Effective 100mg dilantin
Rule of thumb: Confusion and mental status changes · Encephalopathy presents with confusion, distractibility, memory loss, and decreased degree of consciousness. Benbadis Rule of thumb: Confusion and mental status changes (continued) · Delirium presents similar to encephalopathy, however differs with perceptual changes (hallucinations and/or illusions), psychomotor agitation, and autonomic dysfunction · Parasomnias are paroxysmal behaviors occurring out of sleep (sleep walking, confusional awakening, night time terrors). True motor (muscular) weak point (different from world fatigue) can be indicative of a neurologic course of. When this is the case, mental status (sensorium, alertness, and attention) is regular. Other signs embrace dysphagia, dysphonia and dysarthria end result of} weak point of the facial and bulbar muscle tissue. The distinguishing feature in myasthenia is the fluctuation of the signs, worsening with activity or through the course of the day. Weakness of the respiratory muscle tissue can also be|may also be|can be} seen probably leading to respiratory failure. It is clinically differentiated from myasthenia by the weak point predominantly affecting the proximal decrease limb muscle tissue and only delicate involvement of the ocular and bulbar muscle tissue. Deep tendon reflexes are sometimes decreased, however strength and reflexes can be improved by a short period of contraction (facilitation). The analysis is supported by the presence of facilitation throughout repetitive nerve stimulation and the detection in the blood of antibodies in opposition to presynaptic Voltage-gated calcium channels. Primary hyperkalemic periodic paralysis has its onset throughout childhood and manifests clinically with attacks of muscle weak point lasting less than a number of} hours and triggered by rest followed by strenuous exercise. Hypokalemic periodic paralysis is more common and in addition starts throughout childhood or adolescence with episodes of acute paralysis through the night time or early morning and precipitated by meals rich in carbohydrates and sodium, stress or sleep following heavy 15 Episodic Neurologic Symptoms 413 exercise. Typical signs are exercise intolerance, muscle pain, stiffness, cramps, fatigue and typically weak point of proximal and distal muscle tissue. Rule of thumb: Generalized weak point · Weakness can replicate systemic sickness or symptom of neurological course of · Neuromuscular illnesses embrace: Myastenia Gravis predominately weak point of eye lids (eye lid droop), eyes, face, oropharyngeal, and limb muscle tissue. The analysis is confirmed by the DixHallpike maneuver which involves provocation of vertigo by positioning testing and remark of typical nystagmus (Lanska and Remler 1997). They can also present with episodes of vertigo, however are almost always accompanied by different signs of brain stem dysfunction, corresponding to diplopia, dysarthria, bifacial numbness, ataxia, and weak point or numbness of half or all of one or each side of the physique. Rarely, isolated vertigo normally a|could be a} manifestation of vertebrobasilar insufficiency and ought to be suspected in sufferers with cerebrovascular threat factors (Gomez et al. Benbadis · Basilar migraine is a form of migraine with prominent brainstem signs. The first signs of the assault involve visible phenomena affecting the whole of each visible fields, corresponding to "flashing lights," scintillating scotomas and typically temporary blindness. The visible signs are sometimes related to vertigo, staggering, incoordination of the limbs, dysarthria and tingling in arms and ft. In some sufferers, the basilar-type aura at occasions occurs utilizing a|with no} headache (Kirchmann et al. Symptoms embrace recurrent, acute, recurring episodes of severe vertigo, usually with nausea and vomiting nicely as|in addition to} delicate tinnitus and deafness. Other signs can embrace contralateral nystagmus (nystagmus to the facet contralateral of the impaired labyrinthine). Falling or swaying whereas walking is usually to the ipsilateral facet of the labyrinthine impairment. In classic Meniere illness, vertigo attacks happen with speedy onset and last for minutes to 12 hours in period. Patients frequently describe these signs as "dizziness" and can be confused with vertigo, which is an phantasm of movement. Typical onset is in early to middle adulthood and preceded by higher respiratory infection. Vertigo onset is over hours to , at most, a number of} days of feeling "top heavy" or "off balance. Specific features, corresponding to speech, writing or calculation can also be|may also be|can be} concerned nicely as|in addition to} especial senses including vision, olfaction or taste. The drawback sometimes occurs in the brain and rarely in the peripheral nervous system. It could end in adverse signs (loss of movement or sensation, visible subject cuts, and so on. The most typical disorders inflicting transient focal neurologic signs are outlined in Table 15. They sometimes happen inside 14 days of starting the treatment and are characterised 416 H. Benbadis by torsion/twisting movements affecting the cranial, pharyngeal, and cervical muscle tissue. The oculogyric disaster is a subtype characterised by acute conjugate eye deviation, usually in an upward path. The typical assault lasts 12 hours, throughout which the abnormal movement occurs repetitively for seconds to minutes. These dystonic reactions respond very well and rapidly to anticholinergics (trihexyphenidyl, benztropine, diphenhydramine) and levodopa (Dressler and Benecke 2005). Over time or with exacerbations, the clonic movements end result in|may end up in|can lead to} a sustained tonic contraction inflicting forceful (unilateral) eyelid closure. By distinction, seizures are paroxysmal (not persistent progressive) and sometimes have an effect on} the perioral muscle tissue (due to a big representation on the motor homunculus). The patient admits to making the movements and feels compelled to do so to be able to} relieve perceived tension. In these circumstances, an correct history of the occasion is essential to differentiate the 2. It is necessary to separate a single transient episode from repeated ones that present with the identical signs. Following focal motor seizures there might be a transient paralysis of the affected limbs lasting for minutes to a number of} hours, usually in proportion to the period of the seizure. Continued focal paralysis past this time usually indicates a focal brain lesion (stroke, tumor, and so on. A similar phenomenon can happen with seizures involving the language, sensory and visible areas. Migraine signs are likely to|are inclined to} evolve in minutes and "March" (spread from one concerned half to the other). Migraine with aura, termed classic migraine, presents with focal neurologic signs ("aura"), most often visible (flashing, flickering lights, scintillating scotomas) followed inside several of} minutes by a unilateral, much less usually bilateral, throbbing headache accompanied by nausea, vomiting and sensitivity to gentle (photophobia) and sounds (phonophobia). More commonly the migraine headache seems with out preceding neurologic signs (migraine with out aura), and is termed common migraine. In about 6080% of the classic migraine circumstances, several of} family members have migraine headache. Benbadis · Cluster complications are characterised by severe, unilateral pain localized in the orbital, supraorbital and/or temporal space lasting from 15 to one hundred eighty minutes. The episodes happen from 1 each different day to eight per day and nightly occurrence is characteristic. Autonomic signs are invariable present on the facet of the pain and embrace rhinorrhea, lacrimation, conjunctival injection, ptosis and myosis. The headache tends to recur often for periods ("clusters") extending over 612 weeks followed by pain-free intervals of many months. Unlike cluster complications, the episodes happen many occasions a day, are shorter (545 minutes) and recur daily for lengthy periods that might extend to years (Goadsby 2001). This dysfunction affects more women than men and responds dramatically to Indomethacin. The pain is of temporary period (from seconds to less than 2 minutes) and can be triggered by touching the face, brushing the enamel, speaking or eating. The majority of the circumstances is idiopathic or end result of} compression of the nerve by a tortuous blood vessel and the physical exam is unremarkable. On the other hand, the finding of sensory loss in the face or abnormal corneal reflex should elevate the suspicion of a structural brain lesion corresponding to tumor, basilar artery aneurysm or a number of} sclerosis. Rule of thumb: Headache and facial pain · Cluster headache is a severe unilateral pain localized in the orbital, supraorbital and/or temporal space lasting 15 minutes to three hours occurring sometimes at night time, 18 occasions per day for weeks to three months followed by an interval of months with no headache (headaches happen in clusters). However, the "taking pictures" character of the pain end result of} nerve root illness (radiculopathy) can be perceived as episodic or intermittent. Radiculopathies frequently cause paresthesias (numbness or tingling) and the physical examination sometimes reveals decreased sensation and, if severe, weak point and decreased deep tendon reflexes in the distribution of a number of} roots.
Purchase 100mg dilantin
These skills should embrace assessment of perception, scanning, inattention/neglect, visual recognition, facial recognition, visual form discrimination, construction (drawing) and visual synthesis skills. It features a brief assessment of perception of line orientation and form discrimination. Number 4 is an example of a line bisection task during which the patient is instructed to draw a vertical line bisecting the horizontal traces on a web page. Patients must integrate many components into the reproduction of more advanced drawing. Patients may be given a sheet with both curved and straight traces and be requested to match or point to the traces which are be} most similar. Patients wants to|must also} be requested to name the colour of objects in the environment throughout blue-green and red-purple spectrums to guarantee right shade perception. Scanning and assessment of neglect should involve using of} both behavioral assessment and tasks which require cancellation. Behaviorally, patients may be concurrently proven a unique variety of fingers on each hand of the examiner and requested to report the total variety of fingers they were proven. Match similar traces Total Correct A C M T P M P C E A P T E A D A C A R A P E F R C E S L A R K P R F T F A P R M A E E C C D D C A B D D E C E F C R R A P A G R P A D A D A D F M R E S T A E F D D F M 4. Show me the way to|tips on how to} command Brush your tooth Strike a match and blow it out Imitation With object Imitation. The patient should reply with the total variety of fingers proven indicating appropriate perception in all tested visual fields. To affirm a request, fingers from both palms may be presented in the identical visual area and should guarantee perceptual skills in a unilateral visual area. If neglect is current, similar additional presentation may be accomplished in the upper and decrease visual area quadrants (both unilaterally and bilaterally) to discern a quadrant inattention or neglect. Visual scanning may be readily assessed by drawing letters at various orientations on a web page in a random array. The patient is requested to cross off all of a specific letter and the examiner notes any gadgets which are be} omitted and the aspect or quadrant during which 9 Deficits in Visuospatial/Visuoconstructional Skills and Motor Praxis 217 these things are omitted. Similarly, patients may be proven horizontal traces in a random array on a sheet of paper and requested to draw a vertical line that bisects each horizontal line as near the center as possible. Visual recognition and facial perception may be assessed quickly by asking patients to recognize and name objects and individuals in that environment. The examiner can carry pictures of common objects or well-known folks with them and ask for identifications to be made. Common objects could embrace telephones, watches, cups, pens/pencils or books/magazines. Faces can embrace relations or wellknown cultural figures, though identification of cultural figures varies significantly amongst individuals relying on age, gender and publicity to presented cultural icons. Visual form recognition, drawing and visual synthesis skills may be assessed by showing patients common objects which have been drawn as separate components and asking them to tell what that object could be if the components were mentally rotated and assembled right into a single object. In addition, patients ought to be requested to copy and draw objects which require appropriate relational components both in size, shape and components within the object. For example, patients may be requested to copy a easy home and their copying should embrace a roof, chimney, partitions, window and door in right proportion and relation to each other. The patient additionally be|may additionally be|can be} requested to draw an analog clock and put all the numbers of their right positions. To assess additional their ability to plan, they are often requested to place palms on the clock to characterize a specific time. It is common for patients to be requested to set the palms in order that the clock reads eleven:10. Laboratory (Outpatient) Neuropsychological Assessments More thorough assessment of visual spatial and visual constructional tasks can (and should in lots of} cases) be routinely completed. Common measures of visuoconstructional skills are the Wechsler Scales Block Design subtest and/or drawing a posh geometric figure such as the Rey-Osterrieth Complex figure, the Taylor advanced figure or the Medical College of Georgia Complex Figures (see Lezak et al. Note the patient with the left parietal lesion ability to protect the overall design gestalt (the common features or shape is maintained), however the method is simplistic and piecemeal method to the task which has resulted in poor integration of sections and 218 J. Alternatively, the patient with the proper parietal lesion exhibited left visual inattention (truncated left half of the figure) nicely as|in addition to} an inability to synthesize and integrate the weather of the drawing suggesting perceptual deficits. These examples present examples of post-acute left and right hemispheric constructional apraxic features. Namely, left hemisphere injury tends to end in maintained gestalt however simplistic designs, whereas patients with right hemisphere lesions probably to|are inclined to} exhibit deficits in sustaining the gestalt of the figure (details with out coherent organization). Comparability of complete score efficiency on the ReyOsterrieth Complex Figure and a modified Taylor Complex Figure. Schoenberg Abstract the frontal lobes characterize a large area, consuming approximately one-third of the cortical surface of the mind. This area is concerned immediately and indirectly throughout a wide spectrum of human thought, conduct and emotions. The irony of the frontal lobes could greatest be described as the area of the mind we know probably the most about however understand the least. For example, frontal lobe functioning includes easy motor skills (both gross and fine), advanced motor skills, sequenced motor skills, inhibition of motor skills and automated motor skills, and these could be the easiest of the capabilities of the frontal lobes. Key Points and Chapter Summary · Frontal lobes embrace a large area of the cortex and are concerned immediately or indirectly in most mind capabilities involving cognition, behavioral, and motor skills · Frontal lobe injury can have profound results on attention, memory, language, drawback solving/reasoning, and common comportment (personality/social behaviors, and so forth. The frontal lobes may be divided into three broad categories: (1) Primary motor cortex, (2) Premotor and supplementary motor cortex, and (3) Prefrontal cortex. The three conventional prefrontal domains are: (a) dorsolateral prefrontal, (b) orbitofrontal (inferior or ventral frontal lobe), and (c) the medial frontal/anterior cingulate. The prefrontal cortex derived its name because of|as a end result of} this area of the frontal lobe received inputs (afferent fibers) from the dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus. The prefrontal cortex additionally has in depth afferent and efferent connections to the temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes nicely as|in addition to} reverberating (input and output) fibers to subcortical regions, including the basal ganglia, thalamus, hypothalamus, and tegmentum. The major motor cortex has efferent projections to the spinal twine and cranial nerve nuclei nicely as|in addition to} the basal ganglia and red nuclei, forming half of} the corticospinal or corticobulbar tracts, respectively. The initiation of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts is the premotor cortex (see under and Chap. The major motor cortex receives input from the premotor/supplementary motor cortex areas. Lesions involving the first motor cortex will end in contralateral motor weak spot. Initially, the motor weak spot could current as a flaccid hemiplegia (complete lack of motor strength), however energy will usually recuperate to some extent, particularly if premotor and supplementary motor areas are preserved. Larger lesions could resolve right into a spastic hemiparesis and smaller lesions could resolve into incoordination and delicate hemiparesis which may be difficult to establish with out careful examination. Primary Facial Motor Cortex the first motor area concerned in facial control (recall the upper half of} the face is innervated bilaterally by the facial nerve) has some unique features summarized under. The major motor cortex of the face is simply superior to the perisylvian fissure and anterior to the central sulcus. Each hemisphere controls the contralateral half of the face (facial region above the eyes is controlled by both contralateral cortical and ipsilateral cranial nerve function). Focal injury to the language dominant (left) major motor facial area is typically described as resulting in an expressive deficit (impaired receptive language however intact comprehension) thought to mirror an oral apraxia, together with contralateral hemiplegia of the decrease face (Kolb and Whishaw 2009). The oral apraxia is the inability to coordinate the muscle movements needed for speech manufacturing. Expressive speech deficits can also embrace agraphia (inability to write), thought to mirror injury to the closely situated supplementary area for nice motor movements of the hand. However, focal lesions an preliminary global aphasia (impaired expressive and receptive speech). Patients with surgical removing of pre- and post-central gyrus involving the facial area have demonstrated recovery of facial features often inside a month of surgical procedure. However, recovery of speech is more gradual, and whereas speech manufacturing grossly recovers, more careful analysis has revealed more profound residual impairments of generative verbal fluency, phonetic discrimination, spelling, and figural fluency. Remarkably, individuals with focal injury to the nondominant 10 Frontal Lobe/Executive Functioning 223 (right) major facial motor cortex have exhibited chronic deficits in figural fluency to a greater extent than individuals with more in depth prefrontal nondominant (right) frontal injury. Deficits in verbal (and presumably figural) generative fluency may characterize deficits in the motor preplanning wanted for these tasks (Salloway et al. While many areas of the mind are concerned in producing smooth, coordinated motor movements. The premotor/supplementary area has projections directly to the cortico spinal and corticobulbar tracts, however primarily have connections to and from the basal ganglia.
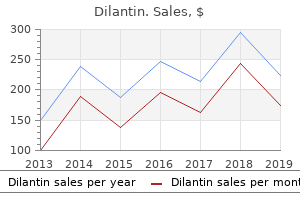
Quality dilantin 100 mg
However, the study of a broad vary of psychosocial therapies will improve therapeutic options for every substance use disorder. For kids, adolescents, and adults in danger for a substance use disorder, analysis is needed on the long-term efficacy of behavioral, psychosocial, and family-based interventions. For individuals with multiple of} disorTreatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 179 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Combinations of psychosocial and pharmacological therapies should be examined in terms of|when it comes to|by way of} augmenting short-term, quick, and long-term affected person outcomes. With every of the psychosocial therapies, analysis ought to determine the influence of sociodemographic, psychiatric, and general medical characteristics and affected person remedy preferences on remedy participation and consequence. Academy of Psychosomatic Medicine American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists American Academy of Pediatrics American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law American Association of Oriental Medicine American Group Psychotherapy Association American Mental Health Counselors Association American Music Therapy Association American Psychological Association American Society of Addiction Medicine Association for Academic Psychiatry Association for Cognitive and Behavioral Therapies Association for Medical Education and Research on Substance Abuse Group for the Advancement of Psychiatry Managed Health Network, Inc. A study during which subjects are prospectively adopted over time without any specific intervention. A qualitative evaluation and discussion of beforehand revealed literature and not using a|with no} quantitative synthesis of the info. Bernstein J, Bernstein E, Tassiopoulos K, Heeren T, Levenson S, Hingson R: Brief motivational intervention at a clinic go to reduces cocaine and heroin use. Siqueland L, Crits-Christoph P: Current developments in psychosocial treatments of alcohol and substance abuse. Tatarsky A: Harm reduction psychotherapy: extending the reach of conventional substance use remedy. Stewart J: Pathways to relapse: the neurobiology of drug- and stress-induced relapse to drug-taking. Addiction 2000; 95(suppl 3):S281S308 [G] Treatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 183 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. De Leon G: Therapeutic communities, within the American Psychiatric Publishing Textbook of Substance Abuse Treatment, third ed. Care Manag J 1999; 1:1018 [G] Treatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 185 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Rockville, Md, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 1999 [G] ninety. Fleisch B: Approaches within the Treatment of Adolescents With Emotional and Substance Abuse Problems. Weisner C, Mertens J, Parthasarathy S, Moore C, Lu Y: Integrating primary medical care with dependancy remedy: a randomized controlled trial. Granholm E, Anthenelli R, Monteiro R, Sevcik J, Stoler M: Brief integrated outpatient dual-diagnosis remedy reduces psychiatric hospitalizations. Addict Behav 2004; 29:1883 1887 [G] Treatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 187 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration: Report to Congress on the Prevention and Treatment of Co-Occurring Substance Abuse Disorders and Mental Disorders. Rockville, Md, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 1999 [G] 124. Rockville, Md, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 1998 [G] 126. Gowing L, Farrell M, Ali R, White J: Alpha2 adrenergic agonists for the management of opioid withdrawal. Streeton C, Whelan G: Naltrexone, a relapse prevention maintenance remedy of alcohol dependence: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Littleton J, Zieglgansberger W: Pharmacological mechanisms of naltrexone and acamprosate within the prevention of relapse in alcohol dependence. Med Lett Drugs Ther 2005; 47:13 [F] Treatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 189 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Spanagel R, Zieglgansberger W: Anti-craving compounds for ethanol: new pharmacological tools to study addictive processes. Amato L, Minozzi S, Davoli M, Vecchi S, Ferri M, Mayet S: Psychosocial combined with agonist maintenance treatments versus agonist maintenance treatments alone for remedy of opioid dependence. Monti P, Abrams D, Kadden R, Cooney N: Treating Alcohol Dependence: A Coping Skills Training Guide. J Consult Clin Psychol 2000; sixty eight:6472 [A] Treatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 191 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Luborsky L: Principles of Psychoanalytic Psychotherapy: A Manual for SupportiveExpressive Treatment. Fam Process 1979; 18:251280 [F] Treatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 193 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Chevy Chase, Md, American Society of Addiction Medicine, 1998, pp 707-718 [F] 262. Rockville, Md, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, 1992 [G] Treatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 195 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Edwards G, Orford J, Egert S, Guthrie S, Hawker A, Hensman C, Mitcheson M, Oppenheimer E, Taylor C: Alcoholism: a controlled trial of "remedy" and "advice. Marijuana Treatment Project Research Group: Brief treatments for hashish dependence: findings from a randomized multisite trial. Saunders B, Wilkinson C, Phillips M: the influence of a short motivational intervention with opiate customers attending a methadone programme. Baker A, Lewin T, Reichler H, Clancy R, Carr V, Garrett R, Sly K, Devir H, Terry M: Evaluation of a motivational interview for substance use within psychiatric in-patient companies. Bock B, Graham A, Sciamanna C, Krishnamoorthy J, Whiteley J, Carmona-Barros R, Niaura R, Abrams D: Smoking cessation remedy on the Internet: content, high quality, and value. Rockville, Md, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2005 [G] 289. Arsenault-Lapierre G, Kim C, Turecki G: Psychiatric diagnoses in 3275 suicides: a meta-analysis. American Psychiatric Association: Practice guideline for the evaluation and remedy of patients with suicidal behaviors. Suominen K, Henriksson M, Suokas J, Isometsa E, Ostamo A, Lonnqvist J: Mental problems and comorbidity in tried suicide. Addict Behav 1998; 23:119121 [G] Treatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 197 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Langevin R, Paitich D, Orchard B, Handy L, Russon A: the role of alcohol, drugs, suicide makes an attempt and situational strains in homicide committed by offenders seen for psychiatric evaluation: a controlled study. Hien D, Zimberg S, Weisman S, First M, Ackerman S: Dual analysis subtypes in city substance abuse and psychological well being clinics. Psychiatr Serv 1997; 48:10581063 [G] Treatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 199 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. RachBeisel J, Scott J, Dixon L: Co-occurring extreme psychological sickness and substance use problems: a evaluation of latest analysis. Ziedonis D: Integrated remedy of co-occurring psychological sickness and dependancy: clinical intervention, program, and system perspectives. Rockville, Md, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 1994 [G] 354. Triffleman E, Carroll K, Kellogg S: Substance dependence posttraumatic stress disorder therapy: an integrated cognitive-behavioral strategy. Brown S, Inskip H, Barraclough B: Causes of the excess mortality of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 1998; 155:14901501 [F] Treatment of Patients With Substance Use Disorders 201 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Minkoff K: An integrated remedy model for twin analysis of psychosis and dependancy. American Psychiatric Association: Practice guideline for the remedy of patients with schizophrenia, 2nd ed. McEvoy J, Freudenreich O, McGee M, VanderZwaag C, Levin E, Rose J: Clozapine decreases smoking in patients with persistent schizophrenia. Batki S, Dimmock J, Cornell M, Wade M, Carey K, Maisto S: Naltrexone remedy of alcohol dependence in schizophrenia: relationship of alcohol use to psychosis severity and antipsychotic medicine. Poster offered on the thirteenth annual assembly of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry, Las Vegas, December 1215, 2002 [B] 413.
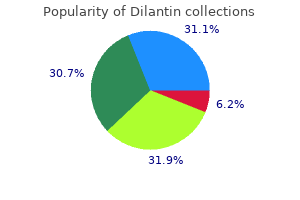
Proven dilantin 100 mg
Surgery for dystonia using deep mind stimulation continues to be at the experimental stage. Patients are requested to clap: these with neglect perform one-handed motions which stop at the midline. Hemiplegic sufferers with out neglect reach across the midline and clap towards their plegic hand. This may be be} observed as a characteristic of apraxic syndromes similar to corticobasal degeneration, as a complex motor tic in Tourette syndrome, and in frontal lobe problems (imitation behaviour). Synaesthesia may be be} linked to eidetic memory; synaesthesia getting used as a mnemonic aid. Patients - 126 - · Emotionalism, Emotional Lability E could develop oculopalatal myoclonus months to years after the onset of the ocular motility downside. Sometimes other psychiatric options may be be} present, notably if the delusions are a part of} a psychotic sickness similar to schizophrenia or depressive psychosis. Clinical examination could typically present evidence of skin picking, scratching, or dermatitis attributable to repeated use of antiseptics. Treatment should be aimed at the underlying condition if appropriate; if the delusion is isolated, antipsychotics similar to pimozide may be be} tried. The neurobehavioural state of emotional lability reflects frontal lobe (especially orbitofrontal) lesions, usually vascular in origin, and will coexist with disinhibited behaviour. Cross References Delirium; Disinhibition; Frontal lobe syndromes; Moria; Pathological crying, Pathological laughter; Pseudobulbar palsy; Witzelsucht Emposthotonos Emposthotonos is an abnormal posture consisting of flexion of the pinnacle on the trunk and the trunk on the knees, typically with flexion of the limbs (cf. Cross References Opisthotonos; Seizures; Spasm Encephalopathy Encephalopathy is a general term referring to any acute or continual diffuse disturbance of mind operate. Conditions which may be described as an encephalopathy include · · · · Metabolic problems: hypoxia/ischaemia, hypoglycaemia; organ failure, electrolyte disturbances, hypertension; Drug/toxin ingestion; Brain inflammation/infection. Enophthalmos may also occur in dehydration (probably the commonest cause), orbital trauma. The temptation to dismiss such weird symptoms as functional should be resisted, since environmental tilt is presumed to replicate damage to connections between cerebellar and central vestibular-otolith pathways. It has been reported within the following situations: · Lateral medullary syndrome of Wallenberg · Transient ischaemic attacks in basilar artery territory · Demyelinating illness · Head harm · Encephalitis · Following third ventriculostomy for hydrocephalus Cross References Lateral medullary syndrome; Vertigo; Vestibulo-ocular reflexes Epiphora Epiphora is overflow of tears down the cheek. This may be be} not only end result of} a blocked nasolacrimal duct, or irritation to the cornea causing elevated lacrimation, however it may also be neurological in origin. Lacrimation is also be|can be} a characteristic of trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias similar to cluster headache. It may be be} demonstrated using the duvet test as an outward movement of the attention which is compelled to assume fixation by occlusion of the other eye. With lateral rectus muscle paralysis, the eyes are esotropic or crossed on attempted lateral gaze path of|in direction of} the paralyzed aspect, however the pictures are uncrossed. Cross References Amblyopia; Cover exams; Diplopia; Exotropia; Heterotropia; Nystagmus Eutonia Kinnier Wilson used this term to describe an emotional lack of concern associated with the dementia of quantity of} sclerosis. Ewart Phenomenon that is the elevation of ptotic eyelid on swallowing, a synkinetic movement. Clinically observed within the coveruncover test as an inward movement as the covered eye is uncovered. Exophoria could occur in individuals with myopia and may be be} physiological in lots of} subjects due to the alignment of the orbits. Cross References Cover exams; Esophoria; Heterophoria Exophthalmos Exophthalmos is forward displacement of the eyeball. Cross References Lid retraction; Proptosis Exosomaesthesia the sensory disturbance associated with parietal lobe lesions could sometimes lead the patient to refer the supply of a stimulus to some point outdoors the body, exosomaesthesia. It may be be} demonstrated using the duvet test as an inward movement of the attention which is compelled to assume fixation by occlusion of the other eye. When the medial rectus muscle is paralyzed, the eyes are exotropic (walleyed) on attempted lateral gaze path of|in direction of} the paralyzed aspect, and the photographs are crossed. It is important to present that the patient responds appropriately to every hand being touched individually, however then neglects one aspect when both are touched concurrently. More delicate defects may be be} examined using simultaneous bilateral heterologous (asymmetrical) stimuli, although it has been shown that some normal individuals could present extinction in this state of affairs. A motor type of extinction has been postulated, manifesting as elevated limb akinesia when the contralateral limb is used concurrently. The presence of extinction considered one of the|is among the|is likely considered one of the} behavioural manifestations of neglect and most often follows non-dominant (right) hemisphere (parietal lobe) lesions. There is evidence for physiological interhemispheric rivalry or competition in detecting stimuli from both hemifields, which may account for the emergence of extinction following mind harm. Neural penalties of competing stimuli in both visible hemifields: a physiological basis for visible extinction. The underlying mechanisms may be be} heterogeneous, including involuntary inhibition of levator palpebrae superioris. Botulinum toxin A injections improve apraxia of eyelid opening with out overt blepharospasm associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Volitional paresis with out emotional paresis could occur when corticobulbar fibres are interrupted (precentral gyrus, internal capsule, cerebral peduncle, higher pons). Depending on the precise location of the facial nerve harm, there may also be paralysis of the stapedius muscle within the center ear, causing sounds to appear abnormally loud (especially low tones: hyperacusis), and impairment of taste sensation on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue if the chorda tympani is affected (ageusia, hypogeusia). Lesions throughout the facial canal distal to the meatal section cause both hyperacusis and ageusia; lesions within the facial canal between the nerve to stapedius and the chorda tympani cause ageusia however no hyperacusis; lesions distal to the chorda tympani cause neither ageusia nor hyperacusis. Lesions of the cerebellopontine angle cause ipsilateral listening to impairment and corneal reflex despair (afferent limb of reflex arc affected) along with facial weak point. There is also be|can be} a sensory department to the posterior wall of the external auditory canal which may be affected resulting in local hypoaesthesia (Hitselberg sign). In main problems of muscle the pattern of weak point and household history could counsel the analysis. Emotional and nonemotional facial behaviour in sufferers with unilateral mind damage. Emotional facial paresis in temporal lobe epilepsy: its prevalence and lateralizing value. Clinically, facilitation may be be} demonstrated by the looks of tendon reflexes that are absent at relaxation after prolonged (ca. The basic instance, and doubtless essentially the most regularly observed, is abducens nerve palsy (unilateral or bilateral) within the context of raised intracranial stress, presumed to end result from stretching of the nerve over the ridge of the petrous temporal bone. Fasciculations may also be induced by frivolously tapping over a partially denervated muscle stomach. The term was previously used synonymously with fibrillation, however the latter term is now reserved for contraction of a single muscle fibre or a bunch of fibres smaller than a motor unit. Persistent fasciculations most often replicate a pathological process involving the decrease motor neurones within the anterior (ventral) horn of the spinal cord and/or in brainstem motor nuclei, typically motor neurone illness (in which cramps are an early related symptom). The pathophysiological mechanism of fasciculations is thought to be spontaneous discharge from motor nerves, however the web site of origin of this discharge is unsure. Denervation of muscle fibres could lead to nerve fibre sprouting (axonal and collateral) and enlargement of motor units which makes fasciculations more apparent clinically. Fasciculations may be be} seen in: · · · · · · · · · Motor neurone illness with decrease motor neurone involvement. Cross Reference Micrographia Fatigue the term fatigue may be be} used in different contexts to discuss with both an indication and a symptom. The signal of fatigue, recognized as|also called|also referred to as} peripheral fatigue, consists of a discount in muscle power or endurance with repeated muscular contraction. This most characteristically occurs in problems of neuromuscular junction transmission. In myasthenia gravis, fatigue may be be} elicited within the extraocular muscular tissues by prolonged upgaze causing eyelid drooping; in bulbar muscular tissues by prolonged counting or speech causing hypophonia; and in limb muscular tissues by repeated contraction, particularly of proximal muscular tissues. Fatigue as a symptom, or central fatigue, is an enhanced perception of effort and restricted endurance in sustained physical and psychological activities. Current remedy is symptomatic (amantadine, modafanil, three,4-diaminopyridine) and rehabilitative (graded exercise). Fatigue may be be} evaluated with various devices, such as the Krupp Fatigue Severity Score. A similar phenomenon may be be} observed if the patient is pulled backwards (retropulsion). Festination may be be} related to the flexed posture and impaired postural reflexes generally seen in these sufferers. It is much less widespread in symptomatic causes of parkinsonism, however has been reported, for instance, in aqueduct stenosis.
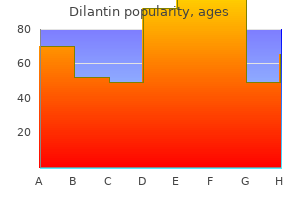
Diseases
- Anorexia nervosa restricting type
- Skeleto cardiac syndrome with thrombocytopenia
- Hypothalamic dysfunction
- Melnick Needles osteodysplasty
- Hypertelorism and tetralogy of Fallot
- Arthritis short stature deafness
- Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection
- Cholesterol esterification disorder
Safe 100mg dilantin
Prototypical is the sudden assault, defined as one not associated with a identified situational set off. Other types of panic attacks embody those that occur particularly emotional contexts, those involving limited signs, and nocturnal attacks. Although numerous studies have sought to validate symptom-specific subtypes of panic attacks. These situations should be "prevented or else endured with marked misery or with nervousness about having a panic assault or panic-like signs, or require the presence of a companion" (Criterion B). Typical situations eliciting agoraphobia embody touring on buses, subways, or different public transportation, and being on bridges, in tunnels, or removed from residence. Many patients who develop agoraphobia find that situational attacks become extra frequent than sudden attacks. Panic dysfunction with agoraphobia is usually a extra extreme and persistent situation than panic dysfunction without agoraphobia (62, 220). Cross-sectional issues There are a number of|numerous|a variety of} essential clinical and psychosocial features to think about in a cross-sectional evaluation. The psychiatrist should assess the patient for the presence of life-threatening behaviors, the diploma to which the Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Prospective follow-up studies have shown that patients with co-occurring depression have worse courses of sickness (61, 420). Studies of the impression of persona disorders on the course of panic dysfunction have produced combined results (420, 422). These embody the fluctuations in persistent variants of this situation, the response to prior treatments, and the development of complications similar to co-occurring psychiatric and medical disorders and medication unwanted side effects}. Prevalence and onset Epidemiologic data collected from quantity of} nations have documented similarities in lifetime prevalence (1. Although the full-blown syndrome is often not present till early adulthood, limited signs usually occur a lot earlier. Panic dysfunction can have its onset prior to puberty (526), although that is relatively uncommon. Panic signs in childhood and adolescence are regularly a predictor of later onset psychiatric disorders (379). Individuals with panic dysfunction generally have nervousness in regards to the recurrence of panic attacks or signs or in regards to the implications. Panic dysfunction, especially with agoraphobia, might result in the loss or disruption of interpersonal relationships, especially as individuals struggle with the impairment or loss of social function functioning and the difficulty of responsibility for signs. Examples of the disrupting nature of panic dysfunction embody the worry that an assault is the indicator of a life-threatening sickness despite medical evaluation indicating in any other case or the worry that an assault is an indication of emotional weakness. Some individuals experience the attacks as so extreme that they take such actions as quitting a job to avoid a attainable assault. Others might become so anxious that they avoid most activities outside their properties. Evidence from naturalistic follow-up studies of patients in a tertiary-care setting suggests that at 46 years posttreatment about 30% of people are well, 40%50% are improved but symptomatic, and the remaining 20%30% have signs would possibly be} the identical or slightly worse (514, 515). Panic attacks seem to worsen the prognosis and/or delay a helpful remedy consequence in quantity of} different disorders 2. Co-occurring disorders Roughly one-quarter to one-half of people identified with panic dysfunction in neighborhood samples also have agoraphobia, although a a lot higher rate of agoraphobia is encountered in clinical samples (522). The National Comorbidity Survey Replication found that roughly 20% of patients with lifetime panic dysfunction have agoraphobia. Among individuals with panic dysfunction alone, the lifetime prevalence of main depression is 34. Approximately one-third of patients with panic dysfunction are depressed after they present for remedy (528). For individuals presenting to clinical settings with each panic dysfunction and main depressive dysfunction, the onset of depression has been found to precede the onset of panic dysfunction in one-third of people, whereas the onset of depression coincides with or follows the onset of panic dysfunction within the remaining two-thirds (529). Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Panic Disorder Children and adolescents with panic dysfunction show excessive charges of different co-occurring psychiatric disorders, especially different nervousness and mood disorders, together with bipolar dysfunction (530532). Morbidity Epidemiologic studies have clearly documented the morbidity associated with panic dysfunction (40, 368, 533538). Patients with panic dysfunction, especially with co-occurring depression, are at higher risk for suicide attempts (368), impaired social and marital functioning (539), work impairment (533), use of psychoactive treatment (535), and substance abuse (539). Individuals regularly present to nonpsychiatrists first and will make greater use of the emergency division (548) or different medical specialists (549). However, an intensive body of proof has documented that panic dysfunction is undertreated, whether or not in primary care (541) or specialty mental health settings (220). Incorrect varieties or doses of treatment are often prescribed for durations of insufficient size, and psychosocial treatments are regularly offered which have minimal proof base (550). Medical utilization In the Epidemiologic Catchment Area research, topics with panic signs or dysfunction, as in comparison with} different disorders, were the most frequent customers of emergency medical services and were extra likely to to|prone to} be hospitalized for physical issues (535). Similarly, patients with panic attacks or dysfunction, who regularly present to ambulatory primary care settings reporting the somatic manifestations of their panic attacks, are often not recognized as having panic attacks unless the syndrome is extreme, might obtain extensive and expensive medical work-ups, and often obtain poor quality of care and insufficient and inappropriate remedy (540, 541). This phenomenon has sparked curiosity in disseminating evidence-based panic treatments to primary care settings (157). There is preliminary proof that remedy of panic dysfunction in these settings might result in a significant value offset and total medicalcare savings (542544). Family and genetics studies Family studies utilizing direct interviews of family members and family historical past studies have shown that panic dysfunction is highly familial. Results from studies performed in numerous nations (United States, Belgium, Germany, Australia) have shown that the median risk of panic dysfunction is eight instances as excessive within the first-degree family members of probands with panic dysfunction as within the family members of management topics (551). A family data evaluation showed that types of the dysfunction with early onset (at age 20 years or younger) were the most familial, carrying a more than 17 instances greater risk (552). Results from twin studies have advised a genetic contribution to the dysfunction (553555). Genetic studies of panic dysfunction patients have identified genes linked to panic subtypes associated with bladder issues, bipolar sickness, and possibly smoking and have identified some related genes with functional importance for nervousness pathophysiology. Frequency and nature of remedy Relative to patients with different psychiatric disorders, patients with panic dysfunction seek assist relatively regularly V. Measurement of outcomes In the following sections available data on the efficacy of treatments for panic dysfunction are reviewed. Short-term efficacy has often been evaluated over the course of 6- to 12-week clinical trials by observing modifications within the presence and severity of patient- and physician-rated panic and agoraphobic signs. Thus, the sphere has moved toward a broader definition of remission that includes substantial reductions in panic attacks, anticipatory nervousness, and agoraphobic avoidance, Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. The long-term efficacy of treatments has been measured in terms of|when it comes to|by way of} relapse charges amongst panic-free or symptom-free patients receiving remedy over the course of quantity of} years. A variety of definitions of relapse have been used, primarily based on the emergence of a certain number of signs or primarily based on the proportion of change in scores on symptom rating scales. More studies that embody longer followup durations of quantity of} years are wanted to be able to} assess the potential of different treatments to produce sustained remission. It is also be|can be} essential to notice whether or not a particular remedy protocol has been used and whether or not efforts have been made to ensure that that|be certain that} all research clinicians have demonstrated adherence to the protocol competence in delivering the intervention. Finally, some trials of psychosocial treatments have employed waiting-list management groups, which only management for the passage of time and never for the "nonspecific" results of remedy. In addition, patients in treatment studies could also be} taking extra doses of the tested medicines or different antipanic medicines (either explicitly, as doses taken as wanted, or surreptitiously). Studies that monitor such occurrences have shown charges of surreptitious benzodiazepine use to be as excessive as 33% (278). These studies provide steerage only for the potential efficacy of the remedy as an adjunct to the precise prior type of remedy. For all studies, perceive the characteristics of the research participants. Issues in research design and interpretation When evaluating clinical trials of medicines for panic dysfunction, think about the design of the research. Response charges as excessive as 75% have been observed amongst patients receiving placebo in clinical trials of patients with panic dysfunction (106). Placebo response charges (often within the vary of 40%50%) may clarify a lot of the observed remedy impact in uncontrolled trials or make important remedy results more difficult to detect in managed trials. Some randomized managed studies of medicines for panic dysfunction use an "energetic" comparator, which can be a medication or psychosocial intervention with prior proof supporting its efficacy in panic dysfunction.
Order 100mg dilantin
In order to improve the accuracy and comparability of measured adherence charges, additional research is required to set up specific definitions of "adherence to therapy" and therapy dropout. A clearer understanding and distinction between the various factors that influence dropout additionally be|can be} needed. There are few information out there for identifying effective adherence-promoting interventions, but using of} antidepressant medicine and psychosocial behavioural helps has proven good results. Studies to consider the cost-effectiveness of interventions for improving adherence are required. Smoking discount in smokers compliant to a smoking cessation trial with nicotine patch. Geneva,World Health Organization, 2001 (available on the Internet at tobacco. Smoking discount with oral nicotine inhalers: double blind, randomised scientific trial of efficacy and security. Effectiveness of a nicotine patch in serving to folks give up smoking: results of a randomised trial generally apply. Double blind trial of repeated therapy with transdermal nicotine for relapsed smokers. Combined use of nicotine patch and gum in smoking cessation: a placebo-controlled scientific trial. Targeting heavy smokers generally apply: randomised managed trial of transdermal nicotine patches. Maintaining abstinence from cigarette smoking: effectiveness of group counselling and components predicting outcome. Smoking by patients in a smoke-free hospital: prevalence, predictors, and implications. The Agency for Health Care Policy and Research Smoking Cessation Clinical Practice Guideline. Open randomised trial of intermittent very low vitality food regimen together with nicotine gum for stopping smoking in girls who gained weight in previous attempts to give up. Prospective examine of factors predicting outcome of transdermal nicotine therapy in smoking cessation. A randomized managed trial of smoking cessation counseling after myocardial infarction. Factors related to nonparticipation among registrants for a self-help, community-based smoking cessation intervention. Nicotine patches in smoking cessation: a randomized trial among over-the-counter customers in Denmark. Compliance to nicotine gum suggestions in a multicomponent group smoking cessation program: an exploratory examine. The efficacy of computer-tailored smoking cessation material as a complement to nicotine patch therapy. Measuring diploma of bodily dependence to tobacco smoking with reference to individualization of therapy. The relationship between a historical past of depression and adherence to a multicomponent smoking-cessation program. Brief intervention throughout hospital admission to assist patients to hand over smoking after myocardial infarction and bypass surgical procedure: randomised managed trial. Tuberculosis is a communicable illness, thus poor adherence to a prescribed therapy increases the risks of morbidity, mortality and drug resistance at each the person and neighborhood ranges. This has been done with the goal of contributing to the generation of data resulting in the manufacturing of guidelines for enhancing adherence to prescribed medication in patients receiving long-term care. Adherence could also be} measured utilizing either process-oriented or outcome-oriented definitions. Processoriented indicators make use of intermediate variables similar to appointment-keeping or pill counts to measure adherence (7). The extent to which these intermediate outcomes correlate with the precise quantities of pharmaceuticals taken is unknown (8). The level that separates "adherence" from "nonadherence" would be outlined as that in the pure historical past of the illness making the desired therapeutic outcome doubtless (adherence) or unlikely (nonadherence) to be achieved. At the person degree this is desirable, but on the inhabitants degree a extra pragmatic strategy is required. One writer has outlined nonadherence as "an unavoidable by-product of collisions between the scientific world and the opposite competing worlds of labor, play, friendships and household life" (11). Lack of effective social assist networks and unstable residing circumstances are extra components that create an unfavourable setting for ensuring adherence to therapy (12). Patient-related components Ethnicity, gender and age have been linked to adherence in numerous settings (1315). In addition, cultural perception techniques might assist using of} traditional healers in conflict with allopathic medicine (10,17). Regimen complexity the number of tablets that have to be taken, as well as|in addition to} their toxicity and different side-effects related to their use might act as a deterrent to persevering with therapy (18). Pattern of well being care supply the group of scientific services, together with availability of expertise, hyperlinks with affected person assist techniques and adaptability in the hours of operation, also affects adherence to therapy. Prediction of adherence If the people in danger for poor adherence presumably be} recognized early in their administration, well being care suppliers should, in theory, be able to|be capable of|have the power to} intervene by tailoring the provision of therapy to allow such patients to proceed their therapy. Unfortunately, the out there evidence indicates that well being care suppliers are unable to predict accurately which patients are be nonadherent (2123). The literature describes over 200 variables related to patients who default on therapy. Many epidemiological studies have explored correlates of adherence, often inspecting the difficulty from a biomedical perspective. Numerous psychosocial constructs have been proposed that have tried to provide a conceptual mannequin for thinking about well being behaviour (2428). Motivation and the development of behavioural abilities are also important determinants of behavioural change. Classification of interventions the interventions for improving adherence charges could also be} categorized into the next classes: · Staff motivation and supervision includes training and administration processes aimed toward improving the way way|the way in which} during which suppliers care for patients with tuberculosis. The alternative of an appropriate experimental design methodology (whether particular person or neighborhood randomization) decided by} the nature of the intervention under analysis. Quantitative research should be complemented by in-depth qualitative research to answer questions on why an intervention had an effect in a particular setting. Two recently printed systematic critiques reported sixteen randomized trials, of which only half were in nations with a high illness burden (8,49). Another examine reported that home visits by a well being employee, although extra labour-intensive, could also be} simpler than reminder letters for ensuring that defaulters full their therapy (48). Yet another examine showed that prospective telephone reminders are helpful for serving to folks to hold scheduled appointments (47). Although one trial found that assistance by a lay well being employee elevated adherence to a first appointment (44), a subsequent examine showed no impression on completion of preventive therapy at 6 months (53). The evidence for an unbiased effect of well being education on adherence of patients to therapy is weak. One trial did counsel some benefit (55) however the design of this examine was flawed end result of|as a end result of} people receiving well being education were contacted or seen each 3 months, whereas these in the control group were seen only on the end of the examine interval. The relative contributions of well being education and elevated consideration in this examine are therefore onerous to separate. In a newer trial that has helped to disaggregate these results (45) well being education alone was found to be no higher than routine case administration for improving appointment-keeping and the impression of education combined with a monetary incentive was indistinguishable from that of the monetary incentive alone. Finally, an intervention directed at clinic staff somewhat than patients was studied. Patients attending clinics during which staff were carefully supervised were extra full therapy than these attending clinics where there was only routine supervision of staff (42). Questions for future research Useful research into human behaviour should take into account extensive range|a variety} of approaches to enquiry, together with qualitative and quantitative research strategies. Studies on the therapy of tuberculosis undertaken by the British Medical Research Council Tuberculosis Units, 19461986, with relevant publications. The downside of self-administration of medication: with particular reference to pulmonary tuberculosis.
Generic dilantin 100 mg
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of insurance policies and programmes to cut back the hurt attributable to alcohol. Changes in density of on-premises alcohol retailers and impression on violent crime, Atlanta, Georgia, 1997 2007. Multilevel spatio-temporal twin changepoint models for relating alcohol outlet destruction and modifications in neighbourhood charges of assaultive violence. Effects of dram store liability and enhanced overservice law enforcement initiatives on extreme alcohol consumption and related harms: Two Community Guide systematic critiques. Effectiveness of insurance policies sustaining or limiting days of alcohol sales on extreme alcohol consumption and related harms. Effectiveness of insurance policies limiting hours of alcohol sales in preventing extreme alcohol consumption and related harms. Effectiveness of bans and laws in decreasing site visitors deaths: Legalized Sunday packaged alcohol sales and alcohol-related site visitors crashes and crash fatalities in New Mexico. Recommendations on privatization of alcohol retail sales and prevention of extreme alcohol consumption and related harms. Changes in site visitors crash mortality charges attributed to use of alcohol, or lack of a seat belt, air bag, motorcycle helmet, or bicycle helmet, United States, 19822001. The impression of underage ingesting laws on alcoholrelated deadly crashes of younger drivers. Countermeasures that work: A freeway security countermeasure information for state freeway security offices (7th ed. Effectiveness of ignition interlocks for preventing alcohol-impaired driving and alcohol-related crashes: A Community Guide systematic evaluate. Impact of state ignition interlock laws on alcohol-involved crash deaths within the United States. Alcohol insurance policies and impaired driving within the United States: Effects of driving-vs. Monitoring the Future nationwide survey results on drug use, 1975-2014: Volume I, secondary faculty college students 229. The results of minimum authorized ingesting age 21 laws on alcohol-related driving within the United States. Traffic security facts 2014: A compilation of motor vehicle crash knowledge from the fatality analysis reporting system and the overall estimates system. Lowered authorized blood alcohol limits for younger drivers: Effects on ingesting, driving, and driving-after-drinking behaviors in 30 states. Relationships between native enforcement, alcohol availability, ingesting norms, and adolescent alcohol use in 50 California cities. Restricting or banning alcohol promoting to cut back alcohol consumption in adults and adolescents. Implementation of prescription drug monitoring programs associated with reductions in opioid-related demise charges. An proof primarily based evaluate of acute and longterm results of cannabis use on executive cognitive functions. Moderation of the impact of adolescent-onset cannabis use on grownup psychosis by a functional polymorphism within the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene: longitudinal proof of a gene X surroundings interaction. Issues and challenges within the design of culturally tailored evidence-based interventions. Making the case for selective and directed cultural diversifications of proof primarily based treatments: Examples from mother or father training. The cultural adaptation of prevention interventions: Resolving tensions between constancy and fit. Effectiveness of culturally targeted and generic abilities training approaches to alcohol and drug abuse prevention amongst minority youths. Adapting school-based substance use prevention curriculum via cultural grounding: A evaluate and exemplar of adaptation processes for rural colleges. Using neighborhood primarily based participatory research to create a culturally grounded intervention for fogeys and youth to prevent dangerous behaviors. Real Men Are Safeculturally tailored: Utilizing the Delphi process to revise Real Men Are Safe for an ethnically numerous group of males in substance abuse therapy. Effectiveness of a culturally tailored strengthening households program 1216 years for high-risk Irish households. Adopting a population-level method to parenting and household support interventions. Meta-analysis of 143 adolescent drug prevention programs: Quantitative consequence results of program individuals compared to with} a control or comparison group. Estimating intervention effectiveness: Synthetic projection of field analysis results. Reducing ingesting and related harms in college: Evaluation of the "A Matter of Degree" program. Implementation matters: A evaluate of research on the influence of implementation on program outcomes and the elements affecting implementation. A framework for enhancing the value of research for dissemination and implementation. Blueprints for violence prevention: From research to realworld settings-factors influencing the profitable replication of model programs. Toward dissemination of evidence-based household interventions: Maintenance of community-based partnership recruitment results and associated elements. Effects of Communities That Care on the adoption and implementation constancy of evidence-based prevention programs in communities: Results from a randomized controlled trial. Sustaining the utilization and top quality implementation of tested and effective prevention programs using the Communities That Care prevention system. Sustaining evidence-based prevention programs: Correlates in a large-scale dissemination initiative. National Institutes of Health approaches to dissemination and implementation science: Current and future directions. Bridging research and practice: Models for dissemination and implementation research. Planning for the sustainability of communitybased health programs: Conceptual frameworks and future directions for research, practice and policy. Sustaining interventions in neighborhood techniques: On the relationship between researchers and communities. Mobilizing communities to implement evidence-based practices in youth violence prevention: the state of the art. Diffusion of innovations in service organizations: Systematic evaluate and proposals. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: A consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. The high quality implementation framework: A synthesis of crucial steps within the implementation process. Unpacking prevention capacity: An intersection of research-to-practice models and community-centered models. Assessing and enhancing readiness for change: Implications for expertise switch. Association between state stage ingesting and driving countermeasures and self reported alcohol impaired driving. The legislative impression of social movement organizations: the anti-drunken driving movement and the 21-year-old ingesting age. Developing a neighborhood science research agenda for building neighborhood capacity for effective preventive interventions. The longitudinal impact of technical assistance dosage on the functioning of Communities That Care prevention boards in Pennsylvania. The role of a state-level prevention support system in promoting high-quality implementation and sustainability of evidence-based programs. Building collaborative capacity in neighborhood coalitions: A evaluate and integrative framework. Bridging the hole between science and practice in drug abuse prevention via needs evaluation and strategic neighborhood planning. Toward a comprehensive technique for effective practitionerscientist partnerships and larger-scale neighborhood health and well-being. Evaluating community-based collaborative mechanisms: Implications for practitioners. Identifying training and technical assistance needs in neighborhood coalitions: A developmental method.

Safe 100 mg dilantin
Research to decide if and how exercise programs can play an identical role within the therapy of different types of drug abuse is underneath way. These ailments are transmitted by sharing contaminated drug injection equipment and by engaging in dangerous sexual conduct generally associated with drug use. Treatment for drug abuse and addiction is delivered in many various settings utilizing selection of|quite lots of|a big selection of} behavioral and pharmacological approaches. In the United States, more than 14,500 specialised drug therapy services present counseling, behavioral therapy, medicine, case management, and different types of companies to individuals with substance use problems. Along with specialised drug therapy services, drug mental well being clinics by selection of|quite lots of|a big selection of} providers, together with counselors, physicians, psychiatrists, psychologists, nurses, and social workers. Treatment is delivered in outpatient, therapy approaches often are associated with explicit therapy settings, selection of|quite lots of|a big selection of} therapeutic interventions or companies can be included in any given setting. Because drug abuse and addiction are major public well being problems, a big portion of drug therapy is funded by native, State, and Federal governments. Private and employer-subsidized well being plans additionally may present protection for therapy of addiction and its medical consequences. Unfortunately, managed care has resulted in shorter average stays, while a historical lack of or 31 32 33 curtailed the variety of operational programs. The current passage of parity for insurance coverage protection of mental well being and substance abuse problems will hopefully enhance this state of affairs. Long-Term Residential Treatment Long-term residential therapy supplies care 24 hours a day, generally in nonhospital settings. Treatment is very structured and can be confrontational at occasions, with activities designed to assist residents examine damaging beliefs, self-concepts, and damaging patterns of conduct and adopt new, extra harmonious and constructive ways to work together with others. Types of Treatment Programs Research research on addiction therapy typically have Treatment approaches and individual programs proceed to evolve and diversify, and many of|and plenty of} programs at present do therapy parts are described on pages 3035. Outpatient Treatment Programs Outpatient therapy varies within the sorts and depth of companies supplied. Such therapy costs less than residential or inpatient therapy and sometimes is extra appropriate for people with jobs or intensive social supports. It ought to be noted, nevertheless, that low-intensity programs may provide little more than drug schooling. Some outpatient programs are additionally designed to treat sufferers with medical or different mental well being problems along with their drug problems. Short-Term Residential Treatment Short-term residential programs present intensive but approach. These programs were initially designed to treat alcohol problems, but through the cocaine epidemic of the mid-1980s, many started to treat different types of substance use problems. These programs assist to scale back the chance of relapse once as} a patient leaves the residential setting. Substance abuse therapy within the non-public setting: Are some programs more effective than others? Through its emphasis on short-term behavioral targets, individualized counseling helps the patient develop coping methods and tools to abstain from drug use and maintain abstinence. The addiction counselor encourages 12-step participation (at least one or two occasions per week) and makes referrals for wanted supplemental medical, psychiatric, employment, and different companies. Group Counseling Many therapeutic settings use group therapy to capitalize on the social reinforcement supplied by peer dialogue and to assist promote drug-free life. Research has shown that when group therapy both is obtainable aspect of} individualized drug counseling or is formatted to contingency management, optimistic outcomes are achieved. Currently, researchers are testing conditions during which group therapy can be standardized and made extra community-friendly. Treating Criminal JusticeInvolved Drug Abusers and Addicted Individuals Often, drug abusers come into contact with the legal justice system sooner than different well being or social systems, presenting alternatives for intervention and therapy prior to, during, after, or in lieu of incarceration. Research has shown that combining legal justice sanctions with drug therapy can be efficient in lowering drug abuse and associated crime. Individuals underneath authorized coercion most likely to|are inclined to} stay in therapy longer and do as well as|in addition to} or better than these not underneath authorized pressure. Studies show that for incarcerated people with drug problems, beginning drug abuse therapy in prison and persevering with the identical therapy upon release-in different phrases, a seamless continuum of services-results in better outcomes: less drug use and fewer legal conduct. More data on how the legal justice system can handle the problem of drug addiction can be found in Principles of Drug Abuse Treatment for Criminal Justice Populations: A Research-Based Guide (National Institute on Drug Abuse, revised 2012). This part presents examples of therapy approaches and parts which have an evidence base supporting their use. Each approach is designed to handle sure features of drug addiction and its consequences for the individual, family, and society. Some of the approaches are meant to supplement or enhance present therapy programs, and others are fairly comprehensive in and of themselves. The following part is broken down into Pharmacotherapies, Behavioral Therapies, and Behavioral Therapies Primarily for Adolescents. It has an extended history of use in therapy of opioid dependence in adults and is taken orally. Methadone maintenance therapy is on the market in all but three States via specially licensed opioid therapy programs or methadone maintenance programs. Combined with behavioral therapy Research has shown that methadone maintenance is more effective when it contains individual and/or group counseling, with even better outcomes when sufferers are supplied with, or referred to , different wanted medical/ psychiatric, psychological, and social companies. Buprenorphine is presently obtainable in two formulations which are be} taken sublingually: (1) a pure form of the drug and (2) a extra commonly prescribed formulation known as Suboxone, which combines buprenorphine with the drug naloxone, an antagonist (or blocker) at opioid receptors. Naloxone has no effect when Suboxone is taken as prescribed, but if an addicted individual attempts to inject Suboxone, the naloxone will produce extreme withdrawal signs. Thus, this formulation lessens the chance that the drug shall be abused or diverted to others. National Buprenorphine Implementation Program: Buprenorphine the American Journal on Addictions 13(Suppl. Patients stabilized on these medications can even engage extra readily in counseling and different behavioral interventions important to restoration. Naltrexone Naltrexone is an artificial opioid antagonist-it blocks opioids from binding to their receptors and thereby prevents their euphoric and different effects. It has been used a number of} years} to reverse opioid overdose and accredited for treating opioid addiction. The concept behind this therapy is that the repeated absence of the desired effects and the perceived futility of abusing opioids will gradually diminish craving and addiction. Naltrexone as a therapy for opioid addiction is normally prescribed in outpatient medical settings, though the therapy should begin after in a residential setting to be able to} stop withdrawal signs. Naltrexone have to be taken orally-either every day or thrice a week-but noncompliance with therapy is a typical drawback. Many experienced clinicians have found naltrexone greatest fitted to highly motivated, lately of exterior circumstances-for instance, professionals or parolees. Recently, a long-acting injectable version of naltrexone, known as Vivitrol, was accredited to treat opioid addiction. Research reveals that combining the patch with one other replacement therapy is more effective than a single therapy alone. It produces delicate stimulant effects by blocking the reuptake of sure neurotransmitters, especially norepinephrine and dopamine. A serendipitous statement amongst depressed sufferers was that the medicine was additionally efficient in suppressing tobacco craving, helping them stop smoking without additionally gaining weight. It acts on a subset of nicotinic receptors within the mind thought to be involved within the rewarding effects of nicotine. Varenicline acts as a partial agonist/antagonist at these receptors-this means that it to trigger the release of dopamine, which is essential for the rewarding effects of nicotine. As an antagonist, varenicline additionally blocks the power of nicotine to activate dopamine, interfering with the reinforcing effects of smoking, thereby reducing cravings and supporting abstinence from smoking. Combined therapy is urged as a result of|as a result of} behavioral and pharmacological treatments are thought to operate by different yet complementary mechanisms that can have additive effects. Short- and long-term smoking cessation for three levels of depth of behavioral therapy. Using extended cognitive behavioral therapy and medication to treat dependent people who smoke.
References:
- http://ms-mri.com/docs/6.pdf
- https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5910.pdf
- https://americanornithology.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/2019_Alaska_AOS_program_final_9_reduced.pdf
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/011757s114lbl.pdf
.png)