Trusted biaxin 250 mg
In immunocompromised hosts, invasive Paecilomyces infections may manifest as fungemia, delicate-tissue infections, pneumonia, or disseminated an infection (Walsh and Groll, 1999). Similar to Fusarium, Scedosporium species and Acremonium species, Paecilomyces species are recovered in blood cultures from sufferers with disseminated illness (Shing et al, 1996). Of note, Paecilomyces species in culture may be confused with Penicillium species owing to the similarity in the conidial buildings of the two genuses (Saberhagen et al, 1997). However, as is the case for mould infections in general, a correlation of susceptibility outcomes on Paecilomyces species with medical end result has not been established, and therapy should be adjusted to medical response (Das et al, 2000; Groll and Walsh, 2001). While the administration of localized Paecilomyces infections depends on the surgical resection of contaminated foci the place possible, the optimal agent for treating systemic infections has not been recognized (Groll and Walsh, 2001). Agents reported to be helpful towards Paecilomyces include miconazole, griseofulvin, amphotericin B, ketoconazole, itraconazole, and terbinafine (Gucalp et al, 1996; Clark, 1999; GutierrezRodero et al, 1999; Gottlieb and Atkins, 2001). However, the results of medical treatment with amphotericin B vary (Shing et al, 1996; Chan-Tack et al, 1999; Das et al, 2000). Of interest, there may be synergism between amphotericin B and flucytosine (Aguilar et al, 1998). By comparison, less compromised sufferers have responded to amphotericin B followed by itraconazole (Walsh and Groll, 1999). In a conservative approach, high-dose amphotericin B deoxycholate should be the initial therapeutic intervention; the lipid formulations of amphotericin B or investigational triazoles are reserved for sufferers refractory to or illiberal of deoxycholate amphotericin B (Groll and Walsh, 2001). The role of itraconazole and voriconazole as well as the investigational triazoles. Triazoles in combination with both amphotericin B or flucytosine may be effective in treating Paecilomyces infections; nevertheless, that is speculative owing to inadequate knowledge (Das et al, 2000). Less Common Agents of Hyalohyphomycosis Localized an infection, extreme invasive an infection, and disseminated an infection attributable to Chrysosporium and Trichoderma species have lately been reported, primarily in the setting of profound immunosuppression (Stillwell et al, 1984; Levy et al, 1991; Warwick et al, 1991; Munoz et al, 1997; Roilides et al, 1999; Wagoner et al, 1999). Less common agents of hyalohyphomycosis, similar to Lecythophora mutabilis (formerly Phialophora mutabilis), Geotrichum candidum, Arthrographis kalrae, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Beauveria bassiana, and Myriodontium keratinophilum, have been reported to trigger infections in both immunocompetent or immunocompromised sufferers (Maran et al, 1985; Ahmad et al, 1985; Rippon, 1988a; Jacobs et al, 1992; Degavre et al, 1997; Guarro et al, 1998; Farina et al, 1999; Kisla et al, 2000; Chin-Hong et al, 2001; Yamamoto et al, 2001; Henke et al, 2002). Trichoderma species have been reported to trigger sinusitis, pneumonia, brain or hepatic abscess, delicate tissue, and disseminated an infection in immunocompromised sufferers (Guarro et al, 1999; Groll and Walsh, 2001; Chouaki et al, 2002). In addition, Trichoderma species are incessantly responsible for continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis-related fungal peritonitis (Loeppky et al, 1983; Chouaki et al, 2002). Most Trichoderma infections are as a result of Trichoderma longibrachiatum and, not often, Trichoderma citrinoviride (Loeppky et al, 1983; Munoz et al, 1997; Furukawa et al, 1998; Guarro et al, 1999; Richter et al, 1999; Hennequin et al, 2000; Chouaki et al, 2002). Chrysosporium species have been reported to trigger keratitis, osteomyelitis, and extreme invasive an infection, together with dissemination, in the setting of immunosuppression (Stillwell et al, 1984; Levy et al, 1991; Warwick et al, 1991; Roilides et al, 1999; Wagoner et al, 1999). Trichoderma species seem as hyaline moulds indistinguishable from other hyalohyphomycetes in tissue (Groll and Walsh, 2001). Most isolates of Trichoderma species present resistance to fluconazole, 5-fluorocytosine and nikkomycin Z in vitro and are both prone or intermediately immune to amphotericin B, itraconazole, ketoconazole, and miconazole (Munoz et al, 1997; Li and Rinaldi, 1999; Chouaki et al, 2002). On the other hand, amphotericin B, itraconazole, Hyalohyphomycoses (other than aspergillosis and penicilliosis) 265 posaconazole, ravuconazole and voriconazole seem to have activity towards Geotrichum species (Pfaller et al, 2002). A reasonable first-selection therapy in the rare case of an infection attributable to Trichoderma species is amphotericin B, both alone or in combination with itraconazole or ketoconazole (Chouaki et al, 2002). The acceptable length for treatment is unclear; treatment should be individualized to each case based on the sort and extent of the an infection and to the underlying predisposing situations (Munoz et al, 1997). In vitro synergistic interactino between amphotericin B and pentamidine towards Scedosporium prolificans. Hyalohyphomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: two world illness entities of public health significance. In vitro susceptibility testing strategies for caspofungin towards Aspergillus and Fusarium isolates. In vitro synergy of caspofungin and amphotericin B towards Aspergillus and Fusarium spp. Fungal endocarditis attributable to Pseudallescheria (Petriellidium) boydii in an intravenous drug abuser. Scedosporium an infection in immunocompromised sufferers: successful use of liposomal amphotericin B and itraconazole. Topical nystatin powder in extreme burns: a brand new treatment for angioinvasive fungal infections refractory to other topical and systemic agents. Berenguer J, Rodriguez-Tudela J L, Richard C, Alvarez M, Sanz M A, Gaztelurrutia L, Ayats J, Martinez-Suarez J V. Carreter de Granda M E, Richard C, Conde E, Iriondo A, Marco de Lucas F, Salesa R, Zubizarreta A. Endocarditis attributable to Scedosporium prolificans after autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Hyalohyphomycosis by Paecilomyces lilacinus in a renal transplant patient and a review of human Paecilomyces species infections. Invasive infections as a result of Trichoderma species: report of 2 circumstances, findings of in vitro susceptibility testing, and review of the literature. Clinical significance of Scedosporium apiospermum in sufferers with cystic fibrosis. Acremonium kiliense endophthalmitis that occurred after cataract extraction in an ambulatory surgical center and was traced to an environmental reservoir. Acute invasive sinusitis as a result of Trichoderma longibrachiatum in a liver and small bowel transplant recipient. Gil-Lamaignere C, Maloukou A, Winn R M, Panteliadis C, Roilides E, the Eurofung Network. Effects of interferon-gamma and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating issue on human neutrophil-induced hyphal damage of Scedosporium spp. Onychomycosis as a potential origin of disseminated Fusarium solani an infection in a patient with extreme aplastic anemia. Girmenia C, Iori A P, Boecklin F, Torosantucci A, Chiani P, De Fabritiis P, Taglietti F, Cassone A, Martino P. Fusarium infections in sufferers with extreme aplastic anemia: review and implications for administration. Bilateral endogenous Fusarium endophthalmitis related to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Treatment of postkeratitis Fusarium endophthalmitis with amphotericin B lipid advanced. Gonzalez G M, Tijerina R, Najvar L K, Bocanegra R, Rinaldi M G, Loebenberg D, Graybill J. Therapeutic efficacy of posaconazole in a murine Pseudallescheria boydii an infection. Successful treatment of cutaneous Paecilomyces lilacinus an infection with oral itraconazole in an immune competent host. Acremonium species: new rising fungal opportunists-in vitro antifungal susceptibilities and review. Guarro J, Antolin-Ayala M I, Gene J, Gutierrez-Calzada J, Nieves- Clancy C J, Nguyen M H. The mixture of amphotericin B and azithromycin as a potential new therapeutic approach to fusariosis. Paecilomyces lilacinus an infection in a coronary heart transplant recipient and successful treatment with terbinafine. Invasive hyalohyphomycosis as a result of Fusarium solani in a patient with acute lymphocytic leukemia. In vitro antifungal activity of pneumocandin L-743,872 towards quite a lot of clinically necessary molds. Disseminated an infection attributable to Fusarium solani in a patient with aplastic anemia. Espinel-Ingroff A, Bartlett M, Bowden R, Chin N X, Cooper C Jr, Fothergill A, McGinnis M R, Menezes P, Messer S A, Nelson P W, Odds F C, Pasarell L, Peter J, Pfaller M A, Rex J H, Rinaldi M G, Shankland G S, Walsh T J, Weitzman I. Paecilomyces sinusitis in an immunocompromised grownup patient: case report and review. Cutaneous hyalohyphomycosis attributable to Paecilomyces lilacinus in an immunocompetent host successfully treated with itraconazole: case report and review. Hachem R, Raad I I, Afif C, Negroni R, Graybill J, Hadley S, Kantarjian H, Adams S, Mukwaya G.
Buy biaxin 250 mg
If the affected person continues to have seizures without any evidence of adverse results at a plasma focus close to the toxic range, there are two approaches. For instance, barbiturates generally trigger despair, with primidone being the worst offender; diazepam and clorazepate are much less prone to trigger despair. Barbiturates, clonazepam, and trimethadione generally trigger cognitive impairment, ranging from sensation to confusion. Deterioration of motor performance and first coordination includes trembling palms, staggering when rounding corners, and gentle limb ataxia. Drugs related to these results embrace hydantoins, methsuximide, carbamazepine, and primidone. These results are much less common with barbiturates and lamotrigine and are not often seen with gabapentin. Two purposed mechanisms embrace (1) A native effect on the abdomen, as within the case of valproic acid; divalproex acid, however, has much less incidence compared with valproic acid. Nausea and vomiting caused by these medicine are related to brainstem involvement; therefore, drug levels play a role in these signs. Administration in smaller, more frequent doses decreases the incidence of these signs by lowering the transient peak focus. Few anticonvulsants affect urge for food separate from nausea and vomiting, together with anorexia or increased urge for food. Headache and dizziness (1) Diffuse headaches may be caused by ethosuximide and, to a lesser extent, by methsuximide and felbamate. Suicidability: increased risk in patients who begin receiving anticonvulsive as single and combination with different anticonvulsive drugs. Administration and dosage (Table 37-7) (1) Adults and youngsters 12 years of age receive an initial oral dose of 200 mg twice day by day. This may be increased gradually to 800 to 1200 mg day by day (normally given in divided doses). Precautions and monitoring results (1) Carbamazepine should be used with caution in patients with bone marrow despair. The commonest unwanted side effects are dizziness, drowsiness, unsteadiness, nausea, and vomiting. If diplopia and ataxia are common and happen after a dose, the schedule could be adjusted to embrace more frequent administration or a larger proportion of the dose at evening. Hyponatremia occurs after a number of weeks to months of remedy, and the incidence increases with age. Fluid restriction should be instituted when levels lower to a hundred twenty five mEq/L with or with out signs. Thrombocytopenia and anemia have a 5% incidence, and they reply to a cessation of drug remedy. Pruritic and erythematous rashes, the Stevens�Johnson syndrome, and lupus erythematosus have been reported. Significant interactions (1) Antiepileptic medicine, similar to phenytoin, primidone, and phenobarbital, lower the level of carbamazepine (enhance metabolism). Mechanism of motion (1) Phenytoin inhibits the spread of seizures on the motor cortex and blocks posttetanic potentiation by influencing synaptic transmission. There is an alternation of ion fluxes in depolarization, repolarization, and membrane stability section and alternating calcium uptake in presynaptic terminals. Administration and dosage (Table 37-7) (1) the standard day by day dose for adults is 300 to seven hundred mg, with adjustments made as needed. The day by day dose of phenytoin can be increased 100 mg day by day till therapeutic blood levels are attained, after which increases of 30 to 50 mg will avoid twofold to threefold increases in blood levels. Seizure Disorders 757 (6) Lymphadenopathy (native or generalized), together with benign lymph node hyperplasia, Hodgkin illness, and lymphoma, has been related to use of phenytoin. Gingival hyperplasia may be reduced by frequent brushing and acceptable oral care. Significant interactions (1) Antiepileptic medicine, similar to carbamazepine, valproic acid, clonazepam, and phenobarbital, lower the level of phenytoin (enhance metabolism). It is transformed to phenytoin by the bloodstream phosphatases, with a half-life of about 8 mins in both adults and youngsters. Administration and dosage (Table 37-7) (1) For adults, valproic acid is run orally in a usual dose of a thousand to 3000 mg day by day in divided doses. There are some reports of hepatotoxicity and increased liver perform tests, that are mostly reversible. The severity and incidence of hepatotoxicity enhance when the affected person is younger than 2 years of age. Significant interactions (1) Antiepileptic medicine (a) Primidone decreases valproic acid clearance (increases metabolism). Administration and dosage (Table 37-7) (1) For adults, phenobarbital is run orally at 90 to 300 mg day by day (in three divided doses or as a single dose at bedtime). Precautions and monitoring results (1) Phenobarbital produces respiratory despair, especially with parenteral administration. The physician should be notified if any of the next adverse results happen: sore throat, mouth sores, easy bruising or bleeding, and any signs of infection. Significant interactions (1) Antiepileptic medicine, similar to valproic acid and phenytoin, enhance the level of phenobarbital (lower metabolism). It has drug characteristics just like phenobarbital, with some variations in dose and half-life. Administration and dosage (Table 37-7) (1) Primidone has a short half-life of seven hrs, which can require thrice day by day dosing. Ethosuximide is normally given orally in an initial dose of 500 mg day by day in adults and older youngsters and 250 mg day by day in youngsters ages 3 to 6 years. Precautions and monitoring results (1) Blood dyscrasias have been reported, making periodic blood counts needed. Patients must also be suggested of the risks of exposure to sunlight and ultraviolet light. Significant interactions (1) Antiepileptic medicine, similar to carbamazepine, lower the level of ethosuximide (increases metabolism). Administration and dosage (1) For adults, clonazepam is an oral agent that could be given in an initial dose of 1. Precautions and monitoring results (1) Patients with psychoses, acute narrow-angle glaucoma, and vital liver illness ought to use this medication cautiously. Significant interactions (1) Antiepileptic medicine, similar to phenytoin, enhance the level of clonazepam (lower metabolism). Clonazepam decreases the efficacy of levodopa and increases the serum degree of digoxin. Felbamate is used as monotherapy or adjunctive remedy or with out secondary generalization in adults and generalized seizures related to Lennox�Gastaut syndrome in youngsters. Administration and dosage (Table 37-7) (1) Adults and youngsters 14 years of age (2) Monotherapy, initially 1. The amount of felbamate may be increased in increments of 15 mg/kg at weekly intervals to 45 mg/kg day by day. There are two very critical toxic results, aplastic anemia and liver failure, which lead to dying for some patients. Phenytoin doubles felbamate clearance, leading to 45% lower in felbamate levels. Felbamate causes a lower in carbamazepine levels and an increase in carbamazepine metabolites. In addition, carbamazepine causes a 50% enhance in felbamate clearance, leading to a 40% lower in steady-state trough levels. Signs and signs related to increased plasma degree and toxicity are anorexia, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, and headache. Its mechanism of motion is at present unknown, though it binds to a specific receptor within the mind and inhibits voltagedependent sodium currents. It has been shown to be efficient as an add-on drug in patients with partial seizure with or with out secondary generalization. Titrating to an effective dose normally can be achieved inside 3 days by initiating remedy with 300 mg and then rising the dose in 300-mg increments over the subsequent 2 days to establish a dosage of 900 mg day by day in three doses. To minimize potential unwanted side effects, especially somnolence, dizziness, or fatigue, the primary dose on day 1 may be administered at bedtime. Antacids scale back the bioavailability of gabapentin by 20%; gabapentin could be taken 2 hrs after antacid use.
Proven biaxin 500mg
These merchandise retard tartar formation; nonetheless, they form an alkaline answer that will irritate the skin. These patients should use regular toothpaste and only occasionally brush with tartar-control toothpaste. Whether or not a affected person receives fluoride depends on the focus in his or her local drinking water (Table 19-1). Agents with antiplaque potential for inclusion in dentifrices embody plant extracts (sanguinarine), metal salts (zinc and stannous), phenolic compounds (triclosan), and essential oils (thymol and eucalyptol). Anticalculous dentifrices embody the elements zinc chloride, zinc citrate, and 33% pyrophosphate to forestall calculus formation. Owing to this expertise, the product accommodates 50% more silica, which significantly enhances the removal of extrinsic stains with out growing abrasiveness. Desensitizing agents cut back the pain in delicate enamel attributable to chilly, warmth, acids, sweets, or contact. Following use, the consumer should rinse the mouth with water and then expectorate. Mouthwashes may comprise astringents, demulcents, detergents, flavors, germicidal agents, and fluoride. They can be used for beauty functions, reducing plaque, or supplementing fluoride consumption. These mouthwashes are categorised by their active Over-the-Counter Otic, Dental, and Ophthalmic Agents 379 elements, alcohol content material, and look. The larger the percent of alcohol, the higher the impact of the flavor inside the mouth. Mouth rinses claiming anticalculus or tartar-control exercise comprise the same active elements as anticalculus dentifrices. Examples of merchandise on this class embody Cepacol, Scope, and Crest Pro-Health Rinse. Chewing gum is associated with elevated salivary circulate, which apparently produces a beneficial buffering impact towards acids in the oral cavity. The gingiva may seem bigger in size with a bluish hue attributable to engorged gingival capillaries and a sluggish venous return. Gingivitis is attributable to microorganisms that eventually damage cellular and intercellular tissues. The gums readily bleed when probed or brushed, and the affected person should seek dental help. Mouthwashes may freshen the breath; nonetheless, it is important to think about the potential of those merchandise to disguise and delay remedy of pathological conditions. The periodontal ligament attachment and alveolar bone support of the tooth deteriorate. Risk components embody gender (men affected greater than ladies), age (35 years old), smoking, lack of oral care and regular dentist visits, diabetes, hypertension, rheumatoid arthritis, and lack of anterior enamel. Periodontitis may be treated with prescription merchandise: (1) Periostat (doxycycline hyclate, 20-mg capsules) (2) Atridox (doxycycline hyclate 10%) in the Atrigel Delivery System. It is postulated that it may be associated with the overgrowth of spirochete and fusiform organisms. Risk components embody anxiousness, stress, smoking, malnutrition, and poor oral hygiene. Signs and symptoms embody a uninteresting, aching pain around the ear, headaches, neck aches, restricted opening of the mouth, and a clicking or popping noise upon opening the mouth. Treatment consists of moist warmth applied to the jaw, muscle relaxants, chunk plates or occlusal splints, a food regimen of soft meals, correcting the occlusion, or surgical procedure. Persisting pain may be treated with a local anesthetic similar to benzocaine (present in Anbesol Baby and Baby Orajel). Canker sores (also known as recurrent aphthous ulcers or recurrent aphthous stomatitis) a. Studies counsel that the sores may be attributable to hypersensitivity to bacteria discovered in the mouth or dysfunction of the immune system initiated by minor trauma or stress. This is why physicians or dentists may use prednisone or a topical steroid to cut back allergic response or have the affected person rinse with a compounded suspension. Products embody protectants, local anesthetics, and debriding and wound-cleaning agents. It supplies oral pain relief by appearing as a protecting adherent barrier over the floor of the mouth and throat. Thalidomide is indicated for aphthous ulcer and stomatitis in severely immunocompromised patients. Cold sores usually happen on the lips and are recurrent, usually arising in the same location. Red papules of fluid-containing vesicles then seem, and these eventually burst and form a crust. These sores are usually self-restricted and heal in 10 to 14 days with out scarring. Patients should apply the cream on the first signal of an outbreak and proceed to apply the cream five instances a day till the lesion is healed. If essential, the affected person should consult a physician for a systemic antibiotic prescription. However, research have produced conflicting data relating to l-lysine and its impact on the period, severity, and recurrence price of chilly sores. Prescription merchandise (1) Valacyclovir (Valtrex) is indicated for the remedy of herpes labialis. Therapy should be initiated on the onset of signal and symptoms and applied five instances per day for 4 days. Patients should apply the cream every 2 hrs whereas awake for 4 days, starting on the first signal of tingling or swelling. Candidiasis (also known as thrush) is attributable to the fungus Candida albicans, which is the most common opportunistic pathogen associated with oral infections. Thrush has a milky curd look, and affected patients should contact a physician. The most common oral most cancers is squamous cell carcinoma, which might seem as red or white lesions, ulcerations, or tumors. Also, remedy usually includes wide local excision for small lesions and en bloc excisions for bigger lesions (in continuity with radical neck dissection if lymph nodes are concerned). Chemotherapeutic agents can produce many attainable unwanted side effects that require quick medical consideration. Nonpharmacological measures, similar to avoiding disturbing environmental odors and vestibular disturbances, may be helpful in minimizing nausea and vomiting. Azithromycin or clarithromycin, 500 mg for adults; 15 mg/kg for youngsters, 30 to 60 minutes before the process F. Denture cleansers are either chemical or abrasive in respect to their cleaning capability. Chemical denture cleansers embody alkaline peroxide, alkaline hypochlorite, or dilute acids. A disadvantage of alkaline hypochlorite is that it corrodes metal denture parts. Refer a affected person to a dentist if the oral criticism involves an abscess with fever, swelling, malaise, lymphadenopathy, or purulent exudate. Remind patients that chilly and canker sores, with appropriate remedy, are usually a self-limiting downside. Patients should be knowledgeable about how to use recommended merchandise, the period of use, the expectations of utilizing the product, and the process to comply with if the product is ineffective. The sclera, also known as the white of the attention, capabilities to defend intraocular contents and maintain the form of the attention. The anterior chamber of the attention houses a steady supply of aqueous humor, which is produced in relation to the intraocular pressure. The iris is the coloured a part of the attention that regulates the entrance of sunshine via the pupil. The pupil is the contractile opening on the center of the iris that dilates and constricts in response to light. The lens is discovered directly behind the iris and pupil and is responsible for enabling the attention to accommodate, focusing for close to and distance vision.
Biaxin 250 mg
By alternative splicing, an organism can make many extra different proteins than it has genes to encode. A current estimate of the number of human proteins is a minimum of one hundred,000, whereas the current estimate of human genes is about solely 20,000�25,000. Alternative splicing could be detected by Northern blot, a technique discussed in Chapter 7. The Composition of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Ribosomes the big and small prokaryotic ribosomal subunits are 50S and 30S, respectively. Apoprotein B100 is expressed within the liver, and apoprotein B48 is expressed within the intestines. There is one intron of 1,000 bps, a 5-untranslated region of one hundred bp, and a three-untranslated region of 200 bp. Many proteins endure posttranslational modifications as they prepare to assume their final roles within the cell. Important features of the genetic code embrace: Medical Genetics � Each codon consists of 3 bases (triplet). Protein synthesis begins with methionine (Met) in eukaryotes, and formylmethionine (fMet) in prokaryotes. Effects of Some Common Types of Mutations on Protein Structure Type of Mutation Silent: new codon specifies same amino acid Missense: new codon specifies different amino acid Nonsense: new codon is cease codon Frameshift/in-frame: addition or deletion of base(s) Large segment deletion (unequal crossover in meiosis) 5 splice web site (donor) or three splice web site (acceptor) Trinucleotide repeat enlargement Effect on Protein None Possible lower in function; variable results Shorter than normal; usually nonfunctional Usually nonfunctional; usually shorter than normal Loss of function; shorter than normal or entirely missing Variable results starting from addition or deletion of a few amino acids to deletion of an entire exon Expansions in coding regions cause protein product to be longer than normal and unstable. In a normal crossover occasion, the homologous maternal and paternal chromosomes exchange equal segments, and although the resultant chromosomes are mosaics of maternal and paternal alleles, no genetic data has been lost from both one. Cri-duchat (mental retardation, microcephaly, extensive-set eyes, and a attribute kittenlike cry) outcomes from a terminal deletion of the quick arm of chromosome 5. A giant number of -globin mutations have been described, together with gene deletions, mutations that slow the transcriptional process, and translational defects involving nonsense and frameshift mutations. It is believed that, just like sickle cell anemia and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, the abnormality of purple blood cells in -thalassemia could protect against malaria. Cases of juvenile onset (age < 10) are extra severe and most incessantly occur when the defective allele is inherited paternally. The normal protein incorporates 5 adjacent glutamine residues, whereas the proteins encoded by the disease-related alleles have 30 or extra adjacent glutamines. A major clinical manifestation of the trinucleotide repeat enlargement issues is neurodegeneration of particular neurons. The enlargement of the trinucleotide repeat within the mutant allele could be in a coding region or in an untranslated region of the gene. The formation of a peptide bond between the carboxyl group on one amino acid and the amino group of one other is illustrated under. Notice that the peptide bond forms between the carboxyl group of the amino acid (or rising peptide) within the P web site and the amino group of the following amino acid within the A web site. The strategy of protein synthesis happens in three phases: initiation, elongation, and termination. There are 2 necessary binding websites on the ribosome referred to as the P web site and the A web site. After formation of the primary peptide bond, the P web site is a binding web site for the rising peptide chain. Acception Assumption Anticipation Mutation Answer: C Medical Genetics Behavioral Science/Social Sciences B. Chloramphenicol is a drug used to battle bacterial infections, together with meningitis. If given to a new child, nevertheless, this drug can trigger a probably lethal reaction. Inhibitors of eukaryotic translation embrace cycloheximide and Diphtheria and Pseudomonas toxins. Generally, four ranges of protein form are distinguished: Primary-sequence of amino acids specified within the gene. Secondary-folding of the amino acid chain into an energetically stable construction. Tertiary structures are stabilized by weak bonds (hydrogen,hydrophobic, ionic) and, in some proteins, strong, covalent disulfide bonds. Agents such as warmth or urea disrupt tertiary construction to denature proteins, causing loss of function. Quaternary-in proteins such as hemoglobin that have multiple subunits, quaternary construction describes the interactions among subunits. Molecular chaperones function in many cell compartments, together with the endoplasmic reticulum, where in depth protein synthesis happens. Whenever protein synthesis happens in a cell, a number of copies of a particular protein could not fold correctly. These defective copies are covalently marked for destruction by the addition of multiple copies of ubiquitin. Proteasomes are giant, cytoplasmic complexes that have multiple protease activities able to digesting broken proteins to peptides. Ubiquitin U U U Proteasome U U U U Peptide fragments Misfolded protein Figure I-four-7. Degradation of Misfolded Proteins by Proteasomes Many proteins require indicators to guarantee delivery to the appropriate organelles. N-glycosylation refers to the addition of sugar chains to the nitrogen of asparagine residues (N-linked). The N-linked sugar chain can additional be modified upon entry within the Golgi (posttranslational modification). O-glycosylation refers to the addition of sugar chains to the hydroxyl group of both serine or threonine residues of the protein, and it happens exclusively within the Golgi (posttranslational modification). Significantly, the construction and sequence of the oligosaccharide chains on proteins and lipids (glycolipids) are the idea of the A, B, O blood teams. This mutation causes the 1-antitrypsin protein to misfold and combination within the endoplastic reticulum, where it damages cells, finally resulting in cirrhosis. Its function is to protect cells by serving as an inhibitor of proteases released throughout a normal inflammatory response. Among the more than 90 allelic variants of the 1-antitrypsin gene, the Z and S variants are most often encountered with 1-antitrypsin deficiency. Genetic defects affecting this phosphorylation produce I-cell disease during which lysosomal enzymes are released into the extracellular area, and inclusion our bodies accumulate within the cell, compromising its function. When a lysosomal enzyme is missing (for example in a genetic disease such as Tay-Sachs), the undigested substrate accumulates within the cell, usually resulting in severe penalties. Major Symptoms of I-Cell Disease A baby aged 5 months was referred to a specialist. Examination of the fibroblasts beneath the microscope revealed the presence of quite a few intracellular inclusions, which on electron microscopy have been revealed to be giant lysosomes. Biochemical analysis confirmed decreased ranges of the lysosomal hydrolase �-glucuronidase within the fibroblasts, but elevated ranges of this enzyme within the tradition medium. It has a considerably distinctive major construction in that a lot of its size is composed of a repeating tripeptide Gly-X-Y-Gly-X-Yetc. Three pro- chains assemble to kind a triple helical construction (procollagen), which might now be transferred to the Golgi. The propeptides are cleaved from the ends of procollagen by proteases to kind collagen molecules (additionally referred to as tropocollagen). Like osteogenesis imperfecta, these syndromes are a results of locus heterogeneity during which defects in several different genes (loci) Behavioral Science/Social Sciences can lead to comparable signs. There are several necessary illnesses related to defective collagen manufacturing. Disorders of Collagen Biosynthesis Disease Scurvy Defect Deficient hydroxylation secondary to ascorbate deficiency Mutations in collagen genes Mutations in collagen genes and proline and lysyl hydroxylases Major Symptoms Petechiae, ecchymoses Loose enamel, bleeding gums Poor wound healing Poor bone growth Skeletal deformities Fractures, blue sclera Hyperextensible, fragile skin Hypermobile joints, dislocations, varicose veins, ecchymoses, arterial, intestinal ruptures Depigmented (steely) hair Arterial tortuosity, rupture Cerebral degeneration Osteoporosis, anemia Osteogenesis imperfecta Ehlers-Danlos syndromes Menkes disease Deficient cross-linking secondary to practical copper deficiency Recall Question Vitreous humor is formed from which kind of collagen Common with Ehlers-Danlos illnesses, Menkes disease has a symptomology due, in part, to weak collagen. Consequently, an affected individual may have severe copper deficiency and all copper-requiring enzymes will be adversely affected. Lysyl oxidase requires copper and plays a direct function in collagen formation by catalyzing the cross-linking of collagen fibrils. A deficiency within the exercise of this enzyme and different copper-dependent enzymes can be immediately liable for the described signs on this infant. For every mutation described within the questions under, choose probably the most carefully related sequence change within the options above.
Purchase 250 mg biaxin
In the setting of hyperammonemia, downregulation of aquaporins occurs (reflecting a protective mechanism of astrocytes to forestall ammonia getting into the cell), however simultaneously, the excretion of K+ and water is altered, and a rise in brain extracellular K+ and water develops, contributing to brain edema formation [41, 42]. Differential diagnosis of hyperammonemia Diagnostically, the presence of acidosis, ketosis, hypoglycemia, and low bicarbonate ranges indicate that the root explanation for hyperammonemia is probably as a result of an natural acidemia, systemic carnitine deficiency, Reye syndrome, toxins, drug effect, or liver illness. The association of elevated liver enzymes with hyperammonemia is most consistent after insult from hepatotoxins, Reye syndrome, or carnitine deficiency [6] (Table 1). The first three reactions are situated intramitochondrially and the remaining are cytosolic. The general incidence of defects presenting clinically is estimated at approximately 1 in forty five,000 live births [1, 44]. Argininosuccinic aciduria: argininosuccinase deficiency-1 the genetic deficiency liable for this disorder is situated on chromosome 7-q11. Distinguishing clinical options embrace psychological retardation, trichorrhexis nodosa (fragile hair with a nodular appearance), and an erythematous maculopapular pores and skin rash. The latter two are associated with arginine deficiency and disappear with arginine supplementation. Liver involvement is characterized by hepatomegaly and elevated transaminases, and the related histopathology displays enlarged hepatocytes and fibrosis [6, forty five] Citrullinemia: argininosuccinate synthetase deficiency the genetic deficiency liable for this disorder is situated on chromosome 9q34. The genetic deficiency liable for this disorder is situated on chromosome 2q35. Biochemical findings on this entity embrace recurrent hyperammonemia, absent citrulline, and low ranges of arginine, urea nitrogen, and urinary orotic acid. Yellow arrows present various pathways used to remove nitrogen in patients with urea cycle defects. Reproduced with permission from Walters and Brophy [43] Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency this represents the most common urea cycle enzyme defect, with an incidence of 1 in 14,000, and is the only one inherited as a sex-linked trait. Around 350 pathological mutations have been reported, and in approximately eighty% of patients, a mutation is discovered. Biochemical diagnostic findings embrace hyperammonemia, absent serum citrulline, and elevated urinary orotic acid. Children develop toe walking as a attribute characteristic, which progresses to spastic diplegia. Finding elevated serum arginine, urine orotic acid, and ammonia ranges makes the diagnosis. Organic acidemias this group of autosomally recessive inherited problems outcomes from enzyme deficiencies in amino acid degradation pathways. This leads to the buildup and excretion of non-amino (natural) acids in plasma and urine. Hallmark findings in natural acid problems embrace high anion hole metabolic acidosis, ketoacidosis (as a result of the buildup of lactate and natural acids), and pancytopenia. Hyperammonemia is seen and is caused by accumulation of coenzyme A (CoA) derivatives, which inhibit carbamyl phosphate synthetase exercise [6]. Propionic acidemia the defect liable for this disorder is in the enzyme propionyl-CoA carboxylase, which converts propionyl CoA to D-methylmalonyl CoA. The diagnosis is confirmed by measuring propionyl-CoA carboxylase exercise in leukocytes or pores and skin fibroblasts [6]. Methylmalonic acidemia this disorder outcomes from the shortcoming to convert methylmalonyl CoA to succinyl CoA. Patients develop metabolic ketoacidosis, hypoglycemia, hyperglycinemia, pancytopenia, and hyperammonemia. Maple syrup urine illness Maple syrup urine illness is characterized by maple syrup odor famous in the urine and elevated serum branched-chain amino acid concentrations (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) through the first 24 h of life. Dibasic aminoacidurias Lysinuric protein intolerance this autosomal recessive condition is characterized by lysinuria and inadequate urea formation with development of hyperammonemia. The main defect resides in renal tubular, intestinal, epithelial, and hepatic dibasic amino acid transport mechanisms. This leads to a drop of available serum ranges of ornithine, lysine, and arginine, main finally to hyperammonemia. There are concomitant will increase in urinary excretion of lysine, ornithine, arginine, and citrulline [49]. Consequently, plasma ornithine ranges rise with an related improve in excretion of homocitrulline in the urine and hyperammonemia [6]. Transient hyperammonemia of the newborn this disorder could also be present in infants with a historical past of perinatal asphyxia, and signs can develop before the toddler is 24 h of age. The former is self-restricted and is believed to occur secondary to a transient deficiency of one of many urea cycle enzymes, a renal transport defect of arginine or ornithine, or a deficient synthesis of ornithine. In the second type (unknown etiology), patients current with respiratory misery, lethargy, and coma. The neurologic consequence in these patients can range from normal mental capability to profound psychological retardation and seizures [6]. Drug associated causes Salicylate Salicylate overdose can result in a Reye-like clinical presentation, including emesis, anorexia, fever, hyperventilation, irritability, and hallucinations. The pathogenesis involves mitochondrial dysfunction and uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation [6]. Carbamazepine Asterixis and hyperammonemia are unusual issues associated with carbamazepine use. The mechanism by which hyperammonemia develops is unknown, and treatment for the latter is solely to discontinue the anticonvulsant [50�52]. Valproic acid Valproic acid use has been associated with the induction of hyperammonemic encephalopathy by way of astrocytic edema, renal tubular interference with glutamine synthesis, and/or elevated renal glutaminase exercise (leading to enhanced ammoniagenesis). Once the valproic-acid-induced hyperammonemic encephalopathy has been recognized, discontinuation of the drug leads to restoration after a couple of days, with normalization of serum ammonia ranges. In addition, topiramate inhibits glutamine synthetase exercise in the brain, resulting in toxic ranges of ammonia [55]. Tranexamic acid this is an antifibrinolytic agent that has been associated with the event of hyperammonemia seen as trigger or result of convulsions caused by the medication [59]. Chemotherapy Hyperammonemic coma has been described postinduction chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. It has also been described in patients with a number of myeloma (as abnormal plasma-cell clones could produce ammonia) in those receiving chemotherapy with asparaginase, 5fluorouracil (transient hyperammonemia), and in those receiving rituximab. The pathogenic mechanism is believed to be associated to an acquired deficiency of glutamine synthetase of unknown trigger. The Jamaican vomiting sickness, which has a high mortality fee (as much as 50%), is characterized by vomiting, lethargy, hallucinations, coma, hypoglycemia, hyperammonemia, and abnormal liver enzymes, which occur when this unripe fruit is ingested [6]. During being pregnant, the wholesome fetus can metabolize ammonia, whereas after delivery, this metabolic process is absent and ammonia accumulates in the mother. In addition, tissue breakdown occurs with postdelivery uterine involution, adding more waste nitrogen merchandise to the urea cycle [sixty six�68]. The renal ammonia manufacturing and tubular reabsorption are stimulated by chronic metabolic acidosis and potassium depletion. Carnitine transport defects Carnitine transport enzyme defects manifest with hypoglycemia, lethargy, and potentially a Reye-like syndrome (hepatomegaly, elevated transaminases, and ammonia). Carnitine plays a key function as cofactor in fatty-acid metabolism and its deficiency can result in abnormal fatty-acid oxidation, resulting in development of hyperammonemia and encephalopathy. Patients with this typically current with hyperammonemia, encephalopathy, hypoglycemia, and myopathies [72]. Urinary tract dilatation Proteus is a bacteria that characteristically produces an alkaline urine pH as a result of the hydrolysis of urea to ammonia by the bacterial urease. Children with massively dilated urinary tracts whose urinary tract is infected/colonized by this bacterium could develop hyperammonemia [seventy three]. Reye syndrome Reye syndrome is a illness of unknown etiology associated with hyperammonemia. Viruses (especially influenza B and varicella), toxins/medicine (valproic acid, salicylate, aflatoxin, pesticides, and bacillus cereus), and a genetic component (elevated risk of prevalence in siblings) have been implicated as causal elements. The key physiologic findings famous are a consequence of hepatic mitochondrial damage (swelling and demise) caused by inhibition of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Abnormal findings embrace acute encephalopathy, hyperammonemia, lactic acidosis, hypoglycemia, elevated liver enzymes, fatty-liver infiltration, and elevated intracranial strain [6, seventy four].
Proven 250 mg biaxin
Plant roots suffer a scarcity of oxygen as a consequence of flooding; this, in turn, causes deleterious results, similar to wilting (epinasty), inhibition of leaf chlorophyll synthesis (chlorosis), cell death (necrosis), and reduced fruit yield. The error bars point out normal errors; the usual errors in panel C were negligible. A gene encoding the enzyme 3rd Proof 4rd Proof make the most of the phytateProof is present in Proof phytase was isolated from the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. In greenhouse experiments, this remodeled bacterium was found to be superior to the wild-type strain in offering phosphorus to tobacco plants cultivated in its presence (Table 15. Notwithstanding these results, it might be some time earlier than this work is commercialized because of political considerations about using genetically engineered micro organism within the setting. Biocontrol of Pathogens Phytopathogens are an ongoing and critical agricultural problem that may scale back crop yields by 25 to 100%. Currently, phytopathogen harm to crops is usually dealt with by the use of chemical agents, although other therapies have also been employed. For most bacterial ailments, plants could also be symptomless for prolonged durations earlier than adjustments in environmental conditions which favor the proliferation of the micro organism cause a fast outbreak of disease. Many of the chemical compounds that are used to control phytopathogens are hazardous to animals and humans, and they persist and accumulate in natural ecosystems. It is due to this fact desirable to replace these chemical agents with organic control agents that are extra "friendly" to the setting. One strategy for the control of phytopathogens is the development of transgenic plants that are resistant to one or more of them (see chapter 18). Alternatively, some plant growth-promoting micro organism can act as biocontrol agents to suppress or prevent phytopathogen harm, and a number of these biocontrol micro organism have been commercialized (Table 15. Plant growth-promoting micro organism can produce a variety of substances that restrict harm to plants by phytopathogens. They include siderophores, antibiotics, other small molecules, and a variety of enzymes. This strategy is still at an early stage of development however appears to have considerable potential. However, the final word utility of a technique primarily based on a particular mechanism could be assessed solely underneath field conditions. Three bidentate functional groups on a siderophore molecule bind with ferric iron. C O C O Siderophores Iron is likely one of the most abundant minerals on Earth and is an important requirement for living organisms. Consequently, to survive on this setting, soil microorganisms synthesize and secrete low-molecularmass (~four hundred- to 1,000-dalton) iron-binding molecules known as siderophores. Control of root rot and damping-off caused by Fusarium, Rhizoctonia, Pythium, Phytophthora, Sclerotinia, Postia, and Verticillium; also suppresses foliar ailments caused by Botrytis A vary of fungal damping-off ailments Crop(s) Fruit timber, nut timber, and ornamental nursery inventory Turf, forage crops, corn Cotton, legumes, barley, tomato, rice Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bacillus pumilis Burkholderia cepacia Burkholderia cepacia Paenibacillus polymyxa Pseudomonas chlororaphis Pseudomonas fluorescens Pseudomonas syringae Streptomyces griseoviridis Streptomyces lydicus Herbs, spices, greens, tree seedlings, ornamentals Fruits and greens, oak, maple, saved seeds Vegetables Alfalfa, barley, beans, clover, corn, cotton, peas, grain sorghum, greens, wheat Cucumber Barley, oat Almond, apple, cherry, mushrooms, peach, pear, potato, strawberry, tomato Citrus and pome fruit, potatoes Field, ornamental, and vegetable crops Useful for cover of cuttings of a variety of plants; also used with turfgrass Especiallyusefulinhydroponicgardens Mixture of B. Once inside a cell, the iron is launched and is then obtainable to help microbial growth. The ensuing lack of iron prevents fungal pathogens from proliferating within the instant vicinity. Fungal phytopathogens also synthesize siderophores, however these generally have a a lot lower affinity for iron than do the siderophores produced by plant growth-promoting micro organism. In effect, the plant growthpromoting micro organism outcompete fungal phytopathogens for obtainable iron. In addition, some studies have shown that iron that has been sequestered by bacterial siderophores is taken up from the soil by the plant, to its benefit. Because the sequestering of iron by a siderophore-producing bacterium can concurrently prevent the proliferation of a number of completely different phytopathogenic microorganisms, siderophore genes are being examined to determine whether or not they can be used to create more practical biocontrol inoculants. Siderophores generally have three functional, or iron-binding, groups connectedbyaflexiblebackbone,oftenapeptide. Eachfunctionalgroup normally presents two atoms of oxygen or, less commonly, two nitrogen atoms, that bind iron. Trivalent ferric iron can accommodate three of those groups to type a six-coordinate advanced. With some exceptions, the functional groups on microbial siderophores are both hydroxamates or catecholates. Different mixtures of functional groups could also be present on a single siderophore. Other functional groups include carboxylate moieties, similar to citrate, and ethylenediamine. In common, hydroxamatetype siderophores are typical of fungi, and catecholates, which bind iron extra tightly than hydroxamates, are widespread in bacterial siderophores. Plant siderophores, however, are linear hydroxy- and aminosubstituted iminocarboxylic acids, similar to mugineic acid and avenic acid. The synthesis and regulation of pseudobactin within the plant growthpromoting bacterium P. Mutagenesis was used to generate a set of 28 mutants that were defective for siderophore manufacturing. Two standards were used for identifying the siderophore-poor mutants: (1) lack of fluorescence underneath ultraviolet mild and (2) incapability to grow within the presence of bipyridyl, a molecule that sequesters many of the iron within the growth medium. When many of the iron is unavailable, solely a cell that produces siderophores can grow. All of the resultant transformants were examined by complementation for restoration of fluorescence and/or the power to grow within the presence of bipyridyl. Thirteen separate complementing cosmid clones, with a mean insert dimension of 26 kilobase pairs (kb), were recognized. After detailed analyses, these clones were found to characterize no less than five separate gene clusters. Thecellsthathavemutations in one of the genes involved in siderophore biosynthesis are unable to grow on medium containing bipyridyl, which sequesters all the free iron within the medium. Transformants that may grow within the presence of bipyridyl are capable of complement the mutation in one of the siderophore biosynthesis genes. The presence of the rpoD gene on the plasmid vector enhanced the activity of the plant growth-promoting bacterium. However, there could also be other methods to enhance the effectiveness of plant growth-promoting micro organism as biocontrol agents. For example, it might be possible to lengthen the vary of iron�siderophore complexes that one bacterial strain can make the most of so that a genetically altered plant growth-promoting biocontrol bacterial strain might take up and use siderophores synthesized by other soil microorganisms, thereby giving it a competitive advantage. This was carried out by cloning the genes for iron�siderophore receptors from one plant growth-promoting control bacterium and introducing them into other strains. Antibiotics One of the simplest mechanisms by which a plant growth-promoting bacterium can prevent phytopathogen proliferation is the synthesis of antibiotics. For example, the antibiotics synthesized by biocontrol pseudomonads include agrocin eighty four, agrocin 434, 2,four-diacetylphloroglucinol, herbicolin, oomycin, phenazines, pyoluteorin, and pyrrolnitrin. The biocontrol activity of a plant growth-promoting bacterium could also be improved by offering it with genes that encode the biosynthesis of antibiotics that are normally produced by other micro organism. In this fashion, the vary of phytopathogens that a single biocontrol bacterium can suppress could be extended. In addition, genetic manipulation can be used to enhance the amount of antibiotic that a bacterium synthesizes. The manufacturing of a number of antifungal metabolites that are produced by pseudomonads appears to be controlled by a protein that acts as a global transcriptional regulator; due to this fact, it ought to be possible to enhance antibiotic manufacturing by modifying this world regulation. The modified strain was more practical at protecting cucumber plants towards a root disease caused by the fungus Pythium ultimum (Table 15. Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria 613 A single copy of the operon carrying all seven of the genes that encode the biosynthesis of the antibiotic phenazine-1-carboxylic acid. This work demonstrates the efficacy of this strategy underneath greenhouse conditions; nevertheless, it stays to be demonstrated whether this altered bacterium is efficient within the field. The regulatory genes that normally control the expression of the seven biosynthetic genes were removed, and the complete operon was placed underneath the control of the tac promoter (ptac). The operon, underneath the control of the tac promoter, was inserted right into a by-product of transposon Tn5 adjacent to a kanamycin resistance gene (not shown) on a plasmid. Transconjugants by which the chromosomal insertion had not inactivated any essential bacterial features were examined for their effectiveness as biocontrol strains. A modified version of Agrobacterium radiobacter K84 has been marketed, first in Australia in 1989, and extra lately everywhere in the world, as a method of controlling crown gall disease, which is caused by the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
Diseases
- Gouty nephropathy, familial
- Visna Maedi complex
- Ectodermal dysplasia osteosclerosis
- Essential hypertension
- Swyer syndrome
- Radio renal syndrome
Cheap 250mg biaxin
In heme containing proteins this reaction is prevented by 134 sequestering the heme deep inside a protein structure where access to the two open coordination bonds is restricted polar amino acids are situated virtually exclusively on the exterior floor of globin polypeptide and contribute to the high solubility of these proteins. Amino acids that are both polar and hydrophobic, corresponding to Threonine, tyrosine and Tryptophan are oriented to the exterior. Hydrophobic amino acid residues are buried with in the interior where they stabilize the folding of the polypeptide and binding of iron porphyrin ring. The solely exceptions to this common distribution of amino acids residues in globins are the two Histidines that play an indispensable position in the heme binding are oriented perpendicular to and on either facet of the planor heme prosthetic group. In the quaternary stucture of human Hb there exists two - globin and two � - globin sub units (2 2). In distinction there are few interactions between identical subunits on the - or � interface so hemoglobin is taken into account more as a heterodmer ()2. The -heterodimer are actually acknowledged as major factors determiners of O2 binding and launch. Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Both Myoglobin and Hemoglobin are built on a common structural motif. Myoglobin incorporates a single polypeptide chain folded about a prosthetic group, the heme, which incorporates the oxygen binding website. Note, for example that myoglobin and every subunit of hemoglobin consists of eight helical segments, that are labeled A via H. In all vertebrates the oxygen transport protein is hemoglobin, a protein that can choose up oxygen in lungs or gills and deliver it to tissues. In tissues, corresponding to muscle, with high oxygen calls for, myoglobin provides giant oxygen reserves. The amino acid sequences of the two sort of subunits are identical at 27 positions. Fetal Hb (HbF) Contains a different sort of Hb simply after conception fetuses synthesize zeta chain (quite like chain) the HbF variant barely detectable and - chains similar to - chain later zeta changed by - and - by. HbF contain 2 and 2 subunits in most adult typically increases as much as 15 - 20% in people with mutant adult Hbs, corresponding to sickle cell disease. The direct advantage of this structural change in Hb isoform is a more environment friendly switch of O2 from maternal HbA to fetal(HbF). At low oxygen concentrations, deoxy HbS polymerizes, types fibers, and distorts erythrocytes in to sickle shapes. The mutation is Glu6 -val a floor localized charged amino acids is changed by a hydrophobic residue as show beneath HbA = Val � His � Leu � Thr � Pro � Glu � Glu � Lys HbS = Val � His � Leu � Thr � Pro � Val � Glu � Lys Such substitution of Valine (non - polar) for Glutamate (polar) have the following consequence 1. Place A non - polar residue on the outside of HbS which markedly reduce solubility of deoxy HbS. Creates sticky patches on the outside floor of each - chains (not present HbA) 3. Sickle Cell Trait the heterozygote people (sickle cell trait) (HbA/HbS) is related to increased resistance to malaria. Specifically growth of the infectious agent, Plasmodium falciparum in the erythrocyte. Sickled erythrocyte exhibits little or much less deformity, they not transfer freely via the micorvasculature and sometimes block blood circulate. Moreover this cells lose water, turn into fragile and have a considerably quick life span leading to anemia. Sickle Cell Disease Sickle cell disease is brought on by an inherited structural abnormality in the �globin polypeptide. Clinically, a person with sickle cell disease present with intermittent episode of haemolytic and painful vaso�occlusive crisis. There is also a prone to be impaired growth, increased susceptibility to infections and a number of organ damage. Digestion and Absorption of Proteins Proteins are larger polypeptide molecules coiled by weaker bonds of their tertiary structure the digestion of proteins includes the gradual breakdown of this polypeptide by enzymatic hydrolysis in to amino acid molecules that are absorbed in the blood stream. The protein load received by the intestine is derived from two sources 70-100g dietary protein which is required every day and 35 200g endogenous protein (secreted enzymes and proteins in the intestine or from intestinal epithelia cell turnover) Only 1-2g of nitrogen equal to 6-12g of proteins are lost in the feces each day. The process of protein digestion may be divided, depending on the sources of peptidases. Gastric Digestion Entry of a protein in to abdomen stimulates the gastric mucosa to secrete a hormone gastrin which in flip stimulates the secretion of Hcl by the parietal cells of the gastric glands and pepsinogen by the chief cells. The acid denatures the protein and the whole protein vulnerable to hydrolysis by the motion other proteolytic enzymes. This active pepsin cleaves the ingested protein at their amino terminus of fragrant amino acids (Phe, Tyr, and Trp. Pancreatic Digestion Pancreatic zymogens proceed digestion because the acidic abdomen contents move in to the small intestine, A low pH triggers the secretion of a hormone Secretin in the blood. Three of these pro-enzyme are trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen and procarboxy peptidase, localized in the exocrine cells. Synthesis of these enzymes as inactive precursors protects the exocrine cells from harmful proteolytic assault. By the sequential motion of these proteolytic enzymes and peptides ingested proteins are hydrolyzed to yield a mix of free amino acids which may be transported across the epithelial lining of the small intestine. The lumenal floor of epithelial cells is wealthy in endopeptidase, and dipptidase aminopeptidase exercise the end products of the cell floor digestion are free amino acids and di and tripeptides. The mechanism of active transport of amino acids are comparable with that of glucose uptake. A comparable H+ dependent symport is present on the comb border floor of di and tripeptides active transport in to the cell. Na+ - independent transporters are present on the contralumenal floor, thus allowing amino acids From both genetic and transporters studies at least six specific symporter systems have been identified for the uptake of L-amino acids from the intestinal lumen. These transporter systems are additionally present in the renal tubules and defects of their constituent protein structure can lead to disease known as Hartnup disease. Neutral amino Aciduria (Hartnup Disease) Transport capabilities, like enzymatic capabilities, are topic to modification by mutations. An instance of a genetic lesion in epithelial amino acid transport is hartnup disease; entry resulting from the defect was first acknowledged. The disease is characterised by the lack of renal and intestinal epithelial cells to take up impartial amino acids from the lumen. In the kidney, by which plasma amino acids attain the lumen of the proximal tubule via the Ultra filtrate, the lack to reabsorb amino acids manifests itself as excretion of amino acids in the Urine (aminoaciduria). Therefore the scientific signs of patients with this are primarily those as a result of essential amino acid and Nicotinamide deficiencies. The pellagra-like features are defined by a deficiency of Tryptophan, which serves as precursor for nicotinamide. Investigations of patients with Hartnup disease revealed the existence of intestinal transport systems for di - or tripeptides, that are completely different from those free of charge amino acids. Amino Acid Catabolism Transamination the nitrogen part of amino acids, the - amino groups, should be eliminated earlier than the carbons can be utilized in other metabolic pathways. The first step in the catabolism of most amino acids is the switch of their - amino group to ketoglutarate where the products are - ketoacids and glutamate. This switch of amino groups from one carbon skeleton to another is catalyzed by a family of transaminases that are additionally 141 known as as aminotransferases. Alanine + -Ketoglutarate <-> Pyruvate + Glutamate Oxaloacetate + Glutamate <-> Aspartate +-ketoglutarate (Urea cycle) In addition to their roles as constructing blocks of proteins, the carbon skeletons could also be used to produce energy in oxidative metabolism by the end levels of glycolysis (corresponding to pyruvate from Alanine) and tricarboxylic acid (corresponding to oxaloacetate from Asparate) thereby offering a metabolic fuel for tissues that requre or favor glucose. In addition, the carbon skeletons of certain amino acids can produce the equal of acetyl-CoA or Acetoacetate termed Ketogenic, indicating that they are often metabolized to give quick precursor of lipids or ketone our bodies. Assays of these enzyme actions in blood serum can be utilized both in diagnosis and in monitoring the progress of a patient throughout therapy. The functional part of pyridoxal phosphate is an aldehyde functional group attached to a pyridine ring. Oxidative deamination Involves the oxidative removing of the amino group, additionally resulting in ketoacids.

Order 500mg biaxin
Patients with neutropenia have a better rate of disseminated skin lesions in contrast with nonneutropenic immunocompromised sufferers (Nucci and Anaissie, 2002). Subcutaneous nodules, palpable and nonpalpable purpura, pink or grey macules, pink or grey papules, macules or papules with progressive central necrosis with central, flaccid pustules, vesicles and hemorrhagic bullae are types of lesions seen in sufferers with disseminated fusariosis (Nelson et al, 1994, Musa et al, 2000; Bodey et al, 2002) (See Color. These skin lesions can involve any web site, with predominance on the extremities (Bodey et al, 2002; Nucci and Anaissie, 2002). The lesions, particularly the subcutaneous nodules are often tender (Bodey et al, 2002) and most sufferers have lesions at varied levels of evolution (Boutati and Anaissie, 1997; Bodey et al, 2002). The variety of disseminated skin lesions is variable and ranges between 4 and greater than 30 based on a latest report from our establishment (Bodey et al, 2002). Skin lesions are an important potential source of diagnostic tissue in some sufferers with fusariosis (Nucci and Anaissie, 2002). Other displays of invasive fusariosis in compromised hosts embody osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, myositis, foot abscesses, sinusitis, endocarditis, myocarditis, external otitis, peritonitis, mind abscesses, cystitis, meningoencephalitis, and chronic hepatic an infection (Jakle et al, 1983; Young et al, 1984; Nuovo et al, 1988; Anaissie et al, 1988; Minor et al, 1989; Agamanolis et al, 1991; Nelson et al, 1994; Mohammedi et al, 1995; Girardi et al, 1999; Walsh and Groll, 1999, Rolston, 2001). Immunohistologic staining of tissues has additionally been used efficiently for diagnosing selected instances (Anaissie et al, 1989). Definitive diagnosis of fusariosis depends on the recovery of Fusarium species from infected tissues or blood cultures (Anaissie et al, 1989; Groll and Walsh, 2001). Fusarium species are extra readily isolated from blood cultures than are Aspergillus species (Fridkin and Jarvis, 1996; Kovacicova et al, 2001). While Fusarium species are a well-recognized reason for true fungemia, Aspergillus species recovered from blood cultures usually replicate pseudofungemia (Kontoyiannis et al, 2000). Fusarium species can also be recovered from urine in the setting of disseminated fusariosis (Richardson et al, 1988). Microscopically, Fusarium colonies start as a white patch, which rapidly develops a pink, purple, or yellow center with a lighter periphery. Fusarium species might produce three types of spores known as macroconidia, microconidia, and chlamydospores (Nelson et al, 1994). The morphology of the macroconidia (canoeshaped) is essential for characterizing the genus Fusarium (See Color. In addition to the morphology of the macroconidia, the presence of microconidia, the morphology of the conidiophores bearing the microconidia, and the presence of chlamydospores are additionally important in Fusarium taxonomy (See Color. Other macroscopic and microscopic features, similar to color of the colony, size and shape of the macroconidia and number, shape, and arrangement of microconidia, are key features for differentiating the varied Fusarium species. However, differentiating species is troublesome, due to their propensity for rapid morphologic change (Anaissie et al, 1988; El-Ani, 1990; Nelson et al, 1994). Polymerase chain reaction-based assays have the potential to be used as an adjunct to standard methods for the early detection and the evaluation of the natural history of this fungal an infection. Fusarium species are one of the most drug-resistant fungi (Sampathkumar and Paya, 2001), and amongst them, F. The molecular mechanism of such resistance has not been studied (Kontoyiannis and Lewis, 2002). However, in vitro susceptibility or resistance to antifungal brokers might not predict the medical end result of Fusarium an infection (Nelson et al, 1994; Mohammedi et al, 1995). Fusarium isolates are resistant to the antifungal brokers miconazole, ketoconazole, 5-fluorocytosine, fluconazole, itraconazole, and nikkomycin Z (Merz et al, 1988; Richardson et al, 1988; Anaissie et al, 1989; Speeleveld et al, 1996; Marco et al, 1998; Johnson et al, 1999; Li and Rinaldi, 1999; Arikan et al, 2001; Capilla et al, 2001). Other latest reports have shown that triazoles exhibit species-dependent fungistatic exercise against Fusarium species, particularly the nonsolani Fusarium species; voriconazole seems to be probably the most potent of the three medication (Huczko et al, 2001; Espinel-Ingroff et al, 2001; Paphitou et al, 2002). However, the remark that voriconazole is efficacious in the remedy of fusariosis in experimental mouse fashions exhibits the potential of this new triazole for treating this refractory invasive fungal an infection (Reyes et al, 2001). Finally, terbinafine, a squalene epoxidase inhibitor, exhibits some in vitro exercise against some isolates of non-solani Fusarium species (Speeleveld et al, 1996; Pont�n et al, 2000). Amphotericin B and natamycin are probably the most lively brokers against Fusarium species in vitro and in vivo (Anaissie et al, 1988; Anaissie et al, 1989; Martino et al, 1994; Johnson et al, 1998). Liposomal amphotericin B at high doses (10 to 20 mg/kg/day) significantly reduces tissue burden in the liver and spleen of immunocompetent mice infected with F. Fusarium species are resistant to the just lately launched glucan synthesis inhibitors, caspofungin, anidulafungin, and micafungin (Espinel-Ingroff, 1998; Pfaller et al, 1998; Tawara et al, 2000; Arikan et al, 2001). One possible explanation is that Fusarium species might possess less 1,three- -D-glucans than 1,6- -glucan or different non-1,three- -D-glucans (Tawara et al, 2000). Of notice, despite the dearth of exercise of caspofungin alone, the in vitro combination of caspofungin and amphotericin B seems to be either synergistic or additive against some Fusarium isolates (Arikan et al, 2002; Kontoyiannis, unpublished information). In view of the innate resistance of Fusarium species to antifungals alone in vitro, different mixtures have been tried. In vitro synergy has been shown between amphotericin B and rifampin, for instance (Stern, 1978), although this combination has been unsuccessful for treating fusariosis in humans (Minor et al, 1989). However, medical information are wanted to help the usage of azithromycin together with amphotericin B. In view of the relative rarity of human infections caused by Fusarium species, the human experience has been derived from uncontrolled case sequence. Furthermore, these reports have been confounded by different factors important for response such because the recovery of neutrophil count. The remedy of disseminated fusariosis in closely immunosuppressed sufferers, in particular, has been disappointing; reported mortality and morbidity charges exceed seventy five% (Martino et al, 1994; Boutati and Anaissie, 1997; Musa et al, 2000). Principles of Therapy in Fusariosis Early aggressive remedy with high doses of lipid amphotericin B Low threshold for switching to a brand new triazole. The most important factors predicting the result of Fusarium an infection are the extent of the an infection and the recovery of immunosuppression of the host (Anaissie et al, 1989; Nelson et al, 1994; Boutati and Anaissie, 1997). An ominous end result is predicted in sufferers with disseminated multiple-organ an infection, even when high doses (1. One of an important medical aspects of extreme Fusarium an infection is the relative lack of responsiveness of this fungus to either amphotericin B deoxycholate or a lipid formulation of amphotericin B in the setting of profound immunosuppression (Anaissie et al, 1988; Anaissie et al, 1992; Martino et al, 1994; Costa et al, 2000; Kovacicova et al, 2001). However, the addition of flucytosine has not been confirmed simpler than high-dose amphotericin B as monotherapy. Walsh and coworkers reported 11 sufferers with fusariosis, together with some with disseminated illness, with an eighty two% response rate (complete or partial) to amphotericin B lipid complicated (5 mg/kg/day). Since the new antifungal triazoles, specifically voriconazole, or posaconazole present preclinical exercise against Fusarium species, they provide some hope in the administration of this extreme an infection (McGinnis et al, 1998; Lozano-Chiu et al, 1999). However, in two pediatric sufferers with fusariosis handled with voriconazole a poor end result was noticed (Walsh el at, 2002). The preliminary experience in our establishment signifies that the response rate to posaconazole in sufferers with fusariosis refractory to or illiberal of ordinary remedy approaches 50% (Hachem et al, 2000). Topical remedy with natamycin is the mainstay of remedy for keratitis or corneal ulcers caused by Fusarium species (Reuben et al, 1989; Hirose et al, 1997). Novel antifungals given either systemically or topical might be of benefit in selected instances. In addition, one other case has been just lately reported of a affected person with amphotericin B and natamycin-resistant Fusarium solani keratitis and endophthalmitis, who responded to systemic and topical posaconazole (Sponsel et al, 2002). Vitrectomy with intravitreal and intravenous administration of amphotericin B and oral flucytosine has been used to deal with Fusarium endophthalmitis with varied results (Rowsey et al, 1979; Gabriele and Hutchins, 1996; Glasgow et al, 1996). Some sufferers with mycetoma due to Fusarium respond to itraconazole (Restrepo, 1994). Interestingly, the appliance of high concentration of nystatin powder (6,000,000 items/g) can effectively halt the development of invasive Fusarium an infection in severely burned pediatric sufferers (Barret et al, 1999). In addition to topical remedy with natamycin, keratoplasty with elimination of the contaminated lens must be a part of the therapeutic regimen for Fusarium keratitis (Nelson et al, 1994). In immunocompetent sufferers, Fusarium onychomycosis must be handled with elimination of the infected keratin and topical or systemic antimycotic remedy (Nelson et al, 1994; Gupta et al, 2000). Nail avulsion followed by the appliance of ciclopirox ointment and bifonazole ointment or eight% ciclopirox nail lacquer has been reported to be effective (Gupta et al, 2000). In sufferers with hematological malignancies, Fusarium onychomycosis must be handled aggressively, together with nail elimination and systemic antifungal remedy. Overall, surgical resection of infected necrotic tissue, when possible, is a vital component of remedy against fusariosis (Nelson et al, 1994). In profoundly neutropenic sufferers with fusariosis, granulocyte transfusion leads to a favorable response rate of 33% to 50% (Martino et al, 1994; Rodriguez-Adrian et al, 1998).
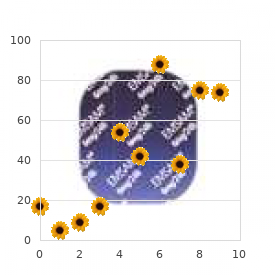
Order biaxin 500mg
For candiduric sufferers with sepsis, not solely is it necessary to get hold of blood cultures, but given the frequency that obstruction and stasis coexist, radiographic imaging of the upper tract is essential. Any febrile affected person for Candidiasis 161 mucosa has been shown experimentally in animals and human volunteers (Stone et al, 1974). Peritoneal contamination with Candida species usually follows spontaneous gastrointestinal perforation on surgical opening of gut (Calandra et al, 1989). Peritonitis is more likely to follow proliferation of accompanying bacterial pathogens but can occur with Candida alone. Several risk elements have been recognized in the improvement of peritonitis including current or concomitant antimicrobial therapy, inoculum size and surgical procedure for acute pancreatitis (Calandra et al, 1989). Pancreatic transplantation, especially with enteric drainage, is associated with intraabdominal Candida abscess formation (Benedetti et al, 1996). Candida species seem to have distinctive affinity for the infected pancreas, leading to intrapancreatic abscesses or an infection of a pseudocyst. With Candida peritonitis, Candida usually remains localized to the peritoneal cavity; dissemination happens in approximately 25% of sufferers. Candidemia complicating intraabdominal an infection is associated with a excessive mortality. The clinical significance of Candida isolated from the peritoneal cavity on the time of surgical procedure or in the postoperative interval is controversial. In a evaluate of Candida isolates from the peritoneal cavity, investigators decided that Candida brought on intraabdominal an infection in 39% (19/forty nine) of sufferers. In 61% of sufferers, Candida isolation occurred with out signs of peritonitis (Calandra et al, 1989). Accordingly, in every particular person affected person, judgement based upon the presence of clinical signs of an infection and different risk elements should be considered in deciding to initiate antifungal therapy (Eggimann et al, 1999). In distinction, a affected person with out sepsis requires performance of no further studies except candiduria persists after removing of the catheter. Candiduria is most often asymptomatic and usually happens in hospitalized sufferers with indwelling catheters. These sufferers usually show not one of the signs or signs associated with urinary tract an infection. Occasionally, sufferers may present with signs of bladder irritation including dysuria, hematuria, frequency, urgency, and suprapubic tenderness. Cystoscopy reveals delicate, pearly white, elevated patches with underlying friable mucosa. Symptomatic Candida cystitis is extraordinarily uncommon in both catheterized and noncatheterized sufferers, implying that the bladder is comparatively resistant to invasion by Candida species. Emphysematous cystitis is a uncommon complication of lower tract an infection, whereas prostatic abscess attributable to Candida species is often seen, especially amongst sufferers with diabetes. Upper urinary tract an infection presents with fever, leukocytosis, and costovertebral angle tenderness. On clinical grounds, ascending pyelonephritis and urosepsis with Candida species are indistinguishable from bacterial pyelonephritis. Ascending an infection nearly invariably happens in the presence of urinary obstruction and stasis, especially in sufferers with diabetes or nephrolithiasis. Candida pyelonephritis is commonly complicated by local suppurative illness, leading to pyonephrosis or focal abscess formation. A major complication of upper urinary tract involvement is obstruction attributable to fungal balls (bezoars), which may also be visualized by ultrasound (Fisher et al, 1979). Renal colic may occur with the passage of fungal "stones" which are literally parts of fungal balls. Patients with hematogenous seeding of the kidneys from candidemia may present with excessive fever, hemodynamic instability, and variable renal insufficiency. Retinal or pores and skin involvement may recommend dissemination, but candiduria and a decline in renal operate are sometimes the only clues to systemic candidiasis in a febrile, excessive-risk affected person. Abdominal Candidiasis Including Peritonitis Candida an infection has been more and more recognized as a cause of stomach sepsis and is associated with a excessive mortality. Abdominal sepsis may occur as monomicrobial or polymicrobial peritonitis and result in single or multiple abscesses (McClean et al, 1994). Candida is an rare cause of cholecystitis and cholangitis usually following extrahepatic biliary tract obstruction (Irani and Truong, 1986). Other risk elements for biliary candidiasis embrace diabetes, immunosuppression and stomach malignancy. A major contributory issue is use of biliary stents positioned to relieve obstruction; Candida an infection usually supervenes when stent drainage is compromised. An uncommon complication of biliary candidiasis is improvement of fungus balls in the gall bladder and dilated bile ducts (Magnussen et al, 1979; Irani and Truong, 1986; Morris et al, 1990). Morris and colleagues reviewed 31 circumstances of biliary candidiasis and classified illness as uncomplicated and complex. Uncomplicated cholecystitis implied that Candida organisms were confined to bile and the gall bladder with out extrabiliary spread. In distinction, complicated infections implied spread to adjoining structures, including liver and peritoneum. Uncomplicated illness has minimal mortality and cure is achieved by cholecystectomy alone. Candida Osteomyelitis and Arthritis Although beforehand uncommon, Candida osteomyelitis has turn into more common. Most circumstances result from hematogenous dissemination with seeding of long bones in children and the axial skeleton in adults. Sites of bone an infection embrace spine (vertebral and intervertebral disks) wrist, femur, humerus, and costochondral junctions (Collette et al, 1989; Herzog et al, 1989). Osteomyelitis may present weeks or months following the causal candidemic episode; hence on the time of the presentation, blood cultures are usually unfavorable and radiologic findings nonspecific. Occasionally, postoperative wound infections may spread to contiguous bone corresponding to sternum and vertebrae (Clancy et al, 1997). Regardless of supply, manifestations resemble bacterial an infection, but run a more insidious course, with a major delay in analysis. Hematogenous vertebral osteomyelitis mostly (ninety five%) affects the lower thoracic or lumbar spine. In one collection, 83% of sufferers had again pain lasting more than 1 month, solely 32% introduced with fever and 19% had associated neurologic issues (Miller and Mejicano, 2001). A prior history of constructive blood cultures was present in 51%�61% of circumstances (Hendrickx et al, 2001). It rarely follows local trauma, surgical procedure, or intraarticular injections (Silveira et al, 1993; Hansen and Anderson, 1995; Murphy et al, 1997; Fukasawa and Shirakura, 1997). Nonalbicans Candida species account for the next than expected frequency of circumstances of fungal arthritis. Candida arthritis can occur in any joint and involves multiple joints in as much as 27% of circumstances. Infection resembles bacterial septic arthritis, but frequent delays in analysis and suboptimal therapy often result in continual an infection with secondary bone involvement. Rarely hematogenous candidiasis may involve single or multiple muscles leading to Candida pyomyositis (Belzunegui et al, 1997). Candida Infections in Burns Fungal an infection is a severe complication of major burns (Spebar and Pruitt, 1981; Prasad et al, 1987; Desai et al, 1987; Grube et al, 1988). Increased survival of sufferers with extensive burns has expanded the pool of in danger subjects. Candida species causing burn-associated an infection are much like these concerned in different nosocomial Candida infections. Burn colonization charges are usually lower than 20% (range 13%�sixty five%), with charges of candidemia ranging from 1. Candidemia and bacteremia frequently coexist in burn sufferers (Spebar and Pruitt, 1981; Prasad et al, 1987; Desai et al, 1987). Mortality attributable to invasive candidiasis in burn sufferers is low (1%) with concomitant bacterial pathogens enjoying a more important function. During the decade of the Eighties, many burn units utilized antifungal prophylaxis with oral nystatin or topical nystatin incorporated into silver sulfadiazine with considerable efficacy in lowering both burn wound colonization by Candida species and candidemia (Desai et al, 1987).
Best 250 mg biaxin
Red circles, mannose; darkish blue squares, N-acetylglucosamine; yellow triangles, glucose; green squares, galactose; orange squares, sialic acid; maroon triangle, fucose. However, in animal cells, transformation refers to changes in the growth properties of cells in tradition after they turn out to be cancerous. Three strategies are commonly used to remodel yeasts: electroporation, lithium acetate therapy, and cell wall removal (protoplast formation). Fungus-Based Expression Systems Fungi share lots of the molecular, genetic, and biochemical options of different, "higher" eukaryotes and are subsequently a good choice for heterologous protein production. Initially, the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae was used extensively as a bunch cell for the expression of cloned eukaryotic genes. It has an extended history of use in traditional biotechnologies in the brewing and baking industries. Today, a variety of fungal expression methods can be found, and they have been optimized for recombinant protein expression. Versatile expression vectors with broad host ranges have been constructed as a result of the optimum host for production of a selected target protein should usually be decided experimentally in a variety of completely different methods. First, 1stgreat deal is 2nd Proof a Proof known concerning the biochemistry, genetics, and cellFinal 3rd Proof 4rd Proof biology of the fungus. It may be grown quickly to high cell densities on comparatively easy media in both small tradition vessels and enormous-scale bioreactors. Second, several strong promoters have been isolated from the yeast and characterised, and a naturally occurring plasmid, referred to as the two�m plasmid, can be used as a part of an endogenous yeast expression vector system. Food and Drug Heterologous Protein Production in Eukaryotic Cells 245 Administration as a "generally recognized as protected" organism. For example, at current, more than 50% of the world supply of insulin is produced by S. Of these, episomal vectors have been used extensively for the production of both intra- or extracellular heterologous proteins. Typically, the vectors include options that enable them to function in both micro organism and S. Such strains are said to be auxotrophic as a result of minimal growth medium have to be supplemented with a specific nutrient. In practice, the vector is provided with a functional (wild-type) version of a gene that complements the mutated gene in the host strain. Generally, tightly regulatable, inducible promoters are most well-liked for producing large quantities of recombinant protein at a specific time throughout large-scale growth. In this context, the galactose-regulated promoters reply quickly to the addition of galactose with a 1,000-fold increase in transcription. Repressible, constitutive, and hybrid promoters that combine the options of various promoters are additionally out there. Also, artificial leader sequences have been created to increase the amount of secreted protein. Plasmid-based yeast expression methods are sometimes unstable underneath largescale (10 liters) growth circumstances even in the presence of choice pressure. To treatment this drawback, a heterologous gene is built-in into the host genome to present a more dependable production system. Different approaches have been devised for the integration of a cloned gene together with a Heterologous Protein Production in Eukaryotic Cells 247 selectable marker gene into an S. The ampicillin resistance (Ampr) gene and the origin of replication (oriE) function in E. The major drawback of this strategy is the low yield of recombinant protein from a single gene copy. Alternatively, the heterologous gene may be built-in into several of the four hundred copies of sequences in the S. In one research, 10 copies of a heterologous gene had been inserted into sequences and produced a major amount of the recombinant protein. In the absence of the product of the marker gene, a colorimetric response is noticed when recipient cells are grown on a specialized medium. In humans, this anion helps both to stimulate the inflammatory response of phagocytes and to direct leukocytes to the location of an an infection. Superoxide anion can be produced when blood is allowed to reenter an organ (reperfusion) after it has been deprived of blood throughout a surgical procedure. A leucine-defective (leu2) yeast strain was transformed with the vector, and the cells had been plated onto medium that lacked leucine. Consequently, the coding sequences of recombinant proteins that require both O-linked or N-linked sugars for organic activity have to be geared up with a leader sequence. Under these circumstances, right disulfide bond formation, proteolytic removal of the leader sequence, and applicable posttranslational modifications usually occur, and an lively recombinant protein is secreted. During this course of, the leader peptide is removed by an endoprotease that acknowledges the dipeptide Lys-Arg. In reality, the development of the first generation of eukaryotic expression vectors was a painstaking course of following a C trial-and-error approach. It additionally stimulated extra analysis that pinpointed intimately the structural prerequisites for the following generation of eukaryotic expression vectors. For example, a correctly processed and lively type of the protein hirudin was synthesized and secreted by an S. Over the last 10 years, the amount of heterologous protein that can be produced per liter of yeast tradition has increased a hundred-fold (from about zero. This increase is principally because of enhancements in rising cultured cells to high cell densities; the level of protein produced per cell has remained largely unchanged. Although there have been vital advances in strategies to increase the number of copies of a target gene in a bunch cell and to increase the expression levels of those genes, the overexpressed proteins tend to type intracellular aggregates, usually associated with molecular chaperones, somewhat than to be secreted into the medium, which facilitates purification. Major issues that have to be addressed to increase heterologous-protein secretion in yeast cells are the incorrect folding of the polypeptide, the activation of cellular mechanisms to cope with the stress of protein overproduction, and the aberrant processing and release of the protein of interest from the endoplasmic reticulum. One of the main reasons for producing a recombinant protein for use in human therapeutics in yeast somewhat than in micro organism is to make sure that the protein is processed accurately following synthesis. Correct protein folding occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotes and is facilitated by a variety of completely different proteins, including molecular chaperones, enzymes for disulfide bond formation, sign transduction proteins that monitor the demand and capability of the protein-folding machinery, and proteases that clear away improperly folded or aggregated proteins. The eukaryotic enzyme protein disulfide isomerase is instrumental in forming the correct disulfide bonds within a protein. For example, the overproduction of molecular chaperones and protein disulfide isomerases may increase the yield of recombinant proteins, particularly those with disulfide bonds. The modified strain confirmed a 16-fold increase in protein disulfide isomerase production in contrast with the wild-type strain. The overproduction of protein disulfide isomerase particularly increases the secretion of proteins with disulfide bonds. Higher levels of secreted products are additionally obtained for the recombinant proteins human erythropoietin, bovine prochymosin, and leech hirudin in S. This is as a result of proper protein folding requires the coordinated efforts of many interacting elements. Even when levels of 1 chaperone are sufficient, the levels of cochaperones or cofactors may be limiting. The unfolded-protein response of yeast cells coordinates the expression of several chaperones, as well as cochaperones. When the demand for protein folding exceeds the folding capability of the endoplasmic reticulum, the unfolded-protein response increases the expression of chaperones, protein disulfide isomerase, and different proteins involved in protein secretion. Engineering the proteins of the unfolded-protein response may be a better approach to increase the overall capability of the cell to fold proteins in a coordinated way by sustaining applicable ratios of all elements required. Pichia pastoris Expression Systems Recombinant proteins have been produced efficiently in S. Although the preliminary phases of addition of glycan chains to proteins in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum are comparable in yeast and humans, following switch of the protein to the Golgi equipment, further processing differs significantly. The end result is the production of a sialylated protein in humans and a hypermannosylated protein in yeast, with a-1,three bonds between the sugar residues that may make the heterologous protein antigenic. Also, proteins that are designed for secretion frequently are retained in the periplasmic house, growing the time and value of purification. For these reasons, researchers have examined different yeast species and eukaryotic cells that might act as efficient host cells for recombinant protein production. Both human and yeast cells add the same small (10-residue), branched oligosaccharide to nascent proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. However, that is the last common precursor between the two cell types, as a result of once the protein is transported to the Golgi equipment, further processing is completely different.
References:
- https://www.vaczine-analytics.com/VAMV024_TOC_190604_Lyme_Disease_vaccines_global_market_forecast.pdf
- https://christianacare.org/documents/COVID-19-Pediatric-Ambulatory-Guidance.pdf
- https://www.bmj.com/content/bmj/294/6566/208.full.pdf
- https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/pb-assets/docs/journals/CAv61nS21-1593018011420.pdf
.png)