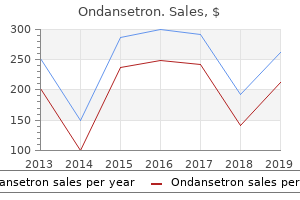
Proven 8mg ondansetron
Incompletely separated duplications might give rise to dysphagia, regurgitation and barely airway obstruction (2). Achalasia: Chronic regurgitation of undigested meals, repeated aspiration pneumonia, retrosternal discomfort in the older baby. Oesophageal foreign body: the patient will usually be drooling and may be dysphagic. Oesophageal inflammatory change: Presentation will depend on the underlying trigger but the patient will usually have retrosternal ache. With persistent change happening to stricture formation they could present with dysphagia. The symptomatic infant will present with recurrent regurgitation of feeds and/or ache. Older sufferers might present with retrosternal ache, meals aversion or much less generally with a stricture. Figure 1 Chest X-ray exhibiting a nasogastric tube coiled in a blind-ending upper pouch in a patient with oesophageal atresia. Imaging Oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula: A chest X-ray will typically present an air-stuffed, dilated and blind-ending upper oesophageal pouch. A Replogle tube (recognized by a dashed radio-opaque marker permitting straightforward identification on X-ray) might have been positioned in the upper oesophagus to permit aspiration of the secretions. This is a dual lumen tube which allows secretions to be continually sucked from the blind-ending upper oesophagus thereby stopping aspiration. Imaging for an H-sort fistula (a fistula between a patent airway and a patent oesophagus) is by a tube oesophagram. With the patient inclined and with lateral screening water-soluble distinction is injected into the oesophagus whilst the nasogastric tube is slowly withdrawn. If a fistula is present, the distinction should flow by way of the fistula from the oesophagus into the airway. This process therefore carries a major risk of acute respiratory compromise and will solely be undertaken if suction, oxygen, nursing help and applicable resuscitation facilities can be found. Ultrasound would usually use an strategy by way of the sternal notch or between the ribs, however in very young sufferers a transsternal strategy can generally be used as the sternum has not ossified. Figure 3 Contrast outlines an oesophageal duplication with two, parallel, fluid-stuffed cavities opacified. Endoscopy allows direct visualisation and simultaneous removing (see entry Foreign body, ingestion, kids). Oesophageal inflammatory change: Very refined superficial modifications may not be detected by imaging and can solely be recognized under direct vision with endoscopy. Ultrasound is more and more used to demonstrate rest of the lower oesophageal sphincter and fluid tracking into the lower oesophagus. Oesophageal Stenosis (corrosive ingestion) 1405 Oesophageal Duplication A congenital abnormality in which there was duplication of a part of the foregut in embryological growth resulting in both a cyst or second lumen of the oesophagus. Oesophageal Disease, Childhood Oesophageal Duplications (and other foregut duplications) Oesophageal Disease, Childhood Oesophageal Dysmotility this may be both irregular contractions of the oesophagus, or a diminution or failure of normal peristalsis. It has many causes, of which the most typical in industrialized nations is gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gastroesophageal Reflux in Adult Patients: Clinical Presentations, Complications, and Imaging Oesophageal Disease, Childhood. Pathology/Histopathology Infectious Esophagitis In Candida esophagitis, plaques encompass heaped-up areas of necrotic epithelial particles or precise colonies of C. Routine histologic stains might present epithelial cells with occasional multinucleation, "floor-glass" nuclear staining, and intranuclear inclusions. Infection happens within submucosal fibroblasts and endothelial cells, not in epithelium, and is usually a part of widespread visceral infection. Routine histologic stains present large cells in the submucosa bearing amphophilic intranuclear inclusions and intracytoplasmic inclusions. Department of Radiology, University Hospital Brno, Brno, Czech Republic 2 Department of Gastroenterology, University Hospital Brno, Brno, Czech Republic vlvalek@med. Reflux esophagitis Drug-induced Esophagitis In drug-induced esophagitis, affected individuals ingest the medication with little or no water immediately earlier than Oesophagitis 1407 going to bed. When such medicine dissolve in the esophagus, they trigger mucosal injury both by creating an acid pH (analogous to a type of caustic esophagitis) or by direct irritating the epithelium. Radiation Esophagitis A radiation dose of 4,500�6,000 rad over a 6- to eight-week period or more to the mediastinum might trigger severe injury to the esophagus. Acute radiation-induced esophagitis usually happens 2�4 weeks after the initiation of radiation therapy. Caustic Esophagitis Caustic esophagitis causes injury similar to that from thermal burns. Liquid lye causes liquefactive necrosis, resulting in probably the most severe type of caustic injury to the esophagus. The severity and extent of esophageal injury depend on the type, concentration, and quantity of the caustic agent. Pemphigus vulgaris affects pores and skin, mouth, and other mucous membranes with weeping bullous lesions. Histology reveals acantholysis and intraepithelial bullae, and particular immunohistology ought to be used. Bullous pemphigoid is a persistent disease of the elderly, in whom tense, pruritic pores and skin bullae arise. The histology reveals subepithelial bullae and circulating antibodies to the basement membrane. Esophageal lesions include ulcerations that can tunnel under the mucosa, strictures, and perforations. The esophagus reveals webs, rings, and tight strictures however typically fails to present generalized desquamation apparent on endoscopy. Candida esophagitis (and infectious esophagitis usually) is usually characterised by the abrupt onset of odynophagia (painful swallowing), chest ache, or dysphagia. Symptoms of tuberculosis esophagitis include dysphagia and chest ache, however esophageal signs are generally absent. Infection also can start with mild symptomatology of nausea and pyrosis (heartburn) or with very severe signs of hematemesis. Symptoms of drug-induced esophagitis are usually sudden in onset and encompass chest ache, odynophagia, or dysphagia. A typical location is the aortic arch stage, where tablets are delayed because of the aortic indentation on the esophagus and the low contractile pressure of peristalsis. Radiation esophagitis usually produces mild heartburn or dysphagia several weeks after the onset of remedy. Some sufferers might have progressive dysphagia Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Esophagitis (Reflux Esophagitis) this kind encompasses reflux esophagitis and is characterised histologically by inflammatory cells and reflux modifications consisting of epithelial hyperplasia with out inflammation. Alkaline reflux esophagitis is brought on by reflux of bile or pancreatic secretions into the esophagus after partial or total gastrectomy. Pemphigus and pemphigoid are nonhereditary conditions in adults, and epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica happens as an autosomal recessive situation in kids. In caustic esophagitis, the preliminary medical signs are the speedy onset of chest ache and dysphagia. Acute problems include shock, fever, respiratory distress, mediastinitis, and perforation. Late problems are associated primarily to fibrosis and stricture, which can trigger dysphagia several weeks after the preliminary injury. In young kids the predominant reflux signs are regurgitation, repetitive vomiting, and failure to thrive. Imaging Barium examination continues to be the first radiologic modality for evaluating sufferers with dysphagia, reflux signs, or other medical findings of esophageal disease. The double-distinction section optimizes the power to detect every kind of esophagitis, notably reflux disease, whereas the one-distinction section optimizes the power to detect hiatal hernia and lower esophageal rings or strictures. Barium distinction research are useful for evaluating mucosal surface lesions however provide little details about the extramucosal extent of disease. Diagnosis Infectious esophagitis: Candida esophagitis is characterised on esophagrams by plaques or a "shaggy" esophagus. Plaquelike lesions are seen as linear or irregular filling defects that are likely to be oriented longitudinally and are separated by normal mucosa.
Safe ondansetron 4 mg
Once the hyperlipidemia is accurately classified, efforts must be directed to rule out any possible secondary causes of the hyperlipidemia (Table 21-5). Although many sufferers with hyperlipidemia have a major or genetic cause of their lipid dysfunction, secondary elements frequently contribute to the hyperlipidemia. A fasting glucose must be obtained within the initial workup of all topics with an elevated triglyceride degree. Nephrotic syndrome and chronic renal insufficiency must be excluded by acquiring urine protein and serum creatinine. Hypothyroidism must be ruled out by measuring serum thyroid-stimulating hormone. Patients with hyperlipidemia, especially hypertriglyceridemia, who drink alcohol or are obese must be inspired to decrease their intake. Often, figuring out the proper analysis requires a detailed family medical historical past and, in some cases, lipid analyses in relations. If the fasting plasma triglyceride degree is >1000 mg/dL, the affected person virtually at all times has chylomicronemia and both has Type I or Type V hyperlipoproteinemia (Table 21-3). The plasma triglyceride-to-cholesterol ratio helps distinguish between these two prospects and is greater in Type I than Type V hyperlipoproteinemia. Recessive forms of extreme hypercholesterolemia are uncommon; a clue to the analysis of sitosterolemia is the response of the hypercholesterolemia to reductions in dietary cholesterol content material and to bile acid resins. The most typical error within the analysis and treatment of lipid issues is in sufferers with a blended hyperlipidemia without chylomicronemia. A direct connection between plasma levels of cholesterol and the atherosclerotic process was made in people when aortic fatty streaks in younger individuals had been shown to be strongly correlated with serum levels of cholesterol. The elucidation of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia was proof that high cholesterol itself brought on atherosclerotic vascular disease. Although most of these studies found a small however significant discount in cardiac occasions, no decrease in complete mortality was seen, which tempered enthusiasm for aggressive, populationbased treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Treatment with simvastatin for an average of 5 years resulted in a 24% discount in major coronary occasions and a extremely significant thirteen% discount in all-cause mortality. The most compelling knowledge supporting the idea that "lower is healthier" come from studies in which completely different statin regimens had been directly compared. Atorvastatin 80 mg was associated with a big 16% relative danger discount in major cardiovascular occasions compared with the much less-intensive pravastatin forty-mg routine. The overall body of data with fibrates concerning cardiovascular outcomes trends is constructive however blended. There was significantly greater "drop-in" of the placebo group into lipid-lowering remedy, largely statins, making the interpretation sophisticated. Interestingly, despite the fact that fibrates are most effective in lowering triglycerides, no fibrate trial has ever been performed particularly in topics with hypertriglyceridemia; in addition, the benefit of the addition of a fibrate to baseline statin remedy has by no means been examined. Management of lipid issues must be primarily based on medical trial knowledge demonstrating that treatment reduces cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, though cheap extrapolation of these knowledge to particular subgroups is typically required. No managed studies have been performed in which a number of of these nonpharmacologic choices have been combined to handle their additive or synergistic results. Weight Loss and Exercise the treatment of weight problems, if present, can have a favorable impression on plasma lipid ranges and must be actively inspired. Regular cardio exercise can even have a constructive impact on lipids, in giant measure because of the related weight discount. For individuals with hypertriglyceridemia, the intake of easy carbohydrates must be curtailed. For extreme hypertriglyceridemia (>1000 mg/dL), restriction of complete fat intake is important. Foods and Additives Certain meals and dietary components are associated with modest reductions in plasma levels of cholesterol. Plant stanol and sterol esters are available in quite a lot of meals corresponding to spreads, salad dressings, and snack bars. An efficient way to estimate absolute danger of a cardiovascular event over 10 years is to use a scoring system primarily based on the Framingham Heart Study database. Diagnosis of the metabolic syndrome also identifies a better-danger particular person who must be targeted for therapeutic life-style adjustments and may be a candidate for extra aggressive drug remedy (Chap. The objective is to scale back plasma triglycerides to below 500 mg/dL to prevent the risk of acute pancreatitis. When triglycerides are 500�1000 mg/dL, the choice to use drug remedy is dependent upon the evaluation of cardiovascular danger. Most major medical endpoint trials with statins have excluded individuals with triglyceride ranges >350�450 mg/dL, and there are therefore few knowledge concerning the effectiveness of statins in reducing cardiovascular danger in individuals with triglycerides greater than this threshold. More knowledge are needed concerning the relative effectiveness of statins, fibrates, niacin, and fish oils for reducing cardiovascular danger in this setting. Severe myopathy can often be averted by cautious affected person choice, avoidance of interacting medicine, and instructing the affected person to contact the physician immediately within the event of unexplained muscle pain. Severe medical hepatitis associated with statins is exceedingly uncommon, and the development is toward much less frequent monitoring of transaminases in sufferers taking statins. The statin-related elevation in liver enzymes resolves upon discontinuation of the medicine. In people, ezetimibe at a dose of 10 mg was shown to inhibit cholesterol absorption by virtually 60%. When utilized in mixture with a statin, monitoring of liver transaminases is recommended. Potential unwanted effects include dyspepsia, headaches, fatigue, and muscle or joint pains. Bile Acid Sequestrants (Resins) Bile acid sequestrants bind bile acids within the intestine and promote their excretion within the stool. To maintain the bile acid pool dimension, the liver diverts cholesterol to bile acid synthesis. Cholestyramine and colestipol are insoluble resins that must be suspended in liquids. Most unwanted effects of resins are restricted to the gastrointestinal tract and include bloating and constipation. They are efficient in combination with statins in addition to in combination with ezetimibe and are significantly useful with one or both of these medicine for troublesome-to-treat sufferers or those with statin intolerance. Nicotinic Acid (Niacin) Nicotinic acid, or niacin, is a B-complicated vitamin that has been used as a lipid-modifying agent for decades. Niacin is also the one at present obtainable lipid-lowering drug that significantly reduces plasma ranges of Lp(a). If correctly prescribed and monitored, niacin is a protected and efficient lipid-lowering agent. Flushing may be reduced by formulations that slow the absorption and by taking aspirin previous to dosing. Immediaterelease crystalline niacin is mostly administered three times per day, over-the-counter sustained-release niacin is taken twice a day, and a prescription form of extended release niacin is taken once a day. Mild elevations in transaminases occur in as much as 15% of sufferers treated with any form of niacin, however these elevations may require stopping the medicine. Niacin potentiates the impact of warfarin, and these two medicine must be prescribed together with caution. Acanthosis nigricans, a darkish-colored coarse pores and skin lesion, and maculopathy are rare unwanted effects of niacin. Niacin is contraindicated in sufferers with peptic ulcer disease and might exacerbate the symptoms of esophageal reflux. It can even increase plasma ranges of uric acid and precipitate gouty attacks in susceptible sufferers. However, in a single research in sort 2 diabetics, niacin treatment was associated with solely a slight enhance in fasting glucose and no significant change from baseline within the HbA1C. Thus, niacin can be used in diabetic sufferers, however every effort must be made to optimize the diabetes administration before initiating niacin, and glucose must be rigorously monitored in nondiabetic sufferers with impaired fasting glucose after initiation of niacin remedy. Successful remedy with niacin requires cautious education and motivation on the part of the affected person. Myopathy and hepatitis occur not often within the absence of other lipid-lowering agents. Fibrates promote cholesterol secretion into bile and are associated with an elevated danger of gallstones. Importantly, fibrates can potentiate the impact of warfarin and sure oral hypoglycemic agents, so the anticoagulation standing and plasma glucose ranges must be intently monitored in sufferers on these agents.
| Comparative prices of Ondansetron | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | Barnes & Noble | 967 |
| 2 | Wegman's Food Markets | 597 |
| 3 | Aldi | 575 |
| 4 | HSN | 236 |
| 5 | Albertsons | 750 |
| 6 | Winn-Dixie Stores | 868 |
| 7 | YUM! Brands | 418 |
| 8 | Ruddick Corp. | 446 |
Cheap 8 mg ondansetron
Axons of those sensory cells pass through perforations within the overlying bone and enter two elongated olfactory bulbs lying on high of the bone. Orexin Neurons Specialized neurons that present an excitatory sign to the arousal system, significantly to the norepinephrine neurons. Symptoms embody slowness of motion, muscular rigidity, and walking and balance impairment. Peptides Chains of amino acids that can perform as neurotransmitters or hormones. Photoreceptor A nerve ending, cell, or group of cells specialised to sense or obtain mild. In humans, the pituitary gland is composed of two lobes and secretes several totally different hormones that regulate the activity of different endocrine organs throughout the physique. Plasticity the power of the mind to modify its neural connections to adapt to challenges within the environment. Pons A a part of the hindbrain that, with different mind buildings, controls respiration and regulates coronary heart rhythms. The pons is a significant route by which the forebrain sends information to and receives information from the spinal twine and peripheral nervous system. Positron emission Tomography (PeT) A technique of measuring mind perform based mostly on the detection of radioactivity emitted when positrons, positively charged particles, endure radioactive decay within the mind. Computers then construct three-dimensional photographs of modifications in blood move based mostly on the amount of radiation emitted in different mind areas. Psychosis A severe symptom of psychiatric problems characterised by an lack of ability to understand actuality. Psychosis can occur in lots of situations, together with schizophrenia, bipolar dysfunction, depression, and drug-induced states. Rapid eye Movement (ReM) Sleep Part of the sleep cycle when active dreaming takes place. Retina A multilayered sensory tissue that traces the back of the eye and accommodates the receptor cells to detect mild. Reuptake A process by which launched neurotransmitters are absorbed for later reuse. The rod is delicate to mild of low intensity and is specialised for nighttime vision. Second Messengers Substances that trigger communication after the actions of neurotransmitters at their receptors have been completed. Second-messenger effects might endure for a few milliseconds to as long as many minutes. Short-Term Memory A phase of reminiscence by which a restricted quantity of data could also be held for several seconds or minutes. Spinal Cord the extension of the mind through the vertebral column that primarily features to facilitate communication between the mind and the remainder of the physique. Stem Cell Unspecialized cells that renew themselves for long durations through cell division. Stress Any external stimulus that threatens homeostasis - the conventional equilibrium of physique perform. Many kinds of stress have a adverse effect on the physique, but some kinds may be useful. A stroke may be brought on by the rupture of a blood vessel, a clot, or strain on a blood vessel (as by a tumor). Suprachiasmatic Nucleus A small group of nerve cells within the hypothalamus that express clock proteins, which go through a biochemical cycle of about 24 hours. This units the tempo for daily cycles of activity, sleep, hormone launch, and different bodily features. Synapse A physical gap between two neurons that features as the positioning of data switch from one neuron to one other. Temporal Lobe One of the four main subdivisions of each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex. The temporal lobe features in auditory perception, speech, and sophisticated visual perceptions. Thalamus A construction consisting of two egg-shaped masses of nerve tissue, each about the size of a walnut, deep throughout the mind. The key relay station for sensory information flowing into the mind, the thalamus filters out information of explicit significance from the mass of signals coming into the mind. Trophic Factors Small proteins within the mind which are essential for the development, perform, and survival of particular teams of neurons. Of the four ventricles, three are situated within the forebrain and one within the brainstem. The lateral ventricles, the 2 largest, are symmetrically positioned above the brainstem, one in each hemisphere. Vertebral Column the column of bones, or vertebrae, that extends down the back and features as a structural component for the physique whereas also surrounding and defending the spinal twine. The white matter gets its color from myelin, the insulation overlaying nerve fibers. No portion of this publication could also be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any kind or by any means, digital, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise without permission of the Society for Neuroscience (SfN). Statistics for ailments and situations were obtained from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, World Health Organization, National Institutes of Health, and voluntary organizations. The Society gratefully acknowledges the invaluable assistance of more than 60 neuroscientists who volunteered their time, expertise, and guidance within the development and replace of this e-book. SfN also acknowledges the necessary contributions of Nicholas Spitzer, PhD, inaugural editor-in-chief for BrainFacts. We focus our assist on a restricted number of areas: � Plantscienceresearch Neuroscienceresearch Scienceandengineeringeducation EconomicdevelopmentinAfrica Publicpolicyresearchandadvice Thearts We are proactive in devising initiatives to achieve our aims. We are analytical as we consider it is very important understand the opportunities and issues we tackle. We are at all times enthusiastic to kind partnerships with different organisations who share our objectives. The Kavli Foundation the Kavli Foundation, established by Fred Kavli, is devoted to advancing science for the good thing about humanity, promoting public understanding of scientific analysis, and supporting scientists and their work. The Foundation is also a founding associate of the Kavli Prizes, biennial $1 million prizes that acknowledge scientists for his or her seminal advances in three analysis areas: astrophysics, nanoscience and neuroscience. Neuroscientists investigate the molecular and cellular levels of the nervous system; the neuronal methods liable for sensory and motor perform; and the basis of higher order processes, similar to cognition and emotion. This analysis offers the basis for understanding the medical fields which are involved with treating nervous system problems. These medical specialties embody neurology, neurosurgery, psychiatry, and ophthalmology. Founded in 1969, the Society has grown from 500 constitution members to more than 42,000 members worldwide. With actions ranging from lectures to networking occasions and information sharing, SfN chapters allow individual members to engage their colleagues at the local level. The mission of the Society is to: � Advancetheunderstandingofthebrain and the nervous system by bringing together scientists of diverse backgrounds, by facilitating the mixing of analysis directed in any respect levels of organic organization, and by encouraging translational analysis and the application of recent scientific information to develop improved illness therapies and cures. Support active and continuing discussions on ethical issues referring to the conduct and outcomes of neuroscience analysis. The trade of scientific information happens at an annual fall meeting where more than sixteen,000 reports of recent scientific findings are presented and more than 30,000 individuals attend. This meeting, the largest of its type on the earth, is the sector for the presentation of recent results in neuroscience. A main goal of the Society is to inform the general public about the progress and benefits of neuroscience analysis. The Society accomplishes this goal by offering details about neuroscience to schoolteachers and encouraging its members to speak to younger individuals about the human mind and nervous system. First revealed 1989 Reprinted 1990, 1992, 1994 Second version 1995 Reprinted 1996, 1999 Third version 2002 Reprinted 2003 Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Hunter, J. As earlier than, every chapter has been up to date extensively, but our goal continues to be the sameato create an simply learn textual content that will assist household medical doctors to get to grips with a subject many nonetheless discover complicated, regardless of the increasingly stodgy units of guidelines that now land often on their desks. However, if we had to embody solely therapies based mostly on flawless proof, we must omit too many elderly favourites that have stood the check of time, but have nonetheless not been evaluated properly. We have also reacted to a survey of our readers, which confirmed that the majority of them spend little time on the chapters devoted solely to the construction, perform and immunology of the pores and skin. We have pruned these back, but have put extra physiology and pathology into the relevant medical chapters where it should be of extra use to a health care provider struggling through a busy surgical procedure.
Proven ondansetron 4 mg
Erythema Multiforme A widespread response pattern (to a wide range of antigenic stimuli) of blood vessels within the dermis with secondary epidermal adjustments. Drugs Sulfonamides, phenytoin, barbiturates, phenylbutazone, penicillin, allopurinol. Dorsa of hands, palms, and soles / forearms / feet / face / elbows and knees / penis and vulva Mucous Membranes: Erosions with fibrin membranes; sometimes ulcerations: - lips, oropharynx, / - Nasal / Vulvar, anal. Nodular vasculitis is a type of lobular panniculitis associated with subcutaneous blood vessel vasculitis with subsequent ischemic adjustments that produce lipocyte harm, necrosis, inflammation, and granulation. On examination: Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema Induratum (Nodular Vasculitis) There are crops of small, tender, erythematous nodules involving the shins and calves may bear necrosis forming slowly healing ulcers. The most common sort of panniculitis: Erythema Nodosum - Panniculitis is the term used to describe illnesses the place the main focus of inflammation is within the S. Clinical Features: - Distribution: - the generally concerned sites: breasts, buttocks, thighs, and stomach. Angioedema is a larger edematous space that entails the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Description: Sharply defined spherical/oval wheals, small (<1 cm) to massive (>eight cm), erythematous. Angioedema: Skin-colored, transient enlargement of portion of face, eyelids, lips, tongue, glottis & larynx, or other sites due to subcutaneous edema - Laryngeal edema may cause airway obstruction and be life threatening. Angioedema occurs due to the professional-inflammatory action of bradykinin, which promotes edema, inflammation and the feeling of pain. Pathophysiology: - C1- esterase inhibitor deficiency, dysfunction or destruction Since C1-esterase inhibitor can be the main inhibitor of the Hageman issue & kallikrein, the two enzymes required for kinin formation elevated levels of the edema-producing factors C2b & bradykinin - Episodes normally observe an infection, dental procedure or trauma. Laboratory Abnormalities: - C1- esterase inhibitor: Decreased levels of (eighty five%) / dysfunctional inhibitor (15%), - Usually presents in late childhood - It is characterized by a speedy onset of the following symptoms: (1) non-inflammatory edema of the face, limbs, genitalia, (2) laryngeal edema, and (3) edema of the bowels leading to colicky belly pain. Distribution: - Most generally on scalp - Any hair-bearing space: Beard, eyebrows, eyelashes, pubic hair. Treatment directed at inflammatory infiltrate and development inhibitor factors produced by inflammation. Classification: 1- Psoriasis vulgaris: - Acute guttate - Chronic stable plaque 2- Psoriatic erythroderma 3- Pustular psoriasis four- Psoriasis arithritis mucous membranes. Description: the basic lesion of psoriasis is: - Sharply marginated, raised red plaque with a white scaly surface. Distribution: (Single lesion or lesions) - Extensor surfaces: elbows, knees, - Scalp, Most obvious at the hair line & behind the ears. Occurs 7 to 14 days after harm - Koebner phenomenon: Systemic triggering factors: May present in a linear arrangement after trauma. Treatment: 1- All patients should use emollients, such as Eucerin, Lubriderm, Aquaphor, and Vaseline or mineral oil. Clinical options: - Description: - hyperkeratotic, hyperpigmented plaques with a basic "velvety" texture. It is associated with insulin-resistant states: (eg, diabetes mellitus, weight problems, polycystic ovarian syndrome) Increased levels of insulin and/or insulin-like development factors are thought to stimulate epidermal and dermal proliferation. Miscellaneous Disorders It is associated with underlying neoplasms, especially of the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts. Ichthyosis Vulgaris Ichthyosis: History of normal pores and skin at birth, with gradual development to dry scaly pores and skin, is typical of ichthyosis. D Section 1 the Use of this Manual: Special Instructions Section 2 the Diagnostic Nomenclature: List of Mental Disorders and Their Code Numbers Section 3 the Definitions of Terms I. The speedy integration of psychiatry with the remainder of medicine additionally helped create a have to have psychiatric nomenclature and classifications closely integrated with these of other medical practitioners. In the United States such classification has for some years adopted closely the International Classification of Diseases. The latter committee is advisory to the Surgeon General of the Public Health Service and was entrusted with responsibility for developing U. Some of those diagnoses have been omitted here; others have been included and certified as controversial. The diagnoses at concern are: Psychosis with childbirth, Involutional melancholia, and Depersonalization syndrome. It has, actually, a wider utilization due to the expansion of psychiatric work generally hospitals, both on psychiatric wards and in consultation companies to the patients in other hospital departments, and in complete group mental well being centers. No listing of diagnostic phrases could possibly be fully enough for use in all these situations and in each nation and forever. Nor can it incorporate all the accrued new information of psychiatry at anybody point in time. The Committee has tried to put down what it judges to be usually agreed upon by nicely-informed psychiatrists right now. In selecting appropriate diagnostic phrases for every rubric, the Committee has chosen phrases which it thought would facilitate most communication within the career and scale back confusion and ambiguity to a minimal. Rationalists could also be vulnerable to believe the old saying that "a rose by any other name would odor as candy"; however psychiatrists know full nicely that irrational factors belie its validity and that labels of themselves situation our perceptions. The Committee accepted the fact that totally different names for a similar factor indicate totally different attitudes and concepts. Inevitably some customers of this Manual will read into it some common view of the character of mental disorders. Consider, for example, the mental disorder labeled in this Manual as "schizophrenia," which, within the first edition, was labeled "schizophrenic response. Until just lately, no other nation had provided itself with an equal official guide of permitted diagnostic phrases. In making ready this new edition, the Committee has been particularly aware of its usefulness in serving to to stabilize nomenclature in textbooks and professional literature. He is particularly responsible for the preparation of the Introduction following and Sections four, and 5 of this Manual. Spitzer, Director, Evaluation Unit, Biometrics Research, New York State Psychiatric Institute, served as Technical Consultant to the Committee and contributed importantly to the articulation of Committee consensus as it proceeded from one draft formulation to the subsequent. The present members of the Committee on Nomenclature and Statistics owe a deep debt to former chairmen and members of the Committee who provided the inspiration upon which the second edition was ready. The exceptions were post-encephalitic character and character disorders among the many continual brain syndromes, alcoholic delirium among the many acute brain syndromes, and gross stress response among the many transient disorders. George Raines, representing the American Psychiatric Association, and three others from the Public Health Service, Dr. General paralysis was classified under syphilis, and post-encephalitic psychosis under the late effects of acute infectious encephalitis, for example. Also, many ol the psychoses associated with natural factors were grouped in a catch-al class of psychoses with other demonstrable etiology. Such a classification was recognized as indispensable for worldwide communication and knowledge collection. Public Health Service then established a series of subcommittees of its National Committee on Vital and Health Statistics, together with a Subcommittee on Classification of Mental Disorders. The National Committee is advisory to the Surgeon General on technical matters and developments within the field of significant and well being statistics. The Subcommittee on Classification of Mental Disorders, appointed by the National Committee on Vital and Health Statistics, comprised Dr. Subcommittee of working with colleagues within the United Kingdom to develop and agree upon a single classification of mental 1 Stengel, E. Brill played a most constructive function in reaching agreement on a single classification. By April of 1963 it was possible to report this achievement to mental well being and hospital authorities within the United States and to solicit their comments on the U. It was quite gratifying that the assembly elicited very appreciable agreement on the classification of schizophrenia; paranoid states; the psychoses associated with infections, natural, and physical situations; nonpsychotic situations associated with infections, natural, and physical situations; mental retardation; physical disorders of presumably psychogenic origin; particular symptom reactions; addictions; and transient situational disturbances. The areas that also remained in disagreement were the affective disorders, neurotic depressive response, a number of of the character disorders (paranoid, delinquent response, and sexual deviation), and mental retardation with psychosocial deprivation. It had become quite clear by now, for example, that there could be little assist for the U. Snezhnevsky, Director of the Institute of Psychiatry of the Academy of Medical Sciences, for the U.
Order ondansetron 4 mg
Necrotic phenomena, when current, are appreciable as non-enhancing intratumoral areas. As sufferers with cirrhosis are at excessive danger of growing portal thrombosis, a differential prognosis between neoplastic and non-neoplastic thrombosis is required. The use of a spiral scanner is obligatory to perform a complete covering of the hepatic parenchyma through the arterial section. Delayed section images can also be useful, notably to consider the presence of a capsule (2). Hepatocellular Carcinoma 865 the degree of fats deposition differs amongst inside portions of the tumour, the characteristic mosaic structure is visualized. Deposition of haemosiderin might occur in regenerative and dysplastic nodules, leading to elevated attenuation on precontrast scans. This sort is characterized by quite a few small hypodense nodules diffusely distributed within the liver (2). These lesions show homogeneous or inhomogeneous contrast-enhancement through the arterial section, thus appearing markedly hyperdense. Satellite lesions are hypervascular like the primary tumour and seem as tiny foci of enhancement within the arterial section. Tumour thrombi in the primary portal branches seem as solid plenty within the vessel with a marked hypervascularity within the arterial section (2). Hyperintensity on T1-weighted images could also be as a result of fatty metamorphosis, haemorrhagic necrosis, glycogen or copper deposition. The tumour capsule is extra likely to be seen on T1-weighted images, detected as a thin hypointense rim. T2-weighted images delineate a single hypointense rim or a double ring with inner hypointensity, similar to the fibrous capsule, and outer hyperintensity, similar to the pseudocapsule. The capsule is optimally depicted on delayed section as a peripheral hyperdense rim. The enhancement within the early arterial section might show totally different patterns: peripheral, central, mixed, full or absent. This is due to the big extracellular areas of the capsular region, which embody vascular lakes within the compressed liver parenchyma. Hepatobiliary contrast agents cross from blood by way of the hepatobiliary system with partial excretion by way of the kidneys and bile ducts. Many of them can be utilized each as vascular contrast agents in dynamic studies and as hepatospecific agents in delayed T1-weighted scans. In the hepatobiliary section, the normally functioning parenchyma shows a transparent enhancement. Cirrhotic livers show a decreased uptake of hepatobiliary agents as compared with normal livers, as a result of a decreased hepato-biliary function (1). The presence of iron particles, captured within the Kupffer cells of the conventional liver, produces a significant signal loss on T2-weighted images through the hepato-particular section. Lesion demarcation and visualization are improved and the detection price is elevated. In basic tumours are iso- or hypointense on T1-weighted scans and iso- or hyperintense on T2-weighted scans. Typically, the scar has low signal depth each on T1 and T2-weighted images (1). For nodules above 2cm in size, imaging strategies are normally able to set up a assured prognosis without needing confirmation with a optimistic biopsy. Dynamic study after bolus administration of gadolinium-chelates utilizing fast T1-weighted sequences demonstrates the everyday enhancement within the arterial section with wash out within the following phases. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography might turn out to be a real-time various to assess therapeutic response (7). Lencioni R, Menu Y (1999) Ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology November 42 (5):1208�1236 Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L et al (2005) Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in sufferers with cirrhosis: lengthy-term results of percutaneous picture-guided radiofrequency ablation. Epub 2005 Jan 21 Hepatocystic Duct H Accessory duct draining the liver parenchyma into the gallbladder. Congenital Malformations, Liver and Biliary Tract Hepatomegaly Abnormal enhance of the liver size. When the growing includes the left lobe, it may cause displacement of the proper anterior wall of the gastric physique. Compression, Extrinsic, Stomach and Duodenum Hereditary or Genetic Hemochromatosis Hemochromatosis, Skeletal Hereditary Spherocytosis Hereditary spherocytosis is the most common dysfunction of the purple blood cell membrane, the bag that contains the hemoglobin molecules that carry oxygen by way of the bloodstream. The abnormal cells cross with greater problem by way of the spleen and are consequently destroyed abnormally shortly. In: Vogl, Lencioni, Hammerstingl, Bartolozzi Eds Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Liver Disease. Thieme, 163�197 Bartolozzi C, Donati F, Cioni D et al (1999) Computed tomography of hepatocellular carcinoma In: Bartolozzi, Lencioni Eds. In this hernia, a portion of the abdomen herniates by way of the oesophageal hiatus. The function of the decrease oesophageal sphincter and the presence of reflux are the components that produce signs and cause issues. In this hernia, the gastro-oesophageal junction is displaced more than 1 cm above the diaphragmatic hiatus. Here the gastro-oesophageal junction remains within the normal location but a portion of the abdomen, normally the fundus, herniates above the diaphragm. If the hernia is large, the herniated abdomen can volvulate and turn out to be strangulated. Bochdalek Hernia If the embryonic pleuroperitoneal canal persists, a defect is current within the diaphragm, and herniation can occur by way of this opening. The bigger hernias are sometimes seen within the neonatal interval and may comprise omentum, spleen, kidney, and retroperitoneal fats. When current within the neonatal interval, the infant might have an ipsilateral hypoplastic lung and respiratory distress. This is presumably because of the protective effect of the liver on the proper, although herniation can even occur by way of the pleuroperitoneal canal on the proper. They might comprise bowel, omentum, bladder, and, every so often, other belly organs similar to liver and gall bladder. Generally, the herniation happens by way of openings or potential areas that exist already. However, weaknesses might occur in muscle tissue or fascia, encouraging the passage of a viscus. The two commonest sites of herniation within the abdomen are the diaphragm and inguinal areas. Morgagni Hernia Clinical Presentation the clinical presentation depends on the location and kind of hernia. Complications of a hernia, similar to obstruction, may be the first clinical presentation in a significant quantity. It is due to a defect within the para-sternal portion of the diaphragm and is invariably right-sided. Hernia, Abdominal and Inguinal 869 Traumatic Hernia Rupture of the hemidiaphragm permits herniation of belly contents by way of the tear. Again, the left side is affected in over 90% of instances because the liver dissipates the traumatic forces and protects the proper hemidiaphragm. Traumatic hernia is suspected when gasoline-filled loops of bowel or abdomen are seen in left decrease thorax following extreme trauma. The left lobe of the liver might herniate, along with the abdomen, small bowel, colon, kidney and spleen. The contour of the left hemidiaphragm can also be vague or elevated on radiographs. Inguinal Hernia In inguinal hernias, bowel, omentum or bladder might herniate into the inguinal canal. The inferior epigastric artery provides off the cremasteric artery at the deep inguinal ring.
Syndromes
- Deficiency of galactose-6-phosphate epimerase
- Since the condom must be put on when the penis is erect, but before contact is made between the penis and vagina, there is usually a brief interruption during foreplay. Many couples solve the problem by making the process of placing the condom on the penis part of foreplay.
- Muscle cramps
- Although foods that contain sugar alcohols may have fewer calories, read labels carefully for the amount of carbohydrates and check your blood sugar levels.
- Close all doors and windows before using the pesticide
- Worsened by deep breathing or coughing
- Marijuana Anonymous (MA)
- Bulky stools
Generic ondansetron 4mg
Renal Disorders Nephrotic syndrome is often associated with pronounced hyperlipoproteinemia, which is often blended but can manifest as hypercholesterolemia or hypertriglyceridemia. Effective remedy of the underlying renal illness normalizes the lipid profile, but most patients with persistent nephrotic syndrome require lipid-lowering drug therapy. Triglyceride lipolysis and remnant clearance are each decreased in patients with renal failure. Severe hepatitis and liver failure are associated with dramatic reductions in plasma cholesterol and triglycerides due to decreased lipoprotein biosynthetic capacity. A major pathway by which cholesterol is excreted from the physique is through secretion into bile, either immediately or after conversion to bile acids, and cholestasis blocks this crucial excretory pathway. Use of low-dose preparations of estrogen or the estrogen patch can minimize the effect of exogenous estrogen on lipids. Drugs Many medication have an effect on lipid metabolism and may end up in important alterations within the lipoprotein profile (Table 21-5). The Frederickson classification scheme for hyperlipoproteinemias (Table 21-three), although less generally used now than in the past, can be useful in this regard. As noted above, the medical trial knowledge with fibrates general suggests cardiovascular profit, but the results are blended. In this setting, the danger of myopathy have to be carefully weighed against the medical good thing about the therapy. Fish oil dietary supplements can be used together with fibrates, niacin, or statins to deal with hypertriglyceridemia. In general, fish oils are properly tolerated and seem to be secure, no less than at doses as much as three�4 g. Although fish oil administration is associated with a prolongation within the bleeding time, no improve in bleeding has been seen in medical trials. In this setting, a cholesterol absorption inhibitor or bile acid sequestrant can be added. Statin-fibrate mixtures are known to be associated with an increased incidence of extreme myopathy (as much as 2. This mixture of medicine must be used cautiously in patients with underlying renal or hepatic insufficiency; within the aged, frail, and chronically unwell; and in those on a number of drugs. A bigger group of patients, most of whom have genetic lipid problems, remain considerably hypercholesterolemic despite mixture drug therapy. Smoking must be discontinued, obese individuals must be encouraged to shed weight, sedentary individuals must be encouraged to train, and diabetes must be optimally controlled. Nevertheless, the concept is useful as a result of the tumors have necessary similarities in addition to some differences (Table 22-1). They can be tentatively identified on routine histology; nevertheless, these tumors are actually principally recognized by their histologic staining patterns due to shared cellular proteins. More lately immunocytochemical localization of chromogranins (A, B, C), neuron-specific enolase, or synaptophysin, which are all neuroendocrine cell markers, are used (Table 22-1). Ultrastructurally, these tumors possess electron-dense neurosecretory granules and incessantly contain small clear vesicles that correspond to synaptic vesicles of neurons. Chromogranins (A, B, C) are acidic monomeric soluble proteins found within the massive secretory granules; chromogranin A is most generally used. Synaptophysin is an integral membrane glycoprotein of 38,000 molecular weight present in small vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine tumors. Frequently synthesize a number of peptides/amines, which can be detected immunocytochemically but will not be secreted. Generally have high densities of somatostatin receptors, which are used for each localization and remedy. Methylation of assorted genes occurs in forty�87% (ras-related area family I, p14, p16, O6 methyl guanosine methyltransferase, retinoic acid receptor). Carcinoid tumors are incessantly categorised according to their anatomic area of origin. Each of the functional syndromes is associated with symptoms due to the specific hormone launched. This classification is additional divided on the basis of tumor location and biology. The incidence of clinically important carcinoids is 7�thirteen cases/million population per 12 months, whereas any malignant carcinoids at post-mortem are reported in 21�eighty four cases/million population per 12 months. With carcinoid tumors, the share exhibiting malignant conduct varies in numerous places. For the three most common websites of incidence, the incidence of metastases varies tremendously from jejunoileum (fifty eight%) > lung/bronchus (6%) > rectum (4%). Particularly necessary within the development of liver metastases is the dimensions of the primary tumor. For example, with small-intestinal carcinoids, the most frequent cause of the carcinoid syndrome due to metastatic illness within the liver (Table 22-2), metastases happen in 15�25% if the tumor diameter is <1 cm, fifty eight�eighty% whether it is 1�2 cm, and >seventy five% whether it is >2 cm. Many are categorised as somatostatinomas as a result of they contain somatostatin immunocytochemically; nevertheless, they uncommonly secrete somatostatin or produce a medical somatostatinoma syndrome. Both hamartin and tuberin work together in a pathway associated to cytosolic G protein regulation. These tumors usually pursue a benign course, with 9�30% associated with metastases. Sporadic carcinoids are often single, massive tumors, 50% have atypical histology, and they could be a cause of the carcinoid syndrome. Gastric carcinoids as a percentage of all carcinoids are rising in frequency [1. They characteristically cause a marked fibrotic reaction, which may result in intestinal obstruction. Distant metastases happen to the liver in 36�60%, to bone in three%, and to lung in 4%. However, even small carcinoid tumors of the small gut (<1 cm) have metastases in 15�25%, whereas it increases to fifty eight�a hundred% for tumors 1�2 cm in diameter. No duodenal tumor <1 cm in two collection metastasized, whereas 33% of those >2 cm had metastases. Small-intestinal carcinoids are the most common cause (60�87%) of the carcinoid syndrome and are mentioned beneath. The presentation is various and associated to the location of origin and extent of malignant unfold. In the appendix, carcinoid tumors are often found by the way during surgical procedure for suspected appendicitis. Because of the vagueness of the symptoms, the analysis is often delayed ~2 years from onset of the symptoms, ranging as much as 20 years. Duodenal, gastric, and rectal carcinoids are most incessantly found by chance at endoscopy. The most common symptoms of rectal carcinoids are melena/bleeding (39%), constipation (17%), and diarrhea (12%). Bronchial carcinoids are incessantly found as a lesion on a chest radiograph, and 31% of the patients are asymptomatic. Ovarian and testicular carcinoids often current as masses found on bodily examination or ultrasound. Metastatic carcinoid tumor within the liver incessantly presents as hepatomegaly in a patient who might have minimal symptoms and near-normal liver function checks. Endocrine Tumors of the Gastrointestinal Tract and Pancreas Rectal Carcinoids Rectal carcinoids are present in ~1 of every 2500 proctoscopies. Most are small, with sixty six�eighty% being <1 cm in diameter, and they not often metastasize (5%). Tumors between 1 and a pair of cm can metastasize in 5�30% and tumors >2 cm, which are uncommon, in >70%. These substances might or will not be launched in adequate quantities to cause symptoms. The most common systemic syndrome with carcinoid tumors is the carcinoid syndrome. Flushing and diarrhea are the 2 most common symptoms, occurring in as much as 73% initially and in as much as 89% in the course of the course of the illness. Flushes may be precipitated by stress, alcohol, train, sure meals corresponding to cheese, or sure agents corresponding to catecholamines, pentagastrin, and serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Flushing episodes may be brief, lasting 2�5 min, especially initially, or might final hours, especially later within the illness course.
Generic ondansetron 8mg
Transabdominal ultrasound will often determine insulinomas, and endoscopic ultrasound has a sensitivity of about 90%. Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy is assumed to detect insulinomas in about half of sufferers. Selective pancreatic arterial calcium injections, with the endpoint of a sharp improve in hepatic venous insulin ranges, regionalize insulinomas with high sensitivity, however this invasive process is seldom essential. Diazoxide, which inhibits insulin secretion, or the somatostatin analogue octreotide can be used to treat hypoglycemia in sufferers with unresectable tumors. Reactive hypoglycemia additionally occurs in sufferers with autoantibodies to insulin and within the noninsulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome. Affected sufferers have symptomatic hyperinsulinemic postprandial hypoglycemia (however adverse seventy two-h fasts) that remits following partial pancreatectomy. A similar syndrome following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery for obesity has been described. The existence of a clinically related idiopathic reactive hypoglycemia syndrome is debated. The issue is whether or not signs are caused by hypoglycemia, an exaggerated sympathoadrenal response to declining glucose ranges late after a meal, or some glucose-impartial mechanism. In any event, caution must be exercised before labeling an individual with a prognosis of hypoglycemia. Frequent feedings, avoidance of straightforward sugars, and high-protein diets are generally really helpful to sufferers thought to have idiopathic reactive hypoglycemia. The efficacy of those approaches has not been established by controlled scientific trials. Even with a quantitative technique, low measured glucose concentrations can be artifactual. Blood must be drawn, each time possible, before the administration of glucose to permit documentation of a low plasma glucose concentration. Thus, the perfect time to measure the plasma glucose stage is throughout a symptomatic episode. A low glucose stage confirms that hypoglycemia is the reason for the signs, offered the latter resolve after the glucose stage is raised. When the reason for the hypoglycemic episode is obscure, extra measurements, whereas the glucose stage is low and before remedy, should include plasma insulin, C-peptide, and ethanol concentrations, as well as ranges of insulin secretagogues. It is most common amongst health care staff, sufferers with diabetes or their relations, and other people with a history of different factitious illnesses. However, it must be considered in all sufferers being evaluated for hypoglycemia of obscure cause. Drugs, particularly these used to treat diabetes or alcohol, must be the first consideration, even within the absence of known use of a related drug, given the potential of surreptitious, unintentional, or malicious drug administration. Other considerations include evidence of a related crucial sickness, less generally hormone deficiencies, and rarely a non�-cell tumor that may be pursued diagnostically. Absent one of these mechanisms, in an in any other case overtly well particular person, one should consider endogenous hyperinsulinism and proceed with measurements and evaluation of signs under fasting situations of enough duration to elicit or exclude fasting hypoglycemia. If the affected person is unable or unwilling, due to neuroglycopenia, to take carbohydrates orally, parenteral therapy is critical. Because it acts by stimulating glycogenolysis, glucagon is ineffective in glycogen-depleted individuals. These treatments increase plasma glucose concentrations only transiently, and sufferers should therefore be urged to eat as quickly as is practical to replete glycogen stores. Failing these treatments, frequent feedings and avoidance of fasting may be required. Administration of uncooked cornstarch at bedtime or even an in a single day intragastric infusion of glucose may be essential in some sufferers. Review:Tight glucose control reduces septicemia, however not dying, and will increase hypoglycemia in critically ill adults. The growth of secure, efficient, and welltolerated pharmacologic agents has significantly expanded the therapeutic armamentarium obtainable to the doctor to treat issues of lipid metabolism. Therefore, the appropriate prognosis and administration of lipoprotein issues is of crucial significance within the follow of drugs. This chapter will review regular lipoprotein physiology, the pathophysiology of major (inherited) issues of lipoprotein metabolism, the diseases and environmental factors that cause secondary issues of lipoprotein metabolism, and the practical approaches to their prognosis and administration. Lipoproteins play an essential function within the absorption of dietary cholesterol, lengthy-chain fatty acids, and fats-soluble vitamins; the transport of triglycerides, cholesterol, and fats-soluble vitamins from the liver to peripheral tissues; and the transport of cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver. Lipoproteins include a core of hydrophobic lipids (triglycerides and cholesteryl esters) surrounded by hydrophilic lipids (phospholipids, unesterified cholesterol) and proteins that work together with physique fluids. The plasma lipoproteins are divided into five main classes based mostly on their relative density. The proteins associated with lipoproteins, known as apolipoproteins (Table 21-2), are required for the assembly, construction, and function of lipoproteins. Apolipoproteins activate enzymes important in lipoprotein metabolism and act as ligands for cell-floor receptors. Each lipoprotein class comprises a family of particles that vary slightly in density, dimension, migration throughout electrophoresis, and protein composition. Dietary triglycerides are hydrolyzed by lipases inside the intestinal lumen and emulsified with bile acids to form micelles. Dietary cholesterol, fatty acids, and fatsoluble vitamins are absorbed within the proximal small intestine. Cholesterol and retinol are esterified (by the addition of a fatty acid) within the enterocyte to form cholesteryl esters and retinyl esters, respectively. The released free fatty acids are taken up by adjacent myocytes or adipocytes and both oxidized to generate energy or reesterified and stored as triglyceride. Some of the released free fatty acids bind albumin before entering cells and are transported to different tissues, especially the liver. Chylomicron remnants are quickly faraway from the circulation by the liver through a process that requires apoE as a ligand for receptors within the liver. Consequently, few, if any, chylomicrons or chylomicron remnants are present within the blood after a 12-h quick, except in sufferers with issues of chylomicron metabolism. During this process, many of the triglyceride within the particle is hydrolyzed, and all apolipoproteins except apoB100 are transferred to different lipoproteins. Apo(a) is synthesized within the liver and attached to apoB100 by a disulfide linkage. In the liver, cholesterol is excreted into the bile, both immediately or after conversion to bile acids. This pathway transports extra cholesterol from the periphery again to the liver for excretion within the bile. A classification scheme based mostly on the molecular etiology and pathophysiology of the lipoprotein issues complements this system and forms the basis for this chapter. The identification and characterization of genes liable for the genetic forms of hyperlipidemia have offered important molecular insights into the crucial roles of structural apolipoproteins, enzymes, and receptors in lipid metabolism (Table 21-four). It has a higher incidence in certain founder populations, such as Afrikaners, Christian Lebanese, and French Canadians. Total levels of cholesterol are normally >500 mg/dL and can be higher than 1000 mg/dL. Atherosclerosis often develops first within the aortic root, where it can cause aortic valvular or supravalvular stenosis, and typically extends into the coronary ostia, which turn out to be stenotic. Carotid and femoral illness develops later in life and is normally not clinically important. Liver transplantation, nonetheless, is associated with substantial risks, including the requirement for lengthy-time period immunosuppression. Corneal arcus is widespread, and tendon xanthomas involving the dorsum of the hands, the elbows, the knees, and particularly the Achilles tendons are present in ~seventy five% of sufferers. These genes are expressed within the intestine and liver, where they form a functional complicated and pump plant sterols, such as sitosterol and campesterol, and animal sterols, predominantly cholesterol, from enterocytes into the intestine lumen and from hepatocytes into the bile. In regular individuals, <5% of dietary plant sterols are absorbed by the proximal small intestine and delivered to the liver. Plant sterols that are carried to the liver on chylomicrons are preferentially secreted into the bile such that the plant sterol ranges in plasma and tissues are usually very low. In sitosterolemia, the intestinal absorption of plant sterols is increased and biliary excretion of the sterols is decreased, resulting in increased plasma and tissue ranges of sitosterol and different plant sterols. Episodes of hemolysis, presumably secondary to the incorporation of plant sterols into the pink blood cell membrane, are a particular scientific function of this illness. The hypercholesterolemia in topics with sitosterolemia is unusually aware of reductions in dietary cholesterol content material.
Ondansetron 8mg
A full laboratory examine have to be carried out in sufferers without evident reason for splenomegaly. Imaging research are helpful to assess the splenic enlargement and identify the cause of the splenomegaly. Splenosis may trigger recurrence of hematologic issues after therapeutic splenectomy. World J Surg 24:183�187 Robertson F, Leander P, Ekberg O (2001) Radiology of the spleen. Split-liver Transplantation Liver transplantation technique consists in cadaveric liver division so that the lateral section of the left lobe could also be transplanted right into a pediatric affected person and the remainder of the liver could also be transplanted into an adult. Transplantation, Hepatic Splenosis Splenosis outcomes from the autotransplantation of splenic tissue occurring after splenic trauma or after splenectomy. The incidence of splenosis after traumatic damage of the spleen varies from 27% to sixty seven%. Splenic implants are often numerous and are spread all through the peritoneal cavity. In sufferers with history of thoraco-stomach trauma with splenic and diaphragmatic damage, splenosis could also be intrathoracic. Splenosis is often an incidental discovering at imaging, and should mimic peritoneal metastases, lymphomegalies and different neoplastic or nonneoplastic lots. Granulation tissue and pannus formation result in cartilage destruction, reflecting the character of the sacroiliac joints as partly synovial joints. Subchondral inflammation progresses to bony erosion, usually with surrounding reactive bony sclerosis. These are systemic autoimmune inflammatory issues of unknown etiology, promoted by an infection and primarily affecting the discovertebral advanced, synovial membranes, articular surfaces, insertion of joint capsules, and tendino-osseous junctions. Clinical Presentation Ankylosing Spondylitis Ankylosing spondylitis is the prototypical form of the spondyloarthropathies. Because sacroiliitis is the primary manifestation, the best diagnostic clue is long-standing low back ache. Patients undergo most critically in the early morning hours, usually waking up with low back ache and feeling aid when strolling around. Motion restriction of the lumbar backbone, neck, hip, and thorax worsens in the middle of the disease. S Source: Dougados M, van der Linden S, Juhlin R et al (1991) the European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group: preliminary criteria for the classification of spondyloarthropathy. Erosions and bony destructions are primarily seen as indistinct and irregular contours. Bony bridges with blurring and disappearance of the joint space are signs of increasing ankylosis. The differential analysis consists of degenerative osteoarthritis, which reveals bandlike subchondral sclerosis or, especially in obese females, multiparae triangular sclerotic areas significantly in the decrease aspect of the iliac bone. Iliacal and sacral bony sclerosis can be signs of insufficiency fractures in extreme osteoporosis and should be considered as a differential in sufferers with low back ache, sacral sclerosis, and generalized osteoporosis. Erosion and destruction of the joint contours and ankylosis in addition to joint effusion as signs of arthritis are detected in unenhanced photographs. Contrast material enhancement can be seen in the joint capsule, erosions, subchondral granulation tissue, and areas of edema in addition to intra-articularly in pannus formation. Spine involvement: the typical function of backbone involvement in ankylosing spondylitis is the syndesmophyte, which grows marginally from the vertebral body nook in the precise position of the annulus fibrosus. Often it begins consecutively in Romanus lesions generally in the thoracolumbar junction segments. Table 2 classification of sacroiliitis �zero �1 �2 �3 �four X-ray Normal Suspicious Minimal arthritis Moderate arthritis Ankylosis Spondyloarthropathies, Seronegative. Contrast material enhancement is found in the areas of bone marrow edema, in the joint space itself, and in the erosions. The sacroiliacal joints are fully postarthritically ankylosed, with only mild residual sclerosis. Square vertebrae and the faint barrel form of the vertebrae are different typical options. Osteitis of the peridiscal bone (discitis, rheumatic spondylodiscitis) is another typical aspect of inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. It could also be restricted to the anterior upper nook and is then called a Romanus lesion. A Romanus lesion consists of a triangular sclerosis and an erosion of the anterior upper vertebral nook. The inflammation of the central part of the disc leads to an aspect resembling spondylitis, with erosions or destructions of the subchondral bone. In comparison to bacterial spondylitis, the destruction remains mild, focal, and unchanged for months and even years. It happens principally in the thoracolumbar junction segments of osteoporotic multisegmentally ankylotic vertebral columns with marked kyphosis. Square and barrel-shaped vertebrae are the result of inflammatory and osteoproliferative affection of the ventral vertebral aspect. Apophyseal joint arthritis with development to fibrous or bony ankylosis and consecutive early stiffness is very common in adolescent sufferers. In late stages, bands of broad ossification over the dorsolateral aspect of the vertebral column are seen. Arthritis of the costotransversal and costovertebral joints gives rise to persistent thoracolumbar ache and is the reason for respiratory S 1736 Spondyloarthropathies, Seronegative movement restriction. Ligament ossification corresponding to of the interspinal and iliolumbar ligaments happens in late stages of ankylosing spondylitis, some of which are specially named: "Dagger signal" is the polysegmental ossification of the interspinal ligaments. If occurring along with prolonged bridging ossification of the intervertebral joint capsules, the term "trolley-truck signal" is used. In ankylosing spondylitis, the massive joints are generally affected: hips, knees, and shoulders. Joint effusion, cartilage destruction with consecutive concentric joint space narrowing, and paraarticular demineralization are the radiologic signs of arthritis. Sometimes, premature degenerative disease is the only signal of postarthritic change. Extraarticular inflammatory proliferation is seen along with arthritic destruction. Bursitis compromising the underlying bone is most frequently seen in bursa subachillea, bursa trochanterica, and iliopsoas bursa. In ankylosing spondylitis, an inflammatory reaction of tendon and ligament insertions is a number one function. Common locations are the iliac crest, tubera ischiadica, higher trochanter, plantar fascia (calcaneopathy), and olecranon, but it can seem wherever. Proliferative adjustments with indistinct, hairy contours in addition to destructions with small grooves or combinations of each are potential options. Synchondritis of the symphysis or manubriosternal junction reveals contour defects or broad indistinct defects and surrounding bony sclerosis. The most up-to-date modification of the New York criteria dates from 1984 and provides high specificity and moderate sensitivity. One or more scientific signs and radiological proof of sacroiliitis have to be present for correct analysis (Table 3). Interventional Radiological Treatment As in rheumatoid arthritis, radiosynovectomy is a promising device for local control in restricted disease of the massive joints. Clinical Presentation Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic arthritis happens in 5�10% of sufferers affected by psoriasis. Lumbar backbone involvement is characterized by ache, morning stiffness, and motion restriction. Imaging Signs and Patterns in Psoriatic Arthritis Peripheral arthritis of the small joints is widespread, but not symmetrical in most sufferers. Table 3 Modified New York criteria (1984) for diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis (1 scientific signal and 1 radiological signal) Clinical signs Low back ache and stiffness >3 months, no ache aid with rest but aid with exercise Motion restriction of the lumbar backbone sagittally and frontally Respiratory motion restriction (age-associated, about <2. Asymmetric huge tracer accumulation could also be an indication of arthritis, but specificity is very low. Bone scanning can present foci of inflammatory affection all over the skeleton, and subsequently can direct the following work-as much as these foci.
Cheap 8mg ondansetron
The sequestration web site of the erythrocytes is localized by way of the uptake measurements (constant measuring occasions) of the liver, spleen, and heart (as a measure for the blood pool). With a thought-about splenectomy, the contribution of the spleen to erythropoiesis must be taken into consideration (compare to ferrokinetic). With an intravascular hemolysis, no organ-particular sequestration web site is noticed. Hereditary spherocytosis (liver-spleen quotient >2) and hereditary nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia (improve from liver and spleen) show attribute uptake patterns. The differential diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia is influenced by the results of the iron resorption examination. Normal values for intestinal iron resorption provide no conclusions to the reason for a proven iron deficiency. If there is an increase in the intestinal iron resorption, the primary line of pondering must be blood loss. Heavy blood loss during the examination time can simulate a normal end result with an really increased resorption. For the diagnosis of hemochromatosis, no essential significance can be attributed to dedication of the intestinal iron resorption. The methodology guarantees a differential diagnostic gain for patients with hypersiderinemia and anemia. Blood samples are taken for two weeks with out congestion so as to measure their radioactivity and compare them against the standards. From the standardized readings, the half-lifetime of the erythrocyte-bound chromium in the blood is determined. The measured common half-lifetime of the lifespan of the erythrocyte is smaller than the true erythrocyte halflife of 25�forty days; this is known as apparent erythrocyte half-life. Beshara S, Sorensen J, Lubberink M et al (2003) Pharmacokinetics and red cellg utilization of 52Fe/59Fe-labelled iron polymaltose in anaemic patients utilizing positron emission tomography. Transfusion 39:156�162 Nielson P, Kongi R, Buggisch P et al (2005) Bioavailability of oral iron drugs as judged by a 59Fe-whole-body counting method in patients with iron deficiency anemia. Definition Esophageal Disease, Childhood Oesophageal Disease, Childhood Esophageal Foreign Bodies Foreign Bodies, Gastrointestinal Imaging of quick, early, and late complications after surgical procedures of the esophagus has two targets: first, to detect morphological changes, corresponding to leaks, stenoses, or extraesophageal lesions, and second, to evaluate the perform of the higher gastrointestinal tract. Morphology and function might intrude in many symptomatic patients after esophageal surgery, and the radiologist has to combine morphological and practical findings to clarify signs and to support therapeutic decisions. Esophageal Rupture (in Blunt Chest Trauma) Esophageal rupture is usually because of penetrating trauma. Most patients with esophageal rupture produce other significant associated thoracic accidents, which is usually adopted by mediastinitis with high mortality (Boerhaave syndrome). The methodology of selection in suspected esophageal perforation is contrast esophagography with water-soluble contrast agents (ninety% sensitivity), if necessary with further endoscopy. Chest Trauma Pathology/Histopathology Complications associated with esophageal surgery are generally associated to the type of operation performed and the extent of surgery. Complications can be roughly divided into technical complications and those associated with cardiopulmonary aberrations. Fistula or leaks Clinical Presentation Immediate complications are usually managed during or just after the procedure. Perforation of the esophagus during dilatation is an indication for an urgent fluoroscopic work-up (Figs 1 and 2). Postoperative hemorrhage happens with an incidence of 3�5% and requires urgent reexploration. For many early postoperative complications, radiologic imaging plays the important thing position in diagnosis. If the patient aspirates, neuromuscular affection of swallowing can be detected by videofluoroscopy. Neuromuscular swallowing issues are associated with longtime intubation and danger components. Anastomotic or staple-line leaks, conduit ischemia, or perforation because of dilatation are among the most feared postoperative and postintervention complications (Figs 1 and 2). The incidence and seriousness are highly variable, relying on the type of operation, the location of the anastomosis, the experience of the surgeon, and the degree of the complication. A cervical leak is less serious than a thoracic leak, and a small anastomotic leak is less serious than a dehiscence associated with conduit necrosis. The peak of medical manifestation of anastomotic failure is between days 5 and seven after surgery. The medical presentation of esophageal leaks can vary from fully asymptomatic to all of the indicators of shock and even death. Hypotony or atony of the esophagus or abdomen and delayed emptying of the esophageal substitute are typical E Esophagus, Postoperative. Figure 1 A 75-12 months-old man after removal of a stent, which was initially inserted endoscopically for therapy of an obstructing squamous cell carcinoma of the distal esophagus. Ischemia of the gastric pull-up or the interposed colon results in extreme medical indicators of shock. A frequent late complication of the postoperative esophagus is a stricture of the anastomosis or a restenosis after dilatation of a stenosis. Intermittent or constant dysphagia for solids or accrued semisolid food (rice, potatoes, and noodles) is the everyday medical presentation. Imaging In the quick period after surgery, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, mediastinal widening, or pneumomediastinum/subcutaneous emphysema on chest X-ray could also be highly suggestive of esophageal perforation. To verify the patency of an anastomosis and the absence of complications after surgery, a swallowing study is initially accomplished. The use of low-osmolar or isoosmolar watersoluble contrast materials is obligatory because of its rapid absorption from the mediastinum in instances of perforation and to keep away from lung edema after aspiration. The examination must be performed in two perpendicular planes-in the majority of instances, in the left and right decubitus position. Small collections of extraluminal contrast materials could also be obscured by the esophagus in the frontal position. Additionally, the investigation of the whole esophagus and the abdomen, duodenum, and first loops of the jejunum in patients with difficult operations is necessary for demonstrating an obstruction, leak, or other possible complication distal to the anastomosis. Dynamic recording of swallowing facilitates the detection of small perforations because of the potential for observing the recorded swallow several occasions in slow motion. Figure 2 A 45-12 months-old lady immediately after endoscopic pneumatic dilatation of the lower esophageal sphincter to treat idiopathic achalasia. The surgeon suspected esophageal injury, however the location was unclear, and makes an attempt to locate the perforation web site by endoscopy failed. In the working theater, fluoroscopy was performed by the radiologist, utilizing a catheter fastidiously introduced under the pharyngoesophageal sphincter. Postoperative motility issues of the esophagus might result in regurgitation and dysphagia for stable food and even liquids. After esophagectomy, up to 10% of patients will develop gastric emptying issues because of vagotomy and the anatomical rearrangement. A prophylactic pyloromyotomy or pyloroplasty (dilatation) is completed routinely in most facilities to keep away from this disabling complication. Diagnosis Neuromuscular affection of swallowing can be an early complication after esophageal surgery, particularly after Esophagus, Postoperative 685 lengthy periods of intubation and in patients with multiple comorbid illnesses. A delayed swallowing reflex, pharyngeal weak spot, and inadequate closure of the larynx are sometimes found. For swallowing rehabilitation, a therapeutic videofluoroscopic study is helpful, by which the radiologist tries to discover which consistency and quantity of contrast materials reveals one of the best outcomes, combined with special maneuvers. Videofluoroscopy or digital sequence should exactly describe the quantity of leakage in relation to the ingested volume of the bolus. If a patient can take solely 5 mL per swallow, the extravasation of 20% of the bolus is comparatively small, measuring 1 mL. If the patient is consuming continually from a cup, an extravasation of 1 mL seems to demonstrate a small leakage with a great prognosis. After consuming 30 mL or much more contrast materials, small leaks of some drops might result in more or less symptomatic strictures. This example reveals how perform can be built-in in the analysis of morphology, with out direct visualization of the lesion traits. Only huge defects of the anastomosis of massive perforations present a visible disintegration of the intestine itself. Usually a leak after dilatation or other esophageal intervention results in a extreme drawback that requires urgent exploration.
Purchase 4 mg ondansetron
External rectal prolapse is an invagination of the rectal wall through the anal canal. Regardless of its extension, inner rectal prolapse may contain all rectal wall layers (fullthickness prolapse;. Enterocele Rectal Prolapse Rectal prolapse is an invagination of the rectal wall and could also be categorised as inner or exterior (1). Enteroceles most regularly happen at the finish of evacuation and may be filled with omental fats (peritoneocele), small bowel (enterocele), or sigmoid colon P Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Anorectal Manifestations. Figure 1 A 63-year-old girl with fecal incontinence and diffuse pelvic ache after hysterectomy. A sagittal T1-weighted spoiled gradient-recalled echo magnetic resonance image with the affected person in sitting position obtained during defecation reveals a full-thickness intraanal rectal prolapse (massive arrow). The anorectal junction (small arrow) is below the pubococcygeal line, with formation of a reasonable rectal descent. Cystoceles are expressions of the descent of the anterior compartment, and descent of the vaginal vault (or any part of the remaining cervix within the case of hysterectomy) represents descent of the center compartment. The descent of those compartments is quantified in a similar way as described for rectal descent. A sagittal T1-weighted spoiled gradient-recalled echo magnetic resonance image obtained during defecation with the affected person in sitting position reveals a full-thickness exterior rectal prolapse (massive arrow). While most enteroceles spontaneously disappear at relaxation, just a few are mounted down at the rectovaginal space. Pelvic floor descent is a common discovering in patients with fecal incontinence and outlet obstruction. Rectal descent is normally associated with descent of the center and anterior pelvic compartments. It is associated with pelvic floor weak spot or with natural or practical neuromuscular problems. Conditions may include pelvic floor ache, urinary incontinence, bowel incontinence, stool outlet obstruction, pelvic organ descent, pelvic organ prolapse, and pelvic floor dyssynergy or spasm. Pathology Anatomically, the pelvic floor is fashioned by the genitourinary diaphragm and the levator ani muscle. The two elements of the levator ani muscle are the puborectalis muscle Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Genitourinary 1467 sling and the iliococcygeus muscle. The puborectalis muscle sling originates from the posterior surface of the pubic symphysis and goes around urethra, vagina, and anus. Contraction of the muscle pulls the rectum toward the symphysis and closes urethra, vagina, and rectum. The iliococcygeus muscle plates originate at the genitourinary diaphragm and insert at the lateral internal surfaces of the pelvis. The underlying trigger for incontinence and organ prolapse is pelvic floor laxity, normally resulting from compromised levator ani and puborectalis muscle perform and endopelvic fascia laxity and fascia defects. Predisposing components are multiple childbirths, vaginal delivery, menopause, age, hysterectomy, and inherited connective tissue laxity from collagen defects. Incontinence correlates with weight problems and smoking, and solely to a lesser extent with pelvic floor laxity and bladder neck hypermobility. The normal means of urination involves coordination between the bladder and pelvic floor muscular tissues; the pelvic floor muscular tissues chill out whereas the bladder contracts. In most patients, the bladder contracts normally but the urine circulate is poor as a result of continued tightening of the pelvic floor. The sensation of urinary frequency and urgency appear to be linked to pelvic floor laxity. The pure tendency for many patients is to pressure and push the last drop of urine out to allow them to prolong the intervals between toilet sessions. Unfortunately, pushing and straining seem to further injury the pelvic floor muscular tissues and worsen the signs. Pelvic organ descent and prolapse is the results of laxity of the connective tissues within the pelvis, particularly defects within the lateral fascial bands of the endopelvic fascia between the vagina and lateral pelvic wall, and defects within the rectovaginal septum. Descent of the posterior bladder wall below the inner urethral orifice is known as a cystocele. An enterocele is the descent of the peritoneal sac between vagina and rectum right down to the extent of the perineum with bulging of the posterior vaginal wall. Partial prolapse of the posterior vaginal wall (white arrow) as results of the enterocele. Descent of the uterus may be quantified by measurement of the change of the vaginal length during Valsalva. Stool outlet obstruction could also be brought on by two circumstances: pelvic floor laxity and pelvic floor dyssynergy. Pelvic floor laxity can result in descent of the peritoneal sac or uterus and to compression of the rectum by these organs. Compression of a rectocele by the peritoneal sac may intussuscept the anterior rectal wall into the anal canal. Detachment of the rectum from the sacrum in pelvic floor descent may result in intussusception of the rectum in itself. Damage to the nerves within the pelvis and pelvic floor could be a results of pelvic floor laxity with permanent stretching of the nerves. P 1468 Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Genitourinary Clinical Presentation Symptoms associated with anterior compartment could also be stress urinary incontinence, urinary urgency with increased frequency of urination and decreased urinary circulate, and sensation of incomplete urination with residual bladder volume. In genital descent, patients may present with protrusion of elements of the anterior vaginal wall by a cystocele or of the posterior vaginal wall by a rectocele or enterocele. Protrusion may go as far as full prolapse and eversion of the vagina to the surface. Descent and prolapse may happen solely during straining, or it could be mounted with permanent vaginal prolapse. If the uterus remains to be present, the portio may descend right down to the pelvic floor, or the uterus may protrude partially or completely to outside the body. In the posterior compartment, rectal mucosa prolapse or rectal wall prolapse may develop in patients with practical problems with permanent excessive-strain defecation. In stool outlet obstruction by rectal descent and intussusception, the affected person complains about defecation in small fractions. Large rectoceles with retention of bowel content increase the necessity to digitize from the vagina to empty the rectocele. In anisms or dyssynergy, defecation needs excessive intraabdominal strain, and the defecation process is extended. Imaging Ultrasound is normally carried out by the gynecologist as part of the diagnostic work-up of stress urinary incontinence and genitourinary prolapse. It permits for the morphological and dynamic assessment of the decrease urinary tract. Transvaginal ultrasound permits the detection of pathologies of the bladder and uterus. Introital ultrasound can detect urethral diverticula, periurethral lots, funneling of the urethra and cystoceles. Translabial ultrasound detects defects within the rectovaginal septum and helps to identify rectoceles. Roentgen colpocystodefecography is the unique imaging technique to evaluate pelvic floor descent. It requires filling of the urinary bladder, vagina, rectum, bowel, and peritoneum with roentgen contrast medium and is associated with a excessive-dose radiation exposure. These pictures give an summary of the pelvic organs and the pelvic floor muscular tissues within the resting position. T1- or proton density pictures could also be used for the pelvic floor muscular tissues moreover. T2-weighted imaging requires filling of the vagina and the rectum with watery contrast material. Normal urine manufacturing leads to adequate opacification of the bladder during investigation. A repetitive single slice within the mid sagittal airplane of 10 mm thickness is acquired during pelvic floor contraction and Valsalva maneuver with defecation. For contraction series, we use 30 pictures per series, for Valsalva and defecation, eighty to a hundred pictures are required. The series is repeated as usually as necessary to see greatest contraction and rest and most descent of pelvic floor, greatest rest of levator ani and puborectalis muscle, most organ descent and organ prolapse and full emptying of the rectum. The investigation is carried out in supine position of the affected person, with the knees slightly flexed and thighs kidnapped.
References:
- https://www.rand.org/content/dam/rand/pubs/external_publications/EP60000/EP66197/RAND_EP66197.pdf
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2017/209606Orig1s000MultidisciplineR.pdf
- https://dp.cdn.sos.ca.gov/forms/sf-dp_yourfuturetogetherbrochure.pdf
- https://www.waterloowellingtondiabetes.ca/userContent/documents/Professional-Resources/nutrition%20guidelines%20diabetes%20and%20kidney%20disease.pdf
.png)