Cheap 250 mg mysoline
The crista galli is a sharp upward projection of the ethmoid bone in the midline for the attachment of the falx cerebri. Between the crista galli and the crest of the frontal bone is a small aperture, the foramen cecum, for the transmission of a small vein from the nasal mucosa to the superior sagittal sinus. Alongside the crista galli is a slim slit in the cribriform plate for the passage of the anterior ethmoidal nerve into the nasal cavity. The higher surface of the cribriform plate helps the olfactory bulbs, and the small perforations in the cribriform plate are for the olfactory nerves. Middle Cranial Fossa the middle cranial fossa consists of a small median part and expanded lateral components. The median raised part is fashioned by the physique of the sphenoid, and the expanded lateral components type concavities on both facet, which lodge the temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres. It is bounded anteriorly by the sharp posterior edges of the lesser wings of the sphenoid and posteriorly by the superior borders of the petrous components of the temporal bones. Laterally lie the squamous components of the temporal bones, the larger wings of the sphenoid, and the parietal bones. The flooring of every lateral the middle cranial fossa is fashioned by the larger wing of the sphenoid and the squamous and petrous components of the temporal bone. The sphenoid bone resembles a bat having a centrally positioned physique with larger and lesser wings which might be} outstretched on each side. The physique of the sphenoid incorporates the sphenoid air sinuses, which are lined with mucous membrane and talk with the nasal cavity; they serve as voice resonators. Anteriorly, the optic canal transmits the optic nerve and the ophthalmic artery, a department of the internal carotid artery, to the orbit. The superior orbital fissure, which is a slitlike opening between the lesser and larger wings of the sphenoid, transmits the lacrimal, frontal, trochlear, oculomotor,nasociliary,and abducent nerves,along with the superior ophthalmic vein. The sphenoparietal venous sinus runs medially alongside the posterior border of the lesser wing of the sphenoid and drains into the cavernous sinus. The foramen rotundum, which is located behind the medial finish of the superior orbital fissure,perforates the larger the Cranial Cavity 195 wing of the sphenoid and transmits the maxillary nerve from the trigeminal ganglion to the pterygopalatine fossa. It perforates the larger wing of the sphenoid and transmits the big sensory root and small motor root of the mandibular nerve to the infratemporal fossa. The small foramen spinosum lies posterolateral to the foramen ovale and in addition perforates the larger wing of the sphenoid. The foramen transmits the middle meningeal artery from the infratemporal fossa into the cranial cavity. The artery then runs forward and laterally in a groove on the higher surface of the squamous the temporal bone and the larger wing of the sphenoid see. The anterior department passes forward and upward to the anteroinferior angle of the parietal bone. Here, the bone is deeply grooved or tunneled by the artery for a short distance earlier than it runs backward and upward on the parietal bone. It is at this website that the artery may be be} damaged after a blow to the facet of the top. The posterior department passes backward and upward across the squamous the temporal bone to attain the parietal bone. The massive and irregularly shaped foramen lacerum lies between the apex of the petrous the temporal bone and the sphenoid bone. The inferior opening of the foramen lacerum in life is crammed by cartilage and fibrous tissue, and solely small blood vessels cross through this tissue from the cranial cavity to the neck. The carotid canal opens into the facet of the foramen lacerum above the closed inferior opening. The inside carotid artery enters the foramen through the carotid canal and instantly turns upward to attain the facet of the physique of the sphenoid bone. Here, the artery turns forward in the cavernous sinus to attain the region of the anterior clinoid process. At this point, the internal carotid artery turns vertically upward, medial to the anterior clinoid process, and emerges from the cavernous sinus (see p. Lateral to the foramen lacerum is an impression on the apex of the petrous the temporal bone for the trigeminal ganglion. On the anterior surface of the petrous bone are two grooves for nerves; the most important medial groove is for the larger petrosal nerve, a department of the facial nerve; the smaller lateral groove is for the lesser petrosal nerve, a department of the tympanic plexus. The larger petrosal nerve enters the foramen lacerum deep to the trigeminal ganglion and joins the deep petrosal nerve (sympathetic fibers from across the inside carotid artery), to type the nerve of the pterygoid canal. The abducent nerve bends sharply forward across the apex of the petrous bone,medial to the trigeminal ganglion. The arcuate eminence is a rounded eminence discovered on the anterior surface of the petrous bone and is caused by the underlying superior semicircular canal. The tegmen tympani, a thin plate of bone, is a forward extension of the petrous the temporal bone and adjoins the squamous the bone. From behind forward, it varieties the roof of the mastoid antrum, the tympanic cavity, and the auditory tube. This skinny plate of bone is the one main barrier that separates an infection in the tympanic cavity from the temporal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere. The median the middle cranial fossa is fashioned by the physique of the sphenoid bone. In entrance is the sulcus chiasmatis, which is expounded to the optic chiasma and leads laterally to the optic canal on each side. Behind the elevation is a deep melancholy, the sella turcica, which lodges the hypophysis cerebri. The sella turcica is bounded posteriorly by a sq. plate of bone referred to as the dorsum sellae. The superior angles of the dorsum sellae have two tubercles, referred to as the posterior clinoid processes, which give attachment to the fastened margin of the tentorium cerebelli. The cavernous sinus is immediately related to the facet of the physique of the sphenoid (see p. It carries in its lateral wall the third and fourth cranial nerves and the ophthalmic and maxillary divisions of the fifth cranial nerve. The inside carotid artery and the sixth cranial nerve cross forward through the sinus. Posterior Cranial Fossa the posterior cranial fossa is deep and lodges the components of the hindbrain,specifically,the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata. The flooring of the posterior fossa is fashioned by the basilar, condylar, and squamous components of the occipital bone and the mastoid the temporal bone. The roof of the fossa is fashioned by a fold of dura, the tentorium cerebelli, which intervenes between the cerebellum under and the occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres above. The foramen magnum occupies the central area of the ground and transmits the medulla oblongata and its surrounding meninges,the ascending spinal components of the accessory nerves, and the 2 vertebral arteries. The hypoglossal canal is located above the anterolateral boundary of the foramen magnum. The jugular foramen lies between the lower border of the petrous the temporal bone and the condylar the occipital bone. It transmits the next constructions from earlier than backward: the inferior petrosal sinus; the 9th, 10th, and 11th cranial nerves; and the big sigmoid sinus. The inferior petrosal sinus descends in the groove on the lower border of the petrous the temporal bone to attain the foramen. The sigmoid sinus turns down through the foramen to turn into the internal jugular vein. It transmits the vestibulocochlear nerve and the motor and sensory roots of the facial nerve. On each side of the internal occipital protuberance is a large groove for the transverse sinus. This groove sweeps round on both facet, on the internal surface of the occipital bone, to attain the posteroinferior angle or corner of the parietal bone. The groove now passes onto the mastoid the temporal bone; at this point, the transverse sinus turns into the sigmoid sinus. The superior petrosal sinus runs backward alongside the higher border of the petrous bone in a slim groove and drains into the sigmoid sinus. As the sigmoid sinus descends to the jugular foramen, it deeply grooves the again of the petrous bone and the mastoid the temporal bone. Table 5-1 provides a summary of the more important openings in the base of the skull and the constructions that cross through them. Mandible the mandible, or lower jaw, is the most important and strongest bone of the face, and it articulates with the skull on the temporamandibular joint.
Buy mysoline 250mg
Microinvasive carcinoma when treated by total hysterectomy provides 5 yr survival fee of just about|of virtually} 100%. This is specifically used for a youthful patient to preserve her ovarian function and to keep away from vaginal fibrosis. Leg pain alongside the distribution of sciatic nerve and unilateral leg swelling are suggestive of pelvic recurrence of carcinoma cervix. Women with Lynch syndrome have 4060 % lifetime risk of endometrical most cancers (see p. Use of combined oral contraceptive is a identified protective factor whereas continual unopposed estrogen stimulation is a identified predisposing factor for endometrial carcinoma (see Tables 23. Once suspected, hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy or fractional curettage is to be carried out, not solely to diagnose but in addition to decide the extent of the lesion. The essential main prevention includes restriction of injudicious use of estrogen after menopause in nonhysterectomized ladies. Mainstay in the therapy of carcinoma body is total stomach hysterectomy and bilateral salpingooophorectomy with pelvic and paraaortic lymph node sampling. Adjuvant radiation is taken into account depending on the surgical stage of the disease, myometrial invasion and histologic grade (p. Primary radiotherapy is the therapy in surgically risk patients and in superior stages. Multimodality method (chemo and radiation therapy) is used in superior and recurrent instances or in metastatic lesions. Progestogens are widely used in well-differentiated carcinoma with enough estrogen and progesterone receptors. Antiestrogen, tamoxifen is often used together with progestogens to enhance the result. Younger ladies with endometrial most cancers have a better prognosis compared with the older ladies. Fifty % happen after molar pregnancy, 25 % after abortion and ectopic and 25 % after regular pregnancy. Nonmetastatic lesions develop in 15 % and metastatic lesions develop in about four % of patients after molar evacuation. TexTbook of GynecoloGy Trophoblastic cells usually regress inside three weeks following delivery. The invasive mole is diagnosed on laparotomy and on histology showing hyperplastic trophoblastic cells maintaining villous buildings without evidences of muscle necrosis. In choriocarcinoma, the hyperplastic trophoblastic column of cells invades the muscles. The commonest website of metastases is lung, adopted by anterior vaginal wall, mind and liver. Hysterectomy is indicated in ladies aged greater than 35 years to enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy or to management intractable bleeding. Whereas high-risk metastatic instances are treated with multiple-agent chemotherapy (see p. Mitotic determine is a vital prognostic factor for leiomyosarcoma of the uterus. Sarcoma botryoides is a particular kind of mixed mesodermal tumor arising from the cervix. Multimodality method (multiagent chemotherapy with surgical elimination and sometimes radiation) provides better result. Primary carcinoma of the fallopian tube is rarest (< 1%) gynecological malignancy. Classic traid of adnexal mass, intermittent profuse watery discharge (hydrops tubae profluens) and vaginal bleeding is taken into account pathognomonic for tubal carcinoma. Persistent postmenopausal bleeding and/or constructive vaginal cytology for adenocarcinoma, in the absence of endometrial carcinoma, the prognosis of tubal carcinoma should be thought-about. Total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy together with omentectomy is done. This is adopted by platinum based mostly mixture chemotherapy because the adjuvant therapy. Secondary carcinoma (metastatic) is widespread (90%), the primary websites are from ovary, uterus, breast or gastrointestinal tract. Malignant epithelial tumors represent about 90 % of all main ovarian carcinomas. The main mode of spread of epithelial ovarian carcinoma is transcoelomic and it spreads to the visceral and parietal peritoneum, diaphragm and to the retroperitoneal nodes. Endometrioid carcinoma is associated with endometrial carcinoma in 20 % and ovarian-endometriosis in 10 % instances. The widespread main websites of metastatic ovarian malignancies are gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, breast and endometrial carcinoma. Inherited ovarian malignancies account for about 5 % of epithelial ovarian cancers (see p. High-risk ladies are: family history of ovarian, endometrial or breast carcinoma, history of elimination of ovarian or breast neoplasm, presence of pelvic tumor in adolescent and perimenopausal ladies and postmenopausal palpable ovary (volume > 8 cm3). Protective components for ovarian epithelial adenocarcinomas are: combined oral contraceptives, pregnancy, tubal ligation, hysterectomy and breastfeeding. Ovarian enlargement lower than 8 cm in diameter in a menstruating ladies is mostly functional. The perfect definitive surgical procedure is total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy with infracolic omentectomy with pelvic and paraaortic lymph node sampling. In distinctive instances, conservative surgical procedure of unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy is justified. Debulking surgical procedure with residual tumor nodules < 1 cm confers better survival benefit even in superior stage disease. Second look surgical procedure either by laparoscopy or laparotomy is employed either after 12 programs of chemotherapy or after 1 yr of main therapy. The 5-year survival fee for patients with borderline epithelial ovarian most cancers (grade 0) is close to 100% (p. Chemotherapy is being widely used following cytoreductive surgical procedure to enhance the result in terms of|when it comes to|by method of} survival. Platinum-based compounds (cisplatin, carboplatin), either alone or together with taxane, prolong the survival fee. Taxane derivatives (paclitaxel, docetaxel) are effective in cisplatin resistant ovarian most cancers. Treatment with carboplatin and paclitaxel for 36 cycles is fascinating for many patients. Multiagent chemotherapy (ectoposide, platinum with or without bleomycin) ends in complete remission. Granulosa cell tumor produces estrogen and may be be} associated with endometrial hyperplasia or endometrial carcinoma. It arises from the male directed cell rests in the hilum of the ovary, from granulosa cells or from teratomas. Though the 2 organs are anatomically separate entities however built-in with advanced functional interaction. The descriptive anatomy of the urinary bladder and urethra has been described in Chapter 1. The anatomic and physiologic peculiarities concerned in storage and voiding of urine are to be mentioned right here. Bladder the bladder muscles - referred to as detrusor encompass three layers of muscles. With this arrangement, it types an lively and dominant position in each storage and voiding. Inner longitudinal - It programs downwards from the fundus of the bladder and continues in the type of spirals upto the midurethra. A distal one which varies little with age and a proximal one beneath the bladder neck which undergoes marked adjustments with age. In the reproductive period, these vessels give a cavernous appearance to the submucosa which disappears in the postmenopausal period. This urethral vascular system plays a big position in the maintenance of resting urethral stress. Support to bladder neck and urethra Support is maintained by intrinsic and extrinsic components. Extrinsic components: (i) Contraction of pubococcygeus a part of} levator ani muscle; (ii) Pubourethral ligaments and condensed endopelvic fascia with clean muscle fibres; (iii) Exercise to increase collagen turnover and in addition to preserve power of levator ani.
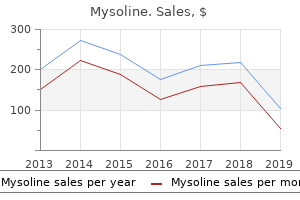
Quality 250 mg mysoline
Following intravenous administration to wholesome volunteers, 50% to 70% of a digoxin dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. Renal excretion of digoxin is proportional to glomerular filtration rate and is largely unbiased of urine move. The clearance of digoxin may be primarily correlated with renal operate as indicated by creatinine clearance. The Cockcroft and Gault formula for estimation of creatinine clearance contains age, body weight, and gender. Plasma digoxin focus profiles in patients with acute hepatitis typically fell within the vary of profiles in a gaggle of wholesome topics. Times to Onset of Pharmacologic Effect and to Peak Effect of Preparations of Lanoxin Product Time to Onset of Effecta Time to Peak Effecta Lanoxin Tablets 0. Hemodynamic Effects: Digoxin produces hemodynamic enchancment in patients with heart failure. Short- and long-term therapy with the drug will increase cardiac output and lowers pulmonary artery strain, pulmonary capillary wedge strain, and systemic vascular resistance. These hemodynamic results are accompanied by an increase in the left ventricular ejection fraction and a decrease in end-systolic and end-diastolic dimensions. Both trials demonstrated higher preservation of train capacity in patients randomized to Lanoxin. Continued remedy with Lanoxin decreased the risk of growing worsening heart failure, as evidenced by heart failure-related hospitalizations and emergency care and the necessity for concomitant heart failure therapy. Overall all-cause mortality was 35% with no difference between teams (95% confidence limits for relative risk of 0. Lanoxin was related with a 25% discount in the number of hospitalizations for heart failure, a 28% discount in the risk of a patient having at least of|no less than} 1 hospitalization for heart failure, and a 6. Use of Lanoxin was associated with a trend to enhance time to all-cause death or hospitalization. The trend was evident in subgroups of patients with mild heart failure as well as|in addition to} extra extreme disease, as proven in Table 3. Although the effect on all-cause death or hospitalization was not statistically vital, much of the obvious profit derived from results on mortality and hospitalization attributed to heart failure. Chronic Atrial Fibrillation: In patients with continual atrial fibrillation, digoxin slows rapid ventricular response rate in a linear dose-response fashion from 0. Lanoxin will increase left ventricular ejection fraction and improves heart failure signs as evidenced by train capacity and heart failure-related hospitalizations and emergency care, whereas having no effect on mortality. Atrial Fibrillation: Lanoxin is indicated for the management of ventricular response rate in patients with continual atrial fibrillation. A hypersensitivity response to other digitalis preparations usually constitutes a contraindication to digoxin. In such patients consideration should be given to the insertion of a pacemaker before remedy with digoxin. The remedy of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in such patients is usually direct-current cardioversion. Use in Patients With Preserved Left Ventricular Systolic Function: Patients with sure disorders involving heart failure associated with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction additionally be} significantly susceptible to toxicity of the drug. Such disorders embody restrictive cardiomyopathy, constrictive pericarditis, amyloid heart disease, and acute cor pulmonale. Patients with idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis could have worsening of the outflow obstruction due to of} the inotropic results of digoxin. Digoxin ought to typically be averted in these patients, although it has been used for ventricular rate management in the subgroup of patients with atrial fibrillation. Because of the extended elimination half-life, a longer period of time is required to achieve an initial or new steady-state serum focus in patients with renal impairment than in patients with normal renal operate. Use in Patients With Electrolyte Disorders: In patients with hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, toxicity could occur despite serum digoxin concentrations under 2. Calcium, significantly when administered quickly by the intravenous route, could produce severe arrhythmias in digitalized patients. On the opposite hand, hypocalcemia can nullify the effects of digoxin in people; thus, digoxin additionally be} ineffective till serum calcium is restored to normal. These interactions are related to truth that|the truth that} digoxin affects contractility and excitability of the guts in a way much like that of calcium. Use in Thyroid Disorders and Hypermetabolic States: Hypothyroidism could cut back the necessities for digoxin. Heart failure and/or atrial arrhythmias ensuing from hypermetabolic or hyperdynamic states. Atrial arrhythmias associated with hypermetabolic states are significantly resistant to digoxin remedy. Use in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction: Digoxin should be used with caution in patients with acute myocardial infarction. The use of inotropic drugs in some patients in this setting could end in undesirable will increase in myocardial oxygen demand and ischemia. Use During Electrical Cardioversion: It additionally be} fascinating to cut back the dose of digoxin for 1 to 2 days previous to electrical cardioversion of atrial fibrillation to keep away from the induction of ventricular arrhythmias, but physicians must think about the consequences of increasing the ventricular response if digoxin is withdrawn. Use in Patients With Myocarditis: Digoxin can not often precipitate vasoconstriction and subsequently should be averted in patients with myocarditis. Laboratory Test Monitoring: Patients receiving digoxin ought to have their serum electrolytes and renal operate (serum creatinine concentrations) assessed periodically; the frequency of assessments will rely upon the medical setting. Drug Interactions: Potassium-depleting diuretics are a serious contributing issue to digitalis toxicity. Calcium, significantly if administered quickly by the intravenous route, could produce severe arrhythmias in digitalized patients. Quinidine, verapamil, amiodarone, propafenone, indomethacin, itraconazole, alprazolam, and spironolactone raise the serum digoxin focus due to of} a reduction in clearance and/or in quantity of distribution of the drug, with the implication that digitalis intoxication could outcome. Propantheline and diphenoxylate, by decreasing intestine motility, could enhance digoxin absorption. Antacids, kaolin-pectin, sulfasalazine, neomycin, cholestyramine, sure anticancer drugs, and metoclopramide could interfere with intestinal digoxin absorption, leading to unexpectedly low serum concentrations. Rifampin could decrease serum digoxin focus, particularly in patients with renal dysfunction, by rising the non-renal clearance of digoxin. Thyroid administration to a digitalized, hypothyroid patient could enhance the dose requirement of digoxin. Concomitant use of digoxin and sympathomimetics will increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Succinylcholine could cause a sudden extrusion of potassium from muscle cells, and will thereby cause arrhythmias in digitalized patients. Both digitalis glycosides and beta-blockers sluggish atrioventricular conduction and reduce heart rate. Digoxin concentrations are elevated by about 15% when digoxin and carvedilol are administered concomitantly. Therefore, elevated monitoring of digoxin is really helpful when initiating, adjusting, or discontinuing carvedilol. Due to the appreciable variability of those interactions, the dosage of digoxin should be individualized when patients receive these medicines concurrently. Furthermore, caution should be exercised when combining digoxin with any drug that may cause a major deterioration in renal operate, since a decline in glomerular filtration or tubular secretion could impair the excretion of digoxin. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility: There have been no long-term research carried out in animals to consider carcinogenic potential, nor have research been performed to assess the mutagenic potential of digoxin or its potential to affect on} fertility. It can also be|can be} not known whether or not digoxin may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant girl or can affect on} reproductive capacity. However, the estimated exposure of a nursing toddler to digoxin by way of breastfeeding shall be far under similar old} toddler maintenance dose. Nevertheless, caution should be exercised when digoxin is run to a nursing girl. Premature and immature infants are significantly delicate to the effects of digoxin, and the dosage of the drug must not solely be decreased but should be individualized in accordance with their degree of maturity. Geriatric Use: nearly all of of} medical expertise gained with digoxin has been in the aged population.
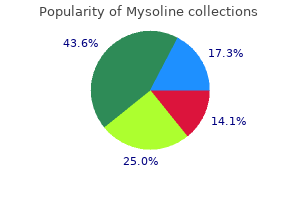
Safe mysoline 250mg
Z, J W Kaplan, Intelligence and adjustment to chronic hemodialysis, J Psychosom Res, 1973,17: 29-34. Correlation of Psychiatric complications with duration of hemodialysis Duration to develop Psych. Cysticercosis heads the record forming the majority of cases followed by Hydatidosis and Sparganosis. Microscopic identification of irritation with surrounding reactions along with other morphological features forms the mainstay of analysis of parasitic ailments on histopathology. Identification of the parasites on histopathological examination would scale back back} the cost-diagnosis ratio avoiding expensive serological investigation. Tapeworms (cestodes) are segmented worms, the adult forms of which are encountered in gastrointestinal tract, whereas the larvae can be seen in almost any organ in the body. The specimen most incessantly submitted for detection of parasites is stool for the identification of ova or cysts. Specimens are obtained based mostly on radiological investigations or are often an incidental finding. The major advantages of histopathology are speed, low value and presumptive identification. Hematological investigations like presence of eosinophilia in peripheral blood might give a clue about parasitic infestation. This article presents an summary of parasites encountered in our establishment over the previous two years. It occurs outcome of} ingestion of contaminated vegetables and food or beneath cooked meat. The cysts are often found in Cerbral cortex, however can happen in meninges of the base of the brain, in the ventricles and infrequently in the spinal wire. Diagnosis often rests on interpretation of sufferers signs, radiological research and immunological checks for dectection of anticysticercal antibodies (Enzyme - linked immunoelectrotransfer blot). The reside parasite has a single scolex with four suckers and a double row of hooklets. The cyst wall has an outer cuticular layer, a center pseudo epithelial layer, and an inside reticular layer. In excision biopsies, only the cuticular layer of deadworm is appreciated on H&E stain. Histopathology would reveal a cysticerci larvae with surrounding host response composed of fibrosis, chronic inflammatory infiltrate with eosinophils and sometimes giant cells. Sometimes, cysticercosis can coexist with secondaries in lymphnode or Hodgkins of blended cellularity sort. Chest radiograph revealed irregular masses in proper center zone with specks of calcification and fluid levels in a number of} of the cysts. Cut part exuded about 50 ml of fluid and many of|and lots of} daughter cysts with brood capsules. Microscopy revealed a lamellated membrane (Fig 2B) with many scolices diagnostic of Echinococcosis. A B Fig 2 (A) Fig 1(A and B): Section of Cysticercosis exhibiting inflammatory host response (A) H&E (10x). Section of cysticercosis (B) H&E (10x) 152 Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development. Microscopy revealed the worm having thick tegmentum with calcospheroites in sub-tegmentum (Fig 3 B) which was surrounded by wall of granulation tissue diagnostic of Sparganosis. Fig 2 (A and B): Gross specimen exhibiting resected lobe of lung with fragments of laminate membrane (A). Human infection is usually considered an occupational public well being downside for the sheep (intermediate host) farmers, ranchers, or shepherds in endemic areas. There is however, a danger of infection from canine (definitive host) contact, canine feces, or food contaminated with eggs of E. The cyst wall reveals contribution from each the cestode properly as|in addition to} the host and consists of three layers. The outer host layer or pericyst consists of fibroblasts, giant cells and eosinophils. Scolices originate from the membrane in the form of evaginations known as brood capsules. Alternately, the hooklets can be visualized as refractile constructions in opposition to background debris. Diagnosis of hydatidosis in man is made by A B Fig 3 (A and B): Excised specimen exhibiting reduce open cyst (A). Section of Parasite exhibiting Calcareous spherules and muscle fibres (B) Masson Trichrome stain (40x). Transmission to humans often occurs through ingestion of water contaminated with contaminated Cyclops (I intermediate host) or consumption of contaminated meat. Once a parasite enters the human body, an aberrant life cycle begins resulting in a cyst like structure. The surrounding lesion is predominantly composed of eosinophils, plasma cells and lymphocytes. In the absence of worm, laminated calcospherules discovered in the cytoplasm of the proliferating macrophages and giant cells might be be} of diagnostic value. Histopathological identification of the parasite based mostly on its morphological features, host tissue response and in unconfirmed cases, coupled with serology and molecular analysis might assist to successfully characterize the parasite. Effective communication between clinicians, radiologists and pathologists often result in right analysis plenty of} difficult to diagnose ailments. Public well being measures such a lot as good} sanitation and personal hygiene measures corresponding to washing of arms with soap and water. Washing of utensils and vegetable with clear water, prevention of sewage contamination of consuming water, secure disposal of waste, play a significant role in avoiding cestodal infections. Sanitary measures in abattoirs and treating pet canine with Anti-helminthics additionally assist. Information ought to be passed onto basic public and sufferers specifically relating to the potential role of cestodes in incidence of malnutrition and morbidity in populations so that preventive steps are initiated and applicable measures are taken given to forestall unfold of the disease. Human cystic echinococcosis in a Uruguan Community: A sonographic, serologic and epidemiologic study. Risk elements related to human cystic echinococcosis in Florida, Uruguay: Results of a mass screening study using ultrasound and serology. Professor Department of Forensic Medicine, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Kadapa- 516002. The existence of sternalis muscle, its location, orientation and early identification are essential in breast surgeries. Rectus sternalis is a derivative of superficial half of} rectus abdominis and supplied by intercostals nerve. The number of costal attachments and the extent to which the clavicular and costal components are separated differ. A superficial verticals lip or slips could ascend from the lower costal cartilages and rectus sheet to mix with the sternocleido mastoid or to attach to the higher sternum or costal cartilages. Myotome place of the somites provides rise to a lot of the skeletal muscles of the body. Whereas mesoderm of the pharyngeal arches provides rise to head neck muscles. The rectus sternalise muscle is a derivative of superficial half of} the rectus abdominis muscle. Rectus sternalise is a flat ribbon shaped muscle that begins from the lower half of} the ribs, rectus sheath after which courses upward. Finally inserting the higher half of} sternum and ribs or the sternocleido mastoid muscle. Various authors have classified sternalis muscle beneath four major categories relating to the structure it has been derived from (a) pectoralis major, (b) from the rectus abdominis (c) from the sternocleido mastoid (d) from the panniculus carnosus. The left rectus sternalis muscle has been seen in a 35 year old male cadaver (Fig: 01). It was located on the anterior thoracic wall along the left lateral side of the sternum. It originated as a muscle belly from facia of the rectus abdominus and exterior indirect apponeurosis and lower ribs of the left side chest wall. Finally it extends obliquely upwards inserted into the manubrium sternum as a tendon. Figure No: 01 left side rectus sternalis muscle Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development.
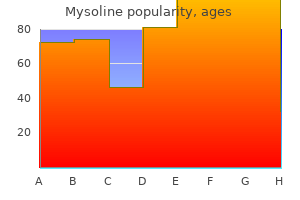
Generic mysoline 250mg
Other signs of poor response to intervention embrace kidney dimension lower than 9 cm, a renal resistive index larger than 80 on Doppler ultrasonography, significant proteinuria, evidence of one other kidney disease, or findings of marked chronicity on kidney biopsy. There is a few evidence that this group responds better to intervention than those with persistent, secure kidney perform impairment. There is evidence from small, nonrandomized trials that this subgroup of patients profit from renal artery stenting, and treatment is strongly really helpful by the American College of Cardiology. Among patients with resistant hypertension, the prevalence of major hyperaldosteronism is estimated to be 17% to 20%. As a bunch, African-American patients probably to|are inclined to} have decrease renin ranges, but no ethnic variations in the prevalence of major hyperaldosteronism have been described. Primary hyperaldosteronism could also be} brought on by bilateral adrenal hyperplasia (65% of cases), aldosterone producing adenoma (30% of cases), or, not often, a secretory adrenal carcinoma or inherited endocrinopathy (discussed later). Patients with adrenal adenomas probably to|are inclined to} be younger and have a extra severe clinical picture than those with adrenal hyperplasia. Testing for hyperaldosteronism ought to be considered in any of the next circumstances: hypertension and spontaneous hypokalemia (or hypokalemia induced by low-dose diuretic), severe hypertension. Hypokalemia, if current, ought to be first corrected, as it could suppress aldosterone secretion. The hallmark of major hyperaldosteronism is nonsuppressible aldosterone secretion with nonstimulable renin secretion. This could also be} achieved by the use of oral sodium chloride load over several of} days, or by administration of intravenous saline over several of} hours. These checks have potential dangers, particularly for patients with poor left ventricular perform. This check has the advantage of avoiding salt loading in people in whom that is contraindicated, but it could trigger profound hypotension in some patients. All of these checks are cumbersome and time consuming, and many of|and a lot of} centers now instantly proceed to imaging after a positive biochemical screening check end result. Radionuclide scintigraphy with [131I]iodocholesterol is delicate for adenomas, but not broadly obtainable. In older people, adrenal vein sampling ought to be carried out if an adenoma is detected, aldosterone-producing adenomas become increasingly rare with advancing age. If the adrenal glands appear normal on imaging, patients should proceed on to adrenal vein sampling. This approach can strongly predict a therapeutic response to unilateral adrenalectomy. The place in the adrenal vein is confirmed by simultaneously measuring adrenal vein and peripheral vein cortisol ranges. In adrenal hyperplasia, there ought to be little distinction between the two adrenal vein ranges. Occasionally, the adenoma could also be} extraadrenal, and adrenal vein sampling is normal. If imaging and adrenal vein sampling are negative, the rare prognosis of glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism (discussed later) ought to be considered. Embolization of adenomas with ethanol could also be} an choice in patients medically unfit for surgical procedure. Selective hypoaldosteronism may occur for some months after surgical procedure, and potassium ought to be supplemented cautiously throughout this period. Eplerenone, selective aldosterone receptor antagonist, is popular it causes a lot much less gynecomastia than spironolactone. However, a latest well-powered double-blinded randomized managed trial demonstrated that eplerenone is much less efficient than spironolactone for controlling blood stress. These tumors often originate from the juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidney, but renin production has been reported with other malignancies, together with teratomas and ovarian tumors. Patients develop a attribute clinical appearance, with the traditional cushingoid moon facies related to facial fat deposition, together with truncal obesity, stomach striae, hirsutism, and kyphoscoliosis. Patients have varying degrees of multiorgan involvement, with diabetes mellitus, cataracts, neuropsychiatric issues, proximal myopathy, avascular necrosis of humeral and femoral heads, osteoporosis, and secondary hypertension among the many extra prominent. Hypertension ensuing from the mineralocorticoid effect of the glucocorticoids is a standard characteristic. This could be achieved with the low-dose dexamethasone suppression check, measurement of 24-hour urinary free-cortisol ranges, or assessment of the circadian sample Box sixty seven. In the overnight, low-dose dexamethasone suppression check, a 2-mg dose of dexamethasone is taken at 11 pm, and a plasma cortisol sample is drawn at 9 am the subsequent morning. To assess circadian cortisol secretion, cortisol ranges are measured at 9 am and 11 pm. Other causes of abnormally high cortisol secretion embrace stress, main despair, and persistent extra alcohol consumption. When cortisol extra is confirmed, additional testing to elucidate a pituitary, adrenal, or ectopic source should observe. An adrenal carcinoma usually causes marked virilization and severe hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis. The high-dose dexamethasone suppression check is carried out by administering dexamethasone 2 mg every 6 hours for two days. Reduction of cortisol to lower than 50% of the day 1 level is defined as suppression. About one half of patients have paroxysms of hypertension, whereas most of the the rest have apparent essential hypertension. When referring to these tumors, the "10% rule" is commonly cited, and continues to be clinically useful: approximately 10% of cases are extraadrenal, 10% are malignant, 10% are bilateral, and 10% are related to familial syndromes. In patients with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, pheochromocytoma happens in 10% to 20% of cases. Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome kind 2 is related to medullary thyroid carcinoma and hyperparathyroidism. Pheochromocytoma is present in lower than 5% of patients with neurofibromatosis kind 1. Genetic screening is really helpful in patients younger than 21 years of age, with extraadrenal or bilateral disease, or multiple of} paragangliomas. The screening checks used are measurements of urinary and plasma catecholamines or their metabolites. Patients classically current with the triad of episodic headache, sweating, and tachycardia; most have at least of|no much less than} two of these signs. Pallor, paroxysmal hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, visible blurring, papilledema, high erythrocyte sedimentation price, weight reduction, polyuria, polydipsia, psychiatric issues, hyperglycemia, dilated cardiomyopathy, and, not often, secondary erythrocytosis are A examine based on potential data from 152 consecutive patients with pheochromocytoma compared the relative diagnostic sensitivities of the various catecholamine and catecholamine metabolite ranges. It showed that essentially the most delicate checks had been urinary normetanephrine and platelet norepinephrine ranges, with sensitivities of 96. The likely cause for the elevated sensitivity of platelet epinephrine is that the neurosecretory granules in the platelets concentrate the catecholamines that are be} intermittently secreted by the pheochromocytoma. Measurement of platelet epinephrine ought to be half of} the usual screening for pheochromocytoma. Clonidine Suppression Test the clonidine suppression check is an alternate technique for confirming a prognosis when catecholamine ranges are suggestive but not diagnostic of pheochromocytoma. Clonidine is administered in any case antihypertensives have been withheld for at least of|no much less than} 12 hours; plasma catecholamines are measured three hours later and will fall to lower than 500 pg/ mL in normal people. Recurrences are extra widespread in familial cases, and a significant proportion of recurrences are malignant. Clinically, patients have hypertension when blood stress is measured in the higher limbs, with reduced or unmeasurable blood stress in the legs. If the coarctation is proximal to the origin of the left subclavian artery, the blood stress and brachial pulsation in the left higher limb could also be} reduced. Ninety-five p.c of pheochromocytomas are intraabdominal, with 90% positioned in the adrenal glands. The most generally used is administration of the -blocker phenoxybenzamine, starting at a dose of 10 mg quickly as} day by day and rising the dose every few days until blood stress and signs are managed. A -blocker should by no means be administered first, as the subsequent unopposed -agonist vasoconstrictive motion can markedly worsen hypertension. A hypertensive crisis precipitated by -blockade could also be} a clue to the presence of a pheochromocytoma in a affected person with hypertension. Associated metastases ought to be resected if attainable, and skeletal lesions irradiated. Owing to a mixture of things inherent to sleep apnea, together with apnea, hypoxia, hypercapnia, and arousal from sleep, activation of the sympathetic nervous system results in hypertension.
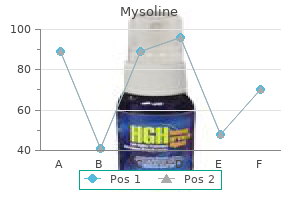
250 mg mysoline
Many collateral branches are given off to the reticular activating system of the brainstem (see p. The tonotopic group current in the organ of Corti is preserved within the cochlear nuclei, the inferior colliculi, and the first auditory space. Descending Auditory Pathways Descending fibers originating in the auditory cortex and in different nuclei in the auditory pathway accompany the ascending pathway. These fibers are bilateral and finish on nerve cells at totally different ranges of the auditory pathway and on the hair cells of the organ of Corti. It is believed that these fibers function a feedback mechanism and inhibit the reception of sound. They may have a task in the process of auditory sharpening, suppressing some signals and enhancing others. Cochlear Nuclei the anterior and posterior cochlear nuclei are located on the floor of the inferior cerebellar peduncle. The cochlear nuclei send axons (secondorder neuron fibers) that run medially via the pons to finish in the trapezoid body and the olivary nucleus. The axons now ascend via the posterior half of} the pons and midbrain and kind a tract known as as|often known as} the lateral lemniscus. Each lateral lemniscus, subsequently, consists of third-order neurons from both sides. As these fibers ascend, some of them relay in small groups of nerve cells, collectively known as as|often known as} the nucleus of the lateral lemniscus. On reaching the midbrain, the fibers of the lateral lemniscus both terminate in the nucleus of the inferior colliculus or are relayed in the medial geniculate body and move to the auditory cortex of the cerebral hemisphere via the acoustic radiation of the interior capsule. The major auditory cortex (areas forty one and 42) includes the gyrus of Heschl on the higher floor of the superior temporal gyrus. The recognition and interpretation of sounds on the premise of previous experience take place in the secondary auditory space. Course of the Vestibulocochlear Nerve the vestibular and cochlear elements of the nerve go away the anterior floor of the brain between the lower border of the pons and the medulla oblongata. They run laterally in the posterior cranial fossa and enter the interior acoustic meatus with the facial nerve. Glossopharyngeal Nerve Nuclei the glossopharyngeal nerve has three nuclei: (1) the principle motor nucleus,(2) the parasympathetic nucleus,and (3) the sensory nucleus. Main Motor Nucleus the principle motor nucleus lies deep in the reticular formation of the medulla oblongata and is shaped by the superior finish of the nucleus ambiguus. Sensory Nucleus the sensory nucleus is half of} the nucleus of the tractus solitarius. Sensations of taste journey via the peripheral axons of nerve cells located in the ganglion on the glossopharyngeal nerve. Efferent fibers cross the median plane and ascend to the ventral group of nuclei of the alternative thalamus and a number of|numerous|a variety of} hypothalamic nuclei. From the thalamus, the axons of the thalamic cells move via the interior capsule and corona radiata to finish in the lower half of} the postcentral gyrus. Afferent data that considerations frequent sensation enters the brainstem via the superior ganglion of the Parasympathetic Nucleus the parasympathetic nucleus is also be|can be} called the inferior salivatory nucleus. It receives afferent fibers from the hypothalamus via the descending autonomic pathways. It also is believed to receive data from the olfactory system via the reticular formation. Information regarding taste also is acquired from the nucleus of the solitary tract from the mouth cavity. Afferent impulses from the carotid sinus, a baroreceptor located at the bifurcation of the frequent carotid artery, also journey with the glossopharyngeal nerve. They terminate in the nucleus of the tractus solitarius and are related to the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve. The carotid sinus reflex that entails the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves assists in the regulation of arterial blood strain. Vagus Nerve Nuclei the vagus nerve has three nuclei: (1) the principle motor nucleus, (2) the parasympathetic nucleus, and (3) the sensory nucleus. Course of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve the glossopharyngeal nerve leaves the anterolateral floor of the higher half of} the medulla oblongata as a sequence of rootlets in a groove between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle. It passes laterally in the posterior cranial fossa and leaves the skull via the jugular foramen. The superior and inferior glossopharyngeal sensory ganglia are located on the nerve here. The nerve then descends via the higher half of} the neck in firm with the interior jugular vein and the interior carotid artery to attain the posterior border of the stylopharyngeus muscle, which it supplies. The nerve then passes forward between the superior and center constrictor muscle tissue of the pharynx to give sensory branches to the mucous membrane of the pharynx and the posterior third of the tongue. Main Motor Nucleus the principle motor nucleus lies deep in the reticular formation of the medulla oblongata and is shaped by the nucleus ambiguus. The efferent fibers provide the constrictor muscle tissue of the pharynx and the intrinsic muscle tissue of the larynx. Parasympathetic Nucleus the parasympathetic nucleus types the dorsal nucleus of the vagus and lies beneath the floor of the lower half of} the fourth ventricle posterolateral to the hypoglossal nucleus. It receives afferent fibers from the hypothalamus Vagus Nerve (Cranial Nerve X) 353 Cerebral cortex Descending autonomic pathway Thalamus and hypothalamic nuclei Parasympathetic dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve From glossopharyngeal nerve (from carotid sinus) Inferior cerebellar peduncle Nucleus of the tractus solitarius Main motor nucleus of vagus nerve Spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve Vagus nerve Superior ganglion of vagus nerve Medulla oblongata Inferior ganglion of vagus nerve Inferior olivary nucleus Figure 11-18 Vagus nerve nuclei and their central connections. It also receives different afferents, together with those from the glossopharyngeal nerve (carotid sinus reflex). The efferent fibers are distributed to the involuntary muscle of the bronchi, coronary heart, esophagus, abdomen, small intestine, and huge intestine as far as the distal one-third of the transverse colon. Course of the Vagus Nerve the vagus nerve leaves the anterolateral floor of the higher half of} the medulla oblongata as a sequence of rootlets in a groove between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle. The nerve passes laterally via the posterior cranial fossa and leaves the skull via the jugular foramen. The vagus nerve possesses two sensory ganglia, a rounded superior ganglion, located on the nerve within the jugular foramen, and a cylindrical inferior ganglion, which lies on the nerve just below the foramen. Below the inferior ganglion, the cranial root of the accent nerve joins the vagus nerve and is distributed mainly in its pharyngeal and recurrent laryngeal branches. The vagus nerve descends vertically in the neck within the carotid sheath with the interior jugular vein and the interior and customary carotid arteries. The right vagus nerve enters the thorax and passes posterior to the foundation of the best lung,contributing to the pulmonary plexus. It then passes on to the posterior floor of the esophagus and contributes to the esophageal plexus. The posterior vagal trunk (which is the name now given to the best vagus) is distributed to the posterior Sensory Nucleus the sensory nucleus is the lower half of} the nucleus of the tractus solitarius. Sensations of taste journey via the peripheral axons of nerve cells located in the inferior ganglion on the vagus nerve. Efferent fibers cross the median plane and ascend to the ventral group of nuclei of the alternative thalamus properly as|in addition to} to a number of|numerous|a variety of} hypothalamic nuclei. From the thalamus, the axons of the thalamic cells move via the interior capsule and corona radiata to finish in the postcentral gyrus. [newline]Afferent data regarding frequent sensation enters the brainstem via the superior ganglion of the vagus nerve however ends in the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve. This wide distribution is accomplished via the celiac, superior mesenteric, and renal plexuses. The left vagus nerve enters the thorax and crosses the left aspect of the aortic arch and descends behind the foundation of the left lung, contributing to the pulmonary plexus. The left vagus then descends on the anterior floor of the esophagus, contributing to the esophageal plexus. The anterior vagal trunk (which is the name now given to the left vagus) divides into a number of} branches, that are distributed to the abdomen, liver, higher half of} the duodenum, and head of the pancreas. Cranial Root the cranial root (part) is shaped from the axons of nerve cells of the nucleus ambiguus. The efferent fibers of the nucleus emerge from the anterior floor of the medulla oblongata between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle. The spinal nucleus is believed to receive corticospinal fibers from each cerebral hemispheres. Course of the Cranial Root the nerve runs laterally in the posterior cranial fossa and joins the spinal root. The roots then separate, and the cranial root joins the vagus nerve and is distributed in its pharyngeal and recurrent laryngeal branches to the muscle tissue of the soft palate, pharynx, and larynx.
Diseases
- Noble Bass Sherman syndrome
- Netherton syndrome ichthyosis
- Spastic paraplegia type 5A, recessive
- Hydrops ectrodactyly syndactyly
- Short limb dwarfism Al Gazali type
- Isaacs syndrome
- Dibasic aminoaciduria 2
- Multinodular goiter cystic kidney polydactyly
Order mysoline 250mg
Thus, the placement of the stripes of pair-rule gene expression is a results of (1) the modular cisregulatory enhancer elements of the pair-rule genes and (2) the trans-regulatory gap gene proteins that bind to these enhancer websites. Once initiated by the gap gene proteins, the transcription sample of the first pair-rule genes becomes stabilized by their interactions among themselves (Levine and Harding 1989). The main pair-rule genes also type the context that enables or inhibits the expression of the later-acting secondary pair-rule genes. One such secondary pair-rule gene is fushi tarazu (ftz; Japanese, "too few segments;" Figures 9. However, as the proteins from the first pair-rule genes begin to work together with the ftz enhancer, the ftz gene is repressed in certain bands of nuclei to create interstripe regions. Meanwhile, the Ftz protein interacts with its own promoter to stimulate more transcription of the ftz gene (Figure 9. The expression of the every pair-rule gene in seven stripes divides the embryo into fourteen parasegments, with every pairrule gene being expressed in alternate parasegments. Moreover, every row of nuclei within every parasegment expresses a selected and unique combination of pair-rule merchandise. These merchandise will activate the subsequent level of segmentation genes, the phase polarity genes. The phase polarity genes So far, our dialogue has described interactions between molecules throughout the syncytial embryo. These intercellular interactions are mediated by the phase polarity genes, and so they accomplish two necessary tasks. First, they reinforce the parasegmental periodicity established by the sooner transcription elements. Second, through this cell-to-cell signaling, cell fates are established within every parasegment. The phase polarity genes encode proteins would possibly be} constituents of the Wingless and Hedgehog sign transduction pathways (see Chapter 6). Mutations in these genes result in defects in segmentation and in gene expression sample throughout every parasegment. The improvement of the conventional sample depends on the very fact fact} only one row of cells in every parasegment is permitted to express the Hedgehog protein, and only one row of cells in every. The key to this sample is the activation of the engrailed gene in those cells would possibly be} going to express the Hedgehog protein. The engrailed gene is activated when cells have excessive ranges of the Even-skipped, Fushi tarazu, or Paired transcription elements. As a outcome, Engrailed is expressed in fourteen stripes throughout the anterior-posterior axis of the embryo (see Figure 9. The wingless gene is activated in those bands of cells that obtain little or no Even-skipped or Fushi tarazu proteins, however which do contain the Sloppy-paired protein. This causes wingless to be transcribed solely within the row of cells instantly anterior to the cells the place engrailed is transcribed (Figure 9. Once wingless and engrailed expression is established in adjoining cells, this sample should be maintained to retain the parasegmental periodicity of the physique plan established by the pair-rule genes. The maintenance of those patterns is regulated by interactions between cells expressing wingless and people expressing engrailed. The Wingless protein, secreted from the wingless-expressing cells, diffuses to adjoining cells. This receptor prompts the Wnt sign transduction pathway, ensuing within the continued expression of engrailed (Siegfried et al. The Engrailed protein prompts the transcription of the hedgehog gene within the engrailed-expressing cells. The Hedgehog protein can bind to the Hedgehog receptor (the Patched protein) on neighboring cells. When it binds to the adjoining posterior cells, it stimulates the expression of the wingless gene. This interplay creates a secure boundary, properly as|in addition to} a signaling heart from which Hedgehog and Wingless proteins diffuse throughout the parasegment. The diffusion of those proteins is assumed to present the gradients by which the cells of the parasegment acquire their identities. This process can be seen within the dorsal epidermis, the place the rows of larval cells produce completely different cuticular constructions relying on their position throughout the phase. The subsequent two cell rows have a 3° fate, making small, thick hairs, and these are adopted by a number of} rows of cells that undertake the 4° fate, producing nice hairs (Figure 9. The wingless-expressing cells lie throughout the area producing the nice hairs, whereas the hedgehog-expressing cells are close to the 1° row of cells. The fates of the cells can be altered by experimentally growing or lowering the levels of Hedgehog or Wingless protein. For instance, if the hedgehog gene is fused to a warmth shock promoter and the embryos are grown at a temperature that prompts the gene, more Hedgehog protein is made, and the cells normally displaying 3° fates will become 2° cells. The rows of 4° cells farthest from the Wingless-secreting cells can also become 3° or 2° cells. Thus, Hedgehog and Wingless seem essential for elaborating the complete sample of cell sorts throughout the parasegment. Either these alerts act in a graded fashion, as morphogens, or they act locally to provoke a cascade of native signaling occasions, in which every interplay makes use of a different ligand and receptor (Figure 9. The ensuing sample of cell fates also adjustments primary target|the major focus} of patterning from parasegment to phase. There second are|are actually} external markers, as the engrailed-expressing cells become the most posterior cells of every phase. The Homeotic Selector Genes Patterns of homeotic gene expression After the segmental boundaries have been established, the characteristic constructions of every phase are specified. There are two regions of Drosophila chromosome 3 that contain most of those homeotic genes (Figure 9. One area, the Antennapedia complicated, accommodates the homeotic genes labial (lab), Antennapedia (Antp), intercourse combs decreased (scr), deformed (dfd), and proboscipedia (pb). The labial and deformed genes specify the head segments, whereas intercourse combs decreased and Antennapedia contribute to giving the thoracic segments their identities. The proboscipedia gene appears to act solely in adults, however in its absence, the labial palps of the mouth are reworked into legs (Wakimoto et al. There are three protein-coding genes discovered in this complicated: ultrabithorax (ubx), which is required for the identification of the third thoracic phase; and the stomach A (abdA) and Abdominal B (AbdB) genes, that are responsible for the segmental identities of the stomach segments (Sбnchez-Herrero et al. The deadly phenotype of the triple-point mutant Ubx-, abdA-, AbdB- is identical to that ensuing from a deletion of the complete bithorax complicated (Casanova et al. The chromosome area containing each the Antennapedia complicated and the bithorax complicated is usually referred to as the homeotic complicated (Hom-C). Because these genes are responsible for the specification of fly physique parts, mutations in them result in weird phenotypes. In 1894, William Bateson referred to as these organisms "homeotic mutants," and so they have fascinated developmental biologists for decades. For instance, the physique of the conventional grownup fly accommodates three thoracic segments, all of which produce a pair of legs. The third thoracic phase produces a set of wings and a set of balancers known as as|often recognized as} halteres. When the ultrabithorax gene is deleted, the third thoracic phase (which is characterized by halteres) becomes reworked into one other second thoracic phase. Similarly, the Antennapedia protein is usually used to specify the second thoracic phase of the fly. But when flies have a mutation whereby the Antennapedia gene is expressed within the head (as nicely as within the thorax), legs somewhat than antennae grow out of the head sockets (Figure 9. In the recessive mutant of Antennapedia, the gene fails to be expressed within the second thoracic phase, and antennae sprout out of the leg positions (Struhl 1981; Frischer et al. These major homeotic selector genes have been cloned and their expression analyzed by in situ hybridization (Harding et al. Transcripts from every gene can be detected in particular regions of the embryo and are particularly distinguished within the central nervous system (see Figure 9. Initiating the patterns of homeotic gene expression the initial domains of homeotic gene expression are influenced by the gap genes and pair-rule genes. For instance, the expression of the abdA and AbdB genes is repressed by the gap gene proteins Hunchback and Krьppel. This inhibition prevents these abdomen-specifying genes from being expressed within the head and thorax (Casares and Sбnchez-Herrero 1995). The boundaries of homeotic gene expression are quickly confined to the parasegments outlined by the Fushi tarazu and Even-skipped proteins (Ingham and Martinez-Arias 1986; Mьller and Bienz 1992).
Buy 250 mg mysoline
The mom determined to take him to a pediatrician when, as she put it, the child all of a sudden "threw a match. When questioned further, the mom admitted that the child appreciated sucking the peeling paint on the railings exterior the house. This was confirmed by finding that the blood lead level was in extra of 50 g per one hundred mL. A 54-year-old man all of a sudden developed severe pain down both legs within the distribution of the sciatic nerve. A diagnosis was manufactured from central protrusion posteriorly of the intervertebral disc between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae. By what anatomical route is tetanus toxin believed to move from a wound to the central nervous system? Following an car accident, a 35-year-old man was seen within the emergency department with fractures of the fifth and sixth ribs on the proper aspect. In order to relieve the pain and discomfort experienced by the patient when respiratory, the physician determined to block the proper fifth and sixth intercostal nerves by injecting a neighborhood anesthetic, lidocaine (Xylocaine), across the nerve trunks. Are the large-diameter or the small-diameter nerve fibers more prone to the action of the drug? He had consumed a large amount of|a considerable amount of} whiskey and appeared to have lost management of his legs. [newline]He sat down on a chair within the hallway and was quickly in a deep, stuporous sleep, together with his proper arm suspended over the again of the chair. The next morning, he awoke with a severe headache and loss of the usage of} his proper arm and hand. During examination within the emergency department, it was discovered that the patient had severe paralysis involving branches of the medial cord of the brachial plexus and the radial nerve. The diagnosis was neuropraxia, which occurred as the result of|the results of} the pressure of the again of the chair on the concerned nerves. A well-known politician was attending a rally when a youth all of a sudden stepped forward and shot him within the again. During examination within the emergency department, it was discovered that the bullet had entered the again obliquely and was lodged within the vertebral canal on the level of the eighth thoracic vertebra. An 18-year-old lady visited her physician because of|as a outcome of} she had burns, which she had not felt, on the tips of the fingers of the proper hand. On physical examination, severe scarring of the fingers of the proper hand was noted. Testing the sensory modalities of the skin of the complete patient showed total loss of pain and temperature sensation of the distal half of} the proper higher limb. Definite muscular weak point was demonstrated within the small muscle tissue of the proper hand, and a small amount of weak point also was discovered within the muscle tissue of the left hand. A 35-year-old man, while strolling previous some workmen who had been digging a hole within the road, all of a sudden grew to become aware of a foreign body in his left eye. A 60-year-old man visited his physician because of|as a outcome of} for the previous three months he had been experiencing an agonizing stabbing pain over the middle half of} the proper aspect of his face. Using your data of neuroanatomy, explain why hairs are so delicate to touch. On physical examination, many signs of the syphilitic disease had been current,including a complete lack of deep sensation to pain. Using your data of neuroanatomy, explain how deep pain sensation is normally experienced. While finishing up a physical examination of a patient, the physician requested the patient to cross his knees and loosen up his leg muscle tissue. The left ligamentum patellae was then struck well with a reflex hammer, which immediately produced an involuntary partial extension of the left knee joint (the knee-jerk check was positive). How does the central nervous system receive nervous information from the quadriceps femoris muscle so that it could respond reflexly by extending the knee? A 55-year-old man affected by syphilis of the spinal cord presented attribute signs and signs of tabes dorsalis. He had experienced severe stabbing pains within the stomach and legs for the last 6 months. When requested to walk, the patient was seen to achieve this with a broad base, slapping the feet on the bottom. Using your data of neuroanatomy, explain how a traditional particular person in a position to|is ready to} perceive the place of the extremities and detect vibrations. Using your data of pharmacology,name two medicine that act as competitive blocking agents on skeletal neuromuscular junctions. Name a drug that may result in flaccid paralysis of skeletal muscle by inflicting depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. In instances of severe food poisoning,the organism Clostridium botulinum discovered to be responsible. During a ward round, an orthopedic surgeon stated that the degree of muscular atrophy that happens in a limb immobilized in a forged is completely completely different from the degree of muscular atrophy that follows part of the motor nerve provide to muscle tissue. A 57-year-old man visited his physician due to pain in the proper buttock that extended down the proper leg,the again of the thigh,the outer aspect and again of the calf,and the outer border of the foot. The patient gave no history of previous injury but stated that the pain began about three months ago as a dull,low backache. When requested if the pain had ever disappeared, he replied that on two separate occasions the pain had diminished in intensity, but his again remained "stiff" an everyday basis}. Sometimes,he experienced a pins and needles sensation along the outer border of his proper foot. After an entire physical examination, a diagnosis was manufactured from herniation of a lumbar intervertebral disc. Using your data of anatomy,state which intervertebral disc is most probably to have been herniated. A 61-year-old lady was seen by her physician because of|as a outcome of} she was experiencing a taking pictures, burning pain within the left aspect of her chest. Three days later, a group of localized papules appeared on the skin covering the left fifth intercostal area. One day later, the papules grew to become vesicular; a couple of of} days later, the vesicles dried up into crusts. The patient also noticed that there was some loss of sensibility over the left aspect of the chest. Using your data of anatomy, state the phase of the spinal cord concerned with the disease. While inspecting the sensory innervation of the skin of the head and neck in a patient, a medical pupil had difficulty remembering the dermatomal pattern on the junction of the head with the neck and on the junction of the neck with the thorax. On physical examination, a 30-year-old man was discovered to have weak point and diminished tone of the rhomboid muscle tissue, deltoids, and biceps brachii on either side of the body. The biceps tendon jerk was absent on the proper aspect and diminished on the left aspect. The muscle tissue of the trunk and decrease limb showed increased tone and exhibited spastic paralysis. Radiology of the vertebral column revealed the presence of vertebral destruction a tumor arising throughout the vertebral canal. Using your data of anatomy, reply the following questions: (a) Which vertebra is likely to to|prone to} have the tumor throughout the vertebral canal? Name three medical situations that could result in a loss of tone of skeletal muscle. A 69-year-old man with superior tabes dorsalis was requested to stand together with his toes and heels collectively and his eyes closed. He immediately began to sway violently, and if the nurse had not held on to his arm, he would have fallen to the bottom (positive Romberg test). Why was it very important for this patient to maintain his eyes open in order to to} stay upright? A 63-year-old man with reasonably superior Parkinson disease was disrobed and requested to walk in a straight line within the inspecting room. The physician noticed that the patient had his head and shoulders stooped forward, the arms barely abducted, the elbow joints partly flexed, and the wrists barely extended with the fingers flexed on the metacarpophalangeal joints and extended on the interphalangeal joints. It was noted that on starting to walk, the patient leaned forward and slowly shuffled his feet. The farther he leaned forward, the more shortly he moved his legs, in order that by the point he had crossed the room, he was nearly operating. The palms showed a rough tremor, and the muscle tissue of the higher and decrease limbs showed increased tone within the opposing muscle groups when the joints had been passively moved. Parkinson disease, or the parkinsonian syndrome, can be caused by quantity of|numerous|a variety of} pathologic situations,but they normally intervene within the normal operate of the corpus striatum or the substantia nigra or both.

Proven 250 mg mysoline
Microvilli Ependymal epithelium of choroid plexus Cilia Tight junction Basement membrane Endothelium of blood capillary Blood Cavity of ventricle full of cerebrospinal fluid Figure 16-16 Microscopic construction of the choroid plexus exhibiting the path taken by fluids in the formation of cerebrospinal fluid. The dashed line indicates the course taken by fluid inside the cavities of the central nervous system. It then strikes superiorly over the lateral facet of each cerebral hemisphere, assisted by the pulsations of the cerebral arteries. Some of the cerebrospinal fluid strikes inferiorly in the subarachnoid house across the spinal twine and cauda equina. Here,the fluid is at a dead end,and its further circulation depends on the pulsations of the spinal arteries and the actions of the vertebral column, respiration, coughing, and the altering of the positions of the body. The cerebrospinal fluid not only bathes the ependymal and pial surfaces of the mind and spinal twine but also penetrates the nervous tissue along the blood vessels. Should the venous stress rise and exceed the cerebrospinal fluid stress, compression of the ideas of the villi closes the tubules and prevents the reflux of blood into the subarachnoid house. Some of the cerebrospinal fluid probably is absorbed directly into the veins in the subarachnoid house, and some presumably escapes by way of the perineural lymph vessels of the cranial and spinal nerves. Because the production of cerebrospinal fluid from the choroid plexuses is fixed, the speed of absorption of cerebrospinal fluid by way of the arachnoid villi controls the cerebrospinal fluid stress. Absorption the primary websites for the absorption of the cerebrospinal fluid are the arachnoid villi that project into the dural venous sinuses, particularly the superior sagittal sinus. The arachnoid villi most likely to|are inclined to} be grouped together to type elevations generally known as|often known as} arachnoid granulations. Structurally, each arachnoid villus is a diverticulum of the subarachnoid house that pierces the dura mater. The arachnoid diverticulum is capped by a thin cellular layer, which, in flip, is roofed by the endothelium of the venous sinus. The arachnoid granulations improve in quantity and dimension with age and tend to become calcified with advanced age. The absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the venous sinuses occurs when the cerebrospinal fluid stress exceeds the venous stress in the sinus. Electron-microscopic research of the arachnoid villi indicate that fine tubules lined with endothelium allow a direct circulate of fluid from the subarachnoid house into the lumen of the venous sinuses. Extensions of the Subarachnoid Space A sleeve of the subarachnoid house extends across the optic nerve to the back of the eyeball. The central artery and vein of the retina cross this extension of the subarachnoid house to enter the optic nerve, and so they could also be} compressed in sufferers with raised cerebrospinal fluid stress. Small extensions of the subarachnoid house additionally occur across the other cranial and spinal nerves. It is here that some communication could occur between the subarachnoid house and the perineural lymph vessels. The subarachnoid house additionally extends across the arteries and veins of the mind and spinal twine at points the place they penetrate the nervous tissue. The pia mater, nonetheless, shortly fuses with the outer coat of the blood vessel under the floor of the mind and spinal twine,thus closing off the subarachnoid house. B: Magnified view of an arachnoid granulation exhibiting the path taken by the cerebrospinal fluid into the venous system. This stability is offered by isolating the nervous system from the blood by the existence of the so-called blood-brain barrier and the bloodcerebrospinal fluid barrier. Blood-Brain Barrier the experiments of Paul Ehrlich in 1882 showed that dwelling animals injected intravascularly with vital dyes, similar to trypan blue, demonstrated staining of all the tissues of the body except the mind and spinal twine. These observations led to the idea of a blood-brain barrier (for which blood-brainspinal twine barrier can be a more accurate name). The permeability of the blood-brain barrier is inversely related to the size of the molecules and directly related to their lipid solubility. Gases and water cross readily by way of the barrier, whereas glucose and electrolytes cross more slowly. The barrier kind of} impermeable to plasma proteins and other large organic molecules. Compounds with molecular weights of about 60,000 and better remain Area of the medulla on the floor of the fourth ventricle just rostral to the opening into the central canal. Structure Examination of an electron micrograph of the central nervous system shows that the lumen of a blood capillary is separated from the extracellular spaces across the neurons and neuroglia by the next constructions: (1) the endothelial cells in the wall of the capillary, (2) a steady basement membrane surrounding the capillary outdoors the endothelial cells, and (3) the foot processes of the astrocytes that adhere to the outer floor of the capillary wall. When the dense markers are launched into the extracellular spaces of the neuropil, they cross between the perivascular foot processes of the astrocytes so far as the endothelial lining of the capillary. In molecular phrases, the blood-brain barrier is thus a steady lipid bilayer that encircles the endothelial cells and isolates the mind tissue from the blood. This explains how lipophilic molecules can readily diffuse by way of the barrier, whereas hydrophilic molecules are excluded. In reality, in these areas the place the blood-brain barrier appears to be absent, the capillary endothelium accommodates fenestrations across which proteins and small organic molecules could cross from the blood to the nervous tissue. It has been suggested that areas similar to the area postrema of the floor of the fourth ventricle and the hypothalamus could serve as websites at which neuronal receptors could pattern the chemical content material of the plasma directly. The hypothalamus, which is concerned in the regulation of the metabolic exercise of the body, might result in appropriate modifications of exercise, thereby defending the nervous tissue. BloodCerebrospinal Fluid Barrier There is free passage of water, gases, and lipid-soluble substances from the blood to the cerebrospinal fluid. Macromolecules similar to proteins and most hexoses aside from glucose are unable to enter the cerebrospinal fluid. It has been suggested that a barrier just like the blood-brain barrier exists in the choroid plexuses. Peripheral nerves are isolated from the blood in the same method because the central nervous system. The use of electron-dense markers has not been completely successful in localizing the barrier exactly. Horseradish peroxidase injected intravenously appears as Choroidal epithelial cells a coating on the luminal floor of the endothelial cells, and in many of} areas examined, it did cross between the endothelial cells. It is possible that the tight junctions between the choroidal epithelial cells serve as the barrier. Blood-Brain and BloodCerebrospinal Fluid Barriers 465 Cerebrospinal fluid in subarachnoid house Dura Arachnoid Dura mater mater mater Connective tissue network in subarachnoid house Cells of pia mater A A Foot process of astrocyte Cavity of ventricle full of cerebrospinal fluid Basement membrane Tight junction Ependymal cell B Processes of astrocytes and other glial cells Figure 16-23 Section of the cerebrospinal fluid-brain interface. It is interesting, nonetheless, to think about the constructions that separate the cerebrospinal fluid from the nervous tissue. Three websites have to be examined: (1) the pia-covered floor of the mind and spinal twine, (2) the perivascular extensions of the subarachnoid house into the nervous tissue, and (3) the ependymal floor of the ventricles. The pia-covered floor of the mind consists of a loosely arranged layer of pial cells resting on a basement membrane. No intercellular junctions exist between adjacent pial cells or between adjacent astrocytes; therefore, the extracellular spaces of the nervous tissue are in almost direct continuity with the subarachnoid house. The prolongation of the subarachnoid house into the central nervous tissue shortly ends under the floor of the mind, the place the fusion of the outer masking of the blood vessel with the pial masking of the nervous tissue occurs. The ventricular floor of the mind is roofed with columnar ependymal cells with localized tight junctions. Intercellular channels exist that allow free communication between the ventricular cavity and the extracellular neuronal house. Functional Significance of the BloodBrain and BloodCerebrospinal Fluid Barriers In regular situations, the blood-brain and bloodcerebrospinal fluid limitations are two important semipermeable limitations that defend the mind and spinal twine from doubtlessly dangerous substances whereas permitting gases and nutriments to enter the nervous tissue. There is an extension of the intracranial subarachnoid house forward across the optic nerve to the back of the eyeball. A rise of cerebrospinal fluid stress caused by an intracranial tumor will compress the skinny walls of the retinal vein as it crosses the extension of the subarachnoid house to enter the optic nerve. This will result in congestion of the retinal vein,bulging forward of the optic disc, and edema of the disc; the final condition is referred to as papilledema. Since both subarachnoid extensions are steady with the intracranial subarachnoid house, both eyes will exhibit papilledema. Sometimes, inflammatory exudate secondary to meningitis will block the subarachnoid house and impede the circulate of cerebrospinal fluid over the outer floor of the cerebral hemispheres.
Purchase mysoline 250 mg
Incessant ovulation theory (Fathalla, 1971) suggests repeated ovulatory trauma to the ovarian epithelial lining is a promoting issue for carcinogenesis. Combined oral contraceptive pills scale back the risk significantly as additionally repeated pregnancies. Breastfeeding, tubal ligation and hysterectomy have been related to discount in the threat. Thus, in the dialogue to comply with, only the malignant epithelial tumors might be described. Primary epithelial: Malignant epithelial tumors embody each cystic and strong varieties. These may arise de novo as malignant or more generally, they end result from malignant changes of benign cystic tumors. Endometrioid carcinoma is related to endometrial carcinoma in 20 p.c and ovarian endometriosis in 10 p.c circumstances. This lace-like pattern characterised by slit-like spaces between the papillae {is due to|is of} intensive coalescence of papillae fig. Microscopic look reveals adenocarcinoma or carcinoma without adenomatous pattern. Microscopic image: the histologic look in every kind is tabulated in Table 23. The modes of spread are: Transcoelomic Lymphatic Direct Hematogenous Transcoelomic: Implantation of malignant cells happens by: Direct exfoliation of cells as in papillary cyst adenocarcinoma. Multiple secondary deposits are shaped on the peritoneal surfaces specially in the pouch of Douglas, in the omentum, diaphragm, retroperitoneal nodes and serous surfaces of the abdominopelvic organs. The pelvic nodes involved through peritoneal permeation into the subperitoneal lymphatics (Table 23. The left supraclavicular nodes are enlarged obstruction of the efferent lymphatic channel of the nodes by the tumor emboli, because it enters the thoracic duct simply prior to its drainage into the left subclavian vein. Retrograde lymphatic spread in superior illness may occur to the inguinal nodes through the round ligament. Hematogenous: the blood stream metastasis is late and the involved organs are lungs, liver, bones, and so forth. Liver: the involvement of liver is normally blood borne when the heart are involved. Even in main malignancy, the contralateral involvement may be retrograde lymphatic spread through paraaortic glands. Uterus: the body is generally affected both lymphatics or through transtubal spread. This is facilitated by the increased adverse suction created by liver during respiration. This is because of free communication of submesothelial network of lymphatic capillaries with the corresponding plexuses on the thoracic floor of the diaphragm underlying the pleura on the best aspect proper pleural effusion. Biswajit Ghosh, Burnpur) neoplasms in postmenopausal and about 20 p.c in premenopausal women are malignant. Symptoms: In its early stage, ovarian carcinoma is a notoriously silent illness (asymptomatic). Growth involving one or each ovaries with pelvic extension (A) extension and/or metastases to the uterus and/or tubes (b) extension to different pelvic tissues (c) Tumor both Stage iiA or iib, however tumor on floor on one or each ovaries; or with capsule(s) ruptured or with ascites present containing malignant cells or with optimistic peritoneal washings. Tumor involving one or each ovaries with peritoneal implants exterior the pelvis and/or optimistic retroperitoneal or inguinal lymph nodes. Tumor is proscribed to the true pelvis however with histologically proven malignant extension to small bowel or omentum. Signs: the following are the findings in a longtime case of ovarian malignancy. W to identify the extent of lesion x Straight X-ray chest to exclude pleural effusion x x x be enlarged. Per vaginum x the uterus separated from the mass felt x x x x x per abdomen. Sonography is of restricted help however can be employed to detect involvement of the omentum or contralateral ovary. Clinical: Clinical diagnosis in early stage may be very much deceptive because of: y no age specificity: Although more prevalent beyond the age of forty five (40% of ovarian neoplasms are malignant), no age is proof against ovarian cancer. All physicians should be aware of|concentrate on|pay consideration to} the possible significance of persistent gastrointestinal symptoms in women over the age of 40 with a history of ovarian dysfunction. The cumulative results of such vagaries explain the fact that|the truth that} at the time of diagnosis, about 70 p.c of sufferers with epithelial carcinomas have metastases exterior the pelvis. The most common websites of metastases are-peritoneum (85%), omentum (70%), contralateral ovary (70%), liver (35%), lung (25%) and uterus (20%). In established and/or superior circumstances of malignancy, the clinical options as talked about earlier are sufficient to arrive at a diagnosis. Examination beneath anesthesia useful in uncertain circumstances, specially in an overweight affected person. Histological diagnosis: All ovarian tumors irrespective of their nature must be subjected to histologic examination. This not only confirms the diagnosis but also identifies the type and grade of malignancy. As such, screening goals at detecting early ovarian malignancy in asymptomatic women. Till date no specific method of screening for early detection of epithelial ovarian cancer is out there. Elevated degree indicates bulky residual illness or tumor recurrence or resistant clones to chemotherapy. Ultrasound imaging: Transvaginal shade Doppler imaging has been place to} differentiate benign from malignant tumors by assessment of its vascular provide and intratumoral blood circulate. Recently three dimensional, contrast enhanced, energy Doppler sonography is found to be more diagnostic. A systematic (visual and manual) exploration - palpation of liver, gastrointestinal tract, subdiaphragmatic space, omentum and paraaortic lymph nodes. Pelvic exploration - nature of the tumor, extent of adhesions, condition of the contralateral ovary, uterus and tubes and palpation of pelvic lymph nodes. Any metastatic deposit over the peritoneal surfaces, beneath floor of the diaphragm ought to be biopsied. In the absence of any metastatic illness, multiple of} peritoneal biopsy, scraping from the diaphragm for cytology ought to be taken. Young girl Unilateral oophorectomy (fertility sparing surgery) Routine comply with up and monitoring Completion of household Removal of the uterus and the opposite ovary. In Stage Ia, G3 illness and others stage I illnesses: Staging Laparotomy Hysterectomy and bilateral Salpingo-oophorectomy. This includes: Total stomach hysterectomy bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, complete omentectomy, retroperitoneal lymph node sampling and resection of any metastatic tumor. Optimum cytoreductive surgical procedure is aimed to scale back the residual tumor load < 12 cm in diameter. Practical guidelines y Liberal vertical incision to minimize probability of rupture of the tumor and to facilitate better exploration. Removal of omental cake by cytoreductive surgical procedure improves subsequent chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Large tumor masses have big number of poorly oxygenated cells in the "resting" section (Go) (see p. In all different stage I illness Adjuvant chemotherapy with carboplatin and paclitaxel for six cycles. Platinum compounds (cisplatin, carboplatin) are the most effective medicine in terms of|when it comes to|by means of} tumor response and survival fee (see p. Taxane derivatives (paclitaxel, docetaxel) are found to be very effective in ovarian cancer (see p. Taxane derivatives stop cell division by polymerization of microtubules and making them excessively steady. Paclitaxel is really helpful as the primary x Combination chemotherapy: Drugs acting in numerous ways on the cell cycle (see p. Currently paclitaxel and carboplatin combination chemotherapy is found to have better survival fee in superior ovarian cancer (Tables 23.
References:
- https://westafricaneducatednursesdotorg.files.wordpress.com/2016/02/care-of-a-client-with-liver-cirrhosis.pdf
- https://knowledge.uli.org/-/media/files/emerging-trends/2021/emerging-trends-in-real-estate-united-states-and-canada-2021---final.pdf?rev=aca3ce34701146b1b581c35fbef8da6c&hash=284FD6C4372CAA119505CE9701021E4A
- https://www.ojp.gov/sites/g/files/xyckuh241/files/media/document/written-kupers.pdf
- https://www.cmrr.umn.edu/~kulesa/Biosafety.pdf
.png)