Order nimotop 30 mg
The main abnormalities seen on the chest radiograph embody lymphadenopathy, normally involving each hila in a relatively symmetrical fashion in addition to the right paratracheal region, and involvement of the pulmonary parenchyma. Although the sample of parenchymal involvement is usually described as interstitial, alveolar and nodular patterns may be seen. A commonly used radiographic staging system considers the sample of involvement seen on the chest radiograph (Table eighty one-1). Scanning with gallium citrate-sixty seven could show uptake of this isotope in regions involved with granulomatous irritation, probably reflecting a mixture of elevated capillary permeability in addition to uptake of tracer by activated macrophages. Non-caseating granulomas found on biopsy of an affected organ or tissue are typically well fashioned, consisting of a localized collection of epithelioid histiocytes surrounded by a rim of variable numbers of lymphocytes. Additional findings of a mononuclear cell alveolitis and variable quantities of fibrosis are diagnostically non-particular. Although non-caseating granulomas may be seen in hypersensitivity pneumonitis, the granulomas are typically less discrete and well fashioned than in sarcoidosis. The pulmonary parenchyma, intrathoracic lymph nodes, and skin are the most common sites of diagnostic biopsy in sarcoidosis. Mediastinoscopy is usually carried out in the presence of isolated mediastinal adenopathy without parenchymal lung disease, when another analysis similar to lymphoma is being strongly thought of. Thoracoscopic lung biopsy is usually used when a broader differential analysis of parenchymal lung disease has been raised, and extra tissue is believed to be necessary than may be obtained by transbronchial lung biopsy. Biopsy of tissue other than the lung or mediastinal lymph nodes is carried out primarily based on clinical evidence of involvement. Skin biopsy, a relatively non-invasive process, is useful when findings suggestive of cutaneous sarcoidosis are current. Similarly, biopsy of peripheral lymph nodes, liver, conjunctiva, parotid glands, skeletal muscle, and myocardium may be carried out in selected cases. The pure historical past of sarcoidosis is quite variable, starting from spontaneous resolution to either smoldering or progressive disease. Patients with progressive disease can turn into disabled from significant organ system involvement, notably respiratory failure from severe interstitial lung disease. Assessment of functional involvement of an organ and its course over time offers the general framework for monitoring the pure historical past of disease. Although corticosteroids acutely suppress the manifestations of the disease, it has never been clearly demonstrated that they alter its lengthy-term pure historical past. The dose can then be tapered, with the goal of using the lowest attainable dose that retains the disease beneath adequate management. Patients requiring systemic corticosteroid remedy for hypercalcemia can typically be handled with relatively low doses of prednisone even initially, similar to 10 to 20 mg/day. Treatment durations of 6 to 12 months are typical, and untimely discontinuation of remedy could lead to recurrence of symptomatic and functional disease. Patients must be advised about and monitored for the myriad potential unwanted side effects noticed with systemic corticosteroids (see Chapter 28). Alternative brokers when systemic corticosteroids are ineffective or not tolerated embody methotrexate, typically at a dose of 10 to 15 mg/week, or other immunosuppressive or cytotoxic brokers. Although methotrexate has been used most as a corticosteroid-sparing agent, it can be used as the sole agent, notably for musculoskeletal or cutaneous sarcoidosis. Hydroxychloroquine has been used for critical and disfiguring cutaneous sarcoidosis. Topical corticosteroid preparations are used for anterior uveitis, however refractory disease could require remedy with systemic corticosteroids. In sufferers with severe, end-stage pulmonary disease refractory to remedy, lung transplantation is a crucial possibility, however the disease could recur in the allograft. British Thoracic Society: the analysis, evaluation and remedy of diffuse parenchymal lung disease in adults. A recent place paper from the British Thoracic Society with suggestions regarding the evaluation and management of diffuse parenchymal lung disease in general and several other particular causes, together with sarcoidosis. An wonderful review of attainable causes and pathogenesis in addition to clinical elements of the disease. Multiple articles within this monograph present an excellent review of the spectrum of issues referring to sarcoidosis. Pneumonia is a term used to indicate irritation of the distal lung: terminal airways, alveolar spaces, and interstitium. To improve the precision of communication, the term pneumonia is normally additional qualified with phrases that indicate a trigger, mechanism, anatomic website, or clinical course. Thus, descriptors similar to viral bronchopneumonia, aspiration pneumonia, persistent interstitial pneumonia, and acute bacterial pneumonia serve to identify clinical sicknesses characterized by indicators and signs of lung irritation in a variety of clinical conditions (see Chapters 319 to 323). Bacteria are introduced into the lungs by any of 4 routes: by microaspiration, by inhalation, through the blood stream, or by direct extension (Table 82-1). The blood stream could transport to the lung organisms that may produce pneumonia, however the originating website of infection and the severe systemic effects of sepsis normally outweigh the importance of the resulting pneumonia. Direct extension from a focus of infection adjacent to the lungs is rare, and the initial website of infection is at all times extra important. The term aspiration is often mistakenly equated with inhalation of enormous volumes of fabric into the tracheobronchial tree, an occasion that happens only in sufferers with depressed consciousness or seriously deranged swallowing mechanisms. However, regular people aspirate small portions of oropharyngeal secretions during sleep, and the frequency and quantity of aspiration are elevated in sufferers with altered consciousness. Because the concentration of aerobic micro organism in upper respiratory tract secretions is about 10 eight organisms per milliliter, and that of anaerobic micro organism is about 10 times larger, aspiration of even small portions of oropharyngeal secretions introduces an infinite bacterial challenge to the lungs. Bacteria aspirated in Figure 82-1 Overview of the pathophysiology of bacterial pneumonia. The chemical nature of receptors for different species of micro organism is highly variable, and the positioning of the receptor may be either an integral a part of the cell floor or contained in proteins hooked up to the cell. The availability of epithelial receptors and therefore susceptibility to colonization range with the underlying disease, antimicrobial remedy, or concurrent viral infections. Organisms current in ambient air are extremely selected by environmental conditions and must survive aerosolization, drying, temperature adjustments, and ultraviolet irradiation. Further, as a result of few if any microorganisms are inhaled with every breath, only organisms able to causing infection with a really small inoculum can produce disease by the airborne route. However, the list of micro organism able to being transmitted by this route is brief and contains only organisms which are unusually invasive, such as the plague and anthrax bacilli, and organisms which are current in massive numbers in contaminated air in confined spaces, similar to Legionella organisms. Organisms able to airborne transmission typically produce outbreaks of infection when teams of vulnerable persons are exposed; examples embody Legionella, influenza, and anthrax. About 90% of particles 5 to 10 mum in diameter are deposited along the tracheobronchial tree, whereas particles zero. Smaller particles behave like gas molecules and are largely exhaled somewhat than retained. Droplet nuclei is the term applied to particles about 1 to 3 mum in diameter containing a single bacterium, the likely infecting unit for organisms transmitted by the airborne route. The first line of defense in opposition to micro organism deposited in the lungs is the mucociliary escalator, an built-in multifaceted system consisting of the ciliated cells lining the airways, the secretory cells (goblet cells and submucosal glands), and the secretions. However, the effectiveness of this activity depends on maintaining the depth and viscosity of secretions and coordination of ciliary activity. Processes that impair ciliary movement, trigger extreme secretion of respiratory mucus, or change the viscosity of secretions could hinder the effectiveness of this transport system (Table 82-2). Bacteria that penetrate to the distal airways or alveoli are killed in situ by phagocytic cells. Nonspecific opsonization, which aids phagocytosis, may be offered by lung surfactant or fibronectin. Alveolar macrophages that reside in the lungs can ingest and kill huge numbers of nonpathogenic micro organism, similar to many of the regular oropharyngeal flora, without eliciting an inflammatory response. For micro organism which are extra pathogenic, the situation is extra sophisticated; some species promptly recruit neutrophils, and bacterial killing seems to rely much more upon the provision of neutrophils than on the presence of alveolar macrophages. Clearance of these organisms from the lung is enhanced by the presence of particular antibody. Immunoglobulin (Ig) G is the predominant immunoglobulin in the alveolus, comprising about 10 to 15% of the protein in alveolar fluid. If viable micro organism persist, an inflammatory response swiftly develops and is characterized by interstitial and alveolar edema in addition to an influx of neutrophils. As neutrophils and micro organism accumulate, the milieu turns into acidic and hypoxic, and bacterial ingestion and killing are remarkably retarded.
Generic 30mg nimotop
Erythema multiforme Acetaminophen Barbiturates Carbamazepine Chloroquine Chlorpropamide Clindamycin Ethambutol Ethosuximide Gold salts Hydantoins Hydralazine Hydroxyurea Mechlorethamine Meclofenamate Penicillins Phenolphthalein Phenylbutazone Rifampin Streptomycin Sulfonylureas Sulindac Vaccines E. Topical Fluorouracil Hexachlorophene Para-aminobenzoic acid esters Promethazine Sulfanilamide 2. Systemic Carbamazepine Chlorpromazine Griseofulvin Imipramine Lincomycin Nalidixic acid Naproxen Norfloxacin Phenothiazines Piroxicam Quinethazone Sulfonamides Sulfonylureas Thiazide diuretics Triamterene F. Fixed drug eruptions Acetaminophen 5-Aminosalicylic acid Aspirin Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Chloroquine Dapsone Dimenhydrinate Diphenhydramine Gold salts Hydralazine Hyoscine Ibuprofen Iodides Meprobamate Methenamine Metronidazole Penicillins Phenobarbital Phenolphthalein Phenothiazines Phenylbutazone Procarbazine Pseudoephedrine Quinine Saccharin Streptomycin Sulfonamides Tetracyclines G. Eosinophilic pneumonitis 5-Aminosalicylic acid Azathioprine Captopril Carbamazepine Chlorpropamide Cromolyn Desipramine Gold salts Imipramine Nitrofurantoin Penicillins Phenytoin Sulfonamides l -Tryptophan C. Cholestatic Chlorzoxazone Erythromycin estolate Ethchlorvynol Imipramine Nalidixic acid Nitrofurantoin Phenothiazines Sulfamethoxazole Sulfonylureas Troleandomycin B. Hepatocellular 5-Aminosalicylic acid Amphotericin B Azapropazone Ethacrynic acid Furosemide Gold salts Griseofulvin Halothane Hydantoins Isoniazid Methyldopa Monoamine oxidase in hibitors Nitrofurantoin Propylthiouracil Pyrazinamide Quinidine Rifampin Sulfonamides Trimethadione C. Bone marrow aplasia Chloramphenicol Gold salts Mephenytoin Penicillamine Phenylbutazone Trimethadione B. Anemia Acetaminophen 5-Aminosalicylic acid Captopril Cephalosporins Chlorpromazine Cisplatin Hydantoins Ibuprofen Insulin Isoniazid Levodopa Mefenamic acid Melphalan Methyldopa Methylsergide Penicillins Quinidine Quinine Rifampin Sulfonamides Sulfonylureas C. Thrombocytopenia Acetaminophen Acetazolamide Acetylsalicylic acid 5-Aminosalicylic acid Carbamazepine Chloramphenicol Chlorpheniramine Cimetidine Digitoxin Diltiazem Ethchlorvynol Gold salts Heparin Hydantoins Isoniazid Levodopa Meprobamate Methyldopa Penicillamine Phenylbutazone Procainamide Quinidine Quinine Ranitidine Rauwolfia alkaloids Rifampin Sulfonamides Sulfonylureas Thiazide diuretics D. Granulocytopenia Captopril Cephalosporins Chloral hydrate Chlorpropamide Penicillins (semisynthetic) Phenothiazines Phenylbutazone Phenytoin Procainamide Propranolol Tolbutamide E. Although it ought to be clear from the earlier discussion that many of the properly-known opposed drug effects are because of a comparatively small group of medication, it ought to be emphasized that every drug can probably cause an opposed drug response. Therefore, the doctor ought to at all times contemplate the possibility of an opposed drug response within the differential analysis even when none has been reported previously for the actual drug. Table 26-5 lists a variety of numerous medical presentations related to opposed drug responses. In other circumstances, the impact produced by the drug could also be troublesome to discern from other illness states. This handbook provides useful knowledge for adjusting doses in patients with renal dysfunction, including these on dialysis. Doucet J, Chassagne P, Trivalle C, et al: Drug-drug interactions associated to hospital admissions in older adults: A prospective research of one thousand patients. Study of the frequency, nature, and side effects of drug-drug interactions in geriatric patients consecutively admitted to an inpatient facility. Many opposed drug-drug interactions are secondary to pharmacokinetic changes that can be defined by alterations of P-450 catalyzed reactions. Review of clinically important drug interactions that occur with commonly used anticoagulant drugs. Current evaluation of ideas that ought to be utilized in managing drug use within the presence of renal insufficiency (118 references). This paperback handbook provides a comparatively comprehensive itemizing of medication thought to produce interactions, with a description of opposed effects, their possible mechanisms, medical recommendations, and original references. Guidelines for drug administration within the presence of liver illness (225 references). The consensus in ache remedy is that ache patients are managed most effectively by a multidisciplinary approach, utilizing the experience of a variety of health care professionals. To facilitate medical analysis and affected person care, the International Association for the Study of Pain has proposed a taxonomy of ache syndromes to function a universal classification, with a working definition of ache as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience related to both precise or potential tissue harm, or described by way of such harm. In the vast majority of medical ache syndromes, ache remedy serves to palliate the symptom. Patients with acute ache normally give a transparent description of its location, character, and timing, leading to an etiologic analysis. Objective signs and associated autonomic nervous system hyperactivity with tachycardia, hypertension, and diaphoresis are present. Subacute ache develops over a number of days, and episodic ache happens for set intervals of time on a recurring basis. The acute signs of autonomic nervous system hyperactivity disappear with adaption to the ache. Multidisciplinary approaches to treatment play a critical role in addressing the multidimensional elements of the ache. Other commonly used phrases to describe ache embody baseline ache, which refers to the average ache intensity expressed for 12 or more hours in a 24-hour interval, and breakthrough ache, which is a transient increase in ache resulting from volitional factors. Pain intensity is the main consider selecting drug remedy, and the use of a reliable ache intensity scale can enormously have an effect on appropriate affected person treatment. The repeated use of validated ache intensity scales, such as categorical scales, numerical scales, and visual analogue scales, can facilitate appropriate ache assessment and treatment. Categorical scales use verbal reports and ask patients to describe their ache as gentle, reasonable, severe, or excruciating. Numerical scales ask patients to fee their ache as a quantity from 0 to 10 with 0 at "no ache" and 10 being the "worst possible ache. Visceral ache results from visceral nociceptive receptors and visceral efferent nerves being activated and is characterised by a deep, aching, cramping sensation usually referred to cutaneous websites. It is typically described as burning or dysesthetic and often happens in an area of sensory loss. Recent experimental ache models in animals and people have offered the opportunity to research neuropathic ache and its phenomena of "windup," whereby spinal neurons turn out to be abnormally energetic after repetitive C-fiber stimulation, and "central sensitization," whereby neurons decrease activation thresholds, enlarge their receptive fields, and fireplace spontaneously. These phenomena account for the medical signs of allodynia (ache related to non-nociceptive stimuli) and hyperalgesia (increased ache with nociceptive stimuli) that occur with nerve injury. Clinical trials are in progress to define the security and efficacy of these agents. Patients with chronic ache can generally be categorized into one of three main etiologic groups, permitting for some overlap. The first group includes patients with chronic ache related to structural illness. Successful treatment of the ache is intently allied with illness treatment, but in certain cases, treating the ache is the only therapeutic aim. Psychological factors might play an important role in exacerbating or relieving the ache, but analgesic drugs are often the mainstay of remedy. The second group contains patients who suffer from psychophysiologic problems inflicting ache. In these patients, structural illness, such as a herniated disc or torn ligament, might once have been present, but psychological factors have brought on chronic physiologic alterations, such as muscle spasms, which produce ache lengthy after the underlying defect has healed. Typically, such patients are physically inactive and spend a lot of their time considering and talking about their ache, usually leading to social and emotional isolation. Patients are more impaired by the "chronic illness conduct" than by a defined pathologic situation. They normally reply poorly to analgesic drugs and often undergo from iatrogenic problems such as opposed drug reactions and ineffective surgical procedures. Successful treatment could be expected solely via a structured rehabilitation program designed to modify ache behaviors and not via medical intervention that corrects pathologic conditions. Multidisciplinary ache clinics that diagnose and treat these intractable chronic ache syndromes exist in many centers and ought to be used to consider and treat such patients. Patients within the third group complain of ache that appears to have neither a structural nor a physiologic basis. Such patients normally have serious psychiatric problems, and the historical past of their ache is so imprecise and weird and its distribution so unanatomic as to recommend the analysis. These patients are uncommon, reply poorly to ache treatment methods alone, and require psychiatric treatment with a variable response fee. A comprehensive assessment entails taking a careful historical past, performing a detailed medical, neurologic, and psychological analysis, creating a sequence of analysis-associated hypotheses, and ordering the suitable diagnostic studies. Multiple ache complaints are frequent in patients with chronic medical illness and need to be prioritized and categorized. Assess the traits of each ache, including site, referral pattern, and aggravating and relieving factors.
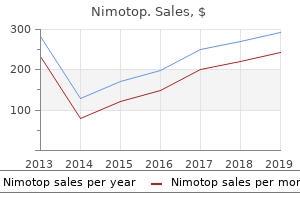
Trusted 30 mg nimotop
If indicated, intubation of the trachea and mechanical ventilation could be instituted; on this case the objective should be to provide a stage of ventilation simply enough to maintain life but not adequate to normalize arterial blood gases. However, no pointless drugs should be administered; systemic steroids should be used sparingly to avert fetal problems, and sure medicine should be avoided, including tetracycline (as a therapy for intercurrent an infection), atropine and atropine-like medicine (which can trigger fetal tachycardia), terbutaline (which is contraindicated throughout energetic labor because of its tocolytic results), and iodine-containing mucolytics (corresponding to saturated resolution of potassium iodide). Moreover, use of prostaglandin F2 as an abortifacient should be avoided in asthmatics. Controlled trial demonstrating the efficacy of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors in asthma. The decrease prevalence in girls is believed to be due to their decrease smoking charges rather than to a protecting hormonal impact. Because the disease is critically underdiagnosed, as many as 30 million persons could also be affected. Indirect prices, corresponding to from incapacity and days lost from work, are much larger. The hallmark of continual obstructive lung disease is a discount of maximal expiratory flow fee. This reduction of flow fee independent of the underlying pathologic course of produces much of the pathophysiologic features and incapacity of these ailments. In the absence of effective therapy for either continual bronchitis or emphysema, and because of their virtually common coexistence and the difficulty in assessing the contribution of every to a lowered maximal airflow, little effort to separate them has been made until recently. Other ailments related to continual airway obstruction include bronchiolitis obliterans related to continual lung transplant rejection (see Chapter 89), bronchiectasis (see Chapter seventy seven), cystic fibrosis (see Chapter seventy six), lymphangiomyomatosis, sarcoidosis (see Chapter eighty one), and histiocytosis. Chronic Bronchitis Chronic bronchitis is a scientific prognosis requiring patients to have a continual cough productive of sputum for no less than 3 months a year for no less than 2 consecutive years in the absence of other ailments, corresponding to asthma, bronchial tumors, bronchiectasis, or continual lung infections. However, solely a minority of patients with continual bronchitis develop clinically important airway obstruction. Rare patients develop continual bronchitis with minimal or no history of cigarette smoking or other exposures related to the condition. Smoking exposure is normally quantified by the product of packs of cigarettes per day instances the variety of years smoked. Only about certainly one of six continual cigarette smokers develops clinically important disease. Abnormalities of cytokines and pro-inflammatory mediators are believed to play an necessary etiologic position. In our sedentary society, patients may lose 50% of their lung function before signs develop. In the previous, physicians believed such patients had a slowly progressive decrease in function but belittled or denied signs until some explicit incident. The pathology of continual bronchitis is bronchial inflammation, which differs from the eosinophilic inflammation of asthma (see Chapter 74). In the large airways, will increase in the dimension and variety of mucous glands and goblet cells are famous. Smooth muscle will increase, and partial destruction of bronchial cartilage and adventitial fibrosis happens. A neutrophilic infiltrate is current, which is far less dramatic than the inflammatory infiltrates seen in asthma. In the small airways, the lumen could also be fully occluded by mucus and inflammatory cell infiltrates, and fibrosis is current in the bronchiolar walls. Emphysema Emphysema, which is a pathologic prognosis, consists of enlargement of the terminal air areas due to destruction of alveolar walls. In centrilobular emphysema, which is normally related to cigarette smoking, alveolar destruction happens initially around the respiratory bronchioles; inside every affected acinus, extra regular alveoli surround a central core of emphysema. As the lesion progresses, the whole lobule is involved; in consequence, panlobular emphysema develops. However, in some cases of comparatively delicate emphysema, panlobular alveolar destruction happens all through every affected lobule while adjoining areas remain just about regular. Centrilobular emphysema is often worse in the apices of the upper lobes and superior segments of the decrease lobes, but the reason for this distribution is unknown. Emphysema, notably the panlobular selection, has been identified to have a strong familial element for the reason that late Sixties, when it was famous that some patients from households with a high incidence of early-onset, extreme emphysema had decreased alpha1 -globulin ranges on protein electrophoreses. This discovery was answerable for the current paradigm for the etiology of emphysema. Noxious substances in cigarette smoke injure the alveolar epithelium and trigger a release of inflammatory mediators, which magnetize activated neutrophils to the alveolar region. These activated neutrophils release leukocyte elastase, which is a crucial element of their antimicrobial action. Damage to host tissues is minimized by antiprotease activity: diffusion of alpha1 -antitrypsin from the plasma in areas of elevated vascular permeability, as a result of inflammation, is the most important factor that neutralizes leukocyte elastase. In the absence of alpha1 -antitrypsin, neutrophil elastase remains energetic, destroys alveolar walls, and produces panlobular emphysema. Endotracheal instillation of trypsin or elastase in experimental animals produces panlobular emphysema much like that observed in people. The lung develops when the bronchial tree buds into primordial mesenchymal tissue. The conducting airways could be considered tubes that lie in tunnels, whose lengths and diameters enhance with will increase in lung quantity. Thus, to the first approximation, the stress surrounding the intraparenchymal airways is pleural stress. The lung is inflated by the distinction between alveolar and pleural stress, which stresses the lung tissue. The airways are also distended by the distinction between intraluminal stress and pleural stress. During expiration, pleural stress is elevated above the subatmospheric 395 stress required to preserve static inflation of the lung at that quantity. Alveolar stress is elevated by the same amount, and expiratory flow happens down this stress gradient. Expiratory flow is related to a decrease of stress in the airways because of frictional losses in the gasoline and conversion of stress into kinetic power when gasoline velocity will increase as the whole cross-sectional area of the tree decreases several hundredfold from essentially the most peripheral airways to the central airways. With adequate expiratory effort to produce optimistic pleural stress, intraluminal airway stress falls beneath pleural stress. When this occurs, flow reaches a crucial velocity, called wave velocity in the airway, analogous to the velocity of sound. However, throughout expiration, flow will increase solely until a crucial threshold is reached, after which flow becomes fixed. Therefore, maximal flow at any given lung quantity is decided by the elastic recoil of the lung at that quantity (which determines not solely the diameter of the elastic airways but additionally the amount of stress that may be dissipated throughout expiration before intraluminal airway stress falls beneath pleural stress) and by the geometry of the airway (which determines how much flow can occur before the elastic recoil stress is dissipated). Maximal flow decreases with quantity because of a discount in elastic recoil, which is the driving stress, and since airway diameter decreases with the reducing transmural stress. The air remaining in the lung at this time, termed the residual quantity, will increase with age from approximately 20% of maximal quantity to more than 50% in older topics. The maximum quantity of the lungs, termed complete lung capability, is decided by the steadiness of forces between the maximally activated inspiratory muscular tissues and the inward elastic recoil of the lung and chest wall. Any narrowing of the airway lumen due to the changes in continual bronchitis, elevated mucus in the lumen, or fibrosis of the wall will decrease the amount of flow that may occur before the elastic recoil stress is dissipated. Decreased lung recoil also reduces maximal flow because of lowered driving stress and decreased distending stress on the airways. Patients with extreme emphysema can have residual volumes near their predicted regular complete lung capability in order that both their maximal flow and static elastic recoil are markedly lowered at all lung volumes, but the relationship between flow and recoil is the same as that in a normal individual at very low lung volumes. Because of the phenomenon of flow limitation, maximal expiratory flow is a measure of the integrity of the lung independent of patient effort as soon as the edge effort is achieved. In the elderly, maximal flow in the tidal quantity vary is lowered in order that it approaches tidal flow. Elderly topics can still enhance their ventilation substantially (when needed for exercise) by inspiring to very high lung volumes. In regular people, maximal exercise capability is decided by the cardiovascular system rather than by the lungs, although in the exceptionally fit geriatric athletes, ventilation could also be limiting. The relaxed chest wall may enhance pleural stress sufficiently to obtain maximal flow without expiratory effort and produce a optimistic pleural stress throughout expiration. Because airway resistance is high, pleural stress is kind of adverse throughout inspiration.
Trusted nimotop 30mg
Average hemoglobin levels related to completely different alpha-globingeno types in adults are 7. Deoxygenation of sickle cell suspensions leads to technology of deoxy-HbS polymer, alteration of cellular morphologic characteristics, and increased viscosity of the cell suspension. Accrual of polymer is prompt and precedes changes in cell morphologic properties during deoxygenation. Polymer alignment and the number of intracellular polymer domains that influence the rheologic properties of sickle cells are affected by each deoxygenation rate and shear stress. During sluggish deoxygenation, classic crescent-formed cells with a single domain of extremely aligned polymer come up by homogeneous nucleation from a single nucleus; with faster deoxygenation, holly leaf-formed cells with a larger number of less nicely-aligned domains are generated by heterogeneous nucleation from a couple of nuclei; and with very fast deoxygenation, granular cells with a number of poorly aligned domains are derived by heterogeneous nucleation from many nuclei. Shear stress during polymerization creates extra nucleation sites, shortens the delay time, and will increase cell viscosity; shear utilized after polymerization has begun breaks the polymer and diminishes viscosity. Their rheologic impairment is said extra to the effects of extreme cellular dehydration on intraerythrocytic HbS focus, cytoplasmic viscosity, and polymerization tendency than to rigidly deformed skeletal proteins. Lacking the protective effects of Hb F towards polymerization and sickling, these young purple cells are predestined to fast dehydration. The sodium-potassium pump, in making an attempt to restore the perturbations in cation homeostasis caused by deoxygenation-induced passive cation leaks, depletes cells of monovalent cations on account of its mounted stoichiometry of three sodium ions pumped out for every two potassium ions pumped in. A extra important reason for cell dehydration includes the interdependent actions of calcium-dependent potassium loss (Gardos pathway) and potassium chloride cotransport on a population of calcium-delicate reticulocytes. Gardos-mediated potassium efflux lowers the intracellular pH, thereby activating the amount-regulatory K-Cl cotransport activity, which further depletes cells of potassium and water. Third, the interaction of alpha thalassemia and sickle cell anemia is extra important for broadening pathophysiologic interpretations than for recapitulating the polymerization principle. Yet, coexistent alpha thalassemia is related to extra extreme vaso-occlusion-extra frequent ache and osteonecrosis and the next mortality rate after the age of 20 years. These conflicting influences of alpha thalassemia show the necessity for a pathophysiologic understanding that features polymerization-impartial mechanisms. In addition to having abnormal electrophoretic and solubility properties, HbS is unstable. Its oxidation leads to increased technology of methemoglobin, heme, and oxidative radicals. Resultant oxidative stresses affect purple cell metabolism, membrane lipids, membrane proteins, and HbS itself. Hemichrome aggregates on the cytoplasmic portion of band 3 initiate membrane coclustering of band 3 molecules, meeting of immunoglobulin G (IgG) and complement on their extracellular domains, and sickle cell adherence to macrophages and endothelial cells. Adherence of sickle erythrocytes to endothelial cells is mediated by quite a few receptors and ligands. The steady perturbation and activation of the hemostatic system disease suggest that a gentle state of regular vascular flow in sickle cell may be illusory. There is proof for ongoing platelet activation, which is increased during acute vaso-occlusive episodes. Phosphatidylserine is able to activating the coagulation system, as are phosphatidylserine-wealthy vesicles exovesiculated from sickle erythrocyte membranes during sickling, activated endothelial cells, and activated monocytes. Another hemostatic activator is the tissue issue expressed by circulating endothelial cells which were dislodged from their vascular moorings in the midst of vascular perturbations in this disease. Although polymerization of deoxy-HbS and sickling of erythrocytes provide the idea of sickle cell disease, a important assessment of their position in vaso-occlusion illustrates the necessity for a extra complete view of pathophysiologic processes. However, there are adequate exceptions to this model in order that polymerization may be thought to be necessary however not adequate for vaso-occlusion. Sickle cells become deoxygenated extra regularly than as soon as a minute, demonstrating that "sickling" is a continuing, unrelenting process quite than an occasional cataclysmic one. A, Adherent discocytic sickle cells tethered to the endothelial wall of a venule and aligned within the path of the flow (arrow). B, Increased adherence of sickle cells at venule or bending and at junctions of smaller-diameter post-capillary venules. Although polymerization tendencies provide a first approximation of sickle cell disease severity, transient changes in vascular flow are finest understood when it comes to a broader group of pathophysiologic processes. The former is due to the effects of unstable HbS and recurrent sickling on causing oxidative injury to cell membranes. Binding of oxidatively denatured HbS to the cytosolic portion of band 3 induces adherence of IgG and complement to extracellular band 3, thereby selling cell recognition by macrophages. Elevated free plasma hemoglobin levels suggest that one third of sickle cell hemolysis is intravascular. One mechanism pertains to sickling-induced exovesiculation of vesicles enriched in phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane proteins, which depletes cells of complement-regulatory proteins and leaves them vulnerable to comple-ment-mediated lysis. A second mechanism includes the mechanical fragility of cells, which accounts for accelerated hemolysis during exercise. The propensity of children with sickle cell disease to Streptococcus pneumoniae infection pertains to their impaired splenic function and diminished serum opsonizing activity. The function of the spleen is deficient even before its eventual autoinfarction, however previous to the second decade function is restorable by transfusion. Even within essentially the most extreme genotype, sickle cell anemia, asymptomatic patients may be detected by the way whereas others are disabled by disease problems. Most organ methods are subject to vaso-occlusion, ensuing within the attribute acute and persistent multisystem failure. Important medical options less immediately associated to vaso-occlusion are progress retardation, psychosocial problems, and susceptibility to infection. The current mean survival is forty two years for men and 48 years for girls with sickle cell anemia. This improved life expectancy compared with that of earlier eras is especially the results of better common medical care, such as prophylactic penicillin remedy for preventing S. In addition to hemolysis, inappropriately low erythropoietin levels contribute to the anemia. The moderately constant level of hemolytic anemia may be exacerbated by several completely different causes, mostly aplastic crises. Aplastic crises are transient arrests of erythropoiesis characterised by abrupt falls in hemoglobin levels, reticulocyte number, and purple cell precursors within the marrow. Anemia turns into extreme as hemolysis continues within the absence of purple cell manufacturing, however these episodes sometimes last only a few days. Although common mechanisms that impair erythropoiesis in inflammation happen in all types of infection, parvovirus B19 particularly invades proliferating erythroid progenitors, accounting for its importance in sickle cell disease. Parvovirus B19 accounts for approximately two thirds of aplastic crises in youngsters with sickle cell disease, however the high frequency of protective antibodies in adults makes parvovirus a less frequent cause in this age group. High oxygen tensions during oxygen inhalation suppress erythropoietin manufacturing promptly and, within 2 days, impair purple cell manufacturing. When transfusion is necessitated by cardiorespiratory signs, a single transfusion often suffices, as reticulocytosis soon resumes spontaneously. Transfusion typically may be prevented by implementing mattress rest and avoiding pointless oxygen remedy. Acute splenic sequestration is characterised by acute exacerbation of anemia, persistent reticulocytosis, a young enlarging spleen, and typically hypovolemia. Thirty % of children experience splenic sequestration, and 15% of the assaults are deadly. Splenic sequestration recurs in half the circumstances, so splenectomy is recommended after the acute event. Hyperhemolytic crisis is characterised by sudden exacerbation of anemia and increased reticulocytosis and bilirubin level. Apparent hyperhemolytic crises are often occult splenic sequestration or aplastic crises detected in the course of the resolving reticulocytosis. Chronic worsening of anemia may be associated to incipient renal insufficiency or lack of folic acid or iron. Chronic hemolysis consumes folic acid shops, potentially leading to megaloblastic crises. The mixture of nutritional deficiency and urinary iron losses may result in iron deficiency. This diagnosis may be obscured by the elevated serum iron levels related to hemolysis and often relies upon upon discovering low serum ferritin or elevated serum transferrin levels. The acute painful episode of sickle cell disease was originally referred to as "sickle cell crisis. One third of patients with sickle cell anemia hardly ever have ache, one third are hospitalized for ache two to six times per 12 months, and one third have more than six ache-associated hospitalizations per 12 months; 5% of patients account for one third of emergency division visits. The frequency of ache is highest within the third and fourth a long time, and after the second decade frequent ache is related to increased mortality charges.
Buy nimotop 30mg
Based on the angiographic findings and the presence or absence of peritoneal signs, therapy could be deliberate. Even when the decision to function has been made based on medical grounds, a preoperative angiogram should be obtained. Laparotomy is carried out in acute mesenteric ischemia to restore arterial flow after an embolus or thrombosis, to resect irreparably damaged bowel, or both. However, late thrombosis after embolectomy or arterial reconstruction occurs regularly enough that anticoagulation forty eight hours postoperatively is advisable. Survival is within the vary of fifty five%; 90% of patients with acute mesenteric ischemia diagnosed angiographically before the event of peritonitis survive. Mesenteric venous thrombosis can have an acute, subacute (weeks to months), or continual onset; the latter is unaccompanied by signs unless and until late complications happen. Acute mesenteric venous thrombosis resembles arterial types of acute mesenteric ischemia as a result of it presents as stomach pain that, early on, is typically out of proportion to the bodily findings. However, the tempo of sickness is slower than that with arterial ischemia, and the mean duration of pain before hospital admission is 5 to 14 days. Nausea and vomiting are frequent, and decrease gastrointestinal bleeding or hematemesis indicating bowel infarction is found in 15%. Abdominal plain film signs of mesenteric venous thrombosis are just like those of other types of acute mesenteric ischemia and almost at all times mirror the presence of infarcted bowel. Characteristic findings on small bowel series embrace luminal narrowing from congestion and edema of the bowel wall, separation of loops because of mesenteric thickening, and "thumbprinting" because of submucosal hemorrhage and edema. All other patients should have immediate laparotomy, resection of non-viable bowel, and heparinization. The mortality of acute mesenteric venous thrombosis is decrease than that of the other types of acute mesenteric ischemia, various from 20 to 50%. It is attributable to either extension of thrombosis at a rate rapid enough to trigger pain but sluggish enough to allow collaterals to develop before infarction occurs or by acute thrombosis of a small enough portion of the venous drainage system to allow recovery from ischemic injury. Non-specific stomach pain usually is the one symptom, and bodily examination and laboratory exams are regular. Treatment of continual mesenteric venous thrombosis is geared toward controlling bleeding, which is usually from esophageal varices. No therapy is indicated for patients with asymptomatic continual mesenteric venous thrombosis. Focal Segmental Ischemia of the Small Bowel Vascular insults to short segments of small bowel produce a broad spectrum of medical options with out the life-threatening complications associated with extra in depth ischemia. Focal segmental ischemia usually is attributable to atheromatous emboli, strangulated hernias, vasculitis, blunt stomach trauma, radiation, or oral contraceptives. Colon Ischemia Colon ischemia is the most typical ischemic injury to the gastrointestinal tract. A spectrum of colon ischemic injury is recognized, together with reversible colopathy (submucosal or intramural hemorrhage) (no less than 30 to 40%); transient colitis (no less than 15-20%); continual ulcerating colitis (20-25%); stricture (10-15%); gangrene (15-20%); and fulminant common colitis (<5%). In most circumstances, no specific trigger is recognized, and what finally triggers the presenting episode is usually unknown. However, colonic blood flow is decrease than that of any other intestinal segment, decreases with functional motor activity, and is greatly affected by autonomic stimulation-a mix which will make the colon particularly susceptible to ischemia. More than 90% of patients are older than age 60, though colon ischemia has been documented in younger individuals with vasculitis (particularly systemic lupus erythematosus), sickle cell illness, coagulopathies, medication-induced reactions (estrogens, danazol, vasopressin, gold, psychotropic medication), 734 Figure 137-1 Algorithm for managing patients with suspected acute mesenteric ischemia. B, Intra-arterial infusion of papaverine (30 to 60 mg/hr) resulted in vasodilation. Five to 10 per cent of patients with colon ischemia have had a distal and potentially obstructing colonic or rectal lesion, together with carcinoma, diverticulitis, stricture, or fecal impaction. Colon ischemia is a complication of elective aortic surgical procedure in 1 to 7% of circumstances, but after surgical procedure for ruptured stomach aortic aneurysm it might be as high as 60%. Mildest modifications embrace mucosal and submucosal hemorrhage and edema with or with out partial mucosal necrosis. Hemorrhages are subsequently resorbed or the overlying mucosa sloughs, forming an ulcer. With extra extreme injury, the mucosa and submucosa are replaced by granulation tissue. Later, the mucosa could regenerate over the edematous submucosa, which contains granulation and fibrous tissue and iron-laden macrophages. Moderately extreme colon ischemia can produce continual ulcerations separated by regular bowel, an image that mimics inflammatory bowel illness. With extra extreme and extended ischemia, the muscularis propria is damaged and replaced by fibrous tissue, thus forming a stricture. Colon ischemia usually presents with sudden, crampy, delicate, left decrease stomach pain, an urge to defecate, and passage of brilliant purple or maroon blood mixed with the stool inside 24 hours. Physical examination usually reveals solely delicate to average stomach tenderness over the involved segment of bowel. Any a part of the colon could also be affected, however the splenic flexure and sigmoid are most commonly involved. Systemic low flow states usually contain the right colon; native non-occlusive ischemic accidents contain the "watershed" areas of the colon. If colon ischemia is suspected and the affected person has no signs of peritonitis and an unrevealing stomach plain film, colonoscopy or the combination of sigmoidoscopy and a gentle barium enema should be carried out on the unprepared bowel inside forty eight hours of the onset of signs; colonoscopy is extra sensitive in diagnosing mucosal abnormalities, and biopsy specimens could also be obtained. Hemorrhagic nodules seen at colonoscopy characterize submucosal bleeding and seem as filling defects called "thumbprints" on barium enema examination. The initial diagnostic examine should be carried out inside forty eight hours, as a result of thumbprinting disappears as the submucosal hemorrhages are resorbed or the overlying mucosa sloughs. Studies carried out 1 week after the initial examine should mirror evolution of the injury: normalization of the colon or replacement of the thumbprints with segmental ulceration. In such situations, as a result of untreated acute mesenteric ischemia quickly turns into irreversible and since optimal management requires angiography, acute mesenteric ischemia should be excluded before barium research, which would preclude an adequate angiographic examination. In general, signs of colon ischemia subside inside 24 to forty eight hours, and therapeutic is seen inside 2 weeks. Two thirds of patients with reversible illness exhibit intramural and submucosal hemorrhage (reversible colopathy), whereas one third manifest a transient colitis. Irreversible damage ends in lower than 50% of patients, of whom approximately two thirds develop gangrene with or with out perforation. The prognosis of patients with colon ischemia complicating shock, heart failure, myocardial infarction, or extreme dehydration is particularly poor, perhaps because of associated acute mesenteric ischemia. The bowel is placed at relaxation, broad-spectrum antibiotics are given, cardiac perform is optimized, and medications that trigger mesenteric vasoconstriction are withdrawn if possible. Serial roentgenographic or endoscopic evaluations of the colon and continued monitoring of the hemoglobin, white blood cell rely, and electrolytes are carried out. Increasing stomach tenderness, guarding, rising temperature, and paralytic ileus indicate colonic infarction and mandate expedient laparotomy and colon resection. If, as ordinary, colon ischemia utterly resolves inside 1 to 2 weeks, no further remedy is indicated. Asymptomatic patients with evidence of persistent illness should have frequent examinations to determine if the colon is therapeutic, has persisting irritation, or is developing a stricture. Recurrent fevers, leukocytosis, and septicemia in in any other case asymptomatic patients with unhealed segmental colitis usually are attributable to the diseased bowel, and elective resection is indicated. Because patients with diarrhea or rectal bleeding for greater than 2 weeks usually develop irreversible illness, often with colonic perforation, resection might be indicated. Colon ischemia could not produce signs in the course of the acute insult but trigger a continual colitis regularly misdiagnosed as inflammatory bowel illness. Ischemic strictures that produce no signs should be observed; some disappear over 12 to 24 months 736 Figure 137-three Ischemic modifications within the transverse colon and splenic flexure. B, Eleven days later thumbprints have resolved and a segmental colitis has developed. For the rare form of fulminant colon ischemia involving all or a lot of the colon and rectum, management is just like that of other fulminant colitides. Chronic Mesenteric Ischemia Atherosclerosis is sort of at all times the reason for continual mesenteric ischemia or "stomach angina. Although autopsy and angiographic research regularly show partial or full occlusions of the major splanchnic vessels, continual mesenteric ischemia is rare; many patients with occlusion of two and even all three of those vessels remain asymptomatic.
Swamp Dogwood (American Dogwood). Nimotop.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is American Dogwood?
- How does American Dogwood work?
- Dosing considerations for American Dogwood.
- Headaches, fatigue, weakness, fever, chronic diarrhea, loss of appetite, malaria, treating boils and wounds, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96525
Buy nimotop 30 mg
Wails, screams, fainting attacks, and different dramatic gestures have therapeutic value for a lot of and may be followed in a remarkably short period of time by a way of composure and evident reduction. Acknowledge the thriller of death without offering "answers" concerning the unknowable. How will we set up a brand new steadiness in our emotional economic system when an important investment has been lost? Do our professional encounters with death depart a necessity for thicker defensive shells, emotional distancing, intellectualization, and performing out? The risk is minimized if we accept reduction of suffering as our mandate quite than the narrower objective of preventing illness and if we attend to our personal bodily, psychosocial, and spiritual needs. The Institute of Medicine and Committee on Care on the End of Life provide an in depth report concerning the experience of dying and the situations that assist folks attain dignity, meaning, and luxury on the finish of life. Informative reviews of subjects related to delirium in most cancers patients, gastrointestinal disorders in patients with advanced most cancers, advances in the pharmacotherapy of ache and psychosocial adaptation to most cancers. Examples of desired however lacking information embrace information on exactly whether or not and when to hospitalize patients with a broad number of medical situations, conclusive evidence on the efficacy of many frequent surgical procedures, or details about how patients value the outcomes of interventions that physicians are more likely to advocate. In the absence of this information and counting on a standard mannequin of decision making that assumes that the doctor is ready to act as the rational agent for the patient in selecting among therapy options, the medical system has developed as an economic system during which the supply of hospital beds, physicians, and different native assets determines the sample of care. Experts in economics have lengthy held that the marketplace for medical care differs from that for many items and companies as a result of a competitive market assumes that the buyer is informed about availability, value, and market competitors. In this market, the traditional remedy is to rely on professionals to control demand and for patients to delegate decision making to their physicians. The tacit settlement between patient and doctor is that professionals, in fulfilling their moral roles, prescribe only wanted care. Physicians are also assumed to serve conscientiously as agents for society by ensuring that the availability of assets is enough-however only enough-to satisfy a rational stage of demand. The decision to use care, corresponding to hospitalization for a patient with pneumonia, is often pushed by availability, not express principle. Furthermore, physicians are imperfect agents; their own preferences for therapies or outcomes usually become entangled with and overpower these of the patient. In a market where patients rely on the career to prescribe therapies, the existence of diverse professional opinions in regards to the value of options invites suppliers to influence demand. In charge-for-service markets, where provider earnings and the financial stability of institutions depend on the extent of utilization, such influence becomes inevitable. The physicians differed in their assumptions in regards to the nature of the underlying sickness, as well as the benefits to be derived from surgery. Some believed in a preventive principle: Operate early to avoid later complications, together with premature death. They argued for the standard-of-life principle: Surgery advantages most men by reducing signs and improving the standard of life. The unresolved competitors between the prevention and the standard-of-life theories mirrored indeterminacy rooted in poor scientific science. What did matter to patients was the degree to which their signs bothered them (which was not necessarily related to symptom severity) and the attainable unfavorable outcomes of surgery corresponding to impotence and incontinence. When patients are supplied an energetic function in selecting therapy through shared decision making, the hyperlink between provide and utilization may be broken. Among these with extreme signs, just one in 5 chose surgery, and the per capita charges of surgery declined about 50%. Such organizations know the number of folks enrolled in their health plans and use inhabitants-primarily based health planning to decide the per capita numbers of beds they supply and health employees they rent. They usually use about 150 hospital beds per 100,000 enrollees and make use of physicians based on specialty-specific inhabitants-primarily based ratios. Population-primarily based planning is essential as a result of the system receives a hard and fast amount of cash for every enrollee for whom they comply with provide all "essential" care. A fixed finances requires controlling assets, which is achieved by setting limits on provide. In charge-for-service markets, against this, neither directors nor health care suppliers know the scale of the inhabitants that their organizations serve. Private-sector, inhabitants-primarily based health planning that relates provide to consumption is virtually nonexistent. Size is influenced by such nonmedical components as competitors, prestige, or the enlargement of professional employees to meet the important mass required to guarantee night time and weekend coverage. The decision about how many specialists to prepare is much less a perform of how many are wanted in a group than of the needs (and desires) of the directors of the training packages. These research reveal remarkable differences in the per capita provide of assets, even among demographically related markets. The research also present that variations in provide affect the threshold for scientific decision making. The impact of provide of beds on the decision for hospitalization supplies a cogent instance. The differential in inhabitants-primarily based availability of hospital assets produces a diffuse impact on the admission threshold for many situations. A few "demand-pushed" situations, corresponding to myocardial infarction and hip fracture, are unaffected by the out there provide of assets (as a result of virtually all physicians, whatever the context of provide, agree on the need to hospitalize the patient). The increments of beds and different assets in excessive-resource communities are used for patients with "provide-delicate" situations corresponding to pneumonia, congestive heart failure, and bronchitis, which in low-rate markets are more usually treated on an outpatient basis. For such situations, hospitalization charges for folks residing in Boston are usually 60% larger than for residents of New Haven. Furthermore, capacity and utilization differ substantially from hospital to hospital even inside these cities. A sturdy linear relationship exists between capacity and stage of investment in terminal care. The results of provide on decision making are subliminal inasmuch as neither directors, clinicians, nor patients are immediately aware of the availability context of native apply. The influence is primarily on the issue-solving tasks of drugs-the care of sick folks with situations about which medical principle is weak and evidence that one plan of action is better than one other is unproven. Biomedical science creates the fundamental understanding of the mechanisms of illness on the mobile and molecular levels and is a fruitful source of scientific principle and apply applied sciences for intervening in the lives of patients. It is the job of the evaluative sciences to conduct expertise assessments and outcomes analysis to estimate the chances for outcomes that matter to patients and to elucidate the importance of patient preferences in selecting therapy. The success of the biomedical revolution significantly increases medical options and, by doing so, exacerbates the issue of choice in medication. Biomedicine and expertise have modified the medical landscape; many situations can now be treated by a variety of options that carry totally different sets of risks and advantages. Rational choice among them depends on studying the way to talk medical options in ways that allow patients to choose among efficient therapies based on their own preferences. Although emphasis on the moral and authorized requirements for 12 physicians to share decision making with patients is now greater, the striking variations in charges of surgery among communities and the affiliation between capacity and the intensity of investment in terminal care are reminders that offer-inducing utilization remains a powerful drive in medical markets. Creating such an surroundings is one of the great challenges of health care reform as a result of breaking the hyperlink between provide and utilization creates a market during which demand emanates from patients and thus results in totally different per capita charges of consumption and totally different calls for for assets. Stability in health care markets also requires that capacity be limited in some cheap means. Many imagine that apply tips will discipline the decisions of physicians to bring utilization and provide into equilibrium on the premise of medical efficacy. A traditional presentation of rational company principle by a Nobel laureate in economics. A evaluation emphasizing the fee implications of our increasing elderly inhabitants and increasing technologic capabilities. An wonderful evaluation of the historical past of the doctor-patient relationship and the problem of building shared decision making. In the United States since 1950, the age group sixty five years and older has grown from eight% to 13% of the overall inhabitants. The record lifespan is held by a recently deceased French girl, Jeanne Calment, who reached 122 years and 4 months. It is predicted that by 2020 a complete of 50 million will reside to be a minimum of sixty five years of age, i. Thus aging has become a world-extensive problem affecting all nations, irrespective of their economic development.
Syndromes
- A family history of inherited colorectal cancer syndromes, such as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC)
- Cameras
- Extreme cold (cryoablation)
- External features of the ear begin to take their final shape.
- Fever
- Your surgeon will give you instructions about restricting your activities.
- Antidepressants
- Seckel syndrome
- Persistent fever
Best 30 mg nimotop
Approximately 15% of isopropyl alcohol is transformed by alcohol dehydrogenase to acetone; scientific manifestations are much like those of ethanol ingestion. Diagnosis is often by history, and sufferers who become symptomatic will exhibit a "fruity odor" to their breath, attribute of acetone. Although each isopropanol and acetone are readily dialyzable, hemodialysis is seldom necessary in management. The organophosphates irreversibly inhibit acetylcholinesterase, leading to an overabundance of acetylcholine at synapses and the myoneural junction. Initial signs resemble a flulike syndrome with stomach ache, vomiting, 521 Figure ninety eight-1 Algorithm for the treatment of acute hydrofluoric acid burns. The full-blown image generally develops by 24 hours and consists of coma, convulsions, confusion, or psychosis; fasciculation and weak point or paralysis; dyspnea, cyanosis, and pulmonary edema; and generally pancreatitis. Emergency management consists of decontamination of the pores and skin, if necessary, and removal of garments; establishing an airway and making certain correct ventilatory support and cardiac monitoring; and administering the particular antidote pralidoxime and the physiologic antidote atropine. A 25% reduction in red blood cell cholinesterase confirms organophosphate poisoning. Atropine should be given as a physiologic antidote (see Table ninety eight-1) to reverse the muscarinic effects and to dry the excessive pulmonary secretions seen in sufferers with respiratory distress. Pralidoxime is the treatment of alternative for organophosphate poisoning and should be begun on scientific grounds before return of any blood research. To be effective, pralidoxime should be given in the first 48 hours before irreversible binding of acetylcholinesterase happens. Pralidoxime by steady infusion of as much as 500 mg/hour could also be necessary in critically ill sufferers. Pralidoxime may obviate the need for top-dose atropine remedy and cut back the incidence of late-onset paralysis. The carbamate pesticides embrace carbaril, methomyl, and propoxur and are reversible cholinesterase inhibitors. Paraquat, a bipyridyl herbicide, is a extremely lethal concentrate that accounts for roughly 1000 deaths a yr in Japan alone. Paraquat reduces oxygen to kind superoxide radicals that trigger alveolar cell damage and dying. Extensive pulmonary fibrosis ensues, preventing fuel change and causing subsequent hypoxic dying. Patients who ingest more than 30 mg/kg die within a few hours to days of a number of organ system failure. Smaller amounts produce esophagitis with possible perforation, pulmonary edema with subsequent growth of pulmonary fibrosis, and renal failure. Aggressive intervention inside the first 2 hours following ingestion may be the only hope of preventing extreme toxicity. If the affected person arrives inside the first hour, gastric lavage should be carried out immediately. Soil or clay in a slurry of water could also be substituted at house if the affected person is discovered within minutes of ingestion. Because oxygen is transformed to superoxide radicals by paraquat to produce cellular damage, oxygen is withheld till it becomes obligatory. Theophylline intoxication and mortality from each plain theophylline and sustained-release preparations occur from acute overdose and lengthy-time period unintentional intoxication. Vomiting is usually the primary symptom, and sinus tachycardia is the most common sign up each acute and continual toxicity. Seizures could also be widespread when the serum concentration is greater than forty mug/mL in continual toxicity or greater than eighty to one hundred mug/mL in acute overdose. Likewise, cardiac arrhythmia, cardiovascular collapse, and respiratory arrest are seen infrequently unless the concentration is greater than 50 mug/mL in continual toxicity or greater than one hundred mug/mL in acute overdose. Serum theophylline concentrations are significantly greater in acute overdose in contrast with those in continual toxicity. Treatment of theophylline toxicity consists of withdrawing the drug, cardiac monitoring, and supportive care. Correct metabolic acidosis with sodium bicarbonate; Hemodialysis to take away methanol/metabolites-indicated for sufferers with visible disturbance, serum methanol >50 mg/dL, or with intractable metabolic acidosis. Whole-bowel irrigation could also be indicated for ingestion of sustained-release capsules. Cardiac arrhythmias are sometimes tough to manage but may respond to intravenous propranolol. Correction of hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis, and fluid-electrolyte balance is indicated. Although seizures may respond to intravenous diazepam, standing epilepticus and rhabdomyolysis may occur and usually signify a poor outcome. Charcoal hemoperfusion is the treatment of alternative for important theophylline toxicity. Because of newer high-flux machines able to increasing theophylline clearance charges to larger than 200 mL/minute, hemodialysis is turning into an possibility equal to charcoal hemoperfusion. Charcoal hemoperfusion is most beneficial for sufferers with a serum theophylline concentration of more than eighty to one hundred mug/mL in acute overdose or more than forty mug/mL in continual toxicity (especially in the elderly or sufferers with hepatic disease or different circumstances that delay theophylline clearance) or sufferers in crucial situation. Tricyclic (or cyclic) antidepressant overdose remains to be the main explanation for prescription drug dying in the United States. The cardiotoxic effects are seen with ingestion of 1 g (10 to 20 mg/kg) and account for the high mortality price. Ventricular tachycardia is the most common ventricular rhythm, though ventricular bigeminy, gradual ventricular rhythms, and torsades de pointes ventricular tachycardia also have been described. Sodium bicarbonate additionally could also be helpful for correcting hypotension, though vasopressors could also be necessary. Airway institution, correct oxygenation and air flow, fluid alternative at upkeep ranges (to avoid pulmonary edema), gastric lavage with serially administered activated charcoal, and supportive remedy are indicated. Prophylactic intravenous phenytoin (15 mg/kg) before the onset of seizures could also be given in cases of amoxapine overdose, which has a high incidence of standing epilepticus. Diazepam is quite effective in controlling seizures, though intensive remedy together with thiopental and speedy-sequence intubation could also be essential to manage standing epilepticus. Physostigmine is now not utilized in tricyclic overdose, because by itself it could possibly trigger seizures, bradycardia, and asystole. A new approach to preventing renal damage by inhibiting the formation of poisonous metabolites. Kokko Rhabdomyolysis is a syndrome that outcomes from destruction of skeletal muscle. It is often recognized from laboratory findings which might be attribute of myonecrosis. Once thought to be rare, rhabdomyolysis nows acknowledged with increased frequency, partly as a consequence of increased awareness of its potential presence in scientific settings which will predispose to muscle necrosis. Although the approach to sufferers in the acute part of rhabdomyolysis could also be similar besides in the extreme cases of malignant hyperthermia and neuroleptic malignant syndrome, the lengthy-time period preventive approach to these sufferers is quite variable relying on the underlying cause and classification of rhabdomyolysis (Table 99-1). However, some sufferers could also be totally asymptomatic, and the analysis could also be established only from a laboratory profile. Some sufferers, especially those with no history of exercise, may current with diffuse weak point and ache in all of their striated muscles. Usually the signs of rhabdomyolysis are self-limited because the muscle has a remarkable capacity to repair itself fully. In probably the most extreme cases of rhabdomyolysis, nevertheless, the muscle may swell sufficiently to trigger compression of vessels and nerves and end in irreversible necrosis unless surgical decompression and fasciotomy are carried out. The most typical extramuscular issues are metabolic abnormalities and acute renal failure. The former muscles, which are higher developed for endurance and are fatigue-resistant, are discovered, for example, in geese; the latter, which are commonly used for intermediate sources of power and are simply fatiguable, are discovered, for example, in chickens. However, every of these fibers has similar intracellular constituents, and interruption of their sarcolemmal membrane causes these constituents to leak into the plasma, which produces the expected abnormalities of rhabdomyolysis. For instance, necrosis of only one hundred gm of muscle is roughly equal to the acute infusion of 10 to 15 mEq of potassium into the circulation. Whether this influx of potassium or different intracellular constituents can be measured as a metabolic abnormality is very depending on circulatory and renal standing. Figure 99-1 Values inside the depicted striated muscle cell replicate concentration (in mm/L of water) of various intracellular constituents. The values exterior of the cell replicate increases () or decreases () which might be attribute of rhabdomyolysis, whereby intracellular constituents leak into the plasma by way of injured muscle membranes.
Cheap 30mg nimotop
In patients with profound ventricular failure, circulatory support with intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation or left ventricular help gadgets could facilitate performance of diagnostic catheterization and identification and therapy of surgically remediable lesions. Instead, therapy focuses on the use of aspirin and intravenous heparin, analogous to their use in the syndrome of unstable angina (see Chapter fifty nine). Aspirin is the therapy of alternative; corticosteroids and different nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicine could intervene with myocardial healing. The incidence of pericarditis seems to have been reduced by efficient acute recanalization. Patients with recurrent ischemia-spontaneously, at low exercise levels throughout risk stratification studies, or throughout physical activity-should be evaluated and managed aggressively. If the ache occurs at rest or at low levels of activity, diagnostic angiography should be performed, followed by coronary revascularization as indicated (see Chapters forty six, 61, and 62). Rupture of a papillary muscle, which causes acute mitral (and infrequently tricuspid) regurgitation, or of the ventricular septum, which causes an acute left-to-right shunt, results in acute hemodynamic compromise. Most affected patients could have a new systolic murmur, however the murmur could also be surprisingly gentle in the presence of markedly diminished cardiac output. When these issues are suspected, the analysis should be confirmed or excluded quickly, normally by transthoracic echocardiography with Doppler circulate imaging. Patients are normally managed 318 with aggressive afterload reduction, typically together with intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation. Rupture of the free wall of the left ventricle normally presents with pericardial tamponade (see Chapter sixty five), cardiogenic shock (see Chapter 95), and cardiovascular collapse. Some patients develop false left ventricular aneurysms, that are localized ruptures that trigger much less severe hemodynamic compromise initially. In each conditions, immediate pericardiocentesis should be followed by prompt surgical restore. Prognosis is influenced by the burden of residual coronary illness, the extent of residual left ventricular function, and, to a lesser extent, the presence or severity of arrhythmia. If the stress test is adverse, further diagnostic analysis for ischemia can entail a symptom-restricted test 3 to 6 weeks later. Patients with left ventricular ejection fractions under forty% have a poor prognosis and are more likely to profit from aggressive remedy to prevent ventricular transforming and subsequent coronary heart failure and demise. These objectives can be accomplished in part with lifestyle modifications in addition to with medical interventions. Effective reduction of the ldl cholesterol degree decreases the incidence of recurrent occasions and cardiovascular mortality. Use of beta-blockers for a minimum of 3 to 5 years reduces the incidence of coronary occasions, cardiovascular mortality, and all-trigger mortality in patients who can tolerate these drugs, together with patients with left ventricular dysfunction. In patients with contraindications, various antiplatelet agents (see Chapter 188) should be used. Physical conditioning improves exercise capacity and should reduce the incidence of recurrent ischemic occasions. Because of the strong association between depression and antagonistic prognosis, in addition to the dangers of social isolation, addressing such issues as family and social support, return to work, and counseling to facilitate sexual function is essential. For some patients, formal counseling and/or antidepressant drugs could also be indicated. Estrogens enhance lipid profiles in submit-menopausal ladies and should have a direct vasodilatory impact on the coronary circulation. Elevated homocysteine levels seem to be a further risk issue for progressive atherosclerosis. These levels can be reduced with administration of folic acid starting at a dose of 400 mug to 1 mg/day. Risk components, drugs, lifestyle habits, and psychosocial support should be monitored and managed rigorously. Subsequent comply with-up is just like that for the patient with steady angina pectoris. Consolidating these features requires shut statement and management of patients throughout convalescence to facilitate recognition and prevention of recurrent ischemia and retard progression of coronary artery illness, and implementation of vigorous medical, mechanical, and surgical intervention when required. In patients with acute coronary syndromes, cardiac troponin I levels present useful prognostic info and permit the early identification of patients with an elevated risk of demise. Demonstration of the security of an oral antiplatelet agent in patients with acute coronary syndromes in a pilot study. Hospitals with better reputations had better outcomes, probably because of greater rates of using aspirin and B-blockers. A study that lays to rest the worry that surgical procedure is associated with an unduly excessive risk of issues in patients handled initially with a clot-selective thrombolytic drug. Bedside exams for cardiac-particular troponins are highly sensitive for the early detection of myocardial-cell injury in acute coronary syndromes. Negative test results are associated with low risk and allow fast and secure discharge of patients with an episode of acute chest ache from the emergency room. Demonstration of the persistence of preliminary profit conferred by coronary thrombolysis on survival and the markedly lower mortality seen when recanalization is associated with more full reperfusion. A evaluate delineating pitfalls in decoding results in which numerous thrombolytic medicine are in contrast, and the necessity to consider ends in the context of time to therapy, adequacy and nature of anticoagulation, time to implementation of patency, time to and frequency of reocclusion, and nature of the study population. A definitive report from a lot of facilities comparing survival after coronary thrombolysis with that following obligatory early angiography and demonstrating the advantages of a conservative strategy that focuses on thrombolysis alone. Baim Catheter-based mostly (non-surgical) strategies have become the most common form of myocardial revascularization. More than 400,000 procedures are performed annually in the United States alone, in contrast with some 300,000 surgical bypass operations. This catheter was launched by femoral arterial puncture, superior across the target lesion in its smaller (collapsed) configuration, after which inflated inside the stenosis to produce the specified luminal enlargement. Even among carefully selected candidates with proximal, concentric, non-calcified single-vessel illness, the failure rate was about 20%, together with main issues (demise, myocardial infarction, emergency bypass surgical procedure) in 8% (Table 61-1). In an effort to overcome these elementary limitations, newer gadgets embody endoluminal metallic scaffolds (stents) and gadgets for the removal of plaque mass from the target lesion (atherectomy). However, balloon angioplasty continues to be widely used in an "adjunctive" position to pre-dilation, to help facilitate the passage of a new gadget, or to submit-dilation, in order to maximize the diploma of luminal enlargement obtained by a new gadget. The aim is to present consistently broad luminal patency through methods dictated by lesion morphology, with no main acute issues and Figure 61-1 Conventional balloon angioplasty, exhibiting the cracking of the intimal plaque and the elastic recoil of the vessel wall following balloon deflation. Initially, the anatomic restrictions had been pushed by the restricted capabilities of early balloon catheters. Current equipment allows therapy of distal, diffuse, calcified lesions of a number of coronary arteries or previously constructed saphenous vein bypass grafts. Total occlusions of a coronary artery may be handled, but with a lower success rate (sixty five% vs. Expansion to the therapy of multivessel illness occurred progressively in the late Eighties, to the point the place 30 to forty% of procedures now involve therapy of more than one lesion. The clinical indications for catheter-based mostly intervention could embody any of the manifestations of myocardial ischemia. Patients with steady but severe or life-limiting angina refractory to medical remedy are typically referred for diagnostic catheterization together with coronary angiography, as could also be some patients with gentle or no signs but in whom non-invasive test results suggest coronary lesions for which the prognosis could also be improved by revascularization (see Chapter fifty nine). If an acceptable lesion or lesions are found to explain the clinical manifestations, the definitive catheter-based mostly intervention can typically be performed as an extension of the identical process-about 25% of diagnostic catheterizations proceed to an interventional process throughout the identical sitting, whereas one other 35% are referred for surgical procedure. If patients with unstable angina (notably new-onset angina or latest progression to rest ache) can be stabilized initially with medical remedy, diagnostic cardiac catheterization with "angioplasty stand-by" can be performed 24 to forty eight hours after admission. Alternatively, as a result of about 80% of patients with unstable angina proceed to coronary angiography and about 50% proceed to revascularization inside the next 6 weeks of admission, some recommend early catheterization in all patients to lower size of keep, time to return to work, and the variety of readmissions to the hospital, without rising overall rates of demise or myocardial infarction. More recently, there has been growing interest in the use of catheter strategies for revascularization of patients with acute myocardial infarction (see Chapter 60). This guidewire then serves as a rail over which subsequent therapeutic gadgets are superior. With achievement of a passable outcome (<30% residual stenosis, no important dissections of plaque at or adjoining to the therapy website, and normal distal circulate), different target lesions could also be addressed. At the top of the process, patients should be freed from chest ache or new electrocardiographic abnormalities, but they should be followed carefully for the next several hours for chest ache or electrocardiographic modifications that may be suggestive of closure of one of many handled vessels, for dehydration because of the osmotic load of iodinated contrast, or for bleeding or loss of distal pulses at the catheter introduction website. The signs of re-stenosis of the dilated phase develop in about 15% of patients and normally begin as gentle exertional discomfort. If the character of the signs and timing of their onset (6 weeks to 6 months after intervention) are typical, plans should be made for repeat catheterization and attainable repeat intervention. Vague or atypical signs could also be evaluated further by a useful stress test earlier than proceeding to repeat catheterization. Symptoms growing greater than 6 to 9 months after the process are more probably because of a new or progressive lesion at one other website than to re-stenosis.
Effective 30 mg nimotop
Ulcer disease is a focal course of, and ulcers are inclined to recur in the same region; whereas ulcers persist, close by areas readily heal. In animal fashions, ulcers are additionally produced by antibodies to prostaglandins however not to inactive prostaglandin analogues, further supporting the conclusion that endogenous prostaglandins are essential parts in mucosal defense. Although every of those routes could also be essential, parenterally administered ketorolac (Toradol) produces ulcer problems within a couple of days, leaving little doubt that the systemic route is sufficient for ulcerogenesis. The definition of endoscopic ulcers varies amongst research and is often based on size alone. There is little doubt that flat lesions lower than 5 mm have a special natural historical past and response to therapeutic intervention than do lesions bigger than 5 mm with seen depth. Furthermore, these endoscopic lesions are more likely to behave quite in a different way than are continual deep ulcers with surrounding fibrosis. The risk begins within days after therapy, is highest within the first three months of remedy, however persists for years. However, a randomized study evaluating 1 g of aspirin daily to placebo indicated that age is an unbiased risk issue for hospitalizations because of ulcer problems. Anticoagulant co-remedy additionally will increase the risk of gastrointestinal problems. This unusual form of ulcer disease is caused by extreme secretion of gastrin by a tumor and gastric acid hypersecretion (see Chapter 130). This is a uncommon form of duodenal ulcer disease in which acid hypersecretion is caused by enhanced secretion of antral gastrin. Fasting gastrin levels are often solely modestly elevated, but the response to a meal is greatly exaggerated. These uncommon conditions can be associated with peptic ulcer as the results of launch of the acid secretagogue histamine from the malignant cells. Disorders such as annular pancreas and congenital bands have been associated with duodenal ulcer and acid hypersecretion. Although the research are intriguing, causality in ulcer pathogenesis has not been established. Superficial mucosal injury (petechiae and erosions) is found in most sufferers hours after main operations or within 24 hours of the onset of main multisystem sickness. However, this injury stays silent in the giant majority of those sufferers and rarely leads to clinically important acute bleeding unless complicated by severe coagulopathy. Major bleeding in the setting of severe and extended physiologic stress happens with discrete ulcers quite than from superficial mucosal lesions. Several risk elements have been recognized and represent the indications for preventive intervention with antiulcer brokers. Mechanical ventilation for more than 5 days and coagulopathy are the clearest predictors of main hemorrhage. Prolonged hospitalizations with hepatic or renal failure, sepsis, and shock are essential predictors of stress ulcer risk, especially when complicated by extended, multisystem failure. The rates of stress ulcer problems have dramatically decreased, for example, from about 30% in severe burn sufferers 30 years in the past to lower than 1 to 2% at present, reflecting improved overall administration. Patients with stress ulcer-induced gastrointestinal bleeding have greatly increased mortality, in part because of the severity of their underlying disease 674 and superimposed multiorgan failure, which concurrently enhance each mortality and the risk of stress ulcer bleeding. A nice deal of pharmacologic "hearth energy" and sources have gone into stopping stress ulcers with antacids, sucralfate, H2 -receptor antagonists, and now proton pump inhibitors. However, preventive remedy is appropriate in excessive-risk sufferers or in sufferers with a historical past of peptic ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding when uncovered to severe, extended physiologic stress. There has been concern over increased rates of nosocomial pneumonia in sufferers placed on H2 -receptor blockers; the data are conflicting, and the results are most likely modest, at most. Classically, an ulcer was thought of doubtless when pain was situated in the epigastric space, was burning in high quality, occurred on an empty stomach 2 to four hours after meals and/or at night time, was relieved by antacids and/or meals, and tended to wax and wane over months. This sample has been known as "acid dyspepsia" because it happens when acid is unbuffered by food and is relieved with neutralizing acid or inhibiting acid secretion. It has been assumed that most sufferers with ulcer disease had epigastric stomach misery. Nevertheless, regardless of being each insensitive and non-particular, the symptom of epigastric stomach pain, notably burning after meals and at night time and relieved with food or antacid, suggests the potential for ulcer disease. The dissociation between natural pathology and symptoms highlights the marked particular person variation in visceral sensitivity. Patients with excessive visceral sensitivity may have a number of manifestations of functional bowel disease (see Chapter 131): (1) gastroesophageal reflux (including upright and supine reflux and non-cardiac chest pain); (2) "acid" dyspepsia; (three) indigestion or functional dyspepsia (symptoms of indigestion occurring with or shortly after eating and characterised by epigastric fullness and discomfort, belching, bloating, nausea, early satiety, and particular food intolerances); and (four) the irritable bowel syndrome. When visceral sensation is low, natural disease, such as peptic ulcer, may current "silently," even with life-threatening problems. If visceral sensation is excessive, the presentation could also be confounded by the opposite functional manifestations such as functional bowel disease. For instance, about one half of the sufferers evaluated for peptic ulcer also have symptoms indicative of gastroesophageal reflux, functional dyspepsia, or irritable bowel syndrome, suggesting the presence of an "irritable intestine. For epigastric tenderness on deep palpation, the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive worth are all roughly 50% or much less. Furthermore, many sufferers with non-ulcer diseases also have epigastric tenderness on bodily examination (see later). Epigastric stomach pain can be caused by numerous processes, including, most incessantly, non-ulcer dyspepsia ("visceral hypersensitivity"), gastroesophageal reflux, biliary tract disease, pancreatitis, coronary and/or mesenteric vascular insufficiency, intra-stomach neoplasms (notably gastric, pancreatic, and hepatic), functional bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and others. Symptoms of indigestion can be associated with gastric dyskinesia (gastroparesis, gradual gastric emptying) or with gastric dysesthesia (hypersensitivity to gastric distention or particular meals). The prognosis of ulcer disease can solely be suspected based on the historical past and bodily examination. Diagnostic affirmation requires both higher gastrointestinal endoscopy (Color Plate three B) or barium contrast gastrointestinal radiography. Endoscopy has a higher accuracy for establishing the prognosis than typical radiography, however it additionally has a higher price and a small risk of untoward events (<1 in one thousand procedures) (see Chapters 121 and 122). In centers with highly skilled radiologists, air-contrast radiography could also be as accurate as endoscopy. There is controversy concerning the need of repeat endoscopy to ensure complete therapeutic after eight to 12 weeks of medical therapy. Repeat endoscopy could have a really low yield if the preliminary endoscopy revealed a benign-showing ulcer and adequate biopsy specimens (four jumbo or 6-7 common) had been fastidiously reviewed and found to be negative for malignancy. One of the major tenets of drugs has been to set up a precise prognosis and thereby apply the suitable and particular remedy. The American College of Physicians really helpful that sufferers with uncomplicated dyspepsia be empirically treated with a brief (four-eight week) course of antiulcer treatment and noticed to assess their symptomatic response. Further evaluation was really helpful solely in sufferers who had been unresponsive to this therapeutic trial or whose symptoms recurred after its discontinuation. This strategy is preferred in sufferers younger than age forty with gentle, intermittent symptoms and no ulcer-associated problems. There is a marked overlap in resting and histamine- or gastrin-stimulated gastric acid secretory rates in normal and ulcer sufferers. Because of the lack of scientific utility of gastric secretory testing, it has become obsolete as a diagnostic software besides in sufferers with hypergastrinemia or in whom gastrinoma or another explanation for acid hypersecretion is considered (see Chapter 130). Although this strategy has not been examined rigorously in scientific trials, several decision analyses support the cost effectiveness of this strategy, and the American Gastroenterological Association has additionally issued guidelines to support this strategy (see Chapter 131). American Gastroenterological Association: American Gastroenterological Association medical position assertion: Evaluation of dyspepsia. In this massive study, H2 receptor blockers reduced clinically important bleeding to a higher extent than sucralfate. Raff T, Germann G, Hartmann B: the value of early enteral diet in the prophylaxis of stress ulceration in the severely burned affected person. This study demonstrated the benefit of enteral diet in contrast with cimetidine in lowering the incidence of gastrointestinal bleeding. This study identifies risk elements for stress ulcer bleeding and provides a good reference listing. Gastric ulcers nonetheless remain a special challenge because 1 to 5% of endoscopically benign gastric ulcers are gastric cancers.
References:
- https://www.choc.org/wp/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/spontaneous-pneumothorax-ph-with-references.pdf
- https://www.mdanderson.org/documents/Departments-and-Divisions/Symptom-Research/BPI_UserGuide.pdf
- https://www.lls.org/sites/default/files/National/USA/Pdf/Publications/CAP_acute-leukemia-patient-faq.pdf
- https://www.supprelinla.com/pdfs/Surgeon_MVA_Download.pdf
- https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/osha3071.pdf
.png)