Singulair 4mg
A method for defect closure within the flooring of the mouth, the tongue, the buccal mucosa, and the lateral pharyngeal wall. Excellent useful end result in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the base of the tongue handled with exterior irradiation and interstitial iodine a hundred twenty five increase. Sector-associated grey scale analysis of video ultrasound recorded tongue movements in swallowing. Cinematographic useful prognosis of swallowing after plastic reconstruction of large tumor defects of the mouth cavity and pharynx. Perfusion manometry within the analysis of postoperative swallowing function following various reconstructive procedures of the higher aero-digestive tract. Objective analysis of the quality of voice following radiation therapy for T1 glottic most cancers. Stroboscopic remark of the larynx after radiation in patients with T1 glottic carcinoma. Normal laryngeal valving patterns throughout three breath hold maneuvers: a pilot investigation. Speech and survival: tradeoffs between high quality and amount of life in laryngeal most cancers. The anatomy and complication of "T" versus vertical closure of the hypopharynx after laryngectomy. Current strategies of rehabilitation of the laryngectomized affected person: seminars in speech and language. Tracheo-oesophageal "puncture speech": an evaluation method for failed oesophageal audio system. British expertise of surgical voice restoration strategies as a secondary procedure following total laryngectomy. Esophageal insufflation and videofluoroscopy for analysis of esophageal speech in laryngectomy patients: medical implications. An improved methodology of flexible endoscopic creation of tracheoesophageal fistula for voice restoration. Problems with tracheoesophageal fistula voice restoration in totally laryngectomized patients. The Indian expertise with instant tracheoesophageal puncture for voice restoration. Surgical voice rehabilitation: affect of postoperative radiotherapy on tracheoesophageal fistulas. Development and medical analysis of a second-generation voice prosthesis (Provox 2), designed for anterograde and retrograde insertion. A self-retaining valveless voice prosthesis for vocal rehabilitation after total laryngectomy. Secondary tracheoesophageal puncture: elements predictive of voice high quality and prosthesis use. Predictive worth of goal esophageal insufflation testing for acquisition of tracheoesophageal speech. Botulinum toxin injection to enhance tracheoesophageal speech after total laryngectomy. Pharyngoesophageal reconstruction using the radial forearm fasciocutaneous free flap: preliminary results. Tubed, folded radial forearm free flap for pharyngeal reconstruction and voice rehabilitation. Primary tracheojejunal shunt operation for voice restoration following pharyngolaryngoesophagectomy. Simultaneous reconstruction of pharyngoesophagus and phonation following laryngopharyngoesophagectomy. Surgical voice restoration with the Blom-Singer prosthesis following laryngopharyngoesophagectomy and pharyngogastric anastomosis. Voice restoration after total laryngopharyngectomy and cervical esophagectomy using the duckbill prosthesis. Speech reconstruction following total laryngo-pharyngectomy with free jejunal repair. A comparative examine of speech after total laryngectomy and total laryngopharyngectomy. Voice restoration following laryngectomy: the role of primary versus secondary tracheoesophageal puncture. A comparative acoustic examine of regular, esophageal, and tracheoesophageal speech manufacturing. Understanding voice issues: physiological perspective for prognosis and treatment. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of tracheoesophageal voice following pectoralis major flap reconstruction of the neopharynx. There is advanced interplay between the varied molecular changes that ultimately end result within the abrogation of key cellular regulatory and progress control pathways. Protooncogenes typically encode proteins which might be constructive effectors of the transformed phenotype and can simplistically be considered constructive progress regulators. Their "activation" results in their useful deregulation, resulting in a acquire in function or "dominant" impact. Interacting with but other biologic changes, these elementary molecular occasions appear to underlie the traits of dysregulated progress, clonal enlargement, and immortality, that are typical of overt lung cancers. In addition, these, and but other to be discovered molecular changes, may have an effect on the processes of invasion, metastasis, and resistance against most cancers therapy. In translating these laboratory discoveries into the clinic, it is important to establish these various changes, determine the frequency of occurrence, and check whether they have clinically important associations. In addition, these abnormalities will most likely also give us important understanding about lung growth and differentiation. Molecular cytogenetic analysis with comparative genomic hybridization has recognized hitherto unrecognized abnormalities, including deletions at 10q26, 16p11. Other sites of hypermethylation, including 3p, 4q34, 10q26, and 17p13, have been implicated in lung most cancers pathogenesis, although the exact gene targets are uncertain. In addition to use as an early detection goal, it might be attainable to reverse methylation pharmacologically. Clinical trials with such brokers have been tried in other illnesses, and brokers with less toxicity must be developed and tested in lung most cancers. Another acquired tumor abnormality is lack of imprinting (lack of methylation) to enable the expression of genes in lung most cancers. Methylation plays a task in mediating genomic imprinting, which is a gamete-particular modification causing differential expression of the 2 alleles of a gene in somatic cells. Activation of this putative autocrine loop may provide a progress benefit, or it might mediate chemoattraction. The frequent progress stimulatory and inhibitory cascades involved in lung most cancers cells. A single circle denotes progress stimulatory molecules, and a number of circles denote activation attributable to some tumor-acquired abnormality. A box denotes progress inhibitory molecules, whereas their inactivation is indicated by a cross inside the box, once more acquired (for instance) by mutation within the tumor. Double arrows indicate transcriptional activation of goal genes that regulate cell progress. Apart from protooncogene merchandise, other progress stimulatory loops are found in lung most cancers. The myc family gene amplification has been differentially observed within the major lung most cancers subtypes. It functions as a transcription issue to activate the expression of genes that control cell-cycle checkpoints. More proof linking smoking harm with p53 mutations is the finding that a significant cigarette smoke carcinogen, benzo(a)pyrene, selectively types adducts at the p53 mutational scorching spots. Missense mutations (the commonest kind of mutation) often extend the half-life of the p53 protein to a number of hours, resulting in elevated levels detectable by immunohistochemistry and thus using immunohistochemistry as a surrogate assay for p53 mutation. Also, systemic methods (such as with lipid vesicles) of delivering p53 gene therapy to disseminated tumors are being developed. Two proteins homologous to p53-p51 and p73-have been discovered, resulting in the hypothesis that they might be mutated in p53 wild-kind tumors. Finally, the Li-Fraumeni syndrome of inherited susceptibility to most cancers determined by an inherited germline mutation of p53 may also result in elevated susceptibility to lung most cancers in adults in these pedigrees.
Best singulair 5 mg
However, most patients are treated with irradiation alone using a mix of exterior-beam remedy and brachytherapy. The altered geometry and brief uterine canal in these patients complicate therapy planning. However, generally the endocervical canal is 2 cm or longer and, after a course of exterior-beam irradiation, patients could be adequately treated with intracavitary remedy. The endocervical canal is usually loaded with 20 to 30 mgRaEq of cesium, depending on the length of the endocervical canal, and vaginal ovoids are loaded based on their diameter and place. Remote afterloading techniques provide somewhat higher flexibility in source loading. Several authors have advocated interstitial remedy, using techniques described for apical vaginal carcinomas, for patients with bulkier lesions. Most investigators have reported survival charges just like those for patients with carcinomas of the intact cervix. Hacker and colleagues 480 reported an incidence of cervical carcinoma in situ of 0. Diagnosis is commonly delayed as a result of bleeding is erroneously attributed to being pregnant-related issues. All pregnant patients should have a careful pelvic examination and Pap smear at their first antenatal go to. Because conization topics the mother and fetus to issues, it should be carried out solely within the second trimester and solely in patients with inadequate colposcopy and strong cytologic proof of invasive cancer. The infant may be delivered by a cesarean section, which is followed immediately by modified radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection. Fetal pulmonary maturity could be decided by amniocentesis, and prompt therapy could be instituted when pulmonary maturity is documented. It is probably sensible to avoid delays in remedy of more than four weeks each time potential though this guideline is controversial. There should be a thorough discussion of the risks and options with both mother and father earlier than any therapy is undertaken. If the being pregnant is within the first trimester, exterior-beam irradiation could be began with the expectation that spontaneous abortion will happen earlier than the delivery of 40 Gy. In the second trimester, a delay of remedy may be entertained to improve the probabilities of fetal survival. If the affected person needs to delay remedy, it is important to guarantee fetal pulmonary maturity earlier than delivery is undertaken. Compared with different cervical cancer patients, those with cervical cancer throughout being pregnant have barely higher overall survival as a result of an elevated proportion have stage I disease. The diagnosis of cancer within the postpartum interval tends to be related to a extra advanced clinical stage and a corresponding decrease in survival. However, studies differ in their conclusions about whether being pregnant has an independent influence on the prognosis of patients with cervical cancer. At least 13 circumstances demonstrating this uncommon sample of failure have been reported. Pride and colleagues 505 instructed that pelvic irradiation might be a predisposing think about some circumstances. However, viral and different risk components independent of the mode of therapy undoubtedly place some of these patients in danger for a number of major tumors. In a review of 301 patients with vaginal cancer, Chyle and associates 495 found that 56 had a previous history of carcinoma in situ of the cervix, 22 had a history of invasive cervical cancer, and two had prior in situ carcinomas of the vagina. This led to the establishment of a registry to collect information about circumstances of clear cell carcinoma within the United States. The oldest affected person reported thus far was forty two years old at diagnosis, however the risk to women older than 40 years continues to be unknown as a result of women within the first exposed cohort are simply reaching their fifth decade. Tumors could invade directly to contain adjoining structures such as the urethra, bladder, and rectum. Vaginal cancers can also unfold laterally to the paravaginal space and pelvic wall. The vagina is equipped with a fine anastomosing network of lymphatics within the mucosa and submucosa. Despite the continuity of lymphatic vessels inside the vagina, Plentl and Friedman 515 found a daily sample of regional drainage from particular regions of the vagina. The lymphatics of the vaginal vault communicate with those of the lower cervix, draining laterally to the obturator and hypogastric nodes. The lymphatics of the posterior wall anastomose with those of the anterior rectal wall, draining to the superior and inferior gluteal nodes. The lymphatics of the lower third of the vagina communicate with those of the vulva and drain either to the pelvic nodes or with the vulvar lymphatics to the inguinofemoral lymph nodes. Plentl and Friedman summarized their description of the lymphatic drainage of the vagina with the comment that, except for the lateral exterior iliac group, all lymph nodes of the pelvis could at one time or different function major sites of regional drainage for vaginal lymph. Approximately one-third of these tumors are keratinizing, and multiple-half are nonkeratinizing, moderately differentiated lesions. Verrucous carcinoma is an uncommon variant of squamous cell carcinoma that presents as a warty, fungating mass. This tumor rarely metastasizes but can extensively infiltrate into surrounding tissues, together with the rectum and coccyx. The differential diagnosis of adenocarcinoma occurring within the vagina is commonly difficult, because it should be distinguished from metastatic tumors originating in different sites. It has been hypothesized that these tumors could come up in foci of adenosis, from mesonephric rests, or from foci of endometriosis within the vagina. The prognosis for youngsters with this tumor has improved with the use 494,495 of multimodality remedy together with surgical procedure, chemotherapy, and radiation. Patients can also current with complaints of vaginal discharge, a palpable mass, dyspareunia, or pain within the perineum or pelvis. All patients should have chest roentgenography, full blood rely, and biochemical profile. Cystoscopy and ureteroscopy are strongly recommended for patients with massive tumors or tumors involving the anterior vaginal wall. Carcinoma of the Vagina: Survival Rates According to Clinical Stage Most investigators have been unable to find a correlation between tumor website and consequence. Tumors that contain the complete vagina are likely to have a poorer prognosis, most likely reflecting the larger size of these lesions. Several investigators have reported a correlation between growing grade of squamous carcinomas and recurrence, 495,538,539 whereas others have found no correlation. These lesions often regress spontaneously, are incessantly multifocal, and recur quickly after attempts at ablative remedy. Local excision is a superb method of therapy for small upper vaginal lesions. Treatment is usually delivered using 137Cs loaded in a plastic vaginal cylinder three to four cm in diameter. The single vaginal recurrence was distal to the area treated with brachytherapy, and the authors emphasize the significance of treating the complete vagina to avoid marginal recurrences. However, Ogino and colleagues 545 reported adhesive vaginitis and rectal bleeding in two patients treated to the complete vagina with a much less conservative fractionation schedule. Stage I Radiotherapy is commonly the therapy of selection for stage I disease as a result of if surgical procedure is used, whole vaginectomy and even exenteration may be wanted to get hold of satisfactory resection margins. Some surgeons advocate broader indications for surgical therapy of stage I disease. One affected person in whom disease recurred had profitable salvage therapy with irradiation, and two patients who acquired postoperative irradiation have been cured of their disease. For patients with a previous history of pelvic irradiation, radical surgical procedure (usually pelvic exenteration) is indicated and is commonly curative. They recommended a dose of 60 to 70 Gy calculated 5 mm beyond the airplane of the implant or vaginal mucosa (vaginal floor dose of 80 to 120 Gy). Thicker stage I tumors should be treated with a mix of exterior-beam irradiation and brachytherapy with an goal to deliver 40 to 50 Gy to the pelvic nodes and 70 to 75 Gy to the tumor.
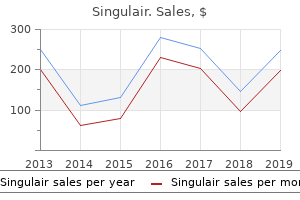
Order singulair 10 mg
A speculation has been proposed that such families inherit a faulty or lost allele encoding a tumor suppressor gene. This speculation was primarily based largely on work by Knudson, who instructed that the inactivation of two alleles of a gene was required within the disease known as retinoblastoma, one hundred sixty and Harris, who demonstrated that sure chromosomes could suppress malignancy in vitro in cell hybrid studies. During the malignant development of breast most cancers to its absolutely metastatic state, mutation, inactivation, loss, or down-regulated expression of tumor suppressing genes commonly occurs. Mutation can confer a loss of tumor suppressor exercise and achieve of tumor promotion perform. It is of explicit significance for the development of many cancers, together with breast most cancers, that mutation of p53 is associated with enhanced genetic instability. Hypophosphorylation of Rb allows its perform as an additional cell-cycle inhibitor. A protein whose transcription is immediately inhibited on this pathway is Bcl-2 174 (Table 37. Bcl-2 is an apoptosis-stopping protein, commonly expressed in breast most cancers in p53-mutated cells. Several other stimulatory and inhibitory members of the family exist, together with Bclx S, a promoter of apoptotic dying. This whole system capabilities to regulate dying by regulating a sequence of regulatory cysteine proteases inside the cell. Current research is concentrated on how these components regulate the apoptotic pathway(s). For example, it has been instructed that estrogen promotes chemotherapy resistance of breast most cancers by induction of Bcl-2,a hundred and eighty that p53 mutation ends in resistance to chemotherapy, 181 and that experimental gene therapy with bclx can differentially kill tumor cells and sensitize them to chemotherapy however spare bone marrow cells. When mutated in one of a number of crucial areas, the perform of the gene product is inactivated. Rb seems to perform to limit mobile entry into the S phase of the cell cycle (Table 37. As necessary regulators of the epithelial cell cycle in breast most cancers, tyrosine kinase receptor-acting growth components and sex steroids induce each c-Myc and cyclin D1. These studies have proven that the genes encoding cyclin D1 and cyclin E are commonly amplified and deregulated, respectively, in breast most cancers. Studies in breast most cancers have served to underscore the role of germline deletion or mutation of suppressor genes within the familial types of the disease, and somatic gene amplifications, mutations, deletions, and rearrangements during malignant development of the disease. Malignant development of breast most cancers involves a progressive deterioration of the normal mechanisms of cell-cycle development. The precise mechanisms for these early hyperactive proliferative controls to induce benign breast disease or premalignant atypical ductal or lobular carcinoma are by no means clear this present day. Some studies have proven that genetic harm is minimal in these early lesions, although this area of examine is just in its earliest levels. Summary of the genetic and phenotypic alteration of mammary epithelial cells associated with the onset and development of breast most cancers. High levels of expression of this enzyme have been proven to result in cell immortalization, a widely hypothesized early step in human tumorigenesis. Thus, telomerase disregulation may serve a delicate, early perform in breast tumorigenesis-replicative immortality. Once these kind of genetic alterations start to happen, a cascade of further genetic modifications occurs, resulting from total genomic and chromosomal instability. In distinction to colon most cancers, centrosomal defects appear to predominate in early breast most cancers, probably causing the chromosomal sort of instability. Chemotherapy resistance in breast most cancers is also not absolutely understood, however probably involves altered cell dying responses and altered metabolism of the medicine. For example, sure frequent patterns of cytogenetic alterations exist in breast tumors, probably the signature of distinct pathways of development. One example already discussed is the unfavorable interaction between cyclin D1 and the estrogen receptor. Mutated p53 may work together unfavorably with c-crbB 2 by blocking apoptotic pathways. A major method for the longer term understanding of this phenomenon will contain elevated use of the transgenic and gene knockout mouse fashions, with the eventual hope of creating the biochemical and mobile bases of various patterns of malignant progressions. At present, nonetheless, few studies in vivo have focused on mixtures of genetic alterations thought to be necessary in human disease or on the usage of transgenic fashions for studies of remedy-induced resistance and disease development to metastasis. Two separate however apparently interactive mobile processes seem to happen to allow metastasis of the disease: tumor angiogenesis and loss of correct tissue compartmentalization (invasion). However, a number of molecular determinants have been proposed to relate to every process. Loss of cell-cell attachment, altered cell substratum attachment, and altered cytoskeletal group play a task in regulating mobile invasion. In addition, cell locomotion, proteolysis, and the flexibility to survive and proliferate at distant sites also must contribute. Women at high risk will undoubtedly be the population of emphasis for future prevention trials. Although the benefits of prophylactic mastectomy and oophorectomy at the moment are established, tamoxifen is also identified to be an efficient prevention strategy. A major, current trial is evaluating tamoxifen to raloxifene (an antiestrogen thought to produce fewer endometrial cancers and to provide other benefits). It is feasible that detection of telomerase expression or the flexibility to detect delicate genetic alterations will provide useful new approaches for marking the onset of most cancers. More just lately, detection of the c-erbB 2 oncoprotein has also proven its worth for characterization of poor-prognosis tumors, as well as for these which might be likely to have a poor response to adjuvant hormonal therapy and chemotherapy. Certain antibodies to the extracellular area of the c-erbB 2 protein seem to sensitize cells to killing by cis-platinum, carboplatinum, and doxorubicin in vivo. This examine noted production of growth-inhibitory antibodies by peripheral lymphocytes from these patients. For example, many established human breast most cancers cell lines overexpressing c-erbB 2 are incessantly of poor tumorigenicity within the nude mouse. This truth could theoretically be as a result of an absence of coexpression of a heterodimeric receptor associate or a ligand, or to coinduction of a suppressive phosphatase. Because the c-erbB 2 protein can heterodimerize with other receptor members of the family, co-overexpression of all members of the family and cross-dimerization must eventually be taken into consideration in prognostic and therapeutic studies. The c-Myc protein has a very short half-life, and only now are high-quality monoclonal antibodies capable of staining paraffin sections becoming available. These studies also suggest that tumors containing both of those two necessary amplicons could also be of such different biologic significance that the amplicons are mutually incompatible. First, loss of Rb detected by immunohistochemistry seems to point out poor prognosis, 267 as does expression of bcl-2 and down-regulation of Bax. To complement the traditional lymph node biopsy measurements, promising new medicine are in scientific trial for blockade of angiogenesis. New medicine, similar to marimastat, are at present in scientific trials learning blockade of proteases. In abstract, although a very giant variety of genetic and phenotypic alterations have been instructed in breast most cancers, only a handful have been absolutely recognized and dropped at scientific examine. It is sort of encouraging that examine of each of those genes and phenotypic modifications has supplied its personal unique perspective to the biology of the disease. It is important that new technologies be dropped at improve tumor analysis and prediction of response to current therapies. These approaches must also end in discovery of latest targets for extra biologic-primarily based therapies and prevention methods for breast most cancers. Prospects for scientific translation of primary molecular biologic results appear to be shiny. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast most cancers, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Germ line transmission of a mutated p53 gene in a most cancers-prone family with Li Fraumeni syndrome. Decreased expression of brca1 accelerates growth and is usually present during sporadic breast most cancers development. Comparative genomic hybridization of formalin mounted, paraffin embedded breast tumors reveals different patterns of chromosomal positive aspects and losses in fibroadenomas and diploid and aneuploid carcinomas. Breast most cancers metastasisassociated genes: role in tumour development to the metastatic state.
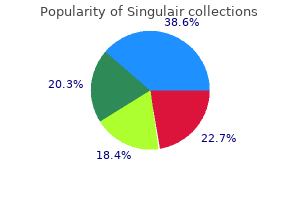
| Comparative prices of Singulair | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | Tractor Supply Co. | 120 |
| 2 | TJX | 719 |
| 3 | Trader Joe's | 910 |
| 4 | Ahold USA / Royal Ahold | 728 |
| 5 | Costco | 476 |
| 6 | CVS Caremark | 634 |
| 7 | A&P | 703 |
| 8 | Nordstrom | 604 |
| 9 | Family Dollar | 413 |
Singulair 10 mg
This case highlights the occasional misdiagnosis of basal cell carcinoma for herpes labialis. The chronic, recurring nature of each, in sure circumstances, may be liable for the confusion. E: Recurrent basal cell carcinoma at upper edge of graft 10 years after original surgical procedure. Surgery and radiation therapy are typically the one treatments presently out there. Photodynamic therapy, incorporating the usage of topical aminolevulinic acid, which avoids systemic opposed results, holds promise for treatment of enormous numbers of lesions. Multiple basal cell carcinomas in a affected person who received radiation therapy for acne 50 years earlier. It is extremely important, however, because patients with this condition characterize a administration challenge. It can be important because the basal cell cancer gene was first identified on this group of patients. A complete strategy using a combination of electrodesiccation and curettage, cryosurgery, Mohs surgical procedure in critical areas, and, sooner or later, photodynamic therapy permits control of the lesions. Intralesional interferon was additionally used on this affected person with some success but has not proven routinely successful. Suppression of new cancers may be achieved with oral isotretinoin or related compounds, but unwanted effects limit its use, and the cancer incidence returns to pre-treatment levels when treatment is discontinued. This affected person has nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome and introduced with multiple in depth basal cell cancers of the scalp, face, and trunk. She received radiation therapy as a baby for medulloblastoma, and this will likely have increased the incidence of basal cell cancers of the scalp. After a persistent effort at removing individual lesions, it was determined that the continued development rate necessitated full removal of the scalp tissue. Multiple basal cell carcinomas of the trunk are famous within the affected person depicted in. On the back, the chance of recurrence have to be considered, because the thickness of the dermis invites deep penetration of recurrent basal cell cancer. A small basal cell carcinoma of the tip of the nostril in a 14-yr-old boy with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. When these lesions are small, simple electrodesiccation and curettage or excision with Mohs micrographic surgical procedure adopted by second intention therapeutic often provides glorious outcomes. Nonetheless, the tendency on this syndrome is to develop quite a few skin cancers that eventually could make surgical procedure impractical. This benign congenital lesion has a well-documented tendency to transform into basal cell cancer. It is presently really helpful that the lesion be considered for excision at or round puberty. Because the location of this lesion makes it troublesome to monitor for the development of basal cell cancer, excision is indicated. Its medical distribution is similar as that of basal cell cancer, but this cancer does have the potential for metastasis. The incidence of squamous cell cancer in these patients is increased in contrast with the overall inhabitants. Approximately 2000 people per yr die from metastatic cutaneous squamous cell cancer. Irregular pigmentation, skin laxity because of photo voltaic elastosis, and actinic keratoses are hallmarks of extreme sun exposure. Studies of such sun-broken skin have demonstrated ultraviolet radiation-induced mutations within the tumor suppressor gene, p53. A: Squamous cell carcinoma within the popliteal fossa of a center-aged lady with in depth photo voltaic injury of the lower extremity. This lesion have to be distinguished from a hypertrophic actinic keratosis by biopsy, and excision is indicated if squamous cell carcinoma is identified. B: Infiltrative squamous cell carcinoma on the base of the fourth toe in the same affected person. Excision by the Mohs micrographic technique is indicated to minimize injury to adjoining anatomic structures and optimize the remedy rate. Multiple actinic keratoses, hypertrophic actinic keratoses, and early squamous cell carcinoma on the lower extremity of a affected person similar to the one depicted in. Squamous cell carcinoma of the lower extremity in girls is a major challenge due to the frequent in depth nature of the lesions. Photodynamic therapy is presently being explored as an option for treatment of widespread illness. Surgical excision remains the standard treatment, but administration of precancerous lesions by cryosurgery and topical drugs similar to 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod (experimental) could minimize the variety of lesions that evolve into squamous cell cancer. The lesions famous on the dorsal hand include hypertrophic actinic keratoses, squamous cell carcinoma, and actinic keratoses. Squamous cell carcinoma on this space, as in other skin websites such because the temple and lip, can metastasize. Aggressive administration of these lesions with monthly visits could help minimize the development of infiltrative squamous cell cancer. Because of therapeutic problems related to the lower extremities, in depth excision is usually problematic. The tissue-preserving advantages of Mohs micrographic surgical procedure in addition to conservative tangential excision with cautery of the wound base contribute to successful administration of the cancers in these patients. This lesion may be handled by cryosurgery, excision, or electrodesiccation and curettage. Because it persisted, a shave biopsy was performed, which confirmed the presence of squamous cell carcinoma. This horn consists of keratin produced by well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma and is finest handled by Mohs micrographic surgical procedure. Note earlier scar superior to the site where a skin cancer was beforehand handled. Note extension of squamous cell carcinoma past the quick space of the protruding horn. In this situation, the tissue-sparing method will doubtless allow preservation of underlying cartilage and optimum therapeutic. Excision is indicated due to the proximity to the eye and the chance of progression to invasion. Concretion of keratin and debris on the scalp of a person with skin type I (which all the time burns and never tans in response to exposure to sunlight). Removal of the debris, which was achieved by pre-moistening with water, revealed the underlying squamous cell carcinoma. Mohs micrographic excision is an option, but the surgical defect can be in depth. A trial of imiquimod, an immunomodulator proven to have some impact on superficial skin cancer, was tried. Note thickened epidermis and large atypical squamous epithelial cells with a wind-blown appearance. The differential prognosis contains chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis, which is often painful, and squamous cell cancer, which may bleed but is often not tender. If chondrodermatitis is suspected due to pain on stress, a trial of intralesional corticosteroid is an inexpensive first strategy. After the cancerous space was prepared with local anesthesia, it was scored in accordance with the Mohs micrographic technique in preparation for removal and mapping of all margins. Because of therapeutic points related to the lower extremity, the tissue preserving method of the Mohs technique is the treatment of alternative for this massive lesion. During full extirpation by Mohs surgical procedure, invasive squamous cell carcinoma was detected and removed. Recurrence of squamous cell carcinoma in situ within a scar line of a earlier Mohs micrographic surgical procedure excision. The differential prognosis contains squamous cell carcinoma, hypertrophic actinic keratosis, and infected seborrheic keratosis.
Best singulair 4 mg
Twelve patients received a lowered dose (20 mCi) because of bone marrow involvement or unsuccessful marrow harvest. Based on these encouraging results, radioimmunotherapy appears to be a brand new promising choice, both alone or in combination with other chemotherapy or immunotherapy (or each). Side effects had been rare and consisted of brief-lasting fever, ache in involved lymph nodes, and a maculopapular rash. In these scientific pilot trials, several transient partial remissions had been achieved in closely pretreated patients with relapsed or refractory disease. Uber eine eigenartige unter dem Bilde der Pseudoleukamie verlaufende Tuberculose des lymphatischen Apparates. Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus sequences and correlations with histologic subtype. Identification of Hodgkin and Sternberg-reed cells as a singular cell kind derived from a newly-detected small-cell inhabitants. Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells in lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin disease represent clonal populations of germinal centerderived tumor B cells. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Nodular paragranuloma and progressively transformed germinal centers:ultrastructural and immunohistochemical findings. Lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin disease: clinicopathologic options and results of treatmentthe Pediatric Oncology Group experience. Anaplastic massive-cell lymphoma: scientific and prognostic evaluation of 90 grownup patients. On the criteria and kinetics related to "curability" of experimental leukemia. Combined intensive alkylating brokers with autologous bone marrow transplantation for metastatic stable tumors. Autologous bone marrow transplantation: proceedings of the primary international symposium. A mathematic model for relating the drug sensitivity of tumors to their spontaneous mutation fee. Lymphoma Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Immunophenotypic and molecular analyses of acquired immune deficiency syndromerelated and Epstein-Barr virus-related lymphomas: a comparative study. Hodgkin disease survivors at elevated threat for issues in psychosocial adaptation. Assessing the standard of lifetime of patients in cancer scientific trials: common issues and customary sense answer. Long-term restoration of immunity in opposition to Epstein-Barr virus infection by adoptive transfer of gene-modified virus specific T-lymphocytes. The cytogenetic study of those malignant cells has revealed that recurrent chromosomal changes occur in over one-half of all cases of leukemia. Most generally, these are structural changes categorised as translocations, inversions, or deletions. Thus, leukemia results, a minimum of partially, from the disruption or deregulation of genes that normally regulate blood cell development, blood cell homeostasis, or each. The genetic mishap often happens at a selected point in normal hematopoiesis, giving rise to leukemia of a selected lineage that has arrested at a distinct maturational stage. This strongly means that the gene or genes altered in a specific kind of leukemia are important in a selected stage of development or homeostasis of its normal cell counterpart. The mechanisms by which disrupted or deregulated genes cause leukemia may be broadly categorised into two classes. The first is gene fusion, whereby a distinct protein, usually both a transcription issue or receptor tyrosine kinase, fuses with an unrelated gene to create a singular chimeric fusion protein that then critically contributes to malignant transformation of the cell. This mechanism predominates in the genesis of myeloid leukemia, but can be found in lymphoid leukemia. Chromosomal translocations that lead to gene activation usually occur in lymphoid tissue and lead to a deregulation in gene expression. The improved techniques for the study of chromosomes and the explosive development in molecular biology are quickly facilitating the elucidation of genes involved at chromosomal breakpoints in cases of leukemia, and the listing of oncogenes is rising nearly every day in the literature. Advances in a fraction of such cases have revealed that comparable genetic mechanisms of leukemogenesis are operative even in the absence of structural cytogenetic abnormalities. Selected Examples of Cytogenetic and Molecular Abnormalities in Leukemia In this chapter, we evaluate the most common genetic disruptions that result from the recurrent cytogenetic aberrations in acute and persistent leukemia, and the place attainable, provide an evidence as to how such alterations contribute to the molecular pathogenesis of the disease. In addition, we evaluate instances in which the molecular basis for leukemia has been decided in the absence of structural cytogenetic abnormalities. Finally, we discuss other genetic alterations, principally in tumor suppressor genes, which are more likely to contribute to the genesis or progression of leukemia. We proceed with a molecular description of leukemia that simply follows the listing of the more common molecular defects supplied in Table 46. There is little or no attention to the more traditional revised histologic classification of leukemia to put more emphasis on the genetic basis of leukemia. Additional elements that act as coactivators of transcription participate on this complicated formation. This whole complicated then facilitates repression of transcription by altering chromatin construction via histone deacetylation. This process might result in the disruption of normal hematopoiesis and may also inactivate tumor suppressor genes and other elements important for neoplastic transformation. The genomic fusion between these two genes is sort of variable, and a minimum of eight different sized fusion transcripts have been described, the biologic and scientific significance of which are unclear. This gene fuses with a unprecedented quantity (over 30) of diverse associate genes, examples of which are proven in Table 46. The fusions manifest in myeloid, lymphoid, or combined lineage leukemias (outlined by markers of more than one hematopoietic lineage) of infants, youngsters, or adults, the scientific particulars of which are supplied in subsequent chapters. Exons are indicated by vertical strains and packing containers, and introns are indicated by the horizontal line for each construction. Most of the cloned companions are novel genes and inference about their features comes from the study of their homologies or in vitro systems. The complicated in turn alters chromatin conformation in such a way that transcription of target genes liable for myeloid differentiation is repressed. Both of the fusion proteins invariably include the two transcriptional activation domains on the amino terminus of E2A. A significant fraction of those patients have also achieved a complete cytogenetic response as properly, again emphasizing how specific targeting of molecular defects is more likely to have a major impact on remedy end result (see Chapter 46. This activation ends in phosphorylation of a large number of mobile and nuclear signaling molecules (some of which are proven) whose pathways in the end have an effect on cell development, differentiation, and cell survival. The earliest of those studies had been the primary to show that rearrangement of specific genes that resulted from chromosomal translocations had been actually on the coronary heart of malignant transformation. How the activation of those downstream occasions in turn induces the malignant B-cell transformation remains to be incompletely understood and an space of intense study (reviewed in references 126 and 127). As a consequence, these regulatory genes turn out to be inappropriately expressed, and their protein merchandise contribute to T-cell leukemogenesis. This process normally requires disruption of each copies of related tumor suppressor genes, which might occur by such genetic alterations as point mutation, frame-shift mutation, and deletion, or by epigenetic alterations such as hypermethylation. This method showed that a median of 608 CpG islands had been aberrantly methylated in these tumors (range, zero to 4500), and it allowed the identification of patterns of CpG island methylation that had been shared within each tumor kind, along with a pattern that was specific for acute leukemia. Which tumor suppressor genes are systematically silenced by this process has not yet been decided. However, these knowledge recommend that the methylation of explicit subsets of CpG islands has specific penalties for leukemogenesis and is probably going an important occasion in disease progression. However, as we be taught more in regards to the evolutionary history of the leukemic clone and the seemingly excessive likelihood that in lots of instances, a large number of genetic alterations are required for leukemogenesis, the simultaneous detection of several such alterations might show to be more predictive of end result following the achievement of a scientific full remission. Translocations, master genes, and differences between the origins of acute and persistent leukemias.
Quality 10 mg singulair
Bacci and coworkers241 evaluated the pattern of metastatic unfold of osteosarcoma in 193 sufferers on the Rizzoli Institute. Thirty sufferers who were handled with surgery alone were in comparison with 163 sufferers who underwent adjuvant chemotherapy. In basic, lung metastases appeared later and were fewer in number after adjuvant chemotherapy but with variable difference on extrapulmonary or bony unfold. Bacci and coworkers evaluated sufferers handled for osteosarcoma between 1972 and 1989. Surgical Resection of Localized Extremity Osteosarcoma Before the early Nineteen Eighties, remedy for localized osteosarcoma was amputation one joint above the tumor-containing bone or, occasionally, transmedullary amputation. No difference in survival was discovered between amputation and resection or between radical resection and a large surgical margin. The investigators concluded that a large surgical resection was enough for native control. In basic, they really helpful amputation if the main neurovascular bundle was concerned. They concluded that native recurrence was as a result of an extremely aggressive tumor or to skip metastases. Rougraff and colleagues 142 updated a combined examine from the Musculoskeletal Tumor Society of 227 sufferers from 26 establishments handled for osteosarcoma of the distal femur. No variations in native recurrence, total survival, or length of illness-free survival were famous between amputation and limb-sparing groups. The most typical causes of failed limb-sparing procedures were infection and native recurrence. Local Recurrence, Tumor Necrosis, and Surgical Margins During the Nineties, many surgeons intuitively believed that a patient with an excellent response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy was extra likely to undergo a limb-sparing process safely than a patient with a poor response. A relationship seems to exist between the protection of limb-sparing resection and the surgical margins achieved with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Patients whose lesions respond well to chemotherapy are less likely to develop native recurrence than these whose lesions respond poorly. The mean time to native recurrence was thirteen months from diagnosis (vary, 2 to fifty six months). Eighty-nine percent of the native recurrences developed within 18 months of the diagnosis. When the type of surgical margin and the response to chemotherapy were analyzed collectively, variations in consequence were dramatic. Treatment by Anatomic Site the distinctive features of analysis, administration, and resection of tumors of the commonest anatomic areas, the shoulder and knee, are described and illustrated on this section. A surgical classification for shoulder girdle resections has been described and is shown schematically in Figure 39. This classification is helpful for all limb-sparing procedures of the shoulder girdle. A and B denote the status of the abductor mechanism: A is undamaged, and B is partially or completely excised. Impact of two cycles of preoperative chemotherapy with intraarterial cisplatin and intravenous doxorubicin on the selection of surgical process for prime-grade bone sarcomas of the extremities. Adequate resection of the proximal humerus requires elimination of 15 to 20 cm of the humerus and shoulder joint with the deltoid, rotator cuff, and parts of the biceps and triceps muscle tissue 249. The process includes suspension of the arm, motor reconstruction, and provision of enough gentle tissue protection. This patient was placed in a shoulder splint and given three cycles of chemotherapy within the hope of avoiding a forequarter amputation. Due to the nice scientific and radiographic response, this patient underwent a limb-sparing resection (kind V). Biopsy beneath fluoroscopy through the anterior one-third of the deltoid by a trocar is most popular. Extraarticular resection of the glenohumeral joint by medial scapulosteotomy is safer than intraarticular resection. Soft tissue reconstruction and suspension are essential to keep away from postoperative pain, instability, and fatiguability. Shoulder motion is minimal, but steady, and scapulothoracic motion provides some inner and exterior rotation. Alternatively, resection of the proximal humerus for osteosarcomas may be performed by an intraarticular resection that preserves the glenoid and the adjoining deltoid muscle. The issues associated with this process embrace important native recurrence charges and instability of the reconstructed prosthesis or allograft. When the glenoid and deltoid are preserved on this process, minimum margins are obtained along the shoulder joint, the deltoid muscle, and the axillary nerve. Adequate en bloc resection consists of 15 to 20 cm of the distal femur and proximal tibia and parts of the adjoining quadriceps. Contraindications to resection are popliteal vessel involvement, massive gentle tissue contamination from earlier biopsy, and fracture. Large tumors requiring elimination of the complete quadriceps or hamstrings may be adequately reconstructed by an arthrodesis. These issues are instantly related to the anatomic constraints: minimal adjoining gentle tissue and the conventional subcutaneous location of the medial tibial border. It is extremely necessary that the biopsy be small and that it keep away from the knee joint. A core biopsy of medial flare is most popular to keep away from contamination of the anterior musculature and peroneal nerve. The popliteus muscle adjoining to the posterior facet of the tibia prevents direct tumor involvement of the neurovascular bundle. The medial gastrocnemius is routinely transferred to provide gentle tissue protection of the reconstructed area. Rehabilitation emphasizes knee extension, but not flexion, for a most of 2 to 3 months. Tumors of the proximal fibula require the identical analysis as do proximal tibial lesions. Contraindications to resection are direct tibial involvement, an anomalously absent posterior tibial artery, and intraarticular knee joint extension. Adequate resection consists of the fibula, the tibiofibular joint, the anterior and lateral muscle compartments, and a portion of the lateral gastrocnemius muscle. After surgery, the one practical deficit is footdrop, which is handled by an orthosis. Hemipelvectomy often is required for pelvic tumors, whereas modified hemipelvectomy is used for tumors of the proximal femur. Detailed anatomic and surgical concerns are discussed within the section on chondrosarcomas (see Chondrosarcoma, later on this chapter), which regularly arise in these websites. Fahey and Spanier 256 reviewed 25 sufferers with osteosarcoma of the pelvis handled on the University of Florida between 1967 and 1990 and described their biologic habits, progress, and histologic and vascular findings. Common issues included delay in diagnosis, widespread invasion into main pelvic veins, microscopic foci of tumor in otherwise regular tissue, and extension into adjoining (and different) pelvic constructions. Eighteen sufferers underwent surgery (ten hemipelvectomies and eight limb-sparing resections). Only two of ten hemipelvectomy sufferers obtained broad margins, and only two of the eight limb-sparing sufferers obtained adverse margins. An sudden intraoperative discovering was obvious tumor invasion into the large veins in nine sufferers: the iliac veins in two sufferers, the inferior vena cava in three sufferers, and unnamed veins in 4 sufferers. The high incidence of venous invasion requires that the iliac vessels be evaluated preoperatively and intraoperatively. Radiographic staging research should embrace a thorough analysis of the iliac vessels. Clinical Analysis of Limb-Sparing Surgery the latest comparison of the outcomes of limb-sparing surgery and amputation were reported by Sluga and colleagues 257 from the University of Vienna. They evaluated one hundred thirty consecutive sufferers younger than 21 years of age handled for osteosarcoma of the extremity. Fourteen amputations, 32 rotationplasties, and eighty four resections with subsequent reconstruction were performed. The surgical margins were categorised as broad in 109 cases and radical in ten cases. The authors emphasize that there was no choice bias by tumor volume for the type of surgical process performed. They emphasize the significance of broad margins to a successful limb-sparing process.
Safe 10 mg singulair
The combination of peripheral stem cell transfusions with hematopoietic development factors has permitted the evaluation of multiple programs of high-dose remedy in sufferers with ovarian cancer. Multiple cycles of high-dose chemotherapy could be safely administered with hematopoietic help. If it can be demonstrated that such an method is possible in a multicenter study, then a bigger potential randomized comparability towards commonplace doses of chemotherapy in beforehand untreated sufferers might be performed. In addition, scientific trials are planned in evaluating the function of multiple cycles of high-dose chemotherapy as a consolidation therapy in sufferers who achieve an preliminary response to induction chemotherapy. At current, high-dose chemotherapy with hematologic help ought to be thought of an experimental process, and sufferers ought to be entered on scientific trials evaluating security and efficacy. New Drug Combinations the usual chemotherapy for ovarian cancer now consists of paclitaxel plus a platinum compound. As noted earlier within the section Chemotherapy for Recurrent Disease, a series of new agents have been shown to have activity in ovarian cancer, including topotecan, gemcitabine, oral etoposide, and encapsulated doxorubicin. New combos based on the activity of paclitaxel and platinum are at present being evaluated. With the massive variety of active compounds obtainable for recurrent disease, quite a few new potential combos and sequences are under consideration. Reversal of Drug Resistance the molecular mechanisms associated with drug resistance, the primary issue that limits the healing potential of any salvage remedy in sufferers with ovarian cancer, are being extensively studied. For the taxanes, a minimum of two mechanisms of acquired resistance have been identified in cells made resistant by extended exposure in vitro. In paclitaxel-resistant cells, elevated expression of the membrane P glycoprotein efflux pump is seen, which leads to partial cross-resistance to bulky natural merchandise, including vinca alkaloids and anthracyclines. In addition, paclitaxel-resistant cells have construction alterations in a and b tubulin protein subunits, which kind an integral a part of microtubules. Combinations of cyclosporin and cisplatin have also been studied in platinum-resistant sufferers. Antibodies to c-erbB-2 in combination with cisplatin have shown synergistic cell kill in vitro. Numerous scientific trials have explored the potential to reverse the multidrug resistance phenotype in ovarian cancer. The scientific significance of each of these mechanisms of drug resistance in ovarian cancer has not been established. The identification of the outstanding function of paclitaxel in ovarian cancer has led to new curiosity in modulation of natural product resistance. One study suggests that an related drug-resistant protein (Lrp) might have prognostic significance in ovarian cancer. In experimental models of gene remedy, sensitivity to cisplatin can be restored in resistant cell lines by reintroduction of p53 into tumor cells. Adenoviral-mediated supply of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase has been shown to selectively synthesize human ovarian cancer cells to ganciclovir, and scientific evaluation is planned for this combination. The immunotherapy of ovarian cancer has advanced from the administration of nonspecific immunostimulants, such as Corynebacterium parvum to extra specific therapies focusing on antigens and surface receptors current on tumor cells. One should always be sure to rule out the potential for a synchronous appendiceal major tumor when dealing with the latter entity. The mean age of women growing tumors of low malignant potential is 40 years, roughly 20 years earlier than the mean age for girls with epithelial cancers of the ovary. Ovarian tumors of low malignant potential have been associated with infertility and ovulation induction. The causes of demise on this evaluation have been radiation-related issues in three sufferers, chemotherapy-related issues in nine, and bowel obstruction in eight. Eight women died from invasive carcinoma, and 18 died of disease without any additional data. Noteworthy was the truth that extra sufferers died of therapy-associated issues than died of bowel obstruction from progressive disease. Management of sufferers with low malignant potential tumors of the ovary is much like that of the surgical administration of invasive cancer. If intraabdominal disease is current, aggressive cytoreductive surgical procedure ought to be performed. The proof is scant to counsel that therapy past that of the preliminary surgical procedure has any useful function. Appropriate adjuvant remedy has but to be identified within the administration of women with tumors of low malignant potential. No variations within the two arms in any of the 4 randomized studies could be identified. In general, they have an inclination to current with stage I disease and regularly are associated with hormonal results, such as precocious puberty, amenorrhea, postmenopausal bleeding, or virilizing symptoms. For instance, granulosa cell tumors have been reported to be associated with virilization. All sufferers within the series underwent ovarian hyperstimulation for the therapy of infertility. In general, premenarchal women or sufferers presenting within the reproductive years are likely to have stage I disease in most series. Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy has been probably the most regularly used therapy. However, few series have been reported, and they involve small numbers of women with granulosa cell tumors. One of the pathologically complete respondents, however, relapsed forty eight months after the onset of chemotherapy. Fourteen of the 18 sufferers had pathologically unfavorable second-look outcomes, 4 sufferers had a partial response, 14 sufferers had stable disease, and two sufferers had progression of disease among the 55 sufferers evaluable for response. Sixteen sufferers obtained the chemotherapy after major surgical procedure, nine of whom had obtained the chemotherapy due to optimistic peritoneal cytology and seven for the therapy of gross residual disease. For women older than 40 or for any girl with superior-stage or recurrent disease, we suggest doxorubicin, cisplatin, and etoposide. Perhaps sooner or later move cytometric studies could also be useful in figuring out which group of sufferers would possibly profit from adjuvant remedy as opposed to remark. Their administration is the same as that of granulosa cell tumors by way of staging, surgical administration, and adjuvant chemotherapy. If the recurrence is isolated and could be encompassed in a radiation field, older literature suggests that radiation remedy could also be of worth if the malignancy is a granulosa cell tumor. Patients with intensive recurrences ought to be treated with cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy. In some sufferers, the primary site is unknown, and peritoneal carcinomatosis can current as a part of the syndrome of adenocarcinomas of unknown major site. Adenocarcinomas of unknown major site who current with peritoneal carcinomatosis can respond to chemotherapy with platinum-based regimens. In a series of 18 women treated with a platinum-based routine, median survival was 23 months, and 5 sufferers had complete remissions and lengthy-term survival. Although embryologically the germinal epithelium of the ovary and the mesothelium of the peritoneal cavity are derived from the same celomic epithelium, a subset of peritoneal tumors can be morphologically identified that have a extra favorable scientific conduct in response to remedy compared with peritoneal mesotheliomas. Using the proposed terminology, when an uncommon subtype apart from serous is current, it can be encompassed within the description. Peritoneal mesotheliomas are extra aggressive tumors, with a survival price of usually lower than 1 yr. Most sufferers with extraovarian peritoneal carcinomatosis have indicators and symptoms much like these women who current with superior-stage ovarian cancer. At surgical procedure, these women regularly have ascites with diffuse peritoneal carcinomatosis. Attempts at cytoreductive surgical procedure usually are made, though no proof helps survival profit in these women with peritoneal carcinomatosis who endure optimum cytoreductive surgical procedure. In a large study from the University of California, Los Angeles, the median survival of sufferers who obtained chemotherapy after major cytoreductive surgical procedure was 28. Based on the sample of metastases and chemosensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy, it seems prudent that present remedy for this group of sufferers ought to embody cytoreductive surgical procedure adopted by chemotherapy with paclitaxel plus a platinum compound. They nearly always occur in youthful women, and their peak incidence is within the early 20s. They are often divided clinically into dysgerminoma and nondysgerminoma germ cell tumors.
5 mg singulair
The lymphatics from the anterior urethra drain into the superficial and deep inguinal lymph nodes and sometimes to the external iliac lymph nodes. The lymphatics from the posterior urethra drain into the external iliac, obturator, and hypogastric nodes. Tumors of the anterior urethra usually metastasize to the inguinal nodes, and tumors of the posterior urethra mostly spread to the pelvic nodes, though exceptions occur. The extent of local involvement is decided by cautious inspection and palpation of the external genitalia and perineum on the time of cystourethroscopy and by bimanual examination with the patient beneath anesthesia. In common, anterior urethral carcinoma is more amenable to surgical control and has a better prognosis than posterior urethral carcinoma. Although some cases of tumor control by irradiation have been reported, generally, radiation has been reserved for patients with early-stage lesions of the anterior urethra who refuse surgical procedure. Combination chemotherapy has achieved encouraging leads to patients with metastatic urothelial cancer and is now being built-in more regularly with irradiation and definitive surgical procedure in patients with locally superior urethral carcinomas. For a tumor infiltrating the corpus and localized to the distal half of the penis, a partial amputation with a 2-cm margin proximal to the seen or palpable tumor is the accepted remedy. If the infiltrating tumor is positioned within the proximal penile urethra or involves the whole urethra, radical amputation is important. This process might involve emasculation if the scrotal skin or genitalia are involved. Ilioinguinal groin node dissection is indicated provided that the inguinal nodes are palpable. Carcinoma involving the distal or penile urethra usually enjoys a more favorable prognosis than cancers involving the whole or more proximal areas of the urethra. Carcinoma of the Bulbomembranous Urethra Transurethral or segmental resection may be enough for remedy of early superficial tumors involving the bulbomembranous urethra, however such cases are uncommon. Most patients present with an infiltrating bulky tumor with invasion of surrounding constructions. Approximately one-third of these patients are locally understaged and later prove to have pelvic or groin metastasis. The total survival of patients in this group is poor regardless of a distinctly radical surgical method, however radical excision presents the best opportunity for long-term illness control and the bottom incidence of local recurrence. Despite the dismal prognosis, expertise suggests that when local control of the tumor can be achieved, total long-term results are favorable. Such tumors are inclined to be locally intensive and are apt to recur locally with inadequate local remedy. Metastasis seems to be a late occasion, which has led to aggressive combined remedy approaches in patients with bulky posterior urethral carcinoma. Treatment Results for Carcinoma of the Bulbomembranous and Anterior Urethra Surgery alone offers suboptimal leads to the administration of male urethral carcinoma. A mixture of preoperative irradiation (20 to 60 cGy) adopted by surgical excision of the inferior pubic rami with partial symphysiectomy, anterior perineum, urogenital diaphragm, and genitalia, en bloc with the pelvic organs and lymph nodes, might enhance local control and survival. The integration of chemotherapy used as systemic remedy, and radiosensitization adopted by surgical procedure, can be profitable in both the bulbomembranous and prostatic urethra. Oberfield 18 reported genital preservation in two patients with an invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the bulbar urethra with this chemotherapy regimen plus radiation. Tumors may be transitional or adenocarcinoma, and the analysis relies on a solitary tumor within the prostatic urethra with out associated coexisting or preexisting urothelial tumors within the bladder and the bladder neck. Superficial lesions of the prostatic urethra are managed successfully by transurethral resection within the majority of patients. In most cases, the tumor involves the bulk of the prostate with variable extension to the bulbomembranous urethra or to the bladder neck and trigone. In this situation, cystoprostatectomy and urethrectomy is the remedy of alternative. In restricted expertise, the general 5-year survival price of patients treated with radical surgical procedure, with or with out preoperative irradiation, is poor. For instance, a total of 11 patients with superior tumors of the prostate, prostatic urethra, or bulbomembranous urethra acquired neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The commonest method has been external-beam radiotherapy, utilizing varied methods to ship 50 to 60 cGy in 5 to 9 weeks. The long-term results of radiotherapy have been combined, with the best results reported for patients with distal lesions, for whom the end result is just like that reported with surgical procedure. Proliferative lesions, similar to caruncles, papillomas, adenomas, and polyps, have been associated with subsequent malignancy. Leukoplakia of the urethra is considered a premalignant lesion and is treated with broad local excision. Tumors might present as a papillary development within the urethra and will later become a soft fungating mass that bleeds easily. The lesion may be detected first as a submucosal mass within the anterior wall of the vagina. Spread from the first lesion is by local extension and infiltration with subsequent involvement of the bladder neck, vagina, or vulva. It may be difficult on initial bodily examination to differentiate malignant tumors of the urethra from these of the vulva or vagina. Lymphatics of the anterior urethra and labia drain to the superficial after which deep inguinal nodes, whereas the posterior urethra drains to the external iliac, hypogastric, and obturator lymph nodes. Tumor histology is a mirrored image of the location, with squamous cell carcinoma being the predominant tumor sort and usually presenting within the proximal two-thirds of the urethra. Carcinomas of the proximal or whole urethra are of higher grade and locally superior. There has been no universally accepted staging system for feminine urethral carcinoma. Five-Year Survival Rate in Female Urethral Cancer Most urethral cancers in women are locally superior when detected and involve the proximal one-third or whole urethra. Such lesions clearly do worse than localized, low-grade, anterior urethral lesions. Poor prognosis attributed to urethral cancers in women is because of the superior stage (excessive tumor quantity), adjoining organ involvement, lack of ability to obtain a clear surgical margin (because of soft tissue infiltration), nodal illness, morbidity of extensive remedy, and inadequate systemic remedy for metastatic tumor. Single-modality remedy typically fails for superior cases and is profitable solely in chosen cases. For instance, meatal tumors, if identified early, are associated with an excellent 5-year survival price. For tumors involving the proximal urethra or extending past the urethra into the adjoining constructions, more aggressive remedy is required. When surgical procedure is considered, intensive resection is important, together with total urethrectomy, cystectomy with pelvic lymph node dissection, and removal of most (if not all) of the vagina. Extended excision to include resection of adjoining pubic symphysis and urogenital diaphragm just like that for proximal male urethral cancer has resulted in local control of some cases of far superior urethral carcinoma. Even intensive surgical procedure, nonetheless, typically fails because of soft tissue infiltration by the tumor past the confines of the bladder neck, urethra, and vagina. No difference was found in survival between women treated with radiation or surgical procedure. Inguinal lymph node dissection is usually not performed within the absence of palpable illness within the groin. Radiation of these small lesions can be completed with brachytherapy with out further external-beam irradiation. Tumors of the proximal urethra, bladder neck invasion, or involvement of the whole urethra require combined external irradiation and brachytherapy. External irradiation is delivered to the first tumor web site and regional lymph node. In the presence of palpable inguinal lymph nodes, bolus is added to the groin and the total dose is elevated from 60 to 65 Gy. The pelvis is treated to 50 Gy by the combined entire pelvis and cut up area technique. The main tumor web site is boosted with brachytherapy (one or two implants utilizing iridium 192) to bring the total tumor dose from 70 to eighty Gy, depending on tumor size. Complications from irradiation include bowel obstruction, fistula formation, urethral stricture, and incontinence.
References:
- https://www.westonaprice.org/wp-content/uploads/Summer2009.pdf
- https://www.flexiblebenefit.com/sites/default/files/docs/032613CC_Combined_Product_Brochure_Cancer_First_Occurrence_IL.pdf
- https://www.stata.com/manuals13/d.pdf
- https://www.ippf.org/sites/default/files/report_for_web.pdf
- https://www.fourleg.com/media/2Cervico-Thoracic-Shoulder%20Differentials%20Handout.pdf
.png)