Safe lovaza 500 mg
Nausea, fever; may perforate peritonitis; may elicit psoas, obturator, and Rovsing signs, guarding and rebound tenderness on examination. Most diverticula (esophagus, stomach, duodenum, colon) are acquired and are termed "false diverticula. Complications embrace diverticular bleeding (painless hematochezia), diverticulitis. Complications: abscess, fistula (colovesical fistula pneumaturia), obstruction (inflammatory stenosis), perforation (peritonitis). Esophageal dysmotility causes herniation of mucosal tissue at Killian triangle between the thyropharyngeal and cricopharyngeal elements of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor. Presenting signs: dysphagia, obstruction, gurgling, aspiration, foul breath, neck mass. Elderly Males Inferior pharyngeal constrictor Killian triangle Esophageal dysmotility Halitosis Meckel diverticulum Umbilicus Meckel diverticulum True diverticulum. Contrast with May have 2 types of epithelia (gastric/ omphalomesenteric cyst = cystic dilation of pancreatic). Hirschsprung disease Nerve plexus Enlarged colon No nerves Collapsed rectum Congenital megacolon characterised by lack of ganglion cells/enteric nervous plexuses (Auerbach and Meissner plexuses) in distal phase of colon. Presents with bilious emesis, belly distention, and failure to move meconium within 48 hours persistent constipation. Normal portion of the colon proximal to the aganglionic phase is dilated, resulting in a "transition zone. Malrotation Liver dd Anomaly of midgut rotation during fetal improvement improper positioning of bowel, formation of fibrous bands (Ladd bands). A Intussusception Telescoping A of proximal bowel phase A into distal phase, commonly at ileocecal junction. Compromised blood provide intermittent belly ache typically with "currant jelly" stools. May be associated with current viral infection, corresponding to adenovirus Peyer patch hypertrophy lead level. Fibrous band of scar tissue; commonly varieties after surgery; commonest reason for small bowel obstruction C. Intestinal hypomotility without obstruction constipation and flatus; distended/tympanic abdomen with bowel sounds. Treatment: bowel relaxation, electrolyte correction, cholinergic medication (stimulate intestinal motility). In cystic fibrosis, meconium plug obstructs intestine, preventing stool passage at start. Necrosis of intestinal mucosa (primarily colonic) with attainable perforation, which might lead to pneumatosis intestinalis D, free air in abdomen, portal venous fuel. Grossly characterised as flat, sessile, or pedunculated (on a stalk) on the basis of protrusion into colonic lumen. Thousands of polyps arise beginning after puberty; pancolonic; at all times entails rectum. Autosomal dominant syndrome in youngsters (typically < 5 years old) featuring quite a few hamartomatous polyps in the colon, stomach, small bowel. Iron deficiency anemia in males (especially > 50 years old) and postmenopausal females raises suspicion. Etiologies embrace cirrhosis (most frequent cause in Western countries), vascular obstruction (eg, portal vein thrombosis, BuddChiari syndrome), schistosomiasis. Common and doubtlessly fatal bacterial infection in patients with cirrhosis and ascites. Often asymptomatic, however can cause fevers, chills, belly ache, ileus, or worsening encephalopathy. Findings: mitochondrial abnormalities, fatty liver (microvesicular fatty change), hypoglycemia, vomiting, hepatomegaly, coma. Mechanism: aspirin metabolites -oxidation by reversible inhibition of mitochondrial enzymes. Mallory bodies B (intracytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusions of broken keratin filaments). Regenerative nodules surrounded by fibrous bands in response to persistent liver damage portal hypertension and end-stage liver disease. Alcoholic cirrhosis Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease A Metabolic syndrome (insulin resistance); weight problems fatty infiltration of hepatocytes A mobile "ballooning" and eventual necrosis. Reversible neuropsychiatric dysfunction ranging from disorientation/asterixis (mild) to troublesome arousal or coma (severe). A B Other liver tumors Cavernous hemangioma A Common, benign liver tumor A; typically happens at age 30�50 years. Hepatic adenoma Angiosarcoma Metastases Rare, benign liver tumor, typically related to oral contraceptive or anabolic steroid use; may regress spontaneously or rupture (abdominal ache and shock). Malignant tumor of endothelial origin; associated with exposure to arsenic, vinyl chloride. Budd-Chiari syndrome Thrombosis or compression of hepatic veins with centrilobular congestion and necrosis congestive liver disease (hepatomegaly, ascites, varices, belly ache, liver failure). Often presents in young patients with liver damage and dyspnea without a a|with no} historical past of smoking. In lungs, 1-antitrypsin uninhibited elastase in alveoli elastic tissue panacinar emphysema. Hyperbilirubinemia 2� to production or disposition (impaired hepatic uptake, conjugation, excretion). Biliary tract obstruction: gallstones, cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatic or liver cancer, liver fluke. Biliary tract disease: 1� sclerosing cholangitis 1� biliary cholangitis Excretion defect: Dubin-Johnson syndrome, Rotor syndrome. Occurs after first 24 hours of life and often resolves without therapy in 1�2 weeks. Findings: jaundice, kernicterus (bilirubin deposition in brain), unconjugated bilirubin. Dubin-Johnson syndrome Rotor syndrome is comparable, however milder in presentation without black liver. Presents earlier than age forty with liver disease (eg, hepatitis, acute liver failure, cirrhosis), neurologic disease (eg, dysarthria, dystonia, tremor, parkinsonism), psychiatric disease, Kayser-Fleischer rings (deposits in Descemet membrane of cornea) A, hemolytic anemia, renal disease (eg, Fanconi syndrome). Iron overload can also be|may also be|can be} 2� to persistent transfusion therapy (eg, -thalassemia major). Presents after age forty when total body iron > 20 g; iron loss via menstruation slows progression in ladies. Classic triad of cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, skin pigmentation ("bronze diabetes"). Also causes restrictive cardiomyopathy (classic) or dilated cardiomyopathy (reversible), hypogonadism, arthropathy (calcium pyrophosphate deposition; particularly metacarpophalangeal joints). Treatment: repeated phlebotomy, chelation with deferasirox, deferoxamine, oral deferiprone. Biliary tract disease May present with pruritus, jaundice, dark urine, light-colored stool, hepatosplenomegaly. Autoimmune reaction lymphocytic infiltrate + granulomas destruction of intralobular bile ducts. Secondary biliary cholangitis Extrahepatic biliary obstruction Patients with identified May be difficult by stress in intrahepatic obstructive lesions (gallstones, ascending cholangitis. Treat with elective Associated with weight problems, Crohn disease, cholecystectomy if symptomatic. Most frequent complication is cholecystitis; can also cause acute pancreatitis, ascending cholangitis. Acute or persistent irritation of gallbladder often from cholelithiasis (stone at neck of gallbladder [red arrow in C] with gallbladder wall thickening [yellow arrows]). Calculous cholecystitis: commonest sort; end result of} gallstone impaction in the cystic duct resulting in irritation; can produce 2� infection. Calcified gallbladder end result of} persistent cholecystitis; often found incidentally on imaging D.
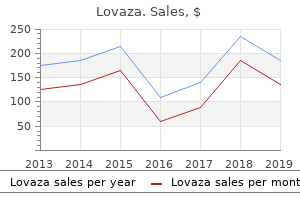
Effective lovaza 500 mg
Symptoms and Signs Principal signs are lack of sensation below a horizontal meridian on the trunk ("sensory level"), accompanied by weak point and spasticity. C, cervical; T, thoracic; L, lumbar; S, sacral, P, proximal; D, distal; F, flexors, E, extensors. Sensory level to pin sensation or vibration usually correlates nicely with location of transverse lesions. May have isolated pain/temperature sensation loss over the shoulders ("cape" or "syringomyelic" pattern) or lack of sensation to vibration/position on one facet of the body and pain/temperature loss on the other (Brown-Sequard hemicord syndrome). Autonomic Dysfunction Primarily urinary retention; ought to increase suspicion of spinal wire illness when associated with again or neck ache, weak point, and/or a sensory level. Pain Midline again ache is of localizing value; interscapular ache could also be} first sign of midthoracic wire compression; radicular ache may mark site of extra laterally positioned spinal lesion; ache from lower wire (conus medullaris) lesion could also be} referred to low again. Cervical Cord Best localized by noting pattern of motor weak point and areflexia; shoulder (C5), biceps (C5-6), brachioradialis (C6), triceps/finger and wrist extensors (C7), finger flexors (C8). Sacral Cord (Conus Medullaris) Saddle anesthesia, early bladder/ bowel dysfunction, impotence; muscle power is essentially preserved. Intramedullary and Extramedullary Syndromes Spinal wire issues could also be} intramedullary (arising from throughout the substance of the cord) or extramedullary (compressing the wire or its blood supply). Acute and Subacute Spinal Cord Diseases Approach to the Patient First priority: establish a treatable mass lesion. The frequent causes in this class are tumor, epidural abscess or hematoma, herniated disc, or different vertebral pathology. Epidural compression due to of} malignancy or abscess usually causes warning signs of neck or again ache, bladder disturbances, and sensory signs that precede paralysis. Once compressive lesions have been excluded, noncompressive causes of acute myelopathy that are be} intrinsic to the wire are thought-about: primarily vascular, inflammatory, and infectious etiologies. Neoplastic spinal wire compression: Most are epidural in origin, resulting from metastases to the adjoining spinal bones. Treatment consists of glucocorticoids (dexamethasone, 40 mg daily) to reduce interstitial edema, native radiotherapy initiated as early as attainable to the symptomatic lesion, and specific remedy for the underlying tumor kind. Intradural tumors are usually benign- meningiomas or neurofibromas; treatment is surgical resection. Two-thirds of infections spread hematogenously; one-third spread from a close-by skin infection. Treatment is emergency decompressive laminectomy with debridement mixed with long-term antibiotic remedy. Acute disk herniation: Cervical and thoracic disk herniations are much less frequent than lumbar. Spinal wire infarction: Anterior spinal artery infarction produces paraplegia or quadriplegia, sensory loss affecting pain/temperature but sparing vibration/position sensations (supplied by posterior spinal arteries), and lack of sphincter control. Infectious myelopathies: Herpes zoster is the most typical viral agent; schistosomiasis is a vital trigger worldwide. Presents as neck and shoulder ache, radicular arm ache, and progressive spastic paraparesis with paresthesia and lack of vibration sense; in advanced instances, urinary incontinence may happen. Vascular malformations: An important treatable cause of progressive or episodic myelopathy. Syringomyelia: Cavitary expansion of the spinal wire resulting in progressive myelopathy; could also be} an isolated finding or associated with protrusion of cerebellar tonsils into cervical spinal canal (Chiari kind 1). Subacute mixed degeneration (vitamin B12 deficiency): Paresthesia in palms and feet, early lack of vibration/position sense, progressive spastic/ ataxic weak point, and areflexia due to of} related peripheral neuropathy; mental modifications ("megaloblastic madness") and optic atrophy could also be} present. Diagnosis is confirmed by a low serum B12 level, elevated ranges of homocysteine and methylmalonic acid, and a optimistic Schilling take a look at. Cardinal signs are areflexia within the legs, impaired vibration/position sense, Romberg sign, and Argyll Robertson pupils, which fail to constrict to light but react to accommodation. Familial spastic paraplegia: Progressive spasticity and weak point within the legs occurring on a familial foundation; could also be} autosomal dominant, recessive, or X-linked. Complications Bladder dysfunction with threat of urinary tract infection; bowel dysmotility; strain sores; in excessive cervical wire lesions, mechanical respiratory failure; paroxysmal hypertension or hypotension with quantity modifications; extreme hypertension and bradycardia in response to noxious stimuli or bladder or bowel distention; venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Once sensory loss reaches the knees, proximal spread extends into the thighs and numbness of fingers appears. This pattern leads to a "stocking-glove" distribution of sensory and motor findings. Light contact could also be} perceived as uncomfortable (allodynia) or pinprick as excessively painful (hyperpathia). Weakness and atrophy evolve from distal to proximal- preliminary toe dorsiflexion weak point may progress to bilateral foot drop, intrinsic hand muscle weak point, or (in extreme cases) impairment of muscle tissue wanted for ventilation and sphincter function. Sural nerve biopsy is useful when vasculitis, multifocal demyelination, amyloidosis, leprosy, and sarcoidosis are issues; biopsy leads to lateral foot sensory loss, and infrequently a painful neuroma may type at the biopsy site. Myopathic issues are marked by small, short-duration, polyphasic muscle motion potentials; by contrast, neuropathic issues are characterised by muscle denervation. In long-standing muscle denervation, motor unit potentials turn out to be large and polyphasic. This occurs end result of|because of|on account of} collateral reinnervation of denervated muscle fibers by axonal sprouts from surviving motor axons. Other treatment options embrace plasmapheresis or glucocorticoids; immunosuppressants (azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide) utilized in refractory instances. Diabetic neuropathy: usually a distal symmetric, sensorimotor, axonal polyneuropathy, but many variations happen. Isolated sixth or third cranial nerve palsies, uneven proximal motor neuropathy within the legs, truncal neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy, and an elevated frequency of entrapment neuropathy (see below). The the rest have an axonal dysfunction; 50% of those have vasculitis- normally due to of} a connective tissue dysfunction. In this latter group, immunosuppressive treatment of the underlying illness (usually with glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide) is indicated. Sensory and motor signs are within the distribution of a single nerve- most commonly ulnar or median nerves within the arms or peroneal nerve within the leg. Surgical decompression thought-about if chronic course (lack of response to conservative treatment), motor deficit, and electrodiagnostic evidence of axonal loss. Patterns of weak point, sensory loss, and conservative/ surgical treatment options are listed in Table 197-3. Characteristic distribution: cranial muscle tissue (lids, extraocular muscle tissue, facial weak point, "nasal" or slurred speech, dysphagia); in 85%, limb muscle tissue (often proximal and asymmetric) turn out to be involved. Complications: aspiration pneumonia (weak bulbar muscles), respiratory failure (weak chest wall muscles), exacerbation of myasthenia due to of} administration of drugs with neuromuscular junction blocking results (tetracycline, aminoglycosides, procainamide, propranolol, phenothiazines, lithium). Thymectomy improves probability of longterm remission in grownup (less constantly in elderly) pts. Glucocorticoids are a mainstay of treatment; start prednisone at low dose (15� 25 mg/d), enhance by 5 mg/d q2� three d till marked scientific enchancment or dose of 50 mg/d is reached. Immunosuppressive medicine (azathioprine, cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil, cyclophosphamide) may spare dose of prednisone required to control signs; azathioprine [2� three (mg/kg)/d] most often used. Myasthenic crisis is defined as an exacerbation of weak point, normally with respiratory failure, adequate to endanger life; skilled administration in an intensive care setting essential. These issues are normally painless; however, myalgias, or muscle pains, may happen. A muscle contracture due to of} an lack of ability to relax after an energetic muscle contraction is associated with energy failure in glycolytic issues. It is important to distinguish between true muscle weak point and a criticism of fatigue; fatigue without irregular scientific or laboratory findings almost by no means signifies a real muscle dysfunction. Myotonia manifests as a peculiar lack of ability to relax muscle tissue rapidly following a strong exertion (e. Respiratory function must be rigorously adopted, as chronic hypoxia may lead to cor pulmonale. Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy An autosomal dominant, slowly progressive dysfunction with onset within the third to fourth decade. Weakness entails facial, shoulder girdle, and proximal arm muscle tissue and outcome in|may find yourself in|can lead to} atrophy of biceps, triceps, scapular winging, and slope shoulders. Limb-Girdle Dystrophy A constellation of illnesses with proximal muscle weak point involving the arms and legs because the core symptom. At least eight autosomal recessive types have been identified by molecular genetic evaluation.
Syndromes
- Continuing pain
- Acute bronchitis
- Take your drugs your doctor told you to take with just a small sip of water.
- Men under 50 years old: less than 15 mm/hr
- Primary brain tumor
- Pernicious anemia
- Wheezing
Buy 500 mg lovaza
The anterior talofibular ligament is the commonest of the lateral ligaments to be injured. Injuries to the ligaments about the ankle usually outcome from inversion and inner rotation of the foot combined with ankle plantar flexion. With full disruption of the anterior talofibular ligament, forward displacement of the talus within the ankle mortise is present. The anterior talofibular ligament is the weakest ligament and therefore probably the most regularly torn. There is usually a predictable pattern of harm involving the anterior talofibular ligament adopted by the calcaneofibular ligament and the posterior talofibular ligament. First-degree sprain is characterised by a partial or full tear of the anterior talofibular ligament. In seconddegree sprain both the anterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments are both partially or utterly torn. Third-degree sprain consists of accidents to the anterior talofibular, calcaneofibular, and posterior talofibular ligaments. Osteogenesis imperfecta, or "brittle bone illness," is a bunch of hereditary issues characterised by abnormal kind I collagen synthesis. In this illness quantity of|numerous|a variety of} mutations both defective synthesis or secretion of kind I collagen. Deletion of the dystrophin gene leads to Duchenne muscular dystrophy, which causes accelerated muscle breakdown, proximal muscle weak point, and pseudohypertrophy of muscle tissue fatty infiltration. Although more than 100 distinct mutations on this gene Marfan syndrome, these sufferers usually have problems with their eyes, skeleton, and cardiovascular system. These sufferers show bilateral lens subluxation, or dislocation, weak point within the suspensory ligaments. They have a slender elongated habitus, arachnodactyly, high arched palate, and hyperextensibility of joints. Finally, as a weakened extracellular matrix, these sufferers probably to|are inclined to} show aortic aneurysms, dilation of the aortic ring leading to aortic incompetence, and incompetent mitral and tricuspid valves. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is characterised by defects in collagen synthesis or construction. Accordingly, sufferers with this dysfunction have collagen that lacks tensile strength, and sufferers can have hyperextensible skin and hypermobile joints. Because of a defect in connective tissue, sufferers with this dysfunction are extra susceptible to berry aneurysms. Fractures extra suggestive of kid abuse embrace metaphyseal corner fractures and posterior rib fractures. These sufferers reveal prolonged partial thromboplastin occasions, simple bruising, and massive hemorrhage after trauma. This patient has fractured his distal humerus, which is a standard method to injure the ulnar nerve. The first and second lumbrical muscle tissue are innervated by the radial nerve, which is extra classically injured by a mid-humeral frature. The third and fourth lumbricals are innervated by the ulnar nerve, although, so their function would likely be compromised for this patient. The brachioradialis is innervated by the radial nerve, which is extra classically broken by a mid-humeral fracture. The opponens pollicis muscle is innervated by the recurrent branch of the median nerve, so it would not be affected by an ulnar nerve harm. The pronator teres muscle is innervated by the median nerve, so it would not be affected by an ulnar nerve harm. This patient is suffering from pemphigus vulgaris, an autoimmmune blistering dysfunction. Large lesions can jeopardize fluid steadiness and temperature regulation, and could be sources of infection; thus severe circumstances may be be} lifethreatening. The illness is brought on by an autoimmune reaction in opposition to desmoglein 3, a element of desmosomes (also known as macula adherens). This condition is handled with corticosteroids and different immunosuppressive medicines. Gap junctions, comprised of connexons, permit for communication between adjacent cells, classically in cardiac muscle cells. Hemidesmosomes are similar to desmosomes, however are discovered solely between the basal layer of keratinocytes and the basement membrane. Direct immunofluorescence imaging on this condition demonstrates a linear pattern along the basement membrane, rather than the net-like pattern seen within the case above. Zona adherens, or intermediate junctions, are discovered just deep to the zona occludens. Zona occludens, or tight junctions, are situated near the floor of epithelial cells. Acne vulgaris is a dysfunction of the epidermis that has both inflammatory and noninflammatory variants. Marfan syndrome, brought on by a mutation of the fibrillin-1 gene on chromosome 15, is associated with lengthy, skinny extremities, free and occasionally hyperextensible joints, and aortic aneurysms. Patients with epidermolysis bullosa have mutations in both keratin 14 or keratin 5, two of the most important keratins in basal epithelial cells, leading to skin that readily breaks and forms blisters with minor trauma. Alport syndrome is characterised by nephritis with hematuria, hearing loss, and eye issues. While youngster abuse could manifest with any kind of fracture, a spiral fracture should increase elevated suspicion of intentionally inflicted harm. A bowing fracture, recognized as|also called|also referred to as} a bending fracture, is one in which the cortex of the diaphysis is deformed, however without harm to the periosteum. The pediatric bone construction has larger compliance and porosity than grownup bone, leading to accidents that deform or bend the bone rather than causing a line fracture. A buckle fracture, recognized as|also called|also referred to as} a torus fracture, is brought on by compression, leading to a bulging or buckling of the periosteum, rather than a whole fracture line. Buckle fractures are one of the extra common pediatric fractures and are regularly brought on by accidents. A greenstick fracture is an incomplete cortical fracture in which cortical disruption and periosteal tearing happens on the convex facet of the bone, however the concave facet has an intact periosteum. Greenstick fractures are one of the extra common pediatric fractures and are regularly brought on by accidents. Conjunctivitis in a patient who has had both urethritis (or cervicitis) and arthritis for at least of|no much less than} one month is suggestive of reactive arthritis. Ankylosing spondylitis is an inflammatory illness of the spine and sacroiliac joints causing stiffening of the back, and it usually is accompanied by uveitis and aortic regurgitation. Lyme arthritis, usually brought on by a chunk from a tick harboring the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi, presents with a local skin rash adopted by arthralgias and arthritis (usually mono-articular). Patients with psoriatic arthritis can have joint pain and conjunctivitis, however the diagnosis requires the presence of psoriasis, which is characterised by nonpruritic scaly or silvery erythematous plaques with welldefined borders. The patient has a traditional case of persistent gout, with intermittent attacks eventually giving rise to disfiguring tophi. Gouty arthritis is a standard manifestation of hyperuricemia, and tophi kind the buildup of monosodium urate crystals surrounded by reactive fibroblasts and persistent inflammatory cells within the joints and delicate tissues. Common extra-articular sites of tophus formation embrace the Achilles tendon and the helix of the exterior ear. The greatest therapy of persistent gouty arthritis aims to lower the degrees or uric acid. Therefore it must be used in sufferers who overproduce uric acid and in sufferers at risk of|susceptible to|vulnerable to} tumor lysis syndrome to stop renal toxicity during therapy for malignancies. Probenecid will increase excretion of uric acid by the kidneys and may therefore even be used in remedy of persistent gout. Colchicine binds tubulin, thereby inhibiting microtubule polymerization, which blocks mitosis as well as|in addition to} neutrophil migration. Colchicine is now considered to be second-line remedy of acute gout due to its slender therapeutic window and threat of toxicity.
Best 500 mg lovaza
Stratified epithelium is outlined as epithelial membrane composed of multiple cell layer. Stratified squamous epithelium is assessed by the flattened shape of the cells within the surface layer. Examples of tissues with stratified squamous epithelium embrace the pores and skin, mouth, anus, vagina, and esophagus. This sort of epithelium solely seems stratified; nevertheless, all cells are in touch with basal lamina and just some cells attain the surface of epithelium. Simple epithelium signifies that the epithelial membrane consists of a single layer of cells, which helps when diffusion is important. Increased temperature is an indicator of metabolic activity (and therefore increased oxygen demand). The illness is brought on by systemic granulomatous irritation, notably of small- and medium-sized arteries such as those supplying the kidneys and lungs. If not treated with immunomodulating medication, focal glomerulonephritis can progress to a crescentic kind, with ensuing renal failure. Eosinophilia is related to Churg-Strauss syndrome, identified as|also called|also referred to as} allergic granulomatous angiitis. The lack of a history of asthma or allergic reactions argues against Churg-Strauss syndrome. IgA nephropathy (such as Berger disease), characterised by deposition of IgA in glomerular mesangium, is a highly variable entity, starting from asymptomatic hematuria to quickly progressive glomerulonephritis. Like Wegener granulomatosis, Goodpasture syndrome is related to hemorrhagic pneumonitis and glomerulonephritis. Polyarteritis nodosa is an immune advanced irritation occurring in medium-sized vessels. It is related to hepatitis B virus in 30% of sufferers, is related to lesions of varied ages, and may happen in nearly any organ. Patients sometimes have fever, weight reduction, malaise, stomach pain, melena, and hypertension, nicely as|in addition to} cutaneous eruptions, neurologic dysfunction, and hematuria. The affected person has indicators and symptoms of sarcoidosis, with classic race, pathology (noncaseating granuloma), and x-ray of the chest revealing outstanding bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, which is present in >90% of sufferers with sarcoidosis. Erythema nodosum, an inflammatory panniculitis, is the most typical cutaneous manifestation of sarcoidosis, and regularly presents as bilateral tender pink bumps on the shins. Additional options of sarcoidosis embrace hypercalcemia as a result of} increased activation of vitamin D by activated macrophages. Erythema infectiosum, or fifth illness, is a standard childhood viral infection brought on by erythrovirus or parvovirus B19. Erythema multiforme is a pores and skin condition brought on by irritation of the microvasculature and mucous membranes. Erythema toxicum is a harmless rash that seems in roughly half of all newborns. This response is an example of a kind I hypersensitivity reaction by which an allergen cross-links antigenspecific IgE on the surface of mast cells and basophils. Subsequently, the mast cells and basophils launch vasoactive amines such as histamine. Because antibodies are preformed in hypersensitivity, the reaction develops fairly quickly. In this reaction, sensitized T lymphocytes launch lymphokines in response to antigen. Loop B is notable for the decreased quantity and increased stress of respiration in comparison with} loops A, C, and D. The decreased quantity in comparison with} the other loops ought to make you think of a lung that had a large lower in area out there for oxygen exchange. There is improved quantity and compliance (change in volume/change in pressure) of the pulmonary system over the baseline loop C. The complete lung quantity and pressures can be anticipated to be larger in a affected person after complete lung resection. This affected person doubtless has diphtheria, an infection brought on by the gram-positive rod Corynebacterium diphthe riae. It is seen very rarely in vaccinated populations however is endemic to sure elements of the world. Culture of C diphtheriae requires tellurite agar (Loeffler medium) to forestall progress of regular higher respiratory tract flora. Pertussis presents with paroxysmal coughing spells and whooping sounds on inspiration. Encapsulated strains of H influenzae trigger invasive ailments such as septicemia, meningitis, cellulitis, septic arthritis, epiglottitis, and pneumonia. Nonencapsulated strains are trigger otitis media, conjunctivitis, bronchitis, and sinusitis. Although the drug typically is well tolerated, its commonest opposed results involve ocular toxicity such as lack of visual acuity and redgreen colour blindness, which usually seems a number of} months after the initiation of therapy. For kids, most literature supports a routine of six months with isoniazid and rifampin, with ad- ditional coverage of pyrazinamide through the first two months. Isoniazid blocks mycolic acid cell-wall synthesis and is bactericidal for quickly multiplying organisms. Major opposed results embrace hepatotoxicity and peripheral neuropathy, however many different opposed results happen, such as lupus-like syndrome and optic atrophy. Like isoniazid, the spectrum of action of pyrazinamide is limited to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The web site of activity for pyrazinamide is assumed to be a fatty acid synthase gene. Histopathology would show a granulomatous reaction, with the attainable presence of big cells. It coats alveoli and small airways and serves to reduce surface tension over the airwater interface. Thus, in a toddler missing surfactant, the compliance of the alveoli shall be decreased. The large anion hole outcome of|as a end result of} of} the overproduction of ketones within the absence of insulin production. Calcium oxalate crystals could also be} seen in ethylene glycol poisoning, which may be another cause of metabolic acidosis with an increased anion hole. In metabolic acidosis, respiratory compensation happens and reduces blood partial stress of carbon dioxide via deep respiration. Elevated blood partial stress of carbon dioxide is seen in sufferers with metabolic alkalosis with respiratory compensation or respiratory acidosis. As may be seen from the anteroposterior chest radiograph, the cardiac define is on the right, as is the gastric bubble. This condition is usually not dangerous if the reversal of viscera is complete, however is fairly debilitating if the reversal is limited to the heart. Often, situs inversus is related to Kartagener syndrome, a condition brought on by an autosomal recessive defect within the molecular motor protein dynein. This genetic defect ends in immotile cilia, impairing a number of|numerous|a selection of} important processes. Patients present with production of enormous quantities of dilute urine, serum hyperosmolality, and hypernatremia. Therefore, as she attempts to inhale, her thoracic cavity expands however air enters via the wound, equalizing the stress; this prevents the normal expansion of the lungs. Intrapleural stress should be less than atmospheric stress during inspiration, permitting air entry. The downside with this affected person is that air is getting into via a penetrating wound, somewhat than solely into the lungs. While it may lower the tidal quantity, it will additionally increase respiratory frequency, resulting in an oxygen saturation nearer to regular. Chronic inhalation of asbestos fibers asbestosis, which is marked histologically by ferruginous bodies that stain positively with Prussian blue.
Effective lovaza 500mg
Intestinal Parasites Most helminths and protozoa exit the body within the fecal stream. Feces must be collected in a clean cardboard container, with the time of assortment recorded. Fecal samples must be collected before the ingestion of barium or different distinction brokers and before remedy with antidiarrheal brokers; these substances alter fecal consistency and interfere with microscopic detection of parasites. Blood and Tissue Parasites Invasion of tissue by parasites could direct the analysis of different samples;. The parasites most commonly detected in Giemsa-stained blood smears are the plasmodia, microfilariae, and African trypanosomes; nonetheless, wet mounts could also be} extra sensitive for microfilariae and African trypanosomes as a result of|as a end result of} these active parasites trigger movement of erythrocytes in microscopic fields. The major mechanisms of resistance utilized by bacteria are drug inactivation, alteration or overproduction of the antibacterial goal, acquisition of model new} drug-insensitive goal, decreased permeability to the agent, and active efflux of the agent. Allergy: anaphylaxis, drug fever, serum illness, maculopapular eruptions, nephritis, hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, Stevens-Johnson syndrome; lowlevel cross-allergy between penicillins and cephalosporins; no cross-allergy between monobactams and different -lactams Miscellaneous reactions. Addition of -lactamase inhibitors extends gram-negative, anaerobic, and Staphylococcus aureus spectrum, but gram-negative bacteria that produce chromosomal -lactamases stay resistant. Cephalosporins No protection of Listeria or Enterococcus or of methicillinresistant S. Cefotetan, cefoxitin: good exercise towards gram-negative bacteria and Bacteroides fragilis, poor exercise towards gram-positive bacteria and H. Cefepime: extra stable to chromosomal -lactamases of Enterobacter and Serratia; higher S. Food consumption could improve tolerance, but absorption is impaired if these medication are taken with meals. However, vacationers must be certain that their routine immunizations are up-to-date as a result of|as a end result of} certain illnesses (e. Recommended immunizations are advisable as a result of|as a end result of} they protect towards illnesses for whose acquisition the traveler is at increased risk. Table 84-1 lists vaccines required or really helpful for travel to different destinations. Prevention of Malaria and Other Insect-Borne Diseases Chemoprophylaxis towards malaria and different measures could also be} really helpful for travel. In the United States, 90% of cases of Plasmodium falciparum infection happen in individuals returning or immigrating from Africa and Oceania. In addition, personal protecting measures towards mosquito bites, especially between nightfall and daybreak (e. Prevention of Gastrointestinal Illness Diarrhea is the leading cause of illness in vacationers. The incidence is highest in parts of Africa, Central and South America, and Southeast Asia. Any dose not given on the really helpful age must be given at any subsequent time when indicated and possible. [newline]Red bars indicate age teams that warrant particular efforts to administer these vaccines not beforehand given. The variety of Haemophilus influenzae kind b (Hib) conjugate vaccine doses decided by} the vaccine used. If possible, influenza vaccination of wholesome kids age 6 to 23 months is encouraged because of a considerably increased risk for influenza-related hospitalizations in this group. Children 12 years old ought to receive influenza vaccine in a dosage applicable for his or her age. Hepatitis A vaccine is really helpful for kids and adolescents in selected states and areas and for certain high-risk teams; hepatitis A immunization can start during any go to, and the two doses must be administered at least of|no less than} 6 months aside. Further data may be obtained by way of the National Immunization Program website ( Vaccination additionally be|can be} indicated in Alaskan natives, certain Native American populations, and residents of nursing properties and different long-term-care services. Persons 65 years old ought to bear one-time revaccination if their prior vaccination was at least of|no less than} 5 years before and was given before age 65. Moderate to extreme diarrhea must be treated with a 3-day course or a single double dose of a fluoroquinolone. High charges of quinolone-resistant Campylobacter in Thailand make azithromycin for that country. Other Infections Travelers are at high risk for (1) sexually transmitted illnesses preventable by condom use; (2) schistosomiasis preventable by avoidance of swimming or bathing in freshwater lakes, streams, or rivers in endemic areas; and (3) hookworm and Strongyloides infections preventable by the avoidance of barefoot strolling outdoors. Travel during Pregnancy the safest a part of} pregnancy by which to travel is between 18 and 24 weeks. The rubella immune status of ladies of childbearing age must be ascertained and counseling offered relating to congenital rubella. Vaccine could also be} given if pregnancy is at second or third trimester during influenza season. Asthma is an indicator condition for influenza vaccination but not for pneumococcal vaccination. In individuals present process elective splenectomy, vaccinate at least of|no less than} 2 weeks before surgical procedure. Viral hepatitis, typhoid fever, bacterial enteritis, arbovirus infections, rickettsial infections, and amebic liver abscess are different prospects. Etiology the causative microorganisms vary, partially because of different portals of entry. Nosocomial endocarditis, regularly Staphylococcus aureus, arises most often from bacteremia associated to intravascular gadgets. Pathogenesis If endothelial harm occurs, direct infection by pathogens such as S. The vegetation is the prototypic lesion on the web site of infection: a mass of platelets, fibrin, and microcolonies of organisms, with scant inflammatory cells. Clinical Features the medical syndrome is variable and spans a continuum between acute and subacute presentations. Nonspecific signs include fevers, chills, sweats, anorexia, myalgias, and again pain. Emboli most commonly come up from vegetations 10 mm in diameter and from these situated on the mitral valve. With antibiotic remedy, the frequency of emboli decreases from thirteen per 1000 pt-days through the first week of infection to 1. Possible endocarditis is defined by 1 major plus 1 minor criterion or by three minor criteria. Vascular phenomena: major arterial emboli, septic pulmonary infarcts, mycotic aneurysm, intracranial hemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhages, Janeway lesions 4. If remedy fails or the isolate is immune to generally used brokers, surgical therapy is suggested (see under and Table 85-3). However, pts who develop acute aortic regurgitation with preclosure of the mitral valve or a sinus of Valsalva abscess rupture into the right heart require emergent surgical procedure. Cardiac surgical procedure must be delayed for 2� three weeks if potential when the pt has had a nonhemorrhagic Table 85-2 Antibiotic Treatment for Infective Endocarditis Caused by Common Organismsa Comments Organism Drug, Dose, Duration Streptococci Penicillin-susceptibleb streptococci, S. Doses of gentamicin, streptomycin, and vancomycin must be adjusted for lowered renal perform. Prophylaxis is really helpful for high-risk sufferers and optionally available for moderate-risk group (see Table 85-5). Table 85-5 Cardiac Lesions for which Endocarditis Prophylaxis Is Advised High Risk Moderate Risk Prosthetic heart valves Prior bacterial endocarditis Complex cyanotic congenital heart disease; different advanced congenital lesions after correction Patent ductus arteriosus Coarctation of the aorta Surgically constructed systemicpulmonary shunts Congenital cardiac malformations (other than high-/low-risk lesions), ventricular septal defect, bicuspid aortic valve Acquired aortic and mitral valve dysfunction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (asymmetric septal hypertrophy) Mitral valve prolapse with valvular regurgitation and/or thickened leaflets Table 85-6 Antibiotic Regimens for Prophylaxis of Endocarditis in Adults at Moderate or High Riska I. Prevention the American Heart Association has recognized procedures that may trigger bacteremia with organisms prone to trigger endocarditis (Table 85-4), pts who ought to receive antibiotic prophylaxis based on their relative risk of creating endocarditis (Table 85-5), and regimens for prophylaxis (Table 85-6). Organisms contained inside the bowel or an intraabdominal organ enter the sterile peritoneal cavity, causing peritonitis and- if the infection goes untreated and the pt survives- abscesses. Peritonitis is either major (without an apparent source) or secondary (bacterial contamination ensuing from spillage from an intraabdominal viscus). Clinical Features Pts expertise an acute onset of signs, with fever, abdominal pain, and indicators of peritoneal irritation. Enteric gramnegative bacilli such as Escherichia coli or gram-positive organisms such as streptococci, enterococci, and pneumococci are the most common etiologic brokers; a single organism is usually isolated. The organism burden is low, however the culture yield is improved if 10 mL of peritoneal fluid is placed instantly into blood culture bottles. However, the chance of serious staphylococcal or antibiotic-resistant infections increases over time. Secondary Peritonitis Secondary peritonitis virtually all the time includes a combined aerobic and anaerobic flora, especially when the contaminating source is colonic.
Trusted 500 mg lovaza
His mother explains that more than 10 kids in his class at college have comparable signs, particularly conjunctivitis. A 40-year-old lady presents with progressive fatigue and bilateral joint irritation characterised by pain, swelling, heat, and morning stiffness. The patient says that the signs started in her palms over one year in the past however have now begun to result on} her knees. A 28-year-old man presents to the first care clinic because of|as a outcome of} his considering has been "sluggish" recently, citing for instance that he has had bother remembering the names of his pals. The patient additionally mentions that he has been feeling depressed, and that he has recently lost a big quantity of weight. Physical examination is notable for purplish skin lesions distributed throughout his torso. Blood was drawn from the 4 males suspected to be the daddy (F1, F2, F3, F4) properly as|in addition to} from the mother (M) and the toddler (C). The resulting fragments had been separated with gel electrophoresis and a Southern blot analysis was performed. On additional questioning, she additionally complains of vaginal dryness and occasional sizzling flashes. The 25-year-old spouse has undergone hormonal analysis, and it has been determined that she menstruates usually and her follicles are viable. Karyotype analysis is performed, and reveals the presence of an extra intercourse chromosome. A 2-week-old premature male toddler is examined in the neonatal intensive care unit, and reveals a wide pulse stress and a holosystolic and holodiastolic murmur. On echocardiography he has blood circulate between the left pulmonary artery and the aorta. Which of the next signs would the mother have skilled throughout being pregnant to increase the chance of having a child with this disorder After injection of the anesthetic agent, the lady complains of palpitations and severe dizziness. Which of the next anesthetic agents was most likely administered for the process Comparing the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curves in the image, which of the next conditions represents curve B as in comparison with} curve A Her physician wish to begin an antihypertensive agent but the patient refuses, totally understanding the dangers, benefits, and outcomes that may outcome with or without remedy. A 19-year-old lady with no vital past medical historical past presents to her major care physician for a sports physical. Her examination is notable for a brachial artery stress of 160/110 mm Hg and a weak femoral pulse. Prompted by the weak pulse, her physician measures her blood stress in the lower extremity and finds it to be 80/40 mm Hg. This lady is presenting with a congenital situation that places her at excessive risk for bacterial endocarditis and which of the next other conditions A 21-year-old man presents to model new} major care physician for routine physical examination. He demonstrates hyperextensible skin and reports a historical past of finger and shoulder dislocations, which he has decreased himself. Her physician notes Test Block 5 � Questions 643 (F) Fibrillin (G) Sphingomyelinase 39. He has no personal or household historical past of medical diseases and denies trauma previous to the onset of his pain. A 7-year-old woman with no vital medical historical past presents with a five-month historical past of persistent weak point regardless of taking nutritional vitamins and dietary supplements. Physical examination is totally benign, with normal blood stress and no peripheral edema. Laboratory research present hyponatremia, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, and an elevated plasma renin degree. A 47-year-old man presents with diarrhea, abdominal pain, lack of urge for food, weight loss, and fatigue. Her physical examination is significant for an lack of ability to totally cowl her eyes with her eyelids and swelling on the anterior floor of both legs. The skin of her anterior legs appears dry and waxy and has quantity of} diffuse, barely pigmented papules. The drug of choice for this disorder acts at what step in thyroid hormone synthesis A 61-year-old alcoholic presents to the emergency division with disorientation, confusion, and an unsteady gait. Horizontal nystagmus, pulmonary r�les, and edematous lower extremities are noted on physical examination. On questioning, the patient states that he started ingesting alcohol when he was a prisoner of struggle in Vietnam. His present alcohol degree is within the authorized limit, a toxicology screen is adverse, and a stroke has been ruled out by imaging. Which of the next additional tests ought to be performed to estimate the extent of his illness A 42-year-old man comes to the physician complaining of abdominal pain for the past three months. A patient with long-standing renal failure secondary to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis undergoes parathyroid biopsy that reveals marked hyperplasia. Which of the next units of laboratory values is most likely to be seen in this patient Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid is a calcitonin-secreting tumor of parafollicular thyroid cells ("C cells"). Microscopically, the tumor consists of nests of tumor cells in an amyloid-filled stroma. Atrophic follicles with prominent germinal middle formation and lymphocyte infiltrate are attribute of Hashimoto thyroiditis. A papillary branching pattern of epithelial cells with ground-glass nuclei and psammoma our bodies (laminated concentric calcified spherules) is seen in papillary carcinoma of the thyroid, the most common form of thyroid cancer and also the form with one of the best prognosis. Sheets of undifferentiated pleomorphic cells are seen in anaplastic, or undifferentiated, thyroid cancer. This form of thyroid cancer is extra frequent in older patients and has a really poor prognosis. It consists of relatively uniform follicles lined with cells which are be} typically bigger than these seen in a traditional thyroid. The appointed sturdy power of lawyer is really sturdy and subsequently supersedes even a residing will. The patient, in good mind-set, believed that the friend would make decisions with which he would agree. The sturdy power of lawyer should all the time make decisions in keeping with} what he believes the patient would need. Many states acknowledge subsequent of kin as sturdy power of lawyer, until it has been in any other case specifically assigned, as in this case. The sturdy power of lawyer is final word|the ultimate word} decision maker and their decision to withdraw life support will be upheld regardless of the existence of a residing will. Hairy cell leukemia is caused by malignant B lymphocytes that commonly present varying numbers of projections from cytoplasm, giving the cell a "furry" or "ruffled" appearance as seen in the image above. It is 4 instances extra prevalent in males than in women, and patients normally complain of abdominal fullness, fatigue, and weight loss test Block 5 Full-length exams Test Block 5 � Answers 647 however hardly ever of evening sweats or fevers. Elevation of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase in the B lymphocytes from bone marrow confirms the analysis of furry cell leukemia. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia a B lymphocyte-derived neoplasm whose presentation is that of furry cell leukemia. All Hodgkin lymphoma variants are differentiated by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells and commonly present clinically with evening sweats, fevers, and weight loss. The nodular sclerosis variant is distinguished by a nodular pattern separated by areas of collagen banding and the presence of lacunar cells.
Serpentine-Wood (Indian Snakeroot). Lovaza.
- Dosing considerations for Indian Snakeroot.
- Nervousness, trouble sleeping (insomnia), mental disorders such as schizophrenia, constipation, fever, liver problems, joint pain, spasms in the legs due to poor circulation, mild high blood pressure, and other conditions.
- What is Indian Snakeroot?
- How does Indian Snakeroot work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96766
Purchase 500mg lovaza
After six months of age, when the degrees of maternal antibodies have declined, sufferers with the illness tend to to|are inclined to} present with recurrent bacterial infections. Low IgM levels and normal T cell numbers are typical of WiskottAldrich syndrome, an X-linked defect associated with elevated IgA levels, elevated IgE levels, normal IgG levels, and low IgM levels. Patients have a traditional number of T cells, but their T cells respond ineffectively to antigens. Recurrent pyogenic infections, eczema, and thrombocytopenia are the standard signs. This patient demonstrates a number of} characteristics classic for neurofibromatosis sort 1 (also generally known as|often known as} von Recklinghausen disease). Potential findings embrace caf� au lait spots, two or extra neurofibromas, optic glioma, iris hamartomas (Lisch nodules), a positive family historical past (autosomal dominant inheritance), and a particular bony lesion corresponding to sphenoid dysplasia or scoliosis. Patients with this illness generally show 95% of the factors by age 8 years and the entire standards by age 20. It is way much less widespread than sort 1 and typically manifests with a number of} central nervous system tumors. Hemophilia (types A and B) is an X-linked recessive disorder, with affected male individuals inheriting a defective copy of the X chromosome from heterozygous (asymptomatic) mothers. This profile describes qualitative platelet defects corresponding to BernardSoulier illness and Glanzmann thrombasthenia. Von Willebrand factor promotes platelet adhesion to broken endopthelium, therefore its deficiency prolongs bleeding time. In this disorder, widespread intravascular coagulation consumes platelets and clotting factors, resulting in lab findings indicative of a deficiency in all parts of the clotting machinery. In the lung, a1-antitrypsin deficiency predisposes to persistent obstructive pulmonary illness, particularly panacinar emphysema. Additionally, misfolded gene products of a1-antitrypsin may be deposited in the hepatocellular endoplasmic reticulum. Therefore, sufferers with a1-antitrypsin deficiency are at elevated danger for developing end-stage liver illness like cirrhosis. Cor pulmonale can present with dyspnea and is outcome of|the results of} dysfunction of the best ventricle attributable to pulmonary hypertension in ailments affecting the lung or its vasculature. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is commonly associated with nosocomial infections via contaminated ventilators or bronchoscopes. Renal cysts are associated with inheritable renal situations corresponding to autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney illness, tuberous sclerosis, and Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. This situation is characterised by acute onset of myelosuppression and the presence of elevated myeloblasts in the peripheral smear and bone marrow. In basic, translocations involving chromosome 14 occur in B-cell lymphomas, as the locus for immunoglobulin manufacturing is on chromosome 14. Translocation t(8:14) is associated with Burkitt lymphoma and induces overproduction of the c-myc oncogene. The Bcr-Abl fusion protein is a constitutively active tyrosine kinase that drives the cells to express a cancerous phenotype. Translocation t(11;14) is associated with mantle cell lymphoma, a kind of lymphoma with a really poor prognosis. The translocation produces elevated exercise of cyclin D1, which causes rapid development of the cell cycle. Misoprostol is a prostaglandin E1 analog that can be used to prevent ulcers produced by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug use. It additionally be|can be} used as a medical abortifacient plenty of} international locations, significantly Latin American international locations, and is therefore strictly contraindicated in pregnant ladies. Prostaglandins E1 (misoprostol) and E2 have been successfully used to induce labor by activating the dissolution of collagen bundles, rising the submucosal water content material of the cervix and potentiating effects of endogenous oxytocin. As an antacid, misoprostol acts on parietal cells to inhibit acid secretion and stimulate bicarbonate and mucus manufacturing. Cimetidine is an H2antagonist and is associated with headache, confusion, gynecomastia, thrombocytopenia, and inhibition of the cytochrome P450 system. It is used to treat hypersecretory states, recurrent ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux illness, and stressrelated gastritis. In this patient, parathyroid involvement sometimes recommended|is recommended} by hypercalcemia; and a pituitary adenoma is most probably causing his bitemporal hemianopsia. These tumors might secrete substances corresponding to serotonin and, when they metastasize, they could cause carcinoid syndrome (symptoms embrace bronchoconstriction, cutaneous flushing, diarrhea, and rightsided valvular heart disease). Gastrinomas are non-b islet cell tumors that generally arise from the pancreas and secrete gastrin, leading to hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid. These tumors are associated with Whipple triad: hypoglycemia, signs of hypoglycemia that embrace mental status adjustments, and aid of signs upon glucose administration. Pheochromocytoma is a tumor arising from the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. Paget illness of the bone is characterised by three stages: an preliminary osteolytic lesion involving marked bone resorption, a period of disorganized bone formation, and a final sclerotic or burned-out section. The major abnormality is the overproduction and overactivity of osteoclasts, that are derived from the bone marrow. Alkaline phosphatase is a marker of bone formation, whereas hydroxyproline signifies bone resorption. Dur- ing the period of haphazard bone formation, bone-specific alkaline phosphatase levels are elevated. Rarely, the whole alkaline phosphatase level is normal while the bone-specific alkaline phosphatase level is elevated. The level of elevation of alkaline phosphatase rarely exceeds 10 times the higher limit of normal. The serum phosphate level stays normal, while the calcium level additionally be} normal or slightly elevated. The phosphate level is elevated; Paget illness is associated with a traditional level of phosphate. Furthermore, the phosphate level in this choice is elevated; Paget illness is associated with a traditional level of phosphate. Highly elevated alkaline phosphatase levels are typically present in sufferers with involvement of the skull and minimal of|no much less than} one other website. Increased secretion of prolactin explains the lactation in the absence of recent being pregnant and breastfeeding. Also, as a result of|as a outcome of} prolactin inhibits gonadotropinreleasing hormone synthesis and release, the patient is experiencing menstrual irregularities. Anti-psychotic agents are dopamine antagonists and lead to elevated secretion of prolactin (dopa- check Block 3 Full-length exams Test Block 3 � Answers 593 mine inhibits prolactin release). The patient has most probably been identified with a psychiatric disorder corresponding to schizophrenia that requires dopamine suppression. Premature menopause is associated with loss of ovarian perform before the age of forty years. Lab checks will reveal high levels of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone, with low levels of estrogen. Parkinson illness is a movement disorder characterised by four cardinal signs: resting tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability. Because the disorder stems from a scarcity of dopamine (which capabilities in the basal ganglia to stimulate the motor cortex), one sort of medicine used to treat Parkinson illness is the dopamine agonist. Typical bodily options embrace a webbed neck, short stature, low-set ears, low hairline, and lymphedema. Females with Turner syndrome additionally be} infertile and may have major amenorrhea, distinction to|not like} this patient, who has menstrual irregularities (secondary amenorrhea). Drugs for treating sort 2 diabetes embrace metformin, sulfonylureas, glitazones, and a-glucosidase inhibitors. This patient also manifests signs of hepatic encephalopathy, together with asterixis (flapping tremor), confusion, and lethargy. It also adjustments the bowel flora in order that fewer ammoniaforming organisms are present.
Order lovaza 500 mg
When a toddler has reached the predetermined ranges for extubation, the next must be done: n A chest radiograph must be obtained as a baseline so that postextubation adjustments can be in contrast. However, these adjuncts additionally be} useful if one or two prior makes an attempt at extubation have failed. When the kid prepared to|is in a position to} be extubated, the tube must be rigorously untaped from the face to prevent any abrasions. This breath overcomes the natural adverse stress created because the tube is withdrawn from the airway. Marked retractions also additionally be} seen and are worrisome, indicating both quantity loss in the lung or upper airway obstruction. Clinical deterioration that occurs 24 to forty eight hours after extubation additionally be} brought on by quantity of|numerous|a selection of} factors, together with increased atelectasis, upper airway edema and obstruction, and muscular fatigue. Neonatal high-frequency air flow makes use of gadgets that provide respiratory assist for critically sick neonates with the use of of} small tidal quantity, fast price assisted air flow. Generally, this means charges above one hundred fifty breaths per minute and tidal volumes under 2 to 3 mL/kg. What are the three kinds of high-frequency air flow, and the way are they distinct from one another The interruption takes place in a patient box positioned close to the infant, by a pinch valve that opens and closes on a piece of plastic tubing. High-frequency circulate interruption generates the signal by interrupting the circulate of gas. It is comparable to the jet ventilator besides that the interruption of the gas circulate occurs at a site a lot farther from the toddler. Have the three kinds of high-frequency air flow been in contrast in scientific trials Because there have been no comparability trials, each type has its advocates and critics. What occurs to tidal quantity delivery to the alveolus when frequency is increased during high-frequency oscillation With commonplace mechanical air flow or spontaneous respiratory, minute air flow = frequency � tidal quantity. In high-frequency air flow, minute air flow = (frequency) � (tidal volume)2 this question emphasizes the significance of understanding the differences between high-frequency oscillation and traditional air flow. In conventional air flow growing the rate will improve carbon dioxide elimination typically. With high-frequency air flow turning up the rate generally causes a decrease in minute air flow owing to the lack of tidal quantity delivery. When air flow is insufficient during high-frequency air flow, turning the rate down can improve carbon dioxide elimination. Rather, inhaled gas spikes down the center of the airway, whereas the exhaled carbon dioxide strikes alongside the periphery in a circuitous trend. As frequencies improve, a whirlpool may very well come up throughout the airway that literally pulls the small-volume puffs of gas to a very deep area of the lung. Just as in conventional air flow, adjustments in respiratory system impedance have an effect on} carbon dioxide elimination during high-frequency air flow. There are a number of} kinds of high-frequency air flow, but the device used additionally be} less essential than the ventilatory technique with which the device is used. If the lung is poorly inflated, a method of lung recruitment (increased mean airway stress in contrast with that being used on a standard ventilator) is acceptable. If air leakage is present or the lung is overinflated, a method that minimizes intrathoracic stress is essential, and a decrease mean airway stress may be the most acceptable strategy. Because of the frequencies used and the small tidal volumes, these adjustments appear to be considerably magnified with highfrequency air flow in contrast with conventional air flow. In neonates with poor lung inflation, ought to high-frequency oscillation be used at decrease, the same, or greater Paw than that being used on conventional air flow High-frequency oscillation permits the use of of} greater Paws than conventional air flow outcome of|as a outcome of} the small tidal volumes promote air flow with out causing lung overinflation. This strategy has been studied in animal fashions of hyaline membrane illness and has been shown to enhance lung inflation, decrease acute lung harm, decrease pulmonary air leaks, and promote survival. Clinically, the objective is to promote lung recruitment whereas avoiding lung overinflation, cardiac compromise, and lung atelectasis. Open lung strategy related to high-frequency oscillatory or low tidal quantity mechanical air flow improves respiratory function and minimizes lung harm in wholesome and injured rats. When high-frequency air flow is used, what measurements assist guide selection of air flow settings If the chest radiograph reveals greater than 9 posterior ribs of inflation, flattened diaphragms, a small coronary heart, or very clear lung fields, the lung additionally be} overinflated. Similarly, if the Paw is high and the FiO2 is low, then Paw must be decreased earlier than FiO2. If the chest radiograph reveals fewer than seven posterior ribs of inflation, domed diaphragms, a standard coronary heart dimension, or diffuse radiopacification, the lung additionally be} underinflated. The assessment of cardiac function essential for the safe use of high-frequency air flow. Monitoring coronary heart price, blood stress, urine output, and capillary refill may help alert the care supplier to adjustments in cardiac output. What adverse occasions have been reported with the use of of} high-frequency air flow The complication of necrotizing tracheobronchitis was reported with early fashions of high-frequency air flow. This complication has disappeared with the event of improved humidification systems. What are the variables used to alter oxygenation during high-frequency air flow Altering Paw to optimum ranges will change lung quantity, enhance ventilation�perfusion matching, and reduce intrapulmonary shunt. In oscillatory air flow Paw can be altered immediately by altering that setting on the ventilator. High frequency oscillatory air flow versus conventional air flow for infants with extreme pulmonary dysfunction born at or near time period. Theoretically, how does high-frequency air flow prevent acute lung harm in hyaline membrane illness Volutrauma occurs most quickly when the lung is repeatedly cycled from a low quantity to a high quantity. Use of zero end-expiratory stress and excessive tidal volumes can create acute lung harm inside minutes. Application of end-expiratory stress reduces "atelectotrauma" by preserving useful residual capacity on the finish of each assisted breath. Thus the extremes of low and high lung volumes are avoided with high-frequency air flow. What other instruments are used in neonatology to promote better lung inflation and cut back the harm related to ventilating a collapsed lung The use of end-expiratory stress, surfactant, susceptible positioning, and liquid air flow all promote lung recruitment over time. To use high-frequency air flow safely, what factors should be rigorously monitored This finding has been observed in quantity of|numerous|a selection of} published research, each with conventional and high-frequency air flow. Currently, no good methods are available for defining optimum lung quantity during high-frequency air flow. In what pulmonary illness states has high-frequency air flow been shown to promote improved oxygenation in contrast with conventional modes of air flow The most dramatic improvements in oxygenation have been reported in sufferers with poor lung inflation. It was adapted in a simplified circuit to provide artificial life assist to pulmonary sufferers in an intensive care unit setting. Both gadgets are sufficiently highly effective to fully assist cardiac output and lung function in neonates. Use of venovenous extracorporeal life assist in pediatric sufferers for cardiac indications: a evaluate of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization registry. Extracorporeal Life Support Registry Report 2008: neonatal and pediatric cardiac instances. Once the aforementioned inclusion and exclusion standards have been thought-about, considered one of a number of} pulmonary indices is used to assess the severity of respiratory sickness and the likelihood of dying if the toddler is treated conventionally.

Generic 500 mg lovaza
The concept is to provide immunity while the virus continues to be in the incubation interval. If the affected person develops signs, the disease may have progressed to an incurable stage. She requires immediate steroids for treatment and subsequent temporal artery biopsy to affirm the prognosis. The elevated erythrocyte sedimentation fee indicates a generalized inflammatory course of, and additional proof is offered by the new-onset jaw claudication and constitutional signs that normally current in patients with temporal arteritis. Analysis of joint fluid would be neither diagnostic nor attainable in this affected person because of|as a result of} she is simply presently affected by synovitis of her wrists and ankles. Testing for rheumatoid factor and anti-cytidine cyclic phosphate ranges would be appropriate to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis, which can produce symmetrical and proximal joint signs. Thiazides work by way of binding to the chloride web site of the sodium-chloride cotransporter on the luminal floor of the early distal tubule and inhibiting sodium-chloride reabsorption. Most diuretic agents, together with thiazides, loop diuretics, and most potassium-sparing diuretics, act at the luminal floor by inhibiting transporters. Exceptions are carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, which inhibit a cytoplasmic enzyme, and the potassium-sparing diuretic spironolactone, which inhibits steroid receptor operate. Loop diuretics such as furosemide, bumetanide, torsemide, and ethacrynic acid bind to the chloride-binding web site of the sodium-potassium-chloride symporter of the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. Aldosterone acts to improve the number of sodium-potassium trade channels in the basolateral membrane at several of} sites, however especially in the amassing duct, successfully increasing sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion. Digitalis agents can act to inhibit the motion of the sodiumpotassium trade pump, however are used as inotropes, not diuretics. Thiazides do bind to the luminal floor of the distal convoluted tubule, however to the chloride-binding sites. Cryptococcus is the most common opportunistic cause of meningitis that presents in a subacute method. Increased opening stress on lumbar faucet is current in most patients with cryptococcal meningitis. Bacterial meningitis results in increased polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and fungal/tubercular meningitis results in lymphocytosis. Toxoplasma is mostly a cause of encephalitis in immunocompromised patients. Treponema, the spirochete that causes syphilis, can even trigger subacute meningitis, however this answer alternative is inconsistent with the picture shown. Each of these shifts the hemoglobin dissociation curve to the right, facilitating oxygen unloading. A shift of the curve to the right signifies that at the same partial stress of oxygen, the p.c saturation of hemoglobin is lower. A shift to the left signifies that at the same partial stress of oxygen, the p.c saturation of hemoglobin is higher, or hemoglobin affinity for oxygen is higher. Temperatures are increased, not decreased, in active tissues and serve to shift the hemoglobin dissociation curve to the right to facilitate oxygen unloading. Test Block 6 � Answers 697 left would produce higher oxygen binding and would oppose oxygen unloading. A shift to the left would produce higher oxygen binding and would oppose oxygen unloading. Subarachnoid hemorrhages begin abruptly, occurring at evening in 30% of instances, and are classically described because the "worst headache of my life. The onset of the headache might or is probably not|will not be} related to a quick lack of consciousness, seizure, nausea, vomiting, focal neurologic deficit, or stiff neck. When current, threat factors for aneurysmal rupture embody hypertension, smoking, alcohol, and conditions causing sudden elevations in blood stress. The pathogenesis of hypertensive hemorrhage is unknown, however is believed to be associated to chronic pathologic effects of hypertension on the small penetrating blood vessels. This affected person is likely going} affected by neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a extreme and probably life-threatening extrapyramidal adverse effect of antipsychotic agents. Classic signs of this syndrome embody hyperpyrexia, autonomic instability, and extreme muscle rigidity. Treatment requires immediate discontinuation of all neuroleptics, supportive care, and the administration of dantrolene. It is first-line treatment for standing epilepticus and is used in most alcohol withdrawal protocols. It is used as a third-line agent for standing epilepticus when first- and second-line agents fail. Although Hunter syndrome and Hurler syndrome are comparable, Hunter syndrome is notable for the absence of corneal clouding, which is current in Hurler syndrome. It is mostly recognized throughout the first 12 months of life and is characterised by a variety of|quite so much of|a wide range of} musculoskeletal abnormalities, corneal clouding, hepatosplenomegaly, and extreme mental retardation. Morquio syndrome is often recognized around the age of one 12 months and is characterised primarily by quick stature and joint laxity. Other musculoskeletal abnormalities are additionally related to this autosomally transmitted disorder. Some patients show hepatosplenomegaly, mild corneal clouding, and valvular heart disease. Some of the physical abnormalities seen in the other mucopolysaccharidoses are additionally observed in Sanfilippo patients, but the hallmarks of this disease are developmental delay and behavioral issues such as aggressive tendencies and hyperactivity that manifest in early childhood. Sleep problems are additionally widespread in these patients, and the physical findings typically develop after the behavioral and sleep sample abnormalities. Patients with Sly syndrome have a defect in the beta-glucuronidase enzyme and are typically recognized as toddlers. The disorder is autosomal recessive, and the presentation can resemble that of Hurler syndrome. P jiroveci pneumonia is handled primarily with sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, however it can possibly} be handled with pentamidine or dapsone. Many antifungal agents inhibit ergosterol synthesis, together with fluconazole and terbinafine. Cell wall synthesis is blocked by many antibiotics, together with penicillins, cephalosporins, and vancomycin. Inhibition of the small ribosomal subunit (30S) is the mechanism of motion antibiotics, together with aminoglycosides and tetracyclines. Inhibition of the bigger ribosomal subunit (50S) is the mechanism of motion of chloramphenicol, erythromycin, clindamycin, and linezolid. The subthalamic nucleus is innervated by the globus pallidus externus in the oblique pathway of the basal ganglia. The web site of the lesion is the substantia nigra, which sends direct projections to the striatum. The striatum consists of the caudate and putamen, that are concerned in both direct and oblique motor pathways of the basal ganglia. The direct pathway, promoted by dopamine launch from the substantia nigra, facilitates motion, and the oblique pathway, inhibited by dopamine launch from the Sn, inhibits motion. The globus pallidus externus is innervated by the striatum in the oblique pathway of the basal ganglia. The globus pallidus internus is a downstream nucleus in both direct and oblique pathways of the basal ganglia. The lateral geniculate nucleus is a thalamic nuclei concerned in visual processing. Construction staff, especially those uncovered to industrial paints (found on bridges), are at risk for lead toxicity that may manifest with wrist and foot drop, in addition to the signs described above. High ranges of iron produce mobile damage by way of the formation of free radicals and lipid peroxidation. N-acetylcysteine is the treatment for acetaminophen toxicity, which is commonly asymptomatic initially. With continued exposure, signs of nephrotoxicity (oliguria and electrolyte abnormalities) develop. Patients with opioid toxicity mostly current with respiratory depression, depressed mental standing, and constricted ("pinpoint") pupils. Symptoms of cyanide poisoning stem primarily from neurologic (headache, confusion, and seizure) and cardiovascular (tachycardia and hypertension) dysfunction. Increased ketone production causes an anion gap metabolic acidosis, characterised by decreased pH and bicarbonate ranges. Ulcerative colitis is a kind of irritable bowel disease that typically begins at the rectum (spares the anus) and spreads continuously up the colon.
500mg lovaza
Tracheal intubation and optimistic strain respiration additionally be} wanted if it is markedly depressed. Most sufferers will recuperate with supportive therapy, maintenance of fluid and electrolyte steadiness and correction of hypoglycaemia by glucose infusion until alcohol is metabolized. It is each pharmacokinetic (reduced price of absorption outcome of} gastritis and sooner metabolism outcome of} enzyme induction) and cellular tolerance. Recent research have confirmed that a genetic basis contributes to progression from social ingesting to Chapter 28 alcoholism in about 50% people. In some societies, alcoholic beverages have turn into a suitable type of extending courtesy and of entertainment. Naltrexone: Several research have demonstrated involvement of opioid system in the pleasurable reinforcing effects of alcohol probably by blunting dopamine mediated reward function. Trials among post-addicts have shown that the long appearing opioid antagonist naltrexone helps stop relapse of alcoholism. It decreased alcohol craving, variety of ingesting days and probabilities of resumed heavy ingesting. In conjunction with social and motivational remedy, it has been discovered to reduce relapse of the ingesting behaviour. Physical dependence happens solely on heavy and round the clock ingesting (if alcohol is current in the body continuously). Astringent action of alcohol is utilized in antiperspirant and aftershave lotions. Intractable neuralgias (trigeminal and others), extreme cancer pain-injection of alcohol around the nerve causes permanent loss of transmission. To ward off cold-may profit by inflicting vasodilatation of blanched mucosae; but additional exposure after taking alcohol additionally be} deleterious as a result of|as a result of} alcohol increases heat loss outcome of} cutaneous vasodilatation. As urge for food stimulant and carminative: 30� 50 ml of 7�10% alcohol additionally be} taken as beverages or tinctures earlier than meal. Side effects of disulfiram (as such) are infrequent, embody rashes, metallic style, nervousness, malaise and stomach upset. Unscrupulous mixing of methylated spirit with alcoholic beverages or its inadvertent ingestion leads to methanol poisoning. Methanol is metabolized to formaldehyde and formic acid by alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases respectively, however the price is 1 /7th that of ethanol. Like ethanol, it follows zero order kinetics and t� of 20�60 hours has been measured. Toxic effects of methanol are largely outcome of} formic acid, since its additional metabolism is sluggish and folate dependent. Manifestations of methanol poisoning are vomiting, headache, epigastric pain, uneasiness, dyspnoea, bradycardia and hypotension. Acidosis is distinguished and Aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitors Disulfiram It inhibits the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase probably after conversion into active metabolites. These are- flushing, burning sensation, throbbing headache, perspiration, uneasiness, tightness in chest, dizziness, vomiting, visual disturbances, psychological confusion, postural fainting and circulatory collapse. Sensitization to alcohol develops after 2�3 hours of first dose, reaches its peak at ~12 hours and lasts for 7�14 Chapter 28 completely outcome of} production of formic acid. Blurring of vision, congestion of optic disc adopted by blindness at all times precede demise which of} respiratory failure. Ethanol 100 mg/dl in blood saturates alcohol dehydrogenase and retards methanol metabolism. Ethanol (10% in water) is run through a nasogastric tube; loading dose of zero. Moreover, Methyl Alcohol 387 the enzyme saturating concentration of ethanol itself produces intoxication and can cause hypoglycaemia. Fomepizole (4-methylpyrazole) is a specific inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase-retards methanol metabolism. Ethylene glycol poisoning Ethylene glycol poisoning has occurred sporadically, particularly among children. It is oxidized in the body by alcohol dehydrogenase to glycoaldehyde and then to glycolic acid-glyoxylic acid- oxylic acid in steps. Ethylene glycol itself may cause intoxication similar to ethanol, but era of metabolites leads to acidosis, cardiopulmonary complications and renal tubular necrosis. Fomepizole used in the same manner as for methanol poisoning is the drug of alternative. Sedation refers to decreased responsiveness to any stage of stimulation; is associated with some decrease in motor activity and ideation. Those with quicker onset, shorter length and steeper dose-response curves are most well-liked as hypnotics whereas more slowly appearing medicine with flatter dose-response curves are employed as sedatives. Alcohol and opium have been the oldest hypnotics and proceed to be used for this purpose as self-medication by folks. In the mean time, quantity of|numerous|a selection of} different sedative-hypnotics have been launched but none was significantly totally different from barbiturates; all are redundant now. The totally different phases of sleep and their traits are- Stage zero (awake) From mendacity means down to} falling asleep and occasional nocturnal awakenings; constitutes 1�2% of sleep time. There are marked, irregular and darting eye movements; goals and nightmares happen, which can be recalled if the topic is aroused. Barbiturates Long appearing Phenobarbitone Ultra-short appearing Butobarbitone Thiopentone Pentobarbitone Methohexitone Short appearing 2. Benzodiazepines Hypnotic Diazepam Flurazepam Nitrazepam Alprazolam Temazepam Triazolam Zopiclone, Antianxiety Diazepam Chlordiazepoxide Oxazepam Lorazepam Alprazolam Anticonvulsant Diazepam Lorazepam Clonazepam Clobazam 3. Newer nonbenzodiazepine hypnotics Zolpidem Zaleplon Chloral hydrate, Triclophos, Paraldehyde, Glutethimide, Methylprilone, Methaqualone and Meprobamate are historical sedative-hypnotics now not used. They are insoluble in water but their sodium salts dissolve yielding extremely alkaline resolution. Hypnotic dose (100�200 mg of a brief appearing barbiturate) shortens the time taken to fall asleep and increases sleep length. The sleep is arousable, however the subject could feel confused and unsteady if waken early. Sedative dose (smaller dose of a longer appearing barbiturate) given at daytime can produce drowsiness, reduction in anxiousness and excitability. The 5-phenyl substituted agents (phenobarbitone) have higher anticonvulsant: sedative ratio. The barbiturate website seems to be situated on or subunit, as a result of|as a result of} presence of solely these subunits is sufficient for their response. However, the dose Sedative-Hypnotics 391 producing cardiac arrest is about 3 times bigger than that inflicting respiratory failure. Skeletal muscle Hypnotic doses have little impact but anaesthetic doses reduce muscle contraction by miserable excitability of neuromuscular junction. Effect of single dose of short appearing barbiturate could last just 6�10 hours outcome of} redistribution, whereas elimination t� is 12�40 hours. It is 2�3 g for the more lipid-soluble agents (short-acting barbiturates) and 5�10 g for less lipid-soluble phenobarbitone. Gastric lavage; go away a suspension of activated charcoal in the abdomen to stop absorption of the drug from intestines. Supportive measures: corresponding to, patent airway, assisted respiration, oxygen, maintenance of blood quantity by fluid infusion and use of vasopressors- dopamine additionally be} most well-liked for its renal vasodilating action. Haemodialysis and haemoperfusion (through a column of activated charcoal or different adsorbants) is very efficient in eradicating long-acting properly as|in addition to} shortacting barbiturates. This is harmful, could precipitate convulsions whereas the patient is still comatose-mortality is elevated. The emphasis may be} on keeping the patient alive until the poison has been eradicated. Acute intermittent porphyria-barbiturates exacerbate it by inducing microsomal enzymes (aminolevulinic acid synthetase) and rising porphyrin synthesis. The enzyme inducing property of phenobarbitone could be utilized to hasten clearance of congenital nonhaemolytic jaundice and kernicterus. Mental confusion, impaired efficiency and visitors accidents could happen (also see Ch.
References:
- https://www.bidmc.org/-/media/2019-anesthesia-biennial-report-_lr.pdf
- https://www.gillettechildrens.org/assets/uploads/general/Newsletter_PDFs/Vol17No2.pdf
- https://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/Factsheets/pdfs/bovine_babesiosis.pdf
- https://medicine.umich.edu/sites/default/files/content/downloads/Behavioral-Activation-for-Depression.pdf
.png)