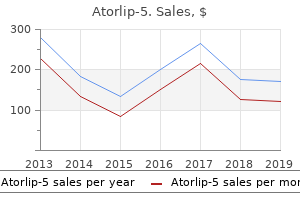
Purchase atorlip-5 5mg
Using coloured feed or inserting brightly coloured marbles in the feed and water might assist. Younger toms for oven-ready dressed birds & older toms for additional processing or restaurant trade. There, nonetheless, should be adequate crude protein to ensure an sufficient nitrogen supply for synthesis of nonessential amino acids. Suggested requirements for crude protein are typical of these derived with corn-soybean meal diets, and ranges may be reduced considerably when artificial-amino acids are used. Chiba Animal Nutrition Handbook Section 12: Poultry Nutrition and Feeding Page 327 2. Suggested requirements for crude protein are typical of these derived with corn-soybean meal diets, and ranges may be reduced considerably when artificial amino acids are used. Chiba Animal Nutrition Handbook Section 12: Poultry Nutrition and Feeding Page 328 three. However, there should be adequate crude protein to ensure an sufficient supply of nonessential amino acids. Chiba Animal Nutrition Handbook Section 12: Poultry Nutrition and Feeding Page 329 four. Body Weight and Feed Consumption of Immature Leghorn-Type Chickensa White-Egg-Laying Strains))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))) Body Weight Feed intake (g) (g/wk) Brown-Egg-Laying Strains))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))) Body Weight Feed Intake (g) (g/wk) 35 50 37 70 100 a hundred and forty one hundred twenty a hundred and sixty 260 260 325 280 450 340 500 350 660 360 750 380 750 380 900 400 980 400 1,100 420 1,100 420 1,240 450 1,220 430 1,380 470 1,375 450 1,500 500 1,475 500 1,600 550 a Average genetic potential when feed is consumed on an advert libitum basis. Different commercial strains might present different development charges and different last mature physique weights. Estimates of Metabolizable Energy Required per Hen per Day by Chickens in Relation to Body Weight and Egg Production (kcal) Rate of Egg Production (%)))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))) 0 50 60 70 80 ninety Body Weight (kg) 1. Temperature of twenty-two°C, egg weight of 60 g, and no change in physique weight have been utilized in calculations. Chiba Animal Nutrition Handbook Section 12: Poultry Nutrition and Feeding Page 330 7. Also, genetic enhancements in physique weight acquire have led to an "earlier implementation" of these requirements. Such energy, when accompanied by the nutrient ranges advised, is expected to present close to-maximum development, notably with pelleted feed. There, nonetheless, should be adequate crude protein to ensure an sufficient nitrogen supply for synthesis of noness ential amino acids. Suggested requirements for crude protein are typical of these derived with corn-soybean meal diets, and ranges may be reduced when artificial amino acids are used. Chiba Animal Nutrition Handbook Section 12: Poultry Nutrition and Feeding Page 331 8. Growth Rate, Feed Intake, and Energy Intake in Large-Type Turkeys Body Weight (kg)))))))))))))))))) Male Female 0. The horse trade has become an important a part of the agricultural scene in lots of areas of the States - An increase in horse research in recent times due to the popularity and the economic influence of the horse trade. After several years of declining horse populations, which started in the mid 1980s, the status of the horse trade has improved in recent times: 1) 2) High feed sales by most major horse feed manufacturers - A reflection of not solely the number of horses, but additionally the demand for prime-quality feeds to hold horses "totally content material" somewhat than merely satisfying the needs or maintaining the well being. Limited experimental info on the dietary want of horses: 1) massive gaps on the published info on many points, 2) "unresolved" and conflicting reviews on many points, and 3) some difficulty in precise application of knowledge obtained beneath diverse conditions. Chiba Animal Nutrition Handbook Section 13: Horse Nutrition and Feeding Page 333 1) 2) three) Digestive and metabolic variations among horses - Should make appropriate changes to compensate the attainable variations!? Variations in the production/efficiency functionality and the expectation of the proprietor? Health status of the animal, variations in the nutrient availability in feed elements, interrelationships among vitamins, earlier dietary status, and weather/environmental conditions. Water Expected daily water consumption (Gal; Lawrence, 1998) Maintenance, 500 kg (Thermoneutral) 6-8 444444444444444444444444444444444444444444 Maintenance, 500 kg (Warm environ) 8-15 A. Like other species, an sufficient supply of Lactating mare, 500 kg 10-15 10-12 clean water is necessary for horses - Should Working (reasonable), 500 kg Working (reasonable), 500 kg (Warm environ) 12-18 have water available on a regular basis by way of buckets, Weanling, 300 kg (Thermoneutral) 6-8)))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))) troughs, ponds, or streams (Table). Sum of the water misplaced from the physique (by way of urine, feces, sweat, and secretions) plus a component of development in younger animals. Dehydration and electrolyte balance 1) 2) three) Dehydration through sweating can lead to the lack of water and electrolytes (mostly, Na & Cl with some K). No conclusive proof, but, oral supplementation could also be useful for a heavily sweating endurance horse in a scorching or humid environment! An sufficient water supply, a balanced diet, and a trace mineralized salt on a freechoice should be adequate in most racing conditions! Chiba Animal Nutrition Handbook Section 13: Horse Nutrition and Feeding Page 334 1) 2) "Easy keeper" - Often used to describe a horse that may maintain physique weight on lower than the common dietary energy supply. Body Condition Scoring System (1 - 9) Description 444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444)))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))) C. If not, can use subjective situation scoring system to monitor physique situation - See the desk: 1) 2) Based on physique fatness using 1 (very thin) to 9 (very fats). Environmental temperatures: 1) 2) Have a big influence on energy)))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))) Henneke et al. Ribs, shoulder, backbone, and pelvis are clearly discernable but some fats cover may be felt. Fiber digestion alone is, often, not adequate to fulfill the energy want for lactation, development, and exercise - May want some supplemental grains or lipids. Diets with a large amount of starch and a low amount of fiber are associated with an increased incidence of colic and laminitis. Mature horses at maintenance: 1) 2) Have relatively low protein needs and deficiency is rare with an sufficient energy. Young horses, lactating mares, and mares in late gestation - Need a diet with larger protein amount and quality. Protein quality - An necessary consideration in growing horses, and Lys seems to be the primary limiting amino acid in diets for growing horses, with Thr being advised as the second limiting. Unclear on the speed of amino acid synthesis and absorption at the cecum, thus, should present an sufficient amount of dietary indispensable amino acids, particularly for growing horses till more info is on the market? Similarly, microbes can synthesize some indispensable amino acids, but their absorption by the hindgut might be limited!? Broodmares - Need protein for the deposition of fetal tissues and milk production. Chiba Animal Nutrition Handbook Section 13: Horse Nutrition and Feeding Page 336 A. Ca & P - Special importance in horses: 1) 2) three) four) the event of quality bone is more necessary in horses than other livestock species just because some athleticactivity might put more stress on bones. Sodium, K, and Cl - Function as electrolytes and important for all lessons of horses. The needs are larger for working horses, lactating mares, and horses that are exposed to high environmental temperatures. Iron - Usually met by the typical feed elements, although the availability of Fe in grains and forages could also be low. Selenium - Low in soils of many areas of North America, thus, feeds are also low in Se. Selenium supplementation is usually needed but should be done rigorously due to its toxicity. Fat-soluble nutritional vitamins: 1) Vitamin A and E are of probably the most sensible importance in horse diets: a) b) One of the richest sources of $-carotene (precursor of vitamin A) is "inexperienced" pasture. Microbes can synthesize compounds with vitamin K exercise, and likewise can get substances with vitamin K exercise from hay and pasture. Pasture should be utilized every time attainable: 1) 2) three) four) 5) Can cut back labor prices and supply a high-quality source of vitamins. Most grasses may be grazed by the horse, and legume-grass mixtures make wonderful high quality pastures. Rotational grazing and(or) clipping are necessary administration practices as a result of horses are selective and have a tendency to graze the youngest and most tender grasses. With plenty of high-quality pasture or hay, solely quickly developing weanling and yearling horses, mares that are lactating and to be bred again, and present and efficiency horses may have supplemental grains. Chiba Animal Nutrition Handbook Section 13: Horse Nutrition and Feeding Page 338 1) 2) Undoubtedly, obtaining good hay, storing, and feeding is usually a major administration downside. Some components associated with feeding hay: a) b) c) d) Moldy or dusty hay might cause colic and heaves in horses.
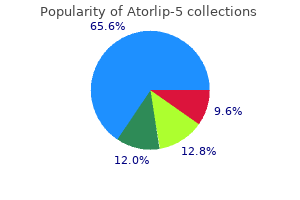
Generic 5 mg atorlip-5
However, metal cyanide particles, particularly water-soluble cyanide particles, are anticipated to be faraway from the air by each moist and dry deposition. Volatilization and sorption are the two physical processes that contribute to the lack of cyanide from water. In outdoor experiments with average winds, the rate of hydrogen cyanide loss increased by a factor of two2. In a research to evaluate the impact of cyanide on biochemical oxidation, there was a 50% lack of 6 ppm (mg/L) cyanide in river water stored in open biochemical oxygen demand bottles (with out aeration) at pH 7. When the bottles have been aerated (fee of aeration not given), 50% loss occurred in solely 10 hours. Data indicated that cyanide volatilization is a more essential destiny process than cyanide loss because of chemical and biodegradation reactions (see Section 6. However, additional data are essential to assess the significance of cyanide sorption to suspended solids and sediments in water. There is some proof that certain metal cyanide complexes bioaccumulate in aquatic organisms. Volatilization of hydrogen cyanide would be a big loss mechanism for cyanides from soil surfaces at a pH <9. Mobility is lowest in soils with low pH and excessive concentrations of free iron oxides, positively charged particles, and clays. Also, leaching of cyanide right into a shallow aquifer can happen, as demonstrated by the excessive focus of cyanide (1,200 g/L) in groundwater sampled from the Biscayne Aquifer in Dade County, Florida, which lies below a strong waste website (Myers 1983). Therefore, it will be anticipated that volatilization from water and soil would be a main route of environmental partitioning for each cyanogen and cyanogen chloride. Similarly, little data could be found in the out there literature on the environmental transport and partitioning of thiocyanate in the setting. The ensuing environmental transformation merchandise within different media are proven in Table 6-three. The fee of hydroxyl radical reaction with hydrogen cyanide in the environment depends on the altitude, and the rate of the reaction is a minimum of an order of magnitude quicker at lower tropospheric altitudes (08 km) than at higher tropospheric altitudes (1012 km) (Cicerone and Zellner 1983). Based on a reaction fee fixed of 3x10-14 cm3/(molecule-sec) at 25 °C (Fritz et al. This worth compares nicely with the atmospheric residence time derived by Cicerone and Zellner (1983) of roughly 2. Cyanogen has additionally been proven to react with hydroxyl radicals in the fuel section (Atkinson 1989). No specific data was found in the out there literature on the transformation and degradation of cyanogen chloride or thiocyanates in air. However, cyanogen chloride has been proven to bear slow hydrolysis in impartial aqueous solution (fee fixed at pH 7 of 6. Therefore, hydrolysis of this compound could also be a possible atmospheric degradation pathway in air. Oxidation, hydrolysis, and photolysis are the three predominant chemical processes that may trigger lack of easy cyanides in aquatic media. In water, hydrogen cyanide and cyanide ion exist in equilibrium with their relative concentrations primarily depending on pH and temperature. As a end result, they readily dissociate into their respective anions and cations when launched into water. The proportion of hydrogen cyanide formed from soluble cyanides will increase because the water pH decreases. As the pH will increase, cyanide ions in the water could form advanced metallocyanides in the presence of excess cyanides; nevertheless, if metals are prevalent, easy metal cyanides are formed. The significance of photolysis in the destiny of cyanides in water has not been totally investigated. In clear water or at water surfaces, some metallocyanides, similar to ferrocyanides and ferricyanides, could decompose to the cyanide ion by photodissociation and subsequently form hydrogen cyanide. For example, diurnal adjustments in free cyanide concentrations in the drainage from spent precious metal ore heaps have been found to maximize around mid-day because of the photodissociation of iron and cobalt cyanocomplexes (Johnson et al. Biodegradation is an important transformation process for cyanide in pure floor waters, and depends on such components as cyanide concentrations, pH, temperature, availability of vitamins, and acclimation of microbes. Although the cyanide ion is toxic to microorganisms at concentrations as little as 510 mg/L (Klecka et al. Mixed microorganisms in sewage sludge or activated sludge acclimated to cyanide additionally considerably biodegrade concentrations 100 mg/L of most straightforward and complicated cyanides (Gaudy et al. These data could characterize a biodegradation half-life; nevertheless, the possibility of loss by chemical reaction was not addressed in this research. A variety of microorganisms have been identified which are able to uptake, conversion, sorption, and/or precipitation of the cyanide ion, cyanate, and thiocyanate, together with species of the genera, Actinomyces, Alcaligenes, Arthrobacter, Bacillus, Micrococcus, Neisseria, Paracoccus, Pseudomonas, and Thiobacillus (Akcil and Mudder 2003). Some of those species, for example Pseudomonas, are able to using the cyanide ion and thiocyanate as the only real source of carbon and nitrogen and subsequently, are particularly effective at cyanide degradation. In reality, Pseudomonas is the premise of economic applications for degrading the cyanide ion to ammonia and carbonate in waste waters generated in mining operations that use the cyanide ion to leach gold and other precious metals for low-grade ores (Akcil and Mudder 2003). Raybuck (1992) has recently reviewed the position of microbes in cyanide degradation and has categorized the microbial enzymes that use the cyanide ion as a substrate according to the next types of reactions: substitution/addition, hydrolysis, oxidation, and reduction. Sulfur transferases similar to rhodanese are involved in substitution reactions that end result in the conversion of the cyanide ion to the much less toxic thiocyanate, whereas pyridoxal phosphate enzymes are involved in substitution/addition reactions that result in production of nitrile derivatives of -amino acids. These natural nitriles could then be in the end degraded by way of enzyme catalyzed hydrolysis to both the corresponding amino acid and ammonia (with out formation of the free amide) or the carboxylic acid and ammonia (by way of formation of the free amide). The cyanide hydratase and cyanidase enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of the cyanide ion to formamide or formic acid and ammonia, respectively. Thus, these hydrolytic systems are a number of the most promising for cleansing of cyanide-containing waste waters (Raybuck 1992). Bacillus pumulus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Pseudomonas paucimobili have all been found to oxidize the cyanide ion to ammonia and carbon dioxide (Meyers et al. In an cardio batch bioreactor experiment, Pseudomonas putida was found to considerably degrade four mM sodium cyanide (cyanide focus roughly 100 mg/L) to ammonia and carbon dioxide (Chapatwala et al. Other proof indicates that formamide and formate are additional transformation merchandise in microbial oxidation of the cyanide ion by this species, inferring that there could also be a couple of pathway of cyanide biotransformation involved (Kunz et al. Several bacterial species have been identified which are able to oxidative degradation of metallocyanides (Silva-Avalos et al. The cyanide oxygenase system involved in this process offers a brand new know-how for the treatment of metal cyanide wastes (Raybuck 1992). However, when an aqueous solution of potassium ferrocyanide was seeded with pure culture of Pseudomona aeruginosa, or E. It was proven that the free cyanide formation was because of biodegradation and not to both photolysis or hydrolysis. The relevance of this research to the destiny of ferrocyanide complexes in pure water or industrial effluents is troublesome to assess as a result of ferrocyanide concentrations utilized in these experiments (three,300 mg/L) are rarely encountered in these media. Biodegradation is also a big transformation process for thiocyanates in pure waters; nevertheless, additional data are wanted to assess the relative importance of this process. Like the cyanide ion, thiocyanate is toxic to microorganisms at excessive concentrations and acclimated cultures have increased tolerance to this compound (Boucabeille et al. Thiosulfate ion (S2O3-2) was identified because the intermediate in this degradation pathway. Several research document the biodegradation of mixtures of cyanides and thiocyanate in waste waters. Complete biodegradation of easy and metal complexed cyanides and thiocyanate from mining waste waters by various micro organism belonging to the households Pseudomonadaceae, Vibrioniaceae, and Enterobacteriaceae has recently been reported (Boucabeille et al. Biodegradation of cyanide and thiocyanate resulted in the formation of ammonia, with or with out accumulation of nitrite and/or nitrate, depending on whether or not a batch, fed-batch, or steady treatment process was used. Cyanogen chloride additionally hydrolyzes slowly to cyanic acid and hydrochloric acid in water at pH 7, with a fee fixed of 6. Hydrolysis of cyanogen chloride is more fast beneath acidic and fundamental conditions, with fee constants of 2x10-2 and 68x102 mol-1sec-1 (pH 10), respectively (U. The half-lifetime of cyanogen chloride at impartial pH ranges between 1 minute at forty five °C and 10 hours at 5 °C (Opresko et al.
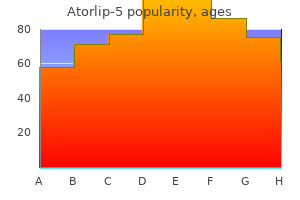
Cheap 5 mg atorlip-5
If the spheroplasts are lysed by the gentle technique of magnetic stirring, nearly all of the chloroplasts are recovered in the lower zone. If, nevertheless, the spheroplasts are damaged in the French press, only about one-third of the entire Chl is recovered in the lower zone. The lowest yields correspond to poor spheroplast formation and to the aggregation of chloroplasts with cell debris previous to density gradient centrifugation. We collected the intact chloroplasts from the lower band of the Downloaded on February 27, 2021. The chloroplasts had been incubated in the light with [35S]methionine over the course of I h. Incorporation into sizzling trichloroacetic acid-insoluble materials occurs rapidly during the first 30 to 40 min. These properties are attribute of protein synthesis by isolated, intact chloroplasts. The development of procedures for the isolation of pure, intact chloroplasts from Euglena able to high rates of protein synthesis opens the door to a wide range of research on the molecular biology of chloroplast development. Yokota and Kitaoka and their associates at Osaka Prefectural University for offering invaluable information on their procedures upfront of publication. Such massive quantitative variations indicate a qualitative difference in the state of the organelles. These rates of protein synthesis are, moreover, among the highest ever recorded for protein synthesis in organello. Euglena thus becomes an organism of selection for studying translation quite aside from its suitability for the examine of development. Two traces of proof indicate that the noticed protein synthesis is accountable to the chloroplasts and to not contaminating bacteria: (a) incorporation in the dark is indistinguishable from that at zero time (cf. It is nonetheless evident from the low and variable yields that the current isolation process remains to be suboptimal. Since chloroplasts of upper vegetation invariably lose both photosynthetic and protein artificial actions following isopycnic sedimentation in sucrose gradients (cf. Li, Chairperson Jon-Paul Bingham Dulal Borthakur Ho Leung Ng Monika Ward Keywords: palm tree, peroxidase, N-glycosylation, mass spectrometry © 2015, Margaret R. Ivan Sakharov graciously supplied the purified windmill palm tree peroxidase, but greater than that, he has been a beautiful mentor by discussing peroxidases, and giving invaluable feedback on my manuscripts. David Tabb and his laboratory had been very gracious in displaying me the ropes in bioinformatics. Li and my committee members for their mentorship and steering throughout this course of. Also, for our discussions on transient expression in tobacco vegetation- hopefully we could have time to collaborate in the future. This project was supported partly by the Agriculture and Food Research Initiative Competitive Grant No. The focus of this work is a novel peroxidase from the leaves of a cold tolerant palm, Trachycarpus fortunei. Like other palm tree peroxidases, windmill palm tree peroxidase is steady at high temperatures and in the presence of denaturants. Because glycosylation is known to play a important function in plant peroxidase stability and activity, this information is essential for structure activity research, selection of an expression system for enzyme production, and engineering the enzyme. The presence of a Cterminal sign peptide predicts vacuolar targeting of the enzyme. Native windmill palm tree peroxidase was analyzed at the glycopeptide stage to give a qualitative and quantitative evaluation of glycosylation at each website. Windmill palm tree peroxidase has thirteen sites for N-linked glycosylation, 2 of that are distinctive. Major glycans are paucimannosidic, which helps the task of windmill palm tree peroxidase as a vacuolar peroxidase. To carry-out this work, a workflow for analyzing the glycopeptide mass spectrometry information was developed. New analytical strategies are needed for the rising field of plant glycoproteomics. The novel v strategies developed in this dissertation shall be helpful for the examine of other necessary plant glycoproteins. This information can be used to examine the roles of glycosylation in this exceptionally steady and distinctive palm peroxidase. There can be as many as 70 different isoforms of peroxidases in a single plant species (Welinder et al. The precise in vivo mechanism of the different peroxidase isoforms is unclear for probably the most half. A current examine recognized a single vacuolar peroxidase concerned in pigment metabolism (Zipor et al. There are many biotechnological uses for plant peroxidases making them extremely valued industrial enzymes (Regaldo et al. Sensitive and quantitative detection of a broad vary of organic molecules have made peroxidase-primarily based biosensors helpful in agricultural, biomedical, and environmental diagnostics (Farrй et al. They can also be used for bioremediation of commercial wastewater containing toxic pollution corresponding to phenols and cresols (Klibanov et al. Peroxidases expressed in alternative expression systems such as the yeast Pichia pastoris have instability problems related to non-native glycosylation (Capone et al. Anionic peroxidases purified from palm tree leaves possess high stability and have glorious catalytic properties (Sakharov 2004). The exceptional stability of palm peroxidases at acidic pH met the requirement for synthesis of conductive and chiral polymers underneath delicate circumstances (Sakharov et al. Develop instruments and a workflow for evaluation of windmill palm tree peroxidase glycopeptide mass spectrometry information 3. The amino acid sequence of a protein gives the primary information about the protein and is requisite to studying the structure additional. These two strategies provide complementary information in addition to confirmation of the outcomes. Characterization of glycosylation involves figuring out the glycans hooked up to each N-glycosylation website and their relative abundance. A glycan is outlined as a compound containing monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds. Analysis of the mass spectrometry information was the largest hurdle encountered in the course of this dissertation. Another notable problem was that many of the available software program had been designed for evaluation of mammalian protein glycosylation. The analytical challenges related to studying glycoproteins result from the truth that the peptide is hooked up a branched polymer, the structure of which is assembled in a non-template driven course of. The course of depends on a number of components including protein-protein interactions between the target and glycosylation enzymes, availability of the sugar nucleotide constructing blocks, quantity and distribution of the glycosylation enzymes, and protein residence time in the Golgi apparatus and its last vacation spot. The interaction of those various components finally results in a heterogeneous population of glycans hooked up to each glycosylation website. The means of N-glycosylation begins with the targeting of proteins containing an Nterminal sign peptide to the secretory pathway (Stanley et al. Local amino acid sequence will affect the efficiency of glycosylation at that website (Petrescu et al. Subsequent secretion to the Golgi puts the glycoprotein in touch with glycosidases and glycosyltransferases which take part in a course of called `maturation. Glycans are then trimmed after being exported to the extracellular matrix or the vacuole (Rayon et al. This is usually a mechanism that developed to add a stage of fantastic-tuning that can be used to the advantage of the organism. A detailed description of the plant N-glycan biosynthesis pathway is presented in Appendix D. Plant glycoprotein N-linked glycans have a number of distinct characteristics: 1) fewer branches, 2) absence of sialylation, and 3) presence of 4 xylosylation and (thirteen)-fucosylation versus (sixteen)-fucosylation (Johnson and Chrispeels, 1987; Tezuka et al. One of the main problems with software program for glycopeptide mass spectrometry information interpretation is the truth that most had been developed with mammalian glycans in mind. Partial deglycosylation of peroxidases results in decreased stability (Tams and Welinder, 1998; Lige et al. Further investigations into the molecular foundation of glycan contribution are needed. A major motivation of this dissertation is that palm peroxidases can be good models for studying roles of glycosylation.
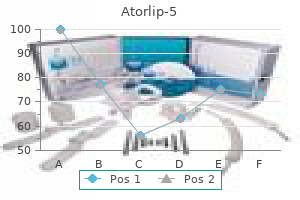
Atorlip-5 5 mg
In usually growing cells the microtubules are thought to be constantly degraded and reformed. Consistent with this, microtubules can polymerize by self-assembly in cell-free systems. This is a two-stage course of: within the first stage, a molecule of the protein -tubulin combines with a (b). Similar hyphae treated with a metabolic inhibitor (sodium azide) showed no proof of dye uptake. Although none of those traces of proof provides definitive proof of the existence of an endosomal system in filamentous fungi, the proof is no less than compatible with an endosomal system during which vesicle trafficking between totally different organelles provides a mechanism for recycling of membranes and their contents between totally different subcellular compartments. Actin is also seen as peripheral plaques (p) and nuclear inclusions (ni) in zones much like these during which microtubules are seen. However, essentially the most compelling proof for a task of the actin cytoskeleton in organizing fungal growth has come from studies on the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yet, actin cables do play a major function in directing secretory vesicles to growth sites in yeast, and by analogy actin may play an identical function in distributing the apical vesicles to sites of wall growth in hyphal ideas. In later chapters we return to the roles of the cytoskeleton in fungal growth (Chapter four), differentiation (Chapter 5), and the behavior of fungal zoospores (Chapter 10). But we finish this chapter by noting that fungal tubulins differ from these of crops and animals. They are inhibited by the antibiotic griseofulvin and by the benzimidazole fungicides, whereas plant and animal tubulins are insensitive to these compounds. This is why griseofulvin can be used to deal with the dermatophytic (ringworm) fungal infections of people, and why the benzimidazoles can be used to deal with fungal infections of crops (Chapter 17). Conversely, the fungal tubulins (excluding Oomycota) are unaffected by colchicine (the toxin from the autumn crocus) which inhibits nuclear division in plant and animal cells. Such close association signifies a possible function for moving the organelle, via the activities of motor proteins. The microtubules formed by this course of work together with two mechanochemical enzymes (motor proteins), kinesin and dynein, and doubtless assist to transport organelles inside the fungal hypha. Actin microfilaments are a lot narrower than microtubules, being about 5eight nm diameter. In the slime mould Physarum polycephalum the actin microfilaments are recognized to perform in cytoplasmic contraction, when actin associates with its motor protein, myosin. Chapter four Fungal growth the key to the fungal hypha lies within the tip (Noel Robertson) coverslip over the margin of a colony on an agar plate. The sequence of nine frames was taken over a 1-hour interval, ranging from the time when the coverslip was added. In the primary body (a) the hyphal tip was growing usually, and two lateral branches had arisen behind the growing tip. Soon afterwards (b and c) the hyphal ideas began to swell (a response to disturbance caused by the coverslip) after which branched repeatedly from the ideas earlier than resuming a extra regular pattern of apical growth. By taking any convenient reference factors, such as the branching factors shown as v1 and v2 in. In reality, the incorporation of latest wall materials is especially confined to the extreme tip. The radiolabel is included maximally on the hyphal tip, and the speed of label incorporation falls off sharply over the primary few micrometres the apical dome of the hypha. For this purpose, what we term apical growth is actually apical extension, as a result of the true rate of growth, defined as improve in biomass per unit of time, is way slower. The size of hypha wanted to help an extending apex could be estimated by making a diagonal cut across a colony margin with a scalpel, in order that individual hyphae are severed at totally different distances from their ideas. Hyphae cut further again proceed to lengthen however extra slowly than usual, and finally a point is reached at which the cut is up to now again that it has no effect on the apical extension rate. This distance is termed the peripheral growth zone of a fungal colony, defined as the size of hypha wanted to maintain the utmost extension rate of the leading hyphae on the colony margin; it varies between fungi, from below 200 µm as much as a number of millimeters for the fastest-extending fungi. We also talk about the ways during which hyphal branches arise and orientate themselves for maximum efficiency of nutrient capture. Apart from the fungus-like Oomycota, which have adopted apical growth by a remarkable degree of convergent evolution (Latijnhouwers et al. The hyphal apex can swell right into a balloon-like structure such as a spore or yeast cell, or it could taper to such a level that it could penetrate a layer of inert gold movie or the wall of a host plant by exerting turgor pressure alone. In other circumstances, the fungal hypha may give rise to advanced tissues and an infection structures, discussed in Chapter 5. Early experiments on the mechanism of apical growth in fungi Robertson (1958, 1959) did many of the key early experiments on apical growth of fungi, using very simple strategies coupled with truly remarkable perception. The other ideas stopped growing for a number of minutes, swelled right into a diamond shape throughout this time, and finally regrew by producing one or more slim ideas simply behind the unique apex. He then repeated the experiments, once more flooding the colonies with water however changing this within forty seconds by a solution of the same osmotic potential as the unique agar (an isotonic resolution). This brought on all of the tricks to cease for a number of minutes, however they swelled throughout this time and finally regrew from slim subapical branches. To interpret these findings, Robertson hypothesized that the normal pattern of apical growth entails two independent processes: (i) continuous extension of a plastic, deformable tip and (ii) rigidification of the wall behind the extending tip. He envisaged these two processes as occurring on the same rate, however with rigidification all the time slightly behind the tip, like two vehicles travelling alongside two lanes of a motorway at precisely the same pace however one is all the time slightly behind the opposite. If the tip readjusts to the brand new osmotic conditions in time it could develop on, however now from a thinner region of the apex the place the wall has not yet rigidified. It is now supported by many traces of proof from wall enzymology and ultrastructural studies. Sometimes the hyphal ideas swell and burst in response to flooding with water, maybe as a result of the wall on the extreme apex is simply too fragile to modify to speedy adjustments in osmotic potential or maybe as a result of the wall on the extreme apex is constantly being degraded by wall-lytic enzymes. Sometimes the ideas develop on as usual after being flooded with water, however a branch develops later from the position the place the apex had reached on the time of flooding. In any case, growing hyphal ideas are very delicate to many forms of disturbance they usually tend to reply in the same means by a "ceaseswellbranch" sequence as shown in. This response could be elicited by mild heat or chilly shock, by exposure to an intense light beam, or even when hyphal ideas encounter bodily obstacles. Some morphological mutants of Neurospora and Aspergillus even show this pattern often throughout growth on agar plates. In Chapter 5 we will see that the ceaseswellbranch sequence happens in the course of the manufacturing of a number of differentiated structures, together with the pre-penetration structures of fungal parasites of crops and animals. Assembly of the wall on the hyphal apex Wall synthesis on the hyphal apex is a fancy course of, the small print of which are nonetheless not absolutely recognized, however from varied traces of proof we will assemble a composite picture of wall growth and subsequent wall maturation (Figs four. Chitin synthase Chitin synthase catalyses the synthesis of chitin chains, and is due to this fact one of the principal enzymes concerned in fungal wall growth. Chitin is thought to be formed in situ on the apex, somewhat than arriving in membrane-bound vesicles. When hyphal homogenates are tested for enzyme exercise in vitro, chitin synthase is present in no less than two varieties: as an inactive zymogen in chitosomes (Chapter three), and as an integral membrane protein. We saw in Chapter three that chitosomes resemble a few of the microvesicles within the hyphal apex (see. Vesicles (V) derived from the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi physique (G) are transported to the apex, most likely by microtubule (M)-associated motor proteins. The vesicles can then be directed to the plasma membrane, maybe by actin-associated motor proteins. The newly formed wall on the extreme hyphal tip is thin and has few cross-linkages, however becomes more and more cross-linked further again. By distinction, the actin cytoskeleton is highly delevoped on the extreme tip (see. Vesicles are thought to ship the principle wallsynthetic enzymes (chitin synthase and glucan synthase) to the tip, the place they lodge within the plasma membrane as integral membrane proteins. Mannoproteins and other glycoproteins are transported in vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulumGolgi secretory system (as a result of the glycosylation of proteins happens solely within the Golgi). Multivesicular bodies, whose functions are nonetheless unclear, may be carried as vesicular cargoes alongside microtubules. Enzyme activators and inhibitors are also thought to be concerned within the orchestration of tip growth, however the substrates for wall synthesis arrive from metabolic reactions within the cytosol. The zymogen form of chitin synthase, when inserted into the membrane, should be activated by a protease which most likely arrives on the apex in other vesicles.
Safe 5 mg atorlip-5
Traditional, silicabased C18 sorbents can simply dry out, particularly on a vacuum manifold if a particular cartridge flows quickly and allows air to be drawn in. Oasis sorbents maintain correct wetting for more constant efficiency (particularly essential for 96-well plates). Oasis sorbents have demonstrated glorious longterm, batch-to-batch reproducibility for over ten years. When the methanol reached the top of the higher frit in each cartridge, vacuum was maintained for different instances to range the cartridge drying time. In some laboratories 10% of samples are retests-this can be reduced using Oasis sorbents. Oasis sorbents work particularly well when you have to seize metabolites (see figure above). The Oasis sorbent has 2-3X more surface space and reveals a dramatic improve in k values compared to silica-primarily based C18, this reduces breakthrough potential. T his novel, water-wettable, polymeric sorbent is stable from pH zero to 14, making method growth easy and fast. If your objective is to seize fundamental analytes and then wash out interferences aggressively, the Load and Wash steps ought to be at low pH to get hold of maximum seize. At excessive pH, the ion-trade retention mechanism shuts-off as a result of the analyte turns into un-ionized. Only reversed-section retention is current, however because the analyte is now un-ionized, we get the utmost of the reversedphase retention. If your objective is to seize acidic analytes and then wash out interferences aggressively, the Load and Wash steps ought to be at excessive pH to get hold of maximum seize. The retention mechanism is blended mode, both ion trade and reversed section, which improves retention for all sorts of fundamental analytes, particularly robust bases. The retention mechanism is blended mode, both ion trade and reversed section, which improves retention for robust acidic compounds. The neutral analyte was processed on all four sorbents, as shown on the earlier web page. Essentially, quantitative restoration and glorious cleanup effectivity were ac hieved for eac h of t he ionic or ionizable take a look at analytes w hen t he really helpful Oasis 2x4 Method sorbent/protocol combination was used. The Waters Oasis µElution plate combines patented plate design, confirmed Oasis chemistries, and easy protocols that deliver excessive analyte restoration and clear extracts in elution volumes as little as 25 L. The progressive options of Oasis µElution plates enable delicate, strong, reproducible outcomes with out evaporation and reconstitution. Analytical efficiency, in terms of sensitivity, selectivity, and ruggedness, is superior. Disk Technology мElution Technology Disk Technology Narrow and Tall Sorbent Bed Ratio Bed H/D = 1. T hese technologies differ tremendously in efficiency primarily because of three options: aspect ratio, holdup volume and elution volume. In distinction, the Oasis µElution tec hnology makes use of an internally tapered well, packed with excessive capability Oasis sorbent, having an aspect ratio, H/D=1. Having 24x much less holdup volume minimizes elution volume and reduces analyte loss throughout elution, improving both restoration and precision. Disk Technology The progressive options of the Oasis µElution plates enable delicate, strong, reproducible outcomes with out evaporation and reconstitution. Methanol is nice as a generic elution solvent, however is commonly not robust sufficient for 25 µL elution volumes. The elution solvent really helpful to be used with the Elution plate must possess a excessive sufficient elutropic energy to absolutely elute analytes in small volumes, and be appropriate for a various set of analytes. Base Strong Acid Acid Strong Base Oasis 2x4 Method Proof-of-Concept Recovery Study: To show the logic, simplicity, and effectiveness of the Oasis 2x4 method, five samples of rat plasma were prepared, each spiked with one of the beforehand characterized take a look at analytes shown under: - Imipramine: pKa = 9. Respective aliquots were then processed using the protocol and the Oasis ion-blended-mode sorbent designated by the Oasis 2x4 Method for the corresponding sample sort. The physicochemical properties of Oasis sorbents are designed to provide exceptionally excessive loading capability, despite the fact that each well in a Waters Oasis µElution plate contains solely 2 mg of Oasis sorbent. To decide the Oasis Elution plate capability, rising volumes of plasma and urine samples (from 50 µL to 350 µL in 50 µL increments) were spiked with 200 ng/mL imipramine (non-polar base) and 200 ng/ mL atenolol (polar base). The Oasis 96-well plates are designed to be used on many manifold configurations and most robotic liquid handling systems. Our design permits optimum recoveries, even with low sorbent weights for smaller elution volumes. Time consuming evaporation and reconstitution steps are eliminated, compressing preparation cycle time and rising throughput capabilities. Extraction Protocols The protein precipitation generic method contains both a centrifugation and an evaporation step, which produces the cleanest sample extract possible for protein precipitation. The Oasis method permits improved sensitivity by eliminating matrix impact and lowering ion suppression. Achieve superior outcomes compared to protein precipitation in much less time using the Oasis µElution plate. Room temperature Waters Alliance 2795 Propranolol, 1 ng/mL one hundred one hundred Amitriptyline, zero. The Oasis µElution plate permits sensitivity features and delivers excessive efficiency with out the time consuming evaporation step. The solvent used for the elution step ought to be selected primarily based on the polarity of the analyte. The second desk under gives a number of elution solvents and every solvent gives you completely different selectivity and elution energy. Capacity and Elution Volume of Oasis 96-Well Plates and Cartridges Sorbent Per Device µElution Plate* 5 mg* 10 mg 30 mg 60 mg Maximum Mass Capacity 60 to 400 µg zero. Solvent Methanol Acetonitrile Tetrahydrofuran Acetone Ethyl Acetate Methylene Chloride Solvent Type proton donor dipole-dipole dipole-dipole dipole-dipole dipole-dipole dipole-dipole Relative Elution Strength** 1. The generic method (1-D) is a superb beginning protocol for strategies growth. Eac h lot is tested for the presence of bisphenol A and different phenols and phthalates, assuring that endocrine disruptors in water samples can be analyzed to half per trillion ranges. The Oasis sorbents in Symbiosis cartridges present the same efficiency benefits as in different Oasis codecs for pharmaceutical compounds when compared to silica-primarily based sorbents. Francis Beaudry, Principal Research Scientist, Phoenix International Life Sciences, Inc. T hese Sorbent Selection Tools have all of the Oasis sorbents, allowing you the flexibility to extract your analyte of interest. Description Oasis µElution Sorbent Selection Plate, 96-well Oasis Sorbent Selection Plate,10 mg/96-well Oasis Sorbent Selection Kit, 30 mg/1 cc cartridge Particle Size 30 µm 30 µm 30 µm Part No. Particle Size: 55-a hundred and five µm Pore Size: a hundred twenty fiveЕ Surface Area: 325 m2/g Carbon Load: 12% Silica-primarily based bonded section with robust hydrophobicity; used to adsorb analytes of even weak hydrophobicity from aqueous solutions. Silica-primarily based bonded section with average hydrophobicity; use for strategies requiring much less retention than C18. Silica-primarily based bonded section with low hydrophobic character; use for strategies requiring much less retention than C8. Particle Size: 37-55 µm Pore Size: a hundred twenty fiveЕ Surface Area: 325 m2/g Carbon Load: 17% Particle Size: 37-55 µm Pore Size: a hundred twenty fiveЕ Surface Area: 325 m2/g Carbon Load: 9% Particle Size: 37-55 µm Pore Size: a hundred twenty fiveЕ Surface Area: 325 m2/g Carbon Load: 2. Silica-primarily based polar bonded section; can be utilized as much less polar different to silica in normalphase purposes or as much less hydrophobic different to C18 or C8 in reversed-section. Silica-primarily based polar bonded section with neutral character; can be utilized as an alternative choice to silica in normal section purposes, where the acidic character of silica is undesirable or as very weakly interacting section in aqueous purposes. Particle Size: 55-a hundred and five µm Pore Size: a hundred twenty fiveЕ Surface Area: 325 m2/g Activity Grade: excessive Polar sorbent, used primarily to adsorb analytes from non polar solvents like hydrocarbons, chloro- or fluoro-substituted hydrocarbons or much less polar esters and ethers; elution with more polar solvents like polar esters, ethers, alcohols, acetonitrile or water; the binding mechanism can be hydrogen bonding or dipole-dipole interplay; silica may also be used in aqueous medium as a cation exchanger of intermediate energy. Similar in use to silica; obtainable in acidic, fundamental and neutral excessive exercise grades; alumina additionally displays particular interactions with the -electrons of aromatic hydrocarbons. Polar, extremely lively, weakly fundamental sorbent for adsorption of low to average polarity species from non-aqueous solutions. Alumina (A, B & N) Al2O3 · Crudeoilfractionation · Acidicandbasicgradescanalsobe used as low capability ion-exchangers 1. Ligand Density: 350 µmoles/g Silica-primarily based, hydrophilic, robust anion-exchanger with giant pore dimension. Larger particle dinitrophenylhydrazine coated silica for use with personal air monitors. Common purposes include the concentrate of pesticides and herbicides in water or meals samples.
Safe 5mg atorlip-5
Since buffalo milk gives higher yield and has a extra fascinating softer physique and easy texture due to the presence of a proportionately higher fat content material, the quality of khoa made from buffalo milk is superior to that made from cow milk because the product has a moist surface and a sticky and sandy texture (Reddy, 1985). Ramamurthy (1976) claimed that the higher emulsifying capability of buffalo milk fat is due to the presence of upper proportions of butyric acid (50 percent) containing triglycerides compared to solely 37 percent in cow milk fat, an element responsible for the smooth and mellow texture of buffalo milk khoa. Heat-acid coagulated milk products the quality of buffalo milk paneer (an acid coagulated milk product) is superior to that of cow milk paneer. The cow milk paneer is simply too soft, weak and fragile and after cooking its pieces loose their id (Sachdeva et al. The low proportion of solid fat, the smaller dimension of casein micelles and fat globules, and the decrease colloidal calcium could be the rationale for the inferior quality of paneer from cow milk. Fermented milk products the superior physique and texture of buffalo milk dahi could be attributed to the higher complete solids content material, particularly fat and protein, the casein micelles and the large fat globules and better calcium content material within the colloidal state (Sindhu and Singhal, 1988). Ghosh (1986) reported that misti dahi made from buffalo milk is popular within the Eastern belt of India. Buffalo milk can be acceptable for making yoghurt with improved physique and texture, due to its higher complete solids content material (thirteen-17 percent) as compared to cow milk. In addition, when buffalo milk is used it requires no prior concentration or addition of milk powder to acquire optimum physique. It is reported that the expansion of yoghurt starter tradition is faster in buffalo milk and produces extra acetaldehyde, a key flavour part, than in cow milk and thus has a excessive organoleptic quality within the ultimate product (Singh and Kaul, 1982). Chakka, a base materials of Shrikhand, is preferentially prepared from buffalo milk because the curd obtained from cow milk is soft, weak and of low curd pressure however the curd from buffalo milk is hard, easy and mellow. The yield of Shrikhand from buffalo milk is about 15-20 percent higher than that from cow milk. Shrikhand and chakka made from buffalo milk are extraordinarily nutritious and are popular among the Indian inhabitants (Patil and Nayak, 2003). Frozen milk products In comparison to cow milk, components from buffalo milk viz. The higher 190 protein content material in buffalo milk might help to make ice cream extra compact and easy and tends to forestall a weak physique and coarse texture. Hence, use of buffalo milk solids in ice cream might enhance sensory enchantment particularly in vanilla ice cream where no colouring is added. Dehydrated milk products Buffalo milk and cream are intrinsically whiter and extra viscous. Hence, buffalo milk is extra acceptable for the production of tea and occasional whitener powders. The whey proteins of buffalo milk are extra immune to heat denaturation compared to the whey proteins of cow milk and thus dried buffalo milk may be most well-liked to dried cow milk for those technological functions where higher ranges of undenatured whey proteins are extra fascinating. Pastillas de leche and other Philippine milk products (Barile photograph, 2004) Figure 9. Italian mozzarella and ricotta (Borghese photograph, 2003) Cheeses In India there are numerous easy buffalo soft cheeses. No old custom of cheese making exists in India, both with regard to technologies or to ripening strategies and hence cheese consumption can be a relatively new habit. Technological problems encountered with buffalo milk fat within the manufacture of milk products. Studies on the preparation of chhana from handled buffalo milk and its suitability for rasogolla-making. Buffalo production and Health: A compendium of latest research data primarily based on Indian research. Although numerous factors affect the lengthy-term estimates for per capita demand for livestock products, the state of affairs predicted for changes in consumption patterns primarily based on economic improvement has been considered (Bouwman, 1997) and the per capita demand (kg/12 months) for all of the developing international locations will enhance from 17 kg in 1989/ninety one to 25 kg in 2010 and to 30 kg in 2025. It is considered that buffalo meat has a powerful potential for meeting this requirement for elevated per capita consumption. The production of buffalo meat has excessive growth prospects and poses a minimal level of threat from pesticides and veterinary medication when compared to beef production in developed international locations. The practical proprieties of buffalo meat for product processing could be improved by rising its recognition on the Indian market. For these reasons the future potential for buffalo meat and meat products is promising for India both on the home and international markets (Murty and Prince Devadason, 2003). The quality and amount of buffalo meat rely upon many factors, an important of that are the water buffalo type and breed, age, feeding depth, management system and environmental situations. Generally, cattle are superior to buffaloes of their growth rate and there are also variations between the two water buffalo subspecies: River and Swamp. The risk of manufacturing buffalo meat in Italy was initially studied by Bartolo Maymone (Maymone, 1945), the primary Director of the Istituto Sperimentale per la Zootecnia (Animal Production Research Institute), and later by Beniamino Ferrara on the Veterinary University in Naples (Ferrara et al. Studies regarding early weaning and growth rate in water buffalo calves had been reported (De Franciscis and Zicarelli, 1974) through the First International Congress on Buffalo Livestock held in Caserta in 1974. The authors found a 154-163 kg live weight at 180 days of age with every day gains between 639 and 707 g with out significant variations at totally different feed ranges, with about 2. The first downside which was tackled in Italy was the question of early weaning so as to save buffalo milk for the market (the actual price is 1. It was also observed that feeding and well being control in particular person bins through the first month of life can reduce calf mortality. But the primary downside affecting the success of early weaning was the chemical composition of milk powders produced at that time for the calve bovine market, which, when reconstituted, had a chemical composition similar to cattle milk: crude protein 19 percent and fat 14 percent on dry matter. Many research had been carried out so as to confirm the effects of different milk powders, totally different concentrations, various ages at weaning and integrations with pre-starter concentrates or lactobacillus compared to bovine or buffalo milk (Palladino et al. Giovanni De Franciscis organized the Second International Congress on Buffalo Livestock on the Royal Palace in Caserta in 1982, where Ferrara (Ferrara et al. These results revealed a excessive every day achieve (904 g) for a low slaughter weight (320 kg), and a low every day achieve (200 g) for a excessive slaughter weight (683 kg); and the dressing percentage was elevated with rising live weight altering from 52. These authors advised that it was not economical to produce animals heavier than 450 kg due to the discount in growth and effectivity in both males and castrated animals, and particularly due to the organoleptic traits of the meat, which smelt badly of musk. In Italy many trials had been carried out by the Istituto Sperimentale per la Zootecnia on water buffaloes and Friesian bovine males, underneath the identical feeding and environmental situations, and at totally different slaughter ages so as to compare the meat efficiency and these had been also referred to on the Second International Congress on Buffalo Livestock. Six trials had been carried out on 116 males: 58 Mediterranean Italian buffaloes and 58 Friesian bovines which had been fed milk substitutes and concentrates and slaughtered at 20, 28 and 36 weeks, or fed milk substitutes, hay and concentrates and slaughtered at 36, 52 and sixty four weeks of age. The Friesians showed better performances than the buffaloes, the latter realized the following every day gains at 20, 28, 36(1), 36(2), 52, and sixty four weeks of age: 795, 807, 746, 963, 930, 949 g/d (Romita et al. These trials proved that buffaloes could be bred until 15 months of age following an early weaning with good performances and a similar physique growth trend compared to Friesians. The head and skin of the buffaloes had been always heavier than that of the bovines, which showed higher intestine length and circumference; the carcasses had been heavier within the bovines at all ages, however buffaloes showed a significantly higher percentage of meat on the carcasses at 20, 28, and 36(1) weeks of age. However at later ages these variations disappeared with the fattening rising in buffaloes. In specific, buffaloes showed significantly extra subcutaneous fat and less intermuscular and intramuscular fat at 36(2), 52, and sixty four weeks of age, so the meat percentage on the carcass transpired as comparable (sixty two-sixty four percent) in both species (Gigli et al. Eight animals from every group had been slaughtered at 10, 14 and 18 months respectively: the buffaloes fed advert libitum realized a similar growth (Table four) to the previous trials with about 970 g/d achieve up until 14 months, reduced to 798 g/d at 18 months; the decrease feeding level strongly affected the animal growth rate; the conversion ratio (feed consumption/achieve) elevated with rising age as did the web dressing percentage with values of greater than 60 percent. Conformation and fatness scores also elevated with the age of the animal as did the subcutaneous and intermuscular fat percentage on the carcass (Table 5), and consequently the meat percentage on the carcass decreased. The carcasses of the animals of group B registered decrease fat and extra meat than the group A buffaloes. In weight achieve checks of young Mediterranean buffaloes, Nascimento and Veiga (1973) demonstrated the good meat potential of this breed, which demonstrated an average every day achieve of zero. In a test involving buffaloes fed with totally different diets from 26 months (330 kg) and slaughtered at about 30 months of age (408 kg), Tonhati et al. Johnson and Charles (1975), in a comparative research involving confined (132 days) buffaloes and Holstein, Angus and Hereford cattle, matured to ages between 20 and 30 months with a diet wealthy in concentrate, concluded that the buffaloes had a decrease yield (53. The decrease carcass yield of buffaloes in relation to cattle was observed by several authors and can be attributed to the fact that these animals have a thicker skin and a bigger percentage of head, horns, hoofs and guts. Preston and Willis (1974) demonstrated that several factors can affect carcass yield values, such because the assessment basis (in relation to live weight or in relation to empty physique weight). When live weight is used, the yield is affected by the diet type and fasting period that the animals have been subjected to prior to slaughter. In South American and Asian international locations buffalo meat production is usually undertaken utilizing in depth methods, using pasture or poor crops, with no incentive to use excessive power diets, realizing low every day gains (500 g) and producing bulls weighing 400 kg at about two years.
Quality 5 mg atorlip-5
Likewise, after we discussed the phosphorylation of proteins by kinases, we needed a source of phosphate for the response, and this phosphate source itself is a substrate of the enzyme. A little bit of reflection will show that lots of the enzymatic reactions in biochemistry proceed with using a number of substrates and/or produce a number of products. In this chapter we explicitly cope with the regular state kinetic strategy to learning enzyme reactions of this kind. For example, a response that makes use of two substrates to produce two products is referred to as a bi bi response, a response using three substrates to form two products is as a ter bi response, and so on (Table 11. Is the order during which the substrates bind random, or should binding happen in a particular sequence? These questions increase the potential for at least three distinct mechanisms for the generalized scheme; these are referred to as random ordered, compulsory ordered, and double-displacement or ``Ping-Pong' bi bi mechanisms. Often a major objective of regular state kinetic measurements is to differentiate between these diversified mechanisms. We shall therefore current an outline of each and describe graphical strategies for distinguishing amongst them. In the treatments that comply with we shall use the final regular state rate equations of Alberty (1953), which cast multisubstrate reactions when it comes to the equilibrium constants that are acquainted from our discussions of the Henri- Michaelis-Menten equation. This strategy works nicely for enzymes that utilize one or two substrates and produce one or two products. At the end of this chapter we shall briefly introduce the method of King and Altman (1956) by which relevant rate constants for complicated response schemes can be decided diagrammatically. Note that the binding of 1 substrate may very nicely have an effect on the affinity of the enzyme for the second substrate. The y intercept of the plot of slope versus 1/[B] yields an estimate of K6/V, and the x intercept of this plot yields an estimate of 1/K. The y and x intercepts of the plot of 1/V versus 1/[B] yield estimates of 1/V and 1/ K, respectively. Thus from the info contained in the two replots, one can calculate the values of K6, K, and V concurrently. For a compulsory ordered bi bi response, the regular state therapy yields Equation 11. It is critical to resort to using isotope incorporation research, or research using product-based mostly inhibitors. For every focus of substrate B, the values of 1/V and 1/K6 can be decided from the y and x intercepts, respectively, of the double-reciprocal plot. The worth of ninety one/K can be decided from the x intercepts of both replot in Figure 11. The y intercepts of the two replots yield estimates of 1/V (for the 1/V versus 1/[B] replot) and 1/K6 (for the 1/K versus 1/[B] replot) for the response, as seen in Figure 11. Because of their structural relationship to the substrate, the product molecules of enzymatic reactions themselves are often competitive inhibitors of the substrate binding website; this case is referred to as product inhibition. The pattern of reciprocal strains noticed with completely different inhibitor concentrations is a nest of strains that converge at the y intercept (see Chapter eight). For an enzyme that requires two substrates, a competitive inhibitor of one of the substrate binding sites will show the habits of a competitive, noncompetitive, or even uncompetitive inhibitor, depending on which substrate is diversified, whether or not the inhibitor is a reversible useless-end. The patterns for both useless-end and product inhibition additionally depend upon whether or not the fastened substrate is at a saturating or nonsaturating (typically at [S]: K) focus with respect to its apparent K. The relationships resulting in these differing patterns of useless-end and product inhibition for bi bi reactions have been derived elsewhere (see. Rather than rederiving these relationships, we current them as diagnostic tools for determining the mechanism of response. The first, and easiest mechanistic test using isotope exchange is to ask whether or not exchange of label can happen between a substrate and product in the presence of enzyme, but in the absence of the second substrate. The similar hyperbolic relationship would also be noticed for a response that proceeded via a random ordered mechanism. Thus isotope exchange in the absence of the second substrate is diagnostic of a double-displacement response, while compulsory ordered and random ordered reactions can be distinguished on the premise of the relation of the rate of radiolabel exchange between one substrate and product of the response to the focus of the opposite substrate and product underneath equilibrium conditions. An alternative methodology, devised by King and Altman (1956), allows the derivation of a velocity equation for primarily any enzyme mechanism when it comes to the individual rate constants of the assorted steps in catalysis. On the premise of the strategies of matrix algebra, King and Altman derived empirical rules for writing down the functional types of these rate fixed relationships. We provide a couple of illustrative examples of their use and encourage interested readers to explore this methodology further. Next, we determine every pathway by which a particular enzyme species could be fashioned in the response scheme. If we invoke the further equality that V = k [E], we see that the King-Altman strategy ends in the same velocity equation we had derived as Equation 5. Now allow us to contemplate the more complicated case of a double-displacement bi bi response using the King-Altman strategy. Hence, the cyclic type of the response scheme is: Consideration of this response yields the relationships given in Table 11. With comparable concerns, the rate equations for random ordered and compulsory ordered bi bi mechanisms can likewise be derived. With some apply, this seemingly cumbersome strategy offers a clear and intuitive technique of deriving the appropriate velocity equation for complicated enzymatic systems. A more thorough therapy of the King-Altman strategy can be discovered in the textual content by Segel (1975) as well as in the original contribution by King and Altman (1956). We have seen that enzyme reactions involving two substrates and two products can proceed by at least three distinct mechanisms: random ordered, compulsory ordered, and double-displacement reactions. Experimental strategies had been introduced to permit the investigator to distinguish amongst these mechanisms on the premise of kinetic measurements, product inhibition research, and radioisotope exchange research. We briefly described the method of King and Altman for deriving the rate equation of complicated enzymatic response, similar to those involving a number of substrates. In reality, the vast majority of enzymatic reactions in nature proceed via the utilization of multiple substrate to yield multiple product. In some oligomeric enzymes, every subunit accommodates an energetic website heart for ligand binding and catalysis. In the simplest case, the energetic sites on these completely different subunits act independently, as if every represented a separate catalytic unit. In different instances, nevertheless, the binding of ligands at one energetic website of the enzyme can increase or lower the affinity of the energetic sites on different subunits for ligand binding. When the ligand binding affinity of 1 energetic website is affected by ligand occupancy at one other energetic website, the energetic sites are said to be acting cooperatively. In optimistic cooperativity ligand binding at one website increases the affinity of the opposite sites, and in adverse cooperativity the affinity of different sites is decreased by ligand binding to the primary website. For cooperative interplay to happen between two energetic sites some distance apart. This concept of transmitted structural modifications in the protein, leading to long-distance communication between sites, has been termed ``allostery,' and enzymes that show these effects are often known as allosteric enzymes. Thus small molecules can bind to sites aside from the enzyme energetic website and, on account of their binding, induce a conformational change in the enzyme that regulates the affinity of the energetic website for its substrate (or different ligands). Such molecules are referred to as allosteric effectors, they usually can function to improve energetic website substrate affinity. Both types of allosteric effector are seen in biology, they usually form the premise of metabolic control mechanisms, similar to suggestions loops. In this chapter we shall describe some examples of cooperative and allosteric proteins that not only illustrate these concepts but additionally have historic significance in the improvement of the theoretical foundation for understanding these effects. We shall then briefly describe two theoretical frameworks for describing the two effects. Finally, we shall focus on the experimental penalties of cooperativity and allostery, and acceptable strategies for analyzing the kinetics of such enzymes. The therapy to comply with discusses the consequences of cooperativity when it comes to substrate binding to the enzyme. The reader ought to notice, nevertheless, that ligands aside from substrate also can show cooperativity in their binding. In reality, in some instances enzymes show cooperative inhibitor binding, but no cooperativity is noticed for substrate binding to these enzymes. Such special instances are past the scope of the current textual content, but the reader ought to concentrate on their existence. A comparatively complete therapy of such instances can be discovered in the textual content by Segel (1975).
Best 5mg atorlip-5
Much work was carried out however, for a variety of causes associated with capital and income costs and the dearth of a market, as a manufacturing process the method seemed doomed to fail. By the late 1990s most main brewers had produced their very own ice manufacturers and sales elevated, backed by huge advertising spends. The fee of development of manufacturing of those beers has slowed however nonetheless ice beer is now an important phase of the alcoholic drinks market. The larger the unique gravity of the beer the lower the temperature at which the beer freezes. The beer is additional cooled and then pumped through three heat exchangers to lower the temperature to Аfour лC (25 лF). Small ice crystals form and the beer is then moved to the recrystallizer where the small crystals deposit on larger ones already present. The beer of high alcohol content is held in a storage tank and adjusted to the required alcohol content with sterile, deaerated, carbonated water. The alcohol content of the processed beer is generally larger than the beginning beer and the removal of polyphenols offers the beer a characteristically easy full taste. The process is pricey and the success for the brewery relies upon in the marketplace permitting the charging of a higher value for the product. Further developments in ice beers will depend upon how the market develops and what costs may be sustained for the beers. A larger proportion of fermentable carbohydrate is therefore made out there to the yeast than is the case in standard brewery fermentations. The ensuing beers have a higher ethanol content however lower dextrin levels from a given original extract in comparison with normal beers. It ought to be noted that these beers seldom have lower calorific values than normal beers, merely lower carbohydrate contents. It follows that these beers are normally derived from fermentations of 100% obvious attenuation. Mashing may be adjusted by extending the 15 Beer maturation and coverings 587 time and by a low temperature stand at 50 лC (122 лF) for a minimum of half-hour however attenuation limits of more than ninety% are seldom produced. Enzymes should therefore be added to the fermenter to degrade residual dextrins throughout fermentation and this can be within the type of malt flour or diastatic malt extract. The -amylase, -amylase, and limit dextrinase so added results in the degradation of dextrin within the fermenting wort. In some international locations the addition of enzymes of fungal origin is permitted (glucoamylase and pullulanase). Beers produced using fungal enzymes are inclined to be extra biologically and non-biologically stable. Fermentation of those highly fermentable worts yields beers of very high alcohol contents and nearly no residual carbohydrate. Pasteurization should be effectively carried out if using malt enzymes, as almost actually bacteria shall be launched into the wort from the malt flour. This pressure was approved for use and is used in-house for the manufacturing of low carbohydrate beers. But, as the result of common public disquiet about the usage of genetic manipulation, there have been no commercial developments using this pressure. Flavour, clarity and stability of beer are improved by the submit-fermentation treatments which were discussed. This is also the area of the whole brewing process where emphasis may be positioned on the development of special beer sorts. There is rising curiosity within the manipulation of beer properties submit-fermentation to produce different beer manufacturers from primarily the identical brewhouse and fermentation techniques. This can result in considerable saving in capital and income cost with fewer requirements to put money into costly maturation storage. In this respect additional improvement in immobilized yeast know-how with its potential for accelerated flavour improvement and manufacturing of novel beers would seem to be worthwhile. Native names are additionally complicated in that different names are used for related merchandise by different tribes and inside one language group different names are used for various sorts or qualities of beers (Daiber and Taylor, 1995; Dendy, 1995; Haggblade and Holzapfel, 1989; Harris, 1997; Miracle, 1965; Novellie, 1966, 1968, 1977; Novellie and De Schaepdrijver, 1986; Peterson and Tressler, 1965; Schwarz, 1956). Traditionally, beers are made by girls brewsters, as was the case in mediaeval Europe, and they may be consumed with some ceremony. However, in southern Africa, as urbanization occurred, men moved into cities as informal labour, leaving their womenfolk behind. To meet the demand for opaque beers commercial brewing began (round 1908±1910) in Bulawayo and Durban. Since then, in some intervals, the speed of increase in manufacturing has risen at an astonishing fee. For instance, in South Africa, at one stage manufacturing elevated by 26% in a single yr and whereas in 1953/four manufacturing was 20 million imp. Estimates of more recent 590 Brewing: science and follow opaque beer manufacturing in different international locations are in millions of hectolitres/yr (Harris, 1997). At first the industrialized manufacturing of those beers was not easy, and many difficulties have been encountered. The publications from this group, and its successors, present practically all of the out there data on the science of opaque beer manufacturing. Brewing may happen within the home, for home consumption or on the market, or it might be produced in a factory. Factory brewing appears to be carried out by men, a change that parallels the historic move from home-based mostly brewsters (girls) to industrial brewers (men) in Europe. The souring fermentation stage produces a desired degree of acidity, caused by lactic acid. Because of the continuing manufacturing of carbon dioxide the beers are held in vented containers. The quick shelf-lives of African beers create many commercial manufacturing and distribution problems. It appears that almost all drinkers are extra concerned with the flavour and physique of a beer than with the (altering) alcohol content. South African beers are described as being as refreshingly bitter as yoghurt, with a characteristic fruity odour. Colours vary from a pale buff to a pinkish-brown, or elsewhere may even have a reddish tinge. However, there are broad variations in beer composition, notably in homebrewed beers (Haggblade and Holzapfel, 1989; Harris, 1997; Novellie, 1966; Novellie and De Schaepdrijver, 1986). Coarsely ground grain, generally combined with slightly malt, is combined with water and a few leaven or some yeast in sourdough. About one-third extra grain is malted and then, typically after drying within the solar, the malt (inexperienced or dry) is ground up with water and lumps of the broken up loaves. The mixture begins to ferment, either spontaneously or after the addition of some older bouza. After a interval of active fermentation the mixture is filtered, for instance through a horsehair sieve. The introduction of air at this stage checks the fermentation, however that is soon resumed. The drink is thick and yeasty, pale yellow, acidic and with a characteristic odour. Raw sorghum grain is ground to a fine flour, which is split into three equal tons, each of which is processed in another way. The third portion is wetted with simply enough water to moisten it, and is set aside for about 36 hours, when a spontaneous, primarily lactic fermentation occurs. It is cooled to room temperature and combined with about 5% malt flour, water and a few good merissa. Portions of the combined two-thirds cooked flour, combined with malt flour, are added in increments to the, strongly fermenting, acid fraction, with out stirring them together. In making busaa maize grits are combined with water and allowed to stand for 2±3 days, at about 25 лC (77 лF), for souring. Malted finger millet (Eleusine coracana) is prepared by steeping for eight±24 h, then germinating for 2±3 days, additionally at about 25 лC (77 лF), adopted by drying within the solar for 1±2 days and coarsely grinding. The soured maize dough is cooked on metal sheets over a charcoal fire at 65±seventy five лC (149±167 лF) for three hours. The cooled maize soured materials is broken into lumps and one part is combined with 1.
References:
- http://www.evolocus.com/Textbooks/Geodakian2012.pdf
- https://azdhs.gov/documents/preparedness/emergency-preparedness/zebra-manual/zm-s4-vhf.pdf
- https://ohdsi.github.io/TheBookOfOhdsi/TheBookOfOhdsi.pdf
- http://www.smgebooks.com/sepsis/chapters/SEP-16-06.pdf
- https://www.who.int/uv/publications/proUVrad.pdf
.png)