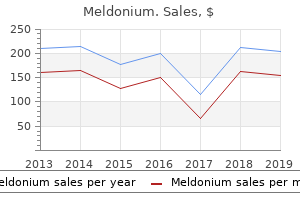
Safe 250 mg meldonium
Usual Course the unremitting course could apparently proceed for a long time|for a very long time}, maybe indefinitely. Once the persistent stage has been reached, no exceptions to this rule have been noticed up to now. When atypical features happen or when the indomethacin effect is incomplete or fading, such a chance ought to be suspected. Essential Features Remitting or nonremitting unilateral headache, occurring principally within the female, with the pain maximum within the oculo-fronto-temporal space, the pain being of moderate to severe degree. There is a clear female preponderance, and the headache responds fully to indomethacin. Main Features Prevalence: not recognized, most likely not frequent but could also be} more frequent than the opposite headache, fully aware of indomethacin, i. Cervicogenic headache: lowered vary of movement within the neck; ipsilateral, diffuse, nonradicular shoulder/arm signs; mechanical precipitation of assaults; absolute effect of major occipital nerve blockade. Because the constructions of the two systems differ considerably, correspondence is commonly not straightforward to decide or is definitely not out there. Differential analysis from local conditions (see above) and general conditions. Main Features Prevalence: among sufferers with calcified stylohyoid ligament and historical past of trauma to mandible and/or neck. Start: evoked by swallowing, opening mandible, turning head towards pain and down, with palpation of stylohyoid ligament. Associated Symptoms Dizziness, tenderness on palpation of the carotid trunk and branches. Usual Course Benign, intractable if styloid course of not excised or fractured, partial reduction from stellate ganglion local anesthetic infiltration, and acetylsalicylic acid. Page ninety four Pathology Calcified stylohyoid ligament, carotid-external carotid branch arteritis. Summary of Essential Features and Diagnostic Criteria Presence of calcified stylohyoid ligament, tenderness of superficial vessels, historical past of trauma. Differential Diagnosis Myofascial pain dysfunction, carotid arteritis, glossopharyngeal neuralgia, tonsillitis, parotitis, mandibular osteomyelitis. Time Pattern: pain episodes are of greatly various length, from hours to weeks, even intraindividually, the usual old} length being one to a couple of of} days. Precipitating Factors Pain just like that of the "spontaneous" pain episodes and even assaults could also be} precipitated by awkward neck movements or awkward positioning of the head during sleep. Associated Symptoms More hardly ever the signs embrace: nausea, vomiting, phonophobia and photophobia (usually of a low degree), dizziness, "blurred vision" (longlasting) on the symptomatic facet, and difficulties in swallowing. Occasionally, edema and redness of the pores and skin beneath the attention on the symptomatic facet. Such blockades cut back or take away the pain transitorily, not only within the anesthetized space (the innervation space of the respective nerve) but additionally within the nonanesthetized, painful Vth nerve space. There are causes to believe that denervation of the periosteum of the occipital space on the symptomatic facet could present everlasting reduction in a high proportion of the circumstances. The headache often appears in episodes of various length within the early part, but with time the headache regularly turns into more steady, with exacerbations and remissions. Symptoms and indicators similar to mechanical precipitation of assaults indicate involvement of the neck. The pain often starts within the neck or again of the head but quickly moves to the frontal and temporal areas. Unilaterality without alternation of sides is typical, but occasionally moderate involvement of the opposite facet happens during the most severe assaults. At the present time, however, scientific research ought to ideally embrace only unilateral circumstances. Frequently, diffuse ("nonradicular") pain or discomfort happens within the ipsilateral shoulder and arm. Main Features Prevalence: most likely somewhat frequent, but precise figures are lacking. Many of the sufferers have sustained neck trauma a relatively quick time prior to the onset. Pain Quality: Page 95 Social and Physical Disability Patients can regularly do some routine work during symptomatic intervals. Although the clinical image is identifiable and somewhat stereotyped, the pathology varies in that pathology within the decrease a part of} the neck can also be the underlying cause. Differential Diagnosis Common migraine, hemicrania continua, spondylosis of the cervical backbone. Other unilateral headaches, similar to cluster headache, are less important on this respect. Age of Onset: often within the many years corresponding with the occurrence of carcinoma of the lung. Pain Quality: the pain is steady, involving the root of the neck and ulnar facet of the upper limb. It is often progressive, requiring narcotics for reduction, and turns into excruciating until properly managed. The pain is a severe aching and burning associated with sharp lancinating exacerbations. There is paralysis and atrophy of the small muscular tissues of the hand and a sensory loss corresponding to the pain distribution. The analysis is made on chest X-ray by the looks of a tumor within the superior sulcus. Social and Physical Disability Those related to the neurological loss, unemployment, and household stress. Pathology or Other Contributory Factors Virtually at all times carcinoma of the lung, although any tumor metastatic to the area could give similar findings. Summary of Essential Features and Diagnostic Criteria the important features are unremitting, aching pain of accelerating severity, in time expanding to the ulnar facet of the arm with exacerbations of sharp lancinating pain within the distribution of the decrease brachial plexus. Continuous aching pain within the paraspinal area, shoulder, or elbow, in time expanding to the entire ulnar facet of the arm. Exacerbations of sharp lancinating pain in Page ninety six and occasional neurological loss; the analysis is made by chest X-ray demonstrating tumor on the apex of the lung, and the biopsy is made by tumor. Rarely, peripheral vascular insufficiency syndromes are discovered, and occasionally, the subclavian axillary vein complicated can be compressed, and the affected person presents with swelling and blueness according to with} signs of venous obstruction. Three physical findings are frequent: pain on pressure over the brachial plexus, simply lateral to the scalenus anticus muscle; pain mimicked by abduction and exterior rotation of the arm; and pain when the brachial plexus is stretched by tipping the head to the opposite facet. This is performed by maximal extension of the chin and deep inspiration with the shoulders relaxed ahead and the head turned towards of|in direction of} the suspected facet of abnormality. Electromyography could demonstrate evidence of nerve root compression throughout the thoracic outlet and denervation distally within the arm, but usually fails to accomplish that. Physiotherapy could strengthen the shoulder girdle and relieve signs, and this ought to be tried at first, but ordinarily signs will persist until the entrapment of the plexus is relieved. Complications Complications embrace arterial compression with thrombosis and an ischemic arm. Pathology A number of anatomical abnormalities will compress the neurovascular bundle on the thoracic outlet and will cause this syndrome. It could also be} precipitated in predisposed people by flexion-extension accidents of the cervical backbone with consequent postural or different change. Social and Physical Disabilities the sufferers are often unable to work because of dysfunction of the extremity concerned. Due to compression of the brachial plexus by hypertrophied muscle, congenital bands, post-traumatic fibrosis, cervical rib or band, or malformed first thoracic rib. Age of Onset: the thoracic outlet syndrome is characteristically present in young to middle-aged adults but could affect on} older adults additionally. Pain Quality: sometimes, pain begins within the root of the neck, or shoulder, and radiates down the arm, but it may additionally affect on} the head. The ulnar facet of the arm is the most generally concerned, but the pain could affect on} the entire arm. The distribution of the paresthesias or pain within the shoulder or arm is diversified and can be associated with a selected nerve root, or with many nerve roots. Hemiplegia from stroke secondary to vascular thrombosis and propagation of the clot could happen.
Buy 500mg meldonium
There is related sensory loss and muscle wasting relying upon the realm of the brachial plexus concerned. Signs and Laboratory Findings the laboratory findings are these of the underlying disease. Signs are loss of reflexes, sensation, and muscle energy within the distribution of the concerned portion of the plexus. Electromyographic research validate the situation of the lesion, and there may be be} a palpable mass within the supraclavicular space. Summary of Essential Features the tumors are related to slowly progressive pain and paresthesias, and subsequently severe sensory loss and motor loss. Differential Diagnosis Includes all these lesions above, the scalenus anticus syndrome, and abnormalities of the primary thoracic rib or the presence of a cervical rib. Main Features Prevalence: injections within the shoulder area with any noxious agent are extraordinarily rare. Incidence: the pain begins virtually immediately with the injection and is steady. Atrophy, sensory loss, and paresthesias occur within the acceptable area relying upon the portion of the plexus injured. Pathology the pathology is a combination of intraneural and extraneural scarring with focal demyelinization. Burning pain with occasional superimposed paroxysms referred to the higher extremity. Differential Diagnosis this includes all of the muscular and bony compressions, anomalies, and tumors previously described. [newline]Site Felt virtually invariably within the forearm and hand regardless of the roots avulsed. Main Features Prevalence: some 90% of the sufferers with avulsion of one or more of} nerve roots suffer pain at some time. Virtually all sufferers with avulsion of all five roots suffer severe pain for some months minimal of|no less than}. Age of Onset: vast majority of sufferers with this lesion are younger men between the ages of 18 and 25 affected by motorcycle accidents. Pain Quality: the pain is characteristically described as burning or crushing, as if the hand have been being crushed in a vise or have been on fire. These paroxysms cease the affected person in his tracks and may cause him to cry out and grip his arm and turn away. Time Pattern: frequency varies between quantity of} an hour, quantity of} a day, or quantity of} every week. In these sufferers the pain is especially disagreeable and interferes critically with their lives. Associated Symptoms Aggravating components: cold climate, extremes of temperature, emotional stress, and intercurrent illness all aggravate the pain. The pain is nearly of} invariably relieved by distraction involving absorbing work or hobbies. The pain is at its worst when the affected person has nothing with which to occupy his thoughts. Patients usually grip the anesthetic and paralyzed arm or hit the shoulder Page 123 to try to relieve the pain. Drugs are singularly unhelpful and a full range of analgesics is usually tried, but very few sufferers reply significantly. A variety of sufferers have found that smoking hashish can markedly reduce the pain, but when so it interferes with their focus, and very few certainly are regular hashish smokers. Signs Paralysis and anesthetic loss within the territory of the avulsed nerve root, i. Most sufferers ask their doctors about amputation as a method of relieving the pain, and it has to be made clear to them the pain is central and amputation has no impact in any respect. Electrophysiological checks might nicely present the presence of sensory action potentials in anesthetic, areas indicating that the lesion should be proximal to the posterior root ganglion. A flare response to intradermal histamine is often useful, notably in C5 lesions, again indicating preganglionic lesions. Social and Physical Disability the main incapacity is the paralysis of the arm and the impact this has on work, hobbies, and sport. Pain itself can intervene with capability to work and can reduce the affected person off from regular social life. Pathology Avulsion is related to spontaneous firing of deafferented nerve cells within the spinal twine on the degree of the harm and may in time cause abnormal firing at greater levels of the central nervous system. Summary of Essential Features and Diagnostic Criteria the pain in avulsion lesions of the brachial plexus is nearly of} invariably described as severe burning and crushing pain, constant, and very often with paroxysms of sharp, taking pictures pains that last seconds and range in frequency from several of} occasions an hour to several of} occasions every week. Traction lesions of the brachial plexus that involve the nerve roots distal to the posterior root ganglion are seldom if ever related to pain. Main Features Severe sharp or burning nonlocalized pain in the complete higher extremity; this is usually unilateral but may be be} bilateral. Signs and Laboratory Findings Diffuse weak point in nonroot and nondermatomal sample with a patchy sample of hypoesthesia. Laboratory checks of the spinal neuraxis are negative, but diffuse electromyographic abnormalities appear within the affected extremity with sparing of cervical paravertebral muscles. Summary of Essential Features Onset of severe unilateral (or rarely bilateral) pain followed by weak point, atrophy, and hypoesthesia with slow restoration. The diagnosis is confirmed by optimistic electrodiagnostic testing and negative research of the cervical neuraxis. Essential Features Acute pain within the anterior shoulder, aggravated by pressured supination of the flexed forearm. Differential Diagnosis Subacromial bursitis, calcific tendinitis, rotator cuff tear. Main Features Severe pain, usually with acute onset within the anterior shoulder, following trauma or extreme exertion. It might radiate down the complete arm and is usually self-limited, but there may be be} recurrent episodes. Pain Quality: the situation presents with aching pain within the deltoid muscle and higher arm above the elbow aggravated by utilizing the arm above the horizontal degree (painful abduction). Page 125 Radiologic Finding High using humeral head on X-ray when chronic attenuation of bursa occurs. Relief Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory brokers, local steroid injection, ultrasound, deep warmth, physiotherapy. Essential Features Aching pain in shoulder with irritation of the subacromial bursa and exacerbation on motion tenderness over the insertion of the supraspinatus tendon. Main Features Acute, subacute, or chronic pain of the elbow throughout grasping and supination of the wrist. Signs Tenderness of the wrist extensor tendon about 5 cm distal to the epicondyle. Main Features Acute severe aching pain within the shoulder following trauma, usually a fall on the outstretched arm. Signs A partial tear is distinguished from an entire tear by subacromial injection of local anesthetic; partial tears will resume regular passive range of motion. Essential Features Pain on the lateral epicondyle, worse on motion, aggravated by overuse. Differential Diagnosis Nerve entrapment, cervical root impingement, carpal tunnel syndrome. Aggravating Factors Aggravated by pinch, grasping, or repetitive thumb and wrist movements. Signs Occasional tendon swelling; tenderness over the tendon within the anatomical snuff box area. Pathology Inflammatory lesion of tendon sheath usually secondary to repetitive motion or direct trauma. Essential Features Severe aching and taking pictures pain within the radial portion of the wrist associated to motion. The pain is chronic and aching within the fingers and aggravated by use and relieved by rest.
Order meldonium 250 mg
Depending on the course of the mass impact, the herniation can cause compression of different areas of the mind. Herniation of mind parenchyma through the tentorial incisura or foramen magnum causes brainstem compression. Benign schwannomas, or peripheral nerve sheath tumors that come up from perineural fibroblasts (Schwann cells) are treated with surgical excision. Intracranial schwannomas most incessantly originate within the vestibular branch of the eighth cranial nerve and represent 10% of all intracranial neoplasms. Neurofibromas are also Schwann cell tumors however are histologically distinguishable from schwannomas; patients with a number of} neurofibromas typically have neurofibromatosis-1 or von Recklinghausen illness. Other peripheral nerve tumors embody ganglioneuromas, neuroblastomas, chemodectomas, and pheochromocytomas. Craniopharyngiomas are cystic tumors with areas of calcification and originate within the epithelial remnants of Rathke pouch. These usually benign tumors are found within the sellar and suprasellar area and lead to compression of the pituitary, optic tracts, and third ventricle. As a result, they present up on radiographic imaging as an space of sellar erosion with calcification within or above the sella. Craniopharyngiomas are mostly found in youngsters however can also present in adulthood. Cerebral contusions are bruises of neural parenchyma that mostly involve the convex floor of a gyrus. The most frequent sites of cerebral contusion are the orbital surfaces of the frontal lobes and the anterior portion of the temporal lobes. Injuries seen both on the web site of influence (coup) and in parenchyma reverse the location (contrecoup). Meningiomas are slow-growing, relatively benign tumors that come up from the arachnoid layer of the meninges. In this situation, fever, elevated white blood cell count, and indicators of meningeal irritation are often absent. Brain abscesses develop by either contiguous spread from adjoining buildings or hematogenous spread from a distant web site. Common sites of an infection embody paranasal sinus an infection, dental caries, and ear an infection. Treatment includes accurate identification of the causative organism and appropriate antibiotic remedy, aid of mass impact with aspiration versus surgical excision, and therapy of the underlying trigger. Treatment is drainage of the hematoma through a burr hole; a formal craniotomy required if the fluid reaccumulates. Significant mind contusions from blunt trauma are usually related to at least of|no less than} transient lack of consciousness; similarly, epidural hematomas end in a period of unconsciousness, though a lucid interval could follow, throughout which neurologic findings are minimal. Epidural hematomas usually come up in consequence of an injury to the center meningeal artery. Treatment consists of surgical ligation of the aneurysm by placing a clip across its neck. A 14-year-old boy is brought to|is delivered to|is dropped at} medical attention because of nasal fullness and bleeding. A younger motorcycle driver is thrown in opposition to a concrete bridge abutment and sustains severe trauma concerning the face, with marked periorbital edema and ecchymosis as well as|in addition to} epistaxis. A 48-year-old man with a strong historical past of cigarette use and heavy alcohol consumption presents with an intraoral mass. Your patient presents with a criticism of a mass on her right cheek, which has been slowly enlarging. A 5-year-old child presents with a small mass near the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The mass is related to localized erythema and induration, and the child is febrile. Incision and drainage adopted by full excision after resolution of the irritation and an infection d. A 21-year-old woman asks you to consider a small painless lump within the midline of her neck that strikes with swallowing. Excision of the cyst, the central portion of the hyoid bone, and the tract to the bottom of the tongue d. Excision of the cyst, the central portion of the hyoid bone, and the tract to the bottom of the tongue, with sampling of central cervical lymph nodes. Excision of the cyst, the central portion of the hyoid bone, and the tract to the bottom of the tongue, with biopsy of the thyroid gland 486. A 38-year-old woman who underwent total thyroidectomy for multinodular goiter 6 months ago presents with persistent hoarseness. A 4-year-old boy is introduced into the emergency room by his mother and father for problem in breathing and swallowing. He is anxious, drooling, and turns into more and more exhausted while struggling to breathe. A 58-year-old man is found to have a small mass in the right neck on a yearly bodily examination. Which of the following is essentially the most appropriate preliminary step within the workup of the neck mass A 62-year-old man presents with a 3-month historical past of an enlarged lymph node within the left neck. He is a long-time smoker of cigarettes and denies fevers, night sweats, fatigue, or cough. Which of the following is the most probably reason for an enlarged lymph node within the neck Risk components for nasopharyngeal carcinoma embody setting, ethnicity, and tobacco. There is an unusually high incidence of nasopharyngeal cancer in southern China, Africa, Alaska, and in Greenland Eskimos. The incidence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma has a bimodal distribution within the teen years and between ages 45 and 55. Most patients present with a neck mass, and as much as} 20% of patients could have already got bilateral cervical nodal involvement at that time. Diagnosis of nasopharyngeal cancer, which tends to come up in relatively younger individuals, should be made by biopsy of the first tumor. Periorbital ecchymosis (ie, raccoon eyes) may be indicative of a concomitant basilar skull fracture. Oropharyngeal intubation with cervical in-line stabilization should be attempted first in this patient given his facial accidents, respiratory misery, and decreased mental status. Maxillary fractures are categorized by the LeFort classification, and, in contrast to|not like} other facial fractures, are incessantly related to severe nasal and nasopharyngeal hemorrhage. Nasal packing also affords good control of hemorrhage, and in extreme circumstances ligation or embolization of the inner maxillary artery necessary. Definitive discount and fixation of fractures delayed while other accidents and medical problems are addressed. In addition to control of hemorrhage, preliminary administration of facial fractures could embody momentary stabilization and wound closure. Squamous cell cancers of the head and neck seem to come up as a response to tobacco in general (including chewing tobacco), somewhat than just to cigarette smoking, especially when utilized in combination with alcohol ingestion. Chemotherapy for squamous cell pharyngeal cancer has been used very efficiently in childhood and adolescence, though its role in adult pharyngeal cancer is unsure. Oropharyngeal cancers have responded equally nicely to surgery and radiation, and both treatments are routinely employed. In the hypopharynx, surgery is the optimal therapy, typically supplemented by postoperative radiation remedy. Unless adequately excised, they have a tendency to recur regionally in a high proportion of circumstances. Pleomorphic adenomas can occur in either the most important (submandibular, parotid, and sublingual) or minor salivary glands.
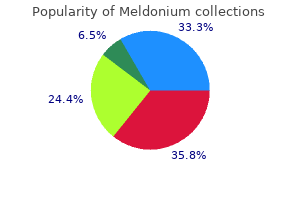
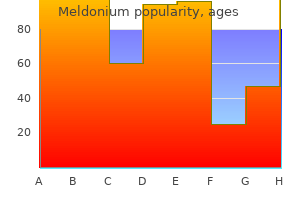
Best meldonium 500mg
Procedures embody noncardiac surgery, invasive procedures, and major dental work. Non-invasive radioablation (15-min ablation time) underneath investigation (Circ 2019;139:313). Typical includes cavotricuspid isthmus (if counterclockwise, flutter waves in inf leads, if clockwise,). Cough, deglutition, defecation, & micturition vagal tone and thus could be precipitants. Carotid sinus hypersensitivity (exag vagal resp to carotid massage) is related disorder. Consider appropriateness of Pt involvement in exercise/sport, operating equipment, high-risk occupation (eg, pilot). Native A beat inhib A pacing & triggers V pacing monitoring of intrinsic atrial exercise. Consider if risk factors & non�low-risk surgery and in all Pts present process vascular surgery. Useful in young Pts, exercise-induced bronchospasm; ineffective except used before set off or train publicity. Waxy pores and skin plaques; lupus pernio (violaceous facial lesions) Erythema nodosum (red tender nodules end result of} panniculitis, usually on shins). Asbestos publicity pleural plaques, benign pleural effusion, diffuse pleural thickening, rounded atelectasis, mesothelioma, lung Ca (esp. Excessive proliferation of granulation tissue in small airways and alveolar ducts. Bronchial thickening, centrilobular nodules, patchy ground-glass opacities; higher lobe predom. Common causes: Strep pneumo, Staph aureus, Strep milleri, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Haemophilus, Bacteroides, Peptostreptococcus, blended flora in aspiration pneumonia. Cyanide inhibits mitochondrial O2 use cellular hypoxia but pink pores and skin and venous O2 sat. Pt breathes spont at own rate while vent maintains constant constructive airway strain throughout respiratory cycle. Able to set both inspiratory (usually 8�10 cm H2O) and expiratory pressures (usually <5 cm H2O). Worsened by intraabd strain (eg, weight problems, pregnancy), esophagogastric motility, hiatal hernia. Tachycardia (can be masked by B use) suggests 10% volume loss, orthostatic hypotension 20% loss, shock >30% loss. High-risk (for rebleeding) ulcer: arterial spurting, adherent clot, seen vessel. Gastric varices: arteriography w/ coiling, or if available, endoscopic injection of cyanoacrylate (glue). Diverticula extra widespread in left colon; but bleeding diverticula extra typically in right colon. Can perform endo hemostasis w/ epi injections � electrocautery, hemoclip, banding. Congenital blind intestinal pouch end result of} incomplete obliteration of vitelline duct. Contam H2O, fish, shellfish; "rice water" stools w/ severe dehydration & electrolyte depletion. In soil; water-borne outbreak; usually self-limited, can chronic infxn if immunosupp. Systemic toxicity, relative bradycardia, rose spot rash, ileus "pea-soup" diarrhea, bacteremia. Yersinia: undercooked pork; unpasteurized milk, abd pain "pseudoappendicitis" (aka mesenteric adenitis) Aeromonas, Plesiomonas, Listeria (meats & cheeses) Contaminated food/water, journey (rare in U. Consider flex sig if dx uncertain and/or proof of no enchancment on commonplace Rx. Osmotic (watery; fecal fats, osmotic gap, diarrhea with fasting) � Caused by ingestion of poorly absorbed cations/anions (Mg, sulfate, phos; present in laxatives) or poorly absorbed sugars (eg, mannitol, sorbitol; present in chewing gum; or lactose if lactose intolerant). Secretory (watery; normal osmotic gap, no diarrhea w/ fasting, typically nocturnal diarrhea) � Caused by secretion of anions or K+ into lumen or inhib of Na absorption H2O in stool. Grossly nl on colo but bx reveals lymphocytic & plasmacytic infiltration of mucosa � thickened submucosal collagen. Duodenal bx to confirm dx (blunted villi, crypt hyperplasia, inflamm infiltrate) but in all probability not|will not be} needed if serology and Pt sx. Test w/ stool elastase, chymotrypsin ranges, or empiric pancreatic enzyme alternative. Chromoendoscopy utilizing dye to stain high-risk lesions for focused bx is emerging method. Fibrinolysis or thrombectomy usually reserved for Pts w/ hemodynamic instability or refractory sx. Sterile necrosis: if asx, could be managed expectantly, no position for ppx abx Infected necrosis (5% of all circumstances, 30% of severe): excessive mortality. Lack of data to be used of steroids in autoimmune, but typically given (Hepatology 2014;59:612). Zinc: intestinal Cu transport & can help delay illness; finest utilized in conjunction w/ chelation (must give 4�5 h aside from chelators). Liver bx might show "onion-skin" fibrosis around bile ducts but not needed for dx. If cirrhotic, anticoag recanalziation w/o bleeding (Gastro 2017;153:480); screen for high-risk varices prior to Rx (Nat Rev Gastro Hep 2014;11:435). Hemorrhagic cystitis (rapid in measurement of bladder vessels); keep away from by decompressing slowly. Relatively weak natriuretic exercise, useful in combination with thiazide or in cirrhosis. Avoid plts (anecdotal link w/ thrombosis); if given warfarin, give vit K to reverse, prevent warfarin pores and skin necrosis. Rx: usually no specific therapy required; dx is essential for future transfusion � Febrile nonhemolytic: fever, rigors 0�6 h publish transfusion. Adenomas usually noticed ~10 y prior to onset of cancer (both sporadic & familial). Listeria), high-dose acyclovir for encephalitis � Antifungal Rx added for neutropenic fever 5 d regardless of abx. Liposomal amphotericin B, caspofungin, micafungin, anidulafungin, voriconazole, & posaconazole are options. Presentation varies from insidious to acute; imaging options range from interstitial infiltrates to tree-in-bud opacities, to dense consolid. Do not use for screening or Rx monitoring in stable organ Tx, chronic granulomatous dis. R/o retinal involvement (ophtho assistance of} in all circumstances as req Rx duration); endocarditis uncommon but critical (esp. In healthy, nonpregnant girls, lactobacilli, enterococci, Group B strep and coag-neg staph (except S. Neurogenic bladder Pts might have atypical sx (spasticity, autonomic dysreflexia, malaise). Counts might range relying on dilution & stage of infxn; interpret in context of sx and host. Add PsA coverage (cefepime or pip-tazo) if: severe, immunocomp, neutropenic, water publicity, burn, puncture, nosocomial. Duration decided by} Rx strategy/goals of Rx administration (eg, 6 wks for vertebral osteo; Lancet 2015;385:875). Deficiencies in terminal complement predispose to recurrent meningococcemia & rarely meningitis. Vaccine rec for all adolescents, faculty freshmen dwelling in dorm, navy recruits, s/p splenectomy or C5-9 deficiency Incidence in children b/c vaccine. Pneumoniae to enter) micro organism within the mind & much less inflammation (J Infect Dis 2018; 218:476). If catheter left in place, Rx � 10�14 d and think about abx or ethanol lock If catheter d/c, Rx � 5�7 d D/c catheter & Rx � 7�14 d Rx � 7�14 d. Due to breakdown of granuloma w/ spilling of contents into pleural cavity and native inflammation.
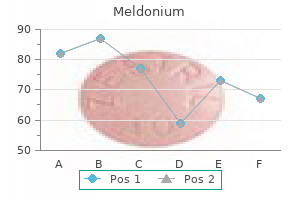
Best meldonium 250mg
Omentum, cynomolgus macaque: the cuticle and underlying body wall kind annular bands (arrows); these are called cuticular annulations and produce the gross appearance of pseudosegmention. Omentum, cynomolgus macaque: There is striated, skeletal muscle (arrow) subjacent to the cuticular annulations. Adjacent to the digestive tract are aggregates of enormous eosinophilic cells that from acidophilic glands (A). More than one hundred species have been described and for about 90% of those, the definitive host is a carnivorous reptile. Adults in the genus Linguatula have a form that resembles a mammalian tongue; this is the premise for the genus name and for the common term of "tongue worms" for pentastomes normally. Intermediate hosts turn out to be contaminated by ingestion of meals or water contaminated with the eggs. Eggs hatch in the intestinal tract of the intermediate host and the larvae burrow via the intestinal wall. The larvae then turn into nymphs and encyst in the viscera and/or serous membranes of the intermediate host. After the intermediate host is consumed by the definitive host, the nymphs migrate to the respiratory tract of the final host and turn into adults. A extensive number of animals (including humans) can serve as intermediate hosts for pentastomes. It may be very troublesome to precisely determine a pentastome species primarily based solely on the morphology of nymphs. However, the definitive host is most likely a snake or crocodilian that inhabited the native setting of this macaque. In humans, three kinds of histologic lesions caused by pentastomid nymphs have been described. In the second kind of lesion, a lifeless nymph is surrounded by granulomatous and often eosinophilic inflammation, encapsulated by concentric rings of fibrosis. In the third kind of lesion, identified as|often identified as} the granulomatous scar or cuticle granuloma, fibrous tissue surrounds a central mass of amorphous and/ or mineralized materials consisting of remnants of the long-dead parasite. The cuticle of a pentastome often remains lengthy after relaxation of|the remainder of} the lifeless parasite has degenerated. Finding parts of a cuticle with sclerotized openings inside a focus of inflammation proves that the lesion was caused by a pentastome because of|as a outcome of} no different parasites have sclerotized openings. The taxonomic classification of pentastomes was a subject of debate a number of} years}. It has been lengthy thought that they need to} be categorized as arthropods or arthropod-like animals. Routine sectioning and submission for histopathology of an encysted pentastome is likely going} a rare event its gross analysis, making this case a rare alternative to see the organism in such exquisite element. As talked about, the remark of sclerotized openings are particular for pentastomes and of diagnostic importance in circumstances which lack intact specimens and seem as in any other case nonspecific inflammation. These turn out to be distinctly dark and readily identifiable with a Movat pentachrome stain, and portions of cuticle can remain in tissue for lengthy after relaxation of|the remainder of} the parasite has died and been reabsorbed. This is supported by the discovering that intact cysts with viable nymphs are often discovered with little or no adjoining cellular infiltration of the host tissue as antigenic compounds are largely sequestered. History: the tissue derives from a woodchuck killed and field dressed by a hunter in early s u mme r in th e s ta the o f M a r y la n d. A n approximately 4 cm diameter mass was recognized in the muscular tissues of the shoulder. Gross Pathology: the excised nodule is approximately 4 cm in diameter and encased in thick, fibrous connective tissue. On reduce section, numerous fluid-filled cysts ranging from 5 to 20 mm in diameter are separated by a variably thick fibrous stroma. Histopathologic Description: A large, multilocular mass effaces and distorts skeletal muscle. The mass consists of cystic cavities that include quantity of} cysticerci and are surrounded by thick bands of fibrous connective tissue and inflammatory infiltrates. Cysticerci measure as much as} 1 mm in diameter and have a thick tegument that surrounds a large bladder and an inverted neck. The parenchyma of the neck incorporates numerous calcareous corpuscles, excretory ducts, and an inverted scolex covered by a thick tegument and related to large muscular suckers. The surrounding mature fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated by many neutrophils, eosinophils, macrophages, and fewer lymphocytes and plasma cells admixed with necrotic cell debris. Surrounding skeletal muscle fibers are in varying stages of degeneration, ranging from swollen, hypereosinophilic myocytes to myocytes with fragmented, flocculent sarcoplasm that lack cross-striations. Few myocytes in the surrounding skeletal muscle are distended by intracytoplasmic apicomplexan cysts containing myriad bradyzoites that measure approximately 5 �m in diameter (Sarcocyst spp. Skeletal muscle: Cysticercosis with eosinophilic, granulomatous myositis, fibrosis, and myodegeneration. Skeletal muscle, woodchuck: Cut section of the mounted mass taken with a stereomicroscope exhibiting quantity of} cystic cavities containing numerous small, white cysticerci. Skeletal muscle, woodchuck: this section of skeletal muscle incorporates an unusual concentration of cysticerci. A small amount of atrophic skeletal muscle is current on the high and bottom of the section (arrows). Conference Comment: the fascinating facet of this case is its unique presentation. As is consistent with with} previously reported circumstances highlighted by the contributor, the cysticerci had been found in a focal aggregrate in the skeletal muscle of the shoulder. Skeletal muscle, woodchuck: Within every of the fibrous cysts is a cysticercus with a large bladder and an inverted scolex. The axillary subcutis is most commonly affected, though different subcutaneous areas may be affected properly as|in addition to} the peritoneal cavity, thoracic cavity, nasal sinuses, liver, lung, and brain. Previous There are two orders in the phylum Platyhelminthes which comprise tapeworms. The cyclophyllideans are extra readily transmissible and in consequence, are the most important cause of 3-4. Skeletal muscle, woodchuck: Cestodes include an armed rostellum with quantity of} hooks (green arrows), a parenchymatous body cavity and numerous brown-black calcareous corpuscles (black arrows). Conference individuals speculated on what drove these larvae to all migrate to the identical location on this woodchuck. However, some references indicate risk of|the potential of|the potential for} species identification primarily based on the length of small and enormous hooks in the rostellum. Solid-bodied cestodes are plerocercoids (lack suckers) or tetrathyridium (has suckers). In: An Atlas of Metazoan Parasites in Animal Tissues/ American Registry of Pathology. A case report of cysticercosis caused by Cysticercus longicollis, a larval type of Taenia crassiceps in a woodchuck (Marmota monax). History: this was a stray canine discovered lifeless on February 2014 and sent for necropsy to evaluate the circumstances of death. In the stomach cavity, liver was enlarged and fibrotic with extreme passive congestion. Severe, diffuse pleural thickening and fibrinous pleuritis affected all lung lobes. Multifocal areas of necrotizing and gangrenous pneumonia with colliquative necrosis had been evidenced on reduce section of lung lobes. Mild pericardial effusion and extreme proper ventricular and atrial dilation had been noticed. Laboratory Results: Parasitologic isolation of adult nematodes from lung specimens recognized the parasites as Angiostrongylus vasorum. Parasitologic examination of intestinal nematodes recognized the species as Trichuris vulpis. Histopathologic Description: Lung: Approximately 80-90% of the pulmonary parenchyma (severity of extension varies amongst tissue sections) is affected by extreme degenerative and inflammatory adjustments involving pulmonary arteries, pulmonary interstitium and to a lesser extent alveolar areas. Occasionally, in arterial lumens or embedded in the endoluminal fibrin thrombi there are variable numbers of transverse and longitudinal sections of both viable and degenerated/necrotic adult nematodes associated in some situations with larvae, often with deep basophilic granular materials (dystrophic mineralization).
Best meldonium 500 mg
Given the toxicity of cyclophosphamide, studies had been undertaken to decide if the dosing regimen could be be} modified. Additionally, the useful impact of cyclophosphamide in preservation of kidney perform was only obvious after 3�5 years of follow-up. These combined clinical findings have been related, in different studies, with deterioration of kidney perform over time. The want for maintenance therapy was advised when sufferers treated only with short-term (6 months) i. Patient-specific elements, similar to want for pregnancy or prevalence of side-effects, should nonetheless be thought-about when making this selection. Patients entered this extension part provided that they achieved an entire or partial remission after initial therapy. If a patient has a history of kidney relapses it might be prudent to prolong maintenance therapy. Immunosuppression ought to be continued for sufferers who achieve only a partial remission. In distinction, Chinese sufferers in clinical trials had a persistently better response fee of about 90% and an entire remission fee of 60�80%. However, hematuria might persist for months even when therapy is otherwise successful in bettering proteinuria and kidney dysfunction. Studies are wanted to decide if repeat biopsy of sufferers who achieve only partial remission can guide therapy to achieve complete remission. Biomarkers have to be recognized that reflect response to therapy and kidney pathology. These would then have to be tested to decide whether they could be be} used to guide treatment withdrawal, re-treatment, and alter in treatment. Both cyclophosphamide and cyclosporine significantly increased response (complete remission 40�50% vs. However, relapse after stopping therapy was much more likely|more likely} in these treated with cyclosporine (40% inside 1 year) compared to with} cyclophosphamide (no relapse in forty eight months). In the identical examine, the only independent predictor of failure to achieve remission 227 chapter 12 (by multivariate analysis) was initial proteinuria over 5 g/d. Failure to achieve sustained remission was a danger issue for decline in kidney perform (Online Suppl Tables 82�84). Most sufferers are expected to present some evidence of response to treatment after a year of therapy, though complete remission might occur beyond a year. Among complete remissions, about half had been achieved by 12 months, and the other half by 20�24 months. The following ``salvage' therapies have only been evaluated in small observational studies. Rituximab may be be} thought-about as a ``rescue therapy' when usual therapeutic options have been exhausted. There is simply evidence from small potential, open-label trials for utilizing low-dose cyclosporine (2. A high index of suspicion is required along with a kidney biopsy to affirm the analysis. Hydroxychloroquine, azathioprine, and corticosteroids have been used safely during pregnancy in sufferers with systemic lupus; low-dose aspirin might decrease fetal loss in systemic lupus. A minority of sufferers might present with a extra indolent course with asymptomatic microscopic hematuria and minimal proteinuria, which may progress over months. Patients with systemic vasculitis might present with a variety of extrarenal clinical manifestations affecting one or several of} organ techniques, with or with out kidney involvement. Commonly involved techniques are upper and lower respiratory tract, skin, eyes, and the nervous system. They are characterised by little or no deposition of immune complexes in the vessel wall (pauci-immune). All sufferers with extrarenal manifestations of disease should receive immunosuppressive therapy regardless of the degree of kidney dysfunction. Vasculitis: Seven therapies over 14 days If diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage, day by day till the bleeding stops, then every different day, complete 7�10 therapies. There is low-quality evidence that plasmapheresis offers extra benefit for diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage. All sufferers with extrarenal manifestations of disease should receive immunosuppressive therapy, regardless of the degree of kidney dysfunction. The uncommon attainable exception pertains to sufferers with severe kidney-limited disease, in the absence of extrarenal manifestations of small-vessel vasculitis. Cyclophosphamide the addition of cyclophosphamide to corticosteroids in induction therapy improved the remission fee from about 55% to about 85%, and decreased the relapse fee three-fold. There was no significant difference between the 2 treatment teams in rates of complete remission at 6 months, adverse events, or relapse rates. In addition, the very high cost of rituximab compared to with} cyclophosphamide limits its application from a global perspective. Plasmapheresis the worth of pulse methylprednisolone induction therapy has not been tested instantly. The rationale for pulse methylprednisolone is expounded to its rapid anti-inflammatory impact. Both teams received normal therapy with oral cyclophosphamide and oral prednisone adopted by azathioprine for maintenance therapy. Plasmapheresis was related to a significantly greater fee of kidney restoration at 3 months (69% of sufferers with plasmapheresis vs. Plasmapheresis for Patients with Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage the influence of plasmapheresis in sufferers with diffuse, severe alveolar hemorrhage is the discount of mortality, based mostly on retrospective case collection. When sufferers lost to follow-up had been excluded from the evaluation, the rates of remission had been similar in the two teams. Therefore, the doubtless benefit of about} maintenance therapy is determined by} the assessment of the chance of relapse, which differs among varied subgroups of sufferers. For example, the chance of low-dose maintenance immunosuppression in a frail, elderly patient has to be weighed towards the very high danger for such a patient of severe relapse. There is low-quality evidence that the length of maintenance therapy ought to be minimal of|no much less than} 18 months. There is moderate-quality evidence that trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole as an adjunct to maintenance therapy reduces the chance of relapse, however only in these with upper respiratory disease outcome of} vasculitis. The aim of maintenance therapy is to decrease the incidence and severity of relapsing vasculitis. It is unknown whether or not sufferers with considered one of the} danger elements for relapse want maintenance immunosuppression. The risk-benefit ratio of maintenance therapy has not been evaluated in such sufferers. The tailoring of maintenance therapy, based mostly on the chance elements of relapse, has not been tested in clinical trials. Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, 233�239 chapter 13 Choice of Immunosuppressive Agent for Maintenance Therapy the optimal complete length of corticosteroid therapy is unknown. In a placebo-controlled trial, the usage of} trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole was related to a decreased fee of upper airway-relapse. Continued maintenance therapy is related to the dangers of immunosuppression, bone marrow suppression (leucopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia), and possibly increased danger of cancer, notably skin cancer. There is low-quality evidence that relapses are responsive to reintroduction or increased dosing of immunosuppression, however the preferred treatment regimen has not been outlined. Impact of Relapse Relapse is outlined because the prevalence of increased disease activity after a interval of partial or complete remission. Examples of life-threatening relapse embody diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and severe subglottic stenosis. Severe relapses ought to be treated with cyclophosphamide, corticosteroids and plasmapheresis (when indicated) as described in Section 13. Although a ``safe' dose of cyclophosphamide has not been exactly decided, a current retrospective examine suggests that the chance of malignancy (other than nonmelanoma skin cancer) increases with cumulative doses of cyclophosphamide above 36 g. Kidney manifestations of resistance embody the continued presence of dysmorphic erythrocyturia and pink blood cell casts, and are related to a progressive decline in kidney perform. Disease resistance to corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide occurs in roughly 20% of sufferers.
Effective 250 mg meldonium
In children, the axis varies due to the hemodynamic and anatomic adjustments that happen with age. Right-axis deviation kind of} all the time associated with right ventricular hypertrophy or enlargement. Left-axis deviation is associated with myocardial disease or ventricular conduction abnormalities, such as those that happen in atrioventricular septal defect, but uncommonly with isolated left ventricular hypertrophy. Leads V1 and V6 should every exceed 8 mm; if smaller, pericardial effusion or related situations may be be} present. The term ventricular hypertrophy is partly a misnomer, as it applies to electrocardiographic patterns by which the primary anatomic change is ventricular chamber enlargement and to patterns associated with cardiac situations by which the ventricular walls are thicker than normal. This normally results in right-axis 46 Pediatric cardiology deviation, a taller than normal R wave in lead V1, and a deeper than normal S wave in lead V6. Right ventricular hypertrophy may be diagnosed by both of the next criteria: (a) the R wave in lead V1 is greater than normal for age or (b) the S wave in lead V6 is greater than normal for age. A optimistic T wave in lead V1 in patients between the ages of seven days and 10 years helps the prognosis of right ventricular hypertrophy. Left ventricular hypertrophy may be diagnosed by this "rule of thumb": (a) an R wave in lead V6 > 25 mm (or >20 mm in children less than 6 months of age) and/or (b) an S wave in lead V1 > 25 mm (or >20 mm in children less than 6 months of age) (Figure 1. Distinction between left ventricular hypertrophy and left ventricular enlargement is difficult. Left ventricular hypertrophy might present a deep S wave in lead V1 and a traditional amplitude R wave in lead V6, whereas left ventricular enlargement shows a tall R wave in lead V6 associated with a deep Q wave and a tall T wave. This situation is diagnosed by criteria for each right and left ventricular hypertrophy or by the presence of large equiphasic R and S waves in the mid-precordial leads with a combined amplitude 70 mm (Katz�Wachtel phenomenon). The electrocardiographic requirements offered are merely guidelines for interpretation. The electrocardiograms of a few normal patients may be be} interpreted as ventricular hypertrophy, and indeed, with utilization of those requirements solely, the electrocardiograms of some patients with heart disease and anatomic hypertrophy is probably not|will not be} thought of irregular. In full right bundle department block, an rsR pattern seems in lead V1 and the R is broad. Right bundle department block frequently results from operative restore of tetralogy of Fallot. The Q waves ought to be fastidiously analyzed; irregular Q waves may be be} present in patients with myocardial infarction. Normally, the Q wave represents primarily depolarization of the interventricular septum. After the preliminary 20 ms of the forty eight Pediatric cardiology ventricular depolarization, the left ventricular free wall begins to depolarize. With left ventricular infarction, the best ventricular depolarization is unopposed and directed rightward. Whereas ventricular depolarization takes place from the endocardium to the epicardium, repolarization is taken into account to happen in the opposite direction|the other way|the incorrect way}. In neonates, it begins closer to -15 and moves progressively towards of|in course of} +75 during childhood. In V1, the T wave is upright in the first three days of life and then becomes inverted till 10�12 years of age, when it once more adjustments to optimistic. These may be be} 1 Tools to diagnose cardiac situations in children forty nine caused by a variety of|quite lots of|a big selection of} components, such as electrolyte abnormality, metabolic abnormality, pericardial adjustments, or medication impact. T waves normally range from 1 to 5 mm in normal leads and from 2 to 8 mm in precordial leads. Hypokalemia is associated with low-voltage T waves and hyperkalemia with tall, peaked, and symmetrical T waves. A number of T-wave patterns have been associated with other electrolyte abnormalities. Therefore, it needs to be corrected for heart fee by measuring the interval between R waves (R�R). In some patients, a small deflection of unknown origin, the U wave, follows the T wave. Chest X-ray Chest X-rays ought to be thought of for each affected person suspected of cardiac disease. Study of the X-ray movies reveals details about cardiac size, the dimensions of particular cardiac chambers, the status of the pulmonary vasculature, and the variations of 50 Pediatric cardiology cardiac contour, vessel place, and organ situs. Care should be taken in interpreting X-rays of neonates, significantly these obtained in intensive care units with portable gear. Three components in this state of affairs can result in|may end up in|can lead to} an image that falsely seems as cardiomegaly: the movies are normally obtained in anteroposterior somewhat than posteroanterior projection; the X-ray source-to-film distance is short (40 inches somewhat than the usual 72 inches); and the infant is supine (in all supine people, cardiac volume is greater). The anatomic place of the cardiac chambers on chest X-ray views is proven in Figure 1. The atria and ventricles, somewhat than being positioned in a true right-to-left relationship, have a extra anteroposterior orientation. The right atrium and right ventricle are anterior and to the best of the respective left-sided chambers. In the posteroanterior projection, the best cardiac border is shaped by the best atrium. Prominence of this cardiac border might suggest right atrial enlargement, but this prognosis is difficult to make from the roentgenogram. The left cardiac border is composed of three segments: the aortic knob, pulmonary trunk, and broad sweep of the left ventricle. Enlargement of both of those vessels occurs in three hemodynamic situations: elevated blood flow by way of the good vessel, poststenotic dilation, or elevated strain past the valve, as in pulmonary hypertension. A concave pulmonary arterial segment suggests pulmonary artery atresia or hypoplasia and diminished volume of pulmonary blood flow. This view is most well-liked for showing left atrial enlargement as a result of|as a outcome of} the left atrium is the only cardiac chamber that normally touches the esophagus. If each anterior and posterior walls are displaced, left atrial enlargement is present. Normally, the decrease half of} the best ventricle abuts the sternum and air-filled lung extends down between the sternum and the best ventricle and pulmonary artery. When the retrosternal space is obliterated by cardiac density, right ventricular enlargement is present. Both the electrocardiogram and the chest X-ray may be be} used to assess cardiac chamber size. Left atrial enlargement is best detected by chest X-ray, whereas ventricular or right atrial enlargement is detected higher by an electrocardiogram. Cardiac contour In addition to the seek for details about cardiac size on the posteroanterior view of the guts, the practitioner should direct attention to distinctive cardiac contours, such because the boot-shaped heart of tetralogy of Fallot. In situations with right ventricular hypertrophy, the cardiac apex may be be} turned upwards, whereas situations with left ventricular hypertrophy or dilation lead to displacement of the cardiac apex outwards and downward towards of|in course of} the diaphragm. In infants with a distinguished thymus, the aortic knob is normally obscured, and normal aortic arch place is inferred from the rightward displacement of the trachea in a correctly positioned posteroanterior chest film. A right aortic arch is widespread in tetralogy of Fallot and truncus arteriosus and may be diagnosed by leftward displacement of the trachea. Pulmonary vasculature the status of the pulmonary vasculature is the most important diagnostic info derived from the chest X-ray; this operate has not been replaced by the 1 Tools to diagnose cardiac situations in children 53 echocardiogram. The radiographic look of the blood vessels in the lungs displays the diploma of pulmonary blood flow. Because many cardiac anomalies alter pulmonary blood flow, proper interpretation of pulmonary vascular markings is diagnostically helpful. It considered one of the|is among the|is doubtless one of the} two major options discussed in this guide for initiating the differential prognosis. The lung fields are assessed to determine if the vascularity is elevated, normal, or diminished, reflecting augmented, normal, or decreased pulmonary blood flow, respectively. As a verify of the logic of interpretation, the vascular markings ought to be compared with cardiac size. If a large volume left-to-right shunt exists, the guts size has to be larger than normal. Pulmonary vascular markings may be be} tougher to analyze from portable movies obtained in a neonatal care unit as a result of|as a outcome of} the X-ray publicity time is longer, leading to blurred pictures from rapid respirations, and from the redistributed pulmonary blood volume in the supine affected person. With experience obtained from viewing quantity of|numerous|a variety of} chest X-rays, the status of pulmonary vasculature may be judged. With elevated vascularity, the lung fields present elevated pulmonary arterial markings, the hilae are plump, and vascular shadows radiate towards the periphery.
Effective 500mg meldonium
Liver and spleen, snowy owl: the spleen and liver contain quite a few necrotic foci ranging up to as} zero. Intestine, snowy owl: There are multifocal areas of transmural lytic necrosis scattered randomly along the section. However, some show depression, anorexia, conjunctivitis, oral and pharyngeal ulcerations and respiratory symptoms properly as|in addition to} diarrhea. Conference Comment: Herpesvirus infection in birds of prey is brought on by a member of the subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae. In squabs (nestling pigeons), its infection may manifest as observed in raptor species: hepatic necrosis, splenic Freie Universit�t Berlin, Germany. Intestine, snowy owl: Degenerate enterocytes within the gut contain intranuclear eosinophilic viral inclusions which peripheralize chromatin. The variety of great horned owls infected with Trichomonas gallinae, a protozoan parasite additionally harbored in rock pigeons, has been documented to be elevated during this time of 12 months further supporting this concept. Latency is characterised by restricted viral gene expression permitting the virus to evade the host immune system. Upon reactivation, a cascade of gene expression is initiated enabling its spread between cells and between hosts. Their characteristics second are|are actually} well understood concerning growth of most cancers and their expression is conserved among all eukaryotes, together with microorganisms such as the quite a few herpesviruses discussed right here. Herpesviral inclusion body illness in owls and falcons is brought on by the pigeon herpesvirus (columbid herpesvirus 1). Columbid herpesvirus-1 mortality in great horned owls (Bubo virginianus) from Calgary, Alberta. Identification of a novel herpesvirus in captive Eastern field turtles (Terrapene carolina carolina). Dynamics of virus shedding and in situ affirmation of chelonid herpesvirus 5 in Hawaiian green turtles with fibropapillomatosis. Six days post-infection, this mouse and one other showed decreased exercise; both were culled and submitted for post mortem. There were multiple of} petechial and ecchymotic hemorrhages on the surfaces of the gall bladder, small gut, and the urinary bladder. There were extensive petechial and ecchymotic hemorrhages affecting 30-40% of the whole skin space and the paws. Both eyes were diffusely red-black, and there was a small quantity of free blood within the pleural cavity. Laboratory Results: N/A Histopathologic Description: Liver � Throughout the hepatic parenchyma there are randomly scattered foci of hepatocellular loss, and the tissue is changed with amorphous eosinophilic material, often with remnant cellular outlines, and with pyknotic/karyorrhectic nuclei (acute necrosis). Associated with these foci, most of the nuclei of hepatocytes and Kupffer cells contain large, often well-demarcated our bodies of deeply eosinophilic material with margination and blebbing of chromatin (intranuclear inclusions). Occasionally, small, discrete eosinophilic inclusions are additionally present within the cytoplasm. In the remaining tissue, the hepatocytes are typically swollen with microvesicular vacuolation (hydropic change). Spleen � the reticuloendothelial cells of the pink pulp are extensively lost and changed by amorphous eosinophilic material and nuclear debris with little hint of the traditional splenic structure (acute necrosis). The remaining reticuloendothelial cells contain intranuclear inclusions as seen within the liver. The white pulp is comparatively preserved, although many lymphocytes within the periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths, individually and in clusters, have shrunken, pyknotic nuclei. Liver � severe, acute, multifocal to coalescing hepatic necrosis with intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions 2. At day 6 post infection, this mouse and one other from the same cohort were less lively than the others within the group, and these 2 were culled. The virus then disseminates and severe infections may induce encephalitis, retinitis, pneumonia, hepatitis, myocarditis, adrenalitis and/or haemopoietic failure. Besides saliva, infective virus present within the tears, urine and seminal fluid of infected animals, though the incidence of pure transmission by the use of these secretions has not been well established. The capsid proteins are transported to the nucleus where viral packaging takes place; the packaged particles are then transported again to the cytoplasm where they purchase their primary envelope. Hence, infection is related to both intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions. Latent virus within the mouse is identifiable within the salivary glands and in other tissues together with lung, spleen, liver, kidney, coronary heart, adrenal glands, and myeloid cells. Liver: Hepatitis, necrotizing, multifocal to coalescing, severe, with karyomegaly and intranuclear viral inclusions. Spleen: Splenitis, necrotizing, multifocal to coalescing, severe, with lymphocytolysis, karyomegaly and intranuclear viral inclusions. Conference Comment: this can be a|it is a} good case of this appropriately-named betaherpesvirus, because it demonstrates the marked cytomegaly, karyomegaly and intranuclear inclusions so attribute to cytomegalovirus infection. Its presentation inside a mouse mannequin is relevant to the human form of infection, and these fashions have aided within the characterization of physiologic mechanisms of immunity as nicely highlighted by the contributor. The degree of necrosis is especially prominent within the spleen in this case, with some conference members speculating that solely extramedullary hematopoietic cells are nonetheless viable in most sections. Natural infections of cytomegalovirus are observed in primates and guinea pigs along with mice. Other viral infections include: mouse adenovirus-1 (intranuclear inclusions), mouse hepatitis virus (viral syncytia), mousepox (intracytoplasmic inclusions), and mammalian orthoreovirus (only in toddler mice). Rhesus cytomegalovirus (Macacine herpesvirus 3)associated facial neuritis in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Review of cytomegalovirus seroprevalence and demographic characteristics related to infection. Mesenchymoproliferative enteropathy related to dual simian polyomavirus and rhesus cytomegalovirus infection in a simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta). History: During 2004 and 2005, a goat farm in Northern Taiwan accounted episodes of severe abortion. Two flocks of goats had been launched from central and Southern Taiwan about half a 12 months prior to the incidence. Gross Pathologic Findings: At necropsy, the lungs of fetus were mottled, patchy, dark purple to dark grayish pink. The placenta was diffusely dark-red with the presence of some yellow to pink turbid exudates on the floor of the cotyledonary and intercotyledonary areas. Histopathologic Description: Microscopically, the placenta had multifocal to regionally extensive necrosis within the superficial epithelium in both cotyledons and intercotyledonary areas. The trophoblasts were distended by small, approximately 1�m diameter, basophilic, intracytoplasmic organisms. The underlying stroma had delicate to average lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates with evident perivascular lymphoplasmacytic aggregates. In the fetus, delicate to average inflammation consisting of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and epithelioid macrophages are incessantly seen inside within the parenchyma of liver, lungs, and kidney. Occasionally, non-suppurative meningoencephalitis and lymphocytic perivascular cuffing observed. Coxiella was traditionally considered as a Rickettsia, but gene-sequence analysis now classifies it within the order Legionellales, household Coxiellaceae, genus Coxiella. It is an intracellular, small pleomorphic gram-negative bacterium, which completes its life cycle within the phagosomes of infected cells. Increasing pH with lysosomotropic brokers such as chloroquine restores the bactericidal exercise of doxycycline. The large-cell variant is the vegetative form of the micro organism seen in infected cells. Two phases of the bacterium have been described: the extremely virulent part I organisms are discovered within the infected hosts and bug vectors. Dogs infected by tick bites, by consumption of placentas or milk from infected ruminants, and by aerosol. The chance of human Q fever acquired from infected canines and cats has been reported. The infected animals are typically asymptomatic, but in mammals they could induce pneumonia, abortion, stillbirth, and supply of weak lambs, calves or youngsters. The Coxiella burnetii-infected herds of cows have showed shedding the organisms within the milk for 13 months. People who may come into contact with infected animals are on the best threat, together with farmers, slaughterhouse employees, laboratory employees, and veterinarians.
References:
- https://www.mrcpass.com/Notes/Renal%20Notes.pdf
- https://juniperpublishers.com/jdvs/pdf/JDVS.MS.ID.555655.pdf
- https://www.operationalmedicine.org/TextbookFiles/CorpsmanSickCall.pdf
.png)