Trusted aggrenox caps 25/200 mg
Noninvasive exams, similar to elastography or fibrosis biomarkers, may be used to assess threat of fibrosis, however referral to a liver specialist and liver biopsy may be required for definitive analysis (43a). Interventions that improve metabolic abnormalities in sufferers with diabetes (weight reduction, glycemic management, and remedy with particular drugs for hyperglycemia or dyslipidemia) are also helpful for fatty liver disease (forty four,45). Treatment with liraglutide and with sodium�glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (dapagliflozin and empagliflozin) In type 2 diabetes, severe hypoglycemia is related to reduced cognitive operate, and people with poor cognitive operate have more severe hypoglycemia. In an extended-time period study of older sufferers with type 2 diabetes, people with one or more recorded episode of severe hypoglycemia had a stepwise improve in threat of dementia (38). Tailoring glycemic remedy may assist to prevent hypoglycemia in people with cognitive dysfunction. Nutrition In one study, adherence to the Mediterranean diet correlated with improved cognitive operate (40). However, a recent Cochrane evaluate found insufficient Age-particular hip fracture threat is considerably increased in people with both care. Fracture prevention methods for people with diabetes are the same as for the overall population and include vitamin D supplementation. For sufferers with type 2 diabetes with fracture threat components, thiazolidinediones (65) and sodium� glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (sixty six) ought to be used with warning. Hearing Impairment Hearing impairment, both in high frequency and low/midfrequency ranges, is more widespread in people with diabetes than in those without, maybe because of neuropathy and/or vascular disease. In those with prediabetes, weight reduction via healthy vitamin and bodily activity may scale back the development toward diabetes. Further testing (similar to luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone ranges) may be needed to distinguish between primary and secondary hypogonadism. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Age-adjusted rates of obstructive sleep apnea, a threat factor for cardiovascular disease, are considerably greater (four- to 10-fold) with obesity, especially with central obesity (seventy five). The prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea within the population with type 2 diabetes may be as high as 23%, and the prevalence of any sleepdisordered respiration may be as high as 58% (76,seventy seven). Sleep apnea remedy (life-style modification, continuous optimistic airway stress, oral appliances, and surgery) considerably improves high quality of life and blood stress management. If initial screening results are regular, checking fasting glucose yearly is advised. B Mean ranges of testosterone are lower in men with diabetes compared with agematched men without diabetes, however obesity is a significant confounder (seventy two,73). Testosterone substitute in men with symptomatic hypogonadism may have benefits together with improved sexual operate, well-being, muscle mass and energy, and bone density (74). In Periodontal disease is more severe, and may be more prevalent, in sufferers with diabetes than in those without (eighty one,eighty two). Current evidence suggests that periodontal disease adversely affects diabetes outcomes, although evidence for remedy benefits stays controversial (24). Psychosocial/Emotional Disorders Prevalence of clinically vital psychopathology diagnoses are considerably more widespread in people with diabetes than in those without the disease (83). Diabetes misery is addressed in Section 5 "Lifestyle Management," as this state is very common and distinct from the psychological disorders mentioned under (eighty four). Common diabetes-particular considerations include fears related to hypoglycemia (87, 88), not meeting blood glucose targets (85), and insulin injections or infusion (89). Onset of complications presents one other crucial point when anxiety can happen (90). General anxiety is a predictor of injection-related anxiety and related to fear of hypoglycemia (88,ninety two). Fear of hypoglycemia and hypoglycemia unawareness typically co-happen, and interventions aimed toward treating one typically profit both (93). Fear of hypoglycemia may explain avoidance of behaviors related to lowering glucose similar to increasing insulin doses or frequency of monitoring. Elevated depressive signs and depressive disorders affect one in four sufferers with type 1 or type 2 diabetes (ninety nine). Thus, routine screening for depressive signs is indicated in this high-threat population together with people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes mellitus, and postpartum diabetes. Regardless of diabetes type, ladies have considerably greater rates of depression than men (a hundred). Routine monitoring with patientappropriate validated measures can help to determine if referral is warranted. Adult sufferers with a historical past of depressive signs or disorder need ongoing monitoring of depression recurrence within the context of routine care (ninety six). When a patient is in psychological remedy (speak remedy), the psychological health provider ought to be included into the diabetes remedy group (one hundred and one). A History of depression, present depression, and antidepressant medication use are threat components for the event of type 2 diabetes, especially if the person has other threat components similar to obesity four. In addition, a evaluate of the medical routine is recommended to determine potential treatmentrelated effects on starvation/ caloric consumption. B Estimated prevalence of disordered consuming behaviors and diagnosable consuming disorders in people with diabetes varies (102�104). For people with type 1 diabetes, insulin omission causing glycosuria in order to shed weight is essentially the most commonly reported disordered consuming behavior (one hundred and five,106); in people with type 2 diabetes, bingeing (excessive food consumption with an accompanying sense of care. For people with type 2 diabetes handled with insulin, intentional omission can be frequently reported (107). People with diabetes and diagnosable consuming disorders have high rates of comorbid psychiatric disorders (108). People with type 1 diabetes and consuming disorders have high rates of diabetes misery and fear of hypoglycemia (109). When evaluating signs of disordered or disrupted consuming in people with diabetes, etiology and motivation for the behavior ought to be thought-about (104,one hundred ten). Adjunctive medication similar to glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (111) may assist people not solely to meet glycemic targets but also to regulate starvation and food consumption, thus having the potential to scale back uncontrollable starvation and bulimic signs. Serious Mental Illness Recommendations olanzapine, require larger monitoring due to an increase in threat of type 2 diabetes related to this medication (113). Multipayer patient-centered medical house implementation guided by the chronic care model. The effect of intensive remedy of diabetes on the event and development of longterm complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Effect of glycemic exposure on the danger of microvascular complications within the Diabetes Control and Complications Trialdrevisited. Is self-efficacy related to diabetes self-administration throughout race/ethnicity and health literacy? Selfefficacy, problem fixing, and social-environmental assist are related to diabetes selfmanagement behaviors. Comparison of the position of self-efficacy and illness representations in relation to dietary self-care and diabetes misery in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Self-efficacy, outcome expectations, and diabetes self-administration in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. B Studies of individuals with serious psychological illness, significantly schizophrenia and other thought disorders, present considerably increased rates of type 2 diabetes (112). People with schizophrenia ought to be monitored for type 2 diabetes due to the known comorbidity. Disordered thinking and judgment can be expected to make it difficult to interact in behaviors that scale back threat components for type 2 diabetes, similar to restrained consuming for weight administration. Coordinated administration of diabetes or prediabetes and serious psychological illness is recommended to obtain diabetes remedy targets. In addition, those taking second-technology (atypical) antipsychotics, similar to 14. The influence of sleep amount and sleep high quality on glycemic management in type 2 diabetes: a scientific evaluate and meta-evaluation. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommended immunization schedule for youngsters and adolescents aged 18 years or youngerdUnited States, 2017. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommended immunization schedule for adults aged 19 years or olderd United States, 2017.
Safe 25/200 mg aggrenox caps
Tracking difficulties and paranoid ideation during hashish and alcohol intoxication. Naltrexone versus acamprosate in the remedy of alcohol dependence: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Intracranial hemorrhage related to cocaine abuse: a potential post-mortem research. Separate mechanisms for behavioral, cardiovascular, and hormonal responses to dextroamphetamine in man. Divalproex sodium in alcohol withdrawal: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Lorazepam and meprobamate dose effects in humans: behavioral effects and abuse liability. Phenomenologic comparison of the idiopathic psychosis of schizophrenia and drug-induced cocaine and phencyclidine psychoses: a retrospective research. Carbamazepine remedy in sufferers discontinuing lengthy-term benzodiazepine therapy: effects on withdrawal severity and outcome. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of baclofen for cocaine dependence: preliminary effects for people with persistent patterns of cocaine use. Caffeine dependence syndrome: evidence from case histories and experimental evaluations. Carbamazepine versus oxazepam in the remedy of alcohol withdrawal: a doubleblind research. Alcohol and reminiscence: amnesia and quick-term reminiscence perform during experimentally induced intoxication. Buprenorphine versus heroin dependence: comparison of toxicologic and psychopathologic traits. Efficacy of bupropion and nortriptyline for smoking cessation among people vulnerable to or with persistent obstructive pulmonary disease. Changes in temper, craving, and sleep during quick-term abstinence reported by male cocaine addicts. Cases of dying and blindness from Columbian spirits and different methylated preparations. Before proceeding further, some words are in order concerning the name of this syndrome. Clinical features the onset is normally inside a day or two of the diminution in dopaminergic tone; exceptionally, the syndrome might seem inside an hour or, at the different extreme, be delayed for weeks (Keck et al. The full syndrome, as famous, is characterised by delirium, fever, rigidity, and autonomic instability, and, though it typically presents with rigidity, any considered one of these parts may be the presenting function (Addonizio et al. Delirium could also be profound, and sufferers may develop stuporous catatonia (Koch et al. Rigidity could also be of either the lead pipe or cogwheel type, is often generalized, and could also be profound, to the purpose of compromising chest wall movement. Rigidity could also be accompanied by a generalized, coarse tremor and, in some cases, dystonia or chorea might happen. Autonomic instability manifests with pallor, diaphoresis, tachycardia, and elevated blood pressure, which may be quite labile. Rhabdomyolysis might happen (Jones and Dawson 1989), with myoglobinuria and, in some cases, acute renal failure. The white blood cell rely is often elevated to round 15 000 cells/mm3, and the creatine phosphokinase degree is likewise increased, typically to round 15 000 models/L. Lactate dehydrogenase, serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, and alkaline phosphatase levels are additionally typically elevated. Aspiration or pulmonary emboli might happen and, in some cases, respiratory failure might happen secondary to extreme rigidity of the chest wall. Rarely, rigidity or catatonia might persist for months, even in cases in which a depot antipsychotic has not been used (Caroff et al. Differential prognosis Malignant hyperthermia is distinguished by its association with the use of inhalational anesthetic brokers or succinylcholine. Recently, a very related syndrome has been described secondary to abrupt discontinuation of lengthy-term remedy with either oral (Turner and Gainsborough 2001) or intrathecal (Coffey et al. Moderate or extreme intoxication with phencyclidine is distinguished by the absence of rigidity and by the presence of nystagmus or myoclonus. As almost all cases of excited catatonia happen in schizophrenia, and as most sufferers with schizophrenia are handled with an antipsychotic, the general clinical image might seem much like the neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Helpful diagnostic points embrace the history of previous excited catatonia and the fact that deadly catatonia first presents with a rise in agitation, in contrast to the neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which generally presents with rigidity and delirium (Castillo et al. Etiology As famous earlier, the syndrome happens secondary to an abrupt diminution of dopaminergic tone, and most commonly this happens secondary to either initiation of remedy with an antipsychotic or a substantial dose improve (Kellam 1990). Although most cases have occurred secondary to remedy with first-era brokers, corresponding to haloperidol, the neuroleptic malignant syndrome has additionally been seen with second-era brokers, corresponding to risperidone (Levin et al. Other dopamine blockers may trigger the syndrome, corresponding to metoclopramide (Friedman et al. There are additionally reports of the syndrome occurring after an antidepressant was added to a secure dose of an antipsychotic, for instance with the addition of venlafaxine to trifluoperazine (Nimmagadda et al. The neuroleptic malignant syndrome has additionally been seen upon the cessation of remedy with not solely levodopa (Friedman et al. In addition, the neuroleptic malignant syndrome has been reported secondary to the use of the dopamine-depleting drug tetrabenazine (Ossemann et al. Intensive supportive care is required, with particular attention to fluid and electrolyte balance; adequate hydration should be assured to reduce the danger of renal failure. Another strategy includes the use of bromocriptine and/or dantrolene (Granato et al. Bromocriptine is given orally, by nasogastric tube if essential, in doses starting from 2. In many cases of the neuroleptic malignant syndrome occurring secondary to an antipsychotic, sufferers require ongoing remedy. In such cases it has been found possible to reinstitute remedy with an antipsychotic (Rosebush et al. Although there are case reports of the successful reinstitution of remedy with the identical agent that caused the syndrome, prudence dictates utilizing a unique antipsychotic. Thus, if a excessive-efficiency first-era agent was used, one should in all probability select either a low-efficiency first-era agent or a second-era one. If the syndrome has occurred secondary to a second-era agent, then one would possibly think about an alternate second-era agent with a statistically lower likelihood of producing extrapyramidal facet-effects bucco-lingual-masticatory actions. Less commonly, one encounters dystonic and akathetic types, and barely one may see tics or ache. Although some authors deal with these less widespread types as separate entities, this distinction seems unwarranted. The general prevalence of tardive dyskinesia in these handled chronically with first-era antipsychotics is in the order of 20 percent (Woerner et al. Clinical features Although some cases of tardive dyskinesia have been reported after solely a month of remedy with an antipsychotic, that is quite uncommon; in general, no less than 6 months are required, and infrequently 1 or more years cross before the irregular actions seem. An exception to this rule is seen in the elderly, in whom the latency between initiation of remedy and the appearance of irregular actions could also be a lot shorter (Kane and Smith 1982; Saltz et al. Conversely, if the dose is maintained, or decreased solely barely, the irregular actions might make their appearance steadily or insidiously. As famous earlier, tardive dyskinesia might manifest with chorea, dystonia, akathisia, tics, or ache, and each of those displays is considered in flip. Choreiform actions in tardive dyskinesia are most commonly found in the lower a part of the face (Burke et al. Classically, one sees buccolinguomasticatory actions in the face, with pursing or puckering of the lips, chewing motions, and repetitive tongue protrusions. Extremity involvement might current with shoulder-shrugging or a stressed piano-taking part in movement of the fingers and hands; in the lower extremities there could also be foot-tapping. Truncal involvement might manifest with axial to-and-fro rocking or with pelvic thrusting. Uncommonly, respiratory dyskinesias might happen, with irregular, grunting respirations (Chiang 22. The most typical, and by far the commonest, type of tardive dyskinesia is a choreiform one, typically with p 22.
Diseases
- Acroosteolysis osteoporosis skull and mandible changes
- Liver neoplasms
- Cerebral cavernous malformations
- Imaizumi Kuroki syndrome
- Usher syndrome, type IA
- Chondrodysplasia punctata 1, x-linked recessive
- Linear nevus syndrome
- Nephrosis deafness urinary tract digital malformation
- Micromelic dwarfism Fryns type
- Chalazion
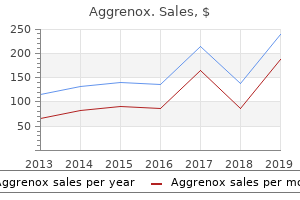
Generic aggrenox caps 25/200mg
There can be many fewer back problems if adults stored their trunk muscular tissues in optimal situation by common sluggish stretching and exercise such as swimming, walking briskly, running, and calisthenic applications. Morning is the perfect time for exercising, because the back of the older grownup tends to be stiffest following an evening of inactivity. Sleeping with the back hyperextended and sitting for lengthy intervals in an overstuffed chair or a badly designed car seat are notably more likely to worsen backache. It is estimated that intradiscal pressures are increased 200 % by changing from a recumbent to a standing position and four hundred % when slumped in a simple chair. Long journeys in a car or airplane with out change in position put maximal strain on discal and ligamentous buildings within the backbone. Lifting from a position by which the back is flexed, as in eradicating a heavy suitcase from the trunk of a car, is risky (one should all the time lift with the thing near the body). Also, sudden strenuous activity with out conditioning and warmup is more likely to injure discs and their ligamentous envelopes. In one large series of patients operated on for proven disc prolapse, 25 % were left with troublesome signs and 10 % required further surgery (Weir and Jacobs). Electromyography and nerve conduction studies, looking for evidence of a radiculopathy, are useful. Various explanations are then invoked- radiculitis, lateral recess syndrome, facet syndrome, unstable backbone, and lumbar arachnoiditis, described earlier on this chapter (see evaluations by Quiles et al and by Long as well as the "Symposium" listed within the References). One would suppose that these patients with chronic ache might be subdivided into a bunch with continued radicular ache and another with referred ache from illness of the backbone. Pressure over the backbone, buttock, or thigh may cause ache to be projected into the leg. Although the distribution of ache from every of those sources may overlap, the patient can often point out its site of origin. Pain of brachial plexus origin is experienced within the supraclavicular region, or within the axilla and across the shoulder; it may be worsened by certain maneuvers and positions of the arm and neck (extreme rotation) and is sometimes associated with tenderness of buildings above the clavicle. A palpable abnormality above the clavicle may disclose the reason for the plexopathy (aneurysm of the subclavian artery, tumor, cervical rib). The mixture of circulatory abnormalities and signs referable to the medial cord of the brachial plexus is characteristic of the thoracic outlet syndrome, described further on. Shoulder ache, like backbone and plexus ache, may radiate into the arm and rarely into the hand, but sensorimotor and reflex modifications- which all the time point out illness of nerve roots, plexus, or nerves- are absent. In most patients the ache subsides gradually with immobilization and analgesics, followed by a program of increasing shoulder mobilization. Osteoarthritis and osteophytic spur formation of the cervical backbone may cause ache that radiates into the back of the head, shoulders, and arm on one or both sides. Coincident compression of nerve roots is manifest by paresthesias, sensory loss, weakness and atrophy, and tendon reflex modifications within the arms and hands. Pain within the neck may project into and cause numbness or burning of one half the tongue (the "neck-tongue syndrome"; see page a hundred sixty five). There could also be difficulty in distinguishing cervical spondylosis with root and spinal cord compression from a major neurologic illness (syringomyelia, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or tumor) with an unrelated cervical osteoarthritis, notably on the C5-C6 and C6-C7 ranges. A mixture of osteoarthritis of the cervical backbone with harm to ligaments and muscular tissues when the neck has been forcibly prolonged and flexed. The harm ranges from a minor sprain of muscular tissues and ligaments to extreme tearing of those buildings, to avulsion of muscle and tendon from vertebral body, and even to vertebral and intervertebral disc injury. Milder levels of whiplash harm are often complicated by psychologic and compensation components (see LaRocca for a evaluate of this subject). Spinal rheumatoid arthritis could also be restricted to the cervical apophysial (facet) joints and the atlantoaxial articulation. The ordinary manifestations are ache, stiffness, and limitation of motion within the neck and ache in the back of the head. Because of major affection of different joints, the analysis is comparatively simple to make, but significant involvement of the cervical backbone could also be overlooked in patients with diffuse illness. In the superior stages of the illness, one or a number of of the vertebrae may turn out to be displaced anteriorly, or a synovitis of the atlantoaxial joint may injury the transverse ligament of the atlas, resulting in ahead displacement of the atlas on the axis, i. In both occasion, severe and even life-threatening compression of the spinal cord may occur gradually or abruptly. Cautiously carried out lateral radiographs in flexion and extension are helpful in visualizing atlantoaxial dislocation or subluxation of the lower segments. Occipital headache and neck ache related to degenerative modifications within the upper cervical facets is mentioned with different cranial pains on page 164 (so-known as third occipital nerve ache). Cervical Disc Herniation (Table 11-1) A common reason for neck, shoulder, and arm ache is disc herniation within the lower cervical region; the method is comparable to disc herniation within the lumbar region but provides rise, in fact, to a different set of signs (Table 11-1). It seems most often and not using a clear and instant cause, but it may develop after trauma, which can be major or minor (from sudden hyperextension of the neck, falls, diving accidents, forceful manipulations). The roots most commonly involved are the seventh (in 70 % of instances) and the sixth (20 %); fifth- and eighth-root involvement makes up the remaining 10 % (Yoss et al). The ache is within the region of the shoulder blade, pectoral region and medial axilla, posterolateral upper arm, elbow and dorsal forearm, index and middle fingers, or all of the fingers. Tenderness is most pronounced over the medial facet of the shoulder blade opposite the third to fourth thoracic spinous processes and within the supraclavicular area and triceps region. Paresthesias and sensory loss are most evident within the second and third fingers or could also be experienced within the tips of all of the fingers. Weakness involves the extensors of the forearm and typically of the wrist; often the hand grip is weak as nicely; the triceps could also be weak and the triceps reflex is diminished or absent; the biceps and supinator reflexes are preserved. With a laterally situated disc protrusion between the fifth and sixth cervical vertebrae, the signs and signs are referred to the sixth cervical root. The full syndrome is characterized by ache on the trapezius ridge and tip of the shoulder, with radiation into the anterior-upper a part of the arm, radial forearm, usually the thumb, and typically the lateral facet of the index finger as nicely. There can also be paresthesias and sensory impairment in the same areas; tenderness within the area above the backbone of the scapula and within the supraclavicular and biceps areas; weakness in flexion of the forearm (biceps) and in contraction of the deltoid when sustaining arm abduction; and diminished to absent biceps and supinator reflexes (the triceps reflex is retained or exaggerated in our experience, but some texts record it as barely diminished in some patients). The fifth cervical root syndrome, produced by disc herniation between the fourth and fifth vertebral bodies, is characterized by ache within the shoulder and trapezius region and by supra- and infraspinatus weakness, manifest by an incapability to abduct the arm and rotate it externally with the shoulder adducted (weakness of the supra- and infraspinatus muscular tissues). There could also be a slight diploma of weakness of the biceps and a corresponding reduction within the reflex, but these are inconsistent findings. The weakness largely involves the muscular tissues supplied by the ulnar nerve, specifically the intrinsic hand muscular tissues (page 1168). These syndromes are often incomplete in that only one or a number of of the everyday findings are present. Particularly noteworthy is the prevalence, in laterally placed cervical disc rupture, of isolated weakness with out ache, particularly with discs on the fifth and sixth ranges. Friis and coworkers have described the distribution of ache in 250 instances of herniated disc or spondylotic nerve root compression within the cervical region. Virtually every patient, irrespective of the particular root(s) involved, showed a limitation within the range of motion of the neck and aggravation of ache with motion (notably hyperextension). Coughing, sneezing, and downward pressure on the head within the hyperextended position often exacerbated the ache, and traction (even guide) tended to relieve it. As already talked about, in many of the cervical radicular syndromes, the onset is acute and no traumatic incident may be documented. It is difficult to relate the syndrome to osseous modifications that will need to have been present for years. Even harder to clarify is the tendency to recovery within a couple of weeks when motion of the neck is proscribed by traction or a collar, as mentioned beneath. Unlike herniated lumbar discs, cervical ones, if large and centrally situated, end in compression of the spinal cord (central disc causing compression of all the cord; paracentral disc, asymmetrical but bilateral components of the cord). The centrally situated disc is commonly painless, and the cord syndrome may simulate a degenerative neurologic illness. Failure to contemplate a protruded cervical disc in patients with obscure signs within the legs, together with stiffness and falling, is a common error. A vague sensory change can usually be detected a number of dermatomes beneath the level of compression. Management of Herniated Cervical Disc Conservative measures should be instituted earlier than turning to surgical removal of the disc until there are signs of a quickly or subacutely progressing myelopathy. In the case of cervical disc with radicular ache, an in depth-becoming foam collar is kind of useful. The patient is advised to put on the collar at all times in the course of the day, particularly while riding in a car, until this turns into fully impractical. While thought of of little value in lumbar disc illness, traction with a halter across the occiput and chin could also be of some benefit in cervical disc syndromes.
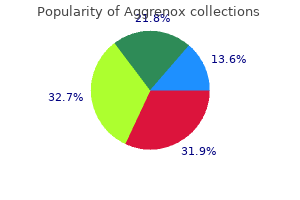
Best 25/200mg aggrenox caps
Some success has been reported by Heitmann and colleagues in coaching aged persons who fall frequently. Ventricular shunting in idiopathic hydrocephalus has restored locomotion in sufferers with this syndrome. Once dementia becomes conjoined with any of the gait disorders that happen in advanced age, rehabilitation stands little chance of success, because the capability to attend to small changes in terrain and posture is lost. Progression from using a cane, to a pronged cane, and eventually to a four-posted walker permits sufferers with all types of gait disorders to preserve some mobility. The optimal use of these orthoses is finest directed by an skilled bodily therapist. Even more problematic are sufferers who search therapy for pain that seems to have little or no structural basis; further inquiry could disclose that fear of significant illness, fear, or despair has aggravated some relatively minor ache or that the criticism of pain has turn into the means of looking for medicine or monetary compensation. They should additionally cope with the "troublesome" pain cases during which no amount of investigation brings to light both medical or psychiatric illness. Finally, the doctor must be ready to manage sufferers who demand aid from intractable pain caused by established and incurable illness. To deal intelligently with such pain problems requires familiarity with the anatomy of sensory pathways and the sensory supply of body segments in addition to insight into the psychologic factors that influence the notion of and reaction to pain. The twin nature of pain is responsible for a few of our problem in understanding it. One aspect, the simpler to comprehend, is its evocation by explicit stimuli and the transmission of pain impulses along sure pathways, i. Far more abstruse is its quality as a mental state intimately linked to emotion, i. Alternatively, interruption of sure neural pathways could abolish all sensation in an affected half, however the symptom of pain could persist. Unlike most sensory modalities- which are aroused by a selected stimulus corresponding to touch-pressure, heat, or cold- pain can be evoked by any considered one of these stimuli if it is intense sufficient. It is clear to the authors that in extremely specialised medical centers and often even in "pain centers," few physicians are able to handling troublesome and weird pain problems in any complete way. Although much has been learned about the anatomy of pain pathways, their physiologic mechanisms, and which constructions to ablate in order to produce analgesia, relatively little is known about which sufferers must be subjected to these destructive operations or how to manage their pain by medical means. Here is a subspecialty that ought to challenge each thoughtful doctor, for it calls for the highest ability in drugs, neurology, and psychiatry. One, often known as the specificity principle, was from the beginning associated with the name of von Frey. He asserted that the pores and skin consisted of a mosaic of discrete sensory spots and that every spot, when stimulated, gave rise to one sensation- both pain, pressure, heat, or cold; in his view, every of these sensations had a distinctive finish organ in the pores and skin and each stimulus-particular finish organ was related by its own private pathway to the brain. A second principle was that of Goldscheider, who deserted his own earlier discovery of pain spots to argue that they merely represented pressure spots, a sufficiently intense stimulation of which could produce pain. According to the latter principle, there have been no distinctive pain receptors, and the feeling of pain was the results of the summation of impulses excited by pressure or thermal stimuli applied to the pores and skin. Originally referred to as the intensivity principle, it later became often known as the sample, or summation principle. The zone of impaired sensation contained an innermost space during which superficial sensation was fully abolished. This was surrounded by a narrower ("intermediate") zone, during which pain sensation was preserved however poorly localized; extreme levels of temperature were recognized in the intermediate zone, however notion of touch, lesser differences of temperature, and two-point discrimination were abolished. To explain these findings, Head postulated the existence of two methods of cutaneous receptors and conducting fibers: (1) an historical protopathic system, subserving pain and extreme differences in temperature and yielding ungraded, diffuse impressions of an all-or-none sort, and (2) a more just lately advanced epicritic system, which mediated touch, two-point discrimination, and lesser differences in temperature in addition to localized pain. The pain and hyperesthesia that follow damage to a peripheral nerve were attributed to a loss of inhibition that was usually exerted by the epicritic upon the protopathic system. This principle was used for a few years to explain the sensory alterations that happen with each peripheral and central (thalamic) lesions. Nevertheless, each fast and slow forms of pain conduction were later corroborated (see below). A later refinement of the sample and specificity ideas of pain was made in 1965, when Melzack and Wall propounded their "gate-management" principle. They observed, in decerebrate and spinal cats, that peripheral stimulation of large myelinated fibers produced a unfavorable dorsal root potential and that stimulation of small C (pain) fibers caused a constructive dorsal root potential. They postulated Copyright � 2005, 2001, 1997, 1993, 1989, 1985, 1981, 1977, by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. The essence of this principle is that the big-diameter fibers excite the I cells, which, in flip, trigger a presynaptic inhibition of the T cells; conversely, the small pain afferents inhibit the I cells, leaving the T cells in an excitatory state. Melzack and Wall emphasized that pain impulses from the dorsal horn should even be under the management of a descending system of fibers from the brainstem, thalamus, and limbic lobes. At first the gate-management mechanisms appeared to provide a proof of the pain of ruptured disc and of sure chronic neuropathies (significantly these with large fiber outfall), and attempts were made to relieve pain by subjecting the peripheral nerves and dorsal columns (presumably their large myelinated fibers) to sustained transcutaneous electrical stimulation. In some scientific situations, these procedures have indeed given aid from pain, however not necessarily as a result of stimulation of large myelinated fibers alone (see Taub and Campbell). But in a number of other instances referring to pain in large- and small-fiber neuropathies, the scientific behavior has been quite out of maintaining with what one would anticipate on the basis of the gate-management mechanism. As with preceding theories, flaws have been uncovered in the physiologic observations on which the theory is based. These and other features of the gate-management principle of pain have been critically reviewed by P. During the previous couple of many years there was a major accrual of information on cutaneous sensibility, demanding a modification of earlier anatomic-physiologic and scientific ideas. Interestingly, much of this information is still finest described and rationalized in the general framework of the oldest principle, that of specificity, as shall be evident from the ensuing discussion on pain and that on other forms of cutaneous sensibility in the chapter that follows. In maintaining with distinctions between nerve varieties, the sensory (and motor) fibers have been classified in accordance with their dimension and performance (Table eight-1). It is now properly established that two types of afferent fibers in the distal axons of primary sensory neurons reply maximally to nociceptive. The peripheral terminations of each these primary pain afferents or receptors are the free, profusely branched nerve endings in the pores and skin and other organs; these are coated by Schwann cells however include little or no myelin. There is considerable evidence, primarily based on their response characteristics, that a degree of subspecialization exists within these freely branching, nonencapsulated endings and their small fiber afferents. Three broad classes of free endings or receptors are recognized: mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, and polymodal nociceptors. Each ending transduces stimulus energy into an action potential in nerve membranes. The first two types of receptors are activated by innocuous mechanical and thermal stimulation, respectively; the mechanoeffects are transmitted by each A- and C fibers and the thermal effects largely by C fibers. Moreover, sure A- fibers reply to light touch, temperature, and pressure in addition to to pain stimuli and are able to discharging in proportion to the depth of the stimulus. These observations on the polymodal features of A- and C fibers would explain the earlier observations of Lele and Weddell that modes of sensation other than pain can be evoked from constructions such because the cornea, which is innervated solely by free nerve endings. The manner during which painful stimuli are translated into electrical depolarizations in nerve endings are starting to be understood. A variety of specialised molecules, when activated by noxious stimuli, open cationic channels in membranes of the nerve ending. Opening of these channels, in flip, prompts voltage-gated sodium channels and generates an action potential in the sensory axon. The regulation and activation of these receptor molecules is summarized by Mannion and Woolf. The peripheral afferent pain fibers of each A- and C varieties have their cell our bodies in the dorsal root ganglia; central extensions of these nerve cells project, through the dorsal root, to the dorsal horn of the spinal twine (or, in the case of cranial pain afferents, to the nucleus of the trigeminal nerve, the medullary analogue of the dorsal horn). The discrete segmental distribution of the sensory models permits the construction of sensory maps, so useful to clinicians (see. This aspect of sensory anatomy is elaborated in the subsequent chapter, which incorporates maps of the sensory dermatomes and cutaneous nerves. The distribution of pain fibers from deep constructions, though not fully similar to these from the pores and skin, additionally follows a segmental sample. The first to fourth thoracic nerve roots are the essential sensory pathways for the center and lungs; the sixth to eighth thoracic, for the upper belly organs; and the lower thoracic and upper lumbar, for the lower belly viscera.
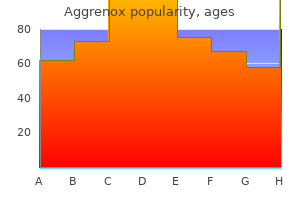
Order aggrenox caps 25/200 mg
In the not too distant past, folks also assumed adult roles at much youthful ages within the United States. This distinction suggested that men could kind an id before coming into an enduring relationship, whereas girls outline themselves in terms of those relationships. For practical and social causes, girls at present extra sometimes set up a profession before coming into a committed relationship. This "quiet revolution" signifies that girls, like men, now are more likely to kind their id in terms of work and outdoors of relationships (Goldin, 2006). Finally, many clinicians recommend that supportive, nondirective remedy is a very acceptable therapy for young people who are trying to "discover themselves. Shereportednohistory of emotional problems, talked at length about her close friends andboyfriend,seemedthoroughlyattachedtoherparents,and wasasuccessfulpsychologymajorwhomaintaineda3. She also was afraid to meet her biological mom, largely as a result of she felt like she could be meeting half ofherself. However, no research has been conducted on different therapies for these young folks. She read abouttheexperiencesofotheradoptedyoungpeoplewhohad met their start dad and mom, and even chatted with some on the Internet. Social scientists often conceptualize family change in terms of the family life cycle-the developmental course of family relationships all through life. Childless families, single-parent families, divorced families, remarried families, gay and lesbian families, and extended family groups all face distinctive obstacles and opportunities, as do families of different ethnic backgrounds. SymptomS of family tRanSitionS All family transitions are characterised by change-changes in time demands, altering expectations, and changes in love and energy in family relationships. Early in marriage, newlyweds negotiate expectations about time together, emotional closeness, and who will assume responsibility for varied duties inside and outdoors the family. The roles that couples assume early in their marriage can set a sample that lasts a lifetime. When youngsters go away the family residence, adults should discover or rediscover interests inside their marriage and outdoors the home. These patterns are Family Transitions Not everyone experiences a midlife crisis, but most adults expertise a variety of challenging family transitions during the center years of adult life. Family transitions could contain the addition or loss of members of a family family and embrace transitions to marriage, parenting, and the empty nest- the adjustment that occurs when adult youngsters go away the family residence. Divorce and remarriage are also widespread family transitions within the United States at present, an remark that underscores the fact that families lengthen beyond the boundaries of 1 family. Family Transitions 457 A specific drawback in intimate relationships is the demand and withdrawal sample, where one companion turns into increasingly demanding and the other withdraws additional and additional. Evidence signifies that demand and withdrawal interactions predict future marital dissatisfaction, especially among girls (Heavey, Christensen, & Malamuth, 1995). Other evidence reveals that conflicts in troubled families are more likely to continue over time and to spill over into other family relationships (Margolin, Christensen, & John, 1996). For example, marital conflicts could lead to fights between dad and mom and kids, as the kids turn out to be another focus of an ongoing marital dispute. Family Conflict Increased battle is a standard con- sequence of changing family relationships. However, psychologists usually have been extra involved with the process than the content of family battle. One analysis suggests that every one disputes during family transitions ultimately contain both energy struggles or intimacy struggles. Power struggles are makes an attempt to change dominance relations, whereas intimacy struggles are makes an attempt to alter the diploma of closeness in a relationship (Emery, 1992). Increased battle may be a standard a part of family transitions, but battle creates great difficulties for some families. One of probably the most constant findings considerations the reciprocity, or social change, of cooperation and battle (Bradbury, Fincham, & Beach, 2000; Gottman & Notarious, 2000). A grouchy remark is dismissed as a part of a "dangerous day," whereas a compliment is readily returned. In contrast, families with troubled relationships get caught in adverse cycles of interaction. An unhappily married spouse may ask her husband to cease studying the paper during dinner, and as a substitute of placing the paper down, he puts her down. In far too many families, such battle can escalate into family violence (Cordova et al. Emotional Distress Whether family battle is expressed through explosive outbursts, constant bickering, or the "silent therapy," fighting often causes emotional distress for all relations. Venting a little anger could be a reduction, but ongoing battle and anger can turn out to be all-consuming. Moreover, anger often is an "emotional cover-up," masking deeper hurts together with loneliness, pain, longing, and grief (Emery, 2004, 2011; MacDonald & Leary, 2005). Interestingly, happily married couples are likely to blame their marital disputes on difficult but momentary circumstances. Unresolved conflicts may cause considerable individual distress (Whisman, Sheldon, & Goering, 2000). The most significant, long-time period consequence of divorce for kids entails painful feelings and recollections, not psychological problems. Identity is closely linked with family roles, and changes in those roles may cause us to doubt ourselves in significant ways. He or she also could really feel like a failure as a father or mom and question his or her success, or objectives, for other life roles. Getting married, turning into a parent, infertility, or the empty nest also could set off doubts that lead to a brand new search for a brand new sense of self. Family transitions also confront folks with a basic battle between acceptance and alter (Christensen et al. Scapegoating can permit other relations to keep away from their very own problems, for instance, unhappily married dad and mom may ignore their very own troubles by worrying about or blaming a troubled baby. A few theorists have developed listings of interaction patterns like scapegoating or of interpersonal diagnoses, classifications of troubled close relationships (Group for the Advancement of Psychiatry, 1995; McLemore & Benjamin, 1979). Census Bureau and other federal businesses regularly acquire information on their frequency. Surveys point out that over ninety p.c of adults within the United States get married during their adult lives. Age at first marriage has elevated, nevertheless, rising from the early to the later 20s over the past several many years. About 5 out of every six girls within the United States bear a toddler, but childbirth increasingly is going down exterior of marriage. Births to teenagers comprised 50 p.c of nonmarital births in 1970, but fell to 23 p.c in 2007 (Ventura, 2009). Although "happily ever after" may be the stuff of fairy tales, at any cut-off date most individuals report their marriage as pleased. Still, one nationwide examine found significant marital discord among 31 p.c of couples (Whisman, Beach, & Snyder, 2008). Divorce rates elevated dramatically within the United States from the late 1960s to the early Eighties but stabilized and fell considerably since then (see Figure 17. Some are heartened by the decline in divorce, but many of the drop is due to will increase in nonmarital childbearing and cohabitation. And estimates point out that about 40 p.c of all existing marriages will nonetheless finish in divorce. About three out of four whites and one out of two blacks remarry following a divorce. Many divorced adults, together with divorced dad and mom, cohabit before remarriage or as a substitute of remarrying (Emery, 1999a). CauSeS of DiffiCulty in family tRanSitionS Most theories of the causes of difficulties in family transitions emphasize psychological and social components. Divorce Rates Have 5 Risen for over 100 Years four three 2 Divorcerateshavetrendedupwardforovera century. Psychological Factors Researchers often blame family difficulties on problems with communication. Communication consists of both meant meaning and nonverbal behaviors that may convey refined or even contradictory meaning. Verbal and nonverbal communication difficulties clearly distinguish distressed from nondistressed family relationships (Gottman, 1994). Based on his intensive studies of marital interaction, John Gottman (1994), a medical psychologist and noted marital interaction researcher, has identified four basic communication troubles.
Spiraea trifoliata (Indian Physic). Aggrenox.
- Digestive disorders, causing vomiting (emetic), and other uses.
- What is Indian Physic?
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Indian Physic work?
- Dosing considerations for Indian Physic.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96520
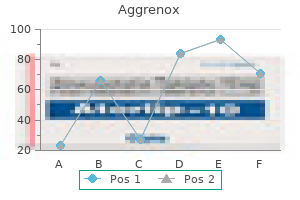
Order 25/200mg aggrenox caps
One is the issue of unequal pupils (anisocoria) and figuring out whether or not this abnormality is derived from sympathetic or parasympathetic denervation. Completely Sector palsy motionless of iris Test for cholinergic sphincter Impaired No dilation lag ``Dilation lag' supersensitivity with light response of smaller Mecholyl 2. Long-standing bilateral Adie pupils are inclined to be small and show tonic close to responses. They can be readily distinguished from Argyll-Robertson pupils, which constrict rapidly to close to (lodging) and redilate rapidly on launch from the close to stimulus. Figure 14-8 is a helpful schematic, devised by Thompson and Pilley, for sorting out the various forms of anisocoria. Sounds alert us to danger; spoken phrases are the universal means of communication; music is one of our most exalted esthetic pleasures. Hence an understanding of the functions of the eighth cranial nerves and their derangements by disease is as much the reliable concern of the neurologist as the otologist. As a general rule, the association of vertigo and deafness signifies a disease strategy of the top organ or eighth nerve. The exact locus of the disease is determined by tests of labyrinthine and auditory function, described beneath, and by findings on neurologic examination and imaging studies that implicate the primary and secondary connections of the eighth cranial nerve. This ganglion consists of bipolar cells, the peripheral processes of which convey auditory impulses from the specialised neuroepithelium of the inner ear, the spiral organ of Corti. This is the top organ of hearing, wherein sound is transduced into nerve impulses. It consists of roughly 15,000 neuroepithelial (hair) cells that rest on the basilar membrane, which extends alongside the entire 2 half turns of the cochlea. Projecting from the inner surface of each hair cell are approximately 60 very fine filaments, or stereocilia, which are embedded within the tectorial membrane, a gelatinous structure overlying the organ of Corti. Sound causes the basilar membrane to vibrate; upward displacement of the basilar membrane bends the comparatively mounted stereocilia and offers a stimulus enough for activating the hair cells. The stimulus is then transmitted to the sensory fibers of the cochlear nerve, which finish synaptically at the base of each hair cell. The basilar membrane vibrates at different frequencies all through its length, according to the frequency of the sound stimulus. In this manner the fibers of the cochlear nerve reply to the complete range of audible sound and may differentiate and resolve complexes of sounds. The so-known as inner hair cells, numbering about 3500, are of particular significance, since they synapse with about 90 percent of the 30,000 afferent cochlear neurons. The central processes of the primary auditory neurons represent the cochlear division of the eighth cranial nerve. In addition, the nerve accommodates approximately 246 500 efferent fibers, which come up from the superior olivary nuclei (eighty percent from the contralateral nucleus and 20 percent from the ipsilateral one) and synapse with the afferent neurons from the hair cells (Rasmussen). It is thought to play some half within the auditory processing generated within the ear itself, presumably to enhance the sharpness of sound perception by some suggestions mechanism (Kemp). The eighth nerve also accommodates adrenergic postganglionic fibers which might be derived from the cervical autonomic chain and innervate the cochlea and labyrinth. This ganglion can also be composed of bipolar cells, the peripheral processes of which terminate in hair cells of the specialised sensory epithelium of the labyrinth (semicircular canals, saccule, and utricle). The hair cells of the maculae are coated by the otolithic membrane, or otolith, which consists of calcium carbonate crystals embedded in a gelatinous matrix. The sensory cells of the cristae are coated by a sail-formed gelatinous mass known as a cupula. The labyrinthine semicircular canals transduce angular actions of the head, and the otoliths transduce linear movement. The central fibers from the cells of the spiral and vestibular ganglia are united in a standard trunk, which enters the cranial cavity via the interior auditory meatus (accompanied by the facial and intermediate nerves). They traverse the cerebellopontine angle and enter the brainstem at the junction of the pons and medulla. The cochlear fibers bifurcate and terminate virtually without delay within the dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei. The fibers from every cochlear nucleus pursue separate crossing and ascending pathways; they move to both inferior colliculi (primarily to the opposite side) via the lateral lemnisci. Secondary acoustic fibers project via the trapezoid physique and lateral lemniscus to the medial geniculate our bodies, a special component of the thalamic sensory system. Some fibers terminate within the trapezoid physique and superior olivary complicated and subserve such reflex functions as auditory consideration, sound localization, auditory startle, and oculopostural orientation to sound. Both excitatory and inhibitory neurons are positioned at each level of those pathways. At all levels there are sturdy commissural connections via which auditory indicators come to be represented bilaterally within the cerebrum. From the medial geniculate our bodies, fibers project to the cortex via the auditory radiations-comparatively compact bundles that course ventrolaterally via the posterior elements of the putamens before dispersing and ending within the transverse gyri of Heschl and other auditory cortical areas (Tanaka et al). The auditory cortical field contains the superior temporal gyrus and the higher financial institution of the sylvian fissure (Brodmann space forty one; see web page 387), or major auditory cortex, and the surrounding secondary and tertiary cortices within the adjacent temporal lobe. The Copyright � 2005, 2001, 1997, 1993, 1989, 1985, 1981, 1977, by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. The proper ear, viewed from the entrance, displaying the external ear and auditory canal, the middle ear and its ossicles, and the inner ear. The perilymph is positioned between the wall of the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. In the cochlea, the perilymphatic space takes the form of two coiled tubes- the scala vestibuli and scala tympani. The endolymph is positioned inside the membranous labyrinth, which includes the three semicircular canals, utricle, and saccule. This is the top organ of hearing; it consists of a single row of inner hair cells and three rows of outer hair cells. Diagram of a crista ampulla, the specialised sensory epithelium of a semicircular canal. The path of head rotation is indicated by the massive arrow, and endolymph move by the small arrow. Note that the ideas of the hair cells are involved with the otoliths (calcareous material), which are embedded in a gelatinous mass known as the cupula. The vestibular fibers of the eighth nerve terminate within the four vestibular nuclei: superior (Bechterew), lateral (Deiters), medial (triangular, or Schwalbe), and inferior (spinal, or descending). In addition, a few of the fibers from the semicircular canals project directly to the cerebellum via the juxtarestiform physique and terminate within the flocculonodular lobe and adjacent vermian cortex (these constructions are therefore known as the "vestibulocerebellum," as famous in Chap. Efferent fibers from this portion of the cerebellar cortex, in flip, project ipsilaterally to the vestibular nuclei and to the fastigial nucleus; fibers from the fastigial nucleus project again to the contralateral vestibular nuclei, again via the juxtarestiform physique. Thus both sides of the cerebellum exerts an influence on the vestibular nuclei of each side. The lateral and medial vestibular nuclei even have important connections with the spinal twine, primarily via the uncrossed lateral vestibulospinal tract and the crossed and uncrossed medial vestibulospinal tracts. Presumably, vestibular effects on posture are mediated via these pathways- the axial muscle tissue being acted upon predominantly by the medial vestibulospinal tract, and the limb muscle tissue by the lateral tract. The nuclei of the third, fourth, and sixth cranial nerves come underneath the influence of the vestibular nuclei via the projection pathways, primarily the medial longitudinal fasciculus described in Chap. In addition, all the vestibular nuclei have afferent and efferent connections with the pontine reticular formation. The latter connections subserve vestibulo-ocular and vestibulospinal reflexes which might be important for clear vision and stable posture. In the monkey, these projections are virtually completely contralateral, terminating close to the "face space" of the primary somatosensory cortex (space 2 of Brodmann). Lesions within the posterior insula impair the sense of verticality, physique orientation, and movement. These temporary remarks convey some notion of the complexity of the anatomic and practical organization of the vestibular system (for a full dialogue, see the monographs of Brodal and of Baloh and Honrubia). In 1969, Konigsmark estimated that there were at least 6 million individuals within the United States with hearing loss of enough severity to impair the understanding of speech; there were in all probability three times this many with some impairment of hearing.
Effective aggrenox caps 25/200 mg
The gait dysfunction could also be accompanied by similarly exaggerated actions of the arms, as if to impress the observer with the nice effort required to stroll and preserve steadiness. Leg actions in mattress could also be unimpaired or the affected person could show a Hoover sign, which belies real leg weak point (web page 52). Some of the patients exhibit extra abnormalities of the voice and visual fields, tremors, and asthenic weak point of muscle contraction. When such patients are positioned on their toes, they could take a few steps after which become unable to advance their legs; they lurch in all instructions and crumple to the ground if not assisted. The antispasticity brokers baclofen and tizanidine are somewhat useful when stiffness of the limbs exceeds weak point. Hypofunction of the labyrinths, as in drug-induced or idiopathic vestibulopathy, has greatly challenged physiatrists. Balance coaching and the more practical use of postural correction and imaginative and prescient have helped some of these patients to be extra steady and better capable of function in the actions of every day dwelling and at work (see Baloh and Honrubia). Likewise, gait ataxia from proprioceptive defects can probably be corrected to some extent by careful attention to visual control and proper placement of the toes. From these cells of termination, second-order axons connect with ventral and lateral horn cells in the identical and adjacent spinal segments and subserve each somatic and autonomic reflexes. The major bundle of secondary neurons subserving pain sensation initiatives contralaterally (and to a lesser extent ipsilaterally) to greater levels; this constitutes the spinothalamic tract, discussed beneath. In latest years, numerous essential observations have been made in regards to the mode of transmission and modulation of pain impulses in the dorsal horn and brainstem. Also, A- pain afferents, when stimulated, release several neuromodulators that play a role in the transmission of pain sensation. Slower neurotransmission by C neurons includes different substances, of which the most important is the 11� amino acid peptide known as substance P. In animals, substance P has been shown to excite nociceptive dorsal root ganglion and dorsal horn neurons; moreover, destruction of substance P fibers produces analgesia. Thus, opiates have been noted to decrease substance P; at the identical time, flexor spinal reflexes, which spring to mind by segmental pain, are decreased. The topic of pain modulation by opiates and endogenous morphinelike substances is elaborated additional on. The principal bundle of these axons decussates in the anterior spinal commissure and ascends in the anterolateral fasciculus because the spinothalamic tract to terminate in several brainstem and thalamic buildings. It is of clinical consequence that the axons carrying pain impulses from every dermatome decussate one to three segments above the level of root entry. For this purpose, a discrete lesion of the lateral spinal cord creates a lack of pain and thermal sensation of the contralateral trunk, the dermatomal degree of which is two to three segments beneath that of the spinal cord lesion. Most of the fibers terminate within the section of their entry into the cord; some prolong ipsilaterally to one or two adjacent rostral and caudal segments; and some project, via the anterior commissure, to the contralateral dorsal horn. The cytoarchitectonic research of Rexed in the cat (the identical organization pertains in primates and probably in people) have shown that secondorder neurons, the sites of synapse of afferent sensory fibers in the dorsal horn, are organized in a sequence of six layers or laminae. Spinal cord in transverse section, illustrating the course of the afferent fibers and the main ascending pathways. Transverse section through a cervical section of the spinal cord, illustrating the subdivision of the gray matter into laminae in accordance with Rexed and the entry and termination of the principle sensory fibers. One such group of fibers initiatives on to the reticular core of the medulla Face and midbrain after which to the medial and intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus; this group of fibers is referred Thalamus to because the spinoreticulothalamic or paleospinothalamic pathway. At the level of the medulla, these fibers synapse in the nucleus gigantocellularis; extra rostrally, Ventral they connect with nuclei of the parabrachial area, posterolateral midbrain reticular formation, periaqueductal grey nucleus of thalamus matter, and hypothalamus. There can be a 3rd, direct spinohypothalamic pathMedial lemniscus means in the anterolateral fasciculus. Nucleus of the conduction of diffuse, poorly localized pain funiculus gracilis arising from deep and visceral buildings (intestine, periNucleus of osteum) has been ascribed to these pathways. Offshoots from the ascending anterolateral fasciculus (spinothalamic tract) to nuclei tensity of the noxious stimulus. Also, the pathways in the medulla, pons, and mesencephalon and nuclear terminations of the tract are indicated. One of these is a longitudinal polysynaptic bundle of the cells of termination of cutaneous nociceptive stimuli and the small myelinated fibers in the heart of the dorsal horn (the dorsal cells of origin of ascending spinal afferent pathways have all been intracornual tract); another consists of axons of lamina I cells that obtained from research in animals (including monkeys). Information about this pathway in Thalamic Terminus of Pain Fibers people has been derived from the examine of postmortem materials and from the examination of patients subjected to anterolateral corThe direct spinothalamic fibers separate into two bundles as they dotomy for intractable pain. The medial contingent terminates mainly in opposite side of the physique, extending to a degree two or three segthe intralaminar complicated of nuclei and in the nucleus submedius. The cortical illustration permits for correct localization of the location of origin of a painful stimulus however the notion that thalamic projections terminate solely in this area is an oversimplification. However, cerebral evoked potentials and elevated cerebral blood flow (by positron emission tomography research) have been demonstrated in the thalamus and pre- and postcentral gyri of patients undergoing rectal balloon distention (Silverman et al; and Rothstein et al). Spinal cord showing the segmental association of nerve fibers inside major tracts. On the left side are indicated the "sensory modalities" that appear to be mediated by the 2 major ascending pathways. Projections from the dorsal column nuclei, which have a modulating affect on pain transmission, are mainly to the ventrobasal and ventroposterior group of nuclei. Each of the four thalamic nuclear teams that receives nociceptive projections from the spinal cord has a definite cortical projection, and each is assumed to play a unique position in pain sensation (see beneath). In general, neurophysiologic proof indicates that as one ascends from peripheral nerve to spinal, medullary, mesencephalic, thalamic, and limbic levels, the predictability of neuron responsivity to noxious stimuli diminishes. Thus it comes as no surprise that neurosurgical procedures for interrupting afferent pathways become less and less profitable at progressively greater levels of the brainstem and thalamus. Of great importance was the invention of a system of descending fibers and means stations that modulate activity in nociceptive pathways. The system that has been studied most extensively emanates from the frontal cortex and hypothalamus and initiatives to cells in the periaqueductal area of the midbrain after which passes to the ventromedial medulla. Several different descending pathways, noradrenergic and serotoninergic, come up in the locus ceruleus, dorsal raphe nucleus, and nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis and are additionally essential modifiers of the nociceptive response. As identified above, the adequate stimulus for pores and skin is one which has the potential to injure tissue, i. These stimuli are ineffective when utilized to the stomach and gut, where pain is produced by an engorged or inflamed mucosa, distention or spasm of smooth muscle, and traction on the mesenteric attachment. In skeletal muscle, pain is brought on by ischemia (the idea of intermittent claudication), necrosis, hemorrhage, and injection of irritating solutions in addition to by accidents of connective tissue sheaths. Joints are insensitive to pricking, chopping, and cautery, however pain may be produced in the synovial membrane by inflammation and by exposure to hypertonic saline. Injuries to the periosteum give rise to pain however probably not to different sensations. Arteries are a supply of pain when pierced by a needle or involved in an inflammatory process. Thalamocortical Projections the ventrobasal thalamic complicated and the ventroposterior group of nuclei project to two major cortical areas: the primary sensory (postcentral) cortex (a small quantity terminate in the precentral cortex) and the upper financial institution of the sylvian fissure. The extent to which either cortical area is activated by thermal and painful stimuli is uncertain. The intralaminar nuclei, which additionally project to the hypothalamus, amygdaloid nuclei, and limbic cortex, probably mediate the arousal and affective aspects of pain and the autonomic responses. Other pain-producing substances corresponding to kinins are released from sensory nerve endings or are carried there by the circulation. In addition, direct stimulation of nociceptors releases polypeptide mediators that improve pain notion. The finest-studied of these is substance P, which is released from the nerve endings of C fibers in the pores and skin throughout peripheral nerve stimulation. It causes erythema by dilating cutaneous vessels and edema by releasing histamine from mast cells; it additionally acts as a chemoattractant for leukocytes. This response, known as neurogenic inflammation by White and Helme, is mediated by antidromic motion potentials from the small nerve cells in the spinal ganglia and is the idea of the axon reflex of Lewis; the reflex is abolished in peripheral nerve diseases and may be studied electrophysiologically as an assist to clinical localization. It has been shown that central transmission in the spinothalamic tract may be inhibited by stimulation of the sensorimotor areas of the cerebral cortex, and, as indicated above, numerous descending fiber systems have been traced to the dorsal horn laminae from which this tract originates.
Aggrenox caps 25/200 mg
If it were to be perfected, testing of olfactory evoked potentials can be of use right here. The nasal epithelium or the olfactory nerves themselves could also be affected in Wegener granulomatosis and by craniopharyngioma. A meningioma of the olfactory groove may implicate the olfactory bulb and tract and may extend posteriorly to contain the optic nerve, typically with optic atrophy; if mixed with papilledema on the other aspect, these abnormalities are known as the Foster Kennedy syndrome (web page 213). A massive aneurysm of the anterior cerebral or anterior communicating artery may produce an identical constellation. In some cases of elevated intracranial strain, olfactory sense has been impaired without evidence of lesions within the olfactory bulbs. In a way, this can be a situation of "smell blindness," analogous to color blindness. During migraine assaults and in some cases of aseptic meningitis, the patient could also be unusually delicate not only to mild and sound however typically to odors as nicely. Dysosmia or Parosmia these terms check with distortions of odor perception the place an odor is current. Parosmia may occur with native nasopharyngeal conditions such as empyema of the nasal sinuses and ozena. In some cases the irregular tissue itself could be the source of disagreeable odors; in others, the place partial accidents of the olfactory bulbs have occurred, parosmia is within the nature of an olfactory phantasm. Parosmia may be a troublesome symptom in middle-aged and elderly individuals with a depressive sickness, who may report that each article of food has a particularly disagreeable odor (cacosmia). Some reviews indicate that repeated anesthetization of the nasal mucosa reduces or abolishes the parosmic disturbance. Most often this is due to temporal lobe seizures ("uncinate fits"), by which circumstances the olfactory hallucinations are brief and accompanied by an alteration of consciousness and other manifestations of epilepsy (web page 277). If the patient is convinced of the presence of a hallucination and likewise offers it private reference, the symptom assumes the standing of a delusion. The combination of olfactory hallucinations and delusions of this type signifies a psychiatric sickness. In most cases, the smells seem to emanate from the patient (intrinsic hallucinations); in others, they appear to come from an exterior source (extrinsic hallucinations). Both sorts differ in depth and are outstanding with respect to their persistence. According to Pryse-Phillips, who took observe of the psychiatric sickness in a sequence of 137 patients with olfactory hallucinations, most were associated with endogenous depression and schizophrenia. In schizophrenia, the olfactory stimulus is normally interpreted as arising externally and as being induced by someone for the purpose of upsetting the patient. The patient uses all manner of how to eliminate the perceived stench, the usual ones being extreme washing and use of deodorants; the situation may lead to social withdrawal. There is some cause to consider that the amygdaloid group of nuclei is the source of the hallucinations, since stereotactic lesions right here have reportedly abolished both the olfactory hallucinations and the psychiatric dysfunction (see Chitanondh). Olfactory hallucinations and delusions may occur along side Alzheimer dementia, however when this happens one must also think about the potential of an related late-life depression. Usually the stimuli appear to be extrinsic, however in this regard it ought to be noted that odors imagined by normal individuals are also perceived as coming from outside the person through impressed air, and unsightly ones are extra clearly represented than nice ones. Loss of Olfactory Discrimination (Olfactory Agnosia) Finally, one should think about a dysfunction by which the first perceptual features of olfaction (detection of odors, adaptation to odors, and recognition of different intensities of the identical odor) are intact however the capability to distinguish between odors and their recognition by quality is impaired or misplaced. In the writings on this subject, this deficit is normally referred to as a dysfunction of olfactory discrimination. In dealing with other sense modalities, however, the inability to establish and name a perceived sensation can be referred to as an agnosia. To acknowledge this deficit requires particular testing, such as matching to pattern, the identification and naming of quite a lot of scents, and figuring out whether or not two odors are similar or completely different. As indicated above, the olfactory dysfunction within the alcoholic Korsakoff patient is more than likely as a result of lesions within the medial dorsal nucleus of the thalamus; several observations in animals indicate that this nucleus and its connections with the orbitofrontal cortex give rise to deficits in odor discrimination (Mair et al; Slotnick and Kaneko). Eichenbaum and associates demonstrated an identical impairment of olfactory capacities in a patient who had undergone in depth bilateral medial temporal lobe resections. The operation was believed to have eliminated a considerable portion of the olfactory afferents to the frontal cortex and thalamus, though there was no anatomic verification of this. In patients with stereotactic or surgical amygdalotomies, Andy and coworkers noted an identical reduction in odor discrimination. Thus it appears that both portions of the upper olfactory pathways (medial temporal lobes and medial dorsal nuclei) are necessary for the discrimination and identification of odors. The taste buds are spherical or oval structures, every composed of as much as 200 vertically oriented receptor cells organized like the staves of a barrel. The superficial portion of the bud is marked by a small opening, the taste pore or pit, which opens onto the mucosal floor. The tips of the sensory cells project through the pore as numerous filiform microvilli ("taste hairs"). The taste receptors are activated by chemical substances in answer and transmit their exercise along the sensory nerves to the brainstem. There are four primary and readily tested taste sensations that have been lengthy known: salty, sweet, bitter, and sour; lately a fifth, "umani"- the taste of glutamate, aspartate, and certain ribonucleotides- has been added. The full range of taste sensations is far broader, consisting of mixtures of these elementary gustatory sensations. Older notions of a "tongue map," which implied the existence of particular areas subserving one or one other taste, are incorrect. In latest years, a G-protein transduction system (gustaductin), just like the one for olfaction, has been discovered to be operative in signaling taste sensations within the tongue receptors. A discussion of this system may be discovered within the commentary by Brand cited within the References. The variety of taste buds, not massive to start with, is steadily decreased with age; also, changes occur within the taste cell membranes, with impaired perform of ion channels and receptors (Mistretta). Both gustatory (and olfactory) acuity diminish (every little thing begins to taste and smell the identical). According to Schiffman, taste thresholds for salt, sweeteners, and amino acids are 2 to 2 half of occasions greater within the elderly than within the younger. The reduction within the acuity of taste and smell with getting older may lead to a distortion of food habits. Interesting genetic polymorphisms within the receptor for sweet substances in rats have been discovered to underlie differences within the proclivity to ingest sweet substances, and an identical system has been proposed in humans (Chaudhari and Kinnamon). The primary pathway arises on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue; these taste fibers first run within the lingual nerve [a significant branch of the mandibular-trigeminal (fifth) cranial nerve]. After coursing within the lingual nerve for a brief distance, the taste fibers diverge to enter the chorda tympani (a branch of the seventh nerve); thence they pass through the pars intermedia and geniculate ganglion of the seventh nerve to the rostral a part of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius within the medulla, the place all taste afferents converge (see beneath). Fibers from the palatal taste buds pass through the pterygopalatine ganglion and greater superficial petrosal nerve, join the facial nerve at the stage of the geniculate ganglion, and proceed to the nucleus of the solitary tract (see. Possibly, some taste fibers from the tongue may reach the brainstem through the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve. The presence of this various pathway most likely accounts for reported cases of unilateral taste loss which have adopted part of the foundation of the trigeminal nerve and cases by which no lack of taste has occurred with part of the chorda tympani. From the posterior third of the tongue, taste bud, and palatal arches, the sensory taste fibers are conveyed through the glossopharyngeal nerve and ganglion nodosum to the nucleus of the tractus solitarius. Taste fibers from the extreme dorsal a part of the tongue and the few that come up from taste buds on the pharynx and larynx run within the vagus nerve. Rostral and lateral parts of the nucleus tractus solitarius, which receive the particular afferent (taste) fibers from the facial and glossopharyngeal nerves, represent the gustatory nucleus. One is the solitariothalamic lemniscus to the ventroposteromedial nu- cleus of the thalamus. A second passes to the ventral parts of the forebrain, to parts of the hypothalamus (which most likely influences autonomic perform), and to other basal forebrain limbic areas in or near the uncus of the temporal lobe. Other ascending fibers lie near the medial lemniscus and are both crossed and uncrossed. Experiments in animals indicate that taste impulses from the thalamus project to the tongue-face area of the postrolandic sensory cortex. This might be the tip station of gustatory projections in humans as nicely, insofar as gustatory hallucinations have been produced by electrical stimulation of the parietal and/or rolandic opercula (Hausser-Hauw and Bancaud).
Cheap 25/200mg aggrenox caps
If retinopathy is progressing or sightthreatening, then examinations will be required more regularly. B Eye examinations should happen before pregnancy or in the first trimester in patients with preexisting type 1 or type 2 diabetes, after which patients ought to be monitored every trimester and for 1 year postpartum as indicated by the degree of retinopathy. B Treatment c c Optimize glycemic management to reduce the danger or slow the development of diabetic retinopathy. A Optimize blood strain and serum lipid management to reduce the danger or slow the development of diabetic retinopathy. A Adults with type 1 diabetes should have an initial dilated and comprehensive eye examination by an ophthalmologist or optometrist inside 5 years after the onset of diabetes. B Patients with type 2 diabetes should have an initial dilated and comprehensive eye examination by an ophthalmologist or optometrist at the time of the diabetes diagnosis. A the standard standard treatment, panretinal laser photocoagulation therapy, is indicated to reduce the danger of vision loss in patients with high-threat proliferative diabetic retinopathy and, in some instances, severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. A Intravitreous injections of anti� vascular endothelial progress issue are indicated for central-concerned diabetic macular edema, which occurs S110 Microvascular Complications and Foot Care Diabetes Care Volume forty one, Supplement 1, January 2018 c beneath the foveal center and will threaten studying vision. A Diabetic retinopathy is a extremely specific vascular complication of each type 1 and kind 2 diabetes, with prevalence strongly related to each the duration of diabetes and the extent of glycemic management (sixty nine). Diabetic retinopathy is the most frequent trigger of new instances of blindness among adults aged 20�seventy four years in developed countries. Glaucoma, cataracts, and other disorders of the eye happen earlier and more regularly in folks with diabetes. In addition to diabetes duration, components that increase the danger of, or are associated with, retinopathy include chronic hyperglycemia (70), diabetic kidney disease (seventy one), hypertension (72), and dyslipidemia (seventy three). Intensive diabetes administration with the aim of achieving close to-normoglycemia has been proven in giant prospective randomized studies to stop and/or delay the onset and development of diabetic retinopathy and probably enhance patientreported visual function (28,seventy four�76). Several case sequence and a controlled prospective examine counsel that pregnancy in patients with type 1 diabetes may aggravate retinopathy and threaten vision, especially when glycemic management is poor at the time of conception (seventy eight,79). Youth with type 1 or type 2 diabetes are additionally in danger for complications and need to be screened for diabetic retinopathy (80). If diabetic retinopathy is current, immediate referral to an ophthalmologist is recommended. Subsequent examinations for patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes are usually repeated annually for patients with minimal to no retinopathy. Exams every 1�2 years may be value-effective after a number of regular eye exams, and in a population with nicely-controlled type 2 diabetes, there was basically no threat of development of significant retinopathy with a 3-year interval after a standard examination (eighty one). Less frequent intervals have been present in simulated modeling to be probably effective in screening for diabetic retinopathy in patients without diabetic retinopathy (82). More frequent examinations by the ophthalmologist will be required if retinopathy is progressing. High-high quality fundus images can detect most clinically vital diabetic retinopathy. Retinal photography may also enhance effectivity and reduce costs when the expertise of ophthalmologists can be utilized for more complex examinations and for therapy (eighty five). In-person exams are nonetheless needed when the retinal photographs are of unacceptable high quality and for follow-up if abnormalities are detected. Results of eye examinations ought to be documented and transmitted to the referring well being care professional. Type 1 Diabetes diagnosis should have an initial dilated and comprehensive eye examination at the time of diagnosis. Pregnancy Pregnancy is associated with a fast development of diabetic retinopathy (87,88). In addition, fast implementation of intensive glycemic administration in the setting of retinopathy is associated with early worsening of retinopathy (79). Treatment Two of the primary motivations for screening for diabetic retinopathy are to stop loss of vision and to intervene with treatment when vision loss can be prevented or reversed. Panretinal laser photocoagulation continues to be commonly used to manage complications of diabetic retinopathy that contain retinal neovascularization and its complications. In addition, it was noticed that patients handled with ranibizumab tended to have less peripheral visual area loss, fewer vitrectomy surgical procedures for secondary complications from their proliferative disease, and a decrease threat of growing diabetic macular edema. Other rising therapies for retinopathy which will use sustained intravitreal supply of pharmacologic agents are currently under investigation. B Assessment for distal symmetric polyneuropathy should include a careful history and assessment of both temperature or pinprick sensation (smallfiber function) and vibration sensation utilizing a 128-Hz tuning fork (for largefiber function). All patients should have annual 10-g monofilament testing to establish ft in danger for ulceration and amputation. B Symptoms and indicators of autonomic neuropathy ought to be assessed in patients with microvascular complications. E Optimize glucose management to stop or delay the development of neuropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes A and to slow the development of neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. B Assess and deal with patients to reduce pain related to diabetic peripheral neuropathy B and signs of autonomic neuropathy and to enhance high quality of life. E Either pregabalin or duloxetine are recommended as initial pharmacologic treatments for neuropathic pain in diabetes. The commonest early signs are induced by the involvement of small fibers and include pain and dysesthesias (unpleasant sensations of burning and tingling). The following scientific exams may be used to assess smalland giant-fiber function and protecting sensation: 1. Protective sensation: 10-g monofilament these exams not only display for the presence of dysfunction but also predict future threat of complications. See American Diabetes Association place assertion "Diabetic Neuropathy" for more details (99). The diabetic neuropathies are a heterogeneous group of disorders with various scientific manifestations. The early recognition and appropriate administration of neuropathy in the affected person with diabetes is important. Nondiabetic neuropathies may be current in patients with diabetes and may be treatable. Recognition and treatment of autonomic neuropathy may enhance signs, reduce sequelae, and enhance high quality of life. Specific treatment for the underlying nerve injury, aside from improved glycemic management, is currently not out there. Glycemic Screening c All patients ought to be assessed for diabetic peripheral neuropathy S112 Microvascular Complications and Foot Care Diabetes Care Volume forty one, Supplement 1, January 2018 Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy the signs and indicators of autonomic neuropathy ought to be elicited fastidiously in the course of the history and physical examination. Major scientific manifestations of diabetic autonomic neuropathy include hypoglycemia unawareness, resting tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, gastroparesis, constipation, diarrhea, fecal incontinence, erectile dysfunction, neurogenic bladder, and sudomotor dysfunction with both increased or decreased sweating. Gastrointestinal neuropathies may contain any portion of the gastrointestinal tract with manifestations together with esophageal dysmotility, gastroparesis, constipation, diarrhea, and fecal incontinence. Gastroparesis ought to be suspected in people with erratic glycemic management or with upper gastrointestinal signs without one other identified trigger. Exclusion of natural causes of gastric outlet obstruction or peptic ulcer disease (with esophagogastroduodenoscopy or a barium examine of the stomach) is needed before contemplating a diagnosis of or specialised testing for gastroparesis. The diagnostic gold standard for gastroparesis is the measurement of gastric emptying with scintigraphy of digestible solids at 15-min intervals for 4 h after meals consumption. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy may also trigger genitourinary disturbances, together with sexual dysfunction and bladder dysfunction. In men, diabetic autonomic neuropathy may trigger erectile dysfunction and/or retrograde ejaculation (99). Female sexual dysfunction occurs more regularly in those with diabetes and presents as decreased sexual need, increased pain during intercourse, decreased sexual arousal, and inadequate lubrication (103). Lower urinary tract signs manifest as urinary incontinence and bladder dysfunction (nocturia, frequent urination, urination urgency, and weak urinary stream). Neuropathic Pain Neuropathic pain can be severe and may impression high quality of life, restrict mobility, and contribute to depression and social dysfunction (110). No compelling proof exists in assist of glycemic management or life-style administration as therapies for neuropathic pain in diabetes or prediabetes, which leaves only pharmaceutical interventions (111). Given the vary of partially effective treatment choices, a tailor-made and stepwise pharmacologic technique with careful consideration to relative symptom improvement, medication adherence, and drugs unwanted side effects is recommended to achieve pain discount and enhance high quality of life (113�115). The majority of studies testing pregabalin have reported favorable effects on the proportion of participants with no less than 30�50% improvement in pain (112,114,116�119). Adverse effects may be more severe in older patients (122) and may be attenuated by decrease beginning doses and more gradual titration.
Safe aggrenox caps 25/200 mg
Should hallucinations and delusions persist in a troubling trend, an antipsychotic, as described in Section 5. Once symptoms have been brought beneath control, the sedative�hypnotic may be steadily tapered in daily decrements approximately equivalent to 10 % of the total daily dose initially required to impact control. Clinical features Intoxication is obtained either by soaking a rag in the volatile substance and holding it to the face or by placing the substance in a plastic or paper bag and then inhaling; when a bag is used it could depart a telltale circular rash on the face. The intoxication (Evans and Raistrick 1987) occurs inside minutes and is characterized by a dreamy euphoria, drowsiness, dizziness, dysarthria, diplopia, nystagmus, and ataxia. Some may experience confusion and hallucinations, which may be either visual or, less commonly, auditory, and others could turn out to be irritable and impulsive. If leaded gasoline is sniffed, intoxication may be accompanied by chorea and myoclonus (Goldings and Stewart 1982). Withdrawal (Evans and Raistrick 1987; Watson 1979) occurs inside 1�2 days of abstinence and is characterized by irritability, sweating, tremulousness, and insomnia, all of which usually remit inside a matter of days. These include airplane or mannequin glue, paint thinner, kerosene, gasoline, fingernail polish remover, the propellants in aerosol sprays and spray paints, and typewriter correction fluid. Each of these merchandise Differential prognosis Intoxication with alcohol or sedative�hypnotics could yield a somewhat similar scientific picture. The odor of solvents on clothes or pores and skin may be a clue, as could a rash on the face; if toluene has been used it could be detected in the blood for days (King et al. In the United States, the two most typical preparations of cannabis are marijuana and hashish. Hashish is a stronger preparation, composed of the resin scraped from the leaves and flowers of the plant, and is normally smoked. Clinical features Intoxication with cannabis (Allentuck and Bowman 1942; Bromberg 1934; Clark and Nakashima 1968; Clark et al. Thinking turns into slowed and patients often develop a heightened sense of the ridiculous, laughing and guffawing at in any other case prosaic things; in some cases depersonalization or derealization could occur. Typically, intoxication is accompanied by conjunctival injection, dry mouth, increased urge for food, mild ataxia, mild tachycardia, and a combination of increased supine blood stress and orthostatic hypotension. In a minority of cases of intoxication, problems could occur, together with anxiety, psychosis, and delirium. Anxiety could occur throughout in any other case unremarkable intoxications and will at instances crescendo to represent an anxiety attack (Bromberg 1934), with tremor, tachycardia, and palpitations; usually the anxiety resolves as does the intoxication. Psychosis (Kroll 1975; Mathers and Ghodse 1992; Talbott and Teague 1969; Weil 1970) may occur throughout an intoxication and patients could develop delusions of persecution, which may be accompanied by auditory or visual hallucinations. Patients could turn out to be quite agitated in the midst of this, and a few will flee the scene or seek safety in another method. Before leaving this discussion of psychosis, mention must also be made of the possible incidence of a continual psychosis secondary to cannabis use. Patients turn out to be confused, agitated, and at instances incoherent; delusions and hallucinations may occur. This delirium could either clear as the intoxication does, or could persist for as much as a couple of days. Tolerance to cannabis can develop and is manifest by a decreased euphoric response and a diminution of the tachycardia and elevated supine blood stress normally seen throughout intoxication. Symptoms are usually mild and consist of anxiety, irritability, restlessness, a nice tremor, diaphoresis, and insomnia. Withdrawal symptoms reach a peak intensity inside 1�2 days and then resolve after a complete of 4�5 days. Course Recreational use of cannabis is extraordinarily common amongst adolescents and young adults, and most of these individuals either cease totally or greatly cut back their use as they begin to assume adult responsibilities. Cannabis abuse is marked by frequent intoxication regardless of social and legal penalties, and dependence is heralded by the onset of tolerance and withdrawal. Overall, abuse and dependence are far less common than leisure use, occurring in not more than 5 % of adolescents and young adults. Differential prognosis Clinical features Uncomplicated intoxication with cannabis may be mimicked by intoxication with alcohol, sedative�hypnotics, inhalants, and opioids, and cannabis intoxication difficult by psychosis or delirium may be confused with hallucinogen or phencyclidine intoxication; moreover, many patients could current with a combined intoxication, having utilized each cannabis and a number of of these other substances. History and urine drug screens may be required to make the differential prognosis. In less than a minute the rush tends to move, to be replaced by a drowsy, vaguely euphoric feeling which will final for hours and which is accompanied by problem with focus and dysarthria. The pupils are usually constricted, peristalsis is slowed, and constipation ensues; urinary hesitancy or retention may occur. Meperidine is metabolized to normeperidine, and this metabolite could cause agitation, tremor, mydriasis, increased deep tendon reflexes, and, sometimes, myoclonus or seizures (Kaiko et al. Pentazocine intoxication, when excessive doses are utilized, may be accompanied by dysphoria, anxiety, hallucinations, and bizarre ideas, together with dizziness and diaphoresis (Challoner et al. Overdose itself is characterized by stupor or coma, accompanied by hypotension and respiratory depression. Pupils are initially pinpoint; nonetheless, with the appearance of cerebral anoxia, mydriasis seems. Pulmonary edema and seizures could occur, and dying is normally due to respiratory arrest. Those who survive may be left with an anoxic dementia or sequelae of watershed infarctions. Tolerance could develop to virtually the entire results of opioids (aside from miosis and constipation) and addicts could progressively improve their doses to obtain intoxication, typically to beautiful ranges of a gram or extra of morphine. Withdrawal is characterized initially by a way of uneasiness and a craving for the drug; quickly after, yawning, lacrimation, and rhinorrhea seem, accompanied in some cases by diaphoresis. Upon awakening, the entire earlier symptoms intensify and patients turn out to be irritable, dysphoric, restless, and demanding. Intense bone and muscle pain, particularly in the again, arms, and legs, additionally occurs, and patients could engage in seemingly Treatment Uncomplicated intoxication usually requires solely statement until the intoxication has passed. Psychosis, if problematic, may be treated with a dose of an antipsychotic, corresponding to 5 mg of haloperidol or 1�2 mg of risperidone, with repeat doses as wanted. Delirious patients should be closely monitored until the delirium has passed, and may be treated as outlined in Section 5. The general goal of therapy in abusers and addicts is abstinence, and numerous types of psychotherapy have been attempted. Unfortunately, many adolescents and young adults merely see nothing mistaken with their use, and infrequently drop out of therapy. Opium is obtained from the juice of the poppy plant, and two opiates are found inside opium, namely morphine and codeine. Synthetic and semi-synthetic derivatives include heroin, oxycodone, hydromorphone, meperidine, pentazocine, methadone, and buprenorphine: these final two derivatives, though often used in the therapy of opioid withdrawal and habit, may be used for intoxication (Torrens et al. Of the entire opioids, oxycodone and heroin are probably the most commonly used for intoxication. Although these drugs may be taken orally for intoxication, most users choose a parenteral route as the impact is extra quick and intense; tablets may be crushed, dissolved, and filtered (often using cigarette filters) to yield a more or less adulterated and contaminated liquid, which p 21. The pupils are dilated and the temperature, pulse, and blood stress are all increased. Nausea, vomiting, intestinal cramping, and diarrhea occur, and the ensuing fluid loss may be so severe that it causes circulatory collapse. Withdrawal normally begins throughout the first day of abstinence, peaks in a matter of days, and then usually subsides over every week or so; in heavy users, nonetheless, a protracted withdrawal syndrome could persist for weeks as much as 6 months, and is characterized by dysphoria, irritability, anhedonia, insomnia, and drug craving (Martin and Jasinski 1969). Intravenous use brings the chance of bacteremia with pulmonary abscess, endocarditis, cerebral abscess, cerebral mycotic aneurysm, meningitis, osteomyelitis, and tetanus. Furthermore, the presence of particulates in the injected fluid (as could occur when cigarette filters are used) could lead to pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, and cor pulmonale. Particulates may acquire in regional lymph nodes inflicting a continual lymphadenopathy with edema, particularly of the palms. Differential prognosis Opioid intoxication may be partially mimicked by intoxication with alcohol, sedative�hypnotics or inhalants; nonetheless, these intoxications usually lack the intense miosis characteristic of most opioid intoxications; in uncertain cases drug screening will resolve the issue. It should be borne in mind, nonetheless, that many patients will use other substances along with opioids: cocaine may be used to cut back sedation, and alcohol or sedative�hypnotics may be employed to ease the pain of withdrawal. Withdrawal should usually solely be attempted on a secure inpatient unit, and, given the intense drug craving seen throughout withdrawal, patients should be confined to the ward until the withdrawal has run its course; visitation, if allowed at all, should be closely and repeatedly supervised. Prochlorperazine may be given for nausea and vomiting, diphenoxylate for diarrhea, and amitriptyline (in a dose of approximately 50 mg at bedtime) for insomnia (Srisurapanont and Jarusuraisin 1998), and these may be made obtainable for many who bear therapy with either opioids or clonidine.
References:
- https://www.thelancet.com/pdfs/journals/lancet/PIIS0140-6736(08)60457-2.pdf
- https://docx2.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/DSM5Conceptual.pdf
- https://www.fmdsa.org/dynamic/files/fmdsa2019-brochure-blu.pdf
.png)