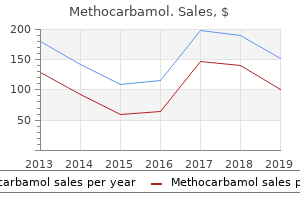
Safe 500 mg methocarbamol
After mask induction with an inhalational agent, topical lidocaine must be used to anesthetize the vocal folds. Direct laryngoscopy must be carried out and a rigid bronchoscope introduced underneath direct imaginative and prescient. Once the bronchoscope has been introduced, the anesthesiologist might connect to the ventilation port. Once the international physique is recognized, removal might require withdrawing, as a unit, the telescopic forceps and bronchoscope (Figure 38�three). Care must be taken to avoid untimely release of the international physique as a result of this can result in an obstructing laryngotracheal international physique. The surgeon also needs to talk with the anesthesiologist to affirm the depth of anesthesia in order that laryngospasm is prevented upon withdrawal of the bronchoscope. The bronchoscope must be advanced once more to rule out further international bodies in the extra distal airway. Flexible suction catheters can be advanced down the side port to take away secretions and facilitate visualization. Depending on the ease of extraction, the kid might require a postoperative chest x-ray and close comply with-as much as rule out the event of pneumonia. Prognosis Most youngsters make a full recovery without everlasting sequelae from aerodigestive tract international physique ingestion. A randomized medical trial of the management of esoph- 527 ageal cash in youngsters. Endoscopic management of international bodies in the tracheobronchial tree: predictive elements for problems. The cricoid cartilage develops abnormally and could also be elliptical or flattened in form, inflicting cartilaginous stenosis. The remainder of subglottic stenosis is taken into account to be iatrogenic; airway instrumentation with both tube dimension relative to the airway and the length of intubation performs a task. Acquired subglottic stenosis extra usually entails gentle tissue stenosis in distinction to the congenital kind, which leads to cartilaginous stenosis. Pressure is taken into account to play a task, inflicting initial mucosal edema and irritation with subsequent ulceration and finally fibrosis (Figure 39�1). The characterization of stenosis throughout diagnostic endoscopy, together with the location, severity, and length of the stenosis, is extremely important and helps to direct management options and predict outcomes. A proportion of those patients developed subglottic stenosis: as much as eight% according to some reports. Further advances in endotracheal tube and ventilation management in the final 30 years have decreased the incidence of subglottic stenosis in the neonatal inhabitants to < 1%. A second inhabitants of infants born with congenital subglottic stenosis has remained stable at approximately 5%. It is these patients who provide some of the best diagnostic and management challenges for the otolaryngologist. Other airway abnormalities-both congenital and iatrogenic-together with laryngomalacia, vocal fold paralysis, and supraglottic and glottic stenosis, have prompted otolaryngologists to proceed to refine surgical airway reconstruction methods. The drawback of pediatric laryngotracheal stenosis: a medical and experimental study on the efficacy of autogenous cartilaginous grafts positioned between the vertically divided halves of the posterior lamina of the cricoid cartilage. The supraglottis, which comprises the epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds, and arytenoid cartilages, prolapses into the airway throughout inspiration. The first proposes that immature cartilage lacks the stiff construction of extra mature cartilage. The second principle suggests immature neural innervation, which is a form of hypotonia. This situation could also be congenital or secondary to an abnormality along the course of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. The commonest etiology is secondary to hydrocephalus from a malformation such as Arnold-Chiari. Reflux in infants with laryngomalacia: results of 24-hour double-probe pH monitoring. Awareness of the risks of aggressive laser use in the airway has additionally contributed to decreased rates of iatrogenic airway lesions such as glottic stenosis and laryngeal net formation. The etiology of supraglottic stenosis may also involve prior airway laser surgery or earlier open airway procedures involving lengthy-time period indwelling stents with subsequent granulation tissue and fibrosis formation. A extra typical presentation of acquired subglottic stenosis, however, could also be of a untimely infant with a E. The pathogenesis of acquired laryngeal net typically entails improvement of an inflammatory course of in reaction to the initial insult, with subsequent maturation and scar formation. For an older child with an initially much less severe airway lesion, voice modifications, feeding difficulties, or progressive respiratory symptoms might develop. This scale, though nonetheless somewhat subjective, is an attempt to provide an objective parameter of stenosis severity. Many of those patients are former untimely infants and should have a component of chronic lung disease, the severity of which must be recognized earlier than proceeding with open airway reconstruction. Voice analysis-Although most earlier research have evaluated only postoperative voice high quality after airway reconstruction surgery, ideally, a preoperative exam would add worth for comparison and, in the future, could also be included extra routinely in the preoperative analysis. Voice issues after pediatric laryngotracheal reconstruction: videolaryngostroboscopic, acoustic, and perceptual evaluation. Airway fluoroscopy might show coexisting pathology, such as tracheomalacia, however depends on the experience of the radiologist for the prognosis. Preoperative barium swallow is really helpful if a child has a historical past of feeding difficulties. Imaging research may also be helpful in diagnosing tracheal compression secondary to a vascular lesion. This check entails a probe in the pharynx (above the upper esophageal sphincter) and in the esophagus (above the decrease esophageal sphincter) for detection of acid over a 24-hour interval. If a repeat pH probe remains to be discovered to be constructive, antireflux surgery is really helpful earlier than considering airway surgery. This planned alteration resulted in G-tube placement for some patients; for other patients, planned surgical reconstruction was modified with the aim of stopping both compromised postoperative recovery secondary to aspiration and the shortcoming to keep adequate diet. Flexible endoscopy-A preoperative dynamic view of the airway is essential when contemplating airway reconstruction. Diagnoses to think about embrace laryngomalacia; vocal fold paralysis; laryngeal net, cyst, or cleft; laryngocele; subglottic hemangioma; tracheoesophageal fistula; tracheal stenosis; tracheal compression secondary to a vascular anomaly; and first tracheomalacia. Some youngsters might require feeding tube placement till stent removal to allow for adequate dietary support. Granulation tissue formation and stenosis-Late problems can embrace granulation tissue formation on the stent tip, and glottic or supraglottic stenosis. These problems could also be prevented if routine postoperative endoscopy is carried out at regular intervals. Posterior glottic stenosis might require growth surgery with a posterior cartilage graft. Problems with voice high quality-Voice high quality postoperatively might worsen and can be secondary to anterior commissure asymmetry, formation of a glottic net, or vocal fold scarring. Care must be taken intraoperatively to avoid incision of the anterior commissure. Postoperative voice therapy could also be indicated since delays in language and communication expertise can be a supply of great morbidity for patients and their families. Tracheocutaneous fistula-A persistent tracheocutaneous fistula is one other potential complication after a protracted-standing tracheotomy and should require restore with excision of the epithelial-lined tract. Suprastomal collapse-Suprastomal collapse can occur in patients with lengthy-standing tracheotomies and should require rigid support with cartilage. Arytenoid prolapse and supraglottic collapse- Arytenoid prolapse might occur, mostly after cricotracheal resection or in depth laryngotracheal growth procedures. A partial arytenoidectomy could also be required, though the potential increased risk of aspiration also needs to be thought-about. Extreme care must be taken when dissecting around the pleura or recurrent laryngeal nerve to avoid damage. Endotracheal tube and stent displacement- Early postoperative problems can be associated to endotracheal tube or stent displacement such as subcutaneous emphysema, pneumothorax, or pneumomediastinum. Care must be taken to secure endotracheal tubes or other stents to avoid these problems. Some surgeons recommend empiric or tradition-directed antibiotic therapy during the postoperative interval. Atelectasis-Atelectasis (with the potential to develop pneumonia) secondary to extended intubation, extended sedation, and paralysis, in addition to narcotic withdrawal, can also be a major postoperative concern.
Safe methocarbamol 500 mg
For the Weimaraner I suggest foods which might be high in animal fats from lamb and poultry. The overall food mix must be poultry first, lamb second, potato third after which a blend of grains like wheat and barley. I feel you must keep away from feeding a Weimaraner any ocean fish, beet pulp, white rice, or soy. Height Standards: m/f - common 17 inches Coat: flat, silky textured with delicate feathering, pink & white in colour Common Ailments: epilepsy, sizzling spots and skin rashes the Welsh Springer Spaniel developed in Wales, which is located on a peninsula of Great Britain. This breed is a direct descendant of the pink and white dogs that the Gauls dropped at Wales in pre-Roman times. In Wales they have been isolated from the rest of the world and bred pure for centuries. The Welsh Springer Spaniel comes from the upper elevations of Wales (2700 to 3500 ft. It was additionally this environment that gave this breed its unique nutritional requirements. Any meats of the world have been from the small herds of cattle or sheep and domesticated poultry, or wild fowl. For the Welsh Springer Spaniel I suggest foods that mix poultry, mutton, and beef meats with corn, wheat, and potato. However, I additionally suggest that you just keep away from feeding any ocean fish, white rice, avocado, or soy bean product to this breed. Height Standards: m/f - common 15 inches Coat: short and wiry in texture, black & tan or grizzle & tan in colour Common Ailments: skin rashes, liver failure, kidney problems the Welsh Terrier, a real Terrier in each sense, is a direct descendant of the old English Black and Tan Terrier. This breed of Terrier developed alongside the Welsh coast to hunt the otter, fox, and badger that inhabited the rookeries of this north Atlantic land. They are very comparable in look to the Airedale Terrier, from Yorkshire County England, besides for his or her physique size. This similarity has led to the speculation that this breed and the Airedale may be related. However, there are data relationship from 1737 that show the Welsh Terrier to be bred out of the old English Black and Tan and bred pure since then. Native food provides for this breed would have been from the coast of Wales and included the otter, badger, fox, fish, poultry, mutton, cabbage, and potato. These foods are the dietary staples for each the humans and the dogs in this space. For the Welsh Terrier I suggest foods which might be a blend of fish, mutton, poultry, corn wheat, and potatoes. I additionally suggest you keep away from feeding any horse meat, avocado, citrus fruit, or white rice to this breed. This space is described as hard rock formations bisected by valleys generally known as "glens" or "straths. Also residing amongst the rocks are many vermin, such as the fox, rabbit, and rodents. Therefore, the farmers from this space developed a breed of dog that would each assist management the vermin inhabitants and save their crops. For the West Highland White Terrier I suggest foods that present meat protein from poultry and lamb, the carbohydrates from potato, barley, and wheat, and the fat from their poultry meat supply. I additionally suggest you keep away from feeding a industrial food that incorporates soy, white rice, yellow corn, beef, or horse meat to this breed. Height Standards: m - 19 to 22 inches, f - 18 to 21 inches Coat: short and sleek, may be any colour or colour combination Common Ailments: monorchidism, sizzling spots and skin rash the Whippet developed in Great Britain however originated in Italy or Northern Africa. The Whippet is the breed instance I use when asked how long it will take a dog to change its nutritional requirements when uncovered to different foods. After twenty-one centuries, the Whippet nonetheless has a coat greatest suited to the nice and cozy and dry environment of its origins and not the heavier double coat discovered on breeds originating in the colder local weather of the British Islands. Likewise, they nonetheless retain the nutritional requirements they developed in their native environment. Fortunately for the Whippet the rabbit was the main food supply in each their native space of the world and in their new homeland. Native food provides for this breed would have been rabbits, domesticated poultry, mutton, goat, and wheat or corn. For the Whippet I suggest foods which might be a blend of lamb, poultry, wheat, and corn. The addition of a linseed oil coat conditioner to this mix will present this breed with an excellent stability of the fatty acids its skin and coat require. However, you must keep away from feeding a soy oil coat conditioner to this breed in addition to any soy bean meal in its food. Other food sources to keep away from feeding a Whippet embody horse meat, beef, or ocean fish. Holland, now generally known as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, is a small European coastal country, north of France and east of Germany. Its highest elevation is a thousand toes and its lowest elevation is 20 toes under sea degree. Yet this coat requires stripping and the feel is like that discovered in many terrier breeds from different climates. This coat, discovered only on the Wirehaired Pointing Griffon, is a technique this breed is different from different breeds of canines. The variations among this breed and others additionally lengthen to its nutritional requirements. Native food provides discovered in their authentic coastal and lowland environment would have been oats, potato, rye, sugar beets, and wheat. Meats have been from domesticated poultry, dairy cattle, and ocean fish of the North Sea. For the Wirehaired Pointing Griffon I suggest foods that comprise ocean fish, poultry, and dairy products blended with potato, oats, and sugar beet. I additionally suggest that you just keep away from feeding yellow corn, avocado, soy bean meal, or horse meat to this breed. Height Standards: m/f - Standard; thirteen to 22 inches, Toy; under thirteen inches Coat: a hairless breed of dog, only a tuft of hair on head and tip of tail Common Ailments: depigmentation, albinism, cryptorchidism, and monorchidism the Xoloitzcuintli (pronounced: show - low - eats - queen - tlee) developed in Western Mexico. The Colima people stored the Xoloitzcuintli as a representative of their god Xolotl. The Xolo has many unique options when compared to different breeds of the canine household. They have an abnormally high physique temperature because of a metabolic price different from some other animal. All of those unique bodily options make this animal a considered one of a form breed of dog. Native food provides for this breed would have been from the western mountains of Mexico, located close to the equator. This is a very hot and humid space the place the native meats (even the wild boar) are very low in physique fat and the crops encompass citrus fruits like the mango and papaya. I do suggest that you just study the nutrients of their immediate space before you try to take considered one of these dogs home with you. Try to meet dietary wants by providing native nutrients to any "exported" member of this breed. Prior to their becoming house pets, they have been used as ratters in the coal mines and mills of the world. The Yorkshire Terrier is likely one of the "slowest" of the toy breeds in relation to the event of its skeletal structure. Thus it requires more of the nutrients present in puppy formulation for an extended time frame than the other toy breeds. Native food provides for this breed would have been rodents, a dairy cattle type of beef, potato, sugar beet, rye, and barley. For the Yorkshire Terrier I suggest foods which might be a blend of horse and beef meats, sugar beet, potato, wheat, and barley. I additionally recommend you keep away from feeding a Yorkie any pink fish, corresponding to salmon, yellow corn, or soy. The sum of the processes concerned in the development, upkeep, and restore of the residing physique as a complete.
Purchase methocarbamol 500mg
Sensory analysis-The sensory analysis quantifies the differences in the equilibrium scores between two circumstances. The equilibrium score for sensory analysis is the average of every of the three trials of the circumstances 1�6. Differences are sought in four ratios: (1) the somatosensory ratio, (2) the visible ratio, (3) the vestibular ratio, and (four) the imaginative and prescient choice ratio. The vestibular dysfunction pattern must also be considered in the sensory analysis. Somatosensory ratio-In the somatosensory ratio, a comparison is made from the equilibrium scores of circumstances 1 and a couple of. Abnormally low ratios are related to dysfunction of the somatosensory system. Visual ratio-The visible ratio is the ratio of the equilibrium scores of circumstances 1 and four. Vestibular ratio-The vestibular ratio compares the equilibrium scores of circumstances 1 and 5. Low scores are considered indicative of a dysfunction of the vestibular system (Figure 46�7B). Vision choice ratio-The imaginative and prescient choice ratio compares the sum of the equilibrium scores of circumstances 3 and 6 with the sum of the equilibrium scores of circumstances 2 and 5. Normal sub- Sensory Organization Test the sensory organization test evaluates whether or not a patient with a stability disorder appropriately does make the most of visible, vestibular, and somatosensory cues, and picks the suitable cue underneath conflicting circumstances to keep stability. Sensory situation four requires the patient to stand on the tilted help surface with eyes open and the visible encompass fastened. In sensory situation 6, the help surface is tilted and the visible encompass leans forward, which signifies that the visible and help circumstances are sway referenced. The vestibular dysfunction pattern in sensory analysis is seen in bilateral vestibular loss or decompensated unilateral vestibular loss. In these instances, the equilibrium scores are anticipated to be within the regular range for circumstances 1 through four, but under the decrease limit of the range for circumstances 5 or 6 (or each) (Figure 46�7A). It could be related to a vestibular dysfunction pattern, relying on whether or not vestibular compensation develops. Utility of Computerized Dynamic Posturography the medical usefulness of computerized dynamic posturography in neurotologic follow has been assessed in the literature. It is agreed that this test is sort of useful in the following circumstances and conditions: (1) chronic dysequilibrium; (2) persistent dizziness or vertigo despite treatment; (3) sufferers with regular leads to different vestibular tests; (four) measuring the baseline postural management previous to treatment; (5) monitoring the results of vestibular ablative therapies; and (6) selecting probably the most useful rehabilitation technique. Strong indicators of a poor response are (1) a substandard performance on the sensory organization test in circumstances 1 or 2 (or each), with nice intertrial differences; (2) a relatively higher performance in circumstances 5 and 6 compared with that in circumstances 1 and a couple of; (3) circular sway with out falling; (four) exaggerated motor responses to small platform translations; and (5) inconsistent motor responses to small and large, forward and backward platform translations. However, controlling the tonic state of the sternocleidomastoid muscle is essential for the correct interpretation of interaural amplitude distinction. The response pathway consists of the saccule, inferior vestibular nerve, lateral vestibular nucleus, lateral vestibulospinal tract, and sternocleidomastoid muscle. The test provides diagnostic details about saccular and/or inferior vestibular nerve perform. The patient is examined whereas seated upright with the pinnacle turned away from the examined ear to improve tension of the muscle. A noninverting surface electrode is positioned at the middle third of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Electromyogenic activity of the muscle is amplified (� 5000) and bandpass filtered from 10 to 2000 Hz. Responses are averaged over a collection of 128 or extra based mostly on the response stability. The test can be useful in detecting vestibular schwannoma originating from the inferior vestibular nerve. However, extended P13 latency was reported to correlate with retrolabyrinthine lesions such as large vestibular schwannoma and a number of sclerosis. Diagnostic worth of extended latencies in the vestibular evoked myogenic potential. Vestibularevoked myogenic potentials in the analysis of superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Characteristics and medical functions of vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials. Augmentation of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials: a sign for distended saccular hydrops. Each pinna is anchored to the skull by pores and skin, cartilage, the auricular muscle tissue, and extrinsic ligaments. The lateral third of the canal is made from fibrocartilage, whereas the medial two thirds are osseous. During early childhood, the canal is straight, but takes on an "S" shape by the age of 9. Cerumen prevents canal maceration, has antibacterial properties, and has a usually acidic pH, all of which contribute to an inhospitable environment for pathogens. Innervation the pinna is innervated laterally, inferiorly, and posteriorly by the nice auricular nerve (cervical plexus). The subcutaneous layer of the cartilaginous portion of the canal accommodates hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and ceruminous glands, and is up to 1 mm thick. The deep auricular department of the maxillary artery supplies the extra medial features of the Copyright � 2008 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. The causes of those problems could also be genetic or secondary to environmental exposures. Patient evaluation requires a radical head and neck examination to exclude additional congenital anomalies. The listing of associated syndromes is intensive and contains Goldenhar (hemifacial microsomia), branchio-otorenal, Treacher Collins, and Robinow syndrome. Pathogenesis Multiple genes might have redundant roles in outer ear formation, which might account for phenotypically related malformations. The sequence of such dysregulation is only starting to be understood with the help of murine knock-out and knock-in models. The mesenchymal tissue of the arches consists of paraxial mesoderm and neural crest cells. The pinna is shaped by the gradual change in shape and fusion of parts of the six auricular hillocks, that are derived from the primary and second branchial arches (Figure 47�5). Formation of the exterior auditory meatus results from an ingrowth of a strong epithelial plate of ectodermal cells, the meatal plug, which finally resorbs with solely the lining of the canal remaining. The tympanic membrane begins to develop through the twenty eighth week of gestation and arises from probably the most medial side of the meatal plug, which finally turns into the exterior layer of the tympanic membrane. Skin of the cartilaginous portion of the exterior auditory canal depicting apopilosebaceous models. However, many anomalies of the exterior ear happen with out recognized patterns of genetic transmission. Isotretinoin, vincristine, colchicine, cadmium, and thalidomide are among the many recognized teratogens related to anomalous hypoplasia of the exterior ear and ought to be averted during being pregnant. This group contains lowset ears, lop ears, cupped ears, and mildly constricted ears. The lop ear is characterized by inferiorly angled positioning of the auricular cartilage, whereas the cup ear protrudes with a deep conchal bowl. Treatment Classically, microtia has been handled by a multistage auricular reconstruction. Patients bear observation till the age of 5 to allow for growth of rib cartilage, which is harvested for reconstruction, and the development of the contralateral ear. This approach provides the benefit of reconstruction with autogenous materials, which ultimately requires little or no maintenance. Postoperatively, the patient should be assessed for pneumothorax, which may arise with rib harvest. Skin for the creation of the sulcus could also be harvested from the groin, decrease abdomen, buttocks, contralateral postauricular sulcus, or back. Audiologic evaluation via behavioral or electrophysiologic measures ought to be performed to verify regular listening to in the contralateral ear in unilateral illness, and to assess for ipsilateral sensorineural listening to loss. The typical pattern of listening to loss in affected ears is a conductive listening to lack of 50�70 dB. Treatment A discussion on reconstruction for aural atresia could be present in Chapter forty eight, Congenital Disorders of the Middle Ear. If the patient selects a bone-anchored prosthesis somewhat than auricular reconstruction, she or he should be conscious that daily maintenance is required and that the anchor might compromise the vascularity of non�hair-bearing pores and skin, complicating future reconstructive surgery if the patient turns into dissatisfied with the prosthesis.
Methocarbamol 500 mg
Take precautions to guarantee the safety of your loved ones and others who might encounter your canine. Every time your canine acts aggressively, back off and use "pleased discuss" to relieve the tenseness of the situation. Your canine off the leash this question is a bit like asking, when will you let your children take independent decisions. Obviously, the best reply can be: When the person is accountable and reliable enough so that you can have the boldness that he can take good decisions. Can you trust your canine not to bounce on folks (especially children), chase joggers, battle with other canines, decide up garbage, invade picnic lunches and so forth Use a protracted leash on outings to give your canine some freedom but nonetheless let you maintain control. His concept was that if a canine needed to anticipate the claws of a bear to sink into his flesh before operating from the danger, he could by no means survive. By the time, you will get to the door; the canine has been displaying the conduct for about 10 seconds. At the first immediate of speeding toward the door, you say the word, "No" to identify which conduct causes the pillow to fly. The use of a warning sign before the actual correction has disrupted the conduct successfully. Over two of three additional trials, the conduct of speeding the door will disappear. If your canine all the time goes ahead of you, you need to get your leash and pull him back. A doggie mattress on the floor beside you is your greatest guess for sustaining the Alpha position. When a child reaches to pet the canine or hug you, he could bite them if allowed to get away with this antisocial conduct. Just as a child appears to his parents for steering and bounds, so does your canine. The canine will eliminate, see the mess and get nervous; you are actually going to be sad. This is the explanation so many canines will relieve themselves in inappropriate places and look really guilty about it, yet they proceed to do it. Use a physique harness and train your puppy to accept it the identical means you train puppy to accept a collar. If you see your puppy starting to forge ahead, abruptly reverse instructions so that puppy finds himself all of a sudden behind or beside you. Since your pup is unable to stroll the streets yet, start educating him to stroll around your home and yard. Go up one step; encourage and entice your canine up with your voice, a meals deal with or a toy. Repeat just one step over and over until your canine goes up and down with ease and braveness. Never pressure your canine to go up or down as this can only frighten him and gradual the method How do you put a collar around his neck Just put the collar on the canine and let him bounce, squirm, roll and paw at it if he wishes. This was developed around the flip of the century as a way of testing and preserving the character and the utility of working canines. It was used then and in lots of instances is still used at present as standards to gauge the suitability of a canine for breeding. Other medical reasons could include viral infections, liver disease, anal gland infections, pores and skin disorders, or other painful situations. A go to to your veterinarian will help determine in case your canine is suffering from any of those situations. This is a compulsion to perform an act repeatedly because of anxiousness, concern or paranoia. Doberman Pinschers are prone to sucking on their pores and skin and causing lick granulomas (thick open sores). If your canine barks when confined or left alone, there are two approaches to take: attempt to make the approach to life more appropriate for the canine, and cease rewarding misbehavior. The resolution to this kind of barking can be very sophisticated, and often requires the use of a canine trainer. Some of the methods used to retrain a canine who barks when pleased involve making the canine sad, and when that becomes too troublesome or maybe even inhumane, the choice of debarking becomes one to contemplate. However, we do know that he originated in Apolda in Thueringen, Germany someday around 1890. His ability to track a scent has made him a favourite among many police departments and even for the game of looking. The accepted colours as defined by the American Kennel Club are black, red, blue and fawn colours with sharply defined rust coloured markings above each eye, on the muzzle, throat, chest, all legs and toes as well as the underside of the tail. No other colours are accepted, nor are any white markings exceeding one-half sq. inch on the chest. The Doberman, like most breeds, is prone to a number of hereditary illnesses As a Doberman proprietor; you should be familiar with the major and minor problems affecting this excellent breed. It is characterised by hematomas, intermittent lameness (from bleeding into joints) and nosebleeds. However, any type of trauma can be life threatening to a canine, since it could possibly lead to extreme blood loss. Clinical trials carried out on 15,000 Dobermans showed seventy p.c of them have been carriers of the disease. In a canine, the reason for the disease is generally unknown, but is extremely breed specific and is widespread to the Doberman. It is more than likely genetic, though this has yet to be proved and the mode of inheritance has not been documented. In this breed, it seems that the disease is first seen around 2 to 5 years of age. As the illness progresses, the affected coronary heart muscle grows weaker and weaker, whereas the left ventricle compensates by enlarging. It is as if the affected animal has become ill only during the previous few days; in reality the canine would have already progressed through the early phases and is now in severe coronary heart failure. If the disease could be very severe, nonetheless, an affected canine might not survive the preliminary remedy. Even if the illness is initially managed, lengthy-time period prognosis is poor and most Dobermans with this situation will die inside one to six months. It might vary from barely poor conformation to gross malformation of the hip joint allowing complete luxation of the femoral head. Fortunately, Hip Dysplasia in Dobermans has been on the decline in recent years, thanks to the diligent efforts of respected breeders. Liver and Pancreas Chronic Active Hepatitis, Doberman Hepatitis, Copper Toxicosis. Mild intermittent scientific signs generally progress to present severe signs of liver disease. These may be weight reduction, loss of urge for food, vomiting, build up of abdominal fluid, bleeding tendencies, and brain damage. Copper concentration in the liver is elevated in some, but not all, indicating the disease is different from the copper toxicosis described in other breeds. Blood chemistry panels are used to display screen for liver disease and should be a part of regular annual examinations in Dobermans. If discovered in the early phases, the use of one or more protocols can, in some instances, lengthen the quality of life for a significant period of time. Diabetes Mellitus Excessive sugar accumulation in the blood and urine causes this disease. Muscular Diseases this muscular disease, the Dancing Doberman Disease, should be thought of hereditary just because no other mammal, let alone a canine, has ever been reported with the disease. They can really experience hair loss as an allergic reaction to their own pure bacteria.
Effective 500 mg methocarbamol
All four genotypes included within the symbol C P, and only these genotypes, have purple flowers. The phenotype of the flowers within the F1 era is purple because the genotype is Cc Pp. Self-fertilization of the F1 crops (indicated by the encircled cross sign) leads to the F2 progeny genotypes shown within the Punnett sq.. Because only the C P progeny have purple flowers, the ratio of purple flowers to white flowers within the F2 era is 9: 7. Formation of the purple pigment requires the dominant allele of both the C and P genes. With this sort of epistasis, the dihybrid F2 ratio is modified to 9 purple: 7 white. In part A are the genotypes produced within the F2 era by unbiased segregation. In every row, the colour coding indicates phenotypes that are indistinguishable due to epistasis, and the ensuing modified ratio is given. For example, within the modified ratio at the bottom, the phenotypes of the "three: three: 1" lessons are indistinguishable, leading to a 9: 7 ratio. This is the ratio noticed within the segregation of the C, c and P, p alleles in Figure three. The most regularly encountered modified ratios are 9: 7, 12: three: 1, 13: three, 9: four: three, and 9: 6: 1. The types of epistasis that lead to these modified ratios are illustrated within the following examples, which are taken from a wide range of organisms. For example, in genetic research of the colour of the hull in oat seeds, a variety with white hulls was crossed with a variety with black hulls. Among 560 progeny within the F2 era, the hull phenotypes noticed had been 418 black, 106 grey, and 36 white. A genetic speculation to clarify these outcomes is that the black-hull phenotype is because of the presence of a dominant allele A and the grey-hull phenotype is because of one other dominant allele B whose effect is apparent only in aa genotypes. If the A, a allele pair and the B, b allele pair bear unbiased assortment, then the F2 era is predicted to have the genotypic and phenotypic composition 9 16 A B (black hull), three 16 A bb (black hull), three 16 aa B (grey hull), 1 16 aa bb (white hull), or 12: three: 1. Both breeds have white feathers because the C allele is necessary for colored feathers, however the I allele in White Leghorns is a dominant inhibitor of feather coloration. The F1 era of a dihybrid cross between these breeds has the genotype Cc Ii, which is expressed as white feathers due to the inhibitory results of the I allele. For example, if the aa genotype has the identical phenotype no matter whether or not the genotype is B or bb, then the 9: four: three ratio outcomes. As an example, in mice the grayish "agouti" coat colour outcomes from a horizontal band of yellow pigment simply beneath the tip of each hair. The agouti sample is because of a dominant allele A, and in aa animals the coat colour is black. A second dominant allele, C, is necessary for the formation of hair pigments of any sort, and cc animals are albino (white). Crosses between F1 males and females produce F2 progeny within the proportions 9 16 A C (agouti), three 16 A cc (albino), three 16 aa C (black), 1 16 aa cc (albino), or 9 agouti: four albino: three black. In Duroc�Jersey pigs, purple coat colour requires the presence of 09131 01 1749P two dominant alleles R and S. Pigs of genotype R ss and rr S have sandy-colored coats, and rr ss pigs are white. The F2 ratio is therefore 9 16 R S (purple), three 16 R ss (sandy), three 16 rr S (sandy), 1 16 rr ss (white), or 9 purple: 6 sandy: 1 white. Among them are different genes within the biochemical pathway for the synthesis of anthocyanin, as well as totally different genes needed for expression of the biochemical pathway in developing flowers. In this selection, the white flowers could be brought on by a mutation in one of many different genes needed for flower colour. Furthermore, a geneticist thinking about understanding the genetic basis of flower colour would hardly ever be satisfied with having recognized the P gene alone or both the P gene and the C gene. The final goal of a genetic evaluation of flower colour would be, by isolating new mutations, to determine each gene necessary for purple coloration after which, through further research of the mutant phenotypes, to determine the traditional function of each of the genes that affect the trait. The Complementation Test in Gene Identification In a genetic evaluation of flower colour, a geneticist would start by isolating many new mutants with white flowers. Although mutations are normally very rare, their frequency may be increased by treatment with radiation or certain chemical compounds. The isolation of a set of mutants, all of which present the identical kind of phenotype, is called a mutant screen. Among the mutants that are isolated, some will comprise mutations in genes already recognized. For example, a genetic evaluation of flower colour in peas may yield a number of new mutations that changed the wildtype P allele right into a recessive allele 09131 01 1718P Photocaption photocaptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotoca ptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotocaptionphotocaption that blocks the formation of the purple pigment. On the opposite hand, a mutant screen should also yield mutations in genes not beforehand recognized. This is because many of the new mutant alleles will encode an inactive protein of some sort, and most protein-coding genes are expressed at such a degree that one copy of the wildtype allele is adequate to yield a standard morphological phenotype. Among all the brand new mutant strains that are isolated, some may have a recessive mutation in one gene, others in a sceond gene, nonetheless others in a third gene, and so forth. Complicating the difficulty are a number of alleles, because two or extra independently isolated mutations could also be alleles of the identical wildtype gene. How can the geneticist determine which mutations are alleles of the identical gene and which are mutations in different genes Because the brand new mutations are recessive, all one has to do is cross the homozygous genotypes. Then the parental mutant strains have genotypes a1a1 and a2a2, and the F1 progeny have the genotype a1a2. This outcome is called noncomplementation, and it means that the parental strains are homozygous for recessive alleles of the identical gene. In part B we suppose the parental mutant strains are homozygous for recessive alleles of various genes, say a1a1 and b1b1. If the phenotype of the F1 progeny is mutant (A), it means that the mutations within the parental strains are alleles of same gene. If the phenotype of the F1 progeny is nonmutant (B), it means that the mutations within the parental strains are alleles of various genes. The A allele masks the mutation a1 and the B allele masks the mutation b1; hence the phenotype is purple (wildtype). This outcome is called complementation, and it means that the parental strains are homozygous for recessive alleles of various genes. Because the outcome indicates the presence or absence of allelism, the complementation test is one of the key experimental operations in genetics. To illustrate the appliance of the test in apply, suppose a mutant screen had been carried out to isolate extra mutations for white flowers. Starting with a true-breeding pressure with purple flowers, we treat pollen with x rays and use the irradiated pollen to fertilize ovules to get hold of seeds. The F1 seeds are grown and the ensuing crops allowed to self-fertilize, after which the F2 crops are grown. A few of the F1 seeds might comprise a new recessive mutation, but in this era the genotype is heterozygous. Self-fertilization of such crops leads to F2 progeny in a ratio of 3 purple: 1 white. As far as we know at this stage, they could all be alleles of the identical gene, or they could all be alleles of various genes. For the second, then, let us assign the mutations arbitrary names in sequence-x1, x2, x3, and so forth-with no implication about which can be alleles of each other. Each box provides the phenotype of the F1 progeny of a cross between the male father or mother whose genotype is indicated within the far left column and the feminine father or mother whose genotype is indicated within the top row. The next step is to classify the mutations into teams using the complementation test. The crosses that yield F1 progeny with the wildtype phenotype (in this case, purple flowers) are denoted with a sign within the corresponding box, whereas people who yield F1 progeny with the mutant phenotype (white flowers) are denoted with a sign. The indicators point out complementation between the mutant alleles within the parents, and the indicators point out noncomplementation.
Best 500mg methocarbamol
Her dad and mom believe her issues started at 6 months of age, when she started eating stable foods, but have considerably worsened over the previous few months. The only current change in her food plan is that she eats a bowl of cereal every morning along with her dad and mom earlier than they go to work. A 26-year-old lady presents to the clinic with joint pain in her hands and wrists, issue respiratory, and redness over her cheeks and nose. She also notes that her fingertips change color from white to blue to pink when she is cold. A clinician is worried that an Rh-unfavorable mother may be pregnant with an Rh-optimistic fetus. The potential pathology that the clinician is worried about is classified as which of the following immune reactions Over the previous year, the affected person has suffered from erysipelas as well as a earlier bout of pneumococcal pneumonia; each were treated efficiently with antibiotics. Which of the following laboratory abnormalities is more than likely to even be present A 30-year-old lady presents to the emergency department with a right-sided facial droop and bilateral swelling on the face near the angles of the mandible. On further questioning she says that for the previous few weeks she has been feeling wanting breath and drained, and has had a dry cough. Physical examination reveals pink, tearing eyes; smooth, nontender bulging of each cheeks; a right-sided drooping of the mouth; cervical nodes; and bilateral dry r�les. A fifty eight-year-old man presents to his physician due to fatigue, edema, and worsening kidney operate. After in depth laboratory work-up, his physician decides to perform a kidney biopsy. The pathologist notes numerous greencolored, proteinaceous deposits when he uses polarized light microscopy to view the pattern. A 7-year-old boy is dropped at the physician by his dad and mom due to recurrent sinus infections. The dad and mom state that the boy also has had multiple lung infections and intermittent diarrheal infections since birth. Which of the following types of hypersensitivity reaction is being examined, and which cells would be expected to mediate a optimistic check end result A 24-year-old, previously healthy lady presents to the outpatient clinic with a two-week historical past of drooping eyelids and issue rising from a chair. Stimulation with a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor leads to the resolution of her signs. A 3-year-old boy is dropped at his pediatrician due to worsening cough and rhinorrhea. His dad and mom state that he has had multiple similar episodes over the previous year with two brief hospitalizations for pneumonia. What different illness is most intently correlated with the identical sort of autoantibodies as present in this affected person A hyperacute rejection is mediated by pre-fashioned antibodies to the transplanted organ. Acute rejection can occur at any time but is more than likely in the first three months after transplantation. It is because of human leukocyte antigen discrepancies between host and graft, and is extra widespread in highly vascular organs such as the liver or kidney. Finally, continual rejection is a gradual process that leads to fibrosis of the transplanted tissue because of elevated fibroblast activity. Plasma cells are liable for antibody production and due to this fact would be the offender in hyperacute rejections. Fibrocytes go away the bloodstream and differentiate into fibroblasts in the transplanted organ. This defect in early stem cell differentiation ends in an absence of T and B lymphocytes. Without T and B lymphocytes, sufferers are at considerably elevated danger of bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. Failure of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches to descend is known as DiGeorge syndrome, and ends in no thymus or parathyroid glands. Tetany from hypocalcemia and viral and fungal infections are widespread because of the lack of T lymphocytes, while regular B lymphocytes are present. An X-linked tyrosine kinase defect causes Bruton agammaglobulinemia, leading to decreased ranges of all immunoglobulin molecules. Infections begin to occur after the maternal IgG antibodies decline, typically after six months of life. This affected person has indicators and signs of rheumatoid arthritis, a disorder of immune dysregulation. Kupffer cells are tissueresident macrophages; the image depicts a Langerhans cell. Langerhans cells are specialized, tissue-resident dendritic cells, not macrophages. As maternal IgG freely crosses the placenta, any subsequent Rh-optimistic fetus is in danger for hemolytic illness. Thus, the oblique Coombs check is a vital laboratory device to monitor for Rh incompatibilities that may complicate fetal well being. The check end result given in this query signifies that the affected person possesses anti-Rh antibodies in her serum. Therefore, it might be logical for the clinician to suspect earlier being pregnant with an Rh-optimistic fetus. Vancomycin could cause two types of hypersensitivity reactions: anaphylaxis, which is a type I hypersensitivity reaction, and the "pink man" syndrome Immunology Answer B is inaccurate. Tumor necrosis factor-b has functions just like tumor necrosis factor-a in that it helps mount an acute-part response. Dendritic cells arise from each myeloid and lymphoid bone marrow precursors after which set up sites of residence inside the peripheral tissues. By contrast, a vancomycin-induced anaphylactic reaction includes histamine release from mast cells and basophils without binding of preformed IgE antibodies to Fc receptors. Examples include autoimmune hemolytic anemia, Goodpasture syndrome, rheumatic fever, and Graves illness. Type I hypersensitivity reactions are mediated by pre-fashioned IgE antibodies that bind a selected antigen to which the affected person has already been uncovered. Binding of the antigen-IgE complexes to Fc receptors on mast cells ends in degranulation and release of vasoactive substances corresponding to histamine. Examples include polyarteritis nodosa, immune complicated glomerulonephritis, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, serum illness, and the Arthus reaction (local complicated deposition). This youngster is suffering from acute epiglottitis, attributable to Haemophilus influenzae sort B (HiB). The incidence of this illness has decreased drastically lately due to immunization efforts. The HiB vaccine consists of two components: the bacterial capsule antigen and diphtheria toxoid protein. Therefore, a protein (the toxoid) is added to the vaccine in order to generate an antibody response. This is a virulence factor found in Staphylococcus aureus that binds the Fc portion of IgG and thus helps stop opsonization. This scientific state of affairs would end in hyperacute rejection (inside minutes of transplantation; scientific presentation inside minutes to hours) mediated by pre-fashioned anti-donor antibodies in the recipient. Hyperacute rejection occurs virtually immediately, as the anti-donor antibodies bind on to vascular endothelial cells, initiating complement and clotting cascades and leading to hemorrhage and necrosis of the transplanted kidney. Hyperacute rejection is typically mediated by pre-fashioned anti-donor antibodies which might be possessed by the recipient. In this state of affairs, hyperacute rejection would be expected to occur first (inside the first few hours after transplant). This condition is attributable to the failure of growth of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches, and thus the thymus and parathyroid glands. The recurrent viral and fungal infections are attributable to a T-lymphocyte deficiency. In lymph nodes, T lymphocytes are found in the paracortical region, thus this region is commonly underdeveloped in sufferers with DiGeorge syndrome.
Order methocarbamol 500mg
Inaccurate saccades suggest the presence of a pathologic condition within the cerebellum, brainstem, or basal ganglia. Saccade Test Saccades are speedy eye movements that bring objects within the periphery of the visual area onto the fovea. Similar central pathways to these of saccadic motion produce clean pursuit motion. Under optimum conditions, healthy subjects can monitor a target with a part angle of zero�. A morphologic abnormality is referred to as a staircase of saccades, during which the trace exhibits staircase-like eye motion whereas the target is adopted. Acute peripheral vestibular lesions can even impair clean pursuit contralateral to the affected side when the eyes are transferring in opposition to the gradual part of a spontaneous nystagmus. The time fixed is the length of time required for the gradual-part velocity to decline to 37% of the preliminary velocity. The gradual cumulative eye place is a perform of both the preliminary velocity and the time fixed. The normative value of the gradual cumulative eye place varies among the many vestibular laboratories. Each target pace needs to be repeated in both clockwise and counterclockwise instructions. The affected person is asked to gaze straight ahead whereas the target is moved in entrance of his or her field of vision. Gaze Test the gaze test is carried out by recording eye movements whereas the affected person fixes his vision on the middle of a target; the affected person then fixes his gaze 30�40� to the best, to the left, after which above and under the middle of the target. Vestibular spontaneous nystagmus is seen during and after unilateral vestibular dysfunction and beats away from the troubled side. Its depth will increase when gaze is directed towards the path of the nystagmus. A symmetrically decreased acquire is noticed in visual problems, fast-part problems, and congenital nystagmus. Asymmetric gaze nystagmus is indicative of a lesion inside the brainstem or the cerebellum. Dissociated (disconjugate) nystagmus is the distinction in eye movements during the gaze. Fixation Suppression Testing Spontaneous nystagmus is determined by placing the affected person, with eyes closed, in a completely darkened room without any visual or positional stimuli. The affected person is then asked to fixate on the middle of a visible target (central gaze). The ratio of the gradual-part velocity with fixation to the gradual-part velocity without fixation is then calculated. Nystagmus that outcomes from a peripheral origin decays to more than 50% with fixation. Positional nystagmus could also be intermittent or persistent, and the path could also be fixed or changing. The clinician must be cautious about the contamination of spontaneous nystagmus with positional adjustments. This statement is very necessary with periodic alternating nystagmus, during which the nystagmus reverses path each 2 minutes. Caloric Tests Caloric exams are based on comparing magnitude of the induced nystagmus on the best and left sides. The temperature gradient produced by a chilly stimulus causes the cupula to transfer away from the utricle, thereby making a nystagmus that beats towards the opposite side. A heat stimulus causes the endolymph to rise, leading to a nystagmus that beats towards the stimulus side. Positional Tests the purpose of positional testing is to determine the impact of various stationary head positions (and never head movements) on eye movements. Another drawback is the truth that a caloric stimulus can present a means of evaluating the vestibular response, but at just one frequency. When it reaches its peak, patients are asked to fixate their eyes on a central point to check the fixation suppression index. The peak gradual-part velocity is averaged over a 10-second period and is calculated for all sides. The values obtained for each caloric stimulus are placed into equations, with each used for specific conditions that outline vestibular perform. Unilateral weakness (ie, canal paresis) indicates a significantly weak response on one side relative to the other. It is formulated as follows: (R 30�C + R 44�C) � (L 30�C + L 44�C) � 100% � (R 30�C + R 44�C + L 30�C + L 44�C) A. In closed-loop systems, the water circulates in an expandable rubber medium to preserve its temperature. Open-loop systems are thought to present extra reliable and reproducible outcomes than closed-loop systems. The test could be carried out with either a bithermal or a monothermal caloric stimulus. The bithermal caloric test offers probably the most useful knowledge on the vestibular system, which is stimulated by heat and chilly water or air. To enhance the nystagmus response, mental tasks are given to the affected person during the test. In performing caloric testing, temperatures seven levels under and above body temperature (30� and 44� C) are used as chilly- and heat-water stimuli. A complete volume of 250 mL of water is given to the outer ear canal over a period of 30 or 40 seconds. As an alternative to the water stimulus, two air stimuli which might be 24� C and 50� C are used with a circulate fee of 8 L/min for 60 seconds. Four caloric stimuli are given with an interval of a minimum of 5 minutes to stop superimposition or conflicting responses. The following order of stimuli is most well-liked: (1) proper�heat, (2) left�heat, (three) proper� chilly, and (four) left�chilly. In response to the caloric stimulus, the nystagmus begins simply earlier than the end of the caloric stimulus and reaches a peak at approximately 60 seconds of stimulation; it then slowly decays over the the distinction between the perimeters 20�25% indicates the presence of a unilateral weakness. However, normative knowledge for this critical proportion ought to be decided for each laboratory. Directional preponderance (ie, unidirectional weakness) refers to a condition during which the imply-peak, gradual-part velocity of the nystagmus beating towards one side is significantly higher than the imply-peak, gradual-part velocity of the nystagmus beating towards the opposite side. It is determined by the next equation: (R 30�C + L 44�C) � (R 44�C + L 30�C) � 100% � (R 30�C + R 44�C + L 30�C + L 44�C) A distinction > 20�30% assumes the existence of a directional preponderance. The directional preponderance is commonly related to a spontaneous nystagmus because a spontaneous nystagmus enhances the nystagmus beating towards its path and eliminates the nystagmus beating towards the opposite direction. The directional preponderance simply exhibits the existence of bias within the tonic exercise of the vestibular system. However, the directional preponderance is taken into account to replicate an asymmetry within the dynamic sensitivity between the left and the best medial vestibular neurons, versus the rationale behind the spontaneous nystagmus, which is reflected in asymmetry within the resting exercise. The directional preponderance is towards the lesion site for labyrinth and eighth nerve lesions, and towards the uninvolved site for lesions of the brainstem and cortex. Directional preponderance and unilateral weakness could also be noticed together, which is suggestive of acute unilateral peripheral lesions. Caloric weakness could also be found in either side, which is referred to as bilateral weakness. For either side, the whole response to a heat stimulus (< eleven�/s) and the whole response to a chilly stimulus (< 6�/s) is taken into account bilateral weakness. A bilateral weakness is commonly related to vestibulotoxic antibiotherapy or bilateral Meniere illness. The numeric standards for these responses varies amongst laboratories from 40�/s to 80�/s. Hyperactive caloric responses are related to a cerebellar lesion or atrophy as a result of elimination of the cerebellar inhibitory impact on the vestibular nuclei. Failure (ie, an abnormal finding) of the fixation suppression test could also be discovered within the caloric test.
Effective methocarbamol 500 mg
The transcochlear approach sacrifices hearing and requires rerouting of the facial nerve. The sort of posterior fossa craniotomy in the combined approach depends on the necessity for hearing preservation and the extent of the surgical exposure required. Radiation therapy must be considered in cases of inoperable tumors, subtotal resection, recurrent tumors, and malignant tumors. The function of stereotactic radiation therapy in meningiomas continues to be defined. Incomplete tumor elimination is commonly associated with both adherence of the meningioma to the brainstem or cavernous sinus involvement. The lengthy-time period recurrence after whole tumor elimination is between 10% and 30%, whereas that of subtotal elimination is greater than 50%. In distinction to vestibular schwannoma, hearing preservation is extra likely and approaches 70%. The facial nerve perform has a 17% price of decay from preoperative ranges. In distinction to vestibular schwannomas, the anatomic location of posterior fossa meningiomas is diversified. The web site of the meningioma is a significant determinant of forms of morbidity from the tumor and the success of remedy. Facial and cochlear nerve perform after surgery of cerebellopontine angle meningiomas. Epidermoid cysts have a higher price of preoperative facial and trigeminal nerve involvement- 40% and 50%, respectively-compared with vestibular schwannomas. Patients could present with hemifacial spasm, facial hypesthesia, neuralgia, or wasting of the muscle tissue of mastication. A distinguishing attribute relative to vestibular schwannomas and meningiomas is that epidermoid lesions present no enhancement with intravenous distinction. General Considerations Epidermoid cysts are much less frequent than vestibular schwannomas or meningiomas. Epidermoid cysts are treated by surgical excision, but whole elimination is tougher than vestibular schwannomas as a result of they become adherent to normal buildings. Pathogenesis Epidermoid cysts likely develop from ectodermal inclusions that become trapped during embryogenesis. The squamous epithelium produces a cyst full of sloughed keratinaceous debris. The cyst is lined with squamous epithelium and full of lamella of desquamated keratinaceous debris. Most epidermoid cysts are benign, with uncommon stories of squamous cell carcinoma arising in epidermoid lesions. The approaches embody a retrosigmoidal approach for hearing preservation and a translabyrinthine approach in patients with vital hearing loss. Any extension into the center fossa can often be eliminated by way of a posterior fossa craniotomy. The capacity to fully remove the tumor is limited by the propensity of epidermoid cysts to adhere to neurovascular buildings. Attempts at complete tumor elimination could increase the speed of postoperative transient or permanent cranial nerve palsies. Prognosis Total tumor elimination is completed in lower than 50% of cases, and the recurrence price may be as high as 50%. These schwannomas may be observed till facial nerve perform has deteriorated or a neurologic complication turns into imminent since resection often requires division and grafting of the facial nerve. Mimetic perform following interposition grafting is poor and is limited to House-Brackmann Grade three functioning at finest. Trigeminal Nerve Schwannomas Trigeminal nerve schwannomas initially present with ipsilateral facial hypesthesia, paresthesias, neuralgia, and difficulties with chewing. These tumors frequently involve each the center and posterior fossa and a combined approach may be necessary for resection. The primary remedy, much like that for vestibular schwannoma, is surgical resection. Resection of cranial nerve schwannomas could result in vital cranial nerve dysfunction; subsequently, preoperative cranial nerve perform and postoperative rehabilitation are important issues to consider. Schwannomas of these cranial nerves produce symptoms primarily based on their cranial nerve functions, thereby causing hypesthesia and weak spot of the palate, vocal cords, and shoulders, respectively. Facial Nerve Schwannomas Facial nerve schwannomas most commonly happen at the geniculate ganglion, but can involve any portion of the facial nerve. These embody paragangliomas (glomus jugulare neoplasms), hemangiomas, and aneurysms. These lesions happen due to errors in embryogenesis that allow vestigial buildings to stay and grow during adult life. The presenting symptoms are similar to, if not indistinguishable from, these of vestibular schwannoma, and solely imaging allows their differentiation. Paragangliomas (Glomus Jugulare Neoplasms) Glomus jugulare tumors arise from paraganglionic tissues (chief cells) and have intracranial extension in 15% of cases. These neoplasms are gradual growing and present initially with pulsatile tinnitus and conductive hearing loss. Further development at the jugular foramen causes decrease cranial nerve neuropathies, after which intracranial extension into the posterior fossa could result in sensorineural hearing loss and dizziness. Paragangliomas cause irregular growth of the jugular foramen, whereas decrease cranial nerve schwannomas cause clean enlargement of the jugular foramen. Extension to the carotid artery or intracranial extension requires an infratemporal fossa approach. This epithelial lining originates from a duplication of the arachnoid membrane and has secretory capabilities. The remedy entails diuretics, shunting procedures, and marsupialization of the cyst into the subarachnoid space. Hemangiomas Hemangiomas of the temporal bone typically involve the geniculate ganglion and the inner auditory meatus. The hemangiomas involving the geniculate ganglion cause progressive facial paresis. The facial paresis occurs sooner with hemangiomas than with facial nerve schwannomas. The small measurement of the soft tissue mass, irregular bony erosion, and presence of calcium in the tumor are all suggestive of a geniculate ganglion hemangioma versus a facial nerve schwannoma. They are as a result of congenital malformations that result in proliferation of adipocytes in subarachnoid cisterns or ventricles. Therefore, the surgical remedy of these lesions, in the event that they become symptomatic, is conservative debulking. Because hearing is commonly intact, the center fossa approach supplies good surgical exposure and allows for hearing preservation. The likelihood of an intact facial nerve after elimination of a hemangioma is greater than with a facial nerve schwannoma. Short-time period tumor management and acute toxicity after stereotactic radiosurgery for glomus jugulare tumors. Cholesterol Granulomas the petrous apex of the temporal bone lies anterior and medial to the inner ear and posterior and lateral to the clivus and incorporates pneumatized air cells in one third of temporal bones. The obstruction of these air cells leads to inflammation and hemorrhage into the air cells. The phagocytosis of pink cells leads to deposition of cholesterol crystals and a foreign physique response in the petrous apex. When symptomatic, the remedy is surgical drainage quite than complete excision. Imaging characteristics suggestive of an extra-axial neoplasm embody bony changes, widening of the subarachnoid cistern, displacement of brain and blood vessels away from the cranium or dura, and sharp definition of the tumor margin. The administration of intra-axial lesions consists of angiography, conservative surgical resection, and adjunctive therapy. Chordomas Chordomas arise from remnants of the notochord, and cranium base chordomas happen at the clivus (sphenooccipital synchondrosis). The midline location and bony destruction without sclerosis are attribute of chordomas.
References:
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/pain/blaustein_pain_center/physicians/christo.pdf
- https://www.aafp.org/afp/2016/0301/afp20160301p371.pdf
- https://erj.ersjournals.com/content/erj/14/6/1418.full.pdf
.png)