Trusted anastrozole 1mg
After a couple of of} days V5-bearing cells decline (upper panel) and are replaced by cells expressing the next most proximal gene, V6. The V5-bearing cells turn into established selectively in the dermis, whereas the V6-bearing cells turn into established in the epithelium of the reproductive tract. Remarkably, given the massive variety of theoretically possible rearrangements, the receptors expressed by these early waves of: T cells are essentially homogeneous. Thus, certain V, D, and J gene segments are chosen for rearrangement at specific instances throughout embryonic improvement; the reasons for this limitation are poorly understood. After these preliminary waves, T cells are produced repeatedly somewhat than in bursts, and: T cells predominate, making up greater than 95% of thymocytes. They have a considerably more diverse receptor repertoire, for which quantity of} different V gene segments have been used, and the receptor sequences have ample N-nucleotide additions. Most of those: T cells, like: T cells, are found in peripheral lymphoid tissues somewhat than in the epithelial sites populated by the early: T cells. The developmental adjustments in V gene phase usage and N-nucleotide addition in murine: T cells parallel adjustments in B-cell populations throughout fetal improvement, which shall be mentioned later (see Section 7-28). Their functional significance is unclear, nonetheless, and not all of those adjustments in the pattern of receptors expressed by: T cells occur in people. Rearrangement of the -chain locus and manufacturing of a series set off quantity of} occasions in growing thymocytes. T cells expressing: receptors first appear a couple of of} days after the earliest: T cells and quickly turn into essentially the most ample kind of thymocyte (see. The rearrangement of the - and -chain loci throughout T-cell improvement follows a sequence that carefully parallels the rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy- and light-chain loci throughout Bcell improvement (see Section 7-9). The sequence of gene rearrangements is shown, along with an indication of the stage at which the occasions happen and the character of the cell-surface receptor molecules expressed at each stage. It is possible to make a lot as} 4 makes an attempt to generate a productive rearrangement at the -chain locus, as there are 4 D gene segments and two units of J gene segments (not shown). The productively rearranged gene is expressed initially inside the cell after which at low ranges on the cell surface. The expression of the pre-T-cell receptor alerts the growing thymocytes via the tyrosine kinase Lck to halt -chain gene rearrangement, and to endure a number of} cycles of division. Rearrangements at the -chain locus can proceed via quantity of} cycles, due to the massive variety of V and J gene segments, in order that productive rearrangements almost all the time occur. The J gene segments are adopted by a single C gene, which incorporates separate exons for the fixed and hinge domains and a single exon encoding the transmembrane and cytoplasmic areas (not shown). The:pT advanced is a functional pre-T-cell receptor analogous to the:VpreB:5 pre-B-cell receptor advanced in B-cell improvement (see Section 7-9). All these occasions require the cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase Lck, which subsequently associates with the co-receptor proteins. The role of the expressed chain in suppressing further -chain locus rearrangement could be demonstrated in transgenic mice containing a rearranged T-cell receptor -chain transgene: these mice express the transgenic chain on just about 100% of their T cells, displaying that rearrangement of the endogenous -chain genes is strongly suppressed. The significance of pre-T has been shown by the hundredfold decrease in: T cells and by the absence of allelic exclusion at the locus in mice deficient in pre-T. Once the cells stop dividing, each of those can independently rearrange its -chain genes, in order that a single functional chain could be associated with many alternative chains in the progeny cells. The expression of those molecules via T-cell improvement is illustrated in. TdT, the protein liable for insertion of Nnucleotides at gene phase junctions in each B and T cells, is expressed throughout the developmental interval in which thymocytes are rearranging T-cell receptor gene segments; N-nucleotides could be found at the junctions of all rearranged and genes. The roles these molecules play in mature T cell signaling are described in Chapter 6. Finally, a set of transcription elements guides the development of thymocytes from one stage to the next. A variety of essential elements have been recognized; in some cases gene knockout studies have shown at which stage of improvement they play essential roles. Thus, transcription elements are turned on at varied developmental phases and are liable for regular improvement via these phases by controlling the expression of essential genes. The temporal expression of quantity of} mobile proteins recognized to be essential for early T-cell improvement. The expression of a set of proteins is depicted with respect to the phases of thymocyte improvement as decided by cell-surface marker expression. The proteins listed here are|listed beneath are} a selection of these recognized to be associated with early T-lineage improvement, and have been included due to their proven significance in the developmental sequence, largely on the basis of studies in mice. T-cell -chain genes endure successive rearrangements until optimistic selection or cell dying intervenes. As with the immunoglobulin light-chain genes, repeated makes an attempt at rearrangement are possible. This means that T cells with an preliminary nonproductive gene rearrangement are to be rescued by a subsequent rearrangement than are B cells with a nonproductive light-chain gene rearrangement. Multiple successive rearrangement occasions can rescue nonproductive T-cell receptor -chain gene rearrangements. The -chain rescue pathway resembles that of the immunoglobulin light-chain genes (see Section 7-10), however the variety of possible successive rearrangements is greater. The potential lots of} successive rearrangements at each alleles of the -chain locus just about ensures that a functional chain shall be produced in each growing T cell. Moreover, many T cells have in-frame rearrangements on each chromosomes and thus can produce two kinds of chain. Thus, rearrangement of -chain genes continues even after manufacturing of a T-cell receptor at the cell surface. This part of gene rearrangement lasts for 3 or 4 days in the mouse and solely ceases when optimistic selection happens as a consequence of receptor engagement, or when the cell dies. The regulation of -chain gene rearrangement by optimistic selection therefore ensures that every T cell has solely a single functional specificity, even when two different chains are expressed. Thus, the part of -chain gene rearrangement marks an essential change in the forces shaping the future of the T cell. As lymphocytes differentiate from primitive stem cells, they proceed via phases which might be} marked by the sequential rearrangement of the antigen-receptor gene segments at the different genetic loci. As each full receptor-chain gene is generated, the protein it encodes is expressed as a part of} a receptor, and this alerts the growing cell to progress to the next developmental step. If rearrangement is profitable and a pre-B-cell receptor is made, heavy-chain gene rearrangement ceases and the resulting pre-B cells proliferate, adopted by the start of rearrangement at a light-chain locus. If the preliminary light-chain gene rearrangement is productive, a whole immunoglobulin B-cell receptor is shaped, gene rearrangement ceases, and B-cell improvement proceeds. In growing T cells, receptor loci rearrange according to a defined program just like that in B cells. There is, nonetheless, the added complication that individual precursor T cells can observe certainly one of two distinct strains of improvement. Rearrangement at these loci leads to cells bearing both: T-cell receptors or: T-cell receptors. Early in ontogeny,: T cells predominate, however from delivery onward greater than 90% of thymocytes express T-cell receptors encoded by rearranged and genes. In growing thymocytes, the, and loci rearrange first, and begin rearranging just about concurrently. Productive rearrangements of each a and a gene might lead to the manufacturing of a functional: T-cell receptor and the development of a: T cell. In these cells the technology of a -chain gene earlier than each and have rearranged leads to the expression of a functional chain and a pre-T-cell receptor. Thus gene rearrangement follows an ordered sequence in each B and T lineages to produce immature lymphocytes that every bear antigen receptors of a single specificity on their surface. These antigen receptors can now be tested for their antigen-recognition properties and the cells chosen accordingly; these selection processes are described in the next a part of} this chapter. Interaction with self antigens selects some lymphocytes for survival however eliminates others. We have adopted the development of a lymphocyte from a dedicated precursor to the purpose at which a whole antigen receptor is expressed on the cell surface. Development a lot as} this level has been targeted on testing for productive gene rearrangements and multiplying these cells which might be} profitable, while at the similar time controlling the rearrangement process in order that cells express just one receptor.
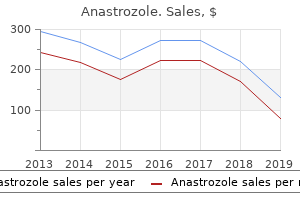
Effective anastrozole 1mg
The humoral immune response is initiated when B cells that bind antigen are signaled by helper T cells or by sure microbial antigens alone. It is a common rule in adaptive immunity that naive antigen-specific lymphocytes are difficult to activate by antigen alone. Naive T cells require a co-stimulatory sign from professional antigen-presenting cells; naive B cells require accent signals that can come either from an armed helper T cell or, in some cases, directly from microbial constituents. Thus, protein antigens binding to B cells each present a specific sign to the B cell by cross-linking its antigen receptors and allow the B cell to attract antigenspecific T-cell help. A second sign is required for B-cell activation by either thymus-dependent or thymusindependent antigens. The first sign required for B-cell activation is delivered via its antigen receptor (top panel). For thymus-independent antigens, the second sign could be delivered by the antigen itself (lower panel), or by non-thymus-derived accent cells (not shown). When mice are immunized with hen egg lysozyme coupled to three linked molecules of the complement fragment C3dg, the modified lysozyme induces antibody with out added adjuvant at doses a lot as} 10,000 instances smaller than unmodified hen egg lysozyme. Although armed peptide-specific helper T cells are required for B-cell responses to protein antigens, many microbial constituents, such as bacterial polysaccharides, can induce antibody production within the absence of helper T cells. T-cell dependent antibody responses require the activation of B cells by helper T cells that reply to the same antigen; that is called linked recognition. This presumably occurs by interaction with an antigen-presenting dendritic cell (see Section 8-1). Indeed, we saw in Chapter 5 that T cells can acknowledge inside peptides which might be} fairly distinct from the floor epitopes on the same protein acknowledged by B cells. It is, nevertheless, crucial that the peptide acknowledged by the T cell be a bodily part of of} the antigen acknowledged by the B cell, which may thus produce the suitable peptide after internalization of the antigen certain to its B-cell receptors. For example, by recognizing an epitope on a viral protein coat, a B cell can internalize a whole virus particle. Helper T cells which were primed earlier in an an infection by macrophages or dendritic cells presenting these inside peptides can then activate the B cell to make antibodies that acknowledge the coat protein. B cells and helper T cells must acknowledge epitopes of the same molecular complex have the ability to} work together. An epitope on a viral coat protein is acknowledged by the floor immunoglobulin on a B cell and the virus is internalized and degraded. Here, these complexes are acknowledged by helper T cells, which help to activate the B cells to produce antibody in opposition to the coat protein. Armed helper T cells will thus help only these B cells whose receptors bind an antigen containing the peptide they acknowledge. The requirement for linked recognition has necessary consequences for the regulation and manipulation of the humoral immune response. One is that linked recognition helps ensure self tolerance, as might be described in Chapter thirteen. An necessary software of linked recognition is within the design of vaccines, such as that used to immunize infants in opposition to Haemophilus influenzae type B. This bacterial pathogen can infect the lining of the mind, called the meninges, inflicting meningitis and, in severe cases, neurological harm or dying. Protective immunity to this pathogen is mediated by antibodies in opposition to its capsular polysaccharide. Although adults make very effective thymusindependent responses to these polysaccharide antigens, such responses are weak within the immature immune system of the infant. To make an efficient vaccine for use in infants, due to this fact, the polysaccharide is linked chemically to tetanus toxoid, a overseas protein in opposition to which infants are routinely and successfully vaccinated (see Chapter 14). B cells that bind the polysaccharide part of the vaccine could be activated by helper T cells specific for peptides of the linked toxoid. Linked recognition was initially discovered via studies of the production of antibodies to haptens (see Appendix I, Section A-1). When coupled at excessive density to a provider protein, nevertheless, they become immunogenic, as a result of|as a result of} the protein will carry a number of} hapten teams that can now cross-link B-cell receptors. In addition, T-cell dependent responses are attainable as a result of|as a result of} T cells could be primed to peptides derived from the protein. Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine is a conjugate of bacterial polysaccharide and the tetanus toxoid protein. After a number of} rounds of proliferation, B cells can additional differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells. Armed helper T cells stimulate the proliferation and then the differentiation of antigen-binding B cells. Antibodies are outstanding not only for the diversity of their antigen-binding websites but in addition for their versatility as effector molecules. A given heavy-chain V area can become associated with the C area of any isotype via the process of isotype switching (see Section 4-16). We will see later on this chapter how antibodies of every isotype contribute to the elimination of pathogens. All naive B cells express cell-surface IgM and IgD, but IgM makes up less than 10% of the immunoglobulin found in plasma, the place probably the most ample isotype is IgG. Much of the antibody in plasma has due to this fact been produced by B cells that have undergone isotype switching. Little IgD antibody is produced at any time, so the early stages of the antibody response are dominated by IgM antibodies. Later, IgG and IgA are the predominant isotypes, with IgE contributing a small however biologically necessary part of of} the response. The total predominance of IgG results, in part, from its longer lifetime within the plasma (see. IgM is so called due to its dimension: though monomeric IgM is only 190 kDa, it normally varieties pentamers, recognized as|often recognized as} macroglobulin (hence the M), of very massive molecular weight (see. When fixed to tissue mast cells, IgE has a a lot longer} half-life than its half-life in plasma proven here. The activation of the choice pathway of complement by IgA1 is caused not by its Fc portion however by its Fab portion. In pentameric IgM, the monomers are cross-linked by disulfide bonds to one another and to the J chain. In dimeric IgA, the monomers have disulfide bonds to the J chain properly as|in addition to} to one another. These experiments present that totally different cytokines preferentially induce switching to totally different isotypes. Some of these cytokines are the same as those who drive B-cell proliferation within the initiation of a B-cell response. The function of cytokines in directing B cells to make the totally different antibody isotypes is summarized in. The particular person cytokines induce (violet) or inhibit (red) production of sure isotypes. Isotype switching is preceded by transcriptional activation of heavy-chain C-region genes. Resting naive B cells transcribe the and genes at a low price, giving rise to floor IgM and IgD. Each of the cytokines that induces switching appears to induce transcription from the switch regions of two totally different heavy-chain C genes, selling specific recombination to one or other of these genes only. Such a directed mechanism is supported by the remark that particular person B cells incessantly undergo switching to the same C gene on each chromosomes, even though fact} that|although} the antibody heavy chain is only being expressed from one of the chromosomes. Thus, helper T cells regulate each the production of antibody by B cells and the isotype that determines the effector perform of the antibody. Antigen-binding B cells are trapped within the T-cell zone of secondary lymphoid tissues and are activated by encounter with armed helper T cells. One of probably the most puzzling options of the antibody response is how an antigenspecific B cell manages to encounter a helper T cell with an applicable antigen specificity. This question arises as a result of|as a result of} the frequency of naive lymphocytes specific for any given antigen is estimated to be between 1 in 10,000 and 1 in 1,000,000. Thus, the prospect of an encounter between a T lymphocyte and a B lymphocyte that acknowledge the same antigen should be between 1 in 108 and 1 in 1012. Achieving such an encounter is a lot more} difficult challenge than getting effector T cells activated, as a result of|as a result of}, within the latter case, only one of the two cells involved has specific receptors. Moreover, T cells and B cells largely occupy fairly distinct zones in peripheral lymphoid tissue (see.
Diseases
- Osteogenic sarcoma
- Muscle-eye-brain syndrome
- Mental retardation short stature wedge shaped epiphyses
- Shprintzen syndrome
- Ulbright Hodes syndrome
- Connexin 26 anomaly
Buy 1 mg anastrozole
Although affected kids seem to be regular at birth, signs gradually seem over the course of the primary 3 years. Among the signs first seen by the mother and father of autistic kids are a failure to communicate by 16 months of age, poor eye contact, an incapability to play with toys, an obsessive attachment to a toy or object, and a failure to smile. Although all people with an autism prognosis will show these traits, the severity varies significantly from one particular person to the next, as does the association or "comorbidity" with other diagnosable disorders corresponding to intellectual disability and seizures. Individuals at one finish of the spectrum could never develop language and exhibit severe cognitive impairment. At the other finish, people could develop a lot as} be socially awkward but intellectually gifted. In some instances, the gene mutations conferring danger for autism happen de novo, meaning that they happen sporadically either within the sperm or egg cells of the mother and father. One danger issue for such sporadic mutations is superior parental age, particularly of fathers. The variety of genetic etiologies partly explains why the signs range a lot from one particular person to the next. Imaging studies have proven that autistic kids also tend to to|are inclined to} have accelerated progress of the brain, each gray and white matter, after birth. This discovering suggests the brains of autistic infants have too many neurons and too many axons, though changes in glia are also potential. Brain progress is controlled by balancing the genesis and destruction of cells, axons, and synapses and the proteins that comprise them. Neuroscientists hope that understanding how the brain usually becomes wired together will suggest therapies to appropriate the altered trajectory of brain progress in kids in danger for autism. By knocking this gene out in mice and fruit flies, researchers have been in a position to} determine how brains operate differently way|in another way} with this mutation. These studies have raised the tantalizing chance that the veil of autism and intellectual disability may be lifted in some instances with appropriate drug remedy. The development of correct brain operate requires a careful stability between the genesis and elimination of cells and synapses (Box 23. Cell Death Entire populations of neurons are eliminated throughout pathway formation by a process known as as|often identified as} programmed cell death. Cell death displays competitors for trophic components, life-sustaining substances which are be} provided in restricted portions by the goal cells. The enter neurons are believed to compete with each other for restricted portions of trophic components produced by the goal neurons. Most of the receptors are neurotrophin-activated protein kinases, known as trk receptors, that phosphorylate tyrosine residues on their substrate proteins (recall phosphorylation from Chapter 6). The essential discovery of cell death genes by Robert Horvitz on the Massachusetts Institute of Technology was acknowledged with the 2004 Nobel Prize. It is now understood that neurotrophins save neurons by switching off this genetic program. The expression of cell death genes causes neurons to die by a process known as apoptosis, the systematic disassembly of the neuron. Apoptosis differs from necrosis, which is the accidental cell death resulting from injury to cells. Changes in Synaptic Capacity Each neuron can receive on its dendrites and soma a finite variety of synapses. Throughout the nervous system, synaptic capacity peaks early in development after which declines as the neurons mature. For instance, within the striate cortex of all species examined so far, the synaptic capacity of immature neurons exceeds that of adult cells by about 50%. In other phrases, visual cortical neurons within the infant brain receive one-and-a-half occasions as many synapses as do the neurons in adults. Yale University scientists Jean-Pierre Bourgeois and Pasko Rakic performed an in depth research to tackle this query within the striate cortex of the macaque monkey. They discovered that synaptic capacity was remarkably constant within the striate cortex from infancy until the time of puberty. However, through the subsequent adolescent period, synaptic capacity declined sharply-by nearly 50% in just over 2 years. A quick calculation revealed the following startling reality: the lack of synapses within the main visual cortex throughout adolescence happens at a mean price of 5000 per second. Simply blocking a subset of receptors with -bungarotoxin can also stimulate synapse elimination. Eventually, nonetheless, this polyneuronal innervation is lost, and every muscle fiber receives synaptic enter from a single alpha motor neuron (Figure 23. Silencing the exercise of the muscle fiber leads to a retention of polyneuronal innervation, whereas stimulation of the muscle accelerates the elimination of all but one enter. The answer seems to be inadequate receptor activation in an otherwise lively muscle. Another arrangement is that neuron A offers one synapse and neuron B offers 5. The goal cell receives the identical variety of synapses in each instances, however the innervation pattern has changed. There is abundant proof for widespread synaptic rearrangement within the immature brain. Unlike many of the earlier steps of pathway formation, synaptic rearrangement happens as a consequence of neural exercise and synaptic transmission. In the visual system, a few of this activity-dependent shaping of connections happens prior to birth in response to spontaneous neuronal discharges. However, significant activity-dependent development happens after birth and is influenced profoundly by sensory experience throughout childhood. In a very real sense, we be taught to see throughout a critical period of postnatal development. Macaque monkeys and cats have been utilized by Hubel and Wiesel as fashions for studies of activity-dependent visual system development as a result of|as a outcome of}, like people, each of those species have good binocular imaginative and prescient. Synaptic Segregation the precision of wiring achieved by chemical attractants and repellents can be impressive. In some circuits, nonetheless, the final refinement of synaptic connections seems to require neural exercise. Somewhat later, the ipsilateral projection arrives and intermingles with the axons of the contralateral eye. Then the axons from the two eyes segregate into the eye-specific domains which are be} attribute of the adult nucleus. Studies by Carla Shatz and her colleagues at Stanford University indicate that ganglion cells fireplace in quasisynchronous "waves" that spread across the retina. The origin of the wave and its course of propagation random, but throughout every wave, the exercise in a ganglion cell is extremely correlated with the exercise of its nearest neighbors. This hypothetical mechanism of synaptic plasticity was first articulated by Canadian psychologist Donald Hebb within the 1940s. Consequently, synapses modified on this way are known as Hebb synapses, and synaptic rearrangements of this type are known as Hebbian modifications. Inputs from the two eyes initially overlap after which segregate underneath the influence of exercise. The lively inputs onto the lively goal endure Hebbian modification and turn out to be more effective. Notice also that enter cells that fireside out of sync with the goal lose their hyperlink. This segregation happens before birth and seems to be a mixture of molecular guidance cues and retinal exercise differences (Box 23. However, this notion was challenged by the remark that eye-specific inputs to the visual cortex of ferrets can be detected even when development proceeds without any retinal exercise in any respect. This discovering means that molecular guidance mechanisms, somewhat than exercise patterns, trigger segregation into ocular dominance stripes. It is essential to recognize, nonetheless, that some problems in development can have a couple of solution. The branches of the mammalian family tree resulting in fashionable carnivores and primates diverged very early in evolutionary history, about ninety five million years in the past.
Order anastrozole 1 mg
We demonstrate that Ehmt1D6cre/+ knockouts have deficits in sensorimotor gating utilizing the acoustic startle task, and impaired studying and reminiscence utilizing the novel object recognition task and 1-choice serial reaction time task. We aim to define developmental gene expression variations amongst these populations and generate a toolbox of genetic markers to help research these disorders. Gene expression was validated with database analysis, in situ hybridization, and analysis of mouse Cre reporter traces. In addition to this, cortical neurons overlying the heterotopia were shown to exhibit a large increase of ongoing glutamatergic synaptic currents (Ackman et al. We subsequently postulate that neuronal networks in normotopic cortex experience a major transforming that might contribute to the event of scientific manifestations. Physiologically, barrel cortex circuits are organized in practical columns spanning a number of} layers (L1-L6). These results strongly counsel that the presence of band heterotopia associates a major reorganization of the normotopic cortex network that might impair the normal operation of somatosensory cortex. Although the survival rate of extraordinarily preterm infants has improved, many survivors (25% to 50%) develop cognitive impairment in later life. The mice showed delayed neuronal migration, ectopic neurons in the white matter, altered neuronal alignment, and irregular cortico-cortical axonal wiring. Left and right cerebral hemispheres are functionally uneven and small deviations have been correlated with pathologies such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorders. Bilateral asymmetry is genetically and developmentally outlined as a third axis besides the anterior/posterior and dorsal/ventral axes. We are utilizing Caenorhabditis elegans as a mannequin to research the molecular genetic bases of left/right (L/R) asymmetry. Mutants affecting early growth and spindle orientation have been reported to lead to bilaterally reversed embyos, and deletion of a G protein coding gene expressed at the 4-6 cell stage has been shown to yield as much as} 50% sinistral worms. We are taking a look at} initial or early symmetry-breaking steps by recording the speed of sinistral embryos, lethality rates, and the behavior of surviving adults. Our results with varied mutants show that surviving adults are impaired in each associative and non-associative studying. We are currently focusing on whether or not the reversed asymmetry immediately correlates with the observed results on behavior, and mapping potentially atypical neuronal circuits. Using the identical stimulation parameters, we evaluated the response to steady optical stimulation at 15Hz for an hour, and observed nearly 100 percent spike entrainment for the entire duration of the take a look at (n=3). Field recordings at M2 at 5Hz intervals (5mW, 2ms for 3s) demonstrate near complete spike entrainment at as much as} 8Hz, before falling at larger frequencies. We observe almost 100 percent spike entrainment to one hour of steady optical stimulation at 7 Hz. A self-grooming assay shall be employed to quantify changes in self grooming following bouts of stimulation. Our lab makes use of an inbred mouse pressure (C58) that reveals sturdy repetitive motor behavior phenotype (vertical jumping, backward somersaulting). Previous histochemical work from our lab means that alterations in basal ganglia circuitry mediate the expression of this repetitive behavior. We additionally carried out probabilistic tractography to assess intra-basal ganglia connectivity. Developmental Disorders Support: Lou Lou Foundation Hope4Harper Title: Hippocampal-specific ampa receptor dysregulation in cdkl5 ki mice Authors: *M. This technique is based on the quantitative autoradiographic willpower of the quantity of labeled product shaped (labeled protein) divided by the built-in specific activity of the tissue leucine pool for protein synthesis. There are two possible sources of leucine in the precursor pool: plasma and protein degradation. In this technique, the fraction of leucine derived from arterial plasma (lambda) is included in the calculation. However, the mechanisms linking chromatin organizers to neurological defects stay unclear. These proteins perform together in regulating chromatin structure and gene transcription. Our goal is to determine how cohesin and cohesin-related proteins regulate reminiscence, studying and social behavior in Drosophila. In a nonassociative social studying and reminiscence paradigm, we will to} measure how mutations in cohesin or NipB are able to to} remember and study. We are continuing to examine these phenotypes to evaluate how cohesin and cohesin-related proteins influence reminiscence and studying in adult organisms. Additionally, cortical layer and neuron type specific results on developmental connectivity, motor perform, and studying have but to be investigated fully. Moreover, our data indicates this coincides with a discount in activity-dependent Arc and c-Fos expression all through the motor cortex. Our experiments will look at whether or not these behavioral deficits are additionally linked to altered corticostriatal or callosal projection neuron outgrowth. Importantly, we find that the alteration in corticospinal connectivity is certainly layer 5 autonomous. These mutants additionally exhibit a major reduction in corticostriatal and callosal innervation. Craniofacial anomalies, together with cleft palate and other structural defects of the palate, as well as|in addition to} defects in sensory/motor coordination that impair speech and swallowing, are apparent in most people carrying with 22q11. Mice with homozygous null mutations of Ranbp1 have a severe, strongly penetrant cleft palate phenotype, with a whole failure of palatal closure, and a concomitant failure to kind key neural-crest derived palatal bone structures together with the palatal processes of the maxilla and premaxilla. Conditional neural-crest specific knockout of Ranbp1 yields a highlypenetrant however less-severe phenotype: Wnt1-Cre::Ranbp1 null embryos have closed however extremely dysmorphic palatal structure. Heterozygous Ranbp1 mutants display a more delicate and variable phenotype: heterozygous mutants show a delay in palatal shelf elevation/extension, as closure seems to be complete in most by E15. This delay seems to prefigure minor anomalies in palatal bone structure that are be} apparent at E17. Latrophilin three is produced by neuronal cells, localised at synapses and has putative roles in neuronal migration and synapse growth. Promisingly, earlier studies in Lphn3 -/- mice have reported elevated locomotive activity and altered gene expression of dopaminergic and serotoninergic receptors and transporters. In this research we look at the characteristics of Lphn3-deficient mice in a number of} behavioural domains. Movement analysis described altered limb positioning of Lphn3 -/- mice in comparison to|compared to} Lphn3 +/+ mice. However, Arx remains expressed in mature interneurons, suggesting a divergent, but unknown, perform. Preliminary investigation into the molecular mechanisms mediating these results counsel a dysregulation in homeostatic basal Ca2+ levels. Here, we further investigated the molecular pathways involved on this dysregulation of basal Ca2+ levels. Developmental Disorders Title: Defective heterochromatin transforming due to of} Nde1 loss leads to nuclear structure aberration of cortical neurons Authors: *Y. The genome and epigenome defects in Nde1 poor neurons were heterogeneous and shared the hallmarks of malignant transformation and degeneration. The mannequin has slight difficulty in motor coordination with out neuron cell loss, which accompanied with oligodendrocyte progenitor cell loss and dysmyelination in the sensorimotor cortex (Misumi et al, Cell Transplantation, 2016). To clarify a question why the motor deficits are induced in our mannequin with no apparent neuron loss, we targeted on the histological changes in the sensorimotor cortex. The mannequin was made by right frequent carotid artery occlusion adopted by 6% oxygen for one hour in P3 Wistar rat. Coronal sections in the hindlimb motor cortex (M1) were ready from adult mannequin rat and processed for the immunostaining. We used contactin related protein 1 (Caspr) antibody to detect dysmyelination and Golgi-staining to see dendritic morphological alterations. Caspar staining revealed that the constructive particle was often detected as twin-dots and the number of Caspr constructive particles was decreased in the H-I side cortex, where much less staining of myelin primary protein was shown in our earlier data. Golgi-staining revealed that the neurite morphology was totally different between H-I side and contralateral side. Furthermore, the more dendritic extension was observed in the H-I side of the cortex. For every dysfunction, genetic and environmental risk elements disrupt normal cognition and alter neuronal connectivity, as exemplified by alterations in dendrite and dendritic spine structure. These mice together with sex-matched, wild type littermates were evaluated utilizing a variety of|quite a lot of|a wide selection of} behavioral tests. Mice heterozygous for Trio in excitatory neurons exhibit elevated anxiety-like behavior, decreased locomotor activity, and deficits in sociability.
Order anastrozole 1mg
An important route of virus transmission is from an contaminated mom to her baby at start or through breast milk. At current, the best indicator of future illness is the extent of virus that persists in the blood plasma once as} the symptoms of acute viremia have passed. At this point, which can happen anyplace between 2 and 15 years or extra after the primary an infection, the period of clinical latency ends and opportunistic infections begin to appear. The first few weeks are typified by an acute influenza-like viral illness, typically called seroconversion illness, with high titers of virus in the blood. However, it has turn out to be increasingly clear that the course of the illness can vary extensively. These viruses persist and proceed to replicate for a few of} years} before causing overt signs of illness. Before fusion and entry of the virus, gp120 should additionally bind to a co-receptor in the membrane of the host cell. The chemokine receptors (see Chapters 2 and 10) are a closely associated family of G protein-coupled receptors with seven transmembrane-spanning domains. After binding of gp120 to the receptor and co-receptor, the gp41 then causes fusion of the viral envelope and the plasma membrane of the cell, allowing the viral genome and related viral proteins to enter the cytoplasm. The reverse transcriptase, integrase, and viral protease enzymes are packaged in the virion and are proven schematically in the viral capsid. The gene frequency of this mutant allele in Caucasoid populations kind of|is sort of} high at 0. The mutant allele has not been present in Japanese or black Africans from Western or Central Africa. Different promoter variants had been related to totally different rates of development of illness. Such low molecular weight inhibitors may be the precursors of useful drugs that could be be} taken by mouth. The gag gene encodes the structural proteins of the viral core, pol encodes the enzymes concerned in viral replication and integration, and env encodes the viral envelope glycoproteins. The product of the env gene, gp160, has to be cleaved by a bunch cell protease into gp120 and gp41, which are then assembled as trimers into the viral envelope. We will talk about the perform of two of these Tat and Rev in the following part. This binding releases gp41, which then causes fusion of the viral envelope with the cell membrane, and the release of the viral core into the cytoplasm. The genome can be learn in three frames and a number of|various|a variety of} other|and several of} other} of the viral genes overlap in several reading frames. The three major protein products Gag, Pol, and Env are synthesized by all infectious retroviruses. At least two of the viral genes, tat and rev, encode proteins, Tat and Rev respectively, that promote viral replication in activated T cells. Tat accommodates two binding sites, contained in one domain, named the transactivation domain. The expression of cyclin T1 is tremendously elevated in activated in contrast with quiescent T lymphocytes. When the provirus is first activated, Rev levels are low, the transcripts are translocated slowly from the nucleus, and thus quantity of} splicing occasions can happen. Thus, extra Tat and Rev are produced, and Tat in turn ensures that extra viral transcripts are made. Later, when Rev levels have elevated, the transcripts are translocated rapidly from the nucleus unspliced or solely singly spliced. These unspliced or singly spliced transcripts are translated to produce the structural parts of the viral core and envelope, along with the reverse transcriptase, the integrase, and the viral protease, all of which are needed to make new viral particles. As levels of Rev increase, much less extensively spliced and unspliced viral transcripts are transported out of the nucleus. The singly spliced and unspliced transcripts encode the structural proteins of the virus and the unspliced transcripts, which are the brand new} viral genomes, are packaged with these to type many new virus particles. Two viral proteins specifically have been the target of drugs aimed toward arresting viral replication. These are the viral reverse transcriptase, which is required for synthesis of the provirus, and the viral protease, which cleaves the viral polyproteins to produce the virion proteins and viral enzymes. Inhibitors of these enzymes stop the establishment of further an infection in uninfected cells. This phase reflects the decay in virus manufacturing from cells that had been actively contaminated initially of drug remedy, and indicates that the half-life of productively contaminated cells is similarly about 2 days. The outcomes additionally present that free virus is cleared from the circulation very rapidly, with a half-life of about 6 hours. After the initiation of such remedy, the virus produced by beforehand contaminated cells is now not infectious, and virus manufacturing is curtailed as these cells die and no new cells are contaminated. The first phase has a half-life of approximately 2 days and lasts for roughly 2 weeks, during which period viral manufacturing declines because the lymphocytes that had been productively contaminated at the onset of remedy die. Measurement of this phase of viral decay is unimaginable at current as viral levels in plasma are beneath detectable levels. When antiviral drugs are administered, variants of the virus that carry mutations conferring resistance to their effects emerge and broaden till former levels of plasma virus are regained. Resistance to variety of the} nucleoside analogues would possibly be} potent inhibitors of reverse transcriptase develops in a similarly short time. It might also be important to treat early in the middle of|in the midst of} an an infection, thereby reducing the probabilities that a variant virus has accumulated all the required mutations to resist the entire cocktail. Current treatments observe this technique and use combos of viral protease inhibitors along with nucleoside analogues (see. Within days of starting the drug, mutant drug-resistant variants can be detected in plasma (bottom panel) and in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Reprinted with permission from Nature 373:117-122, ©1995 Macmillan Magazines Limited 11-24. Macrophages and dendritic cells appear to ready to|be capable of|have the flexibility to} harbor replicating virus with out essentially being killed by it, and are subsequently believed to be an important reservoir of an infection, nicely as|in addition to} a method of spreading virus to other tissues such because the brain. These T-cell responses are unable to clear the an infection completely and might trigger some pathology. In other cases, variant peptides produced by the virus have been found to act as antagonists (see Section 6-12) for T cells conscious of the wild-type epitope, thus allowing each mutant and wild-type viruses to survive. Mutant peptides performing as antagonists have additionally been reported in hepatitis B virus infections, and similar mutant peptides might contribute to the persistence of some viral infections, especially when, as typically occurs, the immune response of an individual is dominated by T cells particular for a specific epitope. Infectious virus is current at relatively low levels in the peripheral blood of contaminated individuals during a prolonged asymptomatic phase, during which the virus is replicated persistently in lymphoid tissues. Typically, resistance is misplaced early to oral Candida species and to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which shows as an elevated prevalence of thrush (oral candidiasis) and tuberculosis. The first problem is the character of the an infection itself, featuring a virus that proliferates extremely rapidly and causes sustained an infection in the face of robust cytotoxic T-cell and antibody responses. The fourth problem is the flexibility of the virus to persist in latent type as a transcriptionally silent provirus, which is invisible to the immune system. This might stop the immune system from clearing the an infection once as} it has been established. In abstract, the flexibility of the immune system to clear infectious virus remains uncertain. However, against this pessimistic background, there are grounds for hope that profitable vaccines can be developed. Subunit vaccines, which induce immunity to only some proteins in the virus, have additionally been made. One such vaccine has been produced from the envelope protein gp120 and has been tested on chimpanzees. This vaccine proved to be particular to the precise pressure of virus used to make it, and was subsequently ineffective in protection against pure an infection. Subunit vaccines are additionally much less environment friendly at inducing prolonged cytotoxic T-cell responses. It can be unethical to conduct a vaccine trial with out attempting at the same time to reduce the exposure of a vaccinated population to the virus itself. However, the effectiveness of a vaccine can solely be assessed in a population during which the exposure price to the virus is high sufficient to assess whether or not vaccination is protecting against an infection. Balanced against that is the success of therapy with combos of the brand new} protease inhibitors and reverse transcriptase inhibitors, which supplies an incentive for probably contaminated folks to establish the presence of an infection and acquire the benefits of remedy.
Best 1mg anastrozole
Reassessing Solitary Confinement: the Human Rights, Fiscal, and Public Safety Consequences: Hearing Before the Subcomm. Prisoners spend virtually all of their time in these cells, forcing them to "sleep, eat, and defecate. Prisoners in solitary confinement could be imprisoned for years without touching one other particular person with affection. In addition to bodily isolating prisoners, solitary confinement socially isolates them. Prisoners have "no alternative for regular dialog or association with others. Even interactions between prisoners and workers are minimal, as cameras, intercoms, and computerized locking and tracking systems allow workers to monitor prisoners without interacting with them. And outcome of|as a result of} every cell has solid steel doors (which forestall communication between inmates, Grassian, 22 Wash. He has no alternative to participate in education or work applications, and his out-of-cell exercise time takes place in a steel cage roughly the same dimension as his cell. Psychological research on isolation and sensory deprivation exterior of the prison context establishes that social contact and environmental stimuli are important to maintaining mental well being. Studies on sensory deprivation-interfering with the stimulation a person usually receives from his environment-well illustrate the importance of sensory and perceptual stimuli. Placement in an "unchanging monotonous environment" "deprives the sensory organs of regular ranges of stimulation. More extreme sensory deprivation can cause "perceptual distortions, hallucinatory experiences, and sometimes high ranges of hysteria. For instance, air drive pilots flying alone at high altitudes, the place auditory and visible stimulation is restricted, have reported severe nervousness and detachment from reality, together with hallucinations. And isolated individuals can "endure from signs that resemble posttraumatic stress disorder-including `anxiety, nervousness. In particular, the "more indeterminate" the period of deprivation is, the larger the damaging results. Change at 501 ("[I]nforming topics of the higher time limit of the study enhanced their capacity to tolerate the isolation. In short, imposing social isolation and sensory deprivation has "drastic" results on individuals. Indeed, that solitary confinement, involving stimulus deprivation and a near-total loss of management, "is among the many most regularly used psychological torture strategies appears to underscore its aversive nature and damaging potential. Prolonged Solitary Confinement Causes Strikingly Similar Psychological Harms In A Substantial Percentage Of Prisoners. These conclusions about social isolation and sensory deprivation are strongly confirmed by research specific to solitary confinement, which "constantly and unequivocally" establish that solitary confinement causes antagonistic psychological results. While the signs are wide-ranging, their manifestation is each remarkably consistent and extremely prevalent amongst inmates in solitary confinement-prisoners in solitary confinement develop an "isolation" syndrome. These consistent and widespread psychological results establish prisoners in extended solitary confinement are danger of|susceptible to|vulnerable to} psychological deterioration. Prisoners in solitary confinement endure varied negative psychological results, ranging from nervousness and panic to self-mutilation and suicide to adjustments in brain perform. Among different psychological results, inmates turn into hypersensitive to external stimuli, similar to smells and noises. For instance, a prisoner reported that he "turned enraged by routine noises-the sound of doors opening because the guards made their hourly checks, the sounds of inmates in nearby cells. An inmate in one study famous that noises "start[ed] to sound like sticks beating men. Prisoners have "hallucinated that the colors on the walls have been altering," Gawande, Hellhole. Inmates in solitary confinement also have "described hearing voices, typically in whispers and often saying scary issues to them. Such results are signs of adjustments that occur within the brain the extreme idleness imposed by solitary confinement. Prisoners "turn into so desperate and despondent that they engage in self-mutilation. Terry Anderson, an Associated Press reporter held hostage for seven years, "snapped" after three years in solitary confinement, and beat his head in opposition to a wall until he was bleeding. Another "amputated certainly one of his pinkie fingers and chewed off the other, removed certainly one of his testicles and scrotum, sliced off his ear lobes, and severed his Achilles tendon with a pointy piece of steel. Individuals in solitary confinement additionally report suicidal impulses, and "a disturbingly high quantity" of inmates in solitary confinement resort to suicide. While less than 10 % of prisoners live in solitary confinement, half of prison suicides occur there. Senator John McCain, for instance, has mentioned that solitary confinement "crushes your spirit and weakens your resistance more successfully than some other mistreatment," and he "was overwhelmed often; denied enough medical remedy for two broken arms, a broken leg, and continual dysentery; and tortured to the point of having an arm broken again. The strikingly consistent and prevalent psychological results of solitary confinement indicate that it causes a definite psychological syndrome. Change at 496-503, 511-29 (discussing empirical research, descriptive accounts, and case research on the psychological results of solitary confinement). These modern research also are preserving with} observations of solitary-confinement prisoners within the nineteenth century, when the United States and European countries experimented with solitary confinement as a method of rehabilitating prisoners. That literature "described a hallucinatory, paranoid, confusional psychosis in which characteristic signs included. Moreover, these psychological signs are extremely prevalent-a substantial share of prisoners endure from them. Specifically, "[r]esearch means that between onethird and greater than 90 % expertise antagonistic signs in solitary confinement. And 8 of the 14 prisoners suffered difficulties with pondering, concentration, and memory. Haney, in a study of a hundred randomly chosen inmates in solitary confinement in Pelican Bay likewise "found terribly high rates of signs of psychological trauma. Hallucinations and different perceptual distortions affected 41% of prisoners, and 27% had thoughts of suicide. In a study of mentally sick prisoners in solitary confinement, 53% had tried suicide a minimum of|no less than} once as}. Correctional Association of New York, Mental Health within the House of Corrections: A Study of Mental Health Care in New York State Prisons fifty seven (2004), obtainable at. The patterns that prisoners develop in adapting to solitary confinement typically are permanent. While in solitary confinement, prisoners turn into desperate for any human response, even a negative one. They would possibly attempt to trigger an emergency "cell extraction"-a "brutal" removal from their cell- merely "to reaffirm their existence. That identical lack of social contact can cause different prisoners to severely withdraw to the point that they turn into frightened by social contact. After three years in prison ready for a trial date, together with 17 months in solitary confinement, "[e]verybody might see that he had modified. Six months after his release, he tried to slit his wrists and, when a friend stopped him, he tried to hold himself from a banister. A year later, he had deteriorated further, throwing out his tv outcome of|as a result of}, he mentioned, "it was watching me. This previous June, two years after he had been released, he committed suicide by hanging himself with an air-conditioning cord from a bed room window. The high rates of similar antagonistic psychological results in solitary-confinement prisoners establish that solitary confinement creates a risk of harm to all prisoners. For instance, extremely educated women with "a historical past of relatively strong psychological functioning" nonetheless "demonstrated vital psychopathological reactions to their extended confinement," together with nervousness, panic assaults, and perceptual disturbances. Similarly, a prisoner in California with no preexisting mental illness turned "catatonic, unresponsive, and incoherent" in isolation. Inmates with mental illness are particularly susceptible to the psychological results of isolation. And "[a]ll too regularly, mentally sick prisoners decompensate in isolation, requiring crisis care or psychiatric hospitalization. This particularly dangerous impact on the mentally sick is important, outcome of|as a result of} roughly one-third of solitary-confinement inmates are mentally sick. Mentally sick prisoners typically lack the capacity to comply with the inflexible rules and procedures of prison life, and so end up in solitary confinement as punishment for rule violations.
Batavia Cinnamon (Cinnamon Bark). Anastrozole.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Cinnamon Bark.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Premature ejaculation. Some evidence suggests that a specific cream containing cinnamon and many other ingredients might prevent premature ejaculation.
- How does Cinnamon Bark work?
- Diabetes, diarrhea, infections, worm infestations, the common cold, influenza, upset stomach, gas (flatulence), spasms, appetite stimulation, and menstrual discomfort.
- What is Cinnamon Bark?
- What other names is Cinnamon Bark known by?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96349
Generic anastrozole 1 mg
Protozoa and worms are usually grouped collectively as parasites, and are the topic of the self-discipline of parasitology, whereas viruses, micro organism, and fungi are the topic of microbiology. The remarkable variety of these pathogens has triggered the pure choice of two essential features of adaptive immunity. First, the benefit of ready to|with the power to|having the power to} recognize broad range|a variety} of different pathogens has pushed the event of receptors on B and T cells of equal or greater diversity. Second, the distinct habitats and life cycles of pathogens should be countered by a variety of distinct effector mechanisms. The characteristic features of each pathogen are its mode of transmission, its mechanism of replication, its pathogenesis or the means by which it causes illness, and the response it elicits. Infectious agents can grow in numerous physique compartments, as proven schematically in. We have already seen that two major compartments can be outlined intracellular and extracellular. Such pathogens can be subdivided additional into those who replicate freely within the cell, such as viruses and certain micro organism (species of Chlamydia and Rickettsia as nicely as Listeria), and those, such as the mycobacteria, that replicate in mobile vesicles. Many microorganisms replicate in extracellular spaces, both within the physique or on the surface of epithelia. Extracellular micro organism are usually susceptible to killing by phagocytes and thus pathogenic species have developed means of resisting engulfment. The encapsulated gram-positive cocci, for instance, grow in extracellular spaces and resist phagocytosis by the use of their polysaccharide capsule. Thus, these extracellular micro organism are cleared by the use of the humoral immune response (see Chapter 9). Different infectious agents trigger markedly different ailments, reflecting the varied processes by which they damage tissues. Many extracellular pathogens trigger illness by releasing specific toxic merchandise or protein toxins (see. Intracellular infectious agents regularly trigger illness by damaging the cells that house them. The specific killing of virus-infected cells by cytotoxic T cells thus not solely prevents virus unfold however removes damaged cells. The immune response to the infectious agent can itself be a significant reason for pathology in a number of} ailments (see. The pathology caused by a specific infectious agent also decided by} the positioning during which it grows; Streptococcus pneumoniae within the lung causes pneumonia, whereas within the blood it causes a rapidly deadly systemic sickness. As we realized in Chapter 2, for a pathogen to invade the physique, it should first bind to or cross the surface of an epithelium. When the an infection is because of|as a result of} of} intestinal pathogens such as Salmonella typhi, the causal agent of typhoid fever, or Vibrio cholerae, which causes cholera, the adaptive immune response occurs within the specialized mucosal immune system associated with the gastrointestinal tract, as described later in this chapter. Some intestinal pathogens even target the M cells of the gut mucosal immune system, which are specialized to transport antigens throughout the epithelium, as a method of entry. However, we should be on the alert always for brand spanking new|for model new} pathogens and new threats to well being. Pathogenic organisms are of 5 major sorts: viruses, micro organism, fungi, protozoa, and worms. Pathogens can be found in numerous compartments of the physique, the place they should be combated by different host protection mechanisms. The mechanisms of injury, consultant infectious agents, and the common names of the ailments associated with each are proven. Exotoxins are released by microorganisms and act at the surface of host cells, for instance, by binding to receptors. Endotoxins, which are intrinsic elements of microbial construction, trigger phagocytes to launch cytokines that produce native or systemic symptoms. Finally, adaptive immune response to the pathogen can generate antigen:antibody complexes that can activate neutrophils and macrophages, antibodies that can cross-react with host tissues, or T cells that kill infected cells. In addition, neutrophils, probably the most abundant cells early in an infection, launch many proteins and small-molecule inflammatory mediators that each management an infection and trigger tissue damage (not shown). The mammalian physique is susceptible to an infection by many pathogens, which should first make contact with the host after which set up a spotlight of an infection to be able to} trigger infectious illness. To set up an an infection, the pathogen should first colonize the pores and skin or the interior mucosal surfaces of the respiratory, gastrointestinal, or urogenital tracts after which overcome or bypass the innate immune defenses associated with the epithelia and underlying tissues. Pathogens differ tremendously in their existence and means of pathogenesis, requiring an equally diverse set of defensive responses from the host immune system. Moreover, deficiencies in nonadaptive defenses are rare, so it has seldom been attainable to study their penalties. Innate immunity does, nevertheless, appear to be essential for effective host protection, as proven by the progression of an infection in mice that lack elements of innate immunity however have an intact adaptive immune system. Adaptive immunity essential, as proven by the immunodeficiency syndromes associated with failure of one or the opposite arm of the adaptive immune response (see Chapter 11). Adaptive immunity is triggered when an an infection eludes the innate protection mechanisms and generates a threshold dose of antigen (see. This antigen then initiates an adaptive immune response, which becomes effective solely after a number of} days, the time required for antigen- specific T cells and B cells to locate their specific international antigen, to proliferate, and to differentiate into armed effector cells. In the earlier chapters of this guide, we discussed the cells and molecules that mediate the adaptive immune response, and the interactions between them. We second are|are actually} able to see how each cell type is recruited in flip the center of|in the midst of} a primary adaptive immune response to a pathogen, and how the effector lymphocytes and antibodies may be} generated in response to antigen are dispersed to their sites of motion. The yellow curve reveals the traditional course of an an infection in immunocompetent mice or people. The nonspecific responses of innate immunity are essential for an adaptive immune response to be initiated. The institution of a spotlight of an infection in tissues and the response of the innate immune system to it produce changes within the instant environment of the an infection. In a bacterial an infection, the very first thing that usually occurs is that the infected tissue becomes inflamed (see. The cytokines trigger the release of Weibel-Palade bodies from within the endothelial cells, which deliver P-selectin to the endothelial cell surface. Macrophages encountering micro organism within the tissues are triggered to launch cytokines that increase the permeability of blood vessels, permitting fluid and proteins to cross into the tissues. They also produce chemokines that direct the migration of neutrophils to the positioning of an infection. Later in an immune response, activated lymphocytes may also contribute to irritation. Neutrophils go away the blood and migrate to sites of an infection in a multistep course of mediated by way of adhesive interactions may be} regulated by macrophage-derived cytokines and chemokines. The first step (top panel) involves the reversible binding of leukocytes to vascular endothelium by way of interactions between selectins induced on the endothelium and their carbohydrate ligands on the leukocyte, proven right here for E-selectin and its ligand the sialyl-Lewisx moiety (s-Lex). The electron micrograph reveals a neutrophil extravasating between endothelial cells. These two selectins trigger leukocytes to adhere to and roll on the endothelial surface in massive numbers. Among these might be polymorphonuclear leukocytes, primarily neutrophils, and monocytes. This strengthens the interplay between leukocytes and endothelial cells, and aids the neutrophils and monocytes to enter the infected tissue in massive numbers to form an inflammatory focus (see. As monocytes mature into tissue macrophages and turn into activated in their flip, increasingly inflammatory cells are attracted into the infected tissue and the inflammatory response is maintained and strengthened. The inflammatory response can be considered placing up a flag on the endothelial cells to signal the presence of an infection, however as but, the response is entirely nonspecific for the pathogen antigens. A second essential impact of an infection is the activation of potential skilled antigen-presenting cells the dendritic cells that reside in most tissues. Once dendritic cells arrive within the lymphoid tissues, they seem to have reached their ultimate destination. They ultimately die in these tissues, however before this their role is to activate antigen-specific naive T lymphocytes.
Quality 1 mg anastrozole
It is combined with a heterogeneous population of lymphocytes and poured over an iron wool mesh in a column. The analysis of specificity and effector function in T cells depends closely on the study of monoclonal populations of T lymphocytes. First, as for B-cell hybridomas (see Section A-12), normal T cells proliferating in response to specific antigen can be fused to malignant T-cell lymphoma traces to generate T-cell hybrids. The hybrids specific the receptor of the normal T cell, however proliferate indefinitely owing to the cancerous state of the lymphoma parent. T-cell hybrids can be cloned to yield a population of cells all having the identical T-cell receptor. T-cell hybrids are wonderful instruments for the analysis of T-cell specificity, as they grow readily in suspension tradition. Functional analysis of T-cell hybrids additionally be|can be} confounded by the fact that|the fact that} the malignant associate cell affects their behavior in functional assays. Therefore, the regulation of T-cell development and the effector functions of T cells must be studied using T-cell clones. These are clonal cell traces of a single T-cell type and antigen specificity, which are derived from cultures of heterogeneous T cells, known as T-cell traces, whose development depends on periodic restimulation with specific antigen and, frequently, on the addition of T-cell development elements. T-cell clones additionally require periodic restimulation with antigen and are extra tedious to grow than T-cell hybrids however, as a result of|as a result of} their development depends on by} specific antigen recognition, they maintain antigen specificity, which is usually lost in T-cell hybrids. Cloned T-cell traces can be utilized for studies of effector function each in vitro and in vivo. In addition, the proliferation of T cells, a critical side of clonal choice, can be characterized solely in cloned T-cell traces, the place such development depends on antigen recognition. Thus, each kinds of monoclonal T-cell line have valuable purposes in experimental studies. Studies of human T cells have relied largely on T-cell clones as a result of|as a result of} a suitable fusion associate for making T-cell hybrids has not been recognized. This simple assay system has yielded a lot information about sign transduction in T cells. This has allowed mutants missing the receptor or having defects in sign transduction pathways to be chosen just by culturing the cells with anti-receptor antibody and selecting people who proceed to grow. Thus, T-cell tumors, T-cell hybrids, and cloned T-cell traces all have valuable purposes in experimental immunology. Finally, primary T cells from any source can be isolated as single, antigen-specific cells by limiting dilution quite than by first establishing a combined population of T cells in tradition as a T-cell line after which deriving clonal subpopulations. During the expansion of T-cell traces, explicit T-cell clones can come to dominate the cultures and provides a false picture of the quantity and specificities within the authentic sample. T cells from an immune donor, comprising a mixture of cells with completely different specificities, are activated with antigen and antigen-presenting cells. T cells are tougher to characterize as there are completely different lessons with completely different functions. It additionally be|can be} technically tougher to study the membrane-bound T-cell receptors than the antibodies secreted in massive amounts by B cells. On many occasions it is important to|it could be very important|you will want to} know the frequency of antigen-specific lymphocytes, particularly T cells, find a way to} measure the efficiency with which an individual responds to a particular antigen, for instance, or the degree to which specific immunological reminiscence has been established. There are methods for doing this, either by detecting the cells instantly by the specificity of their receptor, or by detecting activation of the cells to present some explicit function, such as cytokine secretion or cytotoxicity. The first strategy of this sort to be established was the limiting-dilution tradition (see Section A-25), during which the frequency of specific T or B cells responding to a particular antigen probably be} estimated by plating the cells into 96well plates at growing dilutions and measuring the number of wells during which there was no response. However, in assay it became laborious to ask detailed questions concerning the phenotype of the responding cells, and to compare responses from completely different cell subpopulations. It was due to this fact important to develop assays that would make these measurements on single cells. Measurements based mostly on move cytometry (see Section A-22) proved the answer, with the development of methods for detecting fluorescently labeled cytokines within activated T cells. The drawback of intracellular cytokine staining (see Section A-27) was that the T cells should be killed and permeabilized by detergents to allow the cytokines to be detected. This led to the extra refined strategy of capturing secreted labeled cytokines on the surfaces of the dwelling T cells (see Section A-27). The response of a lymphocyte population is a measure of the general response, however the frequency of lymphocytes capable of to} respond to a given antigen can be decided solely by limiting-dilution tradition. This assay makes use of the Poisson distribution, a statistical function that describes how objects are distributed at random. For occasion, when a sample of heterogeneous T cells is distributed equally right into a series of tradition wells, some wells will obtain no T cells specific for a given antigen, some will obtain one specific T cell, some two, and so forth. The T cells within the wells are activated with specific antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and development elements. After allowing days for his or her development and differentiation, the cells in every nicely are examined for a response to antigen, such as cytokine release or the ability to kill specific goal cells. If cells of 1 type, sometimes antigen-specific T cells due to their rarity, are the only limiting issue for obtaining a response, then a straight line is obtained. Thus, the frequency of antigen-specific cells within the population equals the reciprocal of the number of cells added to every nicely when 37% of the wells are adverse. After priming, the frequency of specific cells goes up considerably, reflecting the antigendriven proliferation of antigen-specific cells. The limiting-dilution assay used to measure the frequency of B cells that can make antibody to a given antigen. The frequency of specific lymphocytes can be decided using limiting-dilution assay. After days, the wells are examined for a particular response to antigen, such as cytotoxic killing of goal cells. Each nicely that initially contained a particular T cell will make a response to its goal, and from the Poisson distribution one can decide that when 37% of the wells are adverse, every nicely contained, on common, one specific T cell initially of the tradition. In the example shown, for the unimmunized mouse 37% of the wells are adverse when one hundred sixty,000 T cells have been added to every nicely; thus the frequency of antigen-specific T cells is 1 in one hundred sixty,000. When the mouse is immunized, 37% of the wells are adverse when solely 1100 T cells have been added; hence the frequency of specific T cells after immunization is 1 in 1100, a rise in responsive cells of 150-fold. Usually, cytokine specific antibodies are certain to the surface of a plastic tissue-culture nicely and the unbound antibodies are eliminated (top panel). Activated T cells are then added to the nicely and settle onto the antibody-coated surface (second panel). If a T cell is secreting the appropriate cytokine, it will then be captured by the antibody molecules on the plate surrounding the T cell (third panel). After a period of time the T cells are eliminated, and the presence of the specific cytokine is detected using an enzyme-labeled second antibody specific for a similar cytokine. Each T cell that originally secreted cytokine provides rise to a single spot of color, hence the name of the assay. You can see the higher response to the cytomegalovirus peptide in comparison with} the melanA peptide by the higher number of spots. One downside with the detection of cytokine production on a single-cell stage is that the cytokines are secreted by the T cells into the encircling medium, and any affiliation with the originating cell is lost. Two methods have been devised that enable the cytokine profile produced by individual cells to be decided. The cytokine thus accumulates throughout the endoplasmic reticulum and vesicular community of the cell. If the cells are subsequently fastened and rendered permeable means of} gentle detergents, antibodies can acquire access to these intracellular compartments and detect the cytokine. This technique uses hybrid antibodies, during which the 2 separate heavy- and light-chain pairs from completely different antibodies are combined to give a combined antibody molecule during which the 2 antigen-binding websites acknowledge completely different ligands. In the bispecific antibodies used to detect cytokine production, one of the antigen-binding websites is particular for a T-cell surface marker, while the opposite is particular for the cytokine in question. The bispecific antibody binds to the T cells via the binding site for the cell-surface marker, leaving the cytokinebinding site free. It can then be detected by including a fluorochrome-labeled second antibody specific for the cytokine to the cells. The cytokines secreted by activated T cells can be decided by using fluorochrome-labeled antibodies to detect cytokine molecules which were allowed to accumulate contained in the cell.

Quality anastrozole 1mg
The invariant chains are required each for transport of the receptors to the cell surface and, most importantly, for initiating signaling when the receptors bind to an extracellular ligand. Antigen binding to the receptor generates indicators that lead in the end to the activation of nuclear transcription factors that activate new gene expression and turn off genes sometimes expressed only in resting cells. In this half of} the chapter we additionally see how clustering of the antigen receptors with co-receptors helps to generate these indicators. The variable chains of lymphocyte antigen receptors are related to invariant accent chains that carry out the signaling operate of the receptor. The antigen-binding portion of the B-cell receptor advanced is a cell-surface immunoglobulin that has the same antigen specificity because the secreted antibodies that the B cell will eventually produce. This implied that other molecules have been required for the immunoglobulin receptor to be expressed on the cell surface. Two proteins related to heavy chains on the B-cell surface have been subsequently identified and known as Ig and Ig. One Ig chain and one Ig chain associates with every surface immunoglobulin molecule. Thus the entire B-cell receptor is thought to be a posh of six chains two identical light chains, two identical heavy chains, one Ig, and one Ig. The Ig and Ig genes are carefully linked in the genome and encode proteins composed of a single amino-terminal immunoglobulin-like area connected through a transmembrane area to a cytoplasmic tail. Ig and Ig present the only substantial cytoplasmic domains current in the receptor advanced and are essential for signaling. The transmembrane type of the immunoglobulin heavy chain has a very quick cytoplasmic tail and it was onerous to understand how this might signal into the cell that the surface immunoglobulin was ligated. The B-cell receptor advanced is made up of cell-surface immuno-globulin with one every of the invariant proteins Ig and Ig. Optimal expression and maximum signaling, nevertheless, additionally require the chain, which is encoded elsewhere in the genome. The T-cell receptor advanced is made up of antigen-recognition proteins and invariant signaling proteins. The cell-surface receptor advanced related to a homodimer of chains, which signal to the interior of the cell upon antigen binding. The transmembrane regions of every chain have both a net constructive or negative cost as proven. It is thought that every full receptor advanced incorporates two: heterodimers related to the six accent chains proven in the figure, during which case the charges would steadiness. Thus the antigen receptors of B and T lymphocytes are created from distinct units of proteins but are similarly constructed. In B cells, three protein tyrosine kinases of the Src family Fyn, Blk, and Lyn are thought to be responsible for this. The enzyme exercise of the Src-family kinases is itself regulated by the phosphorylation status of the kinase area and the carboxy-terminal area, every of which has regulatory tyrosine residues. Phosphorylation of the tyrosine in the kinase area is activatory, whereas phosphorylation of a tyrosine on the carboxy terminus is inhibitory. Even after being phosphorylated on the activating tyrosine, Src-family kinases could be stored inactive by a protein tyrosine kinase known as Csk (C-terminal Src kinase), which phosphorylates the inhibitory tyrosine. As Csk exercise is constitutive in resting cells, the Src proteins are usually inactive. This is a technique during which the threshold for initiating receptor signaling is regulated in lymphocytes. Src-family kinases comprise two tyrosine residues (red bars) that are be} targets for phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of the tyrosine in the kinase area (bottom left panel) stimulates kinase exercise, and this tyrosine is a goal for phosphorylation by receptor-associated tyrosine kinases. Src-family kinases could be covalently modified with ubiquitin, a signal that targets proteins for degradation by the proteasome, and this degradation pathway is managed through affiliation with a regulatory protein, Cbl. This course of used to set a maximum level of response by limiting the focus of kinases throughout the cell. However, Cbl is itself a goal of tyrosine phosphorylation after receptor aggregation, and it appears extra doubtless that its role is to switch off cascades of activated Src-family kinases after the cell has turn into activated. In signaling from the antigen receptor, the activation of Src-family kinases is the first step|is step one} in a signaling course of that passes the signal on to many alternative molecules. One means during which this advanced could be co-ligated with the B-cell receptor is thru the recognition of an antigen that has activated complement. Clustering of the T-cell receptor and a co-receptor initiates signaling throughout the T cell. To turn into active it must itself be phosphorylated, and this is thought to happen by transphosphorylation mediated by Syk itself or by Src kinases. Each B-cell receptor advanced incorporates two molecules of Syk, sure to the Ig and Ig chains. Once the receptors are clustered, these receptor-associated kinases are brought into contact with one another and are thus in a position to} phosphorylate, and hence activate, one another. Once activated, Syk phosphorylates goal proteins to provoke a cascade of intracellular signaling molecules, which shall be described in the subsequent part. Because there are at least of|no much less than} two receptor complexes in every cluster, Syk molecules turn into sure in shut proximity and might activate one another by transphosphorylation, thus initiating further signaling. Downstream occasions are mediated by proteins that affiliate with the phosphorylated tyrosines and bind to and activate other proteins. These three pathways propagate the signal from the activated receptors on the plasma membrane and carry it to the nucleus, as illustrated in. We will discuss in additional element under how every of these pathways is initiated and, in Section 6-11, how they lead to adjustments in gene expression in the nucleus. Other Tec kinases with an important role in lymphocytes are Btk, which is expressed in B lymphocytes and Itk, which is expressed in T lymphocytes. The importance of the Tec kinases in lymphocytes could be seen from inherited deficiencies in these enzymes. Simplified outline of the intracellular signaling pathways initiated by cross-linking of B-cell receptors by antigen. Cross-linking of surface immunoglobulin molecules activates the receptor-associated Srcfamily protein tyrosine kinases Blk, Fyn, and Lyn. This scheme is a simplification of the occasions that truly happen during signaling, showing only the principle occasions and pathways. Simplified outline of the intracellular signaling pathways initiated by the T-cell receptor advanced and its co-receptor. The activation of Ras is achieved by adaptor proteins and guanine-nucleotide exchange factors (see Section 6-5) recruited to the phosphorylated receptors. In B lymphocytes, the adaptor protein Shc binds to tyrosine residues which were phosphorylated by the receptor-associated tyrosine kinases. Adaptor proteins thus form the scaffolding of a signaling advanced, related to lipid rafts, that links ligand binding by the antigen receptor on the cell surface to the activation of Ras, which then triggers further signaling occasions downstream. Another small G protein is activated through the B-cell co-receptor advanced (see Section 6-8). We now flip to the question of how indicators are transmitted to the nucleus, there to activate transcription factors that can regulate specific genes. Antigen recognition leads in the end to the induction of new gene synthesis by activating transcription factors. The final response of lymphocytes to extracellular indicators is the induction of new gene expression. It seems that each pathways are required to drive the clonal expansion of naive lymphocytes. Calcineurin is itself activated by the rise in intracellular free Ca2+ that accompanies lymphocyte activation (see. This illustrates how advanced the process of signal transduction could be, and the way proteins that regulate transcription can integrate indicators that come from different pathways. These medication are used broadly to stop graft rejection, which they do by inhibiting the activation of alloreactive T cells. Erk finally phosphorylates and activates the transcription factor Elk, which enters the nucleus to provoke new gene transcription, significantly of the Fos gene. These peptides are normally known as antagonist peptides, as they antagonize the action of the agonist peptide.
Buy 1mg anastrozole
Exactly how this selective course of works, and how it it} maximizes the usefulness of the T cell repertoire is a central question in immunology and is a serious topic of Chapter 7. On recognizing their targets, the three forms of T cell are stimulated to release different units of effector molecules. These can directly have an effect on} their goal cells or assist to recruit other effector cells in methods we shall talk about in Chapter 8. These effector molecules include many cytokines, which have a crucial position within the clonal growth of lymphocytes properly as|in addition to} in innate immune responses and within the effector actions of most immune cells; thus, understanding the actions of cytokines is central to understanding the varied behaviors of the immune system. We are likely to|are inclined to} take without any consideration the flexibility of our immune techniques to free our our bodies of infection and forestall its recurrence. In probably the most severe of those immunodeficiency diseases, adaptive immunity is totally absent, and dying happens in infancy from overwhelming infection unless heroic measures are taken. Other less catastrophic failures result in recurrent infections with particular forms of pathogen, relying on the actual deficiency. Much has been learned in regards to the features of the different parts of the human immune system via the study of those immunodeficiencies. This disease destroys the T cells that activate macrophages, leading to infections caused by intracellular bacteria and other pathogens usually managed by these T cells. Such infections are the most important reason for dying from this more and more prevalent immunodeficiency disease, which is discussed fully in Chapter eleven along with inherited immunodeficiencies. Such methods are typical of many profitable pathogens and we shall look at a variety of|quite a lot of|a wide selection of} them in Chapter eleven. Understanding adaptive immune responses is necessary for the control of allergy symptoms, autoimmune disease, and organ graft rejection. Many medically necessary diseases are associated with a standard immune response directed in opposition to an inappropriate antigen, often within the absence of infectious disease. Immune responses directed at noninfectious antigens occur in allergy, where the antigen is an innocuous foreign substance, in autoimmune disease, where the response is to a self antigen, and in graft rejection, where the antigen is borne by a transplanted foreign cell. What we name a profitable immune response or a failure, and whether the response is considered dangerous or useful to the host, depends not on the response itself however rather on the character of the antigen. Immune responses may be useful or dangerous relying on the character of the antigen. Allergic diseases, which include bronchial asthma, are an more and more common reason for disability within the developed world, and lots of|and plenty of} other necessary diseases at the moment are|are actually} acknowledged as autoimmune. An autoimmune response directed in opposition to pancreatic cells is the main reason for diabetes within the younger. In allergy symptoms and autoimmune diseases, the powerful protecting mechanisms of the adaptive immune response cause critical harm to the patient. Immune responses to harmless antigens, to physique tissues, or to organ grafts are, like all other immune responses, extremely specific. At present, identical old} approach to deal with these responses is with immunosuppressive drugs, which inhibit all immune responses, fascinating or undesirable. If it had been possible to suppress solely those lymphocyte clones answerable for the unwanted response, the disease probably be} cured or the grafted organ protected without impeding protecting immune responses. We shall see in Chapter 10 how the mechanisms of immune regulation are beginning to emerge from a greater understanding of the useful subsets of lymphocytes and the cytokines that control them, and we shall talk about the current state of understanding of allergy symptoms, autoimmune disease, graft rejection, and immunosuppressive drugs in Chapters 12, thirteen, and 14. Mass immunization applications have led to the digital eradication of quantity of} diseases that used to be associated with vital morbidity (illness) and mortality. Immunization is considered so protected and so necessary nearly all} states within the United States require youngsters to be immunized in opposition to as much as} seven common childhood diseases. Impressive as these accomplishments are, there are still many diseases for which we lack effective vaccines. And even where vaccines for diseases similar to measles or polio can be utilized successfully in developed nations, technical and financial issues can prevent their widespread use in growing nations, where mortality from these diseases remains to be excessive. The tools of recent immunology and molecular biology are being utilized to develop new vaccines and improve old ones, and we shall talk about these advances in Chapter 14. The assure of excellent well being is a important step towards inhabitants control and financial growth. Lymphocytes have two distinct recognition techniques specialised for detection of extracellular and intracellular pathogens. B cells have cell-surface immunoglobulin molecules as receptors for antigen and, upon activation, secrete the immunoglobulin as soluble antibody that gives protection in opposition to pathogens within the extracellular spaces of the physique. Thus, T cells are crucially necessary for both the humoral and cell-mediated responses of adaptive immunity. The adaptive immune response appears to have engrafted specific antigen recognition by extremely diversified receptors onto innate protection techniques, which have a central position within the effector actions of both B and T lymphocytes. The very important position of adaptive immunity in preventing infection is illustrated by the immunodeficiency diseases and the issues caused by pathogens that succeed in evading or subverting an adaptive immune response. The antigenspecific suppression of adaptive immune responses is the aim of treatment for necessary human diseases involving inappropriate activation of lymphocytes, whereas the precise stimulation of an adaptive immune response is the idea of profitable vaccination. Innate immunity serves as a first line of protection however lacks the flexibility to acknowledge sure pathogens and to present the precise protecting immunity that forestalls reinfection. Adaptive immunity relies on clonal choice from a repertoire of lymphocytes bearing extremely various antigenspecific receptors that enable the immune system to acknowledge any foreign antigen. In the adaptive immune response, antigen-specific lymphocytes proliferate and differentiate into effector cells that eliminate pathogens. Host protection requires different recognition techniques and a wide variety|all kinds} of effector mechanisms to hunt down and destroy the wide variety|the huge variety|the extensive range} of pathogens in their numerous habitats throughout the physique and at its surface. Not solely can the adaptive immune response eliminate a pathogen however, within the course of, it additionally generates elevated numbers of differentiated memory lymphocytes via clonal choice, and this permits a extra speedy and effective response upon reinfection. The regulation of immune responses, whether to suppress them when unwanted or to stimulate them within the prevention of infectious disease, is the most important medical aim of analysis in immunology. Research in Immunology Seminars in Immunology the Immunologist the Immunologist, three: Proceedings Issue, 9th International Congress of Immunology Advanced textbooks in immunology, compendia, and so forth. The microorganisms may be} encountered daily within the lifetime of a standard wholesome particular person solely sometimes cause perceptible disease. The time course and different phases of an encounter with a new new} pathogen are summarized in. Only if an infectious organism can breach these early lines of protection will an adaptive immune response ensue, with the generation of antigen-specific effector cells that particularly goal the pathogen, and memory cells that may prevent reinfection with the same microorganism. The energy of adaptive immune responses outcome of|as a end result of} of} their antigen specificity, which we will be learning within the following chapters. The effector mechanisms that take away the infectious agent (for instance, phagocytes and complement) are related or identical in every part, however the first two phases depend on recognition of pathogens by germline-encoded receptors of the innate immune system, whereas adaptive immunity makes use of variable antigen-specific receptors may be} produced gene rearrangements. Adaptive immunity happens late, the uncommon B and T cells specific for the invading pathogen should undergo clonal growth earlier than they differentiate into effector cells that may clear the infection. Whereas the adaptive immune system makes use of a large repertoire of receptors encoded by rearranging genes to acknowledge a huge variety of antigens (see Section 1-10), innate immunity depends upon germline-encoded receptors to acknowledge features may be} common to many pathogens. The second a part of} the chapter is devoted to a system of plasma proteins identified as|often known as} the complement system. This necessary factor of innate immunity interacts with microorganisms to promote their removal by phagocytic cells. Next, we take {a closer|a better|a extra in-depth} a glance at|have a look at} the receptors used by the immune system to acknowledge pathogens, and the final a part of} the chapter describes how the activation of phagocytic cells firstly of the innate immune response to infection leads to the induced or adaptive immune response. Microorganisms that cause pathology in humans and animals enter the physique at different websites and produce disease by a variety of|quite a lot of|a wide selection of} mechanisms. Many different infectious agents could cause pathology, and people who do are referred to as pathogenic microorganisms or pathogens. Invasions by microorganisms are initially countered, in all vertebrates, by innate protection mechanisms that preexist in all people and act inside minutes of infection. Only when the innate host defenses are bypassed, evaded, or overwhelmed is an induced or adaptive immune response required. Infectious agents should overcome innate host defenses to set up a spotlight of infection. Our our bodies are continuously exposed to microorganisms present within the environment, including infectious agents which were shed from contaminated people. Contact with these microorganisms may occur via exterior or inner epithelial surfaces: the respiratory tract mucosa supplies a route of entry for airborne microorganisms, the gastrointestinal mucosa for microorganisms in food and water; insect bites and wounds permit micro-organisms to penetrate the pores and skin; and direct contact between people offers opportunities for infection of the pores and skin and reproductive mucosa. The epithelial surfaces of the physique function an efficient barrier in opposition to most microorganisms, and are rapidly repaired if wounded.
References:
- https://www.ijbs.com/v16p1686.pdf
- https://www.arkleg.state.ar.us/Calendars/Attachment?committee=490&agenda=3445&file=Exhibit+F1c+AAA+ebook+Med+Studies+Support+MDs+Prescribing+Hydroxychloroquine+for....pdf
- https://jdh.adha.org/content/jdenthyg/81/suppl_1/117.full.pdf
- https://gmpua.com/RD/RD/Drug%20Abuse%20Handbook.pdf
.png)