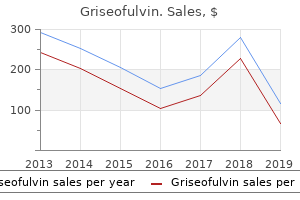
Buy 250mg griseofulvin
Absorption of Toxicants by the Lungs Toxic responses to chemical compounds can happen from absorption following inhalation exposure. A frequent cause of demise from poisoning-carbon monoxide-and an important occupational disease-silicosis-both result from absorption or deposition of airborne poisons in the lungs. Because the absorption of inhaled gases and vapor differs from that of aerosols, aerosols are mentioned individually beneath. However, the absorption of gases and vapors is governed by the same principles, and subsequently the word gasoline is used to symbolize both on this part. However, when inhaled, gases first pass through the nose, filtering through delicately scrolled, simple epithelial-lined turbinates, which serve to enhance the floor space of exposure. Therefore, the nose acts as a "scrubber" for water-soluble gases and extremely reactive gases, partially defending the lungs from doubtlessly injurious insults. Although these actions might serve to reduce systemic exposure or to shield the lungs, in addition they enhance the risk that the nose could possibly be} adversely affected. Second, the epithelial cells lining the alveoli-that is, kind I pneumocytes-are very thin and the capillaries are in close contact with the pneumocytes, in order that the distance for a chemical to diffuse could be very short. Third, chemical compounds absorbed by the lungs are eliminated quickly by the blood, and blood strikes through the in depth capillary community in the lungs. When a gasoline is inhaled into the lungs, gasoline molecules diffuse from the alveolar house into the blood and then dissolve. Table 5-4 pH of the Gastrointestinal Contents of Various Species pH species Monkey Dog Rat Rabbit abdomen 2. The magnitude of this variety can translate into differences a lot as} two orders of magnitude in the concentration of the nonionized versus ionized moiety of a weak organic acid or base out there for absorption. In basic, the intestinal Table 5-5 Number of Microbes and their Distribution along the Gastrointestinal Tract of Various Species species Monkey Dog Rat Rabbit Man abdomen 23 19 18 4 2 jejunum 24 20 23 5 4 colon forty one 40 37 13 10 feces 38 forty three 38 13 - Expressed as log10 of viable counts. As the contact of the impressed gasoline with blood continues in the alveoli, extra molecules dissolve in blood until gasoline molecules in blood are in equilibrium with gasoline molecules in the alveolar house. At equilibrium, the ratio of the concentration of chemical in the blood and chemical in the gasoline part is fixed. When equilibrium is reached, the rate of switch of gasoline molecules from the alveolar house to blood equals the rate of elimination by blood from the alveolar house. For example, chloroform has a relatively excessive bloodto-gas partition coefficient (approximately 20), whereas ethylene has a low coefficient (0. By comparability, a smaller share of the entire ethylene in the lungs is eliminated into the blood throughout each circulation the low blood-to-gas partition coefficient dictates that blood is rapidly saturated with this gasoline. It has been calculated that the time to equilibrate between the blood and the gasoline part for a relatively insoluble gasoline is about 10�20 minutes. A gasoline with a excessive blood-to-gas partition coefficient, such as chloroform, is readily transferred to blood throughout each respiratory cycle in order that little if any stays in the alveoli just before the subsequent inhalation. The extra soluble a poisonous agent is in blood, the extra of goes to be|will in all probability be} dissolved in blood by the point equilibrium is reached. Consequently, the time required to equilibrate with blood is a lot longer} for a gasoline with a excessive blood-to-gas partition coefficient than for a gasoline with a low ratio. This has been calculated to take a minimal of 1 hour for compounds with a excessive solubility ratio, although it may take even longer if the gasoline additionally has excessive tissue affinity. With extremely soluble gases, the principal factor limiting the rate of absorption is respiration. However, the rate may be accelerated tremendously by growing the rate of respiration. In each tissue, the gasoline molecules are transferred from the blood to the tissue until equilibrium is reached at a tissue concentration dictated by the tissue-to-blood partition coefficient. After releasing half of} the gasoline to tissues, blood returns to the lungs to take up extra of the gasoline. The process continues until a gasoline reaches equilibrium between blood and every tissue according to the tissue-to-blood partition coefficients characteristic of each tissue. This equilibrium is referred to as regular state, and presently, no net absorption of gasoline takes place lengthy as|so lengthy as} the exposure concentration stays fixed. Aerosols and Particles Absorption of aerosol and particles is distinguished from gases and vapors by the factors that decide absorption from the inhalation route of exposure. The absorption of gases and vapors by inhalation is decided by the partitioning of the compound between the blood and the gasoline part along with its solubility and tissue reactivity. In contrast, the important traits that affect on} absorption after exposure to aerosols are the aerosol size and water solubility of any chemical current in the aerosol. The site of deposition of aerosols and particulates relies upon largely on the scale of the particles. In basic, the smaller the particle, the additional into the respiratory tree the particle will deposit. Particles starting from 5 m or larger, described as "course particles" usually are deposited in the nasopharyngeal area. The mucous blanket of the ciliated nasal floor propels insoluble particles by the movement of the cilia. These particles and particles inhaled through the mouth are swallowed inside minutes. Soluble particles might dissolve in the mucus and be carried to the pharynx or absorbed through the nasal epithelium into the blood. Toxicants or viral infections that injury cilia might impair the efficiency of this process. Coughing and sneezing tremendously enhance the movement of mucus and particulate matter towards the mouth. Those particles which might be} roughly 10�20 nm in size have the greatest likelihood of depositing in the alveolar area. These extraordinarily small particles absorbed into blood or cleared through the lymphatics after being scavenged by alveolar macrophages (Oberdorster et al. In addition to being a serious determinant of lung deposition, as particle size decreases, the variety of particles in a unit of house increases along with the entire floor space of the particles. This relationship, illustrated in Table 5-6, indicates that nanoparticles have the propensity to deliver excessive quantities of particulates to the lung. The contribution of nanoparticles to poisonous responses, with special emphasis on their disposition (and factors that affect disposition together with size, composition, floor construction, floor group modification, solubility, and aggregation) are major areas of toxicological and human well being effects analysis (Nel et al. The mechanisms answerable for the elimination or absorption of particulate matter from the alveoli are less clear than those answerable for the elimination of particles deposited in the tracheobronchial tree. The origin of the thin fluid layer in the alveoli might be a transudation of lymph and secretions of lipids and other parts by the alveolar epithelium. The principal cells answerable for engulfing alveolar debris are the resident alveolar macrophages. These phagocytic cells are found in large numbers in regular lungs and include many phagoTable 5-6 Particle Number and Surface Area for 10 g/m3 Airborne Particles particle diameter (m) 5 2 0. They apparently migrate to the distal finish of the mucociliary escalator and are cleared and eventually swallowed. The endothelial cells lining lymphatic capillaries are permeable to very large molecules (molecular weight >106) and for particles, although the rate of penetration is low above a molecular weight of 10,000. Nevertheless, the lymphatic system plays a distinguished position in collecting high-molecular-weight proteins leaked from cells or blood capillaries and particulate matter from the interstitium and the alveolar areas. Particulate matter might remain in lymphatic tissue for lengthy periods, and this explains the phenomenon of "dust retailer of the lungs. Thus, seems that|it seems that} elimination of particles that enter the alveoli is largely the dissolution and vascular transport. Overall, human skin comes into contact with many poisonous chemical compounds, however exposure is usually restricted by its comparatively impermeable nature. However, some chemical compounds may be absorbed by the skin in adequate quantities to produce systemic effects. For example, there are several of} pesticides for which deadly exposures have occurred in agricultural employees after absorption through intact skin (see Chap. In addition, there are numerous chemical compounds that enhance tumor improvement in other organs after dermal utility. The dermis is the outermost layer and includes keratinocytes which might be} metabolically competent and capable of to} divide. Dividing keratinocytes in the stratum germinativum displace maturing keratinocyte layers upward until they attain the outermost layer, the stratum corneum. The stratum corneum includes densely packed keratinized cells which have lost their nuclei and are biologically inactive.
Best 250mg griseofulvin
Cardiac Arrhythmia Cardiac rhythms beneath physiological conditions are set by pacemaker cells may be} usually capable of creating spontaneous depolarization and responsible for generating the cardiac rhythm, the so-called automated rhythm. A cardiac rhythm that deviates from the conventional automated rhythm is called as} cardiac arrhythmia, usually manifested in the type of tachycardia (fast heart rate). There are a number of} courses of tachycardia, together with sinus tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and torsade de pointes (TdP) (a life-threatening ventricular tachycardia). In addition, subclasses such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and accelerated idioventricular rhythm present further description of the manifestations of arrhythmia. Recognition of persistent cardiac toxicity in the pathogenesis of cardiomyopathy is of clinical relevance, and this knowledge can be utilized to stop and deal with patients with toxicologic cardiomyopathy. Myocardial Degeneration and Regeneration Myocardial degeneration is final word|the final word} response of the center to toxic publicity, which could be measured by each morphological and functional degenerative phenotypes. In the past, the center has been considered incapable of regenerating, in order that cardiac damage in the type of cell loss or scar tissue formation was considered everlasting injury to the center. However, proof now signifies myocardial regeneration and recovery from cardiomyopathy. Cardiac toxic responses or injury are now are|are actually} divided into reversible and irreversible. Myocardial Degenerative Responses Myocardial cell death, fibrosis (scar tissue formation), and contractile dysfunction are considered as degenerative responses, finish up} in|which might find yourself in|which can lead to} cardiac arrhythmia, hypertrophy, and heart failure. Both acute and persistent toxic stresses can result in irreversible degeneration, depending on whether or not or not the cardiac repair mechanisms are overwhelmed. Both apoptosis and necrosis occur in the process of myocardial cell death, which will be discussed in the subsequent section. Myocardial cell death is accompanied by hypertrophy of the remaining cardiac myocytes in order that in the hypertrophic heart, the whole number of cardiac myocytes is decreased however the dimension or quantity of individual cells is elevated. During myocardial remodeling after cell death, not solely is there a rise in the dimension of cardiac myocytes, but additionally cardiac fibrosis occurs. The activities of these enzymes are altered during the processes of fibrogenesis and fibrinolysis. Under toxic stress situation, the imbalance between fibrogenesis and fibrinolysis leads to enhanced fibrogenesis and extra collagen accumulation- fibrosis. Toxic Effect on Myocardial Regeneration the mainstay of cardiac medication and remedy has centered on the idea that the center is a terminally differentiated organ and that cardiac myocytes are incapable of proliferating. Thus, cell death would result in a everlasting loss of the whole number of cardiac myocytes. However, this view has been challenged just lately because of of} the identification of cardiac progenitor cells (Anversa et al. These cells are characterized and proposed to be responsible for cardiac repair as a result of|as a end result of} these cells can make myocytes and vascular constructions. They are self-renewing, clonogenic, and multipotent, as demonstrated by reconstitution of infarcted heart by intramyocardial injection of cardiac progenitor cells or the local activation of these cells by growth components. One speculation is that when extreme injury to cardiac progenitor cells occurs, the potential for recovery from extreme cardiac damage would be restricted. The elimination of scar tissue or fibrosis in the myocardium prior to now has been considered unimaginable. Many toxic insults affect on} the capability of angiogenesis in the myocardium, in order that cardiac ischemia occurs. The combination of cardiac ischemia and the direct toxic insults to cardiomyocytes represent synergistic injury to the center. During regeneration, coronary arterioles and capillary constructions are fashioned to bridge the lifeless tissue (scar tissue) and supply nutrients for the survival of the regenerated cardiomyocytes. There is an orderly organization of myocytes within the myocardium and a well-defined relationship between the myocytes and the capillary community. This proportion is altered beneath cardiac toxic conditions; both toxicologic hypertrophy or diminished capillary formation can result in hypoperfusion of myocytes in the myocardium. Unfortunately, our understanding of the toxic results on myocardial angiogenesis is proscribed. The issue associated to whether or not or not toxicologic cardiac lesions are reversible has not been explored. However, speculated that there would be reversible and irreversible manifestations of the cardiac response to toxic insults. Myocardial Cell Death and Signaling Pathways Apoptosis and Necrosis Toxic insults set off a series of reactions in cardiac cells leading to measurable changes. However, extreme injuries will result in cell death in the modes of apoptosis and necrosis. If the cell survives the insults, structural and functional adaptations will happen. The loss of cardiac myocytes is a fundamental half of} myocardial damage, which initiates or aggravates cardiomyopathy. An important mode of myocardial cell loss is apoptosis, which has been demonstrated in heart failure patients (Olivetti et al. Myocardial apoptosis has been shown to play an important position in cardiac toxic results induced by Adriamycin (Kang et al. Exposure of major cultures of cardiomyocytes to cadmium additionally induces apoptosis (El-Sherif et al. At first glance, this quantity appears to be too insignificant to account for myocardial pathogenesis. Myocytes that undergo apoptosis are misplaced and may not be not|will not be} changed beneath toxicologic conditions. Although chance of|the potential of|the potential for} myocardial regeneration has been recognized (Anversa et al. Adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy is an efficient example for the pathogenesis resulting from each degeneration and inhibition of regeneration. Necrosis is a time period that had been widely used to describe myocardial cell death prior to now. Myocardial infarction, particularly, had been considered as a consequence of necrosis (Eliot et al. It is now recognized that apoptosis contributes considerably to myocardial infarction (Yaoita et al. The contribution of necrosis to cardiomyopathy induced by environmental toxicants and pollution is particularly important. Apoptosis and necrosis have been initially described as two distinct forms of cell death clearly distinguished (Wyllie, 1994). However, these two modes of cell death can occur concurrently in tissues and cultured cells. A downstream controller, nonetheless, might direct cells toward a programmed execution of apoptosis. If the apoptotic program is aborted earlier than this management point and the initiating stimulus is extreme, cell death might occur by necrosis (Leist et al. The specificity of this molecular probe to determine apoptosis has been confirmed by different strategies such as twin labeling of TdT and caspase-3 (Frustaci et al. Proportion of apoptotic and necrotic cell death in the heart could be estimated by the mix of the above procedures. Distinguishing apoptotic myocytes from non-myocytes in the myocardium is one other downside to overcome. The gold standard for identification of apoptotic cells is morphological examination by electron microscopy. Mitochondrial Control of Cell Death the position of mitochondria in myocardial response to toxicants nicely as|in addition to} therapeutic medication has long been a focus of investigation. Mitochondrial management of cell death is an important subject of apoptotic analysis during the last decade. Because the inside membrane has a bigger floor area than the outer membrane, mitochondrial swelling may cause the rupture of the outer membrane, releasing intermembrane proteins into the cytosol (Reed et al. Another possible mechanism that leads to mitochondrial cytochrome c release is the action of Bax, a proapoptotic protein of the Bcl-2 family (Adams and Cory, 1998). Mitochondrial cytochrome c release is a crucial issue controlling cardiomyocyte apoptosis. It has been shown that Bax is translocated from cytosol to mitochondria and types pores in mitochondrial outer membranes, leaving the inside membranes intact (Jurgensmeier et al. The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into the cytosol is a crucial initiation step in myocardial apoptosis.
Syndromes
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Chronic kidney failure
- Color of the area changes as the amount of oxygen supplying the area decreases
- Seizures
- A diet high in meat products or cranberries can decrease your urine pH.
- Acts out social encounters through play activities
Order 250mg griseofulvin
They may be be} associated to each other as parasite and host or may be be} two tissues in a single organism. This biological variety interferes with the flexibility of ecotoxicologists to predict the poisonous results of a chemical in a single species (humans) from experiments performed in one other species (laboratory animals). In agriculture, for instance, there are fungi, insects, and even competitive crops that injure the crop, and thus selective pesticides are needed. Drugs and other chemical substances used for selective poisonous functions are selective for certainly one of two reasons. Selectivity ensuing from differences in distribution normally is caused by differences within the absorption, biotransformation, or excretion of the toxicant. The selective toxicity of an insecticide spray may be be} partly outcome of} a larger floor area per unit weight that causes the insect to take up a proportionally larger dose than does the mammal being sprayed. The effectiveness of radioactive iodine within the remedy of hyperthyroidism (as nicely as its thyroid carcinogenicity) end result of|as a end result of} of} the selective capability of the thyroid gland to accumulate iodine. A major reason why chemical substances are poisonous to one, but to not one other, sort of tissue is that there are differences in accumulation of the last word|the ultimate word} poisonous compound in varied tissues. This, in turn, may be be} outcome of} differences within the capability of varied tissues to transport or biotransform the chemical into the last word|the ultimate word} poisonous product. Selective toxicity caused by differences in comparative cytology is exemplified by a comparison of plant and animal cells. Plants differ from animals plenty of} ways-for instance, absence of a nervous system, an environment friendly circulatory system, and muscular tissues the presence of a photosynthetic mechanism and cell walls. Selective toxicity additionally be|may additionally be|can be} a result of a difference in biochemistry within the two kinds of cells. Species differences in response to carcinogenic chemical substances represent an essential problem in regulatory threat assessment. The validity of this method after all depends on by} the relevance of the experimental animal model to humans. For instance, mice are extremely proof against the hepatocarcinogenic results of the fungal toxin aflatoxin B1. Mice specific this enzyme constitutively, whereas rats normally specific a carefully associated type with much much less detoxifying activity toward aflatoxin epoxide. Thus, dietary remedy can dramatically change the sensitivity of a species to a carcinogen. Other examples during which massive species differences in response to carcinogens have been noticed embody the event of renal tumors from 2,3,5-trimethylpentane and d-limonene in male rats (Lehman-McKeeman and Caudill, 1992), the production of liver tumors from "peroxisomal proliferators" such as the antilipidemic drug clofibrate and the widespread solvent trichloroethylene (Roberts, 1999), and the induction of nasal carcinomas in rats after inhalation publicity to formaldehyde (Monticello and Morgan, 1997). Identifying the mechanistic basis for species differences in response to chemical substances is a crucial a part of} toxicology solely through a thorough understanding of these differences can the relevance of animal information to human response be verified. Individual Differences in Response Even within a species, massive interindividual differences in response to a chemical can happen because of subtle genetic differences. Hereditary differences in a single gene that happen in more than 1% of the inhabitants are referred to as genetic polymorphism and may be be} answerable for idiosyncratic reactions to chemical substances, as discussed earlier on this chapter. However, genetic polymorphism may have other essential but much less dramatic results than those described for acute idiosyncratic responses (such as that occurring in pseudocholinesterase-deficient individuals after succinylcholine exposure). This enzyme has no apparent vital physiologic operate, and thus homozygotes for the gene deletion (e. Chapter 6 offers additional examples of genetic differences in biotransformation enzymes essential determinants of variability in individual susceptibility to chemical exposures. Genetic polymorphism in physiologically essential genes may be answerable for interindividual differences in poisonous responses. For instance, research in transgenic mice have shown that mice possessing one copy of a mutated p53 gene (a so-called tumor suppressor gene; see Chap. For instance, retinoblastoma is a largely inherited type of most cancers that arises because of the presence of two copies of a faulty tumor suppressor gene (the Rb gene) (Wiman, 1993). This is the case each copies of the gene have to be nonfunctional for the disease to develop. With one mutated copy current genetically, the likelihood of buying a mutation of the second gene (potentially from publicity to environmental mutagens) is way greater than the likelihood of buying impartial mutations in each copies of the gene as can be necessary in individuals with two regular Rb alleles. Simple blood exams may finally be developed that enable a person to study whether she or he may be be} notably susceptible to particular medicine or environmental pollution. Although basic public} well being significance of data might be be} immense, the disclosure of such data raises many essential moral and authorized points that have to be addressed earlier than wide use of such exams. The examine of "gene-environment" interactions, or "Ecogenetics" (Costa and Eaton, 2006) is a quickly creating subject of substantial relevance to toxicology. It is probably going} that the majority all} of persistent illnesses develop the complex interaction between multiple of} genes and the myriad of environmental elements, together with food regimen, lifestyle, and occupational and/or environmental exposures to poisonous substances. The first is that the effects produced by a compound in laboratory animals, when properly certified, are applicable to humans. On the basis of dose per unit of physique floor, poisonous results in humans are normally in the same range as those in experimental animals. On a physique weight basis, humans are typically more susceptible than are experimental animals. When one has an consciousness of these quantitative differences, applicable safety elements could be utilized to calculate comparatively protected doses for humans. All recognized chemical carcinogens in humans, with the possible exception of arsenic, are carcinogenic in some species but not in all laboratory animals. It has turn into increas- ingly evident that the converse-that all chemical substances carcinogenic in animals are additionally carcinogenic in humans-is not true (Dybing and Sanner, 1999; Grisham, 1997; Hengstler et al. However, for regulatory and threat assessment functions, optimistic carcinogenicity exams in animals are normally interpreted as indicative of potential human carcinogenicity. This species variation in carcinogenic response appears to be due plenty of} situations to differences in biotransformation of the procarcinogen to the last word|the ultimate word} carcinogen (see Chap. The second precept is that publicity of experimental animals to chemical substances in excessive doses is a necessary and valid method of discovering possible hazards in humans. This precept is predicated on the quantal dose�response idea that the incidence of an impact in a inhabitants is greater as the dose or publicity will increase. Practical concerns within the design of experimental model methods require that the variety of animals used in toxicology experiments at all times be small compared with the dimensions of human populations at risk. Obtaining statistically valid outcomes from such small teams of animals requires utilization of} comparatively massive doses in order that the impact will happen incessantly enough to be detected. At the excessive concentrations fed to rats, saccharin forms an insoluble precipitate within the bladder that subsequently ends in persistent irritation of bladder epithelium, enhanced cell proliferation, and finally bladder tumors (Cohen, 1998, 1999). Examples corresponding to this illustrate the importance of considering the molecular, biochemical, and cellular mechanisms answerable for toxicological responses when extrapolating from excessive to low dose and throughout species. Depending on the eventual use of the chemical, the poisonous results produced by structural analogs of the chemical, the poisonous results produced by the chemical itself, contribute to the determination of the toxicology exams that should be performed. These tips are anticipated to be followed when toxicity exams are carried out in support of the introduction of a chemical to the market. The following sections present an overview of fundamental toxicity testing procedures in use today. For a detailed description of these exams, the reader is referred to a number of} authoritative texts on this topic (Williams and Hottendorf, 1999; Hayes, 2001; Jacobson-Kram and Keller, 2001). Typical Tiered Testing Scheme for the Toxicological Evaluation of New Chemicals (From: Wilson et al. Typically, a tiered method is used, with subsequent exams dependent on outcomes of preliminary research. A general framework for the way new chemical substances are evaluated for toxicity is shown in Fig 2-11. Early research require careful chemical analysis of the compound or mixture to assess purity, stability, solubility, and other physicochemical elements that might impact the flexibility of the test compound to be delivered successfully to animals. Once this data is obtained, the chemical structure of the test compound is compared with comparable chemical substances for which toxicological data is already available. Structure-activity relationships may be be} derived from a evaluation of present toxicological literature, and might present additional steering on design of acute and repeated dose experiments, and what specialized exams need to be completed. Once such fundamental data has been compiled and evaluated, the test compound is then administered to animals in acute and repeated dose research. Acute Toxicity Testing Generally, the primary toxicity test performed on a new new} chemical is acute toxicity, decided from the administration of a single publicity. The aims of acute toxicity testing are to: (1) present an estimate of the intrinsic toxicity of the substance, often occasions expressed as an approximate deadly dose (e.
Cheap 250 mg griseofulvin
Unwanted effects are uncommon; some people expertise gastrointestinal signs which are be} lowered by taking the drug with meals. Resistance to oseltamivir emerged in late 2007 amongst seasonal influenza A H1N1 viruses end result of|because of|on account of} a spontaneous mutation at place 274 (His274Tyr) in the neuraminidase enzyme. It is mostly less nicely tolerated than ganciclovir; adverse effects embrace renal toxicity (usually reversible), nausea and vomiting, neurological reactions and marrow suppression. Foscarnet causes a contact dermatitis which can result in unpleasant genital ulcerations due to of} excessive urine drug concentrations; this is doubtlessly preventable with good urinary hygiene. Other unwanted effects embrace bone marrow suppression, nausea and vomiting, and iritis and uveitis, and trigger about 25% of sufferers to discontinue remedy. Valganciclovir is an oral prodrug of ganciclovir that gives systemic concentrations almost as excessive as these following. Pegylated (bound to polyethylene glycol) interferon a-2a is simpler than normal interferon a and is now the standard of look after sufferers with persistent hepatitis C infection. Over 50% of sufferers with hepatitis C respond to the combination of pegylated interferon plus ribavirin, and 30�40% to peg-interferon alone. Hepatitis D (d agent co-infection with hepatitis B) requires a much larger dose of interferon to get hold of a response, and relapse may yet happen when the drug is withdrawn. Ribavirin is effective by mouth (t� 45 h) for decreasing mortality from Lassa fever and hantavirus infection (possibly also other viral haemorrhagic fevers and West Nile virus) and, when combined with interferon a-2b or peginterferon, for persistent hepatitis C infection (see below). Systemic ribavirin is a crucial teratogen, and it may trigger cardiac, gastrointestinal and neurological adverse effects. Adverse reactions are widespread and embrace an influenzalike syndrome (naturally produced interferon liable for signs in natural influenza infection), fatigue and melancholy, which respond to decreasing the dose however are likely to|are inclined to} enhance after the first week. Other effects are anorexia (sufficient to induce weight loss), alopecia, convulsions, hypotension, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias and bone marrow melancholy (which may respond to granulocyte colony-stimulating components and erythropoietin). Interferons inhibit the metabolism of theophylline, growing its impact, and autoimmune ailments similar to thyroiditis induced or exacerbated. Transient fever and native injection web site reactions are seen and infrequently, gastrointestinal disturbance, rash, leucopenia or disturbed liver perform happen. Treatment for 2�3 months leads to gradual clearance of warts in about 50% of sufferers, and recurrence is less widespread than after physical removing. Inosine pranobex is reported to stimulate the host immune response to virus infection and has been used for mucocutaneous herpes simplex, genital warts and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. It is administered by mouth and metabolised to uric acid, so must be used with caution in sufferers with hyperuricaemia or gout. Interferons are categorized as a, b or g in accordance with their antigenic and physical properties. Interferon a-2a and -2b also enhance the manifestations of viral hepatitis, however responses differ in accordance with the infecting agent. When multiple of} areas are affected, particularly if the scalp or nails are included, and when topical remedy fails, oral itraconazole or terbinafine are used. Classification of antifungal brokers � Drugs that disrupt the fungal cell membrane: n polyenes. Candida infections Cutaneous infection is mostly handled with topical amphotericin, clotrimazole, econazole, miconazole or nystatin. An underlying explanation must be sought when a patient fails to respond to these measures. Candidiasis of the alimentary tract mucosa responds to amphotericin, fluconazole, ketoconazole, miconazole or nystatin as lozenges (to suck, for oral infection), gel (held in the mouth before swallowing), suspension or tablets. Vaginal candidiasis is handled by clotrimazole, econazole, isoconazole, ketoconazole, miconazole or nystatin as pessaries or vaginal tablets or cream inserted a few times a day with cream or ointment on surrounding skin. Failure due to of} a concurrent intestinal infection inflicting re-infection, and nystatin tablets given by mouth 8-hourly with the native treatment. Isolation of candida from the bloodstream or intravenous catheter ideas of sufferers with predisposing components for systemic candidasis. It is handled with excessive dose co-trimoxazole at 120 mg/kg every day in two to four divided doses for 21 days by mouth or. Although co-trimoxazole resistance is uncommon, sufferers who fail to reply or are intolerant may benefit from pentamidine or primaquine plus clindamycin. The ensuing deformity of the membrane allows leakage of intracellular ions and enzymes, inflicting cell dying. Those polyenes which have helpful antifungal exercise bind selectively to ergosterol, the most important sterol in fungal (but not mammalian) cell walls. Amphotericin (amphotericin B) Amphotericin is absorbed negligibly from the gut and should be given by. The authors are grateful to the Chairman of the Editorial Board for permission to publish the material. The t� is 15 days and, after stopping treatment, drug persists in the physique for a number of} weeks. Amphotericin is at current the drug of selection for many systemic fungal infections (but see Table 15. A conventional course of treatment for filamentous fungal infection lasts 6�12 weeks, during which minimal of|no less than} 2 g amphotericin is given (usually zero. Lipid-associated formulations of amphotericin supply the prospect of lowered danger of toxicity whereas retaining therapeutic efficacy. In an aqueous medium, a lipid with hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties will type vesicles (liposomes) comprising an outer lipid bilayer surrounding an aqueous centre. The AmBisome formulation incorporates amphotericin in a lipid bilayer (55�75 nm diameter) from which the drug is launched. Lipid-associated formulations simpler for some indications outcome of|as a result of} greater doses 224 Viral, fungal, protozoal and helminthic infections (3 mg/kg daily) given quickly and safely. Gradual escalation of the dose limits poisonous effects, which may be deemed justifiable in lifethreatening infection if conventional amphotericin is used. Renal impairment is invariable, though lowered by adequate hydration; nephrotoxicity is reversible, minimal of|no less than} in its early phases. Hypokalaemia and hypomagnesaemia (due to distal renal tubular acidosis) may necessitate alternative remedy. Other adverse effects embrace anorexia, nausea, vomiting, malaise, abdominal, muscle and joint pains, loss of weight, anaemia, and fever. Severe febrile reactions are mitigated by hydrocortisone 25�50 mg before each infusion. Lipid-formulated preparations are associated with adverse reactions much less often, however fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, nephrotoxicity, electrolyte disturbance and occasional nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity are reported. Impairment of testosterone synthesis may trigger gynaecomastia and decreased libido in men. Of specific concern is impairment of liver perform, starting from a transient improve in ranges of hepatic transaminases and alkaline phosphatase to severe damage and dying. Nystatin (named after New York State Health Laboratory) Nystatin simply too|is merely too} poisonous for systemic use. Like all imidazoles, ketoconazole binds strongly to a number of} cytochrome P450 isoenzymes, inhibiting their motion and thereby growing effects of oral anticoagulants, phenytoin and ciclosporin, and growing the chance of cardiac arrhythmias with terfenadine. Tioconazole is used for fungal nail infections, and isoconazole and fenticonazole for vaginal candidiasis. Azoles the antibacterial, antiprotozoal and anthelminthic members of this group are described in the appropriate sections. Antifungal azoles comprise the next: � Imidazoles (ketoconazole, miconazole, fenticonazole, clotrimazole, isoconazole, tioconazole) intervene with fungal oxidative enzymes to trigger deadly accumulation of hydrogen peroxide; they also reduce the formation of ergosterol, an important constituent of the fungal cell wall which thus becomes permeable to intracellular constituents. Triazoles (fluconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole) damage the fungal cell membrane by inhibiting lanosterol 14-a-demethylase, an enzyme essential to ergosterol synthesis, resulting in accumulation of poisonous sterol precursors. Fluconazole Fluconazole is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is excreted largely unchanged by the kidney (t� 30 h). It may trigger gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, reversible alopecia, elevated ranges of liver enzymes and allergic rash, however is mostly nicely tolerated. Animal research demonstrate � 225 Section three Infection and irritation triazoles in opposition to yeasts and is more reliably and quickly absorbed than itraconazole by mouth, however cross-resistance between these brokers is common.
Safe griseofulvin 250mg
Oral iron remedy is commenced with 200 mg ferrous sulphate (non-enteric coated) administered 3 times day by day. Reduced iron absorption: coeliac illness, postgastrectomy and gluten-induced enteropathy. Blood loss: menstruation, menorrhagia, gastrointestinal malignancy, other causes of chronic haemorrhage (e. The main causes are: -� Inadequate dietary consumption: young infants with inadequate consumption of solids (18 months to 3 years), poverty and poor nutrition. The serum ferritin concentration correlates with physique iron shops; serum ferritin of <15 mg/L is virtually specific for iron deficiency. Sustained or slow-release iron preparations have iron bound to resins, chelates (sodium feredetate) or plastic matrices (e. Iron is released within the lower small gut and it has subsequently bypassed the duodenum, the positioning of maximal iron absorption earlier than changing into available. These effects can usually be ameliorated by reducing the dose, using divided doses, switching to another iron salt (e. Managing the gastrointestinal disturbance is important to ensure the the} affected person continues remedy. Failure of oral iron remedy is most commonly due to of} poor compliance, persistent bleeding or incorrect analysis. This is more than likely in being pregnant due to of} excessive fetal necessities for both haematinics. In the anaemia of chronic illness a ferritin < 50 mg/L could also be} related to decreased storage iron, whereas ferritin levels of > 50 mg/L usually point out the presence of iron shops. Measurement of serum soluble transferrin receptor (increased in iron deficiency but not by inflammation) may help in differentiating iron deficiency from the anaemia of chronic illness. Management of iron deficiency and prophylactic iron administration Management of iron deficiency requires: 1. Oral iron preparations are the remedy of selection due to of} their effectiveness, security and low value. Administration of 200 mg ferrous sulphate 3 times day by day offers one hundred eighty mg elemental iron per day; as much as} 30% of the orally administered iron shall be absorbed. Therapy must be continued for an extra 3 months and until the haemoglobin has normalised and iron shops replenished. Formulations embrace ferrous sulphate answer (5 mL accommodates 12 mg elemental iron), iron polymaltose solutions and polysaccharide�iron complex (5 mL accommodates one hundred mg elemental iron). Prophylactic oral iron is acceptable in being pregnant, menorrhagia, following partial or complete gastrectomy, for sufferers with chronic renal illness receiving erythropoietin, within the early remedy of Table 30. Iron sucrose (ferric hydroxide complexed with sucrose, 20 mg/mL) which is delivered by gradual intravenous injection or infusion (not beneficial for children). Adverse effects of intravenous iron embrace quick, extreme and probably life-threatening anaphylactoid reactions, fever and arthropathy. Patients ought to subsequently be intently monitored throughout administration and services for cardiopulmonary resuscitation must be available. A historical past of allergic problems including asthma, eczema and anaphylaxis is a contraindication to parenteral iron. This is to stop adverse reactions as a result of|because of|on account of} saturation of transferrin binding capability resulting in a excessive, unbound plasma iron concentration. Chapter 30 the anaemia of chronic illness occurs in response to chronic infective or inflammatory processes and malignancies and should be distinguished from iron deficiency. Increased hepcidin expression reduces intestinal iron absorption and will increase iron stored in macrophages and hepatocytes. If the anaemia is sufficiently extreme to impair quality of life, red cell transfusions could also be} indicated. Drug interactions Iron chelates quantity of|numerous|a selection of} medication including tetracyclines, penicillamine, methyldopa, levodopa, carbidopa, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin, thereby reducing their absorption. Administration of these medication must be separated from the iron remedy by a minimal of 2. Chronic iron overload Severe tissue iron overload may result up} from extreme absorption (hereditary haemochromatosis), frequent or chronic red cell transfusion remedy (> one hundred units as in thalassaemia or myelodysplasia2) resulting in transfusion haemosiderosis and extreme parenteral iron remedy. In haemochromatosis iron is eliminated by weekly venesection (450 mL blood eliminates 200�250 mg iron) until the ferritin has normalised and thereafter, as required, to maintain the ferritin at < 50 mg/L. Iron chelation remedy has been available the explanation that} Seventies and is used when venesection is contraindicated, most commonly for transfusion haemosiderosis. In thalassaemia, iron chelation remedy is generally commenced after 1 yr of month-to-month blood transfusions. Her blood film shows normochromic normocytic red cells with a light neutrophilia. Analysis of her iron standing shows serum iron of three mmol/L (normal � 14�32), transferrin 1. A 26-year-old topic with b-thalassaemia main had been transfused with 404 units of blood over his lifetime. His iron shops were so excessive (estimated at above one hundred g) that he triggered a metal detector at an airport security checkpoint (Jim R T S 1979 Lancet ii:1028 [letter]). Severe circumstances have acidosis and cardiovascular collapse which can proceed to coma and dying. Desferrioxamine is run by subcutaneous injection or intravenously (30�50 mg/kg/day) over an 8�12 h interval, 5�7 nights per week. Compliance with remedy is a problem due to the gradual parenteral administration. Desferrioxamine complexes with ferric iron to form ferrioxamine which is excreted in urine and in bile. Simultaneous administration of ascorbic acid must be prevented; although ascorbic acid will increase the availability of free iron for chelation, it additionally mobilises iron from reticuloendothelial storage sites to a probably poisonous pool in parenchymal cells. Serious adverse effects of desferrioxamine are unusual but do embrace anaphylactic reactions. There is danger of potentially deadly adult respiratory misery syndrome if infusion proceeds beyond 24. Orally absorbed iron chelators have turn into available up to now decade and provides improved compliance and quality of life for those who|for many who|for individuals who} require lifelong iron chelation. The two main products available are: Deferiprone (3-hydroxy-1,2-dimethylpyridin-4-one). It can stop iron accumulation but not essentially defend in opposition to iron-induced organ harm. Deferiprone is absorbed within the higher gastrointestinal tract and is principally excreted through the kidneys; the elimination half-life is 2�3. It is much less efficient than desferrioxamine and carries a threat of arthropathy, neutropenia and agranulocytosis. Combination remedy of deferiprone with desferrioxamine is efficient within the management of cardiac siderosis. This is a tridentate oral iron chelator that mobilises stored iron by binding selectively to ferric iron. Side-effects embrace gastrointestinal disturbances, skin rash, cytopenias and increased creatinine. Phase 2 Improvement occurs, lasting 6�12 h; could also be} sustained or may deteriorate to subsequent part. Phase 3 Jaundice, hypoglycaemia, bleeding, encephalopathy, metabolic acidosis and convulsions are followed by cardiovascular collapse, coma and sometimes dying 48�60 h after ingestion. Phase 4 1�2 months later: scarring and stricture may cause higher gastrointestinal obstruction. Poisoning is extreme if the plasma iron concentration exceeds the entire iron binding capability (upper limit seventy five mmol/L) or plasma becomes pink due to of} the formation of ferrioxamine. Desferrioxamine is run by intravenous infusion (not exceeding 15 mg/kg/h and maximum 80 mg/kg in 24 h) to chelate serum free iron. Vitamin B12 is produced solely by microorganisms and humans get hold of it by ingesting foods of animal origin. Iron poisoning and acute overdose Iron poisoning is commonest in children, is normally accidental and significantly harmful. Most vitamin B12 (70%) within the blood is bound to haptocorrin (holohaptocorrin, formerly transcobalamin I) which is taken up by and stored within the liver.
Safe griseofulvin 250 mg
The examine of perinatal lung toxicology is a growing area that guarantees to have appreciable impact on future hazard evaluations and risk evaluation of environmental pollutants for infants and younger youngsters. Table 15-2 lists widespread toxicants which are be} identified to produce acute and chronic lung injury in humans. In the following sections, quantity of} examples of our present understanding of lung injury on the mechanistic degree are mentioned, with emphasis on agents instantly liable for human lung illness. Airborne Agents That Produce Lung Injury in Humans Asbestos the term asbestos describes silicate minerals in fiber kind. The most commonly mined and commercially used asbestos fibers embody the serpentine chrysotile asbestos and the amphiboles crocidolite, anthophyllite, amosite, actinolite, and tremolite. Exposure to asbestos fibers occurs in mining operations and in the construction and shipbuilding industries, where asbestos was at one time broadly used for its highly fascinating insulating and fireproofing properties. During final few|the earlier few|the earlier couple of} a long time, concern about asbestos in older buildings has led to the elimination of asbestos-based insulating material; abatement workers may now characterize an extra population at risk. Fibers 2 m in length may produce asbestosis; mesothelioma is associated with fibers 5 m long, and lung most cancers with fibers larger than 10 m. Once asbestos fibers have been deposited in the lung, they might turn out to be phagocytized by alveolar macrophages. Short fibers are utterly ingested and subsequently eliminated via the mucociliary escalator. Longer fibers are incompletely ingested, and the macrophages turn out to be unable to depart the alveoli. Activated by the fibers, macrophages release mediators corresponding to lymphokines and growth elements, which in turn attract immunocompetent cells or stimulate collagen manufacturing. The surface properties of asbestos fibers seem to be an essential mechanistic component in toxicity. The protection afforded by superoxide dismutase or free radical scavengers in asbestos-related cell injury in vitro means that the generation of active oxygen species and concomitant lipid peroxidation are essential mechanisms in asbestos toxicity. The interplay of iron on the surface of asbestos fibers with oxygen may result in the manufacturing of hydrogen peroxide and the highly reactive hydroxyl radical-events that have been associated with asbestos toxicity (Upadhya and Kamp, 2003). In humans, asbestos causes three forms of lung illness: asbestosis, lung most cancers, and malignant mesothelioma. Asbestosis is characterized by a diffuse increase of collagen in the alveolar partitions (fibrosis) and the presence of asbestos fibers, either free or coated with a proteinaceous material (asbestos bodies). Lung most cancers develops in workers in the asbestos mining business and smoking of cigarettes tremendously enhances risk. There is some discrepancy between observations in case of humans and the findings in animals that inhale asbestos fibers. In animal experiments, chrysotile produces mesothelioma much more readily than do the amphibole fibers. In humans, amphibole fibers are implicated extra often even when the predominant publicity is to chrysotile asbestos. It is possible that in small laboratory animals chrysotile fibers, even if damaged down, are retained longer relative to the life span of the animal than they are in humans, thus explaining the upper price of mesothelioma developed. Silica Inhaled particles of silicon dioxide (silica) trigger a characteristic human lung illness. The illness could also be} acute or chronic; this distinction is essential conceptually because of|as a result of} the pathological consequences are manifested fairly a unique way|in another way}. Acute silicosis occurs solely in subjects uncovered to a very excessive degree of aerosol containing silicon dioxide particles (most often in type of quartz or sand) sufficiently small to be respirable (usually less than 5 m) over a relatively brief interval, typically quantity of} months to quantity of} years. There is fast progression of respiratory failure, normally ending in demise within a yr or two. Uncomplicated silicosis is sort of} completely asymptomatic; little alteration is shown on routine pulmonary operate exams even after the illness is radiographically demonstrable. The X-ray image presents fibrotic nodules, typically in the apical portion of lung. The hilar lymph nodes have peripheral calcifications eggshell calcifications. Simple silicosis may progress into sophisticated silicosis, which is outlined because the presence of conglomerate nodules larger than 1 cm in diameter. As a pure mineral, silicon exists primarily in the type of its dioxide, silica (SiO2), which has a crystalline kind in which a central silicon atom forms a tetrahedron with four shared oxygen atoms. The three principal crystalline isomeric forms are quartz, tridymite, and cristobalite. Stishovite, a rare crystalline variant without the tetrahedral conformation, is biologically inert. Amorphous forms of silica corresponding to kieselguhr and vitreous silica have very low fibrogenic potential. The ubiquitous presence of silica has made it an occupational hazard ever since humans began shaping tools from stone, and silicosis stays a significant industrial hazard all through the world in occupations corresponding to mining and quarrying, sandblasting, and foundry work. The primary elements that affect on} the pathogenicity of silica each in vivo and in vitro, in addition to its structure, are particle size and concentration. Many research have examined the connection of silica particle size to fibrogenicity. In research with humans, probably the most fibrogenic particle size appears to be about 1 m (range 0. In animal experiments (rats, hamsters), the comparable values seem to be 1�2 m (range 0. The pathophysiological foundation of pulmonary fibrosis in chronic silicosis is probably better understood than is the etiology of any other type of lung fibrosis. The function of pulmonary alveolar macrophages in the ingestion of silica as an initiating occasion has been established. Apparently, as a part of} the cytotoxic response of a macrophage to silica ingestion, the macrophage may release cytokines and different substances that trigger fibroblasts to replicate and/or increase their price of collagen biosynthesis. The function of inflammatory cells aside from alveolar macrophages in this process is unknown. Naphthalene Naphthalene occurs in tars and petroleum and is a broadly used precursor chemical for artificial tanning agents, phthalic acid anhydride, carbaryl, and 2-naphthol. In experimental animals, inhaled or parenterally administered naphthalene has shown remarkable species and tissue specificity: it produces extensive and selective necrosis in the bronchiolar epithelium of the mouse but a lot less necrosis in the airways of rats and hamsters. Animals treated with small doses of naphthalene along with inhibitors of cytochrome P-450s present little or no tissue injury, implicating metabolism in the toxicity of this chemical. In rats and different species, together with monkeys, conversion of naphthalene is less stereospecific and the charges of formation of the epoxide are a lot slower than in mice. Naphthalene epoxides may subsequently be conjugated with glutathione and kind adducts which are be} eradicated as mercapturic acids. The epoxide can endure rearrangement to 1-naphthol with subsequent metabolism to quinones, which are doubtlessly poisonous compounds. Naphthalene metabolites bind covalently to cellular proteins which are be} essential in normal cellular homeostasis and protein folding and associated to the mechanism of toxicity by this chemical. Interestingly, in each mice and rhesus monkeys the whole amount of adducted protein is analogous (Lin et al. Animal fashions of belomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis have been used to examine the efficacy of promising antifibrotic medicine (Giri, 2003). Cyclophosphamide is metabolized by the cytochrome P-450 system to two highly reactive metabolites: acrolein and phosphoramide mustard. In the lung, cooxidation with the prostaglandin H synthase system, which has excessive exercise in the lung, is a chance. Although the exact mechanism of action for inflicting lung injury has not been established, research with isolated lung microsomes have shown that cyclophosphamide and its metabolite acrolein initiate lipid peroxidation. In humans, a dose-related pulmonary toxicity is often seen first by a lower in diffusion capacity. Several different chemotherapeutic medicine can produce lung injury and pulmonary toxicity in patients treated with these medicine important drawback (Ramu and Kehrer, 1997). Additional exams consider the distribution of air flow, lung and chest wall compliance, diffusion capacity, and the oxygen and carbon dioxide content material of the arterial and venous blood. The topic is requested first to inhale deeply after which to exhale the air as quickly as attainable.
Kakmachi (Bittersweet Nightshade). Griseofulvin.
- Dosing considerations for Bittersweet Nightshade.
- How does Bittersweet Nightshade work?
- What is Bittersweet Nightshade?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Acne, itchy skin, boils, broken skin, warts, arthritis-like pain, nail bed swelling, eczema, promoting water loss (diuretic), pain relief, and calming nervous excitement.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96584
Safe 250mg griseofulvin
It is administered locally for bladder cancer and subsequently induces solely mild systemic toxicities; however, systemic absorption from the bladder might occur, however valrubicin seems to exhibit a decrease propensity for cardiotoxicity than doxorubicin (Hussar, 2000). Epirubicin is a semisynthetic by-product of daunorubicin approved for treatment of breast cancer. However, epirubicin is more lipophilic than doxorubicin and is biotransformed by the conjugative pathways in the liver, resulting in a shorter half-life and a decrease incidence of cardiotoxicity than with doxorubicin (Hussar, 2000). The free radical speculation has received the most consideration in the understanding of anthrocycline-induced cardiotoxicity. The quinone-like structure of doxorubicin permits this molecule to accept an electron and form a semiquinone radical. Oxidation of the semiquinone back to the mother or father quinone by molecular oxygen results in the formation of superoxide radical ions may be} believed to provoke oxidative stress. Several alternate hypotheses to clarify the cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin have been proposed and tested. It is extremely difficult to dissect the sequences of those modifications, resulting in several of} alternate hypotheses, which can in reality occur sequentially. Many studies have demonstrated that anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity includes induction of apoptosis (Kang et al. Production of superoxide anions by oxidation-reduction biking of doxorubicin on the level of the mitochondria. The semiquinone then additionally be} reoxidized back to the mother or father compound by means of the reduction of molecular oxygen (O2) to the superoxide anion (O-). The mechanism of cardiotoxicity of fluorouracil is unknown, however it may relate to impurities present in business products of the drug, certainly one of which is metabolized to fluoroacetate, a compound that might take part in fluorouracilinduced cardiotoxicity. Cyclophosphamide High doses of cyclophosphamide given to cancer or transplant sufferers might lead to severe hemorrhagic cardiac necrosis. Antimicrobial and Antiviral Agents Cardiotoxicity related to the scientific use of antimicrobial and antiviral drugs is usually noticed in overdosage and in sufferers with preexisting cardiovascular dysfunction. Gentamicin is a representative aminoglycoside and has an inhibitory action on sluggish inward Ca2+ channels in coronary heart muscle. Aminoglycosides inhibit the uptake or binding of Ca2+ at sarcolemmal sites, thus lowering the concentration of membrane-bound Ca2+ obtainable for movement into the myoplasm throughout depolarization of the sarcolemma. The precept mechanism of cardiodepression by gentamicin is the dislocation of Ca2+ from slow-channel-binding sites on the exterior surface of the sarcolemma, outcomes in|which leads to|which finally ends up in} a blockade of the channels (Hino et al. Fluoroquinolones are a group of speedy rising antibacterial chemicals in terms of|when it comes to|by means of} numbers of new drugs launched into the market in the United States. Fluoroquinolone antibacterial drugs embody ciprofloxacin, enoxacin, gatifloxacin, gemifloxacin, grepafloxacin, levofloxacin (levo-rotatory isomer of ofloxacin), lomefloxacin, moxifloxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, sparfloxacin, and trovafloxacin (Pickerill et al. Tetracycline and chloramphenicol have been reported to depress myocardial contractility by direct cardiac myocyte interplay or an oblique impact that lowers Ca2+ concentrations in the plasma or extracellular areas. Tetracylcines are Ca2+ chelating brokers, which clarify the action of tetracyclines on myocardial contractility. Antifungal brokers, similar to amphotericin B, might depress myocardial contractility by blocking activation of sluggish Ca2+ channels and inhibiting the influx of Na+. Ventricular tachycardia and cardiac arrest have been reported in sufferers treated with amphotericin B. Flucytosine is one other antifungal drug that has been related to cardiotoxicity. In fungal cells, flucytosine is transformed to 5-fluorouracil, which then exerts antifungal results. However, flucytosine additionally be} transformed to 5-fluorouracil by gastrointestinal microflora in humans, which then additionally be} absorbed systemically and induce cardiotoxicity as discussed above. In September 2004, Vioxx was voluntarily withdrawn from the market primarily based upon the info from a scientific trial that confirmed after 18 months of use Vioxx increased the relative risk for cardiovascular events, similar to coronary heart attack and stroke (Arellano, 2005). In April 2005, Bextra was faraway from the market primarily based on the potential increased risk for serious cardiovascular adverse events and increased risk of significant skin reactions (e. Emerging data indicates the chance of cardiovascular events additionally be} increased in sufferers receiving Celebrex (Solomon et al. Antihistamines the most severe adverse impact of the secondgeneration histamine H1 receptor antagonists (antihistamines) is their affiliation with life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac dying (Simons, 1994). These antihistamines produce cardiac arrhythmias by blocking the delayed rectifier K+ channel and prolonging action potential duration in cardiac myocytes. The prolonged action potential duration promotes early afterdepolarizations and predisposes the myocardium to ventricular arrhythmias. However, terfenadine also inhibits L-type Ca2+ channels in rat ventricular myocytes at concentrations close to or under that required to inhibit delayed rectifier K+ present (Liu et al. Therefore, both inhibition of Ca2+ and inhibition of K+ present doubtless contribute to the cardiotoxic actions of terfenadine. As a result of cardiotoxicity, both astemizole and terfenadine have been faraway from the United States market. However, the understanding of astemizole- and terfenadine-induced cardiotoxicity continues to be an important consideration in drug growth, and different drugs have demonstrated related scientific limitations (e. Immunosuppressants Rapamycin and tacrolimus might produce adverse cardiovascular results, together with hypertension, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia. Tacrolimus has been proven to be related to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in pediatric sufferers, a situation that was reversed by discontinuation of tacrolimus and administration of cyclosporin A; some of these sufferers developed severe coronary heart failure (Atkison et al. Cisapride is a chemical that has been used as a prokinetic drug for gastrointestinal hypomotility. [newline]Methylxanthines (including caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline), can be present in important portions in coffee, tea, chocolate, soft-drinks, and different meals. Theophylline has been used so much of} decades for the treatment of asthma, although the mechanism of action has not been absolutely understood. The cardiac results of methylxanthines noticed in vivo (including will increase in cardiac output and coronary heart rate) may also be explained by elevated catecholamines, as theophylline has been proven to enhance plasma epinephrine concentrations (Vestal et al. Although it hardly ever occurs, caffeine-associated ventricular arrhythmias have been reported. Interestingly, sildenafil was originally developed as a potential drug for treating angina; however, it was not very efficient for this function and was subsequently developed for treatment of erectile dysfunction, where it produces vasodilation and filling of the corpus cavernosum. Therefore, extrapolation of in vitro data related to cardiac toxicity of natural products to in vivo circumstances is challenging. However, there are some products which have clearly demonstrated cardiac poisonous results, and mechanisms of action of those products have been decided. Catecholamines the naturally occurring sympathomimetic amines, similar to epinephrine and norepinepherine, are potent and may cause deleterious results to the center. The artificial catecholamine, isoproterenol, is able to|is prepared to} cause large necrotic modifications in the myocardium and is usually used as a prototype compound for the research of catecholamine cardiotoxicity, which has been discussed in the therapeutic drugs that cause cardiotoxicity. Steroids and Related Hormones Estrogens, progestins, androgens, and adrenocortical steroids are main steroid hormones produced by mammals together with humans. Myocardial tissue incorporates steroid receptors; subsequently the center serves as a goal organ for steroid results. It also has been proven that cardiac tissue can synthesize steroid hormones, although the capacity for synthesis additionally be} a lot decrease than more classic steroid synthesizing tissues. There are two main mechanisms of action of the hormones: the first is to alter gene expression and the second is to change signaling transduction pathways. Estrogens are synthesized in ovaries, testes, and adrenal glands, and estrogen is an energetic metabolite of testosterone. Synthetic estrogens embody diethylstilbestrol (nonsteroidal), equilin, esterified variations of E2, ethinyl estradiol, mestranol, and quinestrol. Estrogens (frequently in combination with progestins) have been used for over 40 years as oral contraceptive drugs. Naturally occurring and artificial progestins embody desogestrel, hydroxyprogesterone, medroxyprogesterone, norethindrone, norethynodrel, norgestimate, norgestrel, and progesterone. As half of} hormone alternative remedy, progestins serve an opposing position to estrogens. Unfortunately, estrogen treatment opposed with progestins might negate the cardiovascular advantages of estrogens on lipid metabolism (Kalin and Zumoff, 1990). Although progestins could exert deleterious results on the center, more studies are required to investigate mechanisms. Androgens cause adverse cardiovascular results (Rockhold, 1993; Melchert and Welder, 1995).
250mg griseofulvin
Acute inflammatory disease of the liver (viral, alcoholic) and cirrhosis result on} both the functioning of the hepatocytes and blood circulate via the liver. Reduced extraction from the plasma of medication which might be} normally highly cleared in first move via the liver ends in elevated systemic availability of medication such as metoprolol, labetalol and clomethiazole. Many different medication exhibit extended t� and decreased clearance in sufferers with continual liver disease. Renal disease has profound results on the elimination and therefore length of action of medication eradicated by the kidney (see p. Pharmacodynamic modifications � Asthmatic attacks may be precipitated by b-adrenoceptor blockers. Myocardial infarction predisposes to cardiac arrhythmia with digitalis glycosides or sympathomimetics. Myasthenia gravis is aggravated by quinine and quinidine, and myasthenics are intolerant of competitive neuromuscular blocking agents and aminoglycoside antibiotics. More specifically, calcium, for example in milk, interferes with absorption of tetracyclines and iron (by chelation). Substituting protein for fats or carbohydrate within the food plan is related to a rise in drug oxidation rates. Drugs which might be} used long run, where exact plasma concentrations are required. The elderly, for they have a tendency to have multiple of} pathology, and will receive a number of} medication concurrently (see p. Citrus flavinoids in grapefruit (but not orange) juice decrease hepatic metabolism and will lead to toxicity from amiodarone, terfenadine (cardiac arrhythmia), benzodiazepines (increased sedation), ciclosporin, felodipine (reduced blood pressure). For completeness, alterations in drug action attributable to food plan (above) are termed drug�food interactions, and people by herbs drug�herb interactions. We present here an summary of the pharmacological basis for wanted and unwanted, anticipated and surprising results when drug combos are used. Drug interactions are of two principal varieties: � Pharmacodynamic interplay: both medication act on the goal web site of clinical impact, exerting synergism (below) or antagonism. The medication may act on the same or totally different receptors or processes, mediating related biological penalties. Examples include: alcohol � benzodiazepine (to produce enhanced sedation), atropine � b-adrenoceptor blocker (to indirectly reverse b-adrenoceptor blocker overdose). Pharmacokinetic interplay: the medication work together remotely from the goal web site to alter plasma (and different tissue) concentrations in order that the quantity of the drug on the goal web site of clinical impact is altered. Clinical significance of drug interactions the amount of medication listed in any national formulary provides ample scope for potential alteration within the disposition or impact of one drug by one other drug. But, in follow, clinically essential opposed drug�drug interactions become likely with: � � Drugs which have a steep dose�response curve and a small therapeutic index (see p. Purgatives cut back the time spent within the small intestine and give much less opportunity for the absorption of poorly soluble substances such as adrenal corticosteroids and digoxin. Antimicrobials potentiate oral anticoagulants by reducing bacterial synthesis of vitamin K (usually only after antimicrobials are given orally in high dose. Hyaluronidase promotes dissipation of a subcutaneous injection, and vasoconstrictors. Summation or addition occurs when the consequences of two medication having the same action are additive. Potentiation (to make more powerful) occurs when one drug increases the action of one other. Sometimes the 2 medication both have the action concerned (trimethoprim plus sulfonamide), and sometimes one drug lacks the action concerned (benserazide plus levodopa). Inhibitors and inducers of drug transporters can profoundly influence the disposition of medication. Probenecid inhibits the organic anion renal transporter, which decreases the renal clearance of penicillin (usefully prolonging its effect) but additionally that of methotrexate (with hazard of toxicity). Elucidation of the location and function of transport systems will give the reason for, and allow the prediction of, many more drug�drug interactions. Before administration Intravenous fluids provide particular scope for interactions (incompatibilities). Drugs commonly are weak organic acids or bases, produced as salts to improve their solubility. Plainly, the blending of options of salts end result in|may find yourself in|can lead to} instability, which may or most likely not|will not be} visible within the solution. In any scenario involving unfamiliar medication their assist and recommendation ought to be sought. At the site of absorption the complicated setting of the gut provides opportunity for medication to intrude with one another, both instantly and indirectly, by altering gut physiology. Antacids that include aluminium and magnesium form insoluble and non-absorbable complexes with tetracyclines, iron and prednisolone. Milk accommodates adequate calcium to warrant its avoidance as a significant article of food plan with tetracyclines. Colestyramine interferes with the absorption of levothyroxine, digoxin and a few acidic medication. Beneficial interactions are sought in overdose, as with naloxone for morphine overdose (opioid receptor), atropine for anticholinesterase. Unwanted interactions include the loss of the antihypertensive impact of b-blockers with frequent cold remedies containing ephedrine, phenylpropanolamine or phenylephrine, often taken unknown to the physician (their a-adrenoceptor agonist action is unrestrained within the b-blocked patient). Drug-induced hypersensitivity reactions and pharmacogenomics: previous, present and future. Adverse drug reactions as explanation for admission to hospital: potential analysis of 18 820 sufferers. Because of the variety of these components, makes an attempt to make a easy account of the unwanted effects of medication must be imperfect. There is basic settlement that medication prescribed for disease are themselves the cause of|the purpose for} a critical quantity of disease (adverse reactions), starting from mere inconvenience to everlasting incapacity and demise. It is important to take, or to attempt to take, into consideration which results are avoidable (by skilled selection and use) and which unavoidable (inherent in drug or patient). Another drug may be be} pleasant to take, in order that sufferers take it consistently, with benefit, however on uncommon events it may kill someone. More skilful prescribing will cut back avoidable opposed results and which means docs, among all the other claims on their time, must find time better to perceive medication, properly as|in addition to} understanding sufferers and their diseases. Therefore, understand how a lot disease medication do trigger and why they trigger it, in order that preventive measures may be taken. It is humans, in their desire to keep away from suffering and demise, who resolve that some of the the} biological results of medication are fascinating (therapeutic) and others undesirable (adverse). In addition to this arbitrary division, which has 1 From: the treatment worse than the disease. Distinguishing between pure development of a disease and druginduced deterioration is particularly challenging. The following elements are helpful in attributing the cause of|the purpose for} an opposed occasion to a drug: 1. The Toxicity implies a direct action of the drug, often at high dose, damaging cells. All medication, for sensible functions, are toxic in overdose2 and overdose may be absolute or relative; within the latter case an ordinary dose may be be} administered however may be be} toxic because of of} an underlying abnormality within the patient. Mutagenicity, carcinogenicity and teratogenicity (see Index) are particular cases of toxicity. Anaphylactic reactions (within minutes or hours) and hypersensitivity reactions (within weeks) may readily counsel an affiliation, however delayed results such as carcinogenesis or tardive dyskinesia (after years and even decades) present more issue. Most reactions subside when the drug is discontinued, unless an autoimmune response is established, when results persist. This after all invites questions about consistency with the established pharmacology and toxicology of the drug or associated substances. Examples are: vitamin deficiency or opportunistic an infection in sufferers whose normal bowel flora has been altered by antimicrobials; diuretic-induced hypokalaemia inflicting digoxin toxicity. Individuals differ greatly in their susceptibility to medication, these at one excessive of the conventional distribution curve being intolerant of the medication, these on the different, tolerant. The doctor, alchemist and philosopher is thought to be the founding father of chemical therapeutics; he was the primary to use rigorously measured doses of mercury to treat syphilis. Techniques used for postmarketing (Phase 4) research include the observational cohort research and the case�control research. A drug hardly ever or uncommonly induces an in any other case frequent illness: this impact is stay undiscovered.
250 mg griseofulvin
Other binding proteins in the blood embody lipoprotein and a1-acid glycoprotein, both of which carry primary medication similar to quinidine, chlorpromazine and imipramine. Chapter 8 the free, unbound, and due to this fact pharmacologically active percentages of some medication appear in Table 8. In chronic renal failure, hypoalbuminaemia and retention of merchandise of metabolism that compete for binding sites on protein are both liable for the lower in protein binding of medication. Chronic liver illness also leads to hypoalbuminaemia and an increase of endogenous substances similar to bilirubin that may compete for binding sites on protein. Drugs which might be} normally extensively protein sure ought to be used with particular warning, for elevated free concentration of diazepam, tolbutamide and phenytoin have been demonstrated in patients with this situation (see also Prescribing for patients with liver illness, p. Some medication distribute readily to areas of the body other than plasma, as a glance at Table 8. Extensive binding to tissues delays elimination from the body and accounts for the lengthy t� of chloroquine and amiodarone. Metabolism is a common term for chemical transformations that happen within the body and its processes change medication in two major methods by: � lowering lipid solubility � altering organic activity. Altering organic activity the end-result of metabolism often is the abolition of organic activity, but varied steps in between may have the following penalties: 1. Conversion of a pharmacologically active to an inactive substance � this applies to most medication. Conversion of 1 pharmacologically active to one other active substance � this has the effect of prolonging drug motion, as shown beneath. The new metabolite typically has reduced organic activity and completely different pharmacokinetic properties. The principal group of reactions is the oxidations, particularly these undertaken by the (microsomal) mixedfunction oxidases which, as the name indicates, are capable of metabolising extensive variety|all kinds} of compounds. By a posh process, the drug molecule incorporates one atom of molecular oxygen (O2) to type a (chemically active) hydroxyl group and the other oxygen atom converts to water. The following rationalization offers a background to the P450 nomenclature that accompanies accounts of the metabolism of a number of} particular person medication on this book. Induction and inhibition of P450 enzymes is a fruitful supply of drug�drug interactions. Phase I oxidation of some medication results in the formation of epoxides, which are short-lived and extremely reactive metabolites that bind irreversibly through covalent bonds to cell constituents and are poisonous to body tissues. Glutathione is a tripeptide that combines with epoxides, rendering them inactive, and its presence in the liver is part of of} an necessary defence mechanism against hepatic injury by halothane and paracetamol. Conversion of a pharmacologically inactive to an active substance (then called a prodrug). Inactive substance aciclovir colecalciferol Active metabolite(s) aciclovir triphosphate calcitriol and alfacalcidol Comment see p. Wilkinson G R 2005 Drug metabolism and variability among patients in drug response. Hydrolysis (Phase I) reactions create active sites for subsequent conjugation of. Chapter 8 � Renal tubular cells, controlling uptake from the blood, secretion into tubular fluid (and thus excretion) of organic anions. Brain capillary endothelial cells, controlling passage across the blood�brain barrier. The kidney readily eliminates the resulting water-soluble conjugate, or the bile if the molecular weight exceeds 300. Morphine, paracetamol and salicylates type conjugates with glucuronic acid (derived from glucose); oral contraceptive steroids type sulphates; isoniazid, phenelzine and dapsone are acetylated. [newline]Conjugation with a more polar molecule an elimination mechanism for natural substances. Enzyme induction the mechanisms that the body evolved over hundreds of thousands of years to metabolise foreign substances now enable it to meet the fashionable environmental challenges of tobacco smoke, hydrocarbon pollutants, insecticides and medicines. At occasions of excessive publicity, our enzyme systems reply by growing in amount and so in activity. It is convenient here to introduce the topic of carrier-mediated transporter processes whose physiological capabilities embody the passage of amino acids, lipids, sugars, hormones and bile acids across cell membranes, and the safety of cells against environmental toxins. There is an emerging understanding that membrane transporters have a key role in the total disposition of medication to their targeted organs. There are broadly two sorts: uptake transporters, which facilitate, for instance, the passage of organic anions and cations into cells, and efflux transporters, which transport substances out of cells, typically against excessive concentration gradients. Their various places illustrate the potential for transporters extensively to result on} the distribution of medication, particularly in: Inducing substances in general share some necessary properties: they have an inclination to be lipid soluble, are substrates, though typically only minor ones. The time for onset and offset of induction is determined by} the rate of enzyme turnover, but important induction usually occurs within a number of} days and it passes off over 2�3 weeks following withdrawal of the inducer. Thus, certain medication can alter the capacity of the body to metabolise different substances together with medication, especially in long-term use; this phenomenon has implications for drug therapy. More than 200 substances induce enzymes in animals however the record of confirmed enzyme inducers in humans is more restricted, as set out beneath. Substances that cause enzyme induction in humans � barbecued meats � barbiturates � Brussels sprouts � nevirapine � phenobarbital � phenytoin Continued Parts of this section are based mostly on the evaluation by Ho R H, Kim R B 2005 Transporters and drug therapy: implications for drug disposition and illness. A patient who turns into enzyme induced by taking rifampicin is more probably to|prone to} develop liver toxicity after paracetamol overdose by elevated production of a hepatotoxic metabolite. Enzyme inhibition by medication the basis of a number of|numerous|a variety of} clinically necessary drug interactions (see p. Enzyme induction is related to drug therapy end result of|as a result of}: � Clinically necessary drug�drug (and drug�herb18) interactions may result, for instance, in failure of oral contraceptives, lack of anticoagulant control, failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy. Antiepilepsy medication speed up the breakdown of dietary and endogenously formed vitamin D, producing an inactive metabolite � in effect a vitamin D deficiency state, which can result up} in|which may find yourself in|which can lead to} osteomalacia. The accompanying hypocalcaemia can improve the tendency to matches and a convulsion may lead to fracture of the demineralised bones. Tolerance to drug therapy may end in and provide an explanation for suboptimal therapy. Enzyme induction brought on by heavy alcohol drinking or heavy smoking an unrecognised cause for failure of a person to achieve the expected response to a standard dose of a drug. To keep away from repetition the following account refers to the drug whereas the processes cope with both drug and metabolites. The fee at which a drug enters the glomerular filtrate is determined by} the concentration of free drug in plasma water and on its molecular weight. Uptake and efflux transporters in proximal renal tubule cells transfer organic anions and cations between the plasma and the tubular fluid (see p. Clearance Elimination of a drug from the plasma is quantified in terms of|when it comes to|by way of} its clearance. The term has the identical meaning as the familiar renal creatinine clearance, which is a measure of removal of endogenous creatinine from the plasma. [newline]Clearance values can present useful information about the organic destiny of a drug. There are pharmacokinetic strategies for calculating total body and renal clearance, and the difference between these represents hepatic clearance. If a drug has a renal clearance in extra of this, then the kidney tubules must actively secrete it. As the tubular epithelium has the properties of a lipid membrane, the extent to which a drug diffuses again into the blood will rely upon its lipid solubility. If the fluid turns into more alkaline, an acidic drug ionises, turns into less lipid soluble and its reabsorption diminishes, but a primary drug turns into unionised (and due to this fact more lipid soluble) and its reabsorption increases. Manipulation of urine pH features useful expression with sodium bicarbonate given to alkalinise the urine for salicylate overdose. Even small amounts, nonetheless, may typically be of significance for the suckling baby, whose drug metabolic and eliminating mechanisms are immature. While most medication taken by the mom pose no hazard to the kid, exceptions to this remark happen end result of|as a result of} some medication are inherently poisonous, or transfer to milk in important amounts, or there are identified antagonistic effects, as beneath. Faecal elimination When any drug meant for systemic effect is taken by mouth a proportion may remain in the bowel and be excreted in the faeces. Some medication are meant not be absorbed from the gut, as an goal of therapy. The cells of the intestinal epithelium comprise a number of} carrier-mediated transporters that control the absorption of medication. Drug in the blood may diffuse passively into the gut lumen, depending on its pKa and the pH difference between blood and gut contents. The effectiveness of activated charcoal by mouth for drug overdose relies upon partly on its adsorption of such subtle drug, and subsequent elimination in the faeces (see p.
Purchase griseofulvin 250 mg
The era of reactive oxygen species leads to oxidation of lens membrane proteins and lipids. A crucial pathway in the growth of highmolecular-weight aggregates entails the oxidation of protein thiol groups, particularly in methionine or cysteine amino acids, that leads to the formation of polypeptide hyperlinks by way of disulfide bonds, and in flip, high-molecular-weight protein aggregates (Patterson and Delamere, 1992; Ottonello et al. Oxidation of membrane lipids and proteins can also impair membrane transport and permeability. The cornea absorbs about 45% of sunshine with wavelengths under 280 nm, however only about 12% between 320 and four hundred nm. The lens absorbs much of the light between 300 and four hundred nm and transmits four hundred nm and above to the retina (Patterson and Delamere, 1992). Absorption of sunshine vitality in the lens triggers selection of|quite lots of|a wide range of} photoreactions, together with the era of fluorophores and pigments that result in the yellow-brown coloration of the lens. Sufficient exposure to infrared radiation, as happens to glassblowers, or microwave radiation may even produce cataracts by way of direct heating of the ocular tissues. Drugs and different chemicals can function mediators of photoinduced toxicity in the cornea, lens or retina (Dayhaw-Barker et al. Chemical buildings probably to|prone to} participate in such phototoxic mechanisms embody those with tricyclic, heterocyclic or porphyrin ring buildings end result of|as a result of}, with light, they produce secure triplet reactive molecules leading to free radicals and reactive oxygen species. The propensity of chemicals to cause phototoxic reactions can be predicted utilizing photo-physical and in vitro procedures (Roberts, 2001; Glickman, 2002; Roberts, 2002). The resulting covalent corticosteroid�crystallin adducts could be high-molecularweight light-scattering complexes. Whatever mechanism is accountable, these results illustrate the significance of routine ophthalmologic screening of patients receiving chronic corticosteroid remedy. Naphthalene Accidental exposure to naphthalene ends in cortical cataracts and retinal degeneration (Grant, 1986; Potts, 1996). Subsequent studies utilizing biochemical and pharmacologic techniques, in vitro assays, and transgenic mice showed that aldose reductase in the rat lens is a major protein related to naphthalene dihydrodiol dehydrogenase activity and that lens aldose reductase is the enzyme responsible for the formation of naphthalene dihydrodiol (Sato, 1993; Lee and Chung, 1998; Sato et al. In addition, in vivo and in vitro studies have shown that aldose reductase inhibitors stop naphthalene-induced cataracts (Lou et al. Phenothiazines It has been known because the that} Nineteen Fifties that schizophrenics receiving phenothiazine drugs as anti-psychotic medicine develop pigmented deposits of their eyes and skin (Grant, 1986; Potts, 1996). The pigmentation begins as tiny deposits on the anterior surface of the lens and progresses, with increasing dose, to contain the cornea as properly. The phenothiazines combine with melanin to form a photosensitive product that reacts with daylight, inflicting formation of the deposits. The amount of pigmentation is related to the dose of the drug, with the annual yearly dose being essentially the most predictive dose metric (Thaler et al. More latest epidemiologic evidence demonstrates a dose-related improve in the threat of cataracts from use of phenothiazine-like drugs, together with both antipsychotic drugs similar to chlorpromazine and nonantipsychotic phenothiazines (Isaac et al. Corticosteroids Systemic therapy with corticosteroids causes cataracts (Urban and Cotlier, 1986). Observable opacities start in the posterior subcapsular area of the lens and progress into the cortical area as the size of the lesion will increase. It was estimated that 22% of patients receiving corticosteroid immunosuppressive remedy for renal transplants skilled cataracts as a aspect effect of remedy (Veenstra et al. The use of inhaled corticosteroids-commonly prescribed bronchial asthma therapy-was once as} thought to be without this threat, however subsequent epidemiologic evidence documented a big affiliation between inhaled steroidal remedy and growth of nuclear and posterior subcapsular cataracts (Cumming et al. There are two proposed mechanisms by way of which corticosteroids would possibly cause cataracts. The common hexagonal array structure of normal lens epithelial cells is disrupted and appears reticulated, while gaps seem between the lateral epithelial cell borders in lenses of people with steroidinduced cataracts (Karim et al. The involved reader is referred to the superb references in the Introduction to numerous outstanding web sites devoted exclusively to the retina (e. The mammalian retina is highly susceptible to toxicant-induced structural and/or functional damage (1) the presence of a highly fenestrated choriocapillaris that supplies the distal or outer retina a portion of the inner retina; (2) the very high price of oxidative mitochondrial metabolism, especially that in the photoreceptors (Linsenmeier, 1986; Ahmed et al. The histogenic steps of growth of the neurons and glial elements are properly characterised. Therefore, toxicological effects in the rodent retina have relevance for chemical exposure in the course of the early gestation period in people during early postnatal growth. The retina incorporates a large range of synaptic transmitters and second messengers whose developmental patterns are properly described. Moreover, the rodent retina is easily accessible, it has most of the similar anatomical and functional features discovered in the creating and mature human retina, and the rat rod pathway is similar to that in different mammals (Dowling, 1987; Finlay and Sengelbaub, 1989; Berman, 1991; Chun et al. Finally, rat rods have comparable dimensions, photochemistry, and photocurrents as human and monkey rods (Baylor et al. These common and particular features underscore the relevance and applicability of utilizing the rodent retina to examine the effects of chemicals on this target site a model to examine the neurotoxic effects of chemicals during growth. Another evaluate by Wolfensberger (1998) concentrates on toxic effects on the retinal pigment epithelium. The major aim of this section is to talk about intimately quantity of} chemicals and drugs (1) at present used as pharmacological agents or environmentally relevant neurotoxicants; (2) whose behavioral, physiologic, and/or pathologic effects on retina are known; and (3) whose retinal site(s) and/or mechanism of motion are properly characterised. In addition, the effects of natural solvents and organophosphates on retinal function and vision are mentioned, as these are emerging areas of concern. The chemical- and drug-induced alterations in retinal structure and performance are grouped into two major categories. The first category focuses on retinotoxicity of systemically administered therapeutic drugs. Four major drugs are mentioned intimately: chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine, digoxin/digitoxin, indomethacin, and tamoxifen. The second category focuses on well-known neurotoxicants that produce retinotoxicity: inorganic lead, methanol, selected natural solvents, and organophosphates. See chapters sixteen and 23 entitled "Toxic Responses of the Nervous System" and "Toxic Effects of Metals" for information on the effects of lead on the mind and different target organs and chapter 24 entitled "Toxic Effects of Solvents and Vapors," for extra information on methanol and the natural solvents mentioned under. Retinotoxicity of Systemically Administered Therapeutic Drugs Cancer Chemotherapeutics Ocular toxicity is a typical aspect effect of cancer chemotherapy (Imperia et al. Symptoms embody blurred vision, diplopia, decreased colour vision, decreased visible acuity, optic/retrobular neuritis, transient cortical blindness, and demyelination of the optic nerves (Imperia et al. The retina its high metabolic activity and choroidal circulation (vide infra) appears to be particularly susceptible to numerous cytotoxic agents such as the alkylating agents cisplatin, carboplatin, and carmustine; the antimetabolites cytosine arabinoside, 5-fluorouracil and methotrexate; and the mitotic inhibitors similar to docetaxel. However, if not detected at an early stage of toxicity, the ocular problems are often irreversible even after chemotherapy is discontinued (Imperia et al. The ocular of tamoxifen, an estrogen antagonist utilized in oncology, are mentioned under. Although the molecular mechanism of motion is unknown, it has been advised that the primary biochemical mechanism is inhibition of protein synthesis (Bernstein, 1967). Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine Two of essentially the most extensively studied retinotoxic drugs are chloroquine (Aralen) and hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil). The first case of chloroquine-induced retinopathy was reported more than 40 years ago (Jaanus et al. These 4-aminoquinoline derivatives are used as antimalarial and anti-inflammatory drugs. The low-dose remedy used for malaria is basically free from toxic ; nevertheless, the chronic, high-dose remedy used for rheumatoid arthritis, and discoid and systemic lupus erythematosus (initially four hundred to 600 mg/day for 4 to 12 weeks and then 200 to four hundred mg/day; Ellsworth et al. Prolonged exposure of the retina to these drugs, especially chloroquine, might result in an irreversible retinopathy. In fact, small quantities of chloroquine and its metabolites were excreted in the urine years after cessation of drug therapy (Bernstein, 1967). Approximately, 20�30% of patients who obtained high doses of chloroquine exhibited some type of retinal abnormality, while 5�10% showed extreme modifications in retinal function (Burns, 1966; Potts, 1996; Shearer and Dubois, 1967; Sassaman et al. Hydroxychloroquine is now the drug of alternative for therapy of rheumatic ailments end result of|as a result of} it has fewer and fewer ocular toxicity. Doses lower than four hundred mg per day seem to produce little or no retinopathy even after prolonged remedy (Johnson and Vine, 1987). The clinical findings accompanying chloroquine retinopathy can be divided into early and late levels. Interestingly, darkish adaptation is relatively normal even in the course of the late levels of chloroquine retinopathy, which helps distinguish the peripheral retinal modifications from those noticed in patients with retinitis pigmentosa (Bernstein, 1967). As part of of} the extract of the plant foxglove, digitalis was recommended for heart failure (dropsy) over 200 years ago. Digitalisinduced visible system abnormalities similar to decreased vision, flickering scotomas, and altered colour vision were documented during that time (Withering, 1785). Approximately, 20�60% of patients with cardiac glycoside serum levels in the therapeutic vary and 50�80% of the patients with cardiac glycoside serum levels in the toxic vary complain of visible system disturbances inside 2 weeks after the onset of remedy (Robertson et al.
References:
- https://medcraveonline.com/JMEN/JMEN-01-00008.pdf
- https://docs.boehringer-ingelheim.com/Prescribing%20Information/PIs/Spiriva%20Respimat/spirivarespimat.pdf
- https://www.gcamerica.com/downloads/SDS_CA/2018/SDS_CA_GC%20Fuji%20LINING%20LC%20(Liquid).pdf
- https://www.state.gov/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/FY-2019-Agency-Financial-Report.pdf
- https://gynecology-obstetrics.imedpub.com/large-72-kg-subserosal-fibroid-with-monkenbergs-calcification-in-a-postmenopausal-woman-extremely-rare-case-with-review-of-literat.pdf
.png)