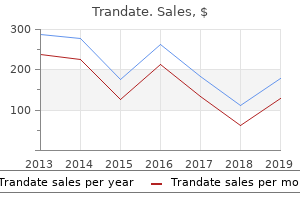
Cheap trandate 100 mg
Normal responses are recorded from abductor digiti minimi muscle and from paraspinal muscular tissues on the T6 stage, whereas no responses are recorded from paraspinal muscular tissues on the T10 stage. The recording from a number of muscular tissues can be used to determine the extent of spinal cord lesion, and this is notably helpful in uncooperative and unconscious sufferers. The functional exploration of the central motor pathways in subacute mixed degeneration may reveal a spinal cord dysfunction even within the early levels of the disease,24 when the scientific manifestation could also be limited to brisk tendon reflexes. In root lesions, needle electromyographic research may document fibrillation potentials within the corresponding paraspinal muscular tissues or myotomes, but these electromyographic changes appear only after 2 to 3 weeks. Magnetic paravertebral stimulation activates the motor axons of peripheral nerves near their exit from the backbone. This website is distal to that of root compression produced by disc issues or spondylotic changes, and the latency of responses evoked by magnetic paravertebral stimulation is normal within the case of root compression. The conduction time alongside the proximal a part of motor roots may be calculated by subtracting the latency of motor responses evoked by magnetic paravertebral stimulation from the entire peripheral conduction time calculated utilizing the formulation of Kimura37 [(F 1)/2]. A pathological increment of the motor root conduction time suggests a demyelination on this portion of the peripheral nervous system. Its assessment could also be notably helpful in pathological circumstances that involve proximal motor segments, similar to spondylotic compression of roots and root involvement in inflammatory peripheral nerve issues that may cause focal demyelination. To determine a delay of conduction alongside the motor roots, a number of roots ought to be concerned, and this is widespread in central disc herniations or lumbar canal stenosis. In these circumstances, dedication of central motor conduction from the latency of the response evoked by magnetic paravertebral stimulation and from the latency of the F wave may reveal functional involvement of the lumbosacral roots. The central motor conduction time calculated from the latency of responses evoked by paravertebral magnetic stimulation is abnormal along with the motor root conduction time, whereas the central motor conduction time calculated from the latency of the F wave is within normal limits. In lumbar canal stenosis, the abnormality of motor root conduction time is evident in a number of lower limb muscular tissues when most lumbosacral roots are concerned (see. The dedication of conduction alongside lumbosacral motor roots is even more helpful in circumstances of acute large central disc protrusions causing multiradicular compression. The scientific presentation of this syndrome is very similar to a lower cord lesion. The electromyographic examine may reveal changes only after 2 to 3 weeks, but the conduction alongside motor roots becomes abnormal with the onset of root compression. An instance in a single patient with a 3-day historical past of acute paraplegia as a result of central disc herniation on the L3 stage is shown in Figure seventy seven. The abnormality of central motor conduction to the tibialis anterior muscle along with the absence of the F wave indicates an L4 and L5 root dysfunction, whereas the conventional central motor conduction for a more caudal muscle such because the abductor hallucis demonstrates a normal lumbosacral cord operate. Conversely, in cervical radiculitis, the marked demyelination of the roots may result in a pronounced delay of conduction alongside the roots. An instance in a single patient with C8-T1 radiculitis related to a spondylodiscitis is represented in Figure seventy eight. The analysis of conduction alongside motor roots is particularly helpful in sure circumstances of acute and persistent inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies and of multifocal motor neuropathies as a result of, notably within the preliminary phases of those issues, a root involvement could also be exclusive or predominant. The most pronounced abnormalities of proximal conduction may be present in these issues. Central motor conduction time for rectus femoris and abductor hallucis muscular tissues is normal. He had had acute, severe ache in his proper arm with a distribution alongside the C8 and T1 roots. The infectious disease compromises the proper lateral recesses and intervertebral foramen. Figure 70 Motor evoked potentials have been recorded from the abductor digiti minimi muscle after cortical and paravertebral magnetic stimulation in a patient with multifocal motor neuropathy. Abnormal radicular conduction can be demonstrated in sufferers with multifocal motor neuropathy. In some circumstances, when the conduction block is localized at proximal motor roots, the central motor conduction time calculated from the latency of the F wave could also be abnormally short54. A potential clarification for this finding is an impaired security margin for repeated discharge of faster fibers of motor roots, which makes them more refractory than normal during backfiring of larger spinal motoneurons. Normally, the antidromic and orthodromic volleys generating the F-wave travel twice at a really quick interval the proximal motor roots. When the excitability of the biggest motor axons at proximal root segments is decreased, the conduction of the orthodromic volley could also be blocked. The preserved backfiring of some slower conducting root fibers can generate a particularly prolonged F wave. Because the biggest fibers can nonetheless discharge after transcranial stimulation, the inhabitants of root fibers concerned in F-wave technology and the inhabitants recruited after transcranial stimulation have completely completely different conduction velocities and this result in an abnormally quick central motor conduction time estimated from the F-wave latency along with a particularly prolonged root conduction time. The assessment of root conduction utilizing magnetic paravertebral stimulation along with F-wave recording is especially helpful for the peripheral nerve inflammatory issues that involve only the foundation whereas sparing segments which are more peripheral or in diabetic multiradiculopathies. An instance in a single patient with inflammatory lumbosacral multiradiculopathy is shown in Figure seventy one. Myelopathy, Radiculopathy, and Thoracic Nerve Evaluation Inflammatory lumbosacral multiradiculopathy one hundred twenty five Extensor digitorum brevis F wave 58. Chokroverty and colleagues46 recorded muscle responses from the rectus abdominis, external indirect, and intercostal muscular tissues after paravertebral root stimulation and after distal intercostal nerve stimulation. Using this method, the identical investigators demonstrated a thoracoabdominal radiculoneuropathy in a single diabetic patient. Examination of motor operate in lesions of the spinal cord by stimulation of the motor cortex. Motor evoked potentials in sufferers with spinal issues: higher and lower motor neuron affection. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in sufferers with cervical spondylotic myelopathy: scientific and radiological correlations. Transcranial magnetic stimulation for detection of preclinical cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Motor and somatosensory evoked potentials in asymptomatic spondylotic cord compression. Ischaemic myelopathy related to cocaine: scientific, neurophysiological, and neuroradiological options. Experience with transcranial magnetic stimulation in analysis of spinal cord harm. Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies and hereditary spastic paraplegia: a magnetic stimulation examine. Abnormalities of somatosensory and motor evoked potentials in adrenomyeloneuropathy: comparison with magnetic resonance imaging and scientific findings. Clinical use of the magnetic stimulator within the investigation of peripheral conduction time. Transcutaneous magnetic and electrical stimulation over the cervical backbone: excitation of plexus rots quite than spinal roots Surgical therapy of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: time for a controlled trial. Conduction instances of cortical projections to paravertebral muscular tissues in controls and in sufferers with a number of sclerosis. Responses in human intercostal and truncal muscular tissues to motor cortical and spinal stimulation. Effects of voluntary contraction on descending volleys evoked by transcranial stimulation in acutely aware humans. Electrophysiological recordings in sufferers with spinal cord harm: significance for predicting outcome. Lumbosacral nerve root stimulation comparing electrical with floor magnetic coil strategies. The contralateral cortex has a predominant control over cranial muscular tissues that produce lateral movements and may act independently. Conversely, symmetrically bilateral cortical projections reach the motoneurons of muscular tissues. The importance of the bilaterality of innervation is clearly completely different from that for limb motor control and is useful in understanding scientific phenomena similar to restoration from stroke. The greatest understood state of affairs is the seventh nerve, thanks in part to an anatomical examine within the rhesus monkey by Morecraft and colleagues. Perioral muscular tissues, prototypical for the lower face, are innervated largely contralaterally from the first motor cortex (M1), ventral and dorsal areas of the lateral premotor cortex, and caudal cingulate (M4). For higher face muscular tissues, orbicularis oculi are innervated principally by rostral cingulate (M3) and auricular muscular tissues by the supplementary motor space (M2), both bilaterally.
Generic trandate 100 mg
Central apnea lasting lower than 10 seconds is frequent in healthy infants and could be present in normal youngsters throughout sleep, particularly after a sigh breath. Central apnea is extra frequent in infants, and obstructive apnea, particularly throughout sleep, is extra frequent in older youngsters. Premature infants can have apnea of prematurity, which consists of recurrent apneic episodes which are typically of central origin, although they are often mixed central/obstructive. Older infants and youngsters with apnea warrant thorough investigation (Table 134-2). Central apnea outdoors of infancy is a rare occurrence and could also be main or secondary. Genetic syndromes related to abnormal central respiratory control and developmental delays include Rett, Joubert, and Prader-Willi syndromes and tuberous sclerosis. It presents as episodes of respiratory pauses, gasping, and restless sleep that can result in hypoxia and hypercarbia. Children might have issue awakening in the morning, daytime somnolence, behavioral adjustments, poor faculty performance, and poor somatic progress because of poor sleep quality. Nighttime hypoxia or hypercarbia can result in morning complications and, in severe cases, to pulmonary hypertension and cor pulmonale. Thus, when the diagnosis is in query, it should be confirmed with a polysomnogram. This requires a tight-becoming nasal mask, which will not be nicely tolerated in young youngsters. In excessive cases, particularly these related to craniofacial abnormalities or hypotonia, tracheostomy could also be indicated. In youngsters, nasal obstruction is usually extra of a nuisance than a danger because the mouth can serve as an airway, however it might be a serious problem for neonates, who breathe predominantly by way of their noses. The differential diagnosis of airway obstruction varies with patient age and can be subdivided into supraglottic, glottic, and subglottic causes (Tables a hundred thirty five-1, a hundred thirty five-2, and a hundred thirty five-three). Stridor typically decreases throughout sleep, because of lower inspiratory flow rates, and increases throughout feeding, excitement, and agitation, because of higher flow rates. Laryngomalacia (floppy larynx) is the commonest cause of inspiratory stridor in infants and could also be aggravated by swallowing problems and gastroesophageal reflux. Asymmetry suggests subglottic stenosis or a mass lesion, whereas tapering suggests subglottic edema. Flexible nasopharyngoscopy/laryngoscopy, which could be carried out with out sedation, is extremely useful in assessing airway patency, the presence of adenoid tissue, vocal cord and different airway lesions, and laryngomalacia. Bronchoscopy could be useful in assessing the subglottic house and intrathoracic massive airways, however this process requires sedation. Adenoidal and tonsillar hyperplasia could also be aggravated by recurrent an infection, allergy, and inhaled irritants. The eustachian tubes enter the nasopharynx on the choanae and could be obstructed by enlarged adenoids, predisposing to recurrent or persistent otitis media. Diagnostic Studies Adenoidal hypertrophy is assessed by a lateral radiograph of the nasopharynx or by flexible nasopharyngoscopy. If the tonsils are massive and the obstruction is severe, then removing the tonsils in addition to the adenoids could also be needed. Stridor Etiology Laryngomalacia is because of exaggerated collapse of the glottic constructions, particularly the epiglottis and arytenoid cartilages, throughout inspiration. It could also be as a result of decreased muscular tone of the larynx and surrounding constructions or to immature cartilaginous constructions. Inspiratory stridor beginning at or shortly after start should elevate the suspicion of laryngomalacia (see Table a hundred thirty five-1). Clinical Manifestations the first sign of laryngomalacia is inspiratory stridor with little or no expiratory component. The stridor is typically loudest when the infant is feeding or lively and decreases when the infant is relaxed or placed susceptible, or when the neck is flexed. Any condition that increases higher airway inflammation will exacerbate laryngomalacia, including viral respiratory infections, dysphagia (swallowing dysfunction), and gastroesophageal reflux. Laryngomalacia usually peaks by three to 5 months of age and resolves between 6 and 12 months of age. However, often it could possibly persist in in any other case normal youngsters up until 24 months of age and even longer in youngsters with underlying situations, particularly these with neurologic ailments affecting control of higher airway muscle tissue (such as cerebral palsy). Diagnostic Studies In many infants with presumed laryngomalacia, the diagnosis could be tentatively established by history and bodily examination. If the patient follows the standard course for laryngomalacia, then no additional workup is important. However, to firmly set up the diagnosis, which is essential in additional severe or atypical cases, the patient should bear flexible nasopharyngoscopy to assess the patency and dynamic movement (collapse) of the larynx and surrounding constructions. This process can also establish vocal cord abnormalities and airway lesions above the vocal cords. The infant should be observed carefully throughout instances of respiratory an infection for evidence of respiratory compromise. Infants with severe laryngomalacia resulting in hypoventilation, hypoxia, or progress failure might profit from a surgical process (aryepiglottoplasty) or, in excessive cases, a tracheostomy to bypass the higher airway. Choanal Stenosis (Atresia) Choanal stenosis/atresia is a congenital downside presenting in the neonatal interval. Neonates are generally obligate nose breathers, so obstruction of nasal passages can cause significant respiratory distress, particularly when feeding. Crying bypasses the obstruction because crying infants breathe although their mouths. Inability to simply pass a small catheter by way of the nostrils should elevate the suspicion of choanal atresia. An oral airway could also be useful in the brief term, but the definitive remedy is surgical procedure. Foreign body should be considered in any infant or youngster able to ingesting small objects who develops acute onset of stridor. Clinical manifestations usually start in infancy and include biphasic stridor and hoarse voice/cry. Treatment choices, which are restricted and barely healing, include laser remedy and interferon. Tracheostomy could also be required to ensure an sufficient airway, however should be avoided if attainable as stories recommend a related seeding of the distal airways with tumor. Endotracheal intubation, particularly extended or repeated intubation required in some premature infants, can result in inflammation and scarring of the subglottic house. Very small infants might not have the ability to breathe with enough drive to generate a sound. Subglottic stenosis may also be related to a barky cough similar to that famous with croup. Respiratory infections can cause subglottic edema, exacerbating the medical manifestations of subglottic stenosis. Diagnostic Studies Definitive diagnosis requires endoscopic analysis, either by flexible or rigid bronchoscopy. Treatment Mild subglottic stenosis could be managed conservatively and may improve sufficiently with airway progress alone. Depending on the nature of the lesion, endoscopic laser remedy could also be effective. A tracheostomy tube could also be required to bypass the subglottic house until the airway is patent enough to allow sufficient airflow. Paralysis could also be unilateral or bilateral and is extra typically attributable to injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve than by a central lesion. The left recurrent laryngeal nerve passes across the aortic arch and is extra vulnerable to injury than the right laryngeal nerve. Peripheral nerve injury could also be attributable to trauma (neck traction throughout supply of infants or thoracic surgical procedures) and mediastinal lesions. Central causes include Arnold-Chiari malformation (meningomyelocele), hydrocephalus, and intracranial hemorrhage. Clinical Manifestations Vocal cord paralysis presents as biphasic stridor and alterations in voice and cry, including a weak cry (in infants), hoarseness, and aphonia. Children with vocal cord paralysis are in danger for aspiration, typically manifested as coughing/choking with ingesting and coarse airway sounds audibly and by auscultation. Treatment and Prognosis Patients with traumatic injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve typically have spontaneous enchancment over time, usually inside three to 6 months. In some cases, Gelfoam injection of a paralyzed vocal cord can reposition the cord to improve phonation and airway protection.
Order 100 mg trandate
First incidence and recurrence of neural tube defects are decreased significantly by maternal supplementation during embryogenesis. Because closure of the neural tube happens earlier than ordinary recognition of being pregnant, all ladies of reproductive age are beneficial to have a folate intake of a minimum of 400 g/day as prophylaxis. The cobalt ion is on the energetic middle of the ring and serves as the positioning for attachment of alkyl groups during their transfer. The vitamin capabilities in single-carbon transfers and is intimately associated to folate function and interconversions. Vitamin B12 is essential for regular lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in energy manufacturing and in protein biosynthesis and nucleic acid synthesis. In contrast to different water-soluble nutritional vitamins, absorption of vitamin B12 is complex, involving cleavage of the vitamin from dietary protein and binding to a glycoprotein known as intrinsic issue, which is secreted by the gastric mucosa (parietal cells). The cobalaminntrinsic issue complex is efficiently absorbed from the distal ileum. Efficient enterohepatic circulation normally protects from deficiency for months to years. Early prognosis and remedy of this disorder in childhood are necessary due to the hazard of irreversible neurologic damage. Most circumstances in childhood result from a specific defect in absorption (see Table 31-2). Gastric or intestinal resection and small bowel bacterial overgrowth additionally cause vitamin B12 deficiency. Exclusively breastfed infants ingest sufficient vitamin B12 until the mother is a strict vegetarian without supplementation. Depression of serum vitamin B12 and the looks of hypersegmented neutrophils and macrocytosis (indistinguishable from folate deficiency) are early clinical manifestations of deficiency. Vitamin B12 deficiency additionally causes neurologic manifestations, together with despair, peripheral neuropathy, posterior spinal column signs, dementia, and eventual coma. Patients with vitamin B12 deficiency also have increased urine levels of methylmalonic acid. Maintenance remedy consists of repeated monthly intramuscular injections, although a form of vitamin B12 is administered intranasally. Ingested plant carotene or animal tissue retinol esters launch retinol after hydrolysis by pancreatic and intestinal enzymes. Chylomicron-transported retinol esters are stored in the liver as retinol palmitate. Retinol is transported from the liver to target tissues by retinol-binding protein, releasing free retinol to the target tissues. Diseases of the kidney diminish excretion of retinol-binding protein, whereas liver parenchymal illness or malnutrition lowers the synthesis of retinol-binding protein. Specific mobile binding proteins facilitate the uptake of retinol by target tissues. In the eye, retinol is metabolized to kind rhodopsin; the action of sunshine on rhodopsin is the first step of the visible course of. The clinical manifestations of vitamin A deficiency in humans appear as a bunch of ocular signs termed xerophthalmia. The earliest symptom is night blindness, which is adopted by xerosis of the conjunctiva and cornea. Untreated, xerophthalmia may end up in ulceration, necrosis, keratomalacia, and a permanent corneal scar. Clinical and subclinical vitamin A deficiencies are related to immunodeficiency; increased danger of infection, particularly measles; and increased danger of mortality, particularly in creating nations. Hypervitaminosis A additionally has severe sequelae, together with complications, pseudotumor cerebri, hepatotoxicity, and teratogenicity. Absorption of fats-soluble nutritional vitamins depends on regular fats intake, digestion, and absorption. The complexity of regular fats absorption and the potential for perturbation in many illness states explains the more widespread incidence of deficiencies of those nutritional vitamins. The most energetic of those, -tocopherol, accounts for ninety% of the vitamin E current in human tissues and is commercially out there as an acetate or succinate. Vitamin E acts as a biologic antioxidant by inhibiting the peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids current in cell membranes. It scavenges free radicals generated by the discount of molecular oxygen and by the action of oxidative enzymes. Vitamin E deficiency happens in youngsters with fats malabsorption secondary to liver illness, untreated celiac illness, cystic fibrosis, and abetalipoproteinemia. In these youngsters, without vitamin E supplementation, a syndrome of progressive sensory and motor neuropathy develops; the primary signal of deficiency is loss of deep tendon reflexes. Deficient preterm infants at 1 to 2 months of age have hemolytic anemia characterized by an elevated reticulocyte count, an increased sensitivity of the erythrocytes to hemolysis in hydrogen peroxide, peripheral edema, and thrombocytosis. All the abnormalities are corrected after oral, lipid, or water-soluble vitamin E remedy. Characteristic radiographic modifications of the distal ulna and radius include widening; concave cupping; and frayed, poorly demarcated ends. The increased house seen between the distal ends of the radius and ulna and the metacarpal bones is the enlarged, nonossified metaphysis. Toxic results of excessive chronic vitamin D might include hypercalcemia, muscle weak point, polyuria, and nephrocalcinosis. Clothing, lack of daylight exposure, and pores and skin pigmentation decrease era of vitamin D in the epidermis and dermis. The antirachitic action of vitamin D probably is mediated by provision of appropriate concentrations of calcium and phosphate in the extracellular house of bone and by enhanced intestinal absorption of those minerals. Vitamin D deficiency appears as rickets in youngsters and as osteomalacia in postpubertal adolescents. Inadequate direct solar exposure and vitamin D intake are enough causes, however different components, such as varied drugs (phenobarbital, phenytoin) and malabsorption, might enhance the risk of improvement of vitamin-deficiency rickets. Breastfed infants, particularly those with darkish-pigmented pores and skin, are at risk for vitamin D deficiency. The pathophysiology of rickets outcomes from defective bone growth, particularly on the epiphyseal cartilage matrix, which fails to mineralize. The uncalcified osteoid leads to a large, irregular zone of poorly supported tissue, the rachitic metaphysis. This gentle, somewhat than hardened, zone produces many of the skeletal deformities through compression and lateral bulging or flaring of the ends of bones. The clinical manifestations of rickets are commonest during the first 2 years of life and will turn into evident solely after several months of a vitamin Deficient food plan. Craniotabes is caused by thinning of the outer table of the cranium, which when compressed seems like a Ping-Pong ball to the contact. Enlargement of the costochondral junction (rachitic rosary) and thickening of the wrists and ankles may be palpated. Bowlegs or knock-knees may be evident in older infants, and greenstick fractures may be observed in lengthy bones. The prognosis of rickets is based on a history of poor vitamin D intake and little exposure to direct ultraviolet daylight. The serum calcium often is regular however may be low; the Vitamin K Available @ StudentConsult. Another kind is menaquinone, or vitamin K2, one of a collection of compounds with unsaturated side chains synthesized by intestinal bacteria. The post-translational conversion of glutamyl residues to carboxyglutamic acid residues of a prothrombin molecule creates effective calcium-binding sites, making the protein energetic. Other vitamin Kependent proteins include proteins C, S, and Z in plasma and -carboxyglutamic acidontaining proteins in several tissues. Bone incorporates a major vitamin Kdependent protein, osteocalcin, and lesser amounts of different glutamic acidontaining proteins. The rarity of dietary vitamin K deficiency in humans with regular intestinal function means that the absorption of menaquinones is feasible. Vitamin K deficiency has been observed in subjects with impaired fats absorption caused by obstructive jaundice, pancreatic insufficiency, and celiac illness; often these issues are mixed with using antibiotics that change intestinal flora. Hemorrhagic illness of the newborn, a illness more widespread among breastfed infants, happens in the first few weeks of life. It is rare in infants who receive prophylactic intramuscular vitamin K on the primary day of life. There are seven essential main minerals: calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, chloride, and sulfur.
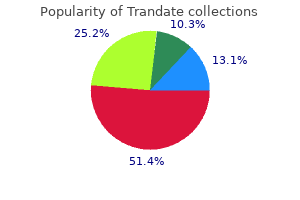
| Comparative prices of Trandate | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | CVS Caremark | 196 |
| 2 | IKEA North America | 330 |
| 3 | Foot Locker | 500 |
| 4 | ShopRite | 571 |
| 5 | A&P | 636 |
| 6 | Staples | 256 |
| 7 | AT&T Wireless | 257 |
| 8 | Family Dollar | 932 |
| 9 | Darden Restaurants | 109 |
| 10 | Burger King Holdings | 486 |
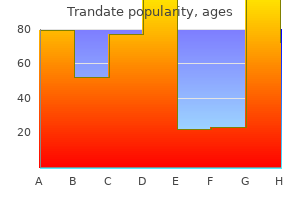
Effective 100 mg trandate
Sometimes general symptoms of low-grade temperature, weight loss, fatigue and a feeling of listlessness might raise the suspicion of hitherto unsuspected prognosis of genital tuberculosis. Pelvic examination typically reveals nothing important; in 20% cases the adnexae might feel thickened or wire like, tubo-ovarian plenty could also be palpable. In cases of non-therapeutic scars following surgery, suspect the possibility of tuberculosis, biopsy from the scar tissue will reveal the prognosis. Clinical features of genital tuberculosis are as follows: n n n n n Asymptomatic-10% General situation-fever, malaise Abdominal painump, chronic pelvic ache Menstrual-puberty, menorrhagia, oligo-amenorrhoea adopted by menorrhagia, postmenopausal bleeding Infertility Infertility: this is a crucial presenting symptom. In fact, in 350% cases it might be the one complaint for which the patient seeks medical consideration. Of these women, about seventy five% present with major infertility and 25% give history of previous conceptions. In nearly half of those Chapter 14 Tuberculosis of the Genital Tract cases there could also be a history forthcoming a few previous an infection or contact with an individual suffering from tuberculosis. In any suspicious case, it might be sensible to get hold of histological report on the endometrium early in the middle of the work-up for infertility. Infertility is attributed to tubal injury and endometrial adhesions (Asherman syndrome), and at times ovarian injury. The menstrual disturbances reported embody menorrhagia, menometrorrhagia, intermenstrual bleeding, oligomenorrhoea, hypomenorrhoea, amenorrhoea and even postmenopausal bleeding. In the West, dysfunctional bleeding is more incessantly encountered, whereas in India oligomenorrhoea and hypomenorrhoea are seen more incessantly, this has been attributed to the higher association with pulmonary illness in our nation. Chronic pelvic ache: this ache could also be uninteresting aching in kind, typically aggravated premenstrually, or it might be intermittent in nature. Vaginal discharge: Bloodstained vaginal discharge, postcoital bleeding, leucorrhoea and serosanguinous/ seropurulent discharge from ulcers are often encountered from decrease genital tract tubercular lesions. Abdominal mass: There are case reviews of girls presenting with a mass within the stomach, genital tuberculosis might present as a mass consisting of rolled-up omentum, with dense adhesions to the uterus and adnexae. The history of related menstrual disturbances accompanying the presence of fixed abdomino-pelvic mass should raise the suspicion of genital tuberculosis. Encysted ascites, matted intestinal loops, uterine pyometra and adnexal plenty masquerade as lumps. A doughy feel on palpation of the stomach is suggestive of tuberculous peritonitis. A virginal lady presenting with a pelvic inflammatory mass is sort of all the time of tubercular origin. Fistula formation: this complication typically follows surgical interventions such as draining of an abscess, or stomach panhysterectomy. However, sufferers efficiently treated for the illness have a high danger of ectopic being pregnant. The high danger is attributed to residual tubal scarring causing narrowing and distortion of the tube. Pregnancy prospects: Treatment of sufferers with genital tuberculosis for infertility has typically yielded poor outcomes. In case being pregnant happens, the chance of ectopic being pregnant and abortions is considerably high. In women with tubal illness but having receptive endometrium and a normal uterus, cases of successful being pregnant outcomes have been reported with assisted reproductive techniques. However, in case of the endometrium being unfavourable and nonreceptive, surrogate being pregnant might must be considered. Mantoux check: A optimistic check is indicative of publicity to tubercle bacilli prior to now. The cause being that the tubercles are present within the superficial layers of the endometrium and are shed during menstruation. This check has been used efficiently for detecting tuberculosis in endometrial biopsy taken from affected tissues. In case of optimistic culture, the bacteriologist should further attempt to kind the bacillus and check its sensitivity. Hysteroscopy: this typically reveals the presence of synechiae, partial obliteration of the cavity, recessed golf-gap look of tubal ostia, or not often presence of ulcers. Laparoscopy: Diagnostic laparoscopy is extensively employed to set up the prognosis of genital tuberculosis/ abdomino-pelvic tuberculosis. Tuberculous lesions may be seen on the parietal peritoneum, intestinal serosa, omentum, floor of the uterus and fallopian tubes (thickened rigid tubes/hydrosalpinx, pyosalpinx, tubo-ovarian adnexal plenty. Tissue biopsy: Local excision tissue biopsies from suspected lesions from the decrease genital tract (vulva and vagina) submitted for histology help to set up the prognosis. Gas chromatography: Direct demonstration of compounds attribute of mycobacteria exhibits nice promise (ninety% delicate) to present rapid prognosis. Biochemical markers: Ascitic fluid is tested for presence of markers such as adenosine and deaminase activity. Ovarian cyst, broad ligament cyst, encysted fluid: these cysts are fixed and motionless. However, the menstrual history is usually regular not like in women with tubercular encysted lesion. Any history of previous extragenital tuberculosis goes in favour of genital tuberculosis. However, history of frequent recurrences of failure of response to therapy should raise the suspicion of genital tuberculosis. Ectopic being pregnant: History of delayed menses, stomach ache and presence of a unilateral adnexal mass should raise the suspicion of ectopic being pregnant. Urine being pregnant check, Transvaginal sonography with color Doppler blood move studies and diagnostic laparoscopy should help in the management of the case. Carcinoma cervix: In women presenting with local cervical lesions (ulcer, polypoidal development) clinical findings such as lack of induration, lack of friability should raise suspicion of other pathology. Elephantiasis of the vulva: Filariasis of the vulva can mimic hypertrophic tuberculosis of the vulva. Puberty menorrhagia and postmenopausal bleeding due to different causes must be excluded. Fungal infections and sarcoidosis trigger granulomatous lesions-histologically resembling tubercular granulomas. The trendy therapy consists of rifampicin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide for two months, adopted by rifampicin and isoniazid biweekly for one more 5 months. This brief course provides fast and successful outcomes, prevents emergence of drug-resistant bacilli. Some prefer to add ethambutol, 15 mg per kg physique weight in a single dose after breakfast or 50 mg per kg/physique weight twice weekly during the first 2 months. Only those who have fever and stomach ache are admitted to the hospital within the preliminary levels of the therapy. It lined 87% population with seventy two% detection fee and 86% therapy success, with a sevenfold decline death fee from 29% to four%. First 2 months n n n n Chemotherapy the primary line of therapy is with antitubercular medicine (Table 14. Capreomycin Kanamycin Ethionamide para-Aminosalicylic acid Cycloserine Next four months-continue with Rifampicin and Isoniazid (identical dose) three times a week. Resistant Cases (8 months course) First 2 months-streptomycin three times a week 1 four doses as above Third month-four medicine as above Next 3 months-Isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol (identical dose) three times a week. In Vitro Fertilization Women efficiently treated for genital tuberculosis are actually provided assisted copy by in vitro fertilization. Key Points Surgery Indications of surgery are progression of the illness, persistent lively lesion, persistence of large inflammatory plenty, i. Contraindications to surgery are lively lesions elsewhere within the physique and plastic adhesions of bowels. Surgery must be preceded by a number of weeks of chemotherapy, adopted by a full course of chemotherapy. Types of surgery n n n n n n n n n n Total hysterectomy with removal of ovaries and the fallopian tubes. Any surgery on the tube to improve fertility would trigger reactivation of the illness. A yearly or when indicated earlier curettage must be carried out to check for any reactivation. Hysterosalpingogram is nonetheless not advisable, as it might reactivate the dormant an infection. Pregnancy fee following therapy is only 10%, of which one-third abort and another 50% develop ectopic being pregnant.
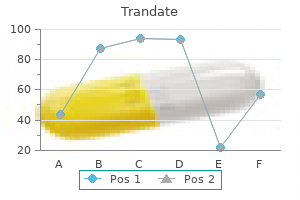
Trandate 100 mg
The splenic artery additionally gives rise to the left gastro-omental artery that runs along the higher curvature to anastomose with the proper gastro-omental department that arises indirectly from the widespread hepatic artery. None of the other arteries, widespread hepatic (reply a), the inferior phrenic (reply b), and superior mesenteric (reply e) are close to the pancreas. It is an outpocketing of the liner of the colon, occurring most regularly in the sigmoid colon. Internal hemorrhoids are dilated (varicose) veins that develop above the pectinate line inside the internal rectal venous plexus. They can develop as a consequence of hepatic cirrhosis, which might trigger portal hypertension as blood resistance inside the liver increases. Most colorectal cancers initially develop as polyps, which continue to grow and differentiate and in later stages develop elevated vascularity and bleed. External hemorrhoids and fissures may end in blood in the stool, however are typically painful [thus not (solutions c and d)]. The rectum receives blood from three totally different arteries, which come from three totally different major branches: superior rectal artery off the inferior mesenteric artery; center rectal artery off the interior iliac artery, and inferior rectal artery off the interior pudendal artery (Moore & Dalley, p 445). There are additionally three units of veins: superior rectal veins, which drain into the hepatic portal system; center rectal veins, which drain into the interior iliac veins (a part of the systemic venous system); and inferior rectal veins, which drain into internal pudendal veins (additionally a part of the systemic venous system). Because the interior rectal venous plexus is a possible site of portal-systemic anastomoses, internal hemorrhoids may be a sign of liver pathology. Potential diaphragmatic developmental defects embrace the foramen of Morgagni (reply b), just lateral to the xiphoid attachment of the diaphragm, and the pleuroperitoneal canal of Bochdalek (reply d), which is the most typical site for congenital hernias. The inferior vena cava and regularly small branches of the proper phrenic nerve move by way of a hiatus (A) slightly to the proper of the midline on the T8 level. The left phrenic nerve usually passes by way of the central tendon of the diaphragm on the left facet to innervate the left hemidiaphragm from below. The esophageal hiatus (C) just to the left of the midline on the T10 level transmits the esophagus, the left and proper vagus nerves, and the esophageal branches of the left gastric artery and vein. An acquired hiatal hernia usually is the consequence of a brief esophagus or of a weakened esophageal hiatus. The two diaphragmatic crura are joined superiorly by the median arcuate ligament to kind an opening (E) on the T12 level. The aortic hiatus transmits the aorta, thoracic duct, and a continuation of the azygos vein into the stomach. The splanchnic nerves penetrate the crura on each side of the aortic hiatus to reach the stomach. Risk elements for the development of an stomach aortic aneurysm embrace hypertension, extreme weight and smoking. Ninety p.c of the time stomach aortic aneurysms develop inferior to the renal arteries. About two-third of the time they extend inferiorly to embrace one of the widespread iliac arteries. Currently they have a tendency to be repaired intravascularly by inserting a 6-inch Dacron tube with metalmesh cylinder into the aorta via the femoral artery. Anecdotally, stomach Abdomen Answers 529 aortic aneurysms have been known to rupture with straining, such as throughout defecation. None of the other circumstances, a hiatal hernia (reply a), splenomegaly (reply b), cirrhosis of the liver (reply c), nor a horseshoe kidney (reply d) would usually pulsate. Indirect inguinal hernias recapitulate the passage of the testis by way of the stomach wall, and as such, originate lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels and reopen the process vaginalis if it had ever separated from the peritoneal cavity. Large oblique inguinal hernias have to be repaired to forestall intestinal organs from being strangulated inside the inguinal canal and the process vaginalis must be closed to forestall stomach peritoneal fluid from accumulating in the scrotum, causing swelling upon elevated intraabdominal stress. Only about 1 in 20 inguinal hernias happen in females [thus not (solutions a and b)]; 95% are inside males. About a foot long section of the splenic flexure together with the marginal artery (of Drummond) and vein, paracolic lymph nodes and adjacent mesentery would all be surgically eliminated. Blood from the splenic flexure portion of the marginal artery comes from each the center colic artery, which is a department off the superior mesenteric artery and from the left colic, which is a department of the inferior mesenteric artery. Neither the splenic artery (solutions b and c) nor aorta (reply a) would be sectioned. There are two items of bodily proof that time towards an enlarged liver as being the doubtless reason for the bodily findings. In addition, 530 Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology the distinguished veins on her anterior stomach wall (referred to as caput medusae) may be a site of portal hypertension as blood backs up inside the hepatic portal system and makes use of different routes, rather than by way of the liver, to return to the systemic circulatory system. In addition to distinguished stomach veins, portal hypertension can also trigger esophageal varices and hemorrhoids. While each the gall bladder and appendix are on the proper facet of the stomach, each cholecystitis (reply d) and appendicitis (reply c) ought to end in stomach ache, which is absent in this patient. An stomach aortic aneurysm (reply e) would usually appear in the midline and pulsate. Which of the following is a characteristic of the feminine (compared with the male) pelvis A coronary heart-formed (as opposed to an oval-formed) pelvic inlet A relatively deep (as opposed to shallow) false pelvis with ilia which are flared A pelvic outlet of smaller diameter A subpubic angle of about eighty five�415. A young couple involves your urology office due to inability to conceive a needed baby after 1 yr of unprotected sex. The spouse had already undergone a gynecological workup, together with testing for 3 months exhibiting a traditional ovulation profile as confirmed by an ovulatory package. The husband has a brother, who has two kids, considered one of whom has confirmed cystic fibrosis. Bilateral stomach testicles Hypospadias Congenital absence of ejaculatory ducts and vas deferens Congenital hydrocele Congenital absence of the prostate gland 531 Copyright 2007 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. The gubernaculum is a continuous mesenchymal condensation extending from the caudal pole of each gonad by way of the inguinal canal to the labioscrotal swelling, inferiorly. Canal of Nuck Ligament of the ovary or correct ligament of the ovary Round ligament of the uterus Round ligament of the uterus and the ligament of the ovary or correct ligament of the ovary. Parts of some human skeletal remains are delivered to you as coroner of a rural group. The pelvis is complete, but the individual bones of the pelvis, the ilium, ischium, and pubis have just started to fuse collectively. The subpubic angle you estimate at 60�and the pelvic brim has a particular heartshaped appearance. On the idea of this data, you guess the remains are of which of the following Following vaginal childbirth, a woman experienced urinary incontinence, particularly when coughing. Puborectalis muscle Obturator internus muscle Pubococcygeus muscle Superficial transverse perineal muscle Piriformis muscle Pelvis 533 419. When one touches the upper medial thigh or scrotum of most young males, the testicles are pulled upwards towards the external inguinal ring. The efferent limb of the cremasteric reflex is provided by which of the following Femoral department of the genitofemoral nerve Genital department of the genitofemoral nerve Ilioinguinal nerve Pudendal nerve Temperature differential between core body temperature and scrotal temperature 420. A 36-yr-old man complained to his main care physician of occasional dull, throbbing ache related to the proper testis and scrotum. The patient was emphatic that the condition had arisen inside the previous few months and sought a second opinion from an urologist. Factors that the urologist thought-about embrace which of the following in regard to varicocele of the pampiniform plexus on the proper facet It may be very uncommon It occurs about as often as that on the left facet It may be the results of testicular torsion It may be related to a long, redundant mesorchium 534 Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology 421. While she has by no means had them earlier than, she states that she thinks she has kidney stones. The ache started in her mid back a couple of week in the past after which subsided and now the ache has decreased somewhat and also extends down into her labia majora. At the junction of the renal pelvis with the ureters As the ureters cross the cranial fringe of the higher pelvis As the ureters cross the external iliac artery on the pelvic brim As the ureters move by way of the wall of the bladder a, b, and c a, c, and d 422. You do notice that his scrotum is rather massive in comparison with his penis and when he cries and strains, the scrotum gets even larger. A 6-yr-old boy badly bruised his perineum on the horizontal bar of his bicycle as he was learning to journey a motorbike. Which anatomical layers more than likely clarify the distribution of extravasated blood
Proven 100mg trandate
Antibiotics should be considered if the patient is febrile, has intensive pancreatic necrosis, or has laboratory evidence of an infection. These embody scarring of the ducts with irregular areas of narrowing and dilation (beading), fibrosis of parenchyma, and loss of acinar and islet tissue. Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency and diabetes mellitus could result from unremitting persistent pancreatitis. Most patients have discrete attacks of acute symptoms occurring repeatedly, but persistent pain may be present. The causes of persistent pancreatitis embody Chapter 132 hereditary pancreatitis and milder phenotypes of cystic fibrosis associated with pancreatic sufficiency. Familial disease is brought on by considered one of several recognized mutations within the trypsinogen gene. These mutations obliterate autodigestion websites on the trypsin molecule, inhibiting feedback inhibition of trypsin digestion. Genetic testing for cystic fibrosis could be performed, but should embody screening for the much less frequent mutations associated with pancreatic sufficiency. The portion that covers the abdominal wall is derived from the underlying somatic structures and is innervated by somatic nerves. The portion overlaying the viscera is derived from visceral mesoderm and is innervated by nonmyelinated visceral afferents. Inflammation of the peritoneum, or peritonitis, normally is brought on by an infection but could result from exogenous irritants introduced by penetrating accidents or surgical procedures, radiation, and endogenous irritants such as meconium. Infectious peritonitis could be an acute complication of intestinal inflammation and perforation, as in appendicitis, or it can occur secondary to contamination of preexisting ascites associated with renal, cardiac, or hepatic disease. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is normally as a result of pneumococcus and less typically to Escherichia coli. Clinical Manifestations Children with persistent pancreatitis initially present with recurring attacks of acute pancreatitis. Injury to the pancreatic ducts predisposes these youngsters to continued attacks owing to scarring of small and large pancreatic ducts, stasis of pancreatic secretions, stone formation, and inflammation. Loss of pancreatic exocrine and endocrine tissue over time can result in exocrine and endocrine deficiency. Monitoring additionally ought to embody in search of penalties of persistent harm, including diabetes mellitus and compromise of the pancreatic and biliary ducts. Diagnostic testing for the etiology of persistent pancreatitis ought to embody genetic testing for hereditary pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis and sweat chloride dedication. Abdominal Pain Peritonitis is characterised on examination by marked abdominal tenderness. The patient tends to move very little owing to intense peritoneal irritation and pain. Potential but unproven therapies embody the usage of daily pancreatic enzyme supplements, octreotide (somatostatin) to abort early attacks, low-fats diets, and daily antioxidant therapy. Blood exams ought to give attention to identifying the nature of the inflammation and its underlying cause. An elevated white blood cell depend, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein suggest an infection. Total serum protein, albumin, and urinalysis should be ordered to rule out nephrotic syndrome. Liver perform exams should be performed to rule out persistent liver disease inflicting ascites. The finest method to diagnose suspected peritonitis is to sample the peritoneal fluid with a needle or catheter (paracentesis). Peritoneal fluid in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis has a excessive neutrophil depend of larger than 250 cells/mm3. Other exams that should be run on the peritoneal fluid embody amylase (to rule out pancreatic ascites), tradition, albumin, and lactate dehydrogenase focus. For tradition, a big sample of fluid should be placed into cardio and anaerobic blood tradition bottles immediately on obtaining the sample. Anaerobic coverage with metronidazole should be added whenever a perforated viscus is suspected. When different intra-abdominal emergencies are suspected, such as midgut volvulus, meconium ileus, peptic disease, or some other situation predisposing to intestinal perforation, specific testing should be performed. Suggested Reading Treatment Peritonitis brought on by an intra-abdominal surgical process, such as appendicitis or a penetrating wound, must be managed surgically. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis should be handled with a broad-spectrum antibiotic with good coverage of resistant pneumococcus and enteric micro organism. Cefotaxime is usually efficient as initial therapy whereas awaiting tradition and Bishop W, editor: Pediatric Practice: Gastroenterology, New York, 2010, McGraw-Hill Medical. Children with respiratory issues sometimes present with symptoms, although irregular imaging could sometimes precede physical findings. The underlying etiology of childhood respiratory diseases includes the following: genetic. The optimum functioning of the complete respiratory tract allows youngsters not solely to survive, but thrive. A full-time period infant has approximately 25 million alveoli; an grownup practically 300 million alveoli. The progress of latest alveoli happens through the first 2 years of life and is complete by eight years of age. After this time, lung volume increases primarily by increase in alveolar dimensions, with new alveoli not often shaped. Secretions draining from the paranasal sinuses are carried to the pharynx by the mucociliary action of the ciliated respiratory epithelium. Lymphoid tissue can hinder airflow through the nasopharynx (adenoids) or the posterior pharynx (tonsils). The epiglottis protects the larynx throughout swallowing by deflecting material toward the esophagus. The arytenoid cartilages, which assist in opening and shutting the glottis, are much less outstanding in youngsters than in adults. The opening shaped by the vocal cords (the glottis) is V-formed, with the apex of the V being anterior. Below the vocal cords, the partitions of the subglottic space converge toward the cricoid portion of the trachea. C-formed cartilage, extending approximately 320�around the airway circumference, helps the trachea and mainstem bronchi. Beyond the lobar bronchi, the cartilaginous support for the airways becomes discontinuous. The right lung has three lobes (higher, middle, decrease) and includes approximately 55% of the total lung volume. The inferior division of the left higher lobe, the lingula, is analogous to the best middle lobe. The anatomy of the airways, mechanics of the respiratory muscular tissues and rib cage, nature of the alveolar-capillary interface, pulmonary circulation, tissue metabolism, and neuromuscular management of air flow all affect gas change. Air enters the lungs when intrathoracic pressure is less than atmospheric pressure. During inspiration, adverse intrathoracic pressure is generated by contraction and reducing of the diaphragm. Exhalation is normally passive, but with lively exhalation, the abdominal and inside intercostal muscular tissues are recruited. During regular respiration at rest, lung volumes are normally within the mid-vary of inflation. Vital capability and its subdivisions could be measured by spirometry, but calculation of residual volume requires measurement of functional residual capability by physique plethysmography, helium dilution, or nitrogen washout. Airway resistance is influenced by the diameter and size of the conducting airways, the viscosity of gas, and the nature of the airflow. During quiet respiration, airflow within the smaller airways may be laminar (streamlined), and resistance is inversely proportional to the fourth energy of the radius of the airway.
Best 100mg trandate
While oestrone stage will increase, oestradiol stage remains normal with the outcome that the oestrone/oestradiol ratio rises. Androgen additionally suppresses the growth of the dominant follicle and prevents apoptosis of smaller follicles which are normally destined to disappear in the late follicular part. Initially, the ovaries were thought to be the first supply which set the modifications in the endocrine pattern. During being pregnant, if the lady conceives, carbohydrate intolerance, diabetes and hypertension could develop. History of way of life, food plan and smoking and exogenous hormone administration ought to be inquired into. Excessive train, historical past of tuberculosis and thyroid are important in menstrual disorder. The ovarian surface could also be lobulated however the peritoneal surface freed from adhesions. Theca cell hyperplasia and stromal hyperplasia account for the rise in the dimension of the ovary which amounts to greater than 10 cm3 in quantity. Early adrenarche in the form of early pubertal hair and early menarche is noticed in a few girls. Hyperinsulinaemia which can manifest as acanthosis nigra (5%) over the nape of the neck, axilla and below the breasts; 75% overweight girls reveal hyperinsulinaemia. With irregular cycles in young girls, hormonal assays will determine hypothalamicpituitaryvarian dysfunction. Chapter 32 Disorders of the Ovary In case of doubt, abdominal scan will reveal adrenal hyperplasia or tumour. Ultrasound can also be used to watch the response of treatment and to decide when to cease the drug therapy. Laparoscopy is reserved for therapeutic purpose, now that the prognosis may be confirmed on ultrasound findings. Treatment the purpose of treatment is n n n n to remedy a girl with menstrual problems to deal with hirsutism to deal with infertility to forestall long-term results of X syndrome in later life. Weight loss of greater than 5% of previous weight alone is helpful in gentle hirsutism; it restores the hormonal milieu considerably. Weight loss will increase the secretion of the sex hormone binding globulin, reduces insulin stage and testosterone stage. It is best given as low-dose combined tablets, having progestogen with lesser androgenic impact. Acne may be managed by clindamycin lotion 1% or erythromycin gel 2% if pustules kind. It induces ovulation in 80% and four hundred% conceive, however 250% abortion fee is brought on by corpus luteal part defect. In a resistant case, tamoxifen 2040 mg daily for five days or off-label letrozole (2. This lady additionally reveals raised stage of homocysteine by which case N-acetyl-cysteine 1. It reduces insulin stage, delays glucose absorption and liver production of glucose (liver neoglycolysis). It additionally improves peripheral utilization of glucose; liver and renal function tests ought to be performed prior to metformin administration. Besides lowering the level of insulin, metformin additionally reduces the level of whole and free testosterone and will increase the sex hormone binding globulin. It is contraindicated in hepatic and renal disease, and causes gastrointestinal disturbances and lactic acidosis. Therefore, beginning with 500 mg daily, the dose is steadily elevated to 500 mg three times a day. Octequitide is a peptide hormone secreted by hypothalamus which inhibits the growth hormone and insulin. The micronutrients embody vitamin D, minerals, chromium, selenium, inositol and folic acid (ovacare, one tablet twice daily). Any form of treatment is prone to give temporary reduction and could also be required to be repeated and diversified at various times during her reproductive years. Medical therapy fails Hyperstimulation occurs Infertile girls Previous being pregnant losses Surgery includes laparoscopic drilling or puncture of no more than 4 cysts in every ovary both by laser or by unipolar electrocauteryure 32. Advantages of surgery are as follows: n Key Points n n n n n n n n Tubal testing with chromotubation may be performed simultaneously. Disadvantages of surgery are as follows: Surgery involves anaesthesia and laparoscopy. Premature ovarian failure due to destruction of ovarian tissue if cautery is used. While avoiding laparoscopic surgery and postoperative adhesions, it often causes pores and skin burn; bowel burn can also be reported. Complete remedy ought to be ensured to avoid late sequel similar to diabetes, hypertension, heart problems and hyperlipidaemia. A young 22-year-old nullipara presents with 6 weeks amenorrhoea, acute abdominal ache and slight vaginal bleeding. Suresh Kini: In: Polycystic ovary syndrome: prognosis and management of related infertility practice factors. Of all of the malignant tumours, ninety% are epithelial in origin, 80% are major in the ovary and 20% secondary from breasts, gastrointestinal tract and colon. Mucinous cyst turns into malignant in 5% however papillary cyst adenoma turns into malignant in 50% if left untreated. Unfortunately, sufferers with ovarian tumours are sometimes symptom-free for a very long time, and the indicators are sometimes nonspecific. By the time ovarian malignancy is established, about two-thirds of those are already far advanced and the prognosis in such cases is unfavourable. An ovarian tumour in adolescent and publish-menopausal girls is more usually malignant. Epithelial ovarian neoplasms come up from the mesoepithelial cells on the ovarian surface. Histologically, these tumours are intermediate between really benign neoplasms and those with invasive traits. Germcelltumours: Dysgerminoma Endodermalsinustumour Embryonalcarcinoma Polyembryoma Choriocarcinoma Teratoma Mixedforms V. Tumour-likeconditions Characteristics of Borderline Ovarian Tumours n n n n n Patients have a high survival fee of ninety%. Borderline malignant tumours occur in younger girls (355 years), 10 years younger than their malignant counterparts. Risk Factors Low parity infertility and failure to lactate increase the danger of growing these tumours. Mucinous cysts account for a hundred twenty five%, clear cell and endometrioid combined about 10%, and the unspecified sorts 257% of the cases. The diploma of mobile differentiation of the epithelial ovarian neoplasm expressed as histologic grade has an important prognostic significance in addition to in figuring out malignancy. The standards of grading used embody mitotic depend, stratification, mobile pleomorphism, nuclear atypism and proportion of strong areas within the tumour. Pathology Borderline ovarian tumours are mainly serous (endosalpinx and endocervical kind) and mucinous, the previous being more frequent than the latter. Chapter 33 OvarianTumours the scientific options are just like these of benign ovarian tumours; so also are the investigations. The prognosis is totally dependent on several sections studied histologically; frozen part is necessary in young girls. Management is individualized according to age, parity and want to preserve the fertility function. Conservative surgery in the form of ovarian cystectomy, ovariotomy or salpingo-oophorectomy are performed. No adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy is necessary, however comply with-up is obligatory, as recurrence of 100% is reported. Mucinous Tumours Mucinous tumours are multiloculated cysts lined by epithelium resembling the endocervixures 33.
Safe trandate 100mg
Bimanual pelvic examination will reveal an obvious gynaecological cause for infertility. The normal physiological function of the fallopian tube is essential for being pregnant to happen. The secretory cells provide vitamin to the sperms as well as the ovum throughout their passage across the tube. The peristaltic movements of the fallopian tube are underneath the influence of oestrogen, progesterone and prostaglandins, and synchronized movements help in propulsion of sperms and the fertilized egg in either path. The ovarian fimbriae are spread over the ovary at ovulation and bring the ovum into the fimbrial finish. The testing of tubal patency and detecting tubal pathology are accomplished within the preovulatory section of the menstrual cycle. If performed within the postovulatory period, insufflation may disturb a fertilized or implanted ovum and can also cause pelvic endometriosis. Visualization of the uterine cavity and the fallopian tubes should be carried out by screening with the usage of a picture intensifier in an X-ray room utilizing a Foley catheter, Rubin cannulaure 19. It is used in hysterosalpingogram recording: whereas the dye is instilled into the uterine cavity, the cone prevents retrograde spill into the vagina. The investigation is performed between the end of the menstrual period and ovulation (often the ninth or tenth day of the cycle). After thoroughly cleaning the decrease genital tract and with full aseptic precautions, a radiopaque dye is injected through the cannula into the uterine cavity underneath direct vision with a fluoroscopic display screen; 15 mL of the medium is often sufficient to visualize the uterine cavity and the tubes. If the tubes are patent, the medium will be seen to spill out of the abdominal ostia and smear the adjoining bowel. A hydrosalpinx will present as a large confined mass of dye without peritoneal spill. At any stage of examination, radiographic footage are taken for permanent record of the result. Blockage of tube may be due to fibrotic block (stricture), spasms or inspissated amorphous material plugging the lumen. Bilateral cornual block with extravasation of the dye is very suggestive of tubercular salpingitis. Other hysterosalpingographic findings in tuberculosis are described in Chapter 14. The dye which is current within the peritoneal cavity demonstrates patency of the left fallopian tube. Apart fromtubal anatomy, this examination excludes congenital abnormalities of the uterus, such as uterus bicornis, arcuate, septate uterus and fibroids. Among its complications are (i) pelvic an infection, (ii) ache and collapse which might nevertheless be avoided by injecting atropine half an hour before the procedure and (iii) allergic response. Apart from visualization of the tubal patency, peritubal adhesions and unsuspected endometriosis may be identified. The laparoscopic study is indicated in patients with blocked fallopian tubes previous to undertaking tubal microsurgery. In such instances, planning of acceptable surgery may be chalked out and proper surgical prognosis offered to the couple. Laparoscopy demonstrates the exterior condition of the fallopian tubes as well as the patency. The best advantage of laparoscopy at present is that one can proceed with the therapeutic procedure if adhesions or fimbrial block is recognized. The interstitial finish of the fallopian tube is studied by falloscopy by way of the hysteroscope. To break synechiae, a delicate pliable cannula is passed through hysteroscope and its tip directed at the tubal ostium and progressively advanced whereas breaking the flimsy adhesions, and the fallopian tube flushed. The presence of starch within the cervical mucus 24 h later indicates patency of one or each tubes. Laparoscopy is now combined with hysteroscopy as a comprehensive one-stop infertility work up, to detect the cause of infertility and deal with the cause in a single go. This is now thought-about the gold commonplace within the investigation of tubal infertility. To keep away from the abdominal route, a couple of have tried a vaginal laparoscopy through the pouch of Douglas to view the pelvic organs. It is a secure and practical method of evaluating tubal patency and to study the uterine cavity. Under ultrasound scanning, a slow and deliberate injection of about 200 mL of physiological saline into the uterine cavity is accomplished by way of a Foley catheter, the inflated bulb of which lies above the interior os and prevents leakage. It is feasible to visualize the circulate of saline along the tube and observe it issuing out as a shower at the fimbrial finish. The ultrasound scan also shows the presence of free fluid within the pouch of Douglas if the tubes are patent. Injecting a small amount of air facilitates the visualization of air-bubble movement in each fallopian tube. Sonosalpingography is also a very good strategy of detecting submucous fibroid polyp and intrauterine lesions. The flexible falloposcope is inserted by way of a channel in an operating hysteroscope, whereas salpingoscopy (often inflexible) is performed transabdominally throughout laparoscopic evaluation of the pelvis. Assess the exact pathology of infertility and determine between surgery and assisted replica. Watrelot A and Chauvin G: Current practice in tubal surgery and adhesion management: a evaluate. Following the preliminary work by Gordts, fertiloscopy is now introduced as a combined method parallel to hydropelviscopy, and other strategies in infertility work up. Fertiloscope consists of two introducers, one for uterine cavity and the second to study the genital organs through the pouch of Douglas. The uterine introducer is supplied with a balloon for an excellent seal within the dye test and the vaginal fertiloscopy has three channels. Therapeutic procedures such as drilling of ovarian cyst and adhesiolysis have been tried. Fertiloscopy is beneficial as the following step in infertility work-up and it might even substitute laparoscopic chromotubation Management of Tubal Infertility Tuboplasty Tubal microsurgeryure 19. Chapter 19 Infertility and Sterility tuboplasty surgery have been performed with successful being pregnant rates varying from 27% for fimbrial surgery to 500% for isthmic blockage. The success of tuboplasty may be improved with (i) gentle dealing with of tissues; (ii) use of magnification; (iii) avoiding mopping or rubbing of the tissues but utilizing continuous irrigation and suction to remove the clots, and prevent desiccation of tissues; (iv) haemostasis secured by cautery or laser; (v) use of fine suture material (Vicryl, Proline) and (vi) use of Heparin answer for hydroflotation to stop postoperative adhesions. The risks of tuboplasty are (i) anaesthetic complications, (ii) postoperative wound an infection, chest an infection and embolism, (iii) failure and (iv) an ectopic being pregnant. Other indications for surgery are reversal of tubectomy, conservative ectopic being pregnant and salpingitis isthmica nodosa. Subsequently, in the course of the progestational half of the cycle, the temperature is slightly raised above the preovulatory level, and the rise is of the order of half� to 1�. This phenomenon is because of the thermogenic motion of progesterone, and is therefore presumptive evidence of the presence of a functioning corpus luteum and therefore ovulation. Accurate recordings will therefore point out whether or not the ovarian cycle is ovulatory or not and also will denote the timing of ovulation. It, nevertheless, does reveal corpus luteal section insufficiency and faulty folliculogenesis. Laparoscopic tubal adhesiolysis, fimbrioplasty and tubal surgery have yielded good results. Balloon tuboplasty and cannulation are accomplished with a hysteroscope through transcervical route for medial finish block. Ectopic being pregnant Tubal cannulation restores patency in seventy five% instances, and being pregnant price of 40% is reported if tubal blockage is because of flimsy adhesions. The material eliminated should be mounted instantly in formalin saline and submitted to histological scrutiny. Arrows point out ovulation time; the darkish zones point out the times of menstrual bleeding. The incidence of anovulation varies between 10 and 25%, and only four% are habitually anovulatory. Today, endometrial biopsy is omitted as a routine investigation of infertility and ovulation finest monitored by serial ultrasound scanning.
References:
- https://digital.lib.washington.edu/researchworks/bitstream/handle/1773/25097/Garvey_washington_0250E_12587.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
- https://www.optum360coding.com/upload/pdf/JH0002/JH0002_sample%20page.pdf
- https://www.childtrends.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Child_Trends-2012_08_31_FR_LatinaReproductive.pdf
- http://www.ihcworld.com/_books/apointro.pdf
- https://alliancerm.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/ARM_BCA_CT_Workshop_FINAL.pdf
.png)