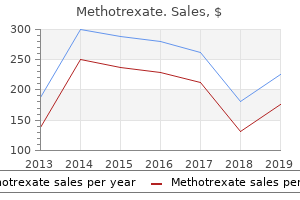
Best 5 mg methotrexate
Screening for secondary causes this ought to be considered in all patients, and especially when there are atypical features. Prevention and remedy As all the time, prevention is healthier than treatment and efforts ought to be directed in direction of prevention in these with identifiable risk factors. Postmenopausal ladies with a earlier fragility fracture ought to be considered for remedy with out further want for risk evaluation. Commonly used preparations range from these given once weekly, to monthly and even annually. Oral preparations may cause oesophageal irritation and ought to be taken before breakfast on an empty stomach with the patient upright. In addition, concern has arisen lately that extended use may be linked to atypical fractures of the femur. Osteonecrosis of the jaw is a rare however doubtlessly serious complication most commonly seen in these with pre-existing dental disease receiving intravenous therapy. Strontium ranelate this acts by rising bone formation and lowering bone resorption. Teriparatide (recombinant parathyroid hormone) this is very effective however currently very costly and reserved for severe/refractory osteoporosis. Clinical features Adult osteomalacia Patients may be aymptomatic or can present with. Serum calcium is often low/low regular (maintained by secondary hyperparathyroidism). Serum vitamin D levels: 25-hydroxycholecalciferol is low in vitamin D deficiency, however in any other case usually regular. Generalised osteopenia with cortical thinning may be related to a number of fractures, notably within the ribs. Aetiology Familial clustering and the finding of viral inclusions in osteoclastic nuclei has been taken to recommend that the disease may be triggered by viral infection in genetically predisposed people. Treatment Vitamin D the dosage and formulation rely upon the underlying aetiology. Serum calcium must all the time be monitored, particularly in these receiving bigger (pharmacological) doses and activated varieties. Pain is the most typical symptom, generally with a rise in temperature over the site of the lesion. Deficiency states: in delicate deficiency four hundred�800 models/ day (of easy ergocalciferol or colecalciferol) is sufficient in most patients; rarely, in severe osteomalacia pharmacological doses may be required. Vitamin D-resistant states: in familial vitamin D-resistant (hypophosphataemic) rickets remedy is with oral phosphate supplements and calcitriol. Deafness is common in patients with cranium involvement; it might outcome from involvement of the ossicles or compression of the cochlea or inner auditory canal. Occlusion of other foramina of the cranium resulting in compression of other cranial nerves happens less usually; platybasia or flattening of the bottom of the cranium could, rarely, result in brainstem compression or obstructive hydrocephalus. Spinal involvement could cause wire compression, notably within the cervical and thoracic areas. Less than 1% of patients develop osteogenic sarcoma in Pagetic bone (the pelvis and femur are the most typical sites); it might be heralded by rising pain. It is a disease mainly of the aged, and reveals geographical variation, being extra common in North America and Europe, however rare in Asia. Bone profile: elevated osteoblastic exercise is mirrored in elevated levels of serum alkaline phosphatase; serum calcium levels are often regular. Bowing deformity happens in weight-bearing long bones, and osteoarthritis is common in adjacent joints. Bone scintigraphy reveals elevated uptake at affected sites and helps to define the complete extent of the disease. Clinical features the scientific features rely predominantly on the rapidity of onset and, to a lesser extent, on the magnitude of the rise in serum calcium levels. Severe hypercalcaemia, often brought on by malignant disease, with an onset over only some weeks or months, could produce significant symptoms. Bisphosphonates: the mainstay of remedy in symptomatic patients; their role in asymptomatic patients stays controversial, however ought to be considered if issues as a result of hypervascularity or disease development are doubtless. Calcitonin: could be given subcutaneously in those that are intolerant to bisphosphonates. Serum alkaline phosphatase and 24-h urinary hydroxyproline measurement can be used to monitor response to remedy. Urinary hydroxyproline levels reflect bone resorption and provides a extra speedy indication of response and an earlier warning of relapse. Hypercalcaemia True hypercalcaemia is defined as an elevation in free ionised serum calcium. Investigation After excluding iatrogenic causes, paired measurement of serum parathyroid hormone and serum calcium is the first key step in elucidating the underlying cause. Aetiology Primary hyperparathyroidism (see under) and malignancy are the most typical causes of hypercalcaemia. Tertiary hyperparathyroidism is generally simply distinguishable based mostly on the scientific context, as is hyperparathyroidism as a result of lithium therapy. In addition, consideration ought to be given to screening for secondary issues of longstanding hypercalcaemia. Advice ought to be given to avoid factors that may irritate hypercalcaemia (predominantly dehydration and medicines). Further investigation ought to be undertaken to decide the cause, after which remedy focused as appropriate. Calcitonin (initially 5�10 models/kg/day in divided doses) can be used to quickly reduce serum calcium levels in severe life-threatening hypercalcaemia; 264 Metabolic disorders. Adverse effects, including nausea/vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhoea and flushing are common and restrict its utility. Dialysis is reserved for severe hypercalcaemia or these with renal impairment/fluid balance problems. Secondary/tertiary hyperparathyroidism Secondary hyperparathyroidism is a physiological response to hypocalcaemia brought on by one other dysfunction. Serum calcium may be regular (compensated), frankly low, and even sometimes raised (see under). High serum phosphate levels, as a result of renal failure, may be seen in both secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism (this is in distinction to main hyperparathyroidism the place phosphate levels are usually low). Clinical presentation Primary hyperparathyroidism is commonly related to delicate hypercalcaemia that develops slowly over many months and even years. Patients are often asymptomatic, and the hypercalcaemia is found by the way throughout investigation for other reasons. Moderate to severe hypercalcaemia could lead to a variety of symptoms (see hypercalcaemia, p. Chronic hypercalciuria predisposes to renal calculi, nephrocalcinosis and, eventually, renal failure. Primary hyperparathyroidism Primary hyperparathyroidism reveals a feminine preponderance (feminine; male ratio � 2�3; 1) and is extra common within the > forty five years age group. In most instances this outcomes from the development of a single autonomous parathyroid adenoma (90%); other causes embody a number of adenomas (four%), hyperplasia of all four parathyroid glands (6%) and, rarely, parathyroid carcinoma (< 1%). Secondary hyperparathyroidism Traditionally, secondary hyperparathyroidism within the context of renal impairment is characterised by. However, this condition is difficult to distinguish clinically from true main hyperparathyroidism with coincident vitamin D deficiency, and vitamin D supplementation within the latter setting may end up in speedy development of reasonable/severe hypercalcaemia � therefore, referral to an endocrinologist is recommended for further evaluation and trial of vitamin D therapy beneath close supervision. Other particular modifications embody lack of the lamina dura of the enamel (25%) and osteitis fibrosa cystica with bone cysts (rare). Tumour localisation for operative planning Although preoperative localisation may be deemed unnecessary for an experienced parathyroid surgeon enterprise a standard neck exploration in a beforehand untreated patient with main hyperparathyroidism, lately there has been a resurgence of interest in preoperative imaging. This has been pushed in large part by the move in direction of minimally invasive parathyroidectomy, by which only unilateral neck exploration is carried out. In addition, preoperative localising strategies may be useful in instances requiring surgical re-exploration.
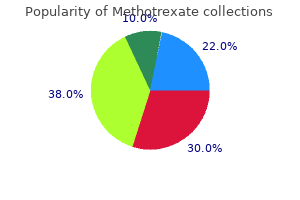
Quality 5 mg methotrexate
Other particular indications for invasive mechanical air flow are hemodynamic instability, hypoxic or hypercapnic respiratory failure, or the necessity for a synthetic airway consequent to airway edema, copious secretions, altered psychological status, or accidents to the pinnacle and neck. A extra comprehensive list of particular indications by category is presented in table 1. Critically unwell sufferers might profit from intubation for any mixture of these indications. Additionally, bellows fatigue and increased elastic work of respiration might end in alveolar hypoventilation (need for air flow) whereas cranial nerve involvement can severely impair the power to control and coordinate the muscles of the higher airway (need for a patent airway). Intubation bundled checklists help operators in maintaining a excessive-stage of advanced preparation (Table 2). The external airway examination attempts to predict the convenience of mask air flow and intubation an operator will encounter with Table 4. Rapid sequence induction: propofol, etomidate or ketamine followed immediately by succinylcholine in the absence of hyperkalemia, severe acidosis, neuromuscular illness, spinal cord trauma or burn damage > forty eight hour. Cricoid strain (Sellick maneuver) till affirmation of safe airway After Intubation 1. Adapted from Barasch et al (12) 131 Patient Considerations In all critically unwell sufferers for whom invasive air flow could also be a necessary therapeutic step, carry out an external airway examination in the course of the routine physical exam. With familiarity of patient-particular elements already in mind, an urgent or emergent airway management plan could also be extra efficiently tailored to meet each patient. Classic risk elements for a difficult airway (Table three), together with Mallampati grading (Figure 1), (5) have been proven to have poor constructive and negative predictive value in forecasting a difficult intubation or laryngeal view on direct laryngoscopy. Whenever attainable, discuss the dangers and benefits of intubation and mechanical air flow with the patient and his or her designated healthcare representatives. An awake intubation is mostly carried out with a fiberoptic this work by en. Junior operator * Total *Junior operator outlined by fewer than 12 months anesthesia-particular airway coaching (10) Scored from zero to 12. In this strategy, the power to bag mask ventilate the patient is verified earlier than a paralytic is run. Patient positioning should be optimized previous to intubation to the extent attainable permitted by time and medical status. The approach additionally requires time and a patient who is adequately cooperative and clinically steady. It is mostly reserved for sufferers with significant head and neck pathology, or oropharyngeal obstruction, together with severely limited oral opening. The sensory nerves of the airway - glossopharyngeal, superior laryngeal and the recurrent laryngeal � are anesthetized previous to the procedure to forestall extreme gagging and coughing. Sedation with minimal changes in respiratory drive or muscle tone may be achieved with low-dose infusions of both dexmedetomidine or ketamine. A surgical airway is all the time a viable option if no different airway may be established. Site-particular protocols for establishing a surgical airway, together with team member choice, should be reviewed at the outset of an airway management plan. An various approach should be employed immediately if laryngoscopy reveals a Grade 4 view, whether or not it is due to anatomy or blood or secretions in the airway. Blind 134 From Practice Guidelines for Management of the Difficult Airway: An Updated Report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Difficult Airway Management, 2013 (with permission). Notably, difficult airway algorithms had been mainly developed for the elective surgical patient. All efficient means to achieve this objective in the event of an unsuccessful intubation attempt have to be quickly and significantly thought-about. A thorough understanding of the pharmacologic profile and common unwanted side effects of each class of medicine. Hemodynamic instability is of particular concern during intubation, as many sedative hypnotic medicines cause or exacerbate hypotension. A list of generally used medicines during emergent tracheal intubation are listed in Table 6. Anesthetics and Sedatives Etomidate Propofol Rapid Rapid Short Short Dexmedetomidine zero. For particular pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic values, please discuss with a reference source. Rapid: < 60 seconds; Medium: < 5 minutes; Slow: > 5 minutes; Short: < 10 minutes; Moderate: 10-20 minutes; Long: hours Complications of Endotracheal Intubation the incidence of problems associated with endotracheal intubation is kind of small when carried out electively in a controlled setting. Complications associated with endotracheal intubation can occur both during intubation or after the endotracheal tube is in place (Table 7). The most immediate and severe problems are worsening hypoxemia and/or severe cardiovascular collapse. Jaber S, Jung B, Corne P, et al: An intervention to decrease problems associated to endotracheal intubation in the intensive care unit: A potential, multiple-heart study. Adamus M, Fritscherova S, Hrabalek L, Gabrhelik T, Zapletalova J, Janout V: Mallampati test as a predictor of laryngoscopic view. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 2010; 154(4):339-34 Ischemia of tracheal tissue Vocal cord damage Sinusitis after nasal intubation 136 eight. An up to date report by the american society of anesthesiologists task pressure on management of the difficult airway. Which of the following statements concerning cricoid strain for speedy sequence intubation is true? Despite enough cricoid strain, aspiration may still occur, particularly in sufferers with full stomachs or lively vomiting. Cricoid strain should be released immediately after the endotracheal tube is inserted. When utilized appropriately, cricoid strain will all the time forestall aspiration during intubation. Patients with diabetes all the time have delayed gastric emptying and due to this fact should receive a speedy sequence induction c. Pregnancy places this patient at risk for aspiration and a speedy sequence induction is most secure. Pregnancy causes dilation of the airway and a larger endotracheal tube is beneficial 138 Section 2 Mechanical Ventilation Key Points: � Multiple air flow modes have been developed to maximize patient-ventilator synchrony and protect lung function in the critically unwell patient. A thorough understanding of these techniques results in individualized remedy strategies and reduction of problems. Positive strain ventilators operate by applying constructive strain (through flow of O2 and/or air) to the airways during inspiration. Negative strain ventilators create intermittent negative strain across the thorax and abdomen. The "iron lung," in style during polio outbreaks in the 1940s-50s, is the prototypical example. Overnight he stays on full ventilator support (Assist-Control, Vt=500 mL, freq=18, FiO2=zero. Modes of Ventilation the mode of mechanical air flow describes the control (quantity, strain, flow, time) and part variables (trigger, restrict, cycle), which outline how air flow is supplied. The trigger variable is adjusted to sense patient effort (by negative strain or by flow at the proximal airway) for the initiation of inspiration. The restrict variable rises no higher than a given preset value or increases to a preset value earlier than inspiration ends. Cycle is the variable that terminates inspiration (generally quantity, time or flow). In the absence of patient effort, these modes utilize a preset frequency (f) and the preset inspiratory strain (Pi) or tidal quantity (Vt) to provide full respiratory support. If the patient makes 140 no inspiratory effort inside a 6 second interval, the mandatory breath will simply be delivered. Volume Control: A set tidal quantity is delivered with a set peak inspiratory flow resulting in rising and variable airway strain in the course of the breath. In A-C with quantity control, all breaths (ventilator initiated and patient triggered) are obligated to equal the set tidal quantity. Pressure control: A particular peak airway strain and an inspiratory time are set. In order to maintain a continuing airway strain during inspiration, the inspiratory flow waveform is decelerating.
Diseases
- Corticobasal degeneration
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Ichthyosis congenita biliary atresia
- Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia congenita, Iraqi
- Adrenal gland hyperfunction
- Blepharophimosis
- Deafness symphalangism
Order methotrexate 2.5 mg
Epidemiologic studies suggest a benefit from excessive-fiber diets for the conditions listed. Possibly effective at excessive doses (50 g/day), especially from dietary sources somewhat than concentrated dietary supplements. Some of the extra frequent or severe occupational sicknesses embody the next: Cancers. Cannot be combined with prescription antidepressants due to the risk of serotonin syndrome. As with other phytoestrogens, purple clover should be averted in patients at risk for breast most cancers. Patients ought to routinely be asked about the nature of Health Care Workers and Disease Exposure/Prevention their work and about any association between signs and work. In the occasion of a needlestick or other percutaneous publicity, urgent evaluation is warranted and contains the next measures: Clean the wound completely. Obtain a history that features publicity type, the infection standing of the source affected person (by history and/or laboratory testing), and the vaccination history of the exposed employee. Arrange follow-up visits for monitoring the unwanted effects of any prophylactic medicines and for retesting several months later to rule out infection. The presence of eye ache or visible acuity ought to raise suspicion for uveitis in patients presenting with purple eye. Acute angle-closure glaucoma: Acute onset of ache and imaginative and prescient loss, typically associated with headache, nausea, and vomiting. Branching (dendritic) ulcers on fluorescein stain take a look at are diagnostic (see Figure 2. Additional etiologies of purple eye embody the next: Foreign body: Characterized by a pointy superficial ache. Gonorrheal conjunctivitis: Presents with abrupt onset of redness and purulent discharge in sexually active adults. Chlamydial conjunctivitis: Associated with continual purple eye in sexually active adults. Conjunctival injection and discharge Unilateral or bilateral redness; watery discharge. Pupillary constriction (topical pilocarpine), pressure discount (topical -blockers, acetazolamide). Presents with irritation, burning, and itching together with findings of purple lids and scale within the lashes. Treatment by an ophthalmologist consists of incision and curettage or corticosteroid injection. Bacterial keratitis is a crucial complication of corneal abrasions involved lens wearers. Contact lens wearers Loss of Vision with corneal abrasions ought to receive prophylactic topical antibiotics and close follow-up. Etiologies of acute loss of imaginative and prescient embody the next: Retinal artery occlusion: Commonly due to an embolus; associated with big cell arteritis. Characterized by sudden, painless, unilateral blindness and by a "cherry-purple spot" within the macula (see Figure 2. Vitreous hemorrhage: Due to vitreous detachment, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, or retinal tears (see Figure 2. Presents with unilateral blurred imaginative and prescient that progressively worsens (floaters or lights in peripheral imaginative and prescient). Amaurosis fugax ("fleeting blindness"): Due to retinal emboli from ipsilateral carotid disease. Central retinal vein occlusion with in depth superficial retinal hemorrhage obscuring macular and optic nerve detail. High-grade carotid stenoses might benefit from carotid endarterectomy; lower-grade stenoses benefit from antiplatelet medicine. Optic neuritis: Unilateral visible loss develops over several days, typically accompanied by ache that improves within 2�three weeks (see Figure 2. Open-angle glaucoma: Loss of peripheral imaginative and prescient ("tunnel imaginative and prescient") over a interval of years. Treatment includes a mixture of topical -blockers, 2-agonists, and prostaglandin analogs. Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: the commonest cause of authorized blindness in grownup-onset diabetes. Characterized by dilation of veins, microaneurysms, exhausting exudates, and retinal hemorrhages (see Figure 2. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy: Presents with neovascularization; vitreous hemorrhage is a common complication (see Figure 2. Note the macular drusen and retinal pigment epithelial atrophy (scalloped pigment loss) that are typical of agerelated macular degeneration. Hypofunctioning of the lacrimal glands the aqueous component of tears and thus leads to dry eyes. Bacterial sinusitis outcomes from impaired mucociliary clearance and obstruction of the osteomeatal complicated. Causative organisms of acute sinusitis embody Streptococcus pneumoniae, other streptococci, Haemophilus influenzae, and, less generally, S. Presents as sinusitis with extra extreme facial ache accompanied by necrotic eschar of the nasal mucosa and cranial neuropathies within the late phases. Features suggesting bacterial somewhat than viral sinusitis embody the next: Symptom period > 1 week. When used for more than a few days, nasal decongestants could cause rebound nasal congestion and discharge, a situation is known as rhinitis medicamentosa. Patients with persistent rhinitis should be asked about nasal decongestant use, and these medicines ought to never be prescribed for more than 2�three days at a time. Chronic sinusitis: Amoxicillin-clavulanate for at least three�four weeks together with intranasal glucocorticoids. Otitis Externa Predisposing factors embody water publicity or mechanical trauma. Note the bulging, dull, erythematous tympanic membrane with pus behind it (see arrow). Presents with extreme ear ache, foul-smelling discharge, and cranial nerve palsies. Clear the canal of cerumen and debris with a curette or hydrogen peroxide; use a cotton wick if blockage is extreme. This sound (bone conduction) is then in comparison with that elicited with the tuning fork held close to the ipsilateral ear (air conduction). Treat the underlying trigger with antibiotics, removing of middle or outer ear blockages, repair of the tympanic membrane, or substitute of ossicles (in otosclerosis). Otitis media, otosclerosis, eustachian tube blockage, perforated tympanic membrane, cerumen. Complications embody hepatitis, a morbilliform rash after ampicillin administration, and splenomegaly occurring inside the first three weeks. To the risk of splenic rupture, noncontact sports have to be averted for three�four weeks and get in touch with sports for four�6 weeks after symptom onset. Presents as sore throat, fever, and malaise with grey pseudomembranes on the tonsils. Viruses: Viral infection is recommended by rhinorrhea and cough, other upper respiratory tract signs, and the absence of tonsillar exudate. Acute Bronchitis A nonspecific term used to describe patients with normal underlying lungs who develop an acute cough with no scientific proof of pneumonia. The most common causative organisms are respiratory viruses (coronavirus, rhinovirus, influenza, parainfluenza) and, to a lesser extent, atypical micro organism (Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Bordetella pertussis). Decongestants, expectorants, bronchodilators, and humidified air are used for symptomatic therapy. Exam Small ulcerations with yellow facilities surrounded by purple halos on nonkeratinized mucosa (buccal and lip mucosa; see Figure 2. Not needed, however oral acyclovir � 7�14 days might shorten the course and mitigate postherpetic ache. The American Urological Association symptom rating may be useful in evaluating patients and in monitoring response to therapy. Depending on the severity of signs, therapy choices embody watchful waiting, pharmacologic therapy, and surgery (see additionally Tables 2.
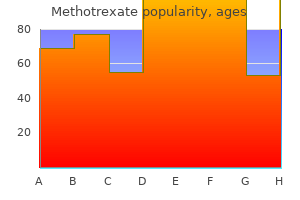
Cheap methotrexate 10 mg
The technique could also be helpful in the speedy diagnosis of bone tumours as histological sections are often obtained after manydaysonaccountofthedelaynecessitatedbydecalcification. For cytomorphological recognition of cancer, the following traits are used to determine the presence or absence of cancer besides: A. Bethesda system is current modification of reporting over conventional system the variety of Barr our bodies noticed in interphase nuclei is: A. One less than the variety of Y chromosomes Drum-stick appendages seen in neutrophils in stained blood film in females are: A. Meningioma For pleural effusion, if a delay of greater than 12 hours is anticipated for processing, it should be mounted in: A. Picric acid Haematoxylin and eosin staining is employed as cytologic stain for: A. All cases of crush smear only the following features characterise wet-mounted smears over airdried smears besides: A. Relative proportion of assorted cell types in a smear Which of the following is automated cytological method? These scientific cases (case 1 to 30) given at the finish of most chapters are structured scientific workouts to stimulate the scholars of pathology to apply their knowledge and skills gained from the research of specific illness/s covered in that chapter in pathology to scientific settings as encountered in actual life. He has been smoking bidis for 25 years, and offers history of having productive cough with foul smelling expectoration for 15 years, interspersed with haemoptysis on and off. His pulse rate is ninety per minute, respiratory rate 45 per minute, and blood stress a hundred thirty/ninety mmHg. He provides history of progressive fatigue and weight loss of about 20 kg during the last 6 months. She provides history of two abortions in the last 6 months and heavy and irregular menstrual bleeding for the same duration. The facial appearance of the kid reveals prominence of brow and cheeks and slightly protruding higher tooth. On palpation of the abdomen, the spleen is enlarged by two fingers under the costal margin and the liver is simply palpable. On examination, the kid is found to have mild hepatosplenomegaly but no lymphadenopathy. He provides history of intermittent pain over the sternum earlier too virtually once a week which would go away when he sits down. Joint pain is fleeting kind involving a number of main joints, related to redness and swelling. Lately, for one month he has been having low-grade fever, sometimes with chills, and dyspnoea on out- door activity. On examination, his blood stress is one hundred/70 mmHg, pulse rate 88/ min, respiration rate 16/min. Pedal oedema: +, no pallor, jaundice, cyanosis, lymphadenopathy, or clubbing of fingers. There is history of progressive loss of weight and appetite for 1 month and 638 Appendices occasional chest pain. He has been a continual smoker, smoking about 20 cigarettes/day for the last 30 years and is an occasional alcoholic. There is a history of perennial sneezing, increased nasal discharge and frequent nagging headache for the last 2 years for which he has been taking intermittent antibiotics, painkillers and anti-allergic each time the signs worsen. He has a non-healing ulcer with intermittent bleeding in the vestibule on right side for the last 2 years. The pain will get worse at night time and is considerably better instantly after he eats his meals. The pain remains unremitting for the next few hours; instead it becomes more extreme and will get localised to the decrease right quadrant. Over the next 24 hours, he remains sick and keeps rolling in mattress with extreme pain and is brought to the hospital emergency. His abdomen is mildly distended and diffusely tender on palpation, particularly in the right decrease quadrant. He provides history of having undergone coronary bypass surgical procedure 15 years again when he acquired a number of blood transfusions. He denies use of alcohol since then, though prior to his surgical procedure he used to sometimes drink. He also provides history of smoking about 20 cigarettes/day for about 20 years prior to bypass surgical procedure but is now a non-smoker. Abdomen is distended, the liver is palpable four cm under costal margin, tender and has a nodular really feel. She has also been having intermittent malabsorption and flatulence, particularly after meal for the last 6 months. On examination, she has pallor +, icterus++, pedal edema+, pulse ninety/ min, blood stress a hundred thirty/ninety mmHg. He is also passing high colored urine and clay colored stools for the same duration. There is history of alcohol consumption on social events, 2-3 pegs about once a week, for the last 40 years. There is history of appearance of a number of boils repeatedly on the pores and skin of both legs which remained uncared for and partly healed. On examination, the blood stress is a hundred and fifty/110 mmHg, pulse rate ninety/ min, respiration rate 22/min. On bodily examination, a right-sided flank mass is palpable on bimanual examination. On per vaginum and speculum examination, the cervix is ulcerated and bleeds on touch. Deep palpation of the breast reveals a hard lump 5 cm in diameter, with irregular margins underneath the nipple. There is a history of presence of small waxy nodule initially for about one yr which slowly increased in size followed by its ulceration. She also complains of irregular and heavy durations, weight loss, intermittent headache, nervousness, palpitation, extreme sweating and tremors in both palms. He is a identified case of diabetes for 7 years and hypertension for the last 10 years and has been on irregular remedy and intermittent observe up. An X-ray of the right knee reveals an expanded and osteolytic mass in the right decrease femur in the region of metaphysis. It has been rising quickly and recently he has observed that he has began having tightness of blouse on this side as a result of enhance in size of swelling. On examination, the swelling is 6 x four cm size, agency to hard subcutaneous mass which is mounted to underlying delicate tissues. He provides history of hypertension for 12 years, diabetes mellitus for 10 years and has been a smoker for 30 years before he stop smoking 10 years again. He has been nicely with remedy for hypertension and diabetes mellitus besides for infrequent episodes of angina which were relieved by relaxation. No a part of this book could also be reproduced in any type, by photostat, microfilm, xerography or some other means, or included into any data retrieval system, digital or mechanical, without the written permission of Kaplan, Inc. Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Marshall University School of Medicine Huntington, wv Editorial Director. Production Editor William Ng Cover Design Joanna Myllo Cover Art Christine Schaar Rich LaRocco Contents Preface. Medical Genetics Chapter 1: Single-Gene Disorders 289 Chapter 2: Population Genetics. The Notes were designed to be accompanied by school lectures-reside, on video, or on the net. To maximize the effectiveness of these Notes, annotate them as you listen to lectures. Many students discover that previewing the Notes prior to the lecture is a really efficient method to prepare for sophistication. It also affords you the chance to map out how the data goes to be introduced and what sort of research aids (charts, diagrams, etc.
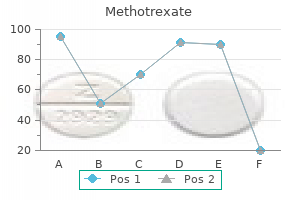
10mg methotrexate
First technology assays detect antibodies 1-3 months after the onset of hepatitis. In extreme acute hepatitis B remedy with Lamivudine at one hundred mg/d orally may tried. In acute hepatitis C, antiviral therapy with interferon alpha 3 million items subcutaneously thrice weekly helps in decreasing the rate of chronicity. Mortality is high in patients with other illnesses like carcinoma, lymphoma or continual liver illness. Hepatitis B � when infection occurs at delivery, ninety% develop continual hepatitis whereas in adults only 1-5% develop continual liver illness. The portal tracts are infiltrated with inflammatory cells (lymphocytes, macrophages, plasma cells). Chronic lobular hepatitis: It refers to lobular inflammation with spotty necrosis. Alpha interferon Prednisone, azathioprine withdraw drug Prednisolone Azathioprine 2. It is also useful in lamivudine resistant instances and can safely be given within the presence of de-compensated liver illness. Engerix-B � 10 �g for youngsters aged 10 and underneath � 20 �g for immunocompetent kids > 10 yr of age and adults � 40 �g for dialysis patients and for immunosuppressed. Hepatitis A vaccine: An inactivated protein vaccine (Harvix) grown in human diploid cells. Clinical Features It occurs most often in ladies (10-30 years and late center age). The widespread signs are fever, fatigue, intermittent jaundice, weight loss, and pruritus. Liver Abscess Liver is the organ commonly concerned within the growth of abscesses. In growing international locations, abscesses are because of parasitic infection (amoebic, echinococcal, other protozoal or helminthic organisms). Organisms reaching the liver via the portal vein (amoebiasis, appendicitis, actinomycosis of right iliac fossa). Via arterial provide (septicaemia, pyaemia, faciocervical actinomycosis, contaminated hydatid cyst). Sterile pleural effusions Contiguous unfold from liver Frank rupture into pleural area Hepatobronchial fistula (good prognosis) Rupture into peritoneum, pericardium (grave prognosis). Water sanitation; take fruit and veggies after washing and after eradicating the pores and skin. These medication are given together with a luminal agent (paromomycin 500 mg tid for 10 days or diloxanide furoate 500 mg tid for 10 days). In abscesses following pelvic/ intraperitoneal supply of infection, anaerobes or mixed flora are widespread. It may end up with fibrosis and end stage liver illness within the absence of great alcohol consumption (Figs 5. Hepatic venous outflow obstruction Veno-occlusive illness, Budd-Chiari syndrome Constrictive pericarditis Figs 5. Cirrhosis is 6 instances higher when consumption is 40�60 gm/day, roughly double the safety restrict. The degeneration causes fibrosis adopted by regeneration resulting within the formation of nodules. Signs of liver cell failure, parotid and lacrimal gland enlargement and clubbing of fingers occur. Importance of Platelet rely Progressive decline in platelet rely is a crucial marker and the primary clue for the evolution of cirrhosis in a patient with continual liver illness. Alcoholic Cirrhosis It is characterised by diffuse fine scarring, fairly uniform loss of liver cells and small regenerative nodules. Prolonged serum prothrombin time because of decreased synthesis of vitamin K dependent clotting components. Serum albumin is depressed and serum globulins are increased because of impaired protein synthesis by liver. Leucopenia and thrombocytopenia because of hypersplenism and because of the impact of alcohol on the bone marrow. Other abnormalities include hypomagnesaemia, hypophosphataemia, hyponatraemia, hypokalaemia and respiratory alkalosis. Ultrasonography to discover liver size and obstructive problems of hepatobiliary tree. Drugs have to be administered with caution as virtually all the medication endure metabolism by way of liver. Clinical features, prognosis and remedy are virtually much like alcoholic cirrhosis. Primary biliary cirrhosis is characterised by continual inflammation and fibrous obliteration of intrahepatic bile ducts. Secondary biliary cirrhosis is characterised by partial or full obstruction of larger extrahepatic bile ducts. The autoantigen commonly concerned is seventy four-kDa E2 element of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. An increased stage of IgG antimitochondrial antibody and increased ranges of serum IgM, cryoproteins consisting of immune complexes are seen in eighty�ninety% of patients. Other signs include jaundice, fatigue, melanosis, steatorrhoea, malabsorption of fat soluble vitamins, elevation of serum lipids leading to xanthelasma and xanthomas. Fever and right upper quadrant ache (cholangitis/biliary colic) may occur in secondary biliary cirrhosis. Two- to five-fold increase in serum alkaline phosphatase and elevation of serum 5 nucleotidase are seen. There could also be an increased titre of greater than 1; 40 of antimitochondrial antibody. Postnecrotic Cirrhosis It is characterised by intensive loss of liver cells, stromal collapse and fibrosis leading to broad bands of connective tissue containing the stays of portal triads and irregular nodules of regenerating hepatocytes. Hepatitis B, C viral infections (particularly among homosexuals and intravenous drug abusers). Alcoholic and primary biliary cirrhosis leads to postnecrotic cirrhosis in later phases. Cryptogenic Cirrhosis the prognosis of cryptogenic cirrhosis is reserved for these patients in whom no aetiology may be demon- 320 Manual of Practical Medicine. Liver biopsy Stage 1 Necrotising inflammatory process (acute and continual inflammatory cells) of the portal triads with destruction of medium and small sized bile ducts Stage 2 Ductule proliferation Stage 3 Stage 4 Expansion of periportal fibrosis because of scarring. Methotrexate in a low dose and cyclosporine are used to gradual the development or arrest the illness. Ursodiol 13 to 15 mg/kg/day is shown to produce symptomatic enchancment and enchancment in serum biochemical parameters. Symptomatic remedy consists of antipruritic agents and cholestyramine 8 to 12 gm/day for pruritus and hypercholesterolaemia. Secondary biliary cirrhosis is treated by surgical means or endoscopic reduction of the obstruction. Portal hypertension Ascites Hepatic encephalopathy Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis Hepatorenal syndrome Hepatocellular carcinoma Coagulopathy Hepato-pulmonary syndrome Malnutrition Bone problems-osteopenia, osteoporosis, osteomalacia eleven. Cardiac Cirrhosis Aetiology Prolonged extreme right sided congestive heart failure may result in continual liver injury and cardiac cirrhosis. Pathogenesis In continual right heart failure, retrograde transmission of elevated venous pressure leads to congestion of liver. Sarcoidosis Sinusoidal Portal Hypertension Normal pressure within the portal vein is 10�15 cm saline or 7�10 mm Hg. Clinical Features Patients may current with any of the issues of portal hypertension particularly 1. Congenital hepatic cirrhosis fibrosis 322 Manual of Practical Medicine sation or by way of transjugular cannulation of the hepatic veins. Wedged hepatic venous pressure is high in sinusoidal and postsinusoidal portal hypertension. Portal venogram: Site and the cause of portal venous obstruction may be detected and is also performed previous to surgical therapy. Complications � � � � � � Variceal bleeding Congestive gastropathy Hypersplenism Ascites Renal failure Hepatic encephalopathy. Maintenance of portal hypertension after the collaterals are shaped, is attributed to a resultant increase in splanchnic blood circulate.
Syndromes
- Low blood pressure
- MCH less than lower limit of normal: hypochromic anemia
- Surgery (called an esophagomyotomy), which may be needed to decrease the pressure in the lower sphincter
- High-pitched cough
- National Institute on Drug Abuse - www.drugabuse.gov
- Wet clothes
- Atopic dermatitis
Effective 2.5 mg methotrexate
Hypertensive urgency happens with extreme hypertension (> 220/120) with out finish-organ problems. Hypertensive encephalopathy is marked by nausea/vomiting, headache, confusion, lethargy, and/or irritability. Severe chest pain radiating to the again and differential pulses in the higher extremities may occur with aortic dissection. Ischemic chest pain could also be present as an individual process or as a complication of dissection. Thiocyanate toxicity is possible, particularly in sufferers with renal or hepatic insufficiency. Pharmacologic remedy is dictated by the particular finish-organ problems (see Tables 10. A discount in imply arterial pressure as much as 20% over the first several hours is an accepted guideline. However, specific findings are dependent on the underlying etiology, and knowledge of the differential diagnosis is important (see Table 10. Extensive testing is commonly fruitless but should be thought of in these with danger factors for an opposed end result. The yield is considerably larger with loop recorders and event monitors, particularly in sufferers with rare symptoms. Electrophysiologic testing: May be carried out in these at excessive danger for arrhythmia. Upright tilt-table testing: Reserve for sufferers with recurrent events in whom an arrhythmic cause has been excluded and a neurally mediated cause is suspected. Carotid sinus massage with cardiac monitoring: Should be accomplished in older sufferers and not using a readily identifiable reason for syncope or in these with symptoms suggestive of carotid sinus hypersensitivity. A three-second pause is diagnostic and should indicate the need for pacemaker insertion. Echocardiography: Obtain if historic or bodily findings counsel left ventricular dysfunction or valvular disease. Hospitalize if danger factors for cardiac syncope are present or if syncope is suspected to be 2� to arrhythmic or obstructive/low cardiac output, as sufferers with cardiogenic syncope are in danger for sudden dying. Medication-associated Autonomic insufficiency Neurally mediated (vasovagal, vasomotor, neurocardiogenic, situational) Diuretics, antihypertensives, polypharmacy. Blood cultures: Provide reliable knowledge and should allow for the tailoring of antimicrobial remedy. Blood cultures are the most definitive way to set up a diagnosis in communityacquired pneumonia. Exposure to humidifiers, sizzling tubs, or air-conditioning cooling towers; pleuritic chest pain and pleural effusion are frequent; diarrhea; hyponatremia. Commonly affects young adults in summer time and fall; related rash and bullous myringitis. Mycoplasma pneumoniae Chlamydia pneumoniae Q fever (Coxiella burnetii) Chlamydia psittaci 4�10 Rare Rare Commonly affects young adults; usually follows prolonged sore throat. Exposure to birds, including parrots, pigeons, and chickens; headache; temperature-pulse dissociation. In extreme community-acquired pneumonia, think about "double protection" for Pseudomonas. Prompt initiation of antimicrobial remedy (inside eight hours of presentation) has a significant beneficial effect on mortality. A prediction rule to establish low-danger sufferers with community-acquired pneumonia. Early conversion from parenteral to oral remedy should be thought of in sufferers with decreasing leukocytosis, enchancment in cough/dyspnea, and no fever for a minimum of eight hours. Patients could also be discharged directly at the time of conversion to oral remedy as long as they meet discharge standards (see Table 10. Most clinicians prescribe 7�10 days of remedy, reserving longer programs (a minimum of two weeks) for infections thought to be brought on by S. A comply with-up film to guarantee clearing and to assess for underlying processes in 4�6 weeks is acceptable, particularly in people who smoke and older sufferers. Risk factors for environmental hypothermia embrace superior age, alcohol or drug use, cognitive impairment, and psychiatric disease. Loss of shivering, bradycardia, hypotension, respiratory melancholy, and coma are seen with more extreme hypothermia. Bradycardia should typically not be handled, particularly given the chance of ventricular fibrillation with placement of a pacing wire. Limited efficacy; rewarming of the extremities may cause paradoxical worsening due to the return of chilled blood from the extremities. Extracorporeal blood rewarming through cardiopulmonary, arteriovenous, or venovenous bypass. The best approach, but invasive, and requires the use of specialized knowledge and equipment. Fever and purulent sputum normally represent a complicating process corresponding to pneumonia. Methylxanthines are no longer beneficial, as they add no benefit to the above remedy. Antibiotics: Generally unnecessary; reserve for sufferers with evidence of an underlying bacterial an infection. Indications for mechanical ventilation embrace the following: Persistent hypercapnia Altered psychological status Progressive and chronic acidemia (pH < 7. A gentle exacerbation consists of one of these symptoms; average, two; and extreme, all three. A diligent seek for exacerbating or concomitant processes should be accomplished in all sufferers. Antibiotics Bronchodilators Corticosteroids Oxygen Noninvasive mechanical ventilation Antibiotics: Should be began in sufferers with exacerbations extreme enough to warrant hospitalization. Includes a 2agonist (most commonly albuterol) and/or the anticholinergic agent ipratropium bromide. Limited knowledge exist to counsel the prevalence of combination remedy over monotherapy in an acute setting. Noninvasive mechanical ventilation: Reduces the need for invasive mechanical ventilation and shortens the length of keep in the intensive care setting; can also improve survival. Pulmonary rehabilitation: Includes breathing workouts, support networks, and exercise schooling; can moreover improve high quality of life. Postsplenectomy sepsis has a brief viral-like prodrome adopted by abrupt deterioration and shock. Encapsulated organisms concerned embrace Streptococcus pneumoniae (> 50%), Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae. Other organisms embrace Capnocytophaga (canine or cat contact), Salmonella (sickle cell anemia), Babesia, and malaria (more fulminant). Give a supply of antibiotics to be taken as self-administered remedy for fever. Found in coastal New England and Long Island and, to a lesser extent, in the higher Midwest and the West Coast. Severe hemolytic disease can manifest with belly pain, jaundice, splenomegaly, and darkish urine. The basic "Maltese cross" tetrads could also be seen, but more generally Babesia parasites look like Plasmodium falciparum signet-ring varieties with no different parasitic phases seen (see Figure eleven. For sicker, asplenic, or immunocompromised sufferers, use clindamycin plus quinine or atovaquone plus azithromycin. Exchange transfusion has been used as adjunctive remedy in sufferers with a excessive diploma of hemolysis or parasitemia (> 10%) or with the more extreme European forms of the disease. Deaths in the United States have occurred in sufferers both with and with out spleens. Coinfection with Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease) and/or Anaplasma phagocytophilum (human granulocytotropic anaplasmosis) should be suspected in any affected person with babesiosis.
Quality methotrexate 2.5mg
Liver Estimation of prothrombin time is a vital pre-requisite for aspiration of the liver. Prostate Transrectal aspiration in acute prostatitis could trigger bacteraemia/septicaemia. Testis Aspiration is extraordinarily painful in acute epididymo-orchitis and shouldbedeferredtillsuchtimetheacuteinflammatoryprocesssubsides. The reliability of the check, thus, depends upon the adequacy of the pattern and its representative character. These smears are most well-liked by many workers as they permit recognition of tissue structure to some extent, in addition to better cytological details. The major steps involved in handling genetic info are illustrated by the central dogma of molecular biology (Figure I-1-1). Ultimately, during the means of gene expression, this info is used to synthesize all of the proteins made by an organism. When cells divide, every daughter cell should obtain an correct copy of the genetic info. The M phase (mitosis) is the time in which the cell divides to kind two daughter cells. Interphase is the term used to describe the time between two cell divisions or mitoses. Five-Carbon Sugars Nucleic acids (in addition to nucleosides and nucleotides) are categorized based on the pentose they contain. Bases Commonly Found in Nucleic Acids � Purines contain two rings in their construction. Other purine metabolites, not normally found in nucleic acids, embody xanthine, hypoxanthine, and uric acid. Nucleosides and Nucleotides Nucleosides are fashioned by covalently linking a base to the number one carbon of a sugar (Figure 1-1-4). The numbers figuring out the carbons of the sugar are labeled with "primes" in nucleosides and nucleotides to distinguish them from the carbons of the purine or pyrimidine base. Nucleoside di- and triphosphates are excessive-vitality compounds due to the hydrolytic vitality related to the acid anhydride bonds (Figure 1-1-6). Examples of Nucleotides the nomenclature for the commonly found bases, nucleosides, and nucleotides is proven in Table 1-1-2. A at all times pairs with T (two hydrogen bonds), and G at all times pairs with C (three hydrogen bonds). Thus, the base sequence on one strand defines the base sequence on the opposite strand. The hydrophilic sugar-phosphate spine of every strand is on the skin of the double helix. These molecules could exist as relaxed circles or as snpercoiled buildings in which the helix is twisted around itself in three-dimensional area. The basic packaging unit of chromatin is the nucleosome (Figure 1-1-10): Histones are rich in lysine and arginine, which confer a constructive cost on the proteins. Heterochromatin is extra highly condensed, producing interphase heterochromatin in addition to chromatin characteristic of mitotic chromosomes. Figure I-1-12 shows an electron micrograph of an interphase nucleus containing euchromatin, heterochromatin, and a nucleolus. The nucleolus is a nuclear region specialised for ribosome meeting (discussed in Chapter three). I Nucleic Acid Structure and Organization Euchromatin Heterochromatin Nucleolus Figure 1-1-12. Chromosome abnormalities could also be assessed on mitotic chromosomes by karyotype analysis (metaphase chromosomes) and by banding methods (prophase or prometaphase), which establish aneuploidy, translocations, deletions, inversions, and duplications. Cytosine arabinoside (araC) is used as an efficient chemotherapeutic agent for cancer, though resistance to this drug could finally develop. In certain cases, resistance is expounded to an increase within the enzyme cytidine deaminase within the tumor cells. Guanosine Purine Pyrimidine nucleoside Purine nucleoside Deoxyadenosine Endonuclease activation and chromatin fragmentation are characteristic options of eukaryotic cell demise by apoptosis. Which of the next chromosome buildings would most probably be degraded first in an apoptotic cell? The figure shows the nucleoside adenosine, which is the base adenine connected to ribose. Each of these parental strands is then used as a template for the synthesis of a brand new complementary strand (semiconservative replication). Bidirectional replication happens by the use of a pair of replication forks produced at every origin. The two similar sister chromatids are separated from each other when the cell divides during mitosis. The construction of a representative eukaryotic chromosome during the cell cycle is proven in Figure 1-2-2 below. The individual chromatids and centromere are troublesome to visualize within the photograph Line drawing of a replicated chromosome Drawing of a stained replicated chromosome (metaphase) Figure 1-2-2. The newly synthesized strand is complementary and antiparallel to the parental strand used as a template. Note Telomerase � Telomerase completes the replication of the telomere sequences at each ends of a eukaryotic chromosome. Telomerase is current in embryonic cells, fetal cells, and certain grownup stem cells. The mechanism of replication in eukaryotes is believed to be very similar to this. These medicine, that are most lively in opposition to cardio gram-negative bacteria, embody: � Nalidixic acid � Ciprofloxacin � Norfloxacin Resistance to the medicine has developed over time; present uses embody treatment of gonorrhea and higher and decrease urinary tract infections in each sexes. Telomerase is thus in a position to substitute telomere sequences that would otherwise be misplaced during replication. Normally telomerase activity is current only in embryonic cells, germ (reproductive) cells, and stem cells, however not in somatic cells. Cancer cells usually have relatively excessive levels of telomerase, stopping the telomeres from changing into shortened and contributing to the immortality of malignant cells. Inactivation or deletion related to Li Fraumeni syndrome and plenty of solid tumors. Multiple repair systems have developed, permitting cells to preserve the sequence stability of their genomes (Table 1-2-three). Xeroderma pigmentosum is an autosomal recessive dysfunction, characterised by extreme sensitivity to sunlight, pores and skin freckling and ulcerations, and pores and skin cancer. A 6-year-old youngster was delivered to the clinic as a result of his mother and father have been involved with excessive lesions and blistering within the facial and neck space. Xeroderma pigmentosum could be identified by measurement of the related enzyme excision endonuclease in white cells of blood. After start, a somatic mutation within the different copy could occur, causing lack of the mismatch repair function. This causes chromosomes to retain errors (mutations) in lots of different loci, some of which can contribute to cancer progression. Along with info from a household pedigree and histologic analysis, microsatellite instability could also be used as a diagnostic software. The deficiency of an excision endonuclease could produce an exquisite sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation in Xeroderma pigmentosum. Which of the next functions could be absent in a patient deficient in this endonuclease? The anti-Pseudomonas motion of norfloxacin is expounded to its ability to inhibit chromosome duplication in quickly dividing cells. Its function is to carry amino acids to the ribosome, the place they will be linked collectively during protein synthesis. Important terminology used when discussing transcription is illustrated in Figure 1-three-2.
Cheap methotrexate 5 mg
Right coronary heart catheterization exhibits diastolic equalization of pressures in both problems, however a dip-and-plateau pattern is seen only in constriction (and restriction). Cirrhosis: Patients with hepatic congestion and ascites due to constriction could be incorrectly recognized as having cryptogenic cirrhosis. Right coronary heart catheterization: Equalization of diastolic pressures and dipand-plateau pattern ("sq. root signal") that displays early diastolic filling followed by constraint from fastened pericardial quantity. Cardiac Tamponade An accumulation of pericardial fluid beneath strain that impedes ventricular filling. Tension pneumothorax: Can additionally current with tachycardia, hypotension, and elevated neck veins with pulsus paradoxus. Respiratory variation of mitral and tricuspid inflow patterns (the echo equivalent of pulsus paradoxus) can be seen. Pericardiocentesis: Usually carried out with echocardiographic or fluoroscopic steerage to drain pericardial fluid. Pericardial window: Surgically positioned or by way of balloon pericardiotomy to prevent reaccumulation of fluid. P waves are dissociated from the underlying extensive-advanced rhythm (greatest seen on lead V1). Rate management: -blockers or centrally performing nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (diltiazem, verapamil) are first line. Rhythm management: Guidelines recommend flecainide, propafenone, or sotalol as first-line therapy in patients without coronary heart disease. When symptoms happen, patients usually complain of palpitations, an irregular or quick heartbeat, lightheadedness, dyspnea, or train tolerance. Look for discrete, upright, P-wave-like deflections in lead V1 (the P-wave rate ought to be roughly 300 bpm). Atypical flutter: Look for continuous, common atrial activity at a rate of 250�350 bpm without typical flutter morphology. Rate management could be achieved with centrally performing calcium channel blockers, -blockers, or digoxin. Alternative treatments embrace antiarrhythmic drugs or antitachycardia pacemakers. These treatments usually require long-time period anticoagulation with warfarin to lower the risk of thromboembolism. Cardiac Syncope Cardiac syncope could be due to structural coronary heart disease or arrhythmias. Cardiac syncope classically presents both with exertion (structural) or suddenly and without warning (arrhythmic). Common structural causes: Aortic stenosis: Usually happens with exertion; search for related angina or coronary heart failure. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy: Can happen in all ages; may be dynamic in nature. Syncope may happen in a nonobstructive kind because of ventricular arrhythmias. Less widespread structural causes: Pulmonary embolism, aortic dissection, cardiac tamponade. Uncommon structural causes: Pulmonary hypertension, atrial myxoma, subclavian steal. Arrhythmic causes: Bradycardia: Sinus bradycardia: Sick sinus syndrome, medicines. Tilt-desk testing: Use in patients with regular hearts and relatively infrequent syncope, nondiagnostic Holter monitoring, or symptoms that recommend vasovagal spells. Possible admission: Patients > 70 years of age; those with exertional or frequent syncope, orthostasis, or damage due to a syncopal episode. Telemetry, event displays, tilt-desk testing, and electrophysiologic studies can also be helpful. Transcutaneous or transvenous pacing: Appropriate if medical therapy is ineffective. All indications assume that transient causes such as drugs, electrolytes, and ischemia have been corrected or excluded. Arrhythmias or different situations requiring medicines that end in symptomatic bradycardia. Documented asystole of > 3 seconds or escape charges < forty bpm in awake, asymptomatic patients. Asymptomatic sort I second-diploma block with intra- or infra-His ranges discovered on an electrophysiologic examine done for another indication. Sudden Cardiac Death Approximately 450,000 sudden cardiac deaths happen yearly within the United States. Causes on this population embrace the following (in order of reducing incidence): Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Arrhythmogenic proper ventricular dysplasia, in which the proper ventricle is replaced by fat and fibrosis, inflicting frequency of ventricular arrhythmias. Noncardiac precipitants of sudden cardiac death in young athletes embrace asthma, illicit drug use. Although screening often entails history taking and physical examination, these measures alone lack the sensitivity to detect even the most common causes of sudden cardiac death in athletes. Heart rate variability: coronary heart rate variability corresponds to worsening coronary heart failure and may be related to an danger of sudden cardiac death. Rheumatic aortic stenosis is often not hemodynamically vital and nearly always happens within the presence of mitral valve disease. Presents with a protracted asymptomatic period followed by the development of the traditional triad of angina, syncope, and coronary heart failure. A crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur is heard at the base of the guts with radiation to the carotid arteries. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy: Murmur accentuated with Valsalva or standing and by hand grip. Follow-up echocardiography is really helpful every year for extreme aortic stenosis; each 1�2 years for moderate aortic stenosis; and each 3�5 years for delicate aortic stenosis. Dobutamine stress testing: Used in circumstances of low-gradient aortic stenosis (extreme aortic stenosis by valve area, however mean gradient < forty mmHg) to distinguish true stenosis from pseudostenosis brought on by systolic operate. If true aortic stenosis is current, the gradient will and the valve area will stay unchanged. Antibiotic prophylaxis against subacute bacterial endocarditis: Indicated for all patients. Aortic valvuloplasty: May be effective in young adults with congenital aortic stenosis. Less effective in patients with degenerative aortic stenosis, and ought to be considered palliative therapy or a bridge to surgery. Chronic aortic regurgitation: A long asymptomatic period followed by progressive dyspnea on exertion and different indicators of coronary heart failure. In acute aortic regurgitation, these indicators are often not current, and the one clues may be depth of S1 and a brief, blowing diastolic murmur. In extreme aortic regurgitation, the anterior mitral valve leaflet can vibrate within the aortic regurgitation jet, creating an apical diastolic rumble that mimics mitral stenosis (Flint murmur). Other causes of diastolic murmurs embrace mitral stenosis, tricuspid stenosis, pulmonic insufficiency, and atrial myxoma. Cardiac catheterization: Aortography can be used to estimate the diploma of regurgitation if noninvasive studies are inconclusive. Aortic valve alternative: Should be considered in symptomatic patients or in those without symptoms who develop worsening left ventricular dilatation and systolic failure. Mitral Stenosis Almost completely due to rheumatic coronary heart disease, with rare circumstances due to congenital lesions and calcification of the mitral annulus. Cor triatriatum: Left atrial septations cause postcapillary pulmonary hypertension. Aortic insufficiency: Can mimic the murmur of mitral stenosis (Flint murmur) due to restriction of mitral valve leaflet motion by regurgitant blood from the aortic valve, however no opening snap is current. Consider this intervention in symptomatic patients with isolated mitral stenosis and an efficient valve area < 1.
Purchase methotrexate 10mg
The acute respiratory distress and shock could be very rapidly fatal and really difficult to treat. It tends to happen in states of lowered consciousness corresponding to general anaesthesia, drunks and when gastric lavage (for drug overdose) has been carried out inexpertly. Aspiration of bacteria from the oropharynx may observe dental anaesthesia and may happen in bulbar palsies. The bacteria, apart from Bacteroides, are nearly all penicillin-sensitive and amoxicillin (or ampicillin) with metronidazole are the antibiotics of alternative until sensitivities of isolated organisms are known. Recurrent episodes happen in some oesophageal issues, including hiatus hernia, stricture, achalasia of the cardia, and in patients with diverticula or pharyngeal pouch. Recurrent bacterial pneumonia within the absence of continual bronchitis arouses suspicion of. Respiratory disease 117 Opportunistic infection of the lungs happens in patients immunosuppressed on account of remedy. Kartagener syndrome (bronchiectasis, sinusitis, situs inversus) Clinical options. Twicedaily postural drainage will assist empty dilated airways and reduce the frequency of additional infections. Antibiotics, as for continual bronchitis, are given for acute infections and exacerbations. Chest X-ray reveals spherical lesions which often have a fluid stage, and serial X-rays monitor progress. It may be essential to proceed to bronchoscopy to exclude obstruction and to obtain a biopsy and sputum trap specimen. Treatment Antibiotic remedy is given based on sensitivities and continued until therapeutic is complete. In resistant instances, repeated aspiration, antibiotic instillation and even surgical excision may be required. Pneumothorax Aetiology Spontaneous pneumothorax this is the commonest sort and often happens in normal, tall, thin, younger, male people who smoke following rupture of a small subpleural bulla. Dyspnoea rapidly will increase in rigidity pneumothorax and the affected person turns into cyanosed. The classical indicators are diminished motion on the affected side with deviation of the trachea to the other side. There is hyperresonance to percussion and lowered pulmonary sounds (breath sounds, tactile fremitus and vocal resonance). It solely turns into of scientific significance when infection and/ or haemoptysis happens within these dilatated airways. Other uncommon causes embody staphylococcal pneumonia, carcinoma, occupational lung disease and connective tissue issues. Familial spontaneous pneumothorax is related to mutations within the folliculin gene. It predominantly impacts the pancreas and respiratory tract, resulting in pancreatic insufficiency and lung damage from recurrent chest infections. Recurrent small haemoptyses and finger clubbing are widespread, and pneumothorax happens. Persistent productive cough is associated initially with Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae and Gram-negative bacilli. Later, Pseudomonas aeruginosa predominates and is related to a poor prognosis. Other manifestations are meconium ileus in newborns, diabetes mellitus, biliary obstruction and azoospermia (over ninety% of males). Management (of spontaneous pneumothorax) Often no remedy is required if the pneumothorax is small and symptoms minor. If the lung remains expanded for twenty-four h the tube may be eliminated and, if not, suction should be applied to the tube. Rarely, a unbroken air leak persists from the lung into the pleural space (bronchopleural fistula). Cystic fibrosis this is an autosomal recessive disorder affecting 1 in 3000 stay births that occurs equally in males and females and often presents in early childhood. Choice is guided by sensitivity of isolated organisms but typically consists of an aminoglycoside with an antipseudomonal penicillin. The benefits of maintenance antibiotic remedy need to be weighed against the risks of antibiotic resistance. Inhaled aminoglycosides may permit supply of excessive concentrations to the lungs with less risk of toxicity. Clinical presentation the affected person is often a cigarette smoker, generally with tobacco-stained fingertips. Cough or the accentuation of an current cough is the commonest early symptom, and haemoptysis the next. Dyspnoea, central chest ache and pleuritic ache, and slowly resolving chest infection are widespread early manifestations. The social and emotional issues could be monumental and, for this reason, in addition to the complexity of scientific administration, the condition should be supervised from specialist centres. Metastatic deposits involving brain, bone, liver, skin, kidney, adrenal glands or other site. The Pancoast syndrome consists of symptoms from local extension on the apex of the lung. There may be ache within the shoulder, higher again or arm, weak spot and atrophy of the hand muscles from brachial plexus involvement, hoarseness from involvement of the recurrent superior laryngeal nerve, or a Horner syndrome (p. Most non-small cell cancers are squamous cell, but about 5% are undifferentiated giant cell tumours and about 10% are adenocarcinoma. The presence of systemic and non-specific symptoms (anorexia, weight loss and fatigue) often, but not always, implies late and probably inoperable disease. Neuromuscular Dementia or focal neurological deficit (caused by cerebral secondaries or not often cortical atrophy), cerebellar syndrome, combined sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy, proximal myopathy, polymyositis (p. The elevated mortality risk of carcinoma of the bronchus (squamous and small cell) has an roughly straight-line relationship with numbers of cigarettes smoked per day (elevated risk of death � cigarettes smoked per day, numerically). Stopping smoking decreases the danger by one-half in 5 years, and to solely twice that of life-long non-people who smoke in 15 years. Other atmospheric pollution (coal smoke and diesel fumes) may show to be aetiologically relevant, but quantitatively small in contrast with cigarettes. Exposure to chromium, arsenic, radioactive supplies or asbestos (which in addition produces interstitial fibrosis and mesothelioma) is related to a higher incidence of lung most cancers. Skin, connective tissue, bone Clubbing, hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy, dermatomyositis and acanthosis nigricans. The tumour may happen either wherever throughout the thoracic cavity and appear as a wellcircumscribed peripheral mass on chest X-ray or, more typically, within the major bronchi and appear as a pedunculated intrabronchial mass seen bronchoscopically. Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is characterised by a systemic non-caseating granulomatous infiltration that may contain any tissue. Fibreoptic bronchoscopy with biopsy is carried out if possible to set up histological diagnosis and assess operability. The site of the tumour is a information to operability (not less than 2 cm from the carina). It sometimes happens in younger individuals of 20�40 years and in females more commonly than males. It often presents as a subacute syndrome with fever, malaise and lassitude, erythema nodosum, polyarthralgia and mediastinal hilar lymphadenopathy. Less commonly and more critically, it presents as a continual insidious disease with respiratory symptoms of cough and progressive dyspnoea with malaise and fever resulting in progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Surgery is contraindicated by metastasis (current in 60% of instances on the time of presentation � mainly in bone and liver), local unfold and insufficient respiratory perform. Chemotherapy with a 3rd technology drug (docetaxel, gemcitabine, paclitaxel or vinorelbine) plus a platinum drug (cisplatin or carboplatin if tolerated) should be offered to patients with more advanced disease. Small cell carcinoma may be palliated with chemotherapy, utilizing a platinum primarily based multi-drug regime. Radiotherapy may have a job if the disease is restricted or responds to chemotherapy. It is because of the uncontrolled synthesis of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 by macrophages eyes � uveitis and keratoconjunctivitis sicca parotitis hepatosplenomegaly generalised lymphadenopathy bone and joints, producing cystic lesions most commonly within the phalanges nervous system, inflicting isolated cranial nerve lesions and peripheral neuropathy Respiratory disease 121 Nervous system Cranial nerve lesions Peripheral neuropathy Skin Lupus pernio Pulmonary Mediastinal lymphadenopathy Granulolmatous irritation Pulmonary fibrosis Hepatosplenomegaly Occular Uveitis Keratoconjunctivitis sicca Parotitis Cardiac Cardiomyopathy Conduction defects Musculoskeletal Myopathy Arthritis Cystic bone lesions Renal Interstitial nephritis Glomerulonephritis Nephrocalcinosis and stones Skin Erythema nodusum Generalised Lymphadenopathy Hypercalcaemia Figure eleven. Investigation the chest X-ray reveals symmetrical lobulated bilateral hilar and paratracheal gland enlargement (interbronchial somewhat than tracheobronchial) or, less commonly, parenchymal mottling or diffuse fibrosis.

Effective methotrexate 10 mg
These values can be utilized to guide fluid therapy, but consideration have to be given to the medical condition of the patient and the small print of the medical state of affairs, as variations in physiology might affect the interaction between the ventilator and cardiac output in any specific patient. Dynamic arterial elastance is defined as the change in pressure for a given quantity over a single respiratory cycle to estimate arterial load. The larger the dynamic arterial elastance, the greater the slope on the pressure-quantity curve, and the extra likely a patient will respond to a fluid eighty one challenge. This measure might predict quantity responsiveness in both mechanically and spontaneously ventilating patients, however additional research are needed. Liu Y, Wei L, Li G, Yu X, Li G, Li Y: Pulse pressure variation adjusted by respiratory modifications in pleural pressure, quite than by tidal quantity, reliably predicts fluid responsiveness in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. A slow dP/dT on the arterial waveform would favor choice of which of the following drugs? Of the following, which is the best measurement to decide fluid responsiveness? In a hypotensive patient with normal cardiac operate, which of the following may indicate the need for fluid therapy? Its safety and portability enable for fast noninvasive bedside evaluation to aid diagnosis and management of critically sick patients. Bedside cardiac ultrasound is particularly helpful in determining the cause of undifferentiated shock in medically complicated patients. The American College of Chest Physicians and Society of Critical Care Medicine have now made suggestions on critical care ultrasound competencies. Interventions initiated embody: fluid boluses, norepinephrine and epinephrine infusions. He stays tachycardic (123 bpm), hypotensive (87/50), with increasing oxygen requirements. Central venous pressure is estimated at 18 mmHg and pulmonary pressures are estimated at 65/34 with a pulmonary artery occlusion pressure of 30 mmHg. Lung ultrasound has made great advances over the past 10 years, particularly within the evaluation of causes of respiratory distress. As both the clinician managing the patient and ultrasound operator, the intensivist has the benefit of creating quick choices that impression patient care. Although central venous and pulmonary catheter data can be found, the diagnosis stays unclear. The medical picture could possibly be according to ventricular failure (right or left), sepsis, or hemorrhage. Bedside cardiac ultrasound can provide actual time pictures to distinguish between these etiologies. Please check with the following web site to get hold of extra complete assets and discussions on every individual matter listed. Cardiac Critical Care Ultrasound Examinations the case presentation above illustrates the issue that may be encountered when treating hemodynamic instability. Hemodynamic instability 85 a) Ventricular failure b) Hypovolemia c) Pulmonary embolism d) Acute valvular dysfunction e) Cardiac tamponade 2. Complications after Cardiothoracic Surgery a) Infective endocarditis b) Suspected aortic dissection or rupture c) Respiratory distress three. Absolute a) Esophageal pathology � tear, mass, stricture b) Dysphagia/odynophagia unevaluated c) Cervical spine Instability 2. Hypovolemic shock a) Decreased end-diastolic space b) "Kissing" papillary muscle c) Hyperdynamic operate 2. Valvular pathology a) Mitral regurgitation or stenosis b) Aortic regurgitation or stenosis four. In every of these circumstances, decision making was altered via using ultrasound. Areas investigated embody hepatorenal, splenorenal, pericardial area, and bladder (posterior to bladder for fluid). Mayo P, Beaulieu Y, Doelken P, et al: American College of Chest Physicians/La Societe de Reanimation de Langue Francaise Statement on Competence in Critical Care Ultrasonography. Neri L; Storti E; Lichtenstein D: Toward an ultrasound curriculum for critical care drugs. Anesthesiology 2012; 117:801-809 Free fluid in abdomen is shown in a patient who was taken to the working room for hypotension. This was a trauma patient who had no other apparent cause of bleeding and was found to have a liver laceration. The most essential high quality of bedside/ portable/point of care ultrasound is reproducibility. Real-time diagnosis primarily based-on pictures obtained still require correct medical context to be able to make expedient and proper interventions at once. Improvements in picture high quality and acquisition allows additional developments for new functions in ultrasonography. Volpicelli G, et al: International proof-primarily based suggestions for point-of-care lung ultrasound. This involves a multistep process in which exams are ordered, samples are drawn, labeled, and transported to the laboratory. He was admitted to the hospital two days prior for diverticulitis and has a medical history important for insulin dependent diabetes, coronary artery disease, and prior stroke. In addition, time to remedy was reduced for patients with circumstances where timing was thought of to be critical. Rapid turnaround in laboratory exams is required for immediate diagnosis, early therapy, and modifications in management. An instance is using fiberoptic pulmonary artery catheters to constantly measure blended venous oxygen saturation (SvO2). Other in vivo exams embody subcutaneous realtime glucose monitoring or measurement of arterial blood fuel through intra-arterial sensors. However, glucose values obtained with a point-of-care system can differ significantly from these obtained by laboratory analysis. In addition, values drawn from a central venous catheter can differ from these obtained from a finger stick. Life threatening modifications in these parameters can occur all of a sudden and fast results are often key to diagnosis and remedy. When a microanalyzer was applied to analyze electrolytes and blood gases on trauma patients within the emergency room, the reported laboratory values have been correct and fast and offered extra info for evaluation and patient management. Timely evaluation of coagulation status can facilitate acceptable use of blood merchandise and associated drugs. A complete blood sample is added to an activator (diatomaceous earth or clay) and the time to clot formation is measured. It is often used within the working room when monitoring the impact of heparin or direct thrombin inhibitors such as argatroban, bivalirudin, and lepirudin. It measures the movement of a pin positioned in a rotating cup full of complete blood blended with kaolin. As clot varieties, the freely hanging pin turns into sure to the rotating cup and movement of the pin is recorded to produce a graph with parameters (Figure 2). Some units provide standard complete blood counts, together with platelet count and evaluation of platelet operate such as aggregation and inhibition. The point of care ultrasound has been described as "the stethoscope of the longer term. Shearer A, Boehmer M, Closs M, et al: Comparison of glucose point-of-care values with laboratory values in critically sick patients. Gupta S, Bhattacharya A: Point of Care Testing in anaesthesiology and intensive care � An overview. Lee-Lewandrowski E, Corboy D, Lewandrowski K, et al: Implementation of a point-of-care satellite laboratory within the emergency department of a tutorial medical heart. Kendall J, Reeves B, Clancy M: Point of care testing: randomized controlled trial of medical end result. Involves a multi-step process in which exams are ordered, samples drawn, labeled, and transported to the lab d. Cytotoxic edema, which happens between 2-5 days submit ischemia, may cause important mind swelling and presumably herniation. The decision was made to take him to interventional radiology for intra-arterial thrombolysis.
References:
- https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/263362/PMC2477188.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
- https://academicjournals.org/article/article1380019714_Suryawanshi.pdf
- http://images2.advanstar.com/PixelMags/dermatology-times/pdf/2013-05.pdf
.png)