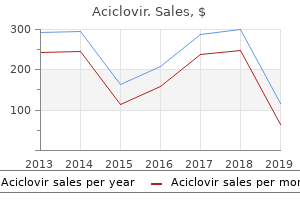
Buy 400mg aciclovir
In deep wounds, new epithelial cells are obtained from the epithelium of the hair follicles and sweat glands situated within the dermis (reply e). The Ruffini endings are the best encapsulated receptor and are related to collagen fibers (reply a). Mechanical stress results in displacement of the collagen fibers and stimulation of the receptor. In the vignette, the Schwannoma (a nerve sheath tumor arising from Schwann cells) results in impairment of proprioception (place sense) and vibratory sense ipsilaterally whereas pain and temperature are impaired contralaterally. Integumentary System Answers 309 It is compressing the spinal wire from its lateral or anterolateral aspect causing impairment of pain and temperature sensation on the contralateral facet to the Schwannoma, with weak point, spasticity and lack of proprioception and vibratory sense on the ipsilateral facet to the tumor. Specific desmogleins are the goal of the autoantibodies in numerous types of the disease. Cadherins are Ca2+-dependent transmembrane-linker molecules essential for cell-cell contact, so their disturbance in pemphigus leads to extreme blistering of the pores and skin because of disrupted cell-cell interactions early within the differentiation of the keratinocyte (epidermal cell) and excessive fluid loss. Therefore, the basal layer of the dermis remains attached to the basal lamina in pemphigus. For more details on junctional complexes, see the desk in feedback for question 199. There is hyperplasia of the dermis and irregular microcirculation within the dermis as venules predominate within the capillaries leading to elevated extravasation of inflammatory cells. Thus, the underlying cause is the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the dermis with further migration of neutrophils into the dermis. There is hyperplasia of the dermis (reply a) as keratinocytes traverse the cell cycle in a shorter period of time (reply b). Microabcesses type within the dermis (reply d) and epithelia are avascular (reply e). The immunofluorescence picture reveals specific labeling of the epidermal-dermal interface. Therefore, the whole dermis separates from the basal lamina in contrast to pemphigus in which the desmosomes disaggregate because of antibodies to the desmogleins causing a disruption of the macula adherens [desmosomes (reply a)] within the stratum spinosum. The gap junction (reply c) is a communicating junction; the zonula occludens (reply d) prevents materials from flowing between cells; and the zonula adherens (reply e) is a belt-like component of the junctional complex that links to the actin cytoskeleton. Below is a helpful "memory grid" to remind you of the elements of the junctional complexes and their attachments to the cell. Memory Grid Cadherins Actin Adhesion Belts Desmosomes Integrins Focal Adhesions Hemidesmosomes Cell to Matrix No Plaque Intermediate Filaments Plaque Cell to Cell No truthful going diagonally! The high ranges of phenylalanine present competitive inhibition for tyrosinase (answers c and d). The variety of melanocytes that differentiate from the neural crest could be normal (reply a). She admits to ingesting a six-pack of beer every day with somewhat more intake on weekends. A biopsy of her liver reveals eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions (Mallory our bodies) derived from intermediate filament proteins. The course of launch of secretion using exocytosis for launch of secretory product from the cell Their presence within the small and enormous gut Their origin from a crypt stem cell Secretion by a regulated pathway 313 Copyright � 2007 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. In regard to the enteroendocrine cells and the cells composing the enteric nervous system of the intestine, which of the following applies to each kinds of cells They are derived from neural crest They secrete comparable peptides They are essential for the intrinsic rhythmicity of the intestine They are turned over rapidly They are discovered solely within the small gut 205. A 17-year-old with counterfeit identification has a piercing accomplished at an area tattoo/piercing institution. She chooses to have a chrome steel barbell inserted within the piercing by way of the anterior 2/three of her tongue. Primary afferents from those buildings journey by way of which of the following cranial nerves The website of this disruption is most probably which of the layers on the accompanying micrograph Layer a Layer b Layer c Layer d Layer e 316 Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology 207. A 48-year-old girl presents to the allergy and rheumatology clinic with itching eyes, dryness of the mouth, issue swallowing, lack of sense of taste, hoarseness, fatigue, and swollen parotid glands. A parotid gland biopsy reveals inflammatory infiltrates within the interlobular connective tissue with damage to acinar cells and striated ducts. In this case, resorption of which of the following shall be most altered by destruction of the striated ducts Antidiuretic hormone Autonomic nervous system Aldosterone Cholecystokinin Secretin Gastrointestinal Tract and Glands 317 209. A younger baby presents with hepatomegaly and renomegaly, failure to thrive, stunted development, and hypoglycemia. A deficiency in glucose 6phosphatase is identified and the prognosis is von Gierke disease. In the liver, the buildings labeled with the arrows within the accompanying transmission electron micrograph accumulate during this disease. Chylomicra Glycogen Mitochondria Peptide-containing secretory granules Ribosomes 318 Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology 210. The branching buildings proven within the photomicrograph below (a scanning electron micrograph taken from the region between two hepatocytes) are concerned in which of the following Communication between the hepatocytes Preventing flow between adjacent hepatocytes Bile flow Blood flow Spot welds between hepatocytes Gastrointestinal Tract and Glands 319 211. The following question refers to the photomicrograph below of a plastic-embedded, thin part. A parasympathetic ganglion A cluster of hepatocytes A serous acinus An intralobular duct An islet of Langerhans 320 Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology 212. The presence of each of those tissues signifies that the sample was taken from the region of the junction between which of the following Anal canal and rectum Esophagus and stomach Skin of the face and mucous epithelium of the lip Stomach and duodenum Vagina and cervix Gastrointestinal Tract and Glands 321 213. A fifty two-year-old girl with a provisional prognosis of celiac disease presents with bouts of diarrhea and extreme fatigue. Verification was sought by way of efficiency of esophagogastroduodenoscopy to obtain small bowel biopsies. Biopsies of the region proven within the accompanying mild micrograph disclose hyperplasia of the buildings labeled with the asterisks. Inflammation within the organ proven within the photomicrograph could result in referred pain to which of the following areas Top of the proper shoulder Neck Spine between the scapulae Groin Umbilical region Gastrointestinal Tract and Glands 323 215. The cells labeled with the asterisks within the heart of the transmission electron micrograph below function in which of the following processes Immune defense mechanisms Mucus secretion Heparin and histamine secretion and launch Endocrine secretion Regulation of the flora of the small bowel 324 Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology 216. In hemolytic jaundice, the structure labeled with the arrow within the accompanying photomicrograph will include which of the following Elevated urobilinogen ranges Elevated bilirubin ranges Decreased urobilinogen ranges Decreased bilirubin ranges Elevated numbers of lymphocytes undergoing diapedesis 217. A four-day-old boy weighing 7 lb, 6 oz is brought to the emergency room by his dad and mom. The examining emergency room doctor notes that his pores and skin and sclerae are icteric. The elevated bilirubin ranges in this patient are most probably the result of which of the following Deficiency of enzymes regulating bilirubin solubility Hepatocellular proliferation Decreased destruction of pink blood cells Dilation of the frequent bile duct Increased hepatocyte uptake of bilirubin Gastrointestinal Tract and Glands 325 218. When seen a number of hours later, she has normal bowel sounds, is tender all through the stomach, particularly in the proper upper quadrant, and is faintly icteric. She recalls occasional episodes of "indigestion" referred to the proper upper stomach and radiating to the shoulder. This has occurred particularly after consuming fried foods or after consuming a meal following a long interval of fasting. The test outcomes out there are a blood rely and blood chemistry together with liver enzymes, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin.
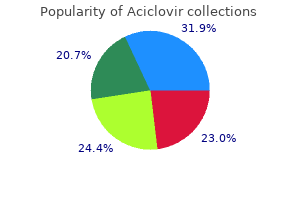
Best aciclovir 400 mg
Diagnosis is by particular antigen detection within the urine or by direct fluorescent antibody staining of the organism within the pleural fluid, sputum or bronchial washings. Treatment contains intravenous ceftazidime, ciprofloxacin, tobramycin or ticarcillin. The medical options and treatment of this and different opportunistic infection are described on web page fifty one. Aspiration usually happens into the posterior segment of the proper decrease lobe due to the bronchial anatomy. It is related to durations of impaired consciousness, structural abnormalities, such as tracheo-oesophageal fistulae or oesophageal strictures, and bulbar palsy. Complications of pneumonia: lung abscess and empyema A lung abscess results from localized suppuration of the lung related to cavity formation, typically with a fluid degree on the chest X-ray. Empyema means 540 Respiratory illness the presence of pus within the pleural cavity, usually from rupture of a lung abscess into the pleural cavity, or from bacterial spread from a severe pneumonia. A lung abscess develops within the following circumstances: � Complicating aspiration pneumonia or bacterial pneumonia caused by S. Clinical options Lung abscess presents with persisting or worsening pneumonia, typically with the production of copious quantities of foul-smelling sputum. With empyema the patient is usually very unwell, with a excessive fever and neutrophil leucocytosis. Investigations Bacteriological investigation is best conducted on specimens obtained by transtracheal aspiration, bronchoscopy or percutaneous transthoracic aspiration. Intravenous cefuroxime, and metronidazole are given for 5 days, adopted by oral cefaclor and metronidazole for several weeks. Empyemas must be treated by immediate tube drainage or rib resection and drainage of the empyema cavity. Rates within the in any other case healthy indigenous white inhabitants have fallen to very low ranges. The main lesion can also occur within the gastrointestinal tract, particularly the ileocaecal region. The main focus is characterized by exudation and infiltration with neutrophil granulocytes. The main focus is almost always accompanied by caseous lesions within the regional lymph nodes (mediastinal and cervical) � together these represent the Ghon complex. In most individuals the primary infection and the lymph nodes heal utterly and become calcified. Post-main tuberculosis refers to all types of tuberculosis that develop after the first few weeks of the primary infection when immunity to the mycobacteria has developed. Patients, especially the elderly, might current with non-particular unwell-well being, fever of unknown origin, weight reduction and some different localizing signs. Occasionally the illness presents as tuberculous meningitis, and within the later phases there may be enlargement of the liver and spleen. Choroidal tubercles (yellowy/white raised lesions about one-quarter the diameter of the optic disc) are often seen within the eye. There are sometimes no bodily indicators, though often indicators of a pneumonia or pleural effusion may be current. Tuberculous illness (as above) should be differentiated from latent tuberculous infection. Infection implies the presence of small numbers of tubercle bacilli within the physique; the tuberculin test is optimistic (as with illness), but the chest X-ray is normal and the patient asymptomatic. Primary three�8 weeks Erythema nodosum Post-main immunity Reactivation (not often reinfection) usually years later because of: Diabetes mellitus Malnutrition Immunosuppression Drugs. This is to reduce the danger of transmission to different sufferers in a confirmed case. With miliary tuberculosis the chest X-ray may be normal or show miliary shadows 1�2 mm in diameter throughout the lung. Culture of sputum is more delicate than microscopy and allows antibiotic sensitivity testing. Where pulmonary tuberculosis is suspected, serial sputum samples on a minimum of three occasions (ideally instantly upon waking) must be collected. Solid culture mediums take four�8 weeks for organism restoration and are steadily being replaced by liquid culture mediums (Bactec) which shorten the restoration time by 2�three weeks. This might contain lymph node biopsy, bone biopsy, urine testing or aspiration of pericardial fluid. A 6-month routine comprising rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide and ethambutol for the preliminary 2 months adopted by rifampicin and isoniazid for an additional four months, is normal treatment. Four medication must be continued for longer than 2 months if susceptibility testing remains to be excellent. Pyridoxine 10 mg daily is given to cut back the danger of isoniazid-induced peripheral neuropathy. A transient asymptomatic rise within the serum aminotransferase degree might occur with rifampicin, but treatment is only stopped if hepatitis develops. The major causes of treatment failure are incorrect prescribing by the physician and inadequate compliance by the patient. Vagrants, alcoholics, homeless and the mentally unwell are most probably to be non-compliant with therapy. Prevention and chemoprophylaxis Close contacts of a case are screened for evidence of illness with a chest X-ray and a Mantoux test (optimistic if space of induration! Antituberculous treatment is given if the chest Xray shows evidence of illness or if the Mantoux test is adverse initially but becomes optimistic on repeat testing 6 weeks later. Patients with tuberculous infection recognized by tuberculin testing are usually treated with one drug for 6 months (chemoprophylaxis) to prevent development to illness. The course of involves not only the interstitial house but additionally the alveoli, bronchioles and blood vessels. Presentation is with shortness 546 Respiratory illness Diffuse parenchymal lung ailments Granulomatous lung illness Inhalation of mud Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias Autoimmune rheumatic ailments Drug induced Other types Organic mud Inorganic mud Idiosyncratic. Pulmonary infection, malignancy and pulmonary oedema might mimic interstitial lung illness. Granulomatous lung illness A granuloma is a mass or nodule of persistent inflammatory tissue formed by the response of macrophages and histiocytes to a slowly soluble antigen or irritant. Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is a multisystem granulomatous dysfunction of unknown cause sometimes affecting younger and center-aged adults. In about half of instances, the illness is detected incidentally on a routine chest X-ray in an asymptomatic individual. Epidemiology Sarcoidosis has a feminine preponderance, is most common in northern Europe and is uncommon in Japan. Diffuse ailments of the lung parenchyma 547 � Depressed cell-mediated reactivity to antigens, such as tuberculin and Candida albicans, and an general lymphopenia with low circulating T cells, because of sequestration of lymphocytes within the lung and slightly elevated B cells. Clinical options Sarcoidosis can affect any organ, particularly the lung, pores and skin and eyes (Table eleven. Lung illness presents with a non-productive cough, breathlessness and sometimes a wheeze. Finger clubbing is uncommon and, when current, various diagnoses must be thought of. Asymptomatic illness may be recognized when a chest X-ray is carried out for different reasons. Common biopsy sites are enlarged lymph nodes, pores and skin lesions and transbronchial biopsy at bronchoscopy. Non-caseating granulomas additionally occur in lymphoma, fungal infection, tuberculosis (additionally caseating) and in response to foreign bodies and occupational exposure to beryllium. Infiltration or abnormal lung function exams that persist for 6 months after prognosis are treated with 30 mg prednisolone for 6 weeks, lowering to 15 mg on alternate days for 6�12 months. Other particular indications for steroid treatment are hypercalcaemia, neurological or myocardial involvement and ocular involvement (topical steroids are used in some instances). Steroid-sparing agents (methotrexate, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide) are sometimes used in sufferers needing lengthy-time period steroids for illness management. Death is mainly because of respiratory failure or renal injury from hypercalciuria. Granulomatous lung illness with vasculitis There are two major teams: � Pulmonary vasculitis related to main autoimmune rheumatic ailments including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis (see Ch.
Aciclovir 200mg
The mother is requested to underline the response that comes closest to how she has been feeling within the earlier 7 days. Care should be taken to keep away from the potential of the mother discussing her solutions with others. The mother should complete the dimensions herself, unless she has restricted English or has problem with studying. The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale could also be used at 6-eight weeks to screen postnatal ladies. The baby health clinic, a postnatal checkup, or a house visit might present an acceptable alternative for its completion. I actually have felt happy: Yes, on a regular basis Yes, most of the time No, not very often No, not at all this is able to imply: "I actually have felt happy most of the time" during the past week. I actually have appeared ahead with enjoyment to things Yes, most of the time As much as I ever did Yes, typically Rather less than I used to Not very often Definitely less than I used to No, not at all Hardly at all *eight. I actually have blamed myself unnecessarily when things went incorrect Yes, most of the time Yes, most of the time Yes, very often Yes, a few of the time Not very often Not very often No, not at all No, by no means *9. I actually have been anxious or worried for no good reason Yes, most of the time No, not at all Yes, very often Hardly ever Only occasionally Yes, typically No, by no means Yes, very often *10. I actually have felt scared or panicky for no very good reason Yes, very often Yes, rather a lot Sometimes Yes, typically Hardly ever No, not much Never No, not at all Response categories are scored 0, 1, 2, and three in accordance with increased severity of the symptom. Users might reproduce the dimensions without further permission providing they respect copyright (which remains with the British Journal of Psychiatry) by quoting the names of the authors, the title, and the source of the paper in all reproduced copies. At the identical time, they type the premise for the rising psychologic relationship between father or mother and baby. Infants come to associate the presence of the father or mother with the pleasurable discount of pressure (as in feeding) and present this preference by calming more quickly for his or her mother than for a stranger. Crockenberg S, Leerkes E: Infant social and emotional development in household context. Section on Breastfeeding, American Academy of Pediatrics: Breastfeeding and the usage of human milk, Pediatrics one hundred fifteen:496�506, 2005. A prenatal pediatric visit permits pediatricians to assess potential threats to bonding (a tense spousal relationship) and sources of social help. Such policies (Baby Friendly Hospital) have been shown four to significantly increase breast-feeding charges (see Chapter ninety four). After discharge, home visits by nurses and lactation counselors can reduce early feeding issues and establish rising medical conditions in either mother or baby. Infants requiring transport to another hospital should be dropped at see the mother first, if at all attainable. On discharge home, fathers can protect moms from unnecessary visits and calls and take over household duties, allowing moms and infants time to get to know one another without distractions. The first office visit should happen during the first 2 wk after discharge to determine how smoothly the mother and toddler are making the transition to life at home. Alternatively, the toddler could also be ready to interact, whereas the mother might appear preoccupied. Asking a brand new mother about her personal emotional state, and inquiring particularly a couple of history of melancholy, facilitates referral for remedy, which may present long-time period benefits to the child. Parents would possibly study that they need to undress their toddler to increase the level of arousal or to swaddle the toddler to reduce overstimulation by containing random arm movements. Some actions previously thought to be "primitive" or "reflexive" end result from complicated methods. Swallowing, quite than a simple reflex, outcomes from a posh highly coordinated process involving a number of ranges of neural management distributed amongst a number of physiologic methods whose nature and relationships mature all through the 1st year of life. Substantial learning of the basic tools of language (phonology, word segmentation) occurs throughout infancy. Speech processing in older people requires defined and exact neuronal networks; imaging studies have revealed that the toddler brain possesses a structural and practical organization much like that of adults, resulting in the idea that structural neurologic processing of speech might information infants to uncover the properties of his or her native language. Myelination of the cortex begins at eight mo gestation and is sort of complete by age 2 yr; much of this process occurs throughout infancy. Given the significance of iron and different vitamins in myelination, sufficient shops all through infancy are critical (see Chapter 42). Inadequate dietary consumption, insufficient interactions with caregivers, or both might alter experience-dependent processes that are critical to brain construction development and performance throughout infancy. Although a few of these processes could also be delayed, as the periods of plasticity close during the fast developmental modifications occurring in infancy, more permanent deficits might end result. Physical progress parameters and normal ranges for attainable weight, size, and head circumference are found within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention progress charts 2 Table eight-1 presents an outline of key milestones by area; Table eight-2 presents comparable information arranged by age. Parents usually search details about "normal development" throughout this era and should be directed to dependable sources, including the American Academy of Pediatrics web site. Physiologic modifications allow the institution of efficient feeding routines and a predictable sleep-wake cycle. The social interactions that happen as mother and father and infants accomplish these duties lay the inspiration for cognitive and emotional development. Nutrition improves as colostrum is replaced by higher-fats breast milk, as infants study to latch on and suck more efficiently, and as moms turn out to be more comfy with feeding methods. Infants regain or exceed birthweight by 2 wk of age and should grow at approxi4 mately 30 g (1 oz)/day during the 1st mo (see Table thirteen-1). Limb movements consist largely of uncontrolled writhing, with apparently purposeless opening and shutting of the arms. Eye gaze, head turning, and sucking are beneath higher management and thus can be utilized to show toddler perception and cognition. Initially, sleep and wakefulness are evenly distributed all through the 24-hr day. Neurologic maturation accounts for the consolidation of sleep into blocks of 5 or 6 hr at night, with brief awake, feeding periods. Learning additionally occurs; infants whose mother and father are persistently more interactive and stimulating during the day study to focus their sleeping during the night. They can recognize facial expressions (smiles) as comparable, even after they appear on different faces. They can also match summary properties of stimuli, similar to contour, intensity, or temporal sample, throughout sensory modalities. Infants at 2 mo of age can discriminate rhythmic patterns in native vs non-native language. Infants appear to search stimuli actively, as if satisfying an innate must make sense of the world. These phenomena level to the integration of sensory inputs within the central nervous system. Caretaking actions present visual, tactile, olfactory, and auditory stimuli; all of these help the development of cognition. Infants habituate to the familiar, attending much less to repeated stimuli and increasing their attention to novel stimuli. Crying occurs in response to stimuli which may be obvious (a soiled diaper), but are sometimes obscure. Cross-cultural studies present that in societies by which infants are carried near the mother, babies cry less than in societies by which babies are solely periodically carried. Crying normally peaks at about 6 wk of age, when healthy infants might cry as much as 3 hr/day, then decreases to 1 hr or much less by 3 mo. Hunger generates increasing pressure; as the urgency peaks, the toddler cries, the father or mother provides the breast or bottle and the tension dissipates. Infants fed "on demand" persistently experience this hyperlink between their distress, the arrival of the 6. Mutual regulation takes the form of complicated social interchanges, resulting in strong mutual attachment and pleasure. Between 3 and four mo of age, the speed of progress slows to roughly 20 g/day (see Table thirteen-1 and. Disappearance of the asymmetric tonic neck reflex means that infants can start to study objects within the midline and manipulate them with both arms (see Chapter 584). Waning of the early grasp reflex permits infants both to hold objects and to allow them to go voluntarily. The high quality of spontaneous movements additionally modifications, from larger writhing to smaller, round movements which have been described as "fidgety.
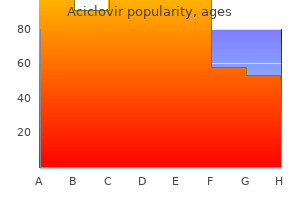
Safe aciclovir 400 mg
The action potential is an all-or-none phenomenon and happens with fixed amplitude and duration for a given axon. An acute childhood infection in the cerebellum (cerebellitis) would end in ataxia: incapability to coordinate voluntary muscle movements, unsteady movements, and staggering gait. Limb ataxia manifests itself with lack of nice motor management of the hands or legs and seems as though the individual is able to coordinate his or her movements. Most often, the cerebellar ataxia that follows a viral infection subsides with out remedy over a period of weeks to months. Occasionally, a toddler shall be left with a persistent movement dysfunction or behavioral problem. Amnesia (reply a) would end result from a cortical harm; reflexive actions (reply c) would occur at the level of the ventral horn cells in the spinal twine; lack of ache sensation is complicated and will contain the dorsal root or trigeminal ganglion, the sensory and frontal cortex, limbic system, and thalamus, but not the cerebellar cortex (reply d); and whole or partial lack of capability to use or perceive language, aphasia (reply e), could be the results of a cortical harm. Damage to the pararhinal�entorhinal� hippocampal�mammillary body�thalamus circuit, the fornix, or the temporal lobe can cause amnesia. For instance, working reminiscence can be affected by prefrontal lesions or by lesions to specific temperoparietal regions subserving the modality getting used. Aphasia can contain a number of completely different areas of the cortex including the frontal, parietal, and/or temporal lobes. Note the three layers forming the cerebellar cortex (molecular layer at left/top, the large Purkinje cell layer, and the granular layer). Basket cells Nervous System Answers 243 make profuse inhibitory dendritic contacts with the flask-formed Purkinje cells. Each Purkinje cell receives about 2 � 105 synapses, largely onto its dendritic spines which splay out throughout the molecular layer. Granule cell axons type the parallel fibers that make excitatory synapses onto Purkinje cell dendrites. Each parallel fiber synapses on about 200 Purkinje cells creating an excitation strip throughout the cerebellum. Shingles begins as erythematous maculopapular eruptions and quickly evolves to vesicles; it often presents with fever. The virus is saved in the dorsal root ganglion, primarily in the satellite tv for pc cells surrounding the perikarya (cell bodies). The dyneins (solutions a and c) are minus-finish directed microtubule motors that transfer organelles, including vesicles, in a retrograde direction towards the cell body (in this case towards the cell bodies of the dorsal root ganglia). The dyneins involved in axonal transport are the cytoplasmic dyneins as in comparison with the axonemal dyneins seen in cilia and flagella. The Tzanck test is a method of testing for the virus; it could detect the presence of the herpesvirus in the cells scraped from a lesion. The nipples are usually discovered in the midst of T4, although T5 can also innervate this area. A dermatome is the world of pores and skin supplied by nerves originating from a single spinal nerve root. The harm causes Wallerian degeneration distal to the level of harm and proximal axonal degeneration to no less than the following node of Ranvier. In extra severe traumatic accidents, the proximal degeneration may prolong beyond the following node of Ranvier. A nerve trunk will regenerate about 1 mm/day (see transport charges discussed in the subsequent paragraph). The endoneurial tubes stay intact (reply d), and, therefore, recovery is full, with axons reinnervating their original motor and sensory targets. The segment distal (reply e) to the wound, including the myelin, is phagocytosed and eliminated by macrophages. The proximal segment is able to regeneration as a result of it stays in continuity with the perikaryon. Transneuronal degeneration happens only when there are synapses with a single broken neuron. Slow axonal transport/dendritic transport (1�5 mm/day) involves the movement of cytoskeletal parts such as actin, tubulin, and neurofilaments from the perikaryon down the axon. Rapid anterograde (away from the perikaryon) transport and retrograde (towards the perikaryon) transport (200�300 mm/day) transports membrane-bound organelles, for example, newly formed secretory vesicles and mitochondria anterogradely. Receptors, recycled membranes, and worn-out organelles are transported retrogradely. Therefore, unfold of depolarization from the nodal area alongside the axon happens till it reaches the following node. This is usually described as a collection of jumps from node to node, or saltatory conduction. Adding to the impermeability are the nonfenestrated nature of the capillary endothelium and the paucity or absence of pinocytotic vesicles that characterize the physiological pores seen in other endothelia. Astrocytes type foot processes around the mind capillaries that induce and preserve the blood-mind barrier. Microglia perform as mind macrophages and are involved in antigen presentation and phagocytosis. Neuromuscular (myoneural), junctions characterize the location at which finish feet (boutons terminaux) approximate the surface of skeletal muscle cells. The arrangement is much like the synapse; a neuromuscular junction can be thought of the most effective-studied synapse. Ca2+ influx into the top feet may have a direct effect on phosphorylation of synapsin I, a vesicular membrane protein, which in its nonphosphorylated 246 Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology state blocks vesicle fusion with the presynaptic membrane. If the proper facet of the mind is broken, movement in the left arm and leg, vision to the left, or hearing in the left ear, could also be affected. An harm to the left facet of the mind impacts speech and movement on the proper facet of the body. Dendrites generally are wider than axons, are of nonuniform diameter, and taper to a degree. Motor neurons, such as these illustrated in the photomicrograph, usually show large amounts of euchromatin, distinct nucleoli, and Nissl (if stained appropriately) attribute of excessive artificial exercise. Perineurial irritation of cutaneous nerves results in distal anesthesia and paralysis, which are major medical features of the early stages of leprosy. Those neuropathic adjustments are eventually liable for the deformities that elicit most of the social stigma related to leprosy. The neuropathy of leprosy primarily impacts the facial, ulnar radial and peroneal nerves with ascending degeneration of the nerves. In the later stages, endoneurial irritation, infection of Schwann cells, demyelination, and lowered conduction velocity happens. In the excessive-magnification light micrograph, a number of cross-sections by way of small peripheral nerves are seen. C signifies the perineurium, a layer of two to three fibroblast-like cells with contractile properties that encompass particular person fascicles. Cells of the perineurium are joined by tight junctions and type a barrier to macromolecules. B signifies the dense, irregular connective tissue part of the epineurium surrounding the entire nerve. There are quite a few nerve fibers surrounded by myelin sheaths (D) produced by Schwann cells (nucleus seen at E). Other nuclei seen within the fascicle embody these of fibroblasts, which secrete the reticular connective tissue parts forming the endoneurium surrounding the person neuronal fibers, and nuclei of capillary endothelial cells. Label A signifies skeletal muscle, identifiable by its striations and peripherally situated nuclei. Nonneuronal buildings formed from the neural crest embody melanocytes of the pores and skin, odontoblasts in enamel, derivatives of the branchial arch cartilages. The adrenal medulla represents postganglionic sympathetic fibers that reply to inputs from preganglionic sympathetic fibers in splanchnic nerves. Ventral horn and pyramidal cells (solutions b and c) as well as astrocytes (reply d) are derived from the neuroepithelium of the neural tube. Parasympathetic stimulation of the salivary glands produces a profuse, watery secretion. Parasympathetic ganglia are situated in close proximity to or in the wall of the organs they innervate.
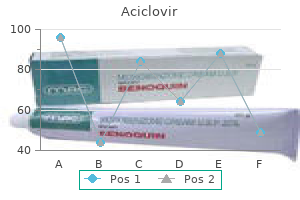
Generic 200 mg aciclovir
At each point where crossover has occurred between two chromatids of the homologous chromosomes, an attachment point known as a chiasma types. Meiosis is the mechanism utilized by the reproductive organs to generate gametes-cells with the haploid number of chromosomes. During meiotic prophase I, maternal and paternal chromosomes are exactly paired, and recombination happens in each pair of homologous chromosomes. The first meiotic prophase consists of 5 substages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis. Homologous chromosomes are aligned on the metaphase plate of the meiotic spindle in metaphase I. The second meiotic division is liable for the discount within the chromosome content material of the cell by 50%. In zygotene (answer b), the synaptonemal advanced begins to kind, which initiates the shut association between chromosomes known as synapsis. The bivalent is formed between the two units of homologous chromosomes (one set maternal and one set paternal equals a pair of maternal chromatids and a pair of paternal chromatids). The formation of chiasmata and desynapsing (separation of the axes of the synaptonemal advanced) happens within the diplotene stage (answer d). Diakinesis (answer e) Cell Biology: Nucleus Answers 151 is an intermediate section between diplotene and metaphase of the primary meiotic division. The formula is the number of Barr bodies equals the number of X chromosomes minus one. The nondisjunction is more frequent in oogenesis than in spermatogenesis, and increased occurrence is immediately proportional to rising maternal age. A combination of irregular and regular genotype happens in mosaic individuals who usually have less extreme symptoms. Only one of many X chromosomes is active within the somatic, diploid cells of the female; the opposite X chromosome remains inactive and is visible in appropriately stained interphase cells as a mass of heterochromatin. Buccal scrapings for Barr physique analysis are getting used less-chromosomal analysis is the usual check now. The lamins are intermediate filament proteins that regulate the nuclear envelope, preserve its stability, and are phosphorylated (prometaphase) and dephosphorylated (telophase) in the course of the cell cycle. Laminin binds to integrins on the cell surface to facilitate attachment of cells to the basement membrane (answer d). Bax is a proapoptotic member of that protein household and inhibits the antiapoptotic actions of bcl-2. Bax can be down-regulated and bcl-2 up-regulated in syndactyly where apoptosis has failed (answer d). The instant effect of mutations within the nucleoporins is decreased import of macromolecules from the cytoplasm. Phosphorylation (breakdown) and dephosphorylation (reconstitution) of the lamins regulates nuclear envelope stability in the course of the cell cycle (answers b and c). A male youngster is born with an absence of the normal structure labeled between the arrows; inclusions of that structure are found within the cells within the photomicrograph. He presents with refractory diarrhea and is chronically depending on parenteral vitamin. What is the primary perform of the structure labeled between the arrows within the photomicrograph beneath Extensive motion of drugs over cell surfaces Increase in surface area for absorption Cell motility Transport of intracellular organelles via the cytoplasm Stretch 153 Copyright � 2007 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. The mechanism for tube formation as happens throughout growth of the neural tube might greatest be explained by which of the following Contraction of microfilament bundles related to the zonula adherens Increased condensation of the transmembrane linkers of the desmosomes Expansion of the sealing strands within the zonulae occludentes Condensation of the hole junctions Contraction of tonofilaments related to desmosomes Epithelium one hundred fifty five 75. In the figure beneath, A is a transmission electron micrograph, and B is a freeze-fracture preparation of a selected mobile structure. Mutations within the proteins that constitute the intramembranous particles labeled within the freeze-fracture image beneath occur in humans. Which of the following would one expect to occur within the presence of such mutations Faster conduction of nerve impulses Increased peristalsis within the small intestine Cardiac arrhythmias More speedy mobilization of glycogen to glucose in response to low blood sugar levels Decreased adherence of epithelial cells to the basement membrane 76. Molecular filtering Contractility Excitability Modification of secreted protein Active ion transport 156 Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology 77. In which specific layer of the accompanying electron micrograph would you expect to see the disruption A fifty four-12 months-old woman presents to the oral surgeon on referral by her general dentist. Her dentist observes a firm mass within the anterior right aspect of the floor of the mouth. Her dentures have been made by a denturist to lower your expenses and her general dentist indicates they fit very poorly. The calcification blocks the submandibular duct resulting in atrophy of the acini and ducts with decreased secretory perform. One would expect which of the following useful changes to occur in association with the basal folds of the striated duct cells Per-Lennart Westesson and Xiang Liu, University of Rochester, Case #98. Increased lipid transport Increased absorption of carbohydrate Decreased active transport Decreased secretion of the primary saliva Decreased lysosomal activity 158 Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology eighty. In the electron micrograph beneath, the structure labeled D primarily does which of the following Forms a spot weld between cells Interacts with actin within the cytoplasm of the apical cytosol Facilitates communication between adjacent cells Seals membranes between cells Moves microvilli Epithelium 159 81. An eleven-12 months-old boy presents with ciliary dyskinesia, sinusitis, and bronchiectasis. In the cross-section of the cilium shown beneath, which of the following is primarily affected on this dysfunction The conversion of sliding to bending within the cilium is achieved by which of the following Restriction of motion by dynein binding of the central microtubules to each other b. Restriction of the microtubule doublets by radial spokes, nexin, and basal bodies a hundred and sixty Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology 83. The structure liable for the linkage of the intermediate filament community of cells to the basal lamina is which of the following Macula adherens Zonula adherens Hemidesmosomes Focal contacts Zonula occludens eighty four. A 42-12 months-old woman, of Mediterranean descent, presents with multiple oral blisters (see photograph), which she says have been present for several months, and a few cutaneous blisters on her again and buttocks that she simply observed over the past week. The bullae are pretty superficial, with the site of skin disruption clearly within the epidermis. Analysis of her sera indicates autoantibodies to a subfamily of cadherins with the distribution shown within the immunofluorescence image (see photomicrograph). Hemidesmosome Zonula adherens Macula adherens Gap junctions Lamina densa of the basal lamina 85. Centrioles Cytoplasmic microtubules Flagellae Axonemes Stereocilia Epithelium Answers 73. Microvilli improve surface area for specialised uptake of molecules by pinocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and phagocytosis. The microvilli additionally contain the comb border enzymes such as lactase and alkaline phosphatase. Microvilli are supported by a core of microfilaments and are capable of motion; however, cilia (answer a) perform within the motion of drugs, such as mucus and foreign materials, over the surface. Cell motion is controlled by interactions between the cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix (answer c), whereas microtubules facilitate organellar motion within the cytoplasm (answer d).
Tuckahoe (Poria Mushroom). Aciclovir.
- How does Poria Mushroom work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Amnesia, anxiety, restlessness, fatigue, tension, nervousness, dizziness, difficult or painful urination, fluid retention, insomnia, inflamed spleen, stomach problems, diarrhea, tumors, and coughs.
- Dosing considerations for Poria Mushroom.
- What is Poria Mushroom?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96271
Effective aciclovir 200 mg
After anesthesia is instituted, the extent of the canthorrhaphy is determined (and marked). The lid margin is break up to the canthal angle, and a segment is excised together with the lash follicles; the adjoining mucosa is abraded. If additional help is required, the canthal tendon (palpebral ligament) is shortened and/or sutured to adjoining orbital periosteum. For Preparation of the Patient, Equipment, Instrumentation, Supplies, and Special Notes, see Excision of Chalazion, pp. Add to Supplies Silicone pegs or different stent material, elective Ectropion Repair Definition Correction of irregular eversion of the eyelid margin away from the globe. Discussion Ectropion normally entails the lower lid and normally happens concurrently with horizontal lid laxity. The lack of regular lid globe opposition results in corneal publicity, tearing, and keratinization of the palpebral conjunctiva. Types of acquired ectropion embody involutional, paralytic, cicatricial (as the result of scarring because of trauma), and mechanical. Various shows may require a lateral tarsal strip to appropriate horizontal laxity or a z-plasty or v-y plasty repair (p. Gold weights (spring wire) may be implanted in sufferers with lagophthalmos; in time, the implant is often extruded. A skin incision is made below the lower lid margin, extending from the punctum to just beyond the lateral canthus. A second incision (an extension of the first) is made within the direction of the earlobe. A skin-muscle flap is developed and elevated across the lower lid; Wescott scissors are normally employed. A vertical incision is made through the tarsus (within the lateral third of the eyelid) and angled into the inferior cul-de-sac ("lazy T" process). The two free edges of the lid are overlapped until tight, and the redundant portion is excised. In younger sufferers, if the punctum is still everted, a tarsal-conjunctival resection may be necessary. The affected person is in supine position; a padded or gel donut headrest may be employed, with the pinnacle turned (affected side up). The process is normally performed bilaterally, employing topical anesthesia with tetracaine ophthalmic drops and a supplemental infraorbital block and subconjunctival injections of lidocaine/xylocaine zero. For Skin Preparation, Draping, Equipment, Instrumentation, Supplies, and Special Notes, see Excision of Chalazion,pp. Add to Draping Microscope drape Add to Equipment Operating fiber-optic microscope. Discussion Entropion results in ocular surface irritation and damage that normally impacts the lower lid; corneal abrasions and scarring may occur. May be because of dysgenesis of the lower lid retractors; instability of the lid follows, with entropion ensuing. Due to hypertrophy of the marginal and pretarsal orbicularis oculi muscle and a paucity of tissue, the eyelid margin is pushed up and towards the globe. Due to spastic closure of the obicularis oculi muscle, usually happens with involutional type. May end result because of horizontal laxity of the medial or lateral canthal tendons, or it might occur as the result of weakness of the retractor muscular tissues of the lower lid when canthal tendons retain their rigidity however the apposition of the lid to the globe is modified. Entropion should be distinguished from lid retraction or epiblepharon, during which the pretarsal obicularis muscle and the skin of the lid override the lid margins and push the lashes inwards. The edges are sutured collectively, and the "canine ear" fringe of remaining tissue is excised. In an alternate technique, skin-tarsal fixation, the orbicular muscle is split and sutured to the lower border of the tarsus. If important scarring (from chronic irritation) is present, a graft of oral mucous membrane may be used. For additional Preparation of the Patient, Equipment, Instrumentation, Supplies, and Special Notes, see Excision of Chalazion, pp. Blepharoptosis Repair/Blepharoplasty Definition Correction of ptosis of the upper eyelid. The commonest reason for congenital myogenic ptosis is due to improper levator muscle improvement. May end result from an accident, from use of contact lenses, or because of ocular surgical procedure. Any considered one of a variety of methods may be employed as remedy, relying on the sort and severity of the deformity. External levator resection is indicated in sufferers with reasonable to severe ptosis and fair to poor levator operate. Unless interference with vision is determined and documented preoperatively, the corrective process is considered beauty surgical procedure. An incision is produced from canthus to canthus and carried through the orbicularis oculi to the superior border of the tarsus. The upper skin edge is grasped, and the orbicularis is separated from the orbital septum. The lower lid is pulled up over the globe by sutures positioned within the lower lid through silicone pegs or bolsters which are taped to the forehead. For Preparation of the Patient, Skin Preparation, Draping, Instrumentation, Equipment, and Supplies, see Excision of Chalazion, p. Special Notes � Apply Special Notes from Ophthalmic Surgery General Information, pp. Chapter 28 Ophthalmic Surgery 883 Excision of Eyelid Lesion Definition Excision of skin lesions of the eyelid. Discussion An excision of an eyelid lesion ought to embody the lid margin; when each benign and malignant tumors are excised, beauty and useful repair of the wound is done. Various benign skin lesions of the eyelid, similar to cysts, nevi, infections, tumors, and so forth. Skin lesions of the eyelid which are malignant embody basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma; basal cell carcinoma is the most common malignant lesion which will have an effect on the eyelid. Treatment as radiation remedy may be employed to ablate neoplastic lesions of the eyelid, however the unwanted side effects of radiation remedy embody dermatitis, keratitis, and scarring. Repair of any wounds following excision contains orientation of the tissue based on skin traces; the closure should be accomplished with out tension for adequate wound therapeutic. For additional data, see the previous entry, Blepharoptosis Repair/Blepharoplasty, p. Procedure In excision of lesions of the eyelid and lid margin, the incision is often pentagon-formed; the bottom of the pentagon is positioned at the lid margin and the apex points upward, away from the lid margin. A number of forms of tarsal/conjunctival flaps may be used, as Tenzel (semicircular is lateral-based mostly) or Cutler-Beard (flap of the opposing lid is handed underneath the lid margin to cowl the defect within the affected lid, which requires closure of the lid with lack of vision for six to 8 weeks); that is inappropriate for sufferers with limited vision or absence of vision within the different eye. Preparation of the Patient Excision of an eyelid lesion may be performed employing topical, local, and/or general anesthesia. Add to Special Notes � Reminder: When a laser is employed, all safety precautions are obligatory. Discussion Eyelid laceration repair may be performed in response to any traumatic eyelid laceration to restore the integrity of the lid. The defects are categorised based on measurement and location; they may involve the lid, lid margins, and canthus. The major causes of the eyelid defect are trauma and tumors; basal cell carcinoma is the second commonest trigger. The skin surfaces (solely) of the wound may be approximated with cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive. Deep sutures should be positioned (on eye muscular tissues and facial areas) to relieve the stress on the wound closure as necessary for wound therapeutic. Dermabond may be employed for skin closure, as it really works Chapter 28 Ophthalmic Surgery 885 as a barrier towards micro organism. To prevent hematoma formation, meticulous hemostasis should be achieved using an ophthalmic diathermy and ice compress dressings postoperatively, somewhat than tight stress dressings.
Syndromes
- Have you noticed any other unusual physical characteristics?
- Blindness - resources
- Drastic weight reduction
- Moving your legs often during long plane trips, car trips, and other situations in which you are sitting or lying down for long periods of time.
- X-ray procedure using a special dye to see the bowel while you have a bowel movement (defecography)
- Stones made of cholesterol, which are by far the most common type. Cholesterol gallstones have nothing to do with cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Flank or back pain
- Constipation
- What other symptoms do you have (for example, have you had any bleeding? Are you dizzy?)
Quality aciclovir 400 mg
A 32-yr-old (gravida 2, para 2) woman who gave start to a child woman 24 hours before is having issue urinating and is retaining urine in her bladder. She is given bethanechol, a muscarinic agonist, which is the ligand shown in the diagram under. Neither his top nor his weight is on the growth chart for his age; mean weight and top for a 6-month-old are 17 lb, 4 oz and 26. You recall out of your cell biology that the phosphotransferase enzymes phosphorylate mannose to type mannose-6-phosphate. Which of the following explains the altered cell organic processes in this affected person Phagocytosis of broken cells occurs by evagination to engulf the IgG-coated surface of the goal. Both processes use acidification of compartments and hydrolases to uncouple receptor and ligand (receptor-mediated endocytosis) or destroy engulfed materials (phagocytosis). Both processes use membrane-enclosed vesicles and are associated with lysosomal exercise (solutions a, b, c, and e). The receptors are bound to clathrin-coated pits, however the ligand is simply directly bound to its cell surface receptor. The acidic setting of the endosome results in the cleavage of the ligand from its receptor. Enzymatic cleavage (answer e) of the sign sequence releases the newly synthesized peptide. The underlying precept in all these features is the popularity by chaperones of proteins of their nonnative states. Chaperones at the side of calreticulin monitor the progress of folding and ensure that solely correctly folded proteins are secreted from the cell or shipped to lysosomes. The determine illustrates the response of the -adrenergic receptor to ligand binding. Phosphorylation (E) stimulates exocytosis and induces nuclear adjustments, together with transcriptional events. Binding of a ligand to its G protein�linked receptor on the cell surface (Gq) activates a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. The protein kinase C phosphorylates (F) specific serine and threonine residues and may alter gene transcription. The two intracellular messenger pathways do interact in that elevated Ca2+ translocates protein kinase C from the cytosol to the internal leaflet of the plasma membrane. The pathway labeled as I (A D) differs from constitutive secretion (C E) in several ways. The most important difference is the requirement for a secretagogue (substance that induces secretion from cells) in the regulated pathway (solutions a and c), which binds to a cell-surface receptor. Regulated secretion (process I) reveals the popularity of a receptor (B) for its ligand (A), ensuing in the release of secretion in response to the stimulus of secretagogue-receptor binding. The vesicles that bud from the Golgi (D) in the regulated pathway are clathrin-coated and include a receptor concerned in the focus of secretory product that normally occurs before release. The constitutive pathway shuttles proteins corresponding to integral membrane proteins and lipids in vesicles to the apical and basolateral membranes. Exocytosis requires vesicle fusion with the membrane in each regulated and constitutive pathways. Cell Biology: Intracellular Trafficking Answers 137 There is an absence or deficiency of N-acetylglucosamine phosphotransferase and an absence of mannose-6-phosphate (M6P) on the lysosomal enzymes. The default pathway is transport to the cell membrane and secretion from the cell by exocytosis for proteins missing M6P. Lysosomal enzymes are secreted into the bloodstream, and undigested substrates build up inside the cells. A newborn boy is born with first arch congenital malformations classified as Treacher-Collins syndrome, which is an autosomal dominant inherited disorder. Treacle is localized to the structure labeled with the arrows in the accompanying transmission electron micrograph. Assembly of ribosomal subunits into mature ribosomes Translation of cytosolic proteins Transcription of nuclear proteins Transcription of ribosomal proteins Organelle degradation 139 Copyright � 2007 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Which of the following is true for the process that the dividing cell shown in the electron micrograph under is present process Which of the following is more than likely to be directly affected by the disruption of nucleosomes in this affected person. A middle aged anatomy professor went to the most popular Indianapolis 500 race in a long time and sat with the solar dealing with him; there was no breeze. When he grew to become dehydrated on the race, it triggered the uric acid crystal formation in his foot. The race was great and he drank about 2 L of water and soda on the race and another couple of liters when he arrived residence. A metaphase-blocking dose of colchicine features by way of which of the following mechanisms Depolymerization of actin Depolymerization of myosin Enhancement of tubulin polymerization Inhibition of tubulin polymerization Binding to and stabilizing microtubules 142 Anatomy, Histology, and Cell Biology 66. The structure labeled A in the accompanying electron micrograph is which of the following Which of the following mechanisms could also be concerned in the lack of cell cycle management that occurs in prostate carcinoma Increased CdkI exercise Decreased transcription of G1/S cyclin Decreased expression of bcl-2 Increased transcription of gene regulatory proteins corresponding to E2F Dephosphorylation of Rb 68. Decreased recombination is associated with the manufacturing of aneuploid sperm in humans. An obese 18-yr-old man presents with small firm testes, a small penis, little axillary and facial hair, azoospermia, gynecomastia, and elevated levels of plasma gonadotropins. He has had issue in social adjustment all through high school, but this has worsened and he has been referred for genetic and endocrine screening. The karyotype from peripheral blood leukocytes would more than likely show what number of Barr physique/bodies He experienced normal fetal and early postnatal growth, but now reveals extreme failure to thrive, some lipoatrophy, bony abnormalities, a small, beaked nostril and receding mandible, hair loss, and speckled hypopigmentation with some areas of tight onerous skin. Which of the following would you almost certainly expect to be directly affected in cells obtained in a biopsy from this affected person He has craniosynostosis, hypoplasia of the center part of his face with retrusion of the eyes, and syndactyly that features fusion of the skin, connective tissue, and muscle of the primary, middle, and ring fingers with average fusion of the bones of those digits. Which of the following have been more than likely decreased in cells in the inter-digital area of the creating hand of this newborn child A 25-yr-old man presents with Triple A (Allgrove) syndrome together with the clinical triad of adrenal failure, achalasia, and alacrima. Expression of treacle is crucial during early embryonic growth in buildings that type bones and other facial buildings. Treacle is energetic in the nucleolus, the structure labeled in the transmission electron micrograph. Ribosomal synthesis occurs in the nucleolus, however the full assembly and maturation of ribosomes requires transport to the cytoplasm (answer a). Ribosomal proteins as well as all proteins that function in the nucleus are synthesized in the cytosol and transported into the nucleus (answer b). Cytosolic proteins are synthesized on isolated ribosomes in contrast with most protein synthesis that occurs on polyribosomes. Cytokinesis requires the motion of the contractile ring composed of actin and myosin. The drive for cytokinesis is generated by the motion of actin and myosin, which may be inhibited by 146 Cell Biology: Nucleus Answers 147 remedy with antimyosin antibodies in vitro. The contractile ring pulls the plasma membrane of the telophase cell into the cleavage furrow. Kinetochore microtubules, which attach the kinetochores to the spindle equipment, shorten and pull the chromatids to reverse poles in anaphase A (answer a). Growth of polar microtubules results in the separation of the spindle poles in anaphase B (answer c).
Cheap 200mg aciclovir
The lesser sac is entered, and the tissues along the lesser curvature of the abdomen to the esophageal hiatus are dissected. The left margin of the best crus of the diaphragm and the abdomen are retracted to the left. The paraesophageal 208 Chapter 17 Gastrointestinal Surgery tissues are dissected to expose the esophagus, which is retracted to the left. Gastric branches are recognized (using dissection of the gastric serosa as needed), clipped, and divided. This process is similar to the one described up to the division of the posterior vagal trunk. As branches of the anterior vagus nerve are sometimes imbedded throughout the seromuscular layer of the abdomen, preventing division of the individual branches, a seromyotomy 1. In addition to histological confirmation that the nervous tissue was eliminated, testing for gastric acidity may be accomplished intraoperatively. Twenty minutes prior to the testing, the abdomen is lavaged through a gastroscope with sodium bicarbonate resolution to take away residual acid. If even partial innervation stays, the affected area will turn black (as seen by way of the scope) and extra nerve transection may be accomplished. A pad underneath the sacral area and/or a pillow may be placed underneath the knees Chapter 17 Gastrointestinal Surgery 209 to relieve strain on back muscle tissue. Bony prominences and all areas susceptible to skin and neurovascular trauma or strain are padded. Skin Preparation Begin at the midline extending from axilla to the pubic symphysis and down to the desk at the sides. Supplies Antiembolitic hose Foley catheter with steady drainage unit, as requested N/G tube. Closure of a Perforated Peptic Ulcer Definition Repair of a full thickness of gastric or duodenal ulcer that has penetrated into the peritoneal cavity. Discussion A complication of peptic ulcer illness is spontaneous perforation with the escape of gastroduodenal secretions and contents into the peri- Chapter 17 Gastrointestinal Surgery 211 toneal cavity, leading to peritonitis. The presentation may be delicate with a spontaneous closure of the perforation handled by nonsurgical means, or it could result in an in depth life-threatening peritonitis. When preexisting peptic ulcer illness has been present and the peritoneal irritation is proscribed, a vagotomy and drainage process may be performed; see Vagotomy and Pyloroplasty, p. If not already partially adherent to the perforation, a portion of adjoining greater omentum (or gastrocolic ligament, etc. After hemostasis is assured and the drains are placed (and secured with a sew), the wound is closed in the traditional method. For Preparation of the Patient, Skin Preparation, Draping, Equipment, Instruments, Supplies, and Special Notes, see Vagotomy and Pyloroplasty, p. Laparoscopic Closure of a Perforated Ulcer (With Vagotomy) Definition Closure of a perforated abdomen or duodenal ulcer and excision of the vagus nerve and its branches; laparoscopically. Procedure Pneumoperitoneum and ports are established as for Laparoscopic Vagotomy; see p. An endoscope is handed transorally, through which a grasping forceps is placed from throughout the abdomen or duodenum into the peritoneal cavity, seizing (with laparoscopic steering) a portion of omentum. The patch is secured with endoscopic suture or staples, and the endoscope is withdrawn. Vagotomy (with drainage process) could then be performed, as described in Laparoscopic Vagotomy, p. For Preparation of the Patient, Skin Preparation, Draping, Equipment, Instruments, Supplies, and Special Notes, see Laparoscopic Vagotomy, p. Gastrostomy Definition Establishment of an artificial opening into the abdomen exiting onto the skin of the stomach wall. A well-lubricated flexible fiber-optic gastroscope is handed into the abdomen; Chapter 17 Gastrointestinal Surgery 213 the abdomen is distended with air. The lighted tip of the scope is impacted on the gastric wall, which is then positioned to be directly underneath the parietal peritoneum, displacing the liver edge and colon. If the affected person is awake, native anesthesia is injected at the website of the meant gastrostomy. A second operator passes a catheter through a percutaneous stab wound, aiming at the transilluminated gastroscope tip. Tissue anchors may be placed percutaneously to safe the gastric wall to the parietal stomach wall about the catheter entry website. An alternative method is to move the catheter transorally, seizing similar from throughout the abdomen with a percutaneously inserted grasper. The peritoneal cavity is entered, the gastric wall is recognized, and concentric purse-string sutures are placed. A small incision is made into the abdomen, throughout the innermost purse-string suture, through which a catheter is handed. The catheter can exit through the incision or ideally through a separate stab wound and secured. The gastric wall is sutured intra-abdominally at a couple of points to the peritoneal floor about the stab wound. A pillow may be placed underneath the sacral area and/or underneath the knees to relieve strain on back muscle tissue. Skin Preparation Begin at the meant website of incision (often transverse left higher stomach), extending from nipples to higher thighs and down to the desk at the sides. Chapter 17 Gastrointestinal Surgery 215 � Surgical group members ought to put on face shields to stop contaminated gastric contents from splashing or spraying into their eyes or onto mucous membranes. Gastrectomy Definition Removal of the entire abdomen or a portion of the abdomen and the reestablishment of the continuity of the gastrointestinal tract. Discussion Subtotal (partial) gastrectomy refers to the excision of a portion of the abdomen performed primarily for peptic ulcer illness or tumor of the distal abdomen. When treating malignancies, the greater omentum, lymph nodes, and adjoining organs. Continuity of the gastrointestinal tract is established by anastomosing distal esophagus to the proximal jejunum, often with the creation of a pouch or reservoir. The greater omentum and generally the spleen are resected in continuity with the abdomen en bloc when malignancy is present. According to the extent of the resection and the type of anastomosis to be fashioned, the duodenum or jejunum is mobilized and anastomosed to the gastric remnant or the distal esophagus anterior to (or posterior to) the transverse colon. The anastomosis is facilitated by means of automatic stapling units, or clamps and all kinds of sutures and suturing methods may be employed. Preparation of the Patient For an higher midline or bilateral subcostal method, antiembolitic hose are utilized. A pillow may be placed underneath the sacrum and/or underneath the knees to relieve strain on back muscle tissue. The affected person is in a modified (45 -) right lateral position with the left aspect uppermost. The right arm is prolonged on a padded armboard; the left arm is supported by a Mayo stand (padded with a pillow), or a double armboard may be used. The left leg is prolonged and the best leg is flexed, or both legs may be flexed with a pillow between the knees. Pad all bony prominences and areas susceptible to neurovascular strain or trauma. The position is secured by broad adhesive tape (after checking chart for affected person allergy symptoms), following the appliance of tincture of benzoin, from the shoulders, hips, and legs to the underside of the desk. Skin Preparation For an higher midline or bilateral subcostal method, start at meant website of incision, extending from the axilla to just above the pubic symphysis and down to the desk at the sides. For a thoracoabdominal method, start at the meant website of incision, extending from the shoulder to the iliac crest and down to the desk, anteriorly and posteriorly. Bariatric Surgery Definition Procedures to deal with morbid obesity that alter the gastrointestinal tract to effect weight loss by decreasing the capacity of the abdomen. Surgery to induce weight loss is performed only after nonsurgical means have failed and the affected person has undergone medical and psychological analysis. Metabolic restriction, by which absorptive capacity of the intestinal tract is altered by short circuiting the small intestine and/or diverting biliopancreatic secretions. Chapter 17 Gastrointestinal Surgery 219 There are quite a few procedures, a few of which have been deserted as a result of long-term metabolic consequences (similar to jejuno-ileal bypass). Other procedures could need to be reversed, revised, or converted to an alternative configuration. Gastroscopic placement of an intragastric balloon has largely been deserted due to erosive unwanted effects and its ineffectiveness.
400mg aciclovir
The surgeon may request a sequential compression system with disposable leg wraps; they can be utilized over the antiembolitic hose, or the leg wraps could also be used alone. Skin Preparation Prep both breasts beginning at the nipples; prolong preparation from the neckline to the level of the iliac crests and right down to the table at the Chapter 25 Plastic Surgery 755 sides. For extremely massive pendulous breasts, the prep could also be extended to the symphysis pubis. Draping Folded towels and a disposable transverse sheet and/or particular person drape sheets may complete the draping. The advantage of using disposable drapes is the adhesive backing on the underside of the fenestration that allows the drape to be secured across the perimeter of the surgical subject. The room must be ready for the laser portion of the process before starting the surgical procedure. A scale is used to weigh the breast tissue; hold tissue removed from each breast in a separate container. The shade change is documented within the postoperative section of the Perioperative Record. Augmentation Mammoplasty Definition Implantation of breast prostheses to enhance the looks of the breasts. Indications for this process include micromastia (unilateral or bilateral), postpartum involution of the breasts, ptosis, postsurgical deformity, and/or simply the desire to improve the cosmetic appearance of the breasts. Prior to surgical procedure, the surgeon and patient choose the form, texture, and volume (measurement). The thickness of the mammary pores and skin and the diploma of breast ptosis (if any) are factors in determining one of the best placement (place) of the prosthesis (implant), either submuscularly (pectoralis) or subglandularly. Breast implants are composed of an outer silicone shell; they can be filled following insertion (saline, only), or they might be prefilled with silicone gel. The advantage of using saline-filled prostheses is that a larger measurement could be positioned while employing a smaller incision. Gelfilled implants look and feel more "pure"; they can be positioned endoscopically, but not through the endoscope. The prosthesis is inserted and pushed along the beforehand made tunnel with the scope. When the implant is to be positioned submuscularly, epinephrine solution 1:10,000 could also be injected into the pectoralis muscle; nonetheless, care should be taken to keep away from penetration of the chest wall. Final adjustment within the placement of the prostheses could also be made after inserting the patient in a sitting place to assess measurement, contour, and symmetry. A aircraft is developed between the pectoralis fascia and the posterior capsule of the breast (subglandular strategy). The retromammary area is enlarged by blunt dissection to accommodate the prosthesis. Hemostasis is accomplished; a fiber-optic lighted retractor could also be employed for better visualization. The pectoralis major fascia is incised and a submuscular aircraft developed by blunt dissection (including finger dissection). A Hopkins rod (rigid) endoscope could also be inserted through the sleeve of a fiber-optic retractor. External palpation (with observance of the endoscopic mild percutaneously) helps to information the scope. An inflatable trial prosthesis or an "expander" could also be inserted, noting the amount of saline required to create the specified pocket measurement. The expander is eliminated and the chosen prosthesis is inserted and pushed by the top of the scope by way of the tunnel and filled (by way of the self-sealing port). The patient could also be positioned in a sitting place following insertion of the implants to assess the dimensions and symmetry of the augmentation. An incision is made within the superior half of the umbilicus and a subcutaneous aircraft of dissection developed. If the implant is to be positioned submuscularly, a solution of native anesthetic with epinephrine (and hyaluronidase) is often injected percutaneously beneath the pectoralis muscle fascia. A subcutaneous tunnel is developed toward the specified placement site for the implant underlying either breast using an endotube dissector. An endoscope is inserted, and under direct vision, the pocket is completed using an "expander. The patient is positioned "symmetrically" on the table in supine place with arms extended, kidnapped, and secured in place on padded armboards at approximately an 80 angle using padded restraints. During the process, the patient will be positioned in sitting place to assess breast measurement and symmetry (with out distortion, as breast distortion may appear within the supine place). Skin Preparation Prep both breasts beginning at the sites of incision (periareolar, transaxillary, inframammary, or transumbilical). Extend prep from the neckline to beneath the umbilicus, using additional care to prep the axilla properly; for terribly massive breasts, prep extends right down to the pubis. Draping Folded towels and a disposable transverse sheet could also be used for all the approaches, aside from transumbilical, for which a laparotomy sheet is most well-liked. The advantage of the adhesive backing on the underside of the fenestration is eradicated. The advantage of using disposable drapes is the adhesive backing on the underside of a fenestration that allows the drape to be secured across the perimeter of the surgical subject. Discussion Abdominoplasty is also referred to as stomach lipectomy and is usually performed in conjunction with panniculectomy, the excision of a redundant apron of subcutaneous tissue (and pores and skin). Techniques employed to carry out abdominoplasty are various; lax, redundant subcutaneous fat (and the overlying stomach pores and skin) are excised and the stomach musculature is tightened. Abdominoplasty is performed to reduce the discomfort associated with performing day by day tasks and considerations relating to private hygiene, and for cosmesis. The surgeon determines the strategy according to fat distribution, amount of stomach wall weak spot or presence of a frank ventral hernia, measurement of the panniculus, and his/her expertise and preference. Tumescent liposuction could also be mixed with an endoscopic-assisted strategy that enables placement of musculofascial sutures employing limited incisions. For intensive presentations, a transverse or transverse curvilinear incision extends from iliac crest to iliac crest. When a big panniculus is excised, a double incision is made, a "lazy" M superiorly and a U inferiorly, the decrease extent of which is at the pubis (this has largely supplanted the W incision). The length of the M is made to equal the length of the U in order that with wound closure there will be no discrepancy. Generally, lesser plastic procedures performed to take away redundant tissue from beneath the umbilicus are referred to as a "tummy-tuck. The M incision is made above the umbilicus and the U incision is made with its center simply above the pubis symphysis, the lateral extent of which meets with the M incision bilaterally. The umbilicus on a pedicle could also be incised in a diamond form, preserving its support and blood provide for later substitute under the flap. Dissection is begun at the decrease portion of the U incision and progresses upward bilaterally; a fine layer of areolar tissue over the fascia is retained. The amount of intervening pores and skin and adipose tissue to be excised is carefully estimated before elimination in order that the defect could be Chapter 25 Plastic Surgery 763 closed with moderate pressure. A ventral hernia, if current, is repaired (massive ventral hernia repair would require synthetic mesh). The umbilicus is brought through an appropriately positioned place within the superior wound flap and sutured. The wound is closed with heavy absorbable suture; the pores and skin could also be closed with a subcuticular operating suture. The surgeon may request a sequential compression system with disposable leg wraps; they can be utilized over the antiembolitic hose, or the wraps could also be used with out the hose. Skin Preparation Begin prepping beneath the umbilicus, extending from the midthorax to the knees and right down to the table at the sides. Draping Folded towels and a transverse sheet and/or particular person drape sheets complete the draping. A sequential compression system with leg wraps could also be utilized over the antiembolitic hose, when ordered, to stop deep vein thrombosis. If the patient has an especially massive panniculus, the surgeon often devises a method of supporting the panniculus that enables the circulator to prep the pores and skin space under the panniculus adequately. Check with the surgeon relating to the kind of mesh to be used for the ventral hernia repair; several types of synthetic mesh must be within the room. When closing the wound, the surgeon may request that the table be flexed to facilitate wound closure.
References:
- https://www.lls.org/sites/default/files/National/USA/Pdf/Publications/CAP_acute-leukemia-patient-faq.pdf
- https://www.hpsc.ie/a-z/respiratory/influenza/seasonalinfluenza/infectioncontroladvice/respiratoryhygieneposters/Primary%20English.pdf
- https://msdh.ms.gov/msdhsite/index.cfm/41,2029,71,pdf/School_Immunization_Requirements.pdf
- https://www.johnscreekpediatrics.net/storage/app/media/2-4-Weeks.pdf
.png)