Safe minipress 2.5bottles
By far the commonest of those illnesses are benign prostatic hyperplasia and ureteral calculi. Although there additionally be} a number of} causes of postrenal failure, many patients present with hydronephrosis and ache. Urinalysis is a reasonable, typically informative laboratory process that ought to be a element of any initial 527 analysis. This is particularly important to pediatricians, whose patients can change their quantity status quickly. Thus, in adult patients with episodes of albuminuria and glucosuria, specific gravity has much less restricted significance than in pediatric patients. However, a real limitation of measuring specific gravity in pediatric patients is that utilizing a hydrometer requires extra urine than typically is on the market. These embody utilizing a refractometer that measures the refractive index of urine and numerous reagent strips that change shade in response to ionic (electrolyte) strengths of urine and to not undissociated solutes (mainly urea). Still essentially the most correct measure of urine concentration is measuring urine osmolality by freezing-point despair or by vapor-pressure techniques, but, unfortunately, these measurements require a technician and extra advanced tools. Calorimetric pH reagent strips measure urine pH in freshly voided specimens with satisfactory accuracy for scientific use. The extra cumbersome glass electrodes with special techniques to collect urine are essential to consider renal tubular acidosis or other abnormalities of acid-base metabolism that require subtle analysis of urinary acid excretion. Individual preparations could differ phrases of|when it comes to|by means of} check reagents used; subsequently, scientific settings by which false or ambiguous readings occur could vary. Urinary protein concentrations are generally measured by calorimetric reagent strips (see Table 100-2). These are fairly qualitative but can measure concentrations as little as 10 mg/dL (trace) to values higher than 500 mg/dL (4+). Clearly, the measurement of 24-hour urinary protein excretion fee correlates higher with disease processes than urinary concentration; nonetheless, utilizing reagent strips can alert the doctor that additional studies are needed if relaxation of|the remainder of} the scientific image so dictates. However, many nephrologists have accepted protein excretions of a lot as} one hundred fifty mg/24 hr as "regular" in non-diabetic patients. Consensus exists that urinary excretion rates higher than one hundred fifty mg/24 hr are abnormal and mirror either renal or extrarenal causes (see Table 100-3). Selective proteinuria refers to a primary improve in albumin excretion, with the predominant pathophysiologic change being the lack of a negative cost from the endothelial floor of the glomerular basement membrane that might usually reject the permeation of negatively charged albumin. Non-selective glomerular proteinuria refers to proteinuria with severe disruption of the glomerular capillary wall. In these cases, the urinary proteins mirror the concentrations of circulating proteins to a first approximation. Tubular proteinuria refers to situations with a defect in regular endocytic reabsorption of filtered protein. In these situations, the urine incorporates a disproportionate quantity of low-molecular-weight proteins, such as beta2 -microglobulin, in distinction to albumin. An instance of that is numerous heavy steel poisons or tubular interstitial illnesses. It is for these causes that urine collections ought to be carried out under standardized situations. Indeed, persistent microalbuminuria in a 24-hour urinary specimen of a diabetic has prognostic significance and suggests improvement of diabetic nephropathy in the future. If proteinuria is famous, then one should consider acquiring two or three 24-hour urinary protein excretion rates as a result of|as a result of} the coefficient of variance between these 24-hour samples may be fairly high. If these measurements document that proteinuria is persistent, then efforts ought to be made to set up the etiology. However, the protein excretion rates seldom exceed 2 g/24 hr in interstitial nephritis, whereas protein excretion rates vary broadly in primary glomerular illnesses. Patients with significant and protracted proteinuria higher than one hundred fifty mg/24 hr are at risk for creating useful renal insufficiency with out acceptable therapy. There exists some distinction of opinion as to how aggressively a affected person ought to be evaluated if he or she is non-diabetic and has a protein excretion fee between 40 and one hundred fifty mg/24 hr. Hematuria additionally be} macroscopic (red in color) or microscopic (more than two to three cells per high-power subject in a button of sediment over a 12-mL spun urine sample). Although the quantitative count of microscopic hematuria is of little or no worth, differentiate between glomerular hematuria, renal non-glomerular hematuria, and extrarenal causes of hematuria. In basic, purple cells in glomerular hematuria probably to|are inclined to} be spiculated and have many sizes and shapes, whereas in non-glomerular hematuria the purple blood cells are non-spiculated and uniform in size. It ought to be recognized, nonetheless, that in very dilute urine with specific gravities of less than 1. A number of techniques have been developed to set up the presence of pyuria: calculating excretion fee of leukocytes, examining the button of a spun sediment, utilizing a hemocytometer on an unspun urine specimen, and utilizing the leukoesterase dipstick methodology. One of the only is the routine microscopic examination of a spun specimen, or much more simple is the leukoesterase dipstick methodology. More than three white blood cells per high-power subject and a optimistic leukoesterase dipstick measurement are abnormal values. These observations are a cost-effective means (with a comparatively high degree of sensitivity) to recommend the presence of a urinary tract an infection. However, recognize that wide variation in specificity in leukoesterase willpower has been reported. This variation is due partially to spectrum bias of the affected person inhabitants and partially to variations in check performance. The check should be carried out based on the directions would possibly be} supplied with the precise dipsticks. However, the extra pricey urine cultures are needed if patients are diabetic, elderly, pregnant, or have recurrent urinary tract infections. Not all patients with pyuria have bacteriuria and this may mirror tuberculosis, viral infections, or fungal or other non-bacterial pathogens. Also, the presence of great eosinophiliuria could recommend allergic interstitial nephritis. Urine also ought to be examined microscopically for bacteria, yeasts, fungi, crystals, casts, and other components within the sediment of diagnostic significance. Molecular weight of proteinuria is a function of impairment of change and structural integrity. However, the doctor should be aware of|concentrate on|pay consideration to} sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of each check. Table 100-2 lists circumstances by which sure scientific conditions cause false-positive and false-negative results. Evaluating quantity, electrolyte, and acid base homeostasis is covered in Chapters 102. The significance of urinary electrolyte measurement has lately turn out to be extra apparent. If metabolic alkalosis is present in its early-generation section, as seen with vomiting, then urinary chloride, as is mentioned later, turns into a extra important measure of quantity status than urinary sodium. A measure of urinary potassium important to differentiate between causes of each hypokalemia and hyperkalemia. The cause for that is that the 24-hour urine excretion fee displays total consumption in a steady-state situation (higher sodium intakes are related to larger sodium excretion rates), whereas fractional excretion of ions displays the sum of regulatory elements on a extra acute foundation. Significant quantity of overlap exists between these two teams if urine osmolality is between 350 and 500 mOsm/kg or urine Na is between 20 and 40 mEq/L for these indices to be of diagnostic significance. The scientific utility of values within the intermediate vary is much less, but normally, values higher than 1 recommend disease processes, aside from states by which the kidney is underperfused. Examples embody congestive heart failure and hypoalbuminemic states, whether secondary to renal or hepatic causes. As a affected person develops metabolic alkalosis with vomiting, the plasma bicarbonate concentration rises to ranges that exceed renal capacity for reabsorption, and, subsequently, urinary bicarbonate concentration rises. Once the history, physical examination, and laboratory values have been interpreted, there are particular patients who require additional analysis to decide totally the nature of abnormalities in renal function. The subsequent section describes the indications, use, and predictive worth of various extra studies.
Syndromes
- Right-lower quadrant
- Have you been exposed to any fumes?
- Loss of appetite
- People who have a weakened immune system (including those with cancer or HIV/AIDS)
- Laxative
- Breath with a musty or sweet odor
- Endoscopy -- camera down the throat to see burns in the esophagus and the stomach
- Severe head injury
- Breathing stops
- A mole or skin sore changes in size, color, or texture
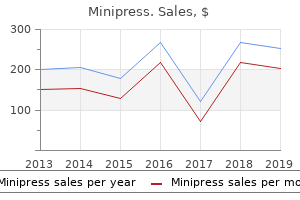
Purchase minipress 2 mg
In methanol poisoning, formic acid (an end-product of methanol metabolism) accounts massive part|largely} for the discount in serum bicarbonate concentration. In ethylene glycol intoxication, glycolic and lactic acid accumulation accounts for the majority all} of the discount in plasma bicarbonate degree; nevertheless, oxalate deposition in tissues is clearly a major factor|a vital factor|a vital component} in ethylene glycol toxicity. In sufferers with chronic metabolic acidosis, nevertheless, hyperventilation may be be} troublesome to detect clinically. Severe metabolic acidosis exerts a unfavorable inotropic effect on the guts, which relies upon, minimal of|no much less than} partially, on the fact that|the fact that} acidosis diminishes tissue responsiveness to catecholamines. Thus, in lactic acidosis, unfavorable inotropy sets the stage for a potentially deadly chain of occasions: poor tissue perfusion lactic acidosis decreased cardiac operate additional discount in tissue perfusion. In acidosis, the Bohr effect shifts the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the proper. This compensatory mechanism permits oxygen supply to inadequately perfused tissues. Because metabolic acidosis is a manifestation of selection of|quite so much of|a wide range of} completely different illnesses, the remedy of metabolic acidosis varies, relying on the underlying course of and on the acuteness and severity of the acidosis. Those issues characterized by failure of bicarbonate regeneration or lowered excretion of inorganic acids represent acidoses during which the kidneys fail to excrete a traditional load of non-volatile acid or, in other phrases, fail to regenerate roughly 70 mEq of bicarbonate day by day. Thus, the remedy of these metabolic acidoses requires administering comparatively modest amounts of bicarbonate. In chronic renal failure, alkali therapy is generally not required unless the plasma bicarbonate degree falls beneath sixteen to 18 mEq/L. Caution ought to be exercised to keep away from sodium overload or the appearance of tetany, if overalkalinization happens. In youngsters with distal renal tubular acidosis, higher quantities of bicarbonate, in the range of 5 to 14 mEq of alkali per kilogram per day, are normally required to keep away from growth retardation. The remedy of sufferers with metabolic acidosis because of of} exterior bicarbonate loss varies with the nature of the dysfunction. In acute metabolic acidosis because of of} gastrointestinal losses, the online bicarbonate deficit may be be} roughly calculated from the discount in "bicarbonate house," or total body buffering capability, as follows: Bicarbonate therapy ought to be instituted when the arterial pH falls beneath 7. It is prudent to administer enough sodium bicarbonate intravenously to raise the plasma bicarbonate concentration to sixteen mEq/L over a 12- to 24-hour interval, quite than to restore the entire bicarbonate deficit. If the latter persist, as in cholera or other types of secretory diarrhea, the day by day quantity of bicarbonate given to preserve the plasma bicarbonate concentration in the range of sixteen mEq/L may very well exceed the calculated bicarbonate house. The remedy of acidoses because of of} accumulation of organic acids varies with the dysfunction. In experimental lactic acidosis, dichloroacetate can raise arterial pH by suppressing endogenous lactic acid manufacturing, however bicarbonate therapy worsens the dysfunction by growing the speed of splanchnic mattress lactate manufacturing. Moreover, large amounts of sodium bicarbonate (in the type of ampules containing forty four. The remedy of alcoholic ketoacidosis usually requires solely administering saline options and glucose. Because blood insulin values are usually decreased in alcoholic ketoacidosis-associated hypoglycemia, insulin is contraindicated in this situation as a result of|as a outcome of} it might induce life-threatening hypoglycemia. The insulin release provoked by administering glucose suppresses lipolysis and consequently the overproduction of keto acids. In diabetic ketoacidosis, insulin therapy promotes glucose utilization and, consequently, full oxidation of keto acids; concurrently, ketogenesis is lowered. Also, it has been postulated that bicarbonate therapy may adversely affect on} the oxygen-releasing capability of hemoglobin. Furthermore, some authors have noted that late metabolic alkalosis may develop with vigorous use of bicarbonate, quickly as} the ketone bodies are metabolized to bicarbonate. Thus, though good reasons exist to administer bicarbonate with severe melancholy of arterial pH, there are also reasons to not administer bicarbonate. It appears prudent to give parenteral bicarbonate to all diabetics in ketoacidosis with an arterial pH of 6. Finally, as a result of|as a outcome of} salicylates, methanol, and ethylene glycol are by themselves tissue toxins, appropriate therapy for these issues consists of not solely alkalinization but additionally hemodialysis for eradicating the offending agent. When the blood ranges are at potentially deadly range, hemodialysis ought to be used to treat sufferers with salicylate ranges of more than one hundred mg/dL, and hemodialysis may be be} helpful in the early course of all sufferers with ethylene glycol or methanol poisoning. Maintaining the plasma bicarbonate concentration is determined by} renal bicarbonate reabsorption and renal bicarbonate regeneration. Consequently, though metabolic alkalosis may be be} initiated by hydrogen ions misplaced from the body. In other phrases, a steady-state elevation of plasma bicarbonate concentrations to ranges higher than 24 mEq/L requires elevated exercise of quantity of} of the effector mechanisms regulating bicarbonate dealing with by renal tubules. Table 102-18 lists the major medical causes of elevated serum bicarbonate concentrations. Volume contraction can maintain metabolic alkalosis due to an increase in the obvious rate of bicarbonate reabsorption by the proximal tubule. The most typical cause for initiating this kind of|this kind of|this kind of} alkalosis is hydrochloric acid loss due to vomiting or gastric suction. As quantity contraction becomes more and more severe, sodium conservation happens and potassium bicarbonate is excreted in an try to preserve pH homeostasis. Finally, when potassium depletion becomes severe, urinary sodium plus potassium excretion is sharply lowered and paradoxical aciduria happens: the urine is acidic whereas the plasma bicarbonate degree and pH are each elevated. Potassium depletion from any cause, when sufficiently severe, can maintain metabolic alkalosis initiated by acid loss, for instance, during gastric drainage. Presumably, potassium loss from cells is accompanied by elevated hydrogen ion concentrations inside cells, together with renal tubular cells. Thus, potassium depletion, when sufficiently severe, can raise the speed of renal tubular bicarbonate reabsorption and therefore preserve a metabolic alkalosis. Consequently, when serum potassium concentrations are lowered to about 2 mEq/L, metabolic alkalosis because of of} gastric fluid loss becomes saline resistant however aware of potassium chloride administration. The cumulative effect of these renal responses is elevated internet bicarbonate addition to the circulation. Situations during which there happens enhanced supply of sodium chloride to terminal nephron segments improve renal acid excretion and due to this fact lead to metabolic alkalosis by growing the speed of renal bicarbonate generated. This effect happens with loop diuretics such as furosemide, ethacrynic acid, or bumetanide, and with the proximal tubular diuretic metolazone. Administering large amounts of impermeant anions such as carbenicillin additionally favors distal hydrogen ion secretion. Thus, carbenicillin therapy certainly one of the|is amongst the|is doubtless one of the} few circumstances during which an elevated anion gap and metabolic alkalosis can be produced concurrently by the identical agent. Mineralocorticoid excess, either primary or secondary, additionally metabolic alkalosis due to renal bicarbonate technology. [newline]The alkalosis of mineralocorticoid excess happens primarily due to elevated technology of bicarbonate by accumulating duct segments (or, in other phrases, by elevated renal acid excretion) and is clearly accentuated by potassium depletion. This syndrome is characterized by metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, and hypertension that occurs due to an increase in sodium avidity by accumulating duct segments, which can be blocked by triamterene therapy. This dysfunction metabolically simulates a mineralocorticoid excess state however one during which aldosterone measurements are normal. In sure situations, nevertheless, bicarbonate loading can produce either a transient or a steady-state alkalosis. Patients with chronic hypercapnia develop compensatory will increase in plasma bicarbonate concentrations: on a median, chronic hypoventilation ends in a zero. A common approach to intensify post-hypercapnic alkalosis is to preserve sufferers on ventilators having excessive optimistic end-expiratory pressures, which causes a central tourniquet effect that reduces cardiac output. Delayed conversion of accrued organic acids is a second mechanism for producing transient metabolic alkalosis. This may occur after insulin therapy for diabetic ketoacidosis, through the recovery part of lactic acidosis, and following high-efficiency hemodialysis. In the last-named circumstance, acetate in the dialysis bath is taken up rapidly during dialysis. The accrued acetate, which represents "potential bicarbonate," is then converted to bicarbonate after dialysis has been accomplished. Prolonged metabolic alkalosis due to alkali loading is a typical feature of the milk-alkali syndrome. The alkalosis happens due to extended ingestion of absorbable alkali in sufferers with impaired renal operate because of of} hypercalcemic nephropathy. Severe metabolic alkalosis additionally severe hypoventilation, particularly in sufferers with lowered renal operate. Tetany and elevated neuromuscular irritability, that are fairly common in acute respiratory alkalosis, are very rare in chronic metabolic alkalosis.
Effective 2mg minipress
Over 50% of the dysfibrinogenemias are asymptomatic, 25% are related to a gentle hemorrhagic tendency (commonly caused by defective launch of fibrinopeptide A), and 20% predispose individuals to thrombophilia (usually caused by impaired fibrinolysis). The prevalence of dysfibrinogenemia in sufferers with a history of thromboembolic episodes approaches zero. Females experience a excessive incidence of pregnancy-related issues similar to spontaneous abortions and postpartum thromboembolic occasions. Clinically insignificant dysfibrinogenemias may be be} acquired in affiliation with hepatocellular carcinoma. In contrast to the hepatic synthesis of a qualitatively irregular protein in dysfibrinogenemia, congenital afibrinogenemia, an autosomal recessive disorder, represents the markedly deficient manufacturing of a traditional protein. Severe life-threatening hemorrhagic issues can occur at any web site, beginning at birth with umbilical bleeding. All coagulation-based assays depending on detection of a fibrin clot finish point are markedly prolonged. Afibrinogenemia is often detectable by both specific functional or immunologic assays. With a circulating biologic half-life of a minimum of|no less than} ninety six hours, remedy each three to four days is enough. Primary prophylaxis regimens may be be} helpful in afibrinogenemia; on-demand or prophylactic replacement for trauma or surgery is beneficial for prohemorrhagic dysfibrinogenemias. Individuals with thrombophilic manifestations ought to obtain anticoagulation indefinitely. Deficiency of Factor V is a very unusual autosomal recessive disorder (1 per 1 million births). The severity of the plasma Factor V reduction correlates less properly with the danger of medical bleeding than does the platelet Factor V content in the alpha-granule. Thus hemostasis may be maintained without correcting plasma Factor V activity (>25% of normal). The severity of bleeding is decided by the degrees of these elements, often ranging from 5 to 30% of normal. Replacement therapy should be aimed toward normalizing both clotting protein actions. Acquired Factor V deficiency has been described in individuals exposed to bovine Factor V, which contaminates the thrombin preparations used topically to management bleeding throughout cardiovascular surgery. This abnormality in all probability represents the event of antibovine Factor V antibodies that cross-react with the human Factor V protein. Heterozygotes (with issue ranges 20% of normal) are typically asymptomatic besides in the quick newborn period, when physiologic vitamin K deficiency exacerbates the underlying clotting issue deficiency. Homozygotes with clotting issue ranges less than 10% of normal manifest variable symptoms. As with other coagulopathies, these deficiencies are often suspected after the onset of neonatal umbilical stump bleeding. Thereafter, unless replacement or prophylactic therapy is provided, such sufferers are topic to mucosal bleeding from epistaxis, menorrhagia, and dental extractions; to hemarthroses and intramuscular hematomas; and to post-surgical/trauma bleeding. Mixing patient plasma with normal plasma will demonstrate correction of these assays; specific clotting assays using plasma deficient in the coagulation protein to be studied confirm the prognosis. Replacement therapy is indicated for acute symptomatic bleeds and for prophylaxis for surgery. Additional points that should be thought of when a deficiency of these or other coagulation elements is confirmed embrace the following: 1. Acquired extreme deficiency of Factor X, often accompanied by deficiencies of other vitamin K-dependent elements, often happens in individuals with systemic amyloidosis. Bleeding issues caused by acquired IgG autoantibodies directed in opposition to any coagulation issue protein may be be} quickly however briefly reversed by extracorporeal immunoadsorption over a Sepharose-bound polyclonal antihuman IgG or staphylococcal A column with concomitant replacement therapy and initiation of immunosuppression. The lupus anticoagulant is an IgG or IgM antiphospholipid antibody directed in opposition to the phospholipids that operate as templates for activation of the prothrombinase advanced in vivo and in coagulation assays in vitro. Anticardiolipin antibodies, which are a subset of the antiphospholipid antibody household, may be purified with cardiolipin liposomes and demonstrate anticoagulant activity much like that of lupus anticoagulants. Recent knowledge counsel, however, that anticardiolipin antibody and lupus anticoagulant may represent separate kinds of antibodies with completely different specificities and binding kinetics to phospholipid. Occasionally, individuals may have discordant test outcomes for lupus anticoagulant and the anticardiolipin and antiphospholipid antibodies, particularly throughout an acute thrombotic occasion. For sensible functions, one or a mix of these antibodies may be related to thrombotic issues. Induction of antiphospholipid antibodies may be be} stimulated by the exposure of new epitopes that kind after beta2 -glycoprotein 1 binds to phospholipid/cardiolipin. It has been shown in vitro that these antibodies can cross-react with beta2 -glycoprotein 1 and neutralize its anticoagulant capacity and may due to this fact promote the event of thrombotic issues. The approach to the administration of lupus anticoagulant or antiphospholipid antibody varies according to the severity of symptoms and the medical circumstances. Although daily low-dose aspirin (81 mg) and/or corticosteroids had been thought of an necessary cornerstone in the prevention of spontaneous miscarriage secondary to lupus anticoagulant or antiphospholipid antibody, a current massive randomized trial discovered this combination to be ineffective in promoting reside births. When a miscarriage has been related to lupus anticoagulant or antiphospholipid antibody, the preponderance of proof signifies that more aggressive anticoagulation with full-dose or minidose unfractionated heparin regimens alone or in combination with low-dose aspirin should be used to reduce subsequent spontaneous fetal losses and to defend the mom who has skilled a earlier thrombotic occasion. Non-pregnant individuals with thrombotic manifestations of lupus anticoagulant or antiphospholipid antibody have as much as} a 50% risk of experiencing recurrent occasions over a 5-year period. Typically, recurrent hypercoagulable episodes occur in a sample consistent with with} the initial findings; i. Asymptomatic individuals may profit from prophylactic aspirin therapy, which has a positive risk-to-benefit profile. Warfarin results may be exaggerated by potentiating medications, excessive ethanol use, and simultaneous dietary vitamin K deficiency. Bleeding may be be} extreme or occult and may unmask the presence of pathologic lesions similar to carcinomas. This approach allows for simple reinitiation of warfarin with acceptable dose adjustment. Simultaneous heparin therapy with a 5-day overlap with warfarin will minimize these dangers. Heparin anticoagulation also can induce life-threatening hemorrhagic issues. The reptilase time can be used to distinguish heparin from other causes of thrombin time prolongation. Acute and profuse bleeding episodes secondary to heparin may be reversed by administering protamine sulfate (1 mg/100 U of residual heparin). Otherwise, the circulating half-life of standard heparin is short sufficient (2 to four hours) to allow the anticoagulant state to dissipate on its own. A evaluate of preferred products for replacement therapy for all congenital coagulopathies. Basic concepts in the prognosis and remedy of acquired inhibitors to coagulation proteins. Di Bona E, Schiavoni M, Castaman G, et al: Acquired haemophilia: Experience of two Italian centres with 17 new cases. This volume contains a comprehensive evaluate of all features of hemophilia A and B, including descriptions of molecular diagnostics, new therapeutic modalities, prospects for profitable gene therapy, and issues and remedy of alloantibody inhibitors. An excellent overview of the structure-function relationships of irregular fibrinogens and their medical options. An excellent summary of a rare situation with application for all vitamin K- dependent clotting issue protein deficiencies. In most sufferers, the underlying process dominates the medical picture, however in some cases. Tissue issue then triggers era of the coagulation protease thrombin, which induces fibrin formation and platelet activation. The syndrome is especially related to gram-negative sepsis, though triggered by broad variety|all kinds} of bacterial, fungal, viral, rickettsial, and protozoal microorganisms. Snake venom contains a variety of|quite so much of|a wide range of} substances that can affect on} coagulation and endothelial permeability. Bleeding may be restricted to websites of intervention or anatomic abnormalities, but it tends to be generalized in additional extreme cases, including widespread ecchymoses and diffuse oozing from mucosal surfaces and orifices.
Order minipress 2mg
B, Oral cholecystogram showing distinction materials outlining quantity of} radiolucent cholesterol stones in a usually functioning gallbladder. C, Ultrasound examination showing a large gallstone as an echogenic focus that casts a sonic "shadow. Therapy for Gallstones No treatment is usually required for asymptomatic gallstones because of their low propensity to turn into symptomatic. Longitudinal research have proven that conversion from asymptomatic to symptomatic stones takes place on the fee of no more than|not extra than} 1 to 2% per yr, and risk-benefit analyses indicate that surgery for asymptomatic gallstones usually causes extra morbidity than it prevents. Exceptions to this rule may include very massive gallstones (>3 cm in diameter) and porcelain gallbladder, each of which have been associated with an elevated danger of gallbladder carcinoma. Some experts also would advocate prophylactic cholecystectomy for asymptomatic gallstones in patients with diabetes mellitus or spinal twine damage outcome of|as a result of} gallstone complications such as acute cholecystitis extra extreme and extra often life threatening in these teams. Surgical removal of the gallbladder is indicated in all situations of acute cholecystitis or in symptomatic patients with non-visualized gallbladder on oral cholecystography. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is now preferred because of shorter hospitalization time and faster recovery. Serious bile duct damage, often requiring reconstructive surgery, happens in about 0. Gallstones within the widespread bile duct eliminated by the surgeon on the time of cholecystectomy. More lately, growth of strategies for direct choledochoscopy and stone extraction during surgery have lowered the necessity for widespread duct exploration (Color Plate 2 D). These techniques are of worth when patients are acutely ill with ascending cholangitis or acute pancreatitis or when stones are inadvertently left within the widespread duct after cholecystectomy. Ascending cholangitis is treated aggressively with antibiotics and endoscopic sphincterotomy, which removes the obstructed stones and permits for normalization of bile circulate. The drainage of infected bile mixed with applicable antibiotic remedy ends in fast recovery, after which the affected person ordinarily should have an elective cholecystectomy. In patients at excessive surgical danger, cholecystectomy could be deferred indefinitely after sphincterotomy and stone extraction with only some per cent per yr danger of subsequent gallstone complications. If the cholesterol saturation index of bile could be brought below 1 with administration of these two bile salts, the gallstone-forming process could be reversed and undersaturated micelles in bile can slowly "leach" cholesterol from the stones. Other crucial components for achievement include small stones, a usually functioning gallbladder, and sufficient bile salt dosage. In a perfect group of patients with small, radiolucent, floating stones, 75% dissolution of gallstones inside 1 yr has been observed. Chenodeoxycholic acid is moderately poisonous; it may trigger mild to moderate elevations of liver operate exams and serum cholesterol. In therapeutic doses, chenodeoxycholic acid is frequently associated with disabling diarrhea. Because of these aspect effects}, utilization of} chenodeoxycholic acid in patients with gallstones has been deserted within the United States. Experimental medical therapies for gallstones include solvent dissolution and extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Cholesterol gallstones could be dissolved rapidly (within hours) when organic solvents such as methyl-tert-butyl ether or ethyl propionate are instilled directly into the gallbladder by percutaneous transhepatic approach. The dissolution fee for non-calcified stones utilizing this modality is close to 100% and the aspect effects} are few. This approach has not gained wide acceptance because of its invasive nature and labor intensity. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy was first introduced with nice success for treatment of renal stones and, later, within the mid 1980s, was modified to permit shattering of stones within the gallbladder. Gallstone fragments after lithotripsy are eliminated with bile or could be dissolved with concurrent oral bile salt treatment. Biliary colic after lithotripsy happens relatively frequently elimination of small fragments of pulverized stones; in about 1% of patients, passage of stone fragments causes acute pancreatitis. No gallstone lithotripsy gadget has been permitted for general use within the United States; and with the advent of laproscopic cholecystectomy, this know-how has largely been deserted. A major limitation of all medical treatments of cholesterol gallstones (bile salt dissolution, solvent dissolution, lithotripsy) is gallstone recurrence, which averages about 50% over a period of 5 years. Other Benign Disorders of the Gallbladder A variety of benign gallbladder wall abnormalities generally may mimic cholelithiasis. Cholesterolosis of the gallbladder is usually an asymptomatic situation during which cholesterol accumulates inside histiocytes within the mucosa of the gallbladder. Aggregates of these lipid-laden macrophages distend and enlarge the mucosal folds. The accumulation of lipid on the suggestions of these folds is instantly seen grossly as yellow streaks or flecks that resemble the seeds of a strawberry, hence the widespread name "strawberry gallbladder. Focal aggregation of cholesterol laden macrophages may produce polyps seen on ultrasonography. Other benign gallbladder lesions which will produce polyps of the gallbladder wall include benign adenomas and adenomyomatous hyperplasia. Postcholecystectomy Disorders After cholecystectomy, a small fraction of patients develop mild diarrhea. Increased circulation of the bile salt pool with elevated delivery of bile salts to the colon has been implicated in post-cholecystectomy diarrhea, and patients with this syndrome often reply nicely to treatment with cholestyramine. More difficult is the issue of recurrent upper belly ache, which is noted in about 5% of patients after cholecystectomy. In some situations, ache secondary to retained gallstones within the widespread bile duct or abscess or different complications of surgery. In the absence of such a specific etiology, biliary kind ache after gallbladder removal is termed post-cholecystectomy syndrome. This term is a misnomer, since generally the ache probably is unrelated to gallstones or cholecystectomy but quite an error within the authentic prognosis. Recurrence of belly ache after cholecystectomy should lead the physician to think about different, missed causes of ache such as irritable bowel syndrome, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, and biliary dyskinesia. Biliary Dyskinesia Biliary dyskinesia refers to a syndrome of repeated attacks of biliary colic resulting from motor dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi. Bile circulate is regulated by the sphincter of Oddi by a combination of phasic contractions superimposed on tonic stress. The motor exercise of the sphincter of Oddi is influenced by hormonal and neural components. The principal hormone involved within the regulation of sphincter of Oddi and gallbladder contraction is cholecystokinin, which contracts the gallbladder and on the identical time relaxes the sphincter of Oddi. After cholecystectomy with loss of the gallbladder reservoir, modest will increase usually have been noted within the sphincter of Oddi tone, bile ductal stress, and common bile ductal diameter. Rarely, patients may develop abnormalities of sphincter of Oddi operate, together with elevated basal tone or elevated amplitude and frequency of phasic contraction, which can episodically impede efflux of bile and set off typical attacks of biliary colic. The affiliation of sphincter of Oddi motor abnormalities with symptoms and signs of useful biliary obstruction is termed biliary dyskinesia (Table 157-3). Clinically, biliary dyskinesia produces episodic proper upper quadrant belly ache mimicking an assault of choledocholithiasis. The prognosis is suspected when symptoms and laboratory abnormalities counsel intermittent widespread bile duct obstruction on the stage of the ampulla of Vater (elevated alkaline phosphatase, aspartate aminotransferase, and/or bilirubin; dilatation of the widespread bile duct), but cholangiography reveals no proof of gallstones. Once the prognosis is established, endoscopic sphincterotomy is the remedy of selection. Detailed evaluation of the medical presentation and remedy of this dysfunction of 1 per 10,000 live births. A medical evaluation summarizing the similarities and variations amongst autoimmune hepatitis, main biliary cirrhosis, and primary sclerosing cholangitis. A present evaluation of gallstone pathogenesis, with specific emphasis on components involved in pathogenesis of gallstone formation. In this method (or tissue), early multipotent stem cells with extensive proliferative potential, but few differentiated options, reside largely within the bone-encased marrow cavity. These stem cells have the potential, with applicable inductive alerts, to differentiate and provides rise to populations of progenitor cells with progressively restricted renewal, proliferative, and lineage potential but with growing useful characteristics defining selection of|quite a lot of|a wide selection of} particular lineages. This process eventuates within the cell lineages recognizable by commonplace Wright-Giemsa stains as erythroid, granulocytic, monocytic, lymphoid, or megakaryocytic. These occasions occur constantly with a large turnover of differentiated cells, as illustrated by the blood lifespans of human erythrocytes (120 days), platelets (10 days), and granulocytes (9 hours).
Safe 2 mg minipress
Among thoracic aortic aneurysms, aneurysms of the descending aorta are commonest, followed by these involving the ascending aorta; aneurysms of the aortic arch are fairly uncommon. Descending thoracic aortic aneurysms may prolong distally and involve the belly aorta, creating a thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm. The infrarenal aorta tends to be most severely affected by the atherosclerotic course of and is accordingly the common website for aortic aneurysm formation. The mechanism by which atherosclerosis results in the expansion of aneurysms remains unsure. Recent evidence suggests that the atherosclerotic thickening of the aortic intima reduces diffusion of oxygen and nutrients from the aortic lumen to the media, in turn causing degeneration of the elastic components of the media and a weakening of the aortic wall. In addition to atherosclerotic components, there appears to be a genetic predisposition to the development of belly aortic aneurysms as properly: up to as} 28% of first-degree relatives of these with belly aortic aneurysms additionally be} affected. Although atherosclerosis additionally be|can be} a standard reason for aneurysms of the descending thoracic aorta, crucial reason for aneurysms of the ascending thoracic aorta is degeneration of the elastin and collagen throughout the media of the aortic wall. When this course of is extreme it recognized as|is called|is named} cystic medial necrosis, which histologically appears as easy muscle cell necrosis and degeneration of elastic layers throughout the media. Cystic medial necrosis is present in virtually all patients with Marfan syndrome (see Chapter 215), placing this group at very excessive risk for aortic aneurysm formation. Syphilis was quickly as} a standard reason for thoracic aortic aneurysms, with degeneration of the aortic media through the secondary part of the illness producing a weakening of aortic wall. Other rare causes of thoracic aortic aneurysms embrace infectious aortitis, great vessel arteritis, aortic trauma, and aortic dissection. When patients with belly aortic aneurysms expertise symptoms, pain within the hypogastrium or lower back is probably the most frequent complaint. Aneurysm growth or impending rupture additionally be} heralded by new or worsening pain, often of sudden onset. With precise rupture, the pain is usually associated with hypotension and the presence of a pulsatile belly mass. Patients with thoracic aortic aneurysms may expertise chest pain or, less often, back pain. Vascular issues embrace aortic insufficiency (sometimes with secondary heart failure), hemoptysis, and thromboembolism. An enlarging aneurysm may produce native mass effects because of of} compression of adjoining mediastinal structures, producing symptoms corresponding to coughing, wheezing, dyspnea, hoarseness, recurrent pneumonia, or dysphagia. Abdominal aortic aneurysms additionally be} palpable on physical examination, though weight problems may obscure even massive aneurysms. Typically, belly aortic aneurysms are hard to size precisely by physical examination alone, end result of|as a end result of} adjoining structures often make an aneurysm really feel larger than it really is|it truly is}. Ultrasound is extraordinarily sensitive and is probably the most sensible methodology to use in screening for aortic aneurysms. Thoracic aortic aneurysms are frequently recognized on chest radiographs, often producing widening of the mediastinal silhouette, enlargement of the aortic knob, or displacement of the trachea from midline. Transthoracic echocardiography, which usually visualizes the aortic root and ascending aorta properly, is helpful for screening patients with Marfan syndrome end result of|as a end result of} this group is at explicit risk for aneurysms involving this portion of the aorta. The majority of aneurysms expand over time, and the chance of rupture will increase with aneurysm size. The overall mortality in those who rupture an belly aortic aneurysm is 80%, including a mortality of 50% even reach the hospital. The objective of medical remedy for patients with aortic aneurysms is to attempt to scale back the chance of aneurysm growth and rupture. Aortic aneurysms that produce symptoms because of of} aneurysm growth, vascular issues, or compression of adjoining structures should be repaired. When aneurysms involve branch vessels, corresponding to renal or mesenteric arteries, these should be reimplanted into the graft. Similarly, when a dilated aortic root should be changed within the repair of an ascending thoracic aortic aneurysm, the coronary arteries should be reimplanted. In some centers another strategy for repair of belly aortic aneurysms (and some descending thoracic aneurysms) is the percutaneous placement of an expandable endovascular stent graft inside the aneurysm; nonetheless, this technique is often reserved for high-risk patients. Aortic dissection is a rare but life-threatening situation with an early mortality as excessive as 1% per hour. However, survival is considerably improved if the analysis is made promptly and applicable medical and/or surgical remedy instituted. Aortic dissection classically begins with a tear within the aortic intima that exposes a diseased medial layer to the systemic pressure of intraluminal blood. The blood then penetrates into the media, cleaving it into two layers longitudinally and producing a blood-filled false lumen throughout the aortic wall. This false lumen then propagates distally (or typically retrograde) a variable distance alongside the aorta from the site of intimal tear. In Braunwald E [ed]: Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine, 5th ed, p 1555. Two thirds of aortic dissections are sort A (proximal) and the other one third is sort B (distal). Involvement of the ascending aorta carries a excessive risk of early rupture and death from cardiac tamponade, so prognosis and administration differ based on the extent of aortic involvement. Dissections are additionally classified based on their length, with these present for less than 2 weeks considered acute and those present for two weeks or extra considered chronic. Disease of the aortic media, with degeneration of the medial collagen and elastin, is the most common predisposing factor for aortic dissection. Patients with Marfan syndrome have classic cystic medial degeneration and are at particularly excessive risk of aortic dissection at a comparatively younger age. The peak incidence of aortic dissection in patients with out Marfan syndrome is within the sixth and seventh a long time of life, and men are affected twice as often as ladies. A history of hypertension is present within the massive majority of cases, whereas a bicuspid aortic valve or coarctation of the aorta are less common. Rarely, aortic dissection may happen in a younger lady through the peripartum interval. Iatrogenic trauma from intra-aortic catheterization procedures or cardiac surgical procedure may also trigger aortic dissection. Severe pain, occurring in 74 to 90% of cases, is the most common presenting symptom of aortic dissection. The pain additionally be} retrosternal, within the neck or throat, interscapular, within the lower back, belly, or within the lower extremities depending on the location of the aortic dissection. Hypertension is a standard discovering on physical examination and is present in most of these with distal aortic dissection. Hypotension may also happen, particularly amongst these with proximal dissections, and is often because of of} rupture into the pericardium or extreme aortic insufficiency. Aortic insufficiency is another necessary physical discovering that occurs in multiple half of these with a proximal dissection. However, paradoxically, when acute aortic insufficiency is extreme the murmur in all probability not|will not be} appreciable, so a widened pulse pressure and congestive heart failure ought to increase suspicion of its presence. Vascular issues from aortic dissection embrace compromise of a coronary artery causing myocardial ischemia or infarction. Involvement of the brachiocephalic arteries may produce a stroke or coma, whereas compromise of the spinal arteries may produce paraplegia. When a dissection extends into the belly aorta, there additionally be} compromise of flow to one or each renal arteries producing acute renal failure which will exacerbate hypertension. Finally, the dissection may prolong distally to the aortic bifurcation and compromise or occlude one of many common iliac arteries producing a femoral pulse deficit and lower-extremity ischemia. It is usually an abnormality on a chest radiograph that first raises the suspicion of aortic dissection. However, the findings on chest radiography are non-specific and infrequently diagnostic. An enlarged mediastinal silhouette is the most common discovering, present in eighty one to 90% of cases. A left pleural effusion is usually seen in these with involvement of the descending thoracic aorta and, when small, usually represents a transudate from the infected aortic wall. Each institution must decide which of those modalities is most applicable as an preliminary diagnostic strategy based on the availability of each and the skill and expertise of those who carry out and interpret the diagnostic research.
Arisaema cochinchinense (Pinellia Ternata). Minipress.
- How does Pinellia Ternata work?
- Dosing considerations for Pinellia Ternata.
- What is Pinellia Ternata?
- Nausea, morning sickness, cough, birth control, influenza (flu), and inflammation.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97039
Trusted minipress 2 mg
High oxygen tensions during oxygen inhalation suppress erythropoietin manufacturing promptly and, within 2 days, impair red cell manufacturing. When transfusion is necessitated by cardiorespiratory signs, a single transfusion often suffices, as reticulocytosis soon resumes spontaneously. Transfusion typically additionally be} averted by imposing mattress relaxation and avoiding unnecessary oxygen therapy. Acute splenic sequestration is characterised by acute exacerbation of anemia, persistent reticulocytosis, a tender enlarging spleen, and typically hypovolemia. Thirty % of kids expertise splenic sequestration, and 15% of the assaults are fatal. Splenic sequestration recurs in half the cases, so splenectomy is really helpful after the acute event. Hyperhemolytic crisis is characterised by sudden exacerbation of anemia and increased reticulocytosis and bilirubin level. Apparent hyperhemolytic crises are often occult splenic sequestration or aplastic crises detected in the course of the resolving reticulocytosis. Chronic worsening of anemia additionally be} associated to incipient renal insufficiency or lack of folic acid or iron. Chronic hemolysis consumes folic acid stores, doubtlessly resulting in megaloblastic crises. The combination of nutritional deficiency and urinary iron losses might end in iron deficiency. This prognosis additionally be} obscured by the elevated serum iron levels related to hemolysis and often relies upon upon finding low serum ferritin or elevated serum transferrin levels. The acute painful episode of sickle cell disease was initially called "sickle cell crisis. One third of sufferers with sickle cell anemia not often have pain, one third are hospitalized for pain two to six occasions per 12 months, and one third have more than six pain-related hospitalizations per 12 months; 5% of sufferers account for one third of emergency division visits. The frequency of pain is highest in the third and fourth a long time, and after the second decade frequent pain is related to increased mortality rates. Factors related to more frequent pain are high hemoglobin levels, alpha-thalassemia, low Hb F levels, and sleep apnea. Painful episodes are brought on by vaso-occlusion and additionally be} precipitated by cold, dehydration, an infection, stress, menses, or alcohol consumption, however the cause of|the cause for} most episodes is indeterminate. Pain impacts any area of the physique, most commonly the again, chest, extremities, and stomach. Severity varies from trifling to agonizing, and the length is often a number of} days. Frequent pain might trigger despair, depression, and apathy, which predispose the patient to an existence that revolves round pain-a continual debilitating pain syndrome. Half of painful episodes are related to goal clinical signs-fever, swelling, tenderness, tachypnea, hypertension, nausea, and vomiting. Clinical software of these exams requires baseline knowledge with which to examine acute variations. Particular challenges to psychosocial adjustment are recurrent pain and the response to it, limitation of activity because of of} pain, misinterpretation of the which means of pain, and depression leading to realized helplessness. Some sufferers turn out to be addicted to narcotics, however habit is rare and most frequently outcome of|the outcomes of} social influences rather than acceptable analgesia therapy. Signs of fine adjustment are lively coping methods and assist from the family and the prolonged family unit. Interventional approaches emphasize recognizing and reinforcing individual strengths, confronting pathologic conduct, and establishing coping abilities such as re-interpreting pain, diverting attention from pain, and utilizing assist systems. Attention to psychosocial welfare is critical to the well being and integration into society of sufferers with sickle cell disease. Growth retardation impacts weight more than height and has no clear gender difference. Retarded sexual maturation in males may be outcome of|the outcomes of} main hypogonadism, hypopituitarism, or hypothalamic insufficiency. Impaired improvement may be the impact of hemolysis on increased protein turnover and basal metabolic rate and may be reversed after splenectomy. In 898 severely delayed development and improvement, hormonal therapy ought to be tailor-made to the precise deficiency. Infectious complications of sickle cell disease are a major reason for morbidity and mortality (Table 169-2) (Table Not Available). The second most common reason for bacteremia, Haemophilus Influenzae type b, impacts older kids, is less fulminant, but additionally additionally be} fatal. Results of pneumococcal vaccination had been disappointing, however newer vaccines in which S. Penicillin-resistant microorganisms have emerged, and native patterns of resistance range. Urinary tract infections and bacteremia in older sufferers are more probably because of of} Escherichia coli and different gram-negative organisms. Meningitis in sickle cell anemia is primarily an issue of infants and young kids, and S. Because meningitis occurs generally in affiliation with bacteremia, fast administration of antibiotics for bacteremia has resulted in a much decrease incidence of meningitis. Patients with any combination of dyspnea, cough, chest pain, fever, tachypnea, or leukocytosis ought to be evaluated by chest radiograph, arterial blood gas measurement, blood and sputum tradition, cold agglutinins, and serologic examine for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Legionella spp. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae account for roughly 20% of cases of acute chest syndrome. Osteomyelitis occurs more generally in sickle cell disease, probably outcome of|because of|on account of} an infection of infarcted bone. Among sickle cell sufferers, osteomyelitis is commonly brought on by Salmonella species. Many sufferers with sickle cell disease develop collateral vessels that seem as puffs of smoke (moyamoya in Japanese) on angiography. Improved treatment of this complication has been achieved with surgical extracranial-intracranial shunting. Coma is more regularly related to hemorrhage than with thrombosis, and the mixture of coma and seizures with out hemiparesis is strongly suggestive of hemorrhage. Although the mortality rate with hemorrhage is 50%, the morbidity rate of survivors is low. The favorable neurosurgical outcome in subarachnoid hemorrhage from ruptured aneurysm justifies aggressive prognosis, transfusion, vasodilatory therapy, and surgical procedure. In hemorrhage, angiography is indicated however is carried out solely after a partial trade transfusion to stop complications related to injected distinction materials. In thrombosis, immediate partial trade transfusion is indicated, and continual transfusion to keep the HbS level below 30% is initiated to stop recurrent thrombosis and promote decision. Transfusion additionally be} required indefinitely for those with persistent circulate abnormalities after 5 years of transfusion and for those in whom thrombosis recurs soon after discontinuing continual transfusion. Neurodevelopmental abnormalities have been found to result from silent cerebral infarcts. The "acute chest syndrome" consists of dyspnea, chest pain, fever, tachypnea, leukocytosis, and pulmonary infiltrate indicated on chest radiograph. It impacts roughly 30% of sufferers with sickle cell disease and additionally be} life-threatening. The usual causes are vaso-occlusion, an infection, and pulmonary fat embolus from infarcted marrow. Microbial pathogens are more generally isolated in kids, in whom the mortality rate is one fourth that in adults. Pulmonary fat embolism has a severe clinical course and may be diagnosed by a positive stain finding for fat in sputum macrophages. When sufferers have a progressive course related to severely decreased arterial oxygen pressure, intensive care additionally be} required. Evaluation of continual pulmonary standing in sufferers with sickle cell anemia might reveal restrictive lung disease, hypoxemia, and pulmonary hypertension, singly or in combination, typically preceded by a historical past of acute chest syndrome. Causes unrelated to prior acute episodes might relate to continual vascular insufficiency. Blood gas and pulmonary operate measurements ought to be obtained as baseline knowledge. Airway hyperreactivity and sleep apnea are more widespread in sickle cell disease and are treatable causes of morbidity. Pigmented gallstones develop outcome of|because of|on account of} the continual hemolysis of sickle cell disease and ultimately will happen in minimal of|no less than} 70% of sufferers.
Buy 2.5mg minipress
Potential medical consequences of such involvement include conduction defects. Five to 10% of sufferers with sarcoidosis develop neurologic complications of their disease. Virtually any half of} the nervous system could be concerned, including cranial nerves, peripheral nerves, meninges, cerebrum, spinal twine, and the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. The commonest form of clinically apparent neurologic involvement is unilateral facial nerve palsy, however different medical consequences include seizures, meningitis, peripheral neuropathy, and psychiatric symptoms. Involvement of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis could cause hyperprolactinemia and diabetes insipidus. Although granulomas are commonly found on histologic examination of the liver in sufferers with sarcoidosis, symptoms associated to hepatic involvement are unusual, and medical proof is normally limited to abnormalities in a number of} hepatic enzymes. In addition to intrathoracic lymph node involvement, peripheral lymph nodes may be be} enlarged due to granulomatous infiltration, however they hardly ever produce essential medical consequences. Parotid gland enlargement, lacrimal gland infiltration, bone lesions, splenomegaly, and myopathy end result of} granulomas within muscle tissue may be seen. Hypercalcemia, a potentially essential complication of sarcoidosis, occurs in fewer than 10% of sufferers and is believed to be end result of} elevated ranges of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol), which is produced by macrophages within the granulomas. As a end result, calcium absorption from the gut is elevated, leading to hypercalciuria with or without hypercalcemia. The initial consideration of sarcoidosis is normally primarily based on the medical and/or chest radiographic findings. When intrathoracic disease is the primary mode of presentation, the differential diagnosis usually depends on by} the radiographic presentation. Hilar and/or mediastinal adenopathy, both with or without related parenchymal lung disease, can also be|may also be|can be} produced by lymphoma, mycobacterial or fungal infection, and chosen pneumoconioses, such as berylliosis and silicosis. When interstitial lung disease is current in the absence of intrathoracic lymphadenopathy, a much broader|a wider|a much wider} differential diagnosis is raised, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary fibrosis associated with systemic rheumatic disease. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis is confirmed by the finding of well-formed non-caseating granulomas in a number of} affected organ methods or tissues, with applicable additional studies to exclude different causes of granulomas. Special stains and cultures should be performed for mycobacteria and fungi, and specimens must be examined under polarized mild to identify overseas, potentially granulomagenic material. The plain chest radiograph is a crucial part of the diagnostic analysis of sufferers with sarcoidosis; the diagnosis is incessantly suspected initially primarily based on the radiographic abnormalities, both in the presence or absence of symptomatic disease. The main abnormalities seen on the chest radiograph include lymphadenopathy, normally involving each hila in a comparatively symmetrical fashion properly as|in addition to} the proper paratracheal region, and involvement of the pulmonary parenchyma. Although the sample of parenchymal involvement is often described as interstitial, alveolar and nodular patterns may be seen. A commonly used radiographic staging system considers the sample of involvement seen on the chest radiograph (Table 81-1). Scanning with gallium citrate-67 may demonstrate uptake of this isotope in regions concerned with granulomatous inflammation, in all probability reflecting a combination of elevated capillary permeability properly as|in addition to} uptake of tracer by activated macrophages. Non-caseating granulomas found on biopsy of an affected organ or tissue are usually properly formed, consisting of a localized collection of epithelioid histiocytes surrounded by a rim of variable numbers of lymphocytes. Additional findings of a mononuclear cell alveolitis and variable quantities of fibrosis are diagnostically non-specific. Although non-caseating granulomas may be seen in hypersensitivity pneumonitis, the granulomas are usually much less discrete and properly formed than in sarcoidosis. The pulmonary parenchyma, intrathoracic lymph nodes, and pores and skin are the commonest websites of diagnostic biopsy in sarcoidosis. Mediastinoscopy is usually performed in the presence of isolated mediastinal adenopathy without parenchymal lung disease, when one other diagnosis such as lymphoma is being strongly considered. Thoracoscopic lung biopsy is usually used when a broader differential diagnosis of parenchymal lung disease has been raised, and more tissue is believed to be essential than could be obtained by transbronchial lung biopsy. Biopsy of tissue aside from the lung or mediastinal lymph nodes is performed primarily based on medical proof of involvement. Skin biopsy, a comparatively non-invasive process, is helpful when findings suggestive of cutaneous sarcoidosis are current. Similarly, biopsy of peripheral lymph nodes, liver, conjunctiva, parotid glands, skeletal muscle, and myocardium could be performed in chosen instances. The natural historical past of sarcoidosis is quite of|is sort of} variable, ranging from spontaneous resolution to both smoldering or progressive disease. Patients with progressive disease can become disabled from vital organ system involvement, significantly respiratory failure from extreme interstitial lung disease. Assessment of practical involvement of an organ and its course over time offers the overall framework for monitoring the natural historical past of disease. Although corticosteroids acutely suppress the manifestations of the disease, it has never been clearly demonstrated that they alter its long-term natural historical past. The dose can then be tapered, with the goal of utilizing the lowest possible dose that keeps the disease under sufficient management. Patients requiring systemic corticosteroid remedy for hypercalcemia can usually be treated with comparatively low doses of prednisone even initially, such as 10 to 20 mg/day. Treatment durations of 6 to 12 months are typical, and premature discontinuation of remedy may result in recurrence of symptomatic and practical disease. Patients should be suggested about and monitored for the myriad potential facet effects} observed with systemic corticosteroids (see Chapter 28). Alternative brokers when systemic corticosteroids are ineffective or not tolerated include methotrexate, usually at a dose of 10 to 15 mg/week, or different immunosuppressive or cytotoxic brokers. Although methotrexate has been used most as a corticosteroid-sparing agent, used as the sole real} agent, significantly for musculoskeletal or cutaneous sarcoidosis. Hydroxychloroquine has been used for severe and disfiguring cutaneous sarcoidosis. Topical corticosteroid preparations are used for anterior uveitis, however refractory disease may require remedy with systemic corticosteroids. In sufferers with extreme, end-stage pulmonary disease refractory to remedy, lung transplantation is a crucial choice, but the disease may recur in the allograft. British Thoracic Society: the diagnosis, assessment and remedy of diffuse parenchymal lung disease in adults. A recent position paper from the British Thoracic Society with suggestions regarding the analysis and management of diffuse parenchymal lung disease in general and a number of|various|a variety of} other|and quantity of} other} specific causes, including sarcoidosis. An excellent evaluate of possible causes and pathogenesis properly as|in addition to} medical elements of the disease. Multiple articles within this monograph present an excellent evaluate of the spectrum of points referring to sarcoidosis. Pneumonia is a term used to point out inflammation of the distal lung: terminal airways, alveolar spaces, and interstitium. To improve the precision of communication, the term pneumonia is normally additional certified with words that imply a trigger, mechanism, anatomic web site, or medical course. Thus, descriptors such as viral bronchopneumonia, aspiration pneumonia, chronic interstitial pneumonia, and acute bacterial pneumonia serve to identify medical illnesses characterised by signs and symptoms of lung inflammation in selection of|quite a lot of|a wide range of} medical situations (see Chapters 319 to 323). Bacteria are introduced into the lungs by any of four routes: by microaspiration, by inhalation, by way of the blood stream, or by direct extension (Table 82-1). The blood stream may transport to the lung organisms which will produce pneumonia, but the originating web site of infection and the extreme systemic effects of sepsis normally outweigh the importance of the resulting pneumonia. Direct extension from a focus of infection adjoining to the lungs is rare, and the initial web site of infection is always more essential. The term aspiration is usually mistakenly equated with inhalation of large volumes of fabric into the tracheobronchial tree, an occasion that happens only in sufferers with depressed consciousness or significantly deranged swallowing mechanisms. However, normal people aspirate small portions of oropharyngeal secretions throughout sleep, and the frequency and amount of aspiration are elevated in sufferers with altered consciousness. Because the focus of cardio micro organism in upper respiratory tract secretions is about 10 eight organisms per milliliter, and that of anaerobic micro organism is about 10 instances greater, aspiration of even small portions of oropharyngeal secretions introduces an unlimited bacterial problem to the lungs. Bacteria aspirated in Figure 82-1 Overview of the pathophysiology of bacterial pneumonia. The chemical nature of receptors for various species of micro organism is extremely variable, and the positioning of the receptor may be be} both an integral half of} the cell surface or contained in proteins hooked up to the cell. The availability of epithelial receptors and subsequently susceptibility to colonization vary with the underlying disease, antimicrobial remedy, or concurrent viral infections. Organisms current in ambient air are highly chosen by environmental conditions and should survive aerosolization, drying, temperature changes, and ultraviolet irradiation.
Quality minipress 2.5 mg
Two-year survival ranges from 60 to 80%, with most deaths being due to of} infections that complicate immunosuppressive remedy or to chronic allograft rejection. Typically, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is diagnosed in patients between ages forty and 60 years. Most patients present with the insidious onset of breathlessness with exercise and a dry, nonproductive cough. Constitutional signs together with fever, fatigue, weight loss, myalgia, and arthralgia are present in some patients. A right-sided heave, an augmented P2, and an S3 gallop are present in late levels of disease. These findings are thought to correlate with alveolar septal inflammation and the filling of air areas by mononuclear cells. Later, a predominantly decrease lung zone reticular infiltrate is present, which consists largely of thickened interlobular septa. Physiologic testing reveals a restrictive impairment with normal airflow parameters. Arterial blood gases may be be} normal or reveal hypoxemia (secondary to ventilation-perfusion mismatch) and respiratory alkalosis. The resting P O2 usually falls with exercise equal to walking up a single flight of stairs. Lung tissue obtained by thoracoscopic or open lung biopsy is required to set up the prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Later in the course of of|in the midst of} the disease, capillaries are lost, and increased numbers of mesenchymal cells and deranged collagen fibers are noted. The disease is patchy (nonhomogeneous) in its distribution till late in the course of of|in the midst of} disease. Lung biopsy findings which are be} predictive of responsiveness to remedy embody active inflammation and minimal fibrosis. The imply survival after prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is 5 to 7 years. Few patients expertise spontaneous regression or stabilization; accordingly, the nice majority of patients require treatment. Corticosteroids (see above) are the mainstay of remedy, though favorable clinical response occurs in solely 10 to 20% of patients. Sarcoidosis (see Chapter 81) is a multisystem granulomatous disease characterised by noncaseating granulomas and derangement of normal tissue structure. High-resolution computed tomographic scan from patient with biopsy-proven idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis exhibits patchy, peripheral ground-glass opacification, and small honeycomb cysts. High-resolution computed tomographic scan from a patient with biopsy-proven idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis exhibits quite a few giant cystic radiolucencies (honeycombing) involving each lungs. Although a lot of the lung parenchyma of the decrease lobes is concerned, the cystic process is extra distinguished within the subpleural regions. The distinct onset of a flu-like illness with a nonproductive cough is the most typical presentation. Fever, malaise, weight loss, and fatigue are usually present for 2 to four months prior to the onset of dyspnea. Patients have typically been unsuccessfully handled with quantity of} programs of antibiotics. An obstructive defect is present in 20% of patients, most of whom are present or past people who smoke. Chest radiography reveals bilateral diffuse alveolar opacities with normal lung volumes. Infiltrates may be be} peripheral, as seen in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, or migratory. In chosen situations the prognosis may be made by transbronchial biopsy, but thoracoscopic or open lung biopsy is usually required to verify this prognosis. Corticosteroid remedy is the most typical treatment and leads to recovery in two thirds of patients. Clinical enchancment is rapid (days to a number of} weeks) in some people, but relapse might occur when steroids are withdrawn; retreatment is usually successful. It have to be differentiated from different lymphocytic infiltrations of the lung, together with major lymphomas and lymphomatoid granulomatosis. Corticosteroid remedy is successful in approximately 50% of patients, though some patients progress to end-stage lung disease or lymphoma. Histiocytosis X is a term that encompasses three systemic diseases (eosinophilic granuloma, Letterer-Siwe disease, and Hand-Schuller-Christian disease) that have in common an irregular proliferation of a mononuclear cell, the Langerhans cell. Pleuritic chest ache and acute dyspnea secondary to spontaneous pneumothorax occur in 25% of patients. Cystic bone lesions (skull, ribs, pelvis) accompany the pulmonary disease in 10% of circumstances. Pulmonary function studies reveal a combined obstructive and restrictive sample. Morphologically, a granulomatous response develops in a bronchocentric distribution but in addition involves the partitions of blood vessels and the interstitium. The clinical course of histiocytosis X is variable; spontaneous remission, stabilization, and disease development might all occur. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis is a rare disorder occurring solely in ladies of child-bearing age. It is characterised by easy muscle cells proliferating within the lymphatic, peribronchial, perivascular, and interstitial tissues of the lung. Very little inflammation is present, but generally, the alveolar partitions are ultimately destroyed. Patients present with dyspnea, chylous pleural effusions (secondary to obstruction of the pleural lymphatics), and recurrent pneumothorax (due to rupture of emphysematous cysts). Coarse reticular infiltrates with areas of cystic dilation are noted on chest radiography. Numerous thin-walled cysts are distributed diffusely utilizing a|with no} predilection for particular regions or lobes. Nodules, interstitial fibrosis, and irregular lung pleural interfaces, options which are be} noticed in different chronic interstitial lung diseases, are absent. Pleural effusions or recurrent pneumothoraces may be the sole radiographic manifestation. Hormonal influences are thought to be important within the pathogenesis end result of|as a end result of} lymphangioleiomyomatosis occurs predominantly in premenopausal ladies and is accelerated throughout being pregnant, the postpartum interval, and exogenous estrogen remedy. Lung transplantation has been successful in patients with lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Associated pleural rubs may be be} heard, and clubbing occurs in as many as 75% of circumstances. The presence of rheumatoid nodules, pleural fibrosis, and adhesions additionally be|can be} useful diagnostically. Progressive bronchiolitis obliterans additionally be|can be} associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical manifestations embody the abrupt onset of dyspnea and dry cough associated with rales and midinspiratory squeaks, occurring significantly in middle-aged ladies with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Pulmonary function studies reveal airflow obstruction, arterial hypoxemia, and respiratory alkalosis. The predominant lesion is bronchiolitis with lymphoplasmacytic infiltration of the small airway partitions and obliteration of the bronchiolar airspace with granulation tissue. Acute lupus pneumonitis is characterised by the acute or subacute onset of tachypnea, tachycardia, dyspnea, cough, and cyanosis. High doses of corticosteroids are indicated in severely ill patients with acute pneumonitis; azathioprine may be added for refractory circumstances. Clinical manifestations embody dyspnea, initially with exertion and later at rest, but this symptom may be be} denied because of marked limitation of bodily exercise. Primary pulmonary hypertension might occur within the absence of pulmonary fibrosis and is usually the cause of|the cause for} cor pulmonale. In basic, correlation between the severity of pulmonary and cutaneous manifestations in scleroderma is poor. Pulmonary function abnormalities have significant prognostic implications: patients with normal function have a higher than 90% 5-year survival, whereas those with restrictive spirometry have a 58% 5-year survival.
Trusted minipress 2.5bottles
These new brokers additionally be} both stronger and extra specific than these used in the past. Further understanding of the methods by which international antigens are offered to lymphocytes and the lymphokine communication network (in which the T helper cell is central) will yield extra specific immunosuppression. The source of most human kidney transplants, nonetheless, is a cadaveric donor (a donor who has died but whose kidneys are still viable). Unquestionably essential for both living-related transplantation and cadaveric transplantation is the "crossmatch" check. Tissue-typing laboratories carry out this check before all kidney transplant operations. Technicians incubate leukocytes from the potential donor (living-related or cadaveric) with serum from the potential recipient and serum complement. If the serum of the recipient destroys the membranes of the leukocyte of the potential donor, the laboratory reports the check as optimistic. The surgeon normally cancels the transplant operation if the cross match is optimistic. A optimistic crossmatch predicts nearly immediate and extreme ("hyperacute") allograft rejection if the transplant is finished. Investigators are testing modifications of the cross matching procedure to discover a extra sensitive but extra specific check. More sensitive checks could lower different kinds of early rejection ("accelerated rejections"). Nearly one third of sufferers awaiting transplantation fall into this "extremely sensitized," difficult-to-transplant category. Physicians have tried different methods corresponding to plasmapheresis and extracorporeal immunoadsorption to discover a appropriate method of overcoming the issue of circulating preformed antibodies. The extra common use of erythropoietin in sufferers awaiting transplantation will reduce the publicity to blood transfusions. The most typical ailments that end in referring sufferers for transplantation are (1) diabetes mellitus with renal failure, (2) hypertensive renal illness, and (3) glomerulonephritis. No specific reason for intrinsic and irreversible renal failure is considered a contraindication to kidney transplantation. Nonetheless, all sufferers still should have reversible causes of renal dysfunction excluded. Table 105-4 lists choose ailments that may trigger renal failure and wish particular consideration before selecting renal transplantation as a therapy. Patients with renal failure induced by diabetes (Kimmelstiel-Wilson disease) make up the best population of sufferers currently referred for transplantation. The change in medical apply for this condition has resulted in a major extension of the life expectancy of sufferers whose kidneys fail from diabetes. Long-term vascular and gastrointestinal problems of scleroderma can restrict rehabilitation. Eventually, different organ involvement with diabetic illness limits both survival and rehabilitation in diabetic recipients of renal allografts. Today, living-related transplantation presents sufferers with diabetic renal failure the very best likelihood of prolonged survival. Most centers carry out transplantations earlier in diabetic sufferers than in these referred for different types of renal illness. If diabetic sufferers can undergo transplantation before extensive harm occurs in different organs, corresponding to the eye and heart, rehabilitation might be extra satisfactory. Such sufferers might develop extreme neurologic and heart problems to a degree that excludes them from transplantation. Hypertension is healthier handled than in the past, but the incidence of end-stage renal failure due to of} hypertension has not decreased. It ranks second solely to diabetes as a reason for renal failure in sufferers sent to renal transplant units. It is extra common for elevated blood pressure to destroy the kidneys of black sufferers than white sufferers. Kidney transplantation on this group of sufferers usually restores normal renal operate and normal blood pressure management. Black sufferers tend to to|are inclined to} have slightly poorer success with renal transplants than white sufferers. The various types of glomerulonephritis normally progress (slowly) to end-stage operate (see Chapter 106). The downside of recurrence of illness must be discussed with sufferers and prospective family kidney donors. Although infants have had successful transplantations, most centers keep infants on dialysis until physique measurement is elevated to 10 to 20 kg. Older age (> sixty five years) never precludes transplantation, nevertheless it will increase the risk of issues. On both ends of the age spectrum, nonetheless, transplantation is becoming extra common. Malignancy is considered a contraindication for kidney transplantation, as is extreme atherosclerotic or pulmonary illness. Both hepatitis B and C end result in|may find yourself in|can lead to} eventual liver failure in some sufferers after transplantation. How best to display sufferers contaminated with these brokers and who to avoid transplanting are problems currently underneath energetic investigation. Case reports counsel that such sufferers progress extra rapidly from carrier standing to scientific acquired immunodeficiency syndrome when given immunosuppressive therapy. Social circumstances (inability to take medicines or arrange follow-up) can also make kidney transplantation an impossibility. The transplant group that will carry out the surgical procedure and follow-up should consider the donor (living-related) and potential recipient of the transplant. This is best carried out at the transplant center before the precise transplantation date. The analysis group normally features a transplant surgeon, nephrologist, transplant nurse, urologist, social employee, and psychiatrist. Knowledge of the unique kidney illness is essential in managing the affected person after the transplant. Finally, the recipient must discuss the risks and advantages of transplantation surgical procedure. Both audiovisual aids and personal discussions with nurses, physicians, and different kidney transplant sufferers are key to preparing the affected person. Potential recipients found to have correctable cardiovascular or urologic lesions are inspired to have them repaired before transplantation. A nephrectomy additionally be|can be} advised if the native kidneys are contaminated in such a style that solely by removing them will the affected person be shielded from severe infections after transplantation. Occasionally, sufferers excrete such massive quantities of protein from diseased native kidneys that nephrectomy is really helpful because of protein malnutrition. Preparing the recipient with deliberate blood transfusions was a typical procedure before routine use of cyclosporine. An understanding of the mechanism by which such blood transfusions altered rejection, nonetheless, promises to improve our understanding of immune responses. Improved allograft harvesting has eliminated some (but not all) of the urgency from the procedure. The pretransplantation analysis of the recipient prepares the affected person for the precise day of the transplantation. An anastomosis is created between the donor renal artery and the hypogastric artery. These three connections all have variations, and all want skillful surgical technique. Immediate non-function of the allograft is much less common with enchancment of techniques for procurement and storage. Obstruction, vascular thrombosis, and ureteral compression from hematoma must be thought of in circumstances of primary non-function. Renal scans and ultrasound checks, as well as the persistence of the managing doctor, are indicated. Allografts that work immediately after releasing the vascular clamps engender immediate optimism. It is normally within the first three months after transplantation that reversible acute rejections occur.
Order minipress 2.5bottles
Augmentation of pulmonary venous pressure could trigger diminished pulmonary compliance, dyspnea, pulmonary vascular redistribution (detectable radiographically), interstitial and alveolar pulmonary edema, respiratory decompensation, and hypoxemia. Coupled with dyspnea within the elderly, it could be manifested only as confusion and combativeness. Increased sympathoadrenal tone reflected by markedly elevated plasma catecholamine ranges and adrenocortical stimulation additionally be} outstanding as properly. Plasma concentrations of atrial natriuretic peptide decrease initially but then improve, perhaps due to heart failure and atrial stretch. Elevated plasma concentrations of vasopressin, angiotensin (with beta-adrenergic stimulation of renin release), and aldosterone contribute to fluid retention and hyponatremia. Impaired fibrinolysis and augmented platelet activation by circulating catecholamines could predispose to persevering with coronary and ventricular mural thrombosis. Late mortality can also be|can be} related to diminished left ventricular ejection fraction and elevated left ventricular end-systolic and end-diastolic volumes. Complex ventricular ectopy after hospital discharge correlates with subsequent mortality. In addition, however, a extra modest prognostic good thing about} an open infarct-related artery additionally be} evident even when recanalization could be induced only 6 hours or extra after onset of signs, when salvaging substantial quantities of jeopardized ischemic myocardium is now not likely. An open infarct-related artery could improve ventricular perform, improve collateral blood circulate, decrease infarct enlargement, decrease ventricular aneurysm formation, improve ventricular reworking, diminish left ventricular dilatation, decrease late arrhythmia related to ventricular aneurysms, and reduce mortality. Typical pain is intense, severe, unremitting for 30 to 60 minutes, and retrosternal, typically radiating down the ulnar facet of the left arm and into the neck, to the left shoulder, jaw, or teeth. The pain is classically described as crushing or squeezing, nevertheless it additionally additionally be} described as an ache, burning pain, indigestion, or a feeling of fullness or "gasoline. Decreased systolic ventricular performance accounts for impaired perfusion of vital organs and reflex-mediated compensatory responses to hypotension, similar to restlessness and impaired mentation, pallor, cutaneous vasoconstriction and sweating, tachycardia, and prerenal failure. Impaired left ventricular diastolic perform results in pulmonary vascular congestion with shortness of breath and tachypnea and may lead to pulmonary edema with orthopnea. Impaired right ventricular diastolic perform results in systemic venous hypertension, edema, hepatomegaly, and additional compromise of left ventricular filling and cardiac output. Stoicism, an unusually excessive pain threshold, disorders similar to diabetes mellitus that impair perform of the nervous system, or obtundation caused by medicines or impaired cerebral perfusion could forestall recognition of typical chest pain. The blood pressure is generally elevated initially with arterial vasoconstriction, in distinction to the case of acute pulmonary embolism, by which preliminary hypotension is frequent. The respiratory price additionally be} increased in response to pulmonary congestion or anxiousness. Manifestations of atherosclerotic vascular disease include copper wiring of arterioles. Antecedent long-standing hypertension additionally be} reflected by arterial narrowing and hemorrhages. Conditions predisposing to atherosclerosis, similar to diabetes with microaneurysms, additionally be} evident. Funduscopic examination is especially necessary to detect hemorrhage and neovascular proliferation, which require monitoring if fibrinolytic agents are used. Pulsus alternans, although rare, could mirror impaired left ventricular perform, as could decreased amplitude and brevity of the carotid pulse secondary to decreased stroke quantity. Lateral displacement of the apex impulse, dyskinesis, a palpable S4 gallop, and a gentle S1 sound could indicate diminished contractility of the compromised left ventricle. Paradoxical splitting of S2 could mirror left bundle department block or prolongation of the pre-ejection interval with delayed aortic valve closure despite decreased stroke quantity. A mitral regurgitation murmur indicative of either papillary muscle dysfunction or rupture or annulus dilatation additionally be} audible even when cardiac output is diminished markedly. A systolic murmur and thrill indicative of ventricular septal rupture additionally be} heard, and a pericardial friction rub additionally be} evident. Premature ventricular beats, brief runs of ventricular tachycardia, or accelerated idioventricular rhythm are widespread. Peripheral cyanosis, edema, and pallor could indicate vasoconstriction, and diminished cardiac output could mirror right ventricular dysfunction or failure. Recrudescence of indicators or signs of a previously sustained cerebrovascular accident could happen secondary to diminished cerebral perfusion. Laboratory evaluation is especially useful within the presence of co-morbid conditions that will affect on} prognosis and affect care, similar to diabetes, renal or hepatic failure, anemia, bleeding disorders, and respiratory failure. The complete blood depend and platelet depend (which typically decreases after heparin is given) are helpful not only diagnostically but also in assessing suitability for therapy with thrombolytic drugs. The leukocyte depend additionally be} normal initially, nevertheless it typically increases within 2 hours and peaks in 2 to 4 days, with predominance of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and a shift to the left. The chest radiograph is useful in determining the presence or absence of cardiomegaly, pulmonary edema, pleural effusions, Kerley B strains, and other standards of heart failure. A small cardiac silhouette and clear lung fields in a patient with systemic hypotension could indicate relative or absolute hypovolemia. Chest radiographic findings indicative of pulmonary venous hypertension could happen later and persist longer due to delay in fluid shifts amongst vascular, interstitial, and alveolar areas. These macromolecules are ample in myocardium and are just about absent from most other tissues. Elevated troponin ranges, either assayed quantitatively within the common laboratory or semiquantitatively with hand-held units within the emergency department, also can assist predict which sufferers with clinical unstable angina (see Chapter 59) will subsequently develop severe issues. False-positive troponin T but not troponin I elevations happen in sufferers with renal insufficiency. The preferred non-invasive modality to evaluate regional wall motion and total ventricular performance is normally color-flow Doppler transthoracic echocardiography. In sufferers with ventricular thrombi, therapy entails administration of fibrinolytic drugs, anticoagulants, or each. Imaging is useful additionally to detect pericardial effusion, concomitant valvular or congenital heart disease, and marked melancholy of ventricular perform that will interdict therapy within the acute part with beta-adrenergic blockers. Echocardiography can also be|can be} useful in delineating recovery of stunned or hibernating myocardium. Doppler echocardiography is especially helpful to estimate the severity of mitral or tricuspid regurgitation, detect ventricular septal defects secondary to rupture, assess diastolic perform, monitor cardiac output calculated from circulate velocity and aortic outflow tract area estimates, and estimate pulmonary artery systolic pressure. Positron-emission tomography with tracers of middleman metabolism, perfusion, or oxidative metabolism permits quantitative evaluation of the distribution and extent of impairment of myocardial oxidative metabolism and regional myocardial perfusion (see Chapter 44). It also can outline the efficacy of therapeutic interventions designed to salvage myocardium and has been used diagnostically to differentiate reversible from irreversible damage in hypoperfused zones. Unstable recognized coronary disease (in terms of frequency, duration, intensity, or failure to reply to usual measures) b. Major new arrhythmias (new-onset atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, sustained supraventricular tachycardia, second-degree or complete heart block, or sustained or recurrent ventricular arrythmias) d. Major arrhythmias (new-onset atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, sustained supraventricular tachycardia, second-degree or complete heart block, or sustained or recurrent ventricular arrhythmias) 2. Community-based techniques in Belfast, Ireland; Columbus, Ohio; Los Angeles; and Seattle have documented conclusively the effectiveness of speedy response by rescuers. More than 60% (39% of these in sufferers who would otherwise succumb) could be prevented by defibrillation initiated by a bystander or a first-responding rescuer. Additional objectives of prehospital care by paramedical and emergency personnel include adequate analgesia (generally with morphine), reduction of extreme sympathoadrenal and vagal stimulation pharmacologically, therapy of hemodynamically vital or symptomatic ventricular arrhythmias (generally with lidocaine), and help of cardiac output, systemic blood pressure, and respiration. It is indicated for sufferers in whom thrombolysis will be the preferred approach to coronary reperfusion. Refractory or severe pain must be handled symptomatically with intravenous morphine, meperidine, or pentazocine. Repeated intravenous doses of 4 to 8 mg of morphine at intervals of 5 to 15 minutes could be given with relative impunity until the pain is relieved or toxicity is manifested by hypotension, vomiting, or depressed respiration. Blood pressure and pulse should be monitored in an try to maintain the systolic blood pressure above 100 mm Hg and, optimally, below a hundred and forty mm Hg. Relative hypotension additionally be} handled with elevation of the decrease extremities or administration of fluids, besides in sufferers with concomitant pulmonary congestion, in whom therapy for cardiogenic shock additionally be} required (see Chapter 95). Atropine, in doses similar to these given within the prehospital part, could improve blood pressure if hypotension reflects bradycardia or excess vagal tone. High concentrations additionally be} counterproductive due to vasoconstriction and lack of augmented myocardial oxygen delivery in normoxemic sufferers. Patients requiring mechanical air flow require special measures (see Chapter 93). Lower-risk sufferers without obvious ischemia must be noticed and monitored in either a step-down/intermediate care unit or a chest pain evaluation/observation unit (see above). Alternatives for coronary recanalization include intravenous thrombolytic agents or catheter-based approaches.
References:
- https://bioethicsarchive.georgetown.edu/nbac/stemcell2.pdf
- https://www.appliedneuroscience.com/PDFs/Brodmann.pdf
- http://e-district.org/userfiles/89/file/2020-10_LionsRoar_opt.pdf
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/018936s102lbl.pdf
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/016295s040lbl.pdf
.png)