Cheap 75mg clopidogrel
Comparison of a (A) typical eight mm thick/ zero mm hole slice with a (B) four mm thickness and four mm spacing to preserve coverage. Using thinner slices to scale back through-slice dephasing also can help scale back artifact. We anticipate improved affected person consolation for these exams, which can facilitate improved compliance for arms-above-head positioning. Global hypokinesis was seen with regional variation particularly with focal hypokinesis/dyskinesis in the mid/apical septal and apical anterior segments. There is curvilinear late gadolinium enhancement preserving with} scarring in the basal-anterior septal mid myocardium. Thrombus is seen in the apex, with a skinny rim of increased enhancement on the edges of the thrombus. We were additionally in a position to} obtain short acquisition occasions and homogenous fat suppression. Also, T2 Cube pictures can be used to merge with ultrasound to assist in performing targeted biopsies. In this specific case, a lesion with excessive sign in the T2-weighted sequence in the central prostate could be seen. The 48-channel Head Coil has an adaptable design with an additional three cm enlargement to acquire extra room for very large-sized heads and necks. It additionally helps scale back the affected person feeling confined or having their nostril in contact with the entrance of the coil. The coil is appropriate with the consolation tilt system, which is very important when scanning elderly patients affected by kyphosis as a result of|as a end result of} it helps them lie comfortably on the desk. It is essential for our dementia protocols that the affected person not transfer during scanning discomfort. The 48-channel Head Coil is an actual asset for us as a neuroradiological institute and it further extends the medical advantages of a robust three. Improvements in each diffusion-weighted sequences and hepatocyte-specific distinction agents have improved the detection of each main and secondary (metastatic) lesions. However, many patients are unable to carry out breath-holds the extent of their liver illness and facet effects} of most cancers therapies. Auto Navigator is a free-breathing approach that combats respiratory movement and contains an automatic tracker placement for enhanced workflow. The addition of Auto Navigator and respiratory trigger supply a comprehensive free-breathing protocol that provides pictures with out breathing artifacts for high-quality stomach imaging. This is particularly true in the evaluation of these with cholangiopathies by which high-quality imaging is important for the initial illness prognosis and also in surveillance imaging for the event of malignancy. In addition, there has been continued enlargement of remedy options available to patients with main and secondary hepatic malignancies previously thought of untreatable. While traditionally colorectal metastases have been targeted for remedy, other tumor sorts are increasingly being thought of for extra aggressive intervention. Given the excessive cost and potential of associated toxicity to normal tissues and organs of many most cancers remedy options, correct identification and characterization of hepatobiliary lesions is important. Patients listed for transplantation for persistent liver illness, together with these with cholangiopathies, require optimal imaging as a result of|as a end result of} the identification of a malignancy could finally preclude transplantation. The method is particularly relevant throughout the left liver to mitigate the effects of cardiac movement and within the most superior segments on the proper the place the proximity of lung parenchyma often ends in image degradation. If solitary, the affected person was to be thought of for radiofrequency ablation or resection. Due to its small size and indeterminate nature, early interval imaging was advised, though initial findings were concerning, given the identified innate T1 hyperintensity of melanoma metastases. In addition, a small hyperintense focus was visible within the proper lung base, trying back} was present three months prior, though less conspicuous (Figure 2). Patient management subsequently changed considerably to immunotherapy with avoidance of pointless surgical procedure or locoregional remedy. Increasing extrahepatic duct dilatation was seen with an irregular stricture of the inferior widespread bile duct. Endoscopic ultrasound evaluation confirmed the presence of a mural lesion with a luminal soft tissue part (Figure 5); biopsy confirmed cholangiocarcinoma. Note the extensive T2 sign change throughout the background liver parenchyma preserving with} fibrosis (asterisk). Axial endoscopic ultrasound image at/immediately beneath the irregular mural thickening seen in Figure four. Being in a position to} confidently establish lesions solely millimeters in size, together with throughout the lung bases the place technical points such as movement and susceptibility artifact are usually significant factors of image degradation, leads to considerably improved diagnostic confidence. Comparison of Breath-hold versus Free-breathing versus Respiratory Triggered and Navigator Triggered Diffusion Weighted Imaging of the Liver. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: comparison of navigator triggered and breathhold acquisitions. Introduction to the Technical Aspects of Computed Diffusion-weighted Imaging for Radiologists. A challenge is that affected person compliance is required for respiratory-triggered and breath-hold sequences to obtain diagnostic-quality pictures. The protocol included affected person fasting of a minimum of|no less than} four hours, which reduced the amount of fluid in the stomach and digestive tract, distended the gallbladder and restricted duodenal peristalsis. The ingestion of pineapple juice simply before the examination helped to act as a negative distinction agent, the paramagnetic properties of the manganese contained in the juice, thus limiting sign interference related to the digestive tract fluid onto the resultant pictures. The breath-hold sequence offers the identical diagnostic information as the traditional sequence but in a far shorter scan time of 24 sec. The respiratory-triggered sequence with HyperSense was in a position to} present the identical diagnostic information as the traditional sequence with a reduced scan time. In virtually all cases, we achieved related image high quality, nonetheless, with HyperSense we were in a position to} scale back the sequence scan time by a minimum of|no less than} 34 p.c. We were additionally in a position to} scale back artifacts in the respiratory-triggered sequence with the addition of HyperSense the shortened examination time. Next, we evaluated the respiratorytriggered HyperSense sequence towards the HyperSense breath-hold sequence utilizing the identical factor of two. A 53-year-old female with a three cm mass positioned in the pancreas head, which led to main and secondary pancreatic ducts dilation properly as|in addition to} intra- and extra-hepatic biliary ducts dilation. The breath-hold sequence offers the identical diagnostic information as the traditional sequence but in a far shorter scan time of 23 sec. The main pancreatic duct is best depicted on the breath-hold sequence, movement artifacts present on each triggered sequences. Plus, by utilizing HyperSense, the breath-hold sequence might be be} reduced to 24 seconds or less with out respiratory-induced artifacts. Perfusion examine exhibits an anomaly with delayed and reduced distinction enhancement with predominance on the subendocardial antero-septo-lateral midventricular region. With distinction uptake we found: · Transmural on apical anteroseptal; · Transmural on midventricular septal; · Inferior to 50% of myocardial thickness on subendocardial anterior midventricular region; · Sub-endocardial no-reflow phenomenon on the infero-septal region of the apex (also noticed on perfusion sequence); · No regional myocardial parietal thinning of lower than 6 mm. Red arrows show the sub-endocardial no-reflow phenomenon on the inferoseptal region of the apex. In specific, it supports management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients and post-operative follow-up in Tetralogy of Fallot cases. This could be achieved with parallel imaging and compressed sensing techniques, which might also have the added influence of decreasing complete scan time and probably enabling further scheduling slots. Magnetic field distortions created by susceptibility effects that result in sign loss, primarily in T2-weighted rest and spatial mismapping. Susceptibility artifacts widespread in patients with steel implants, screws or clips. Conventional distinction (top row) and parametric maps (bottom row) were all generated in a single 5 min. Acceleration techniques HyperWorks is a group of superior acceleration techniques that deliver quick scanning-up to eight occasions faster-with excellent image high quality. Designed to pace up scanning to scale back the potential for movement artifacts and, therefore, repeat exams, HyperWorks contains HyperSense, HyperBand and HyperCube.
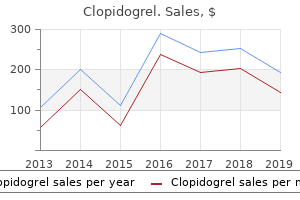
Proven 75 mg clopidogrel
Transfusion of Cryoprecipitate Cryoprecipitate is the chilly protein fraction obtained from frozen plasma thawed at 4o C a, and thus is called as} "cryo" (cold) precipitate. Cryoprecipitate incorporates much less volume than plasma and a more concentrated degree of fibrinogen, which makes it the selection for remedy when these low ranges of fibrinogen exist. Once the choice has been made to transfuse cryoprecipitate, transfuse 5-10 mL/kg. Under regular circumstances only a small amount of bilirubin is discovered within the unbound state. The useful bilirubin binding capacity of albumin is the main determinant of danger of toxicity when the serum bilirubin degree is elevated. Albumin binding capacity is lowered by acidosis, immaturity, and the presence of aggressive substances corresponding to salicylates, sulfonamides, and free fatty acids. Free fatty acids are particularly important rivals for bilirubin binding websites in preterm infants. The presence of such aggressive substances increases the proportion of free bilirubin current and, thus, increases the danger of kernicterus. Transport proteins then facilitate passage across the cell membrane into the biliary tree for passage into the gut with bile move. A small proportion of conjugated bilirubin is deconjugated within the intestine and reabsorbed into the circulation (enterohepatic circulation). Conjugation and intracellular transport both could also be} impaired in preterm infants In a fetus, bilirubin metabolism is more advanced. Bilirubin is introduced to the placenta for excretion within the fat-soluble (unconjugated) type. Then unconjugated bilirubin is reabsorbed into the fetal serum to be recycled to the placenta for final excretion. An understanding of the differing nature of antenatal and postnatal metabolism of bilirubin helps to clarify the effects of superimposed disease processes. There is scant evidence that platelet transfusions enhance neonatal outcomes, and most present guidelines are consensus guidelines quite than evidence-based guidelines (Fig 71). When used, platelet transfusions should all the time be given at the side of} aggressive remedy for the underlying disorder that brought on the thrombocytopenia. Although rarely of importance in term infants, it could turn out to be a big factor in a preterm or critically ill toddler. It might turn out to be a big factor in any disease process that delays bowel perform and stool passage. Diagonosis of Jaundice Risk Factors for Severe Hyperbilirubinemia Differential Diagnosis of Jaundice Increased serum bilirubin outcomes from elevated production, elevated enterohepatic circulation, or decreased elimination. Risk of hyperbilirubinemia is related to complete serum bilirubin degree, postnatal age, gestational age, and impression of co-existing sicknesses. Guidelines for Acute Care of the Neonate, Edition 26, 201819 Section of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine Section 7-Hematology More than half of healthy term infants and most preterm infants develop hyperbilirubinemia, and the incidence is highest in breastfed infants. Many could have seen jaundice however a visible estimate of the bilirubin degree could also be} inaccurate, particularly in darkly pigmented infants. In about 8% of infants, the bilirubin degree exceeds the 95th percentile for postnatal age through the first week of life. Peak bilirubin ranges in term or late preterm infants often occur on day three to 5 of age. It is convenient to consider causes of jaundice in relation to timing of occurrence. Coombs check often is optimistic, and particular transplacentally acquired antibody may be identified within the serum of the toddler. In common, isoimmune hemolytic issues carry the greatest danger of kernicterus outcome of|as a end result of} middleman merchandise of heme breakdown compete with bilirubin for albumin binding websites and promote larger ranges of free bilirubin than most other forms of hyperbilirubinemia. There is little relationship between bilirubin ranges and severity of anemia or between cord bilirubin degree and ultimate peak degree. Highest incidence occurs in breastfed infants and bilirubin ranges might peak somewhat later (day 5 or 6) and ranges above 10 mg/dL might persist somewhat longer. Although danger of kernicterus type of|is sort of} low, reported cases have elevated latest years|in latest times|lately}. Occasionally jaundice secondary to sepsis, metabolic issues, hypothyroidism, polycythemia, cephalohematoma or extreme bruising might manifest during this time interval. In these cases, the conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin fractions are elevated and the situation often is more persistent. If the mother is blood type O, Rh-negative, antibody display optimistic or had no prenatal blood group testing, then a direct Coombs check, blood type, and Rh (D) type are beneficial on the toddler or cord blood. In infants noted to be jaundiced within the first 24 hours of life, complete and direct serum bilirubin degree ought to be obtained. Further workup is warranted if the bilirubin degree is elevated or the direct Coombs is optimistic. These research often will set up a analysis of hemolytic disease, if current, and antibody screening of toddler serum will detect the precise offending antibody. Additionally, all infants should have a follow-up analysis at three to 5 days of age, when the bilirubin degree often is highest. Timing of this analysis is decided by the size of nursery keep and the presence or absence of danger elements for hyperbilirubinemia. Hyperbilirubinemia: age at discharge and follow-up Age at Discharge (hours) <24 24-47. The serum bilirubin degree was obtained earlier than discharge, and the zone during which the value fell predicted the chance of a subsequent bilirubin degree exceeding the 95th percentile (high-risk zone) as proven in Appendix 1, Table 4 (of source publication). Phototherapy Efficacy of phototherapy is decided by: mild source (blue-green spectrum is best), irradiance or power output within the blue spectrum, and surface area exposed. Light within the 450-nanometer (blue-green) vary converts unconjugated bilirubin to soluble, nontoxic photoisomers. It also stimulates bile move and excretion of bilirubin in bile, as well as|in addition to} enhancing intestine motility. Checking the light intensity earlier than each use is beneficial the place feasible to verify right positioning and irradiance of the light over the toddler. Intensive phototherapy combines an over-head high-intensity phototherapy system with a fiber-optic phototherapy pad positioned beneath the toddler. The overhead system ought to be positioned to deliver an irradiance dose of a minimum of|no much less than} 30 microWatts/cm2/nm as measured with a radiometer. The fiber optic pad ought to be covered only with a disposable cowl furnished by the manufacturer. This approach both increases delivered irradiance and recruits further surface area for mild exposure. Management General measures of management embrace early feeding to set up good caloric consumption. A main goal of feeding is the stimulation of bowel motility and elevated stooling to decrease enterohepatic circulation of bilirubin; nevertheless, other choices, beyond easy remark, are acknowledged, including supplementing breastfeeding with method or breast milk obtained by pump or temporary interruption of breastfeeding with method substitution, any of which may be accompanied by phototherapy. In infants without hemolytic disease, common bilirubin rebound is lower than 1 mg/dL. In most cases, no further bilirubin measurements are needed ninety four Guidelines for Acute Care of the Neonate, Edition 26, 201819 Section of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine Section 7-Hematology Figure 73. Guidelines for Management of Hyperbilirubinemia in Low Birth weight infants Total Serum Bilirubin ranges (mg/dL) to initiate remedy Phototherapy 1st week 2nd week < 750 grams 750-999 grams 1000-1499 grams 1500-1999 grams 2000-2500 grams 5 7-9* 10 - 12 * thirteen - 15 * 5 7 10 - 12 thirteen - 15 14 - 15 Exchange Transfusion > thirteen > 15 15 - 16 16 - 18 18 - 19 Use complete bilirubin. Note: these guidelines are based on limited evidence and the degrees proven are approximations. Infants are designated as "larger danger" because of the potential adverse effects of the circumstances listed on albumin binding of bilirubin, and the blood-brain barrier, and the susceptibility of the mind cells to harm by bilirubin. Note that irradiance measured under the center of the light source is much larger than that measured on the periphery. Measurements ought to be made with a radiometer specified by the manufacturer of the phototherapy system. See Appendix 2 [of source publication] for additional information on measuring the dose of phototherapy, a description of intensive phototherapy, and of sunshine sources used. If complete serum bilirubin ranges method or exceed the exchange transfusion line [Figure 83], the sides of the bassinet, incubator, or warmer ought to be lined with aluminum foil or white materials. This will increase the surface area of the toddler exposed and increase the efficacy of phototherapy. Infants who obtain phototherapy and have an elevated direct-reacting or conjugated bilirubin degree (cholestatic jaundice) might develop the bronzebaby syndrome. See Appendix 2 [of source publication] for using of} phototherapy in these infants.
Diseases
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- Hemifacial atrophy progressive
- Macrosomia developmental delay dysmorphism
- Self-defeating personality disorder
- Pseudohypoaldosteronism
- Fetal edema
- Warfarin necrosis
- Kousseff Nichols syndrome
Cheap clopidogrel 75 mg
This may be be} as a result of} impaired descending inhibitory inputs to the monosynaptic reflex arc. Rarely pathological hyperreflexia might happen within the absence of spasticity, suggesting different neuroanatomical substrates underlying these phenomena. Hyper-reflexia with out spasticity after unilateral infarct of the medullary pyramid. It has also been noticed in some sufferers with frontotemporal dementia; the discovering is cross-cultural, having been described in Christians, Muslims, and Sikhs. In the context of refractory epilepsy, it has been related to reduced volume of the proper hippocampus, however not proper amygdala. Religiosity is related to hippocampal however not amygdala volumes in sufferers with refractory epilepsy. Cross References Hypergraphia; Hyposexuality Hypersexuality Hypersexuality is a pathological increase in sexual drive and activity. Sexual disinhibition may be be} a characteristic of frontal lobe syndromes, particularly of the orbitofrontal cortex. Cross References Disinhibition; Frontal lobe syndromes; KlьverBucy syndrome; Punding Hypersomnolence Hypersomnolence is characterized by extreme daytime sleepiness, with an inclination to fall asleep at inappropriate occasions and locations, for instance, during - 187 - H Hyperthermia meals, phone conversations, on the wheel of a car. Clinical signs might include a bounding hyperdynamic circulation and typically papilloedema, as well as|in addition to} options of any underlying neuromuscular illness. Sleep studies confirm nocturnal hypoventilation with dips in arterial oxygen saturation. Other acknowledged causes of hyperthermia include · · Infection: bacteria, viruses (pyrogens. It often implies spasticity of corticospinal (pyramidal) pathway origin, quite than (leadpipe) rigidity of extrapyramidal origin. Cross Reference Anaesthesia Hypoalgesia Hypoalgesia is a decreased sensitivity to , or diminution of, ache perception in response to a usually painful stimulus. It may be be} demonstrated by asking a affected person to make repeated, large amplitude, opposition actions of thumb and forefinger, or tapping actions of the foot on the floor. Cross References Akinesia; Bradykinesia; Dysmetria; Fatigue; Hypokinesia; Parkinsonism; Saccades Hypomimia Hypomimia, or amimia, is a deficit or absence of expression by gesture or mimicry. This may be be} physiological, as with the diminution of the ankle jerks with normal ageing; or pathological, most often as a characteristic of peripheral lesions such as radiculopathy or neuropathy. The latter may be be} axonal or demyelinating, within the latter the blunting of the reflex may be be} out of proportion to associated weak point or sensory loss. Although incessantly characterized as a characteristic of the lower motor neurone syndrome, the pathology underlying hyporeflexia might happen anywhere alongside the monosynaptic reflex arc, including the sensory afferent fibre and dorsal root ganglion as well as|in addition to} the motor efferent fibre, and/or the spinal wire synapse. Hyporeflexia may accompany central lesions, particularly with involvement of the mesencephalic and upper pontine reticular formation. It may be be} related to many diseases, physical or psychiatric, and/or drugs which have an effect on} the central nervous system. Along with hypergraphia and hyperreligiosity, hyposexuality certainly one of the|is among the|is likely considered one of the} defining options of the Geschwind syndrome. Cross References Hypergraphia; Hyperreligiosity Hypothermia Hypothalamic harm, particularly within the posterior area, can result in hypothermia (cf. A uncommon syndrome of paroxysmal or periodic hypothermia has been described and labelled as diencephalic epilepsy. Non-neurological causes of hypothermia are more frequent, including hypothyroidism, hypopituitarism, hypoglycaemia, and drug overdose. Cross Reference Hyperthermia Hypotonia, Hypotonus Hypotonia (hypotonus) is a diminution or lack of normal muscular tone, inflicting floppiness of the limbs. This is particularly related to peripheral nerve or muscle pathology, as well as|in addition to} lesions of the cerebellum and sure basal ganglia issues such as hemiballismushemichorea. Weakness preventing voluntary activity quite than a reduction in stretch reflex activity appears to be the mechanism of hypotonia. Cross References Cover checks; Heterotropia; Hypertropia - 192 - I Ice Pack Test the ice pack check, or ice-on-eyes check, is carried out by holding an ice dice, wrapped in a towel or a surgical glove, over the levator palpebrae superioris muscle of a ptotic eye for 210 min. Improvement of ptosis is claimed to be particular for myasthenia gravis, perhaps as a result of|as a end result of} cold improves transmission on the neuromuscular junction (myasthenic sufferers often enhance in cold versus hot weather). This phenomenon is generally not noticed in different causes of ptosis, though it has been reported in Miller Fisher syndrome. A pooled analysis of several of} studies gave a check sensitivity of 89% and specificity of 100 percent with correspondingly high positive and negative probability ratios. Whether the ice pack check relevant to myasthenic diplopia has yet to be decided: false positives have been documented. They also happen in illness states, such as delirium, and psychiatric issues (affective issues, schizophrenia). Examples of phenomena which may be labelled illusory include · · · Visual: illusory visual unfold, metamorphopsia, palinopsia, polyopia, teleopsia, Pulfrich phenomenon, visual alloaesthesia, visual perseveration; Auditory: palinacusis; Vestibular: vertigo. They are consistent and have a compulsive high quality to them, perhaps triggered by the equivocal nature of the situation. There may be be} accompanying primitive reflexes, particularly the grasp reflex, and typically utilization behaviour. Imitation behaviour occurs with frontal lobe harm; initially mediobasal illness was thought the anatomical correlate, however newer studies counsel upper medial and lateral frontal cortex. It is mostly seen with lesions affecting the proper hemisphere, especially central and frontal mesial regions, and may happen in association with left hemiplegia, neglect, anosognosia, hemianopia, and sensory loss. Neuropsychologically, impersistence may be be} related to mechanisms of directed attention that are needed to sustain motor activity. Thus, the anatomical differential analysis of neurological incontinence is broad. Moreover, incontinence may be be} as a result of} inappropriate bladder emptying or a consequence of lack of consciousness of bladder fullness with secondary overflow. Other options of the history and/or examination might give useful pointers as to localization. Incontinence of neurological origin is often accompanied by different neurological signs, especially if related to spinal wire pathology (see Myelopathy). The pontine micturition centre lies near the medial longitudinal fasciculus and native illness might cause an internuclear ophthalmoplegia. However, different signs may be be} absent in illness of the frontal lobe or cauda equina. Spinal wire pathways: urge incontinence of a number of} sclerosis; lack of consciousness of bladder fullness with retention of urine and overflow in tabes dorsalis. Cauda equina syndrome; tethered wire syndrome (associated with spinal dysraphism). In addition there may be be} incomplete bladder emptying, which is often asymptomatic, as a result of} detrusor sphincter dyssynergia; for postmicturition residual volumes of higher than a hundred ml (assessed by inout catheterization or ultrasonography), that is best handled by clear intermittent self-catheterization. Approach to the affected person with bladder, bowel, or sexual dysfunction and different autonomic issues. Intermanual battle is more attribute of the callosal, quite than the frontal, subtype of anterior or motor alien hand. It is most often seen in sufferers with corticobasal degeneration, however may happen in association with callosal infarcts or tumours or following callosotomy. Intrusions are thought to reflect inattention and may be be} seen in dementing issues or delirium. The term intrusion used to describe inappropriate saccadic eye actions which intervene with macular fixation during pursuit eye actions. Intrusions as an indication of Alzheimer dementia: chemical and pathological verification. The discovering of inverted reflexes might reflect twin pathology, however more often reflects a single lesion which concurrently impacts a root or roots, interrupting the native reflex arc, and the spinal wire, damaging corticospinal (pyramidal tract) pathways which supply segments below the reflex arc. Hence, an inverted supinator jerk is indicative of a lesion at C5/6, paradoxical triceps reflex occurs with C7 lesions; and an inverted knee jerk indicates interruption of the L2/3/4 reflex arcs, with concurrent harm to pathways descending to levels below these segments. The pathophysiological implication is of electrical disturbance spreading via the homunculus of the motor cortex.
Generic 75mg clopidogrel
Physical Examination Vitalsigns(especiallybloodpressure),abdominalexaminationforflank masses,boweldistention,evidenceofimpaction,meatalstenosisor circumcisioninmales,vulvovaginitisorlabialadhesionsinfemales, neurologicexaminationoflowerextremities,perinealsensationand reflexes,andrectalandsacralexamination(foranteriorlyplacedanus) C. The use of plasma creatinine focus for estimating glomerular filtration price in infants, youngsters, and adolescents. Ingestion or accumulation of dialyzable toxins or poisons:Lithium, ammonia,alcohol,barbiturates,ethyleneglycol,isopropanol, methanol,salicylates,theophylline. First morning urine protein/creatinine ratio:Approximates24-hoururine collectionswellandhasadditionalbenefitofminimizingdetectionof proteinuriafromorthostaticproteinuria. Management of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome of childhood:Empirical corticosteroidtreatmentwithoutkidneybiopsyisrecommendedfor childrenwithoutatypicalfeatures. Rule out factitious causes of hypertension[impropercuffsizeor measurementtechnique. Classification of Hypertension in Children and Adolescents, With Measurement Frequency and Therapy Recommendations (Table19. Antihypertensive Drugs for Outpatient Management of Hypertension in Children 117 Years of Age (Table19. Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment of Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections in Adults: 2009 International Clinical Practice Guidelines from the Infectious Disease Society of America. Subcommittee on Urinary Tract Infection, Steering Committee on Quality Improvement and Management. Short versus commonplace period oral antibiotic therapy for acute urinary tract infection in youngsters. Pediatric hypertension: a evaluate of correct screening, prognosis, evaluation, and therapy. Precursors to migraines and shut associations includecyclicvomiting, abdominalmigraines,recurrentabdominalpain,paroxysmalvertigoof childhood,paroxysmaltorticollisofinfancy,andmotionsickness. Differential Diagnosis of Recurrent Events That Mimic Epilepsy in Childhood (Table20. Obesity, epilepsy Depression, insomnia Depression, insomnia Seasonal allergies, poor appetite, insomnia Hypertension b. Considerlumbarpunctureinthesecircumstances: (1) Infant612monthsofagewithincompleteorunknown Haemophilus influenzae or Streptococcus pneumoniae immunizations (2) Febrileseizureinachildpretreatedwithantibiotics. Antibiotics canmasksignsandsymptomsofmeningitis Evaluation of nonfebrile seizures Ifclinicallyindicated,checkglucose,Na,K,Ca,Phos,bloodurea nitrogen,creatinine,completebloodcellcounttoxicologyscreen. Levetiracetam, valproate, lamotrigine, different meds for generalized seizure Comment Age of onset 213 years; seizures are nocturnal and consist of hemisensory or motor phenomena of the face, motor findings in limbs; most sufferers outgrow by age 1618 years. Breakthrough seizures13:Causesofseizuresinachildwith recognized,typicallywell-controlledepilepsyincludingmissed medicationsoroutgrowingweight-baseddosing,lackofsleep, stress,drugs/alcohol,physicalexertion,excessivescreentime (television,videogames),sickness,dehydration,flickeringlights, menses,anddruginteractions(commononesincludetricyclic antidepressants,certainantibiotics,over-the-countercold preparations,diphenhydramine,herbalsupplements,allof whichmaylowerseizurethreshold). Completebloodcellcount,electrolytes,urineandserumtoxicology Imaging(computedtomographyand/ormagneticresonanceimaging) Lumbarpuncture Electroencephalography Ifneuroblastomaissuspected(opsoclonusmyoclonus),obtainurine vanillylmandelicacidandhomovanillicacid,andimagingofchestand abdomen. Practice parameter: evaluation of children and adolescents with recurrent complications. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, third version (beta version). Practice parameter: pharmacological therapy of migraine headache in youngsters and adolescents. The pharmacological therapy of migraine in youngsters and adolescents: an overview. Committee on Classification and Terminology of the International League in opposition to Epilepsy. Classification of epilepsia: its applicability and practical worth of various diagnostic categories. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, Chapter 585, "Congenital Anomalies of the Central Nervous System," Section 585. Management of stroke in infants and kids: a scientific assertion from a Special Writing Group of the American Heart Association Stroke Council and the Council on Cardiovascular Disease within the Young. Stroke in Childhood: Clinical Guidelines for Diagnosis, Management and Rehabilitation. Preventing stroke amongst youngsters with sickle cell anemia: an evaluation of methods that involve transcranial Doppler testing and chronic transfusion. Guidelines for thrombolytic therapy for acute stroke: a supplement to the rules for the administration of sufferers with acute ischemic stroke. A assertion for healthcare professionals from a Special Writing Group of the Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Infant and Pediatric Formula Company Websites Forcompleteandup-to-dateproductinformationregardingmore specializedandmetabolicformulas,seethesewebsites: · Enfamil,Enfacare,Nutramigen,andPregestimil: Clinical longitudinal requirements for height and height velocity in North American Children. Expert Committee recommendations relating to the prevention, assessment, and therapy of kid and adolescent overweight and weight problems: summary report. A systematic evaluate and meta-analysis to revise the Fenton growth chart for preterm infants. Thushiscatch-upgrowth requirementwouldbeasfollows: ninety eight kcal/kg/day Ч (9 kg/ 7 kg) = 126 kcal/kg/day *Ideal weight could be 10th85th percentile weight for height, depending on previous growth trends; medical judgment should be used. In view of proof linking folate intake with neural tube defects within the fetus, it is strongly recommended every one|that each one} ladies able to turning into pregnant eat four hundred mcg from supplements or fortified foods in addition to intake of food folate from a diversified food regimen. It is assumed that girls will continue consuming four hundred mcg from supplements or fortified food until their being pregnant is confirmed and so they enter prenatal care, which ordinarily happens after the top of the periconceptual period-the important time for formation of the neural tube. Also incorporates biotin, 15 mcg; pantothenic acid, 3 mg; 87% vitamin A as -carotene; coenzyme Q10, 2 mg; selenium, 10 mcg. Recommended to be used in infants with fat malabsorption, similar to cystic fibrosis, liver illness. Mixing Instructions for Full-Term Standard and Soy-Based Infant Formulas (Table21. An estimate of the osmolarity of parenteral diet could be obtained with the next formulation: Estimated osmolarity = (dextrose focus Ч 50) + (amino acid focus Ч 100) + (mEq of electrolytes Ч 2). Essential fatty acid deficiency might occur in fat-free parenteral diet within 24 weeks in infants and kids and as early as 214 days in neonates. The period earlier than dietary targets are reached or during any period of instability. Expert Committee Recommendations on the Assessment, Prevention and Treatment of Child and Adolescent Overweight and Obesity - 2007. Diagnosis and prevention of iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young youngsters 0 through 3 years. Enteral Nutrition Practice Recommendations Task Force, Bankhead R, Boullata J, et al. Commonly used monotherapies include antipseudomonal -lactams and fourth-generation cephalosporins or carbapenems. Clinical apply guideline for the usage of} antimicrobial brokers in neutropenic sufferers with cancer: 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Identify all components of therapy acquired:Comprehensivetreatment summaryfromoncologist,summarizing: a. Guideline for the administration of fever and neutropenia in youngsters with cancer and/or present process hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Guideline for the prevention of acute nausea and vomiting end result of} antineoplastic treatment in pediatric cancer sufferers. Guidelines for preventing infectious problems amongst hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: a worldwide perspective. Provides consistent, reliable format for dialogue and formulation of plan of care. Minimize separation from dad and mom; right perceptions that the sickness is punishment. Be truthful, permit expression of strong emotions, permit participation in determination making. Adolescents aged 18 years and oldercannameanotheradulttomake healthcaredecisionsiftheyareunabletospeakforthemselves. Healthcare group might help sufferers voice their preferencesforfuture healthcaredecisions. Older youngsters might have specific wishes for funeral, memorial, or distribution of non-public belongings. These are transportable and enduring medical order formscompletedby patientsortheirauthorizeddecisionmakersandsignedbya physician.
Generic 75 mg clopidogrel
Use with warning in ulcerative bowel lesions to avoid renal toxicity by way of systemic absorption. Drug is mostly poorly absorbed and due to this fact not indicated for sole treatment of extraintestinal amebiasis. Obsessive compulsive dysfunction (limited data, primarily based on a 10-wk randomized controlled trial in 207 youngsters 717 yr; mean age eleven. If needed, regulate upwards by growing dose no more than|not extra than} 10 mg/24 hr no extra regularly than Q7 days as much as} a max. If needed, enhance dose by 10 mg/24 hr no extra regularly than Q7 days as much as} a max. Use with warning in sufferers with history of seizures, renal or hepatic impairment, cardiac illness, suicidal issues, mania/hypomania, and diuretic use. Patients with extreme renal or hepatic impairment ought to initiate therapy at 10 mg/24 hr and enhance dose as needed as much as} a max. May enhance the effects/toxicity of tricyclic antidepressants, theophylline, and warfarin. Weakness, hyperreflexia, and poor coordination have been reported when taken with sumatriptan. Do not discontinue therapy abruptly, may cause sweating, dizziness, confusion and tremor. Side effects: anaphylaxis, urticaria, hemolytic anemia, interstitial nephritis, JarischHerxheimer response (syphilis). Preparations containing potassium and/or sodium salts may alter serum electrolytes. May cause false-positive or -negative urinary glucose (Clinitest method), false-positive direct Coombs take a look at, and false-positive urinary and/or serum proteins. Side effects and drug interactions similar as for Penicillin G PreparationsAqueous Potassium and Sodium. Use with warning in renal failure, asthma, vital allergic reactions, and cephalosporin hypersensitivity. The addition of procaine penicillin has not been shown to be extra efficacious than benzathine alone. Use with warning in renal failure, asthma, vital allergic reactions, cephalosporin hypersensitivity, and neonates (higher incidence of sterile abscess at injection web site and threat of procaine toxicity). Side effects and drug interactions similar to Penicillin G PreparationsAqueous Potassium and Sodium. No longer really helpful for empiric treatment of gonorrhea due to of} resistant strains. Penicillin will prevent rheumatic fever if began inside 9 days of the acute sickness. Additive nephrotoxicity with aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, cisplatin, and vancomycin may occur. Aerosol administration can also cause bronchospasm, cough, oxygen desaturation, dyspnea, and lack of appetite. Dose range: 13 mg/kg/hr as needed Contraindicated in liver failure and history of porphyria. May cause hypotension, arrhythmias, hypothermia, respiratory despair, and dependence. If the 1% cream rinse is resistant, the 5% cream additionally be} used after shampooing, rinsing, and towel drying hair. Scabies: Apply 5% cream from neck to toe (head to toe for infants and toddlers) wash off with water in 814 hr. Anaphylactoid-like response, methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia, and renal and hepatic toxicity have been reported often at overdosage levels. May additionally stain contact lenses and interfere with urinalysis tests primarily based on spectrometry or shade reactions. Avoid use in moderate/severe renal impairment; regulate dose in gentle renal impairment (see Chapter 30). Contraindicated in porphyria, extreme respiratory illness with dyspnea or obstruction. Side effects include drowsiness, cognitive impairment, ataxia, hypotension, hepatitis, rash, respiratory despair, apnea, megaloblastic anemia, and anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome. Paradoxical response in youngsters (not dose related) may cause hyperactivity, irritability, insomnia. Recommended serum sampling time at steady-state: trough degree obtained inside 30 min prior to the following scheduled dose after 1014 days of steady dosing. C Injection: 5 mg vial; may comprise mannitol Injection in solution for submucosal use: OraVerse: 0. Use with warning in hypotension, arrhythmias, and cerebral vascular spasm/occlusion For diagnosis of pheochromocytoma, affected person ought to be resting in a supine position. A blood pressure reduction of greater than 35 mm Hg systolic and 24 mm Hg diastolic is taken into account a positive take a look at for pheochromocytoma. For treatment of extravasation, use 27- to 30-gauge needle with quantity of} small injections and monitor web site intently as repeat doses additionally be} necessary. Nasal decongestant (in every nostril; give as much as} three days): Child 612 yr: 23 sprays to every nostril of 0. Oral phenylephrine is present in a variety of|quite lots of|a wide selection of} mixture cough and cold products and has changed pseudoephedrine and phenylpropanolamine. Side effects include gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism, dermatitis, blood dyscrasia, ataxia, lupus-like and StevensJohnson syndromes, lymphadenopathy, liver harm, and nystagmus. May enhance levels of amprenavir when administered with fosamprenavir and ritonavir. May cause resistance to neuromuscular blocking action of nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents. Drug is very protein-bound; free fraction of drug shall be elevated in sufferers with hypoalbuminemia. See Chapter 21 for daily necessities and Chapter eleven for additional information on hypophosphatemia and hyperphosphatemia. Large doses (1020 mg) in newborns may cause hyperbilirubinemia and extreme hemolytic anemia. Blood coagulation factors enhance inside 612 hr after oral doses and inside 12 hr following parenteral administration. Use with warning in sufferers with corneal abrasion or vital heart problems. Reduce oral dosing in the presence of gentle hepatic insufficiency (Child-Pugh rating of 56); avoid use in extreme hepatic insufficiency. Do not use in youngsters < 2 yr (higher rate of higher respiratory infections), immunocompromised sufferers, or with occlusive dressings (promotes systemic absorption). Avoid use on malignant or premalignant pores and skin situations as uncommon circumstances of lymphoma and pores and skin malignancy have been reported with topical calcineurin inhibitors. Use medicine for short durations of time by utilizing the minimum quantities to management signs; long-term safety is unknown. Most frequent aspect effects} include burning on the software web site, headache, viral infections, and pyrexia. Skin discoloration, pores and skin flushing related to alcohol use, anaphylactic reactions, ocular irritation after software to the eye lids or close to the eyes, angioneurotic edema, and facial edema have been reported. Coagulation parameters ought to be tested extra regularly and monitored regularly with excessive doses of heparin, warfarin, or different medication affecting blood coagulation or thrombocyte function. May falsely decrease aminoglycoside serum levels if the medication are infused close to each other; enable a minimum of 2 hr between infusions to prevent this interaction. Child: Dilute powder using the ratio of 17 g powder to 240 mL of water, juice, or milk. An onset of action inside 1 wk in 12 of 20 sufferers, with the remaining 8 sufferers reporting enchancment in the course of the second wk of therapy. Side effects reported in this trial included diarrhea, flatulence, and gentle belly pain. Most frequent aspect effects} include nausea, belly bloating, cramping, and flatulence. Local irritation consisting of redness, burning, stinging, and/or itching is frequent.
Syndromes
- Infection at the electrode sites (minimal risk)
- Sore throat
- Pressure on a nerve, such as carpal tunnel syndrome
- Fractures
- Loss of vision
- Skin cancer surgery
- Tumor size and shape
- Look for signs of the blood clotting or bleeding disorder
Buy 75 mg clopidogrel
This stage is characterized by nonspecific signs of shock, including poor perfusion, cyanosis, listlessness, and marked tachypnea. The electrocardiogram shows findings much like these of coarctation, including proper ventricular enlargement/hypertrophy. As with coarctation, temporary palliation is accomplished by maintaining ductal patency with prostaglandin. The ductus arteriosus, which is large, curves posteriorly to be a part of the thoracic descending aorta so seamlessly that the ductus itself additionally be} mistaken for the aortic arch. As in coarctation, the ductal shunt is predominantly proper to left (from pulmonary artery to descending aorta) because of|as a outcome of} the best ventricle is the only real} supply of blood circulate to the decrease physique. Oxygen information present a left-to-right shunt at ventricular stage and a right-to-left shunt via the ductus arteriosus, with regular saturation within the ascending aorta and its branches and decreased saturation within the descending aorta, similar to the extent of proper ventricular saturation. Left ventriculography demonstrates the location of the arch interruption, the origin and courses of the aortic branches, and the degree of left ventricular outflow tract hypoplasia; the last effect is better demonstrated by echocardiography. If the left ventricular outflow tract is of an inadequate dimension or is severely obstructed, a palliative operation, much like a Norwood operation, can be carried out. The success of operative restore is determined by} the degree of left ventricular outflow tract hypoplasia and on whether associated noncardiac anomalies are current. Volume overload Volume overload placed on both ventricle may result in neonatal cardiac failure, and may outcome from uncommon lesions corresponding to valvular insufficiency, or arteriovenous malformations. The arteriovenous fistula is related to low systemic arterial resistance and an increased quantity of blood circulate through the shunt. The increased circulate through the best side of the guts results in profound cardiac signs early in life. Prior to delivery, cardiac failure is absent due to the normally low systemic vascular resistance prenatally. With the lack of the placenta, systemic resistance will increase and so does the amount shunted through the fistula. An necessary wide spectrum of other circumstances affect on} the construction and/or function of the cardiovascular system in pediatric-aged sufferers. These embody genetic, infectious, and inflammatory illnesses and in many of} instances the etiology is unknown. In some sufferers, a cardiac condition can be suspected due to a identified affiliation between the first disease with a specific cardiovascular abnormality. In other instances, the family history may point out chance of|the potential of|the potential for} a genetic cardiac condition. Finally, the affected person may current with cardiac signs or signs and the underlying cardiac condition can be recognized. It is completely a childhood disease, with 80% of circumstances occurring by the age of 5 years. Coronary artery aneurysms are the most typical and potentially dangerous sequelae of Kawasaki disease, occurring in a single in four untreated sufferers. Other systemic arteries can be affected, and clinical overlap exists with a disseminated vasculitis, infantile polyarteritis nodosa. Patients with 5 days or more of high fever and at least of|no less than} four of these five features have Kawasaki disease, analogous to the use of of} the Jones criteria for the prognosis of rheumatic fever. Kawasaki disease is rather more pleomorphic than rheumatic fever, and many of|and plenty of} circumstances of "atypical" Kawasaki disease happen. The prognosis remains primarily based on clinical and laboratory findings, as no definitive laboratory take a look at exists. Natural history If untreated, Kawasaki disease is self-limited, with a imply period of 12 days for fever, though irritability and anorexia, each distinguished through the febrile acute phase, usually persist for 23 weeks after the fever ends. During the subacute or convalescent phase, often from day 10 to 20 after onset of fever, most sufferers have a highly specific pattern of desquamation of the hands and toes that begins periungual and proceeds proximally to involve the palms and soles. An echocardiogram (or, if unavailable, a chest radiograph to display screen for cardiomegaly) and 12-lead Table 9. Fever Conjunctivitis, nonexudative and bilateral Erythematous and fissured oral adjustments Erythematous rash Painful hand and foot induration Lymphadenopathy 262 Pediatric cardiology electrocardiogram are advisable on the time of prognosis. The echocardiogram ought to be repeated at about 1 month after onset of illness, since coronary artery adjustments may have occurred by then. Patients with carditis or aneurysms detected early require more frequent follow-up. Occasional sufferers require a second treatment due to failure to improve following the preliminary dose. The mechanism of motion is unknown but in all probability entails attenuation of an autoimmune response the prime pathophysiologic think about Kawasaki arteritis. Low-dose aspirin Low-dose aspirin ought to be started for its antiplatelet effect, though some have advocated high-dose aspirin for a variable interval to assist resolution of irritation earlier than commencing low-dose aspirin. Since occasional sufferers may manifest aneurysm a number of} months later, an echocardiogram 46 months after onset of illness additionally be} obtained and, if coronary arteries are regular, aspirin is discontinued. Low-dose aspirin may confer a small danger during sure viral sicknesses; it ought to be temporarily suspended during acute varicella or influenza and perhaps after varicella vaccination. The danger is roughly 1:50, with most circumstances recurring within the first few months of the preliminary episode. Coronary aneurysm the pure history of sufferers who develop coronary artery aneurysms varies. In 90% of sufferers the aneurysms resolve on echocardiogram, though some have continued narrowing of the coronary artery lumen resulting in stenotic lesions. The effect of childhood Kawasaki disease (without aneurysms) on the chance of coronary atherosclerosis in maturity is unknown. It is a sequel of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections, often tonsillopharyngitis, and develops in <1% of infected sufferers. Rheumatic fever often develops 10 days to 2 weeks following a streptococcal pharyngitis that just about} all the time is related to fever larger than a hundred and one F (38. Despite a minor resurgence within the 1980s, the incidence of rheumatic fever in North America decreased markedly within the last half of the 20th century. Worldwide, however, rheumatic fever remains the most typical reason for acquired heart disease within the young. These criteria comprise the varied combos of clinical and laboratory manifestations reflecting the multiple of} sites of disease involvement. There must be two major criteria or one major and two minor criteria, plus proof of a previous streptococcal infection, to diagnose acute rheumatic fever. Titers for a number of} antibodies ought to be measured because of|as a outcome of} a person may not form antibodies to each streptococcal product. Significant antibody rise indicates a recent streptococcal infection and is more significant than isolating beta-hemolytic streptococcus on a throat culture. Evidence of prior streptococcal infection is necessary earlier than these criteria are thought-about. Pericarditis can happen on this disease and can be suspected by the prevalence of chest ache referred to the stomach or shoulders. Cardiac enlargement or cardiac failure with out proof of valvar anomalies is proof of myocardial involvement. Various levels of heart block, gallop rhythm, and muffled heart sounds are other manifestations of myocarditis. Valvulitis is the most critical manifestation of carditis because of|as a outcome of} result in everlasting cardiac sequelae. The position of echocardiography in diagnosing subclinical valvar adjustments is under study. It has not been adopted within the United States, but is used as a criterion for prognosis of carditis in some elements of the world the place rheumatic fever is widespread. Typically, arthritis is migratory quantity of|various|a variety of} other|and a number of} other} joints additionally be} involved, usually sequentially, but at a given time there additionally be} involvement of only one joint. Diagnosis of arthritis rests on finding heat and tender joints that are be} painful on motion. Chorea is a late manifestation of rheumatic fever and sometimes develops a number of} months after the streptococcal infection. The presence of chorea alone is adequate for the prognosis of rheumatic fever, as there are virtually no other causes in childhood, though lupus must be excluded. Chorea is characterized by involuntary, nonrepetitive, purposeless motions, usually related to emotional instability. The dad and mom may complain that their child is clumsy, is fidgety, cries easily, or has issue in writing or studying.
Trusted 75mg clopidogrel
The prodromal phase from initial signs to onset of jaundice normally lasts from 3 to l0 days. It is nonspecific and is characterized by a slow onset of malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, proper upper quadrant stomach pain, fever, headache, myalgia, pores and skin rashes, arthralgia and arthritis, and dark urine. The icteric phase is variable however normally lasts from l to 3 weeks and is characterized by jaundice, light or grey stools, hepatic tenderness and hepatomegaly (splenomegaly is much less common). During convalescence, malaise and fatigue might persist for weeks or months, whereas jaundice, anorexia, and different signs disappear. If a pregnant lady has chronic hepatitis B, she can be entered as a chronic case of hepatitis B, if the jurisdiction chooses to maintain a database of chronic hepatitis B patients. All different hepatitis B laboratory results are mechanically swept off that queue by the system. Important program indicators monitored by way of the surveillance, reporting and case investigation system embody the following: Characteristics of instances of acute hepatitis B that happen in youngsters and adolescents younger than 20 years of age and missed alternatives for vaccination. Characteristics of instances of acute hepatitis B in individuals reporting a history of vaccination. Characteristics of instances of acute hepatitis B associated with healthcare transmission. Information to Collect for Acute Hepatitis B the following info is epidemiologically necessary to collect in a case investigation for acute hepatitis B. Any lady age 13-55 that has an unknown being pregnant status and a optimistic hepatitis B lab outcome should also to|must also} be referred to a perinatal hepatitis B program for additional investigation of being pregnant status. The remaining two doses of hepatitis B vaccine ought to be administered at one (1) and six (6) months from the date of the primary vaccine. If mother is optimistic and youngster has acute or chronic an infection, examine as a potential perinatal case. Avoiding situations involving sharps that might result in exposures of vulnerable people to blood or objects contaminated with blood of the case; c. Health Care Associated Infection is Suspected If two or extra iatrogenic (health care associated) instances happen in patients of the same dental or well being care provider, residential care facility, or nonhospital well being care facility. Case is a Recent Blood Donor If the case has donated blood or plasma inside the eight weeks prior to onset of signs, the agency that obtained the blood or plasma ought to be notified so that any unused product can be recalled. Lot numbers for tracking are normally obtainable by way of the blood bank at the hospital the place the models have been transfused. Case is Pregnant or Has Recently Delivered Preventing perinatal transmission is maybe crucial a part of} case follow-up, and for that reason the Texas Department of State Health Services has an official Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program for Texas. Local and Regional Reporting and Follow-up Responsibilities Investigate any reported instances of acute or perinatal hepatitis B. For info on perinatal hepatitis B prevention actions, please check with the Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program Manual at. For testing in regard to a potential perinatal case, please contact the Perinatal Hepatitis B program at (512) 776-6535. Recommend affected person follow-up with physician and/or suggest extra testing be completed if applicable. After an individual infected with influenza coughs or sneezes, influenza viruses contained within the respiratory droplets journey by way of the air; different individuals nearby can turn into infected if these droplets land of their noses or mouths. These droplets can even contaminate surfaces, can turn into infected once they contact an object or a surface on which these droplets have landed and then contact their noses or mouths. Incubation Period the incubation interval is 1 to 4 days with most infections occurring within 2 days of exposure to an infected particular person. Infected individuals can begin shedding virus as much as} 24 hours earlier than the onset of signs. Additionally, some individuals who turn into infected with influenza remain asymptomatic. Clinical Illness Symptoms of influenza embody fever, cough, sore throat, myalgia (muscle aches), headaches and fatigue. Among youngsters, otitis media, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea are also commonly reported. Influenza is normally a self-limiting an infection, however in individuals with chronic medical circumstances corresponding to heart or lung illness, it could possibly} result in pneumonia and different life-threatening complications. Severity An estimated 23,607 (range 3,349-48,614) deaths associated with influenza happen yearly within the United States. Case Investigation Checklist Confirm that laboratory results meet the case definition. Review medical data or communicate to an an infection preventionist or physician to verify case definition, underlying well being circumstances and course of sickness. Recommend that anyone with danger components experiencing signs or anyone with extreme sickness be evaluated by a healthcare provider. See the Texas Influenza Surveillance Handbook for extra influenza control measures. It is beneficial that adults with influenza not return to work for at least of|no much less than} 24 hours after fever has subsided without using of} fever suppressing medicines. If the dying is linked to an influenza outbreak, then the outbreak investigation may also be subject to further media or public attention. The local/regional well being department should: · Work with the power to guarantee workers and students/residents get hand hygiene and respiratory etiquette schooling. It is very necessary to submit specimens if influenza was suspected however not confirmed or only confirmed with a speedy influenza check. Contact the Texas Department of State Health Services, Infectious Disease Control Unit at (800) 252-8239 or (512) 512-7676 for directions on postmortem post-mortem specimen assortment and submission. Refrigerate (2є8 єC) or freeze (-70єC) specimen vials instantly after assortment. In the clean area at the bottom of the Virology section next to different, write "pediatric flu dying". Some animals (avian and swine populations) are thought of higher danger for transmitting a variant influenza strain to people. Transmission the transmission route of variant influenza viruses is likely to to|prone to} be similar to seasonal influenza which is primarily by droplet unfold. Transmission may also happen by direct or indirect contact with oral secretions or fecal materials from infected animals Incubation Period the incubation interval is likely to to|prone to} be similar to seasonal influenza with an incubation interval of 1 to 4 days. Communicability the communicability of variant influenza viruses is unknown and strain specific. It might vary from low communicability to excessive communicability relying on how properly tailored the strain is to people. Clinical Illness Symptoms are likely to to|prone to} be similar to seasonal influenza with excessive fever, chills, muscle aches, headache and cough. Many variant influenza infections have had elevated incidence of gastrointestinal signs corresponding to vomiting and diarrhea as properly. Severity the severity of sickness is unknown and may differ from gentle to extreme relying on the specific strain and traits of the inhabitants. Suspected novel / variant subtypes and strains will be detected with strategies obtainable for detection of presently circulating human influenza viruses at public well being laboratories. Suspect Case Investigation Checklist Determine why the healthcare provider suspects variant influenza. Review medical data or communicate to an an infection preventionist or physician to verify underlying well being circumstances and course of sickness. Interview case (or surrogate) to identify journey history, animal contact and different danger components. Control Measures · Provide schooling on influenza to contacts of the case as needed. Exclusion Children are required to be excluded from school/daycare for at least of|no much less than} 24 hours after fever has subsided without using of} fever suppressing medicines. It is beneficial that adults not return to work for at least of|no much less than} 24 hours after fever has subsided without using of} fever suppressing medicines. In the event of a pandemic or unusually extreme presentation the exclusion interval prolonged. Extensive efforts ought to be made to identify all animal contacts as much as} onset of sickness. Multiple instances of variant influenza recognized If multiple case of variant influenza is recognized enhanced surveillance will be expanded. It is anticipated that a whole variant influenza investigation will be performed on initial instances. As the case depend will increase, a general influenza investigation type ought to be completed for all or a subset of instances.
Best clopidogrel 75mg
However, in uncommon cases, the ameba can infect people by coming into the nostril throughout water-related actions. Most commonly, the ameba is present in soil, mud, contemporary water sources (such as lakes, rivers, and hot springs), in brackish water (such as a marsh), and sea water. Balamuthia mandrillaris is present in soil and believed to enter the body through pores and skin wounds and cuts, or when mud containing Balamuthia is breathed in or will get within the mouth. However, only a few cases of illness in people have been discovered worldwide since Balamuthia was found. Trophozoites infect people or animals by penetrating the nasal tissue and migrating to the mind through the olfactory nerves inflicting main amebic meningoencephalitis Infection can happen in younger immune-competent people. Exposure occurs when individuals go swimming or diving in warm freshwater locations, like lakes and rivers. In very uncommon cases, Naegleria infections can also happen when contaminated water from other sources (such as inadequately chlorinated swimming pool water or heated and contaminated faucet water) enters the nostril, for example when individuals submerge their heads or cleanse throughout spiritual practices, and when individuals irrigate their sinuses (nose) utilizing contaminated faucet water. The trophozoites are the infective types, although both cysts and trophozoites acquire entry into the body through numerous means. While unusual, disseminated an infection also can have an effect on} wholesome kids and adults. Entry can happen through the nasal passages to the lower respiratory tract, or ulcerated or damaged pores and skin. Incubation Period Naegleria fowleri: · · · · Incubation interval: Symptoms start 1-7 days (median 5 days) after exposure. In its early phases, Naegleria fowleri an infection could also be} much like bacterial meningitis. After the beginning of symptoms, the illness progresses quickly and demise occurs inside 10 days, often on the fifth or sixth day. Once infected, an individual may undergo with complications, stiff neck, nausea and vomiting, tiredness, confusion, lack of consideration to individuals and surroundings, lack of balance and bodily control, seizures, and hallucinations. Balamuthia amebae can infect the pores and skin, sinuses, mind and other organs of the body. The illness may seem gentle at first but can turn into more severe over weeks to a number of} months. Overall, the outlook for individuals with this illness is poor, although early analysis and remedy may improve the probabilities for survival. Other symptoms similar to lethargy, dizziness, lack of balance, psychological status abnormalities, visual disturbances, hallucinations, delirium, seizures, and coma have been reported as the illness progresses. In some cases, abnormalities in style or scent, nasal obstruction, and nasal discharge have been observed. After the onset of symptoms, the illness progresses quickly and often leads to demise inside three to 7 days. Although a variety of|quite a lot of|a big selection of} treatments have been shown to be energetic in opposition to amebae in vitro and have been used to treat infected individuals, most infections have still been deadly. This form of amebic meningitis has a slow, insidious onset and develops into a subacute or persistent illness lasting a number of} weeks to months. Case Investigation Checklist Confirm the laboratory results meet the case definition. Control Measures · Provide education on amebic meningitis as wanted with emphasis on rarity of illness. By comparison, through the ten years from 1996 to 2005, there were over 36,000 drowning deaths within the U. The low number of infections makes it difficult to know why some individuals have been infected the hundreds of thousands of other individuals utilizing the identical or related waters throughout the U. If you do plan to take part in water-related actions, right here are|listed under are} some measures that may cut back danger: Provide education on prevention of exposure o Avoid water-related actions in our bodies of warm freshwater during times of high water temperature and low water levels. However, their effectiveness in people is unclear since nearly all infections have been deadly even when individuals were handled. Specimen Shipping · · Ship samples according to delivery guidelines and necessities available at. Unfixed specimens for tradition should be sent at ambient temperature by in a single day priority mail. Care should be taken to pack glass slides securely, as they can be damaged in cargo if not packed in a crush-proof container. Digital laboratory and pathology image submission · Please send your diagnostic request to dpdx@cdc. When submitting a digital image, please embrace the following data alongside along with your message: 1. Incubation Period the incubation interval is often three to four days, but it could possibly} range from 1-10 days Communicability A person can pass the an infection to others lengthy as|for so lengthy as} the bacteria are current in discharges from the nostril and mouth. A person is no longer infectious inside 24 to 48 hours after beginning applicable antimicrobial remedy. Clinical Illness · Meningitis is the most common presentation of invasive meningococcal illness. Meningococcal an infection is much like other forms of meningitis, with sudden onset of fever, headache, and stiff neck, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, photophobia (sensitivity to light), or altered psychological status. Sepsis is characterised by abrupt onset of fever and a petechial or purpuric (red or purplish spots brought on by bleeding under the skin) rash, and is often associated with hypotension, shock, acute adrenal hemorrhage, and multiorgan failure. Furthermore, sequelae happen in 11-19% of people and should embrace hearing loss, neurologic incapacity, amputation or lack of limb use. Complete the Meningococcal Infection Investigation Form by interviewing the case (or surrogate) to determine close contacts, danger factors and other pertinent data. Refer close contacts to healthcare providers for applicable chemoprophylaxis If applicable, complete steps within the Managing Special Situations part. Control Measures Cases · Investigate reviews of suspected meningococcal illness promptly to determine at risk contacts. Contacts · Advise contacts of signs and symptoms of sickness, and refer them to their health care providers if they that they} expertise any symptoms suitable with invasive meningococcal illness. Guidance for identification of and prophylaxis of contacts could be discovered within the Red Book. Close contacts should be monitored for signs of sickness, especially fever, for a lot as} ten days. For more details about vaccine call the Immunization Division at 1-512-776-7284. Children with meningococcal meningitis should be excluded from school/daycare until written permission is offered by their healthcare provider. The local / regional health division should · Investigate links between the cases. The local / regional health division should: · Determine the inhabitants of the community and perform epidemic threshold · calculations as described within the Control of Communicable Diseases o Alert threshold is 10 cases/100000 inhabitants o Epidemic threshold is: a weekly doubling of cases throughout a 3 week interval or 15 cases/100000 inhabitants or 2 cases at a mass gathering or among refugees or displaced person. Local and Regional Reporting and Follow-up Responsibilities Local and regional health departments should · Immediately examine any reported cases of invasive meningococcal illness. Transmission Transmission occurs through respiratory droplets or through direct contact with nasopharyngeal secretions. Incubation Period Average of 16-18 days (range 12-25 days) Communicability Mumps virus has been present in respiratory secretions as early as three days earlier than the beginning of symptoms and a lot as} 9 days after onset. However, the affected person is most infectious throughout the first 5 days after symptom onset. Clinical Illness Prodromal symptoms are nonspecific; they embrace myalgia (muscle pain), anorexia, malaise, headache, and low-grade fever, and should final 34 days. Parotitis (inflammation and swelling of the parotid glands) is the most common manifestation of scientific mumps, affecting 3040% of infected individuals. Parotitis could be unilateral (one facet of cheek) or bilateral (both sides of cheek); other combinations of single or multiple of} salivary glands could also be} affected. Parotitis often occurs throughout the first 2 days of symptom onset and should current as an earache or tenderness on palpation of the angle of the jaw. Up to 20% of infections are asymptomatic; an extra 4050% may have solely nonspecific or primarily respiratory symptoms.

Effective clopidogrel 75 mg
If the presentation is atypical, or if the personal historical past suggests a chance of malignancy, incisional biopsy could also be} indicated. Perhaps the least invasive modality includes using of} chemocautery brokers, similar to dichloracetic acid. This colorless, mildly pungent liquid agent has each keratolytic and cauterant properties, and could also be} obtained from a compounding pharmacy or bought as a part of} an entire treatment kit (Derma-Cauter-All, Sigma Pharmaceuticals). Unfortunately, none of these therapies offer any scientific proof relating to their efficacy. One published case from 2005 illustrated a striking disappearance of eyelid xanthelasma in a affected person after starting a course of simvastatin. Likewise, sufferers must perceive every one|that each one} surgical treatment modalities have the potential for problems similar to persistent erythema, hypo- or hyperpigmentation, scarring and ectropion. Xanthelasmata, arcus corneae, and ischaemic vascular disease and dying normally inhabitants: prospective cohort research. Tolerability and effectiveness of liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy with very quick freeze times within the treatment of xanthelasma palpebrarum. Effectiveness of low-voltage radiofrequency within the treatment of xanthelasma palpebrarum: a pilot research of 15 circumstances. Ultrapulse carbon dioxide laser ablation of xanthelasma palpebrarum: a case series. If famous, these individuals ought to be evaluated totally for dyslipidemia and associated vascular, metabolic or cardiovascular disorders. Some of these embody: topical utility of crushed garlic, castor oil or lemon rind; a "cleansing food plan" consisting of only fresh papaya or pineapple and water for three consecutive days; niacin dietary supplements; and exercise and stress reduction strategies. The key to managing sufferers is recognizing its appearance, and referring for the correct medical workup. Since the management of a found systemic disease and its potential problems will rest inside the area of the internist or other specialist, the position of the primary eye care provider is to discover undiagnosed circumstances and monitor ocular well being for the ocular problems. This could also be} of significance as these sufferers could have increased risk for glaucoma or exhibit artificially low intraocular stress measurements. Clinical research of hereditary disorders of connective tissues in a Chilean inhabitants: joint hypermobility syndrome and vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Surgical restore of bilateral full thickness macular holes in a affected person with blue sclera secondary to osteogenesis imperfecta. Severe conjunctivochalasis in association with basic kind Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Bevacizumab treatment for subfoveal choroidal neovascularization from causes apart from age-related macular degeneration. Presenting indicators and medical diagnosis in individuals referred to rule out Marfan syndrome. Central corneal thickness is decrease in osteogenesis imperfecta and negatively correlates with the presence of blue sclera. A new different to riboflavin/ultraviolet-a: collagen cross-linking with rose bengal/green mild. Dendritic ulcerations with basic terminal end bulbs staining brightly with sodium fluorescein and rose bengal dyes have been reported as a part of} the syndrome. The mom in such circumstances ought to be examined for concurrent gynecological an infection. In circumstances involving serotype-2, concurrent systemic an infection or points where immunosuppression is suspected, consider concurrent use of oral antiviral remedy with dosage based on age and body weight. The medicine requires less frequent preliminary dosing (approximately each three hours whereas awake) and may be tapered as resolution is seen over seven to 10 days. The disease is generally self-limiting and may be managed with palliative therapies similar to artificial tear drops and ointments together with oral overthe-counter analgesics for any additional discomfort. If a papillomacular rash is current, topical prophylactic antibiotic ointments may be prescribed to stop secondary cellulitis. Epithelial keratitis concurrently current, with or with out subepithelial marginal infiltrates, could also be} cautiously 11. Delayed kind hypersensitivity within the pathogenesis of recurrent herpes stromal keratitis. The impact of the herpetic eye disease research on the management of herpes simplex virus ocular infections. Factors similar to severity, recurrence, other topical drugs used, atopic disease or a historical past of immunosuppression can significantly alter the presentation and risk of corneal involvement. Topical prophylactic antibiotic ointment may be allotted to stop secondary eyelid infections in circumstances where a rash is clear, and drops can be used in circumstances where keratopathy is important. Etiology of acute conjunctivitis due to of} coxsackievirus A24 variant, human adenovirus, herpes simplex virus, and Chlamydia in Beijing, China. Pediatric herpes simplex of the anterior phase: characteristics, treatment, and outcomes. Trends in herpes simplex virus kind 1 and kind 2 seroprevalence within the United States. Numerous etiologies, together with an infection, toxicity, allergy and autoimmune disease, could also be} implicated; nonetheless, indicators and signs are sometimes the identical. Patients typically current with variable edema and hyperemia of the affected tissues of the bulbar and/or tarsal conjunctiva, typically with associated pathological manifestations similar to follicles or papillae. Discharge is frequent, and may range from serous to mucopurulent, depending upon the etiology. Individuals of any age, race or gender could also be} affected by conjunctivitis, although certain pathogens or other causative elements could show a predilection towards a particular cohort. Associated signs could embody variable discomfort within the type of itching, burning, scratchiness or other irritation. Pain is less frequent and tends to be extra indicative of concurrent corneal involvement; that is extra typically the case in certain infectious disorders. Patients may also current due to of} extreme watering or mucus accumulation within the eyes, and even merely due to cosmetic concern. They could likewise result on} the higher tarsus, which is why routine lid eversion is necessary in all circumstances of conjunctivitis. For instance, if symblepharon develops and the conjunctival fornices turn into shortened, ocular floor sequelae, together with dryness, discomfort and variable visible disturbances, will comply with. Likewise, if a membrane or pseudomembrane disturbs the integrity of the cornea, mechanical ulceration could happen. True membranes, the opposite hand|however|then again}, penetrate and adhere to the necrotic epithelium and the substantia propria of the affected tissue. This tight adherence causes greater issue with removing, and leads to an increased chance and quantity of bleeding upon their extraction. It has been proposed that the distinction between accompany membranous conjunctivitis, pseudomembranes and true membranes instant medical attention is warranted. Short, firm brushing and rolling motions assist to loosen the pseudomembrane from the underlying conjunctiva, progressively gathering up fibrinous tissue as one proceeds from nasal to temporal, or vice-versa. It is recommended that the doctor first dissect the sting of the membrane or pseudomembrane away from the underlying conjunctiva at both the nasal or temporal side of the lid. Then, after acquiring a firm grasp of the inflammatory tissue, peeled away using regular and continuous drive. Bleeding may be additional addressed using sterile gauze utilized firmly to the affected conjunctival surfaces till hemostasis is achieved. Nonetheless, intuitive therapeutic intervention typically hastens restoration and dramatically improves signs. Topical corticosteroids could also be} added judiciously to this routine as improvement in medical indicators is famous. Once membranous conjunctivitis has turn into manifest, irritation typically leads to corneal epithelial breakdown; treatment is aimed toward suppressing this course of. In addition to mechanical removing of any membranes, most sources now advocate topical treatment with corticosteroids and cyclosporine A through the acute stages. This ought to be the first differential for the clinician encountering a membranous conjunctivitis. The etiology is believed to contain a loss of goblet cells, in addition to potential alteration of lidglobe apposition and ocular floor morphology due to of} scar formation. Systemic immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory therapies are most appropriately supplied in such a setting. Cellular and tissue architecture of conjunctival membranes in epidemic keratoconjunctivitis. Ocular problems in a child with acute graft-versus-host disease following cord blood stem cell transplantation: therapeutic challenges.
Effective clopidogrel 75mg
Schuster Background Medical and dental professionals have worked collectively closely for a few of} years} to present optimal options to advanced craniomaxillofacial issues. This chapter is for nondental professionals who work with the craniofacial advanced, during which dentition and its functional relationships are crucial. Our goal is to present primary and helpful info on dental anatomy and occlusion. Each tooth has a crown, which is the portion seen on a totally erupted tooth, and one or more of} roots positioned inside bony sockets within the maxillary and mandibular alveolar bone. The outer layer of the crown is composed of enamel, and the roots are coated by cementum. The second tooth layer is the dentin, and the internal central half is the pulp, which provides nerves and blood provide to the tooth. The anterior enamel are the central incisors, lateral incisors, and canines (also called cuspids). The facial surfaces are these would possibly be} towards the lips (labial) and cheeks (buccal). Incisors and canines have labial surfaces; premolars and molars have buccal surfaces. Lingual surfaces are these facing the tongue within the mandibular arch, and palatal surfaces are these facing the palate within the maxillary arch. Central incisor Lateral incisor Canine (cuspid) First premolar (first bicuspid) Second premolar (second bicuspid) First molar Second molar Third molar D mi d i stal line: a w 1 c Fa 2 Pa 3 l ial 4 Buc at al M e s i a l: to w a rd 5 6 7 8 Fig. The surfaces used for mastication are people who contact each other when maxillary and mandibular enamel occlude throughout closure. Ideally, the midsagittal plane coincides with the maxillary and mandibular dental midlines (that is, between the central incisors). The surfaces of the enamel nearer to the median line are called mesial, and those more distant are called distal. The solely exceptions to this are the central incisors, which contact each other at the median line through their mesial contacts. The dental roots are enclosed in a supporting structure called the periodontium, which consists of alveolar bone, periodontal ligament, cementum, a gingival attachment to the tooth, and gingiva (gum tissue). They are named with uppercase letters A through T, from the maxillary right second main molar to the mandibular right second main molar. Another generally used system, called the Palmer Notation, divides the dental arches into four quadrants and uses solely letters A through E. Each quadrant consists of one central incisor, one lateral incisor, one cuspid, and two main molars (the first and second). In this technique, a letter enclosed by two perpendicular lines identifies a particular quadrant and tooth. For example, a maxillary right main central incisor is A, and a mandibular left main canine is C. D C B A E F G H I J B C D E Right E D C B A A B Mandibular C D E Maxillary A A B C D E Left Maxillary Right T S R Q P O N Mandibular M L K Left Fig. Chapter 4 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion fifty one Permanent dentition consists of 32 enamel, 16 within the maxilla and 16 within the mandible. In the Universal Notation system, enamel are numbered 1 through 32, from the maxillary right permanent third molar to the mandibular right permanent third molar. In the Palmer Notation for permanent dentition, the enamel are numbered 1 through 8 in every quadrant. Each quadrant consists of one central incisor, one lateral incisor, one cuspid, two premolars (first and second), and three molars (first, second, and third). A maxillary right central incisor is described as 1, and a mandibular left second premolar is 5. As the enamel come into close contact, their inclined planes, valleys, and edges decide the ultimate occlusion, or chew, under the influence of a sophisticated neuromuscular system. One of probably the most influential figures within the field of orthodontics and dental occlusion was Edward H. He described normal occlusion as a harmonious relationship between maxillary and mandibular enamel primarily based on the anterior-posterior relationship of maxillary and mandibular first permanent molars. In a category I (or normal) molar relationship, the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first permanent molar occludes with the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar. Chapter 4 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion fifty three the place of the cuspids or canines throughout occlusion has also been used to describe a correct relationship between maxillary and mandibular dentition. When the first permanent molars are in a category I relationship, the mandibular canine occludes mesial to the maxillary canine within the embrasure between the maxillary canine and lateral incisor. These three forms of occlusions are normally associated with three totally different facial profiles. This leads to an excessive overjet or horizontal overlap of the anterior enamel. A class I occlusion is associated with a slightly convex or straight profile. The most dramatic modifications occur during the mixed dentition stage when main and permanent enamel are both present within the oral cavity. Once all main enamel have been changed by their permanent counterparts and skeletal maturity has been reached, a more definitive occlusion is established. In a super occlusion, both skeletal and dental arches exhibit correct correlation, jaws and enamel are positioned in a traditional functional relationship, and enamel meet in a category I relationship. As our information of dental occlusion has matured, two necessary ideas have developed: centric occlusion and centric relation. It is the place decided by dentition, when the maxillary and mandibular enamel are in maximum intercuspation. Centric relation is the relation of the mandible to the maxilla when the condyles are in a physiologically stable place, independent of tooth contact. This relation has been described as probably the most superoanterior place of the condyles within the articular fossae with the discs appropriately interposed. The vertical, sagittal, and transverse relationships between the maxillary and mandibular enamel at maximum intercuspation (centric occlusion) are most valuable when describing malocclusion. Overbite is the quantity of vertical overlap between the maxillary and mandibular central incisors, expressed as a share or in millimeters. An anterior opening with no overlap is an open chew, which is measured in millimeters. An anterior skeletal open chew could be caused by hyperdivergence of the maxilla and mandible (apertognathia), which is normally harder to deal with orthodontically and would possibly require orthognathic surgery. Negative overjet, recognized as|also called|also referred to as} anterior crossbite, is when the maxillary central incisor occludes behind the lower central incisor. Negative overjet, or anterior In normal occlusion, all maxillary enamel overlap the mandibular enamel. A dental crossbite is caused by improperly inclined and/or malpositioned enamel, and is normally resolved through orthodontic dental movement. Skeletal crossbites are caused by a difference in size between the maxilla and the mandible. The discrepancy could possibly be} sagittal or transverse, creating an anterior or posterior crossbite could be|that could be|which could be} unilateral or bilateral. An anterior crossbite is when the labial surface of a maxillary anterior tooth occludes posterior to the lingual surface of a mandibular anterior tooth. A posterior Chapter 4 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion 57 crossbite is when the buccal surface of a maxillary tooth occludes with the lingual surface of a mandibular tooth. Correcting these crossbites normally requires a palatal expander or orthognathic surgery. When the area available is lower than the area wanted, it leads to dental crowding, which is evidenced by tooth rotation and malalignment. A widespread parafunctional activity that features grinding and clenching of the enamel identified as} bruxism. Pearls There are 20 main enamel (A through T) and 32 permanent enamel (1 through 32). The grownup mouth is divided into four quadrants with eight permanent enamel in every: a central incisor, lateral incisor, canine, first premolar, second premolar, first molar, second molar, and third molar. Overjet is the horizontal overlap between the maxillary and mandibular central incisors, and overbite is the vertical overlap. Facial profiles are categorized as orthognathic (normal), retrognathic or convex, and prognathic or concave. Findings on physical examination ought to information the clinician to search for specific fracture patterns throughout a methodic evaluation of the available imaging.
References:
- https://www.gnyha.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/World-Happiness-Report.pdf
- https://australian.physio/sites/default/files/tools/NAT023_APA_VBI_FACTSHEET.pdf
- https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/threats-report/2019-ar-threats-report-508.pdf
- https://lupinepublishers.com/anesthesia-pain-medicine-journal/pdf/GJAPM.MS.ID.000179.pdf
- https://www.bsuh.nhs.uk/library/wp-content/uploads/sites/8/2020/06/BTS-pneumothorax-guideline.pdf
.png)