdomyolysis, and dose reduction in extreme renal impairment is recommended for some statins. As with statins, ezetimibe exerts important antiatherogenic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant actions (Katsiki, 2013). Evidence from animal research demonstrates that diets high in protein result in histologic abnormalities in the kidney and to proteinuria. However, randomized medical trials recommend that the consequences of protein restriction are prone to be small and troublesome to obtain. Recommendations differ from varied guideline teams concerning the advantages of any additional restriction of protein intake. Close comply with-up for any evidence of malnutrition, either by medical parameters or by serum albumin, is important. In stage 4 and 5 sufferers, evidence of failing nutritional standing is one key determinant in the determination to start dialysis therapy. The most common causes are erythropoietin deficiency, iron deficiency, and irritation. Observational research have advised an elevated threat of cardiovascular and renal issues, lower quality of life, and better mortality with a lower Hb level. Thus, the efficient Hb goal, in the United States at least, is 911 g/dL (90one hundred ten g/L). Serum ferritin values are of greatest predictive value for iron deficiency when low (<100 ng/mL), however are of limited value when elevated. Strategies to enhance oral iron absorption embrace solely taking drugs on an empty abdomen, avoiding enteric-coated formulations, and avoiding ingestion of iron with phosphate binders. The use of low-molecular-weight iron therapy is recommended-low-molecular-weight dextrans, ferrous gluconate, iron sucrose, or ferumoxytol. The use of highmolecular-weight iron dextran has been associated with an elevated threat of extreme anaphylaxis. Dosing strategies for oral iron goal at offering approximately 200 mg of elemental iron day by day, which is equal to ferrous sulfate 325 mg three times day by day; each tablet offering sixty five mg of elemental iron. Intravenous iron may be administered as a single giant dose or as repeated smaller doses, relying on the preparation used. The initial course of intravenous iron remedy is to provide approximately 1,000 mg of iron. Even in nonuremic sufferers, gentle serum phosphorus elevation is associated with elevated cardiovascular threat. In a variety of experimental renal failure models, hyperphosphatemia accelerates progression of renal failure. Management features a cautious dietary evaluation to look for abnormally high consumption of meals wealthy in phosphorus, including dairy products, sure colas, and processed meats. A cautious evaluation of the food plan ought to be made with the goal of lowering consumption of meals containing phosphorus additives. Phosphorus intake ought to be restricted to 8001,000 mg per day (2632 mmol per day). This means that if calcium salts are used as phosphorus binders, they might need to be combined with sevelamer, lanthanum, or, presumably, magnesium or one of the newer iron-containing phosphorus binders described in Chapter 36. Alkaline phosphatase is present in bone and is an indicator of bone turnover rate. Vitamin D impacts a number of organ methods; most of those effects are useful, though excess vitamin D has been associated with vascular calcification and even accelerated renal failure. The 1-hydroxylase enzyme exists in varied tissues, suggesting that it may be essential to ensure correct levels of both 25-D and 1,25-D in the circulation for optimum well being. Low serum levels of 25-D have been linked to extreme muscle weakness in aged nonuremic sufferers. Cholecalciferol is on the market in the United States solely as an over-the-counter vitamin complement. Ergocalciferol does have the benefit in the United States of being out there as a formulary drug. A number of electrolyte abnormalities could turn out to be obvious as kidney function declines. In the continual setting, hyperkalemia normally is the result of relatively high dietary potassium intake, and especially, binge intake of high potassium meals such as fruits. It is also extra widespread in sufferers taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as well as trimethoprim. The use of sodium bicarbonate is recommended to maintain the serum bicarbonate level at b. Tasks right here embrace preparation for dialysis or preemptive kidney transplantation; placement of vascular or peritoneal entry; selecting probably the most appropriate mode and location of dialysis. Chlorthalidone for poorly managed hypertension in continual kidney disease: an interventional pilot research. Functional range of creatinine clearance for renal drug dosing: a practical resolution to the controversy of which weight to use in the Cockcroft-Gault equation. Screening for, monitoring, and remedy of continual kidney disease phases 1 to three: a scientific evaluation for the U. Preventive Services Task Force and for an American College of Physicians Clinical Practice Guideline. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Lipid Guideline Development Work Group Members. The impact of antihypertensive drugs on continual kidney disease: a complete evaluation. Ideally, the patient must also be a part of a multidisciplinary predialysis program that features patient and family training, early choice of appropriate renal alternative modality, and, if dialysis is being considered, elective creation of dialysis entry. It is likely that this approach ends in fewer hospital days in the first month after beginning dialysis and substantial price savings. Of key significance is patient training in regards to the varied remedy options out there in the occasion that renal alternative therapy will turn out to be necessary. Would the patient greatest profit from some form of dialysis, from preemptive transplantation, or from continued conservative administration? In some instances, due to extreme patient debility or different reasons, dialysis is probably not an appropriate possibility, and conservative administration may be your best option. Transplantation offers survival superior to the standard types of dialysis being provided today. Transplantation is probably not indicated, however, for a patient who has extreme problems with compliance by way of drugs. Disadvantages Logistics of finding an appropriate donor; want for compliance with immunosuppressive drugs. Usually assisted by a relative or caregiver; uncommonly, by a paid well being-care skilled Automated cycler, with most exchanges accomplished during the night time Three 79hour nocturnal treatments per week (or uncommonly, each different night time) given incenter (either staff assisted or self-care) Either staff assisted (the norm) or self-care Very-lowprotein food plan plus ketoanalogues, cautious fluid administration When given extra than three instances per week, or when given as 810-hour treatments, threethree. Staff does all of the work In-middle conventional hemodialysis Travel to unit; relatively rigid schedule. In observational research, mortality rates are lower in home hemodialysis sufferers than in in-middle hemodialysis sufferers, typically dramatically so, even after adjustments for widespread comorbidities and at comparable total weekly dialysis instances. Some of this home dialysis benefit may be due to unaccounted for patient choice bias, as sufferers enterprise the accountability to dialyze at home normally have a strong positive perspective, good compliance, and powerful caregiver and/or family help structure, factors which are related in their own proper with elevated survival. Normally, whether accomplished at home or in-middle, hemodialysis therapy is offered three instances per week, normally three5 hours per session. When the identical quantity of dialysis time is damaged up into 5 or 6 periods per week, some observational research have shown higher management of blood strain, higher nutrition (weight gain, elevated appetite and albumin), and higher management of anemia.
References:
- https://bipai.org/sites/bipai/files/13-Oral-Manifestations.pdf
- https://anmc.org/wp-content/uploads/guidelines04182018/TreatmentOfacne.pdf
- http://www.colonrectal.org/images/wmimages/OnlineForms/Surgery_Handbook(pdf).pdf
.png)