Trusted speman 60pills
In moderate pimples there are moderate numbers of papules and pustules (10-40) and there may be be} mild illness of the trunk. Moderately severe pimples is characterized by quite a few papules and pustules (40-100) and occasional larger, deeper inflammatory lesions. In severe pimples heaps of|there are numerous} massive, painful nodular or pustular lesions along with smaller papules, pustules, and comedones. Acne is a illness of the pilosebaceous unit characterized by sebaceous gland hyperplasia with elevated sebum manufacturing, altered follicular progress and desquamation, colonization with Propionibacterium acnes and an inflammatory immune response. This follicular plugging and elevated sebum manufacturing causes follicular enlargement or the "microcomedo". The immune response is each cell-mediated (with each instant and delayed sort hypersensitivity reactions) and humoral with anti Propionibacterium acnes antibodies beginning a complement cascade resulting in an inflammatory reaction. Topical antimicrobial agents are effective in the treatment of inflammatory illness. Oral antibiotics must be used for brief time period (3-6 months) whereas topical antibiotics and topical retinoids are used for maintenance remedy. They are effective in each the treatment and prevention of the first lesion of pimples, the comedo, and limit the formation of inflammatory lesions. Topical retinoids must be started with an each 3rd night time schedule and progressively elevated to nightly as tolerated. Isotretinoin reduces the scale and secretions of sebaceous glands, secondarily inhibit the growth of P. Oral retinoid use requires subspecialist referral to a provider who participates in the ipledge program (a necessary program to reduce threat of pregnancy associated complications of oral retinoids). Remember to inform sufferers that remedy can take 6-8 weeks earlier than change is seen and that the pimples may worsen earlier than it gets better. Suggestions for Learning Activities Have the scholar review drugs which are be} related to pimples. An athletic twelve-year-old boy complains of ache just under the best knee when operating and taking part in} soccer. Definition for Specific Terms: Tibial tuberosity- Oblong elevation on the proximal, anterior aspect of the tibia to which the patellar tendon attaches. Review of Important Concepts: Historic Points Time course of presentation-duration of signs will decide if that is acute or persistent. Relation to time of day/activity-the fact that that|proven truth that} his signs are worse with exercise suggests a mechanical issue. If his signs have been worse in the morning and/or after intervals of inactivity, then can be more involved about inflammatory process. Associated symptoms-does he have other joint ache, fever, rash, weight reduction, etc. Signs of inflammation: It is important to examine the knee for indicators of inflammation similar to swelling, redness, warmth, effusion, ache with motion, and decreased range of motion. Tenderness at the tibial tuberosity: Tenderness at the tibial tuberosity suggests some sort of injury/inflammation at the patellar tendon insertion. This is a traction apophysitis of the tibial tubercle outcome of} repetitive strain and persistent avulsion of the secondary ossification middle of the tibial tuberosity. It happens outcome of} the strong pull of the quadriceps muscle during sporting actions. It presents in rising children (typically women 8-12 years and boys 12-15 years) with ache, swelling, tenderness over the tibial tuberosity. Pain is elevated with actions that involve leaping and/or kneeling and sometimes begin quickly after a baby has begun a new new} sporting exercise. However, plain x-rays of the knee may be be} indicated if signs are P a g e 113 unilateral to rule out other circumstances similar to acute tibial apophyseal fracture, infection, or tumor. Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome (traction apophysitis of the inferior patellar pole) b. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (particularly enthesitis-associated arthritis subtype) 4. Most sufferers respond to conservative, nonoperative treatment together with limitation of exercise, ice, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and bodily remedy. If he had bilateral knee ache and swelling how would that change your method to his analysis and treatment P a g e 114 Common Acute Pediatric Illness: Limb & Joint, Case #3 Written by Jennifer Soep, M. Definition for Specific Terms: Limp- A limp is any alteration in the normal two component (stance and swing phases) rhythmic gait. Other types of limp embody spastic, short-leg, stooped, foot drop, toe-walking, vaulting and Trendelenberg. Relation to time of day/activity: If his signs are worse with exercise, then that might counsel a mechanical issue and if his signs are worse in the morning and/or after intervals of inactivity, then that ought to increase concern for an inflammatory process. Has he just lately started any new actions or does he take part in common exercise/sports that could possibly be} inflicting or contributing to his signs Associated signs: Does he have other joint ache to counsel that that is affecting quantity of} joints or simply isolated to one hip Examination of the hip It is important to perform a complete examination of the hip together with palpation, range of motion, strength. One should examine the stomach to rule out referred ache from a primary abdominal/pelvic process. The examiner should examine the opposite joints in his decrease extremity to evaluate for tenderness, swelling, warmth, weak point, or irregular reflexes. Given his lack of fever, infectious etiologies similar to septic joint and osteomyelitis are much less probably l. If that is acute in nature and never very severe, no additional work-up may be be} essential. If he had a historical past of fever, how would that change your method to his analysis and work-up P a g e 116 Common Acute Pediatric Illness: Limb & Joint, Case #6 Written by Jennifer Soep, M. How would your differential analysis change if she later developed swelling of the ankle and wrist Review of Important Concepts: Historic Points Time course of presentation: Duration of signs will decide if that is acute or persistent. Any preceding illness similar to higher respiratory infection, gastroenteritis, or sore throat to counsel a reactive process Any tick bites, cat scratches, unpasteurized dairy product to counsel specific infectious diseases Normally, the knee must be cooler than the shin so if it is warmer, that suggests inflammation of the knee 2. Children with a septic joint often have severe ache with motion and important limitation in motion three. Look for leg length discrepancy Measure from the anterior superior iliac spine to the medial malleolus; the involved leg can grow longer in persistent arthritis (that happens over an extended time period not acutely and this case is acute). Evaluate for muscle atrophy that might counsel that she has had long-standing decreased range of motion and subsequently decreased muscle use. Observation of her gait One should observe her walking to decide limp 7. Examine the skin for rashes that will counsel systemic causes of her knee swelling similar to erythema marginatum (rheumatic fever), erythema migrans (Lyme Disease) or the salmon-colored, migratory rash related to systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Other diagnoses on the differential embody: Post-viral arthritis Post-strep arthritis Rheumatic fever Juvenile idiopathic arthritis Lyme arthritis Osteomyelitis Trauma 2. If she presents with quantity of} joints involved, an infectious etiology similar to a septic arthritis or osteomyelitis turn out to be much less probably. If that is an additive process, then juvenile idiopathic arthritis would turn out to be more probably since this might involve quantity of} joints. If septic arthritis is being thought of, then the joint must be tapped and the fluid sent for cell count, differential, glucose and tradition. Lyme antibodies and Western Blot if the patient has traveled to a Lyme endemic space Rheumatoid Factor d.
Syndromes
- Brain damage
- PPD skin test to check for a prior tuberculosis infection
- Blood poisoning (septicemia)
- Skull x-rays
- General level of comfort
- Tyzine
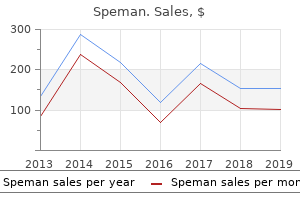
Effective 60pills speman
Consider a bone marrow biopsy Megakaryocyte morphology can recommend essential thrombocythemia. Reactive neutrophilia is readily obvious from the history (inflammation, an infection, extreme burns, glucocorticoid, epinephrine) and from examination of a peripheral smear (D�hle bodies, toxic granulations). A extended eosinophilia of unknown cause with the potential to affect on} multiple of} organs by eosinophil infiltration. Note that a number of} drugs (nitrofurantoin, penicillin, phenytoin, ranitidine, sulfonamides) and toxins (Spanish toxic oil, tryptophan) have been reported to cause eosinophilia. Differentiated as follows: Intrinsic bone marrow failure: Aplastic anemia, myelodysplasia, acute leukemia, myeloma, drugs (chemotherapy, chloramphenicol, sulfonamides, antibiotics). Drugs: Gold, chloramphenicol, clozapine, sulfonamides, tolbutamide, phenytoin, carbamazepine, heaps of|and lots of} others. Abnormal erythropoiesis: Hereditary spherocytosis, sickle cell anemia, drugs (phenytoin, chloramphenicol). Bone marrow biopsy: Abnormal erythroid maturation and characteristic giant pronormoblasts are seen in parvovirus B19 an infection. Its prognosis is said to the share of blasts, cytogenetics, and the number of cytopenias (see Table 9. Supportive care with transfusions and development factors (generally related to a poor response). Both neutrophils in this slide show hypogranulation and hypolobation (pseudo�PelgerHu�t anomaly), suggesting myelodysplasia. The most common of the myeloproliferative problems, it reveals no clear age predominance. Symptoms are associated to greater blood viscosity and expanded blood quantity and embody dizziness, headache, tinnitus, blurred imaginative and prescient, and plethora. Erythromelalgia is regularly related to polycythemia vera and is characterized by erythema, warmth, and ache in the distal extremities. Diagnostic criteria from the Polycythemia Vera Study Group are outlined in Table 9. Helpful drugs embody the next: Hydroxyurea or anagrelide to hold platelet rely < 400,000; each drugs have been proven to stop thromboses. The present normal is to suggest low-dose aspirin in sufferers with erythromelalgia or other microvascular manifestations. B4: Characteristic bone marrow colony development (almost never used) or low serum erythropoietin. The illness has three phases primarily based on the share of blasts in peripheral blood: Chronic part: Bone marrow and circulating blasts < 10%. Major remissions can nearly always be achieved with imatinib mesylate (Gleevec). The sturdiness of these responses remains uncertain, however after five years > 80% of sufferers stay in cytogenetic remission. Myelofibrosis (Agnogenic Myeloid Metaplasia) Fibrosis of bone marrow leading to extramedullary hematopoiesis (marked splenomegaly, bizarre peripheral blood smear). Affects adults > 50 years of age and may be 2� to marrow insults, including other myeloproliferative problems, radiation, toxins, and metastatic malignancies. Note the massive number of teardrop cells suggestive of bone marrow infiltrative illness. Splenectomy or splenic irradiation is acceptable if the spleen is painful or if transfusion requirements are unacceptably excessive. Essential Thrombocythemia A clonal disorder with elevated platelet counts and an inclination towards thrombosis and bleeding. Occasionally presents with erythromelalgia, pruritus, and thrombosis (at risk for each arterial and venous clots). Diagnosed by a persistent platelet rely > 600,000 with no other explanation for thrombocytosis. Not part of of} diagnostic criteria, however may be helpful in distinguishing essential thrombocythemia from other causes of thrombocytosis. Consider platelet pheresis for elevated platelets with extreme bleeding or clotting. Paraprotein: Depression of normal immunoglobulins results in infections; extra protein might cause renal tubular illness, amyloidosis, or narrowed anion hole (due to positively charged paraproteins). Myeloma is characterized by purely osteolytic lesions, so bone scan is and alkaline phosphatase is normal. Autologous stem cell transplantation is usually carried out and appears to delay survival. Amyloidosis A rare disorder characterized by the deposition of amyloid materials throughout the body. Radiation therapy and/or orthopedic surgical procedure for impending pathologic fractures in weight-bearing bones. Soft tissues: Macroglossia, carpal tunnel syndrome, "shoulder pad signal," "raccoon eyes. The choice of biopsy site decided by} the clinical scenario: Biopsy of involved tissue has the very best yield. Fat pad aspirate or rectal biopsies are usually low yield however minimally invasive. One percent per yr convert to myeloma, so monitor frequently for the development of myeloma. Exam findings embody lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, and dilated, tortuous veins on retinal examination ("sausage link" veins). Hyperviscosity syndrome: Elevated serum viscosity from IgM can happen, inflicting blurry imaginative and prescient, complications, bleeding, and strokes. Emergent plasmapheresis can be utilized to lower serum viscosity by removing the IgM paraprotein. Bleeding is often petechial or purpuric, occurring around areas of trauma or pressure. Hemophilia Hemophilias are X-linked deficiencies in clotting factors, so virtually all sufferers are male. Patients should be taught to self-administer factor in the occasion of spontaneous bleeding. Major procedures: Replace with factor focus to one hundred pc activity period of|during|throughout} the procedure with levels of a minimum of|no less than} 50% for 10�14 days (until the wound is healed). Acute bleeding: Minor bleeding: Replace with factor focus to 25�50% activity. Major bleeding (hemarthroses, deep tissue bleeding): Replace to 50% activity for 2�3 days. Exhibits a bleeding sample much like that of a platelet disorder (petechiae, mucosal bleeding/epistaxis, heavy menses, exacerbated by aspirin). Clotting: Digital gangrene, renal cortical necrosis, underlying critical illness (typically sepsis, trauma, or malignancy). Adjuncts embody the next: Cryoprecipitate to achieve a fibrinogen stage > 100�150 mg/dL. Platelet transfusions in the setting of extreme bleeding and a platelet rely < 50. A hematologist should be involved if a heparin drip is being utilized in light of the danger of bleeding. However, if the patient is over the age of 60, a bone marrow biopsy is really helpful to evaluate for myelodysplasia as thrombocytopenia. Risk factors embody being pregnant, surgical procedure, smoking, extended immobilization, hospitalization for any cause, and energetic malignancy. An inherited thrombophilic state additionally be} suspected in the following conditions: An unprovoked clot occurring in a young person|a teenager|an adolescent} (< 50 years of age). Splenectomy Danazol N/A 600 mg/day Anti-RhD 50 g/kg � 1 80�90% response fee Induces hemolytic anemia; works solely with Rhpatients. Diagnostic testing in a nonacute setting proceeds as follows: Best carried out when contemplating whether or not to stop or delay anticoagulation. A typical "hypercoagulable panel" for venous thrombophilia includes the next: Factor V Leiden. Evaluation for rare causes of thrombophilia should be carried out solely after frequent causes have been eliminated and in session with a hematologist. Heterozygotes have a three- to eightfold in the risk of venous thrombosis; homozygotes have a 50to 80-fold risk.
Quality speman 60pills
The student might not have built this pattern but, so questions thirteen under might be be} used to derive an inventory of possibilities, and the most probably answer will be the one which appears on all three lists. Some children could have dacrocystitis and could have eye drainage, however typically they may even have a small swelling over the blocked tear duct on the medial canthus as nicely. Some viruses might trigger both conjunctivitis and pneumonia, however usually concurrently, not 6 weeks later. Asthma might result on} an infant as younger as this and may have an related increase in eosinophils. Premature neonates have been finest studied, and we all know that eosinophilia is fairly common with most infectious processes seen in that inhabitants. Chlamydia is the most probably to be seen in an afebrile youngster, however some viral infections might not have much related fever. If the child acquired the an infection throughout delivery, why is it just now presenting at age 2 months Chlamydia is an intracellular pathogen that probably first infected the conjunctival epithelium after spread from infected maternal secretions, and from there colonized the nasopharyngeal mucosa and eventually spread down the airway to the lungs. Would things be different if the child had been treated for the conjunctivitis at age 10 days Treatment for presumed chlamydial conjunctivitis must be with oral drugs, not just topical, or the nasopharyngeal spread goes unchecked. With topical remedy, the eyes might improve however the youngster continues to be in danger for the pneumonitis; 5-13% of infants who acquire the pathogen will develop pneumonia if untreated. If the child is otherwise stable, ingesting and urinating usually, the decision on location of administration varies by "soft" standards � how far-off does the household reside Many practitioners deal with this condition empirically, without specific laboratory testing. At this age, azithromycin would probably be chosen though some feel the information regarding use of recent macrolides for this condition are sparse and thus use erythromycin. Suggestions for Learning Activities: � Ask the coed the questions in the clinical reasoning section above. This will require them to pare the presentation down to down to} the completely essential elements. Review chest radiographs on-line or along with your pleasant, neighborhood pediatric radiologist to see "hyperinflation with patchy infiltrates". Patients with lower lobe pneumonia might typically current with stomach pain and at times are initially evaluated for appendicitis. Does this patient have a history of earlier pulmonary infections or asthma that will complicate this present an infection If the patient appears unwell or poisonous, they may be more doubtless to|prone to} have a bacterial pneumonia or a complication of bacterial pneumonia similar to empyema. Pediatric patients with pneumonia might current with tachypnea and/or signs of respiratory distress including grunting, flaring, retractions and accessory muscle use. In addition, patients with a lobar pneumonia or consolidation might have bodily findings secondary to their consolidation (see findings listed under under clinical reasoning section: dullness to percussion, increased tactile fremitus, bronchophony, egophony, and whispered pectoriloquy). Since the findings on this case are unilateral, bronchiolitis, chlamydia, mycoplasma, asthma, early congestive heart failure, etc could be much less likely. On percussion you could notice dullness to percussion over airless area (area of pneumonia where the alveoli are crammed with fluid or inflammatory cells as in pneumonia). Pneumococcal pneumonia is more doubtless to|prone to} have a focal infiltrate with lobar consolidation. Indications for hospitalization are: Respiratory distress (retractions, flaring, grunting) Hypoxemia Young infants with suspected bacterial pneumonia Complications similar to empyema, large pleural effusion Septic look, hypotensive, poisonous showing Diagnosis: Bacterial Pneumonia, most probably Pneumococcal Suggestions for Learning Activities: Ask the coed questions under the "clinical reasoning" section to probe their serious about the case. Answer: Findings of pneumonia: focal crackles on auscultation, dullness to percussion, increased tactile fremitus, Bronchophony (where spoken words are louder, clearer over the affected area), Egophony (when the patient says "ee" it his heard as "ay"), Whispered Pectoriloquy (when the whispered words sound louder or clearer vs. P a g e 42 Common Pediatric Acute Illnesses: Cough, Case #6 Written by Kyra Len, M. A two-year-old youngster presents with the abrupt onset of cough, wheeze and tachypnea. Definition for Specific Terms: Tachypnea- As in most things in pediatrics, tachypnea is determined by age dependant regular values. Wheezes are relatively excessive pitched sounds that can occur when there are narrowed airways similar to asthma, bronchiolitis or even the presence of a international physique. What is the significance of the uneven findings on examination ("diminished air exchange and wheezing on the best") Unilateral decreased breath sounds and unilateral wheezing and cough are classic bodily findings of international physique aspiration, however might not all the time be current. Sometimes lung auscultation may be be} regular in a patient with international physique aspiration depending on the fabric and site of the international physique. If the obstruction is in the intrathoracic airway you could be more doubtless to|prone to} hear wheezing. While most patients who current with a international physique aspiration are afebrile, they may current with fever if the aspiration occurred weeks or months earlier and the child now has a ensuing obstructive P a g e 43 pneumonia or lung abscess. Also if the object aspirated was contaminated or chemically irritating, this may additionally manifest as fever. If patient is stable, the following step to evaluate a international physique is chest radiography. Indirect signs of a presence of international physique may be be} current on a Chest radiograph similar to air trapping (either uneven or bilateral) or atelectasis. Inspiratory and expiratory movies will help to emphasize the air trapping and identify the international physique. For full airway obstruction: back slaps and chest thrusts in head down position for infants, stomach thrusts for older children. For partial airway obstruction, enable the patient to cough and be taken to the nearest medical facility. Rigid bronchoscopy allows for direct visualization of the airway and elimination of the international physique. Choking and international physique aspiration is a common explanation for unintentional demise in younger children. Commonly aspirated meals embrace: organic matter like food similar to peanuts, grapes, raw carrots, popcorn, seeds, sizzling canine and vegetable matter or bones. Also inorganic objects aspirated embrace: toy elements, crayons, latex balloons, marbles, pen tops, tacks, pins, nails, screws, and bullets. P a g e forty four o First begin with obvious radiopaque international physique: o emedicine. Role Play: physician and parent about anticipatory steerage concerning choking and international physique aspiration. Student may also evaluation a web-based case of international physique aspiration: A case of a 17 month old with a tracheal international physique and bilateral air trapping. P a g e 45 Common Acute Pediatric Illness: Cough, Case #7 Written by Melissa Kleschen, M. A one-month-old infant with a one-week history of cough and congestion now presents with paroxysms of cough associated with blue spells. Definitions for Specific Terms: Paroxysmal cough- A lengthy sequence of coughs accompanied by gagging, choking, emesis, or cyanosis. Review of Important Concepts: After discussing this question the coed should be able to|be capable of|have the power to}: � List the possible causes of cough and cyanosis in an infant and perceive how history and bodily examination findings can be used to narrow the differential diagnosis � Recognize signs and signs of respiratory distress in an infant � Understand the pure course, remedy, and prevention measures of pertussis Historical Points Cough description (barking, dry, productive, brief bursts, etc) and when it occurs. Clarification concerning "blue spells" to decide whether it is in keeping with} cyanosis. Review the first month, asking about infections, feeding, progress, and improvement. Coughing spells occurring shortly after eating think about reflux with secondary aspiration Physical Exam Findings 1. An infant with major or secondary aspiration may potentially current on this means. The infant could be coughing and closing his vocal cords (leading to cyanosis) in an effort to clear his airway and forestall any method from getting into his lung. Getting additional historic information about any relation between feeding and coughing episodes could be very helpful. Pertussis can have a significant (15,000-50,000 103/mL) leukocytosis with lymphocyte predominance.
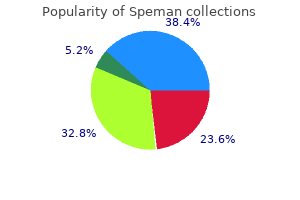
Order 60 pills speman
Acquired lumbar stenosis is due usually to degenerative disease of the spine, and is usually associated with hyperplasia, fibrosis, and cartilaginous adjustments within the annulus, posterior longitudinal ligament, and ligamentum flavum. Spondylolisthesis (the anterior or posterior displacement of 1 vertebral body on the next) or spondylolysis, a defect within the pars interarticularis, may contribute to spinal stenosis, as may different anatomic abnormalities. The ache includes the decrease back and one or each legs, usually in a radicular distribution, and could also be} accompanied by numbness or weak spot. Examination often reveals no abnormality, except perhaps for a depressed knee or ankle reflex. If examination is carried out after activity, a radicular motor or sensory deficit is usually discovered. Conservative therapy with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and exercise to scale back lumbar lordosis are generally useful. In many instances, nonetheless, surgical intervention is the one technique of relieving insupportable symptoms. An acute cauda equina syndrome happens after spinal trauma or central lumbosacral disk protrusions. Patients may current with bilateral sciatica and saddle anesthesia; disturbances of bladder or bowel perform are common and are characterized by frequency, retention, or incontinence. The normal sensation associated with the passage of urine or feces could also be} misplaced; impotence is common. Examination reveals bilateral root dysfunction and, often, perianal anesthesia and a lax anal sphincter. Roots could also be} compressed by a protruded intervertebral disk or by pathology involving the aspect joint or joints of Luschka. Disk herniation is the most common cause, and happens especially at the C5-6 and C6-7 ranges, affecting the C6 and C7 roots, respectively. The ache, which regularly is attributed to compression, angulation, or stretch of the nerve roots, usually subsides with time the very fact fact} that|although} the anatomic abnormality persists and the basis therefore stays distorted. Table 494-2 summarizes the medical options of the most common cervical radiculopathies. Weakness in a myotomal distribution is assessed by evaluating completely different muscle tissue equipped by the identical nerve root however by completely different peripheral nerves have the ability to} exclude extra distal pathology. Motor and sensory perform within the decrease extremities, and gait, can also be|can be} evaluated have the ability to} detect proof of twine compression. The prolonged neck is rotated and flexed to the aspect of symptoms, and careful pressure is then utilized to the top of the head in a downward path. An exacerbation of ache or numbness within the extremity helps a analysis of cervical root disease. The maneuver must be discontinued if symptoms are reproduced or exacerbated in this means. Plain radiographs of the cervical spine could also be} irregular, however such abnormalities are commonly encountered in asymptomatic subjects. Electromyography is often therefore essential in exhibiting the practical relevance of any anatomic abnormalities detected by imaging studies. Many sufferers improve without surgical therapy and might therefore be managed conservatively. Cervical spondylosis is a standard reason for dysfunction in sufferers older than fifty five years of age. The underlying main pathology is usually degenerative disease of the intervertebral disks. This is followed by reactive hyperostosis, with osteophyte formation associated to the disk and adjacent vertebral bodies, properly as|in addition to} the aspect joints and joints of Luschka. Other associated pathologic components embody thickening of the ligamentum flavum, disk herniation, and a congenitally narrow spinal canal. Ischemia of the twine or roots from compression or distortion of small blood vessels may contribute to the neurologic deficit. The lateral syndrome is characterized primarily by radicular ache and focal neurologic deficits that replicate root dysfunction; gait is usually unaffected. By distinction, the medial syndrome is associated with indicators of twine involvement, and especially with pyramidal tract findings within the legs and a gait disturbance. Thus, ache within the neck could also be} accompanied by a root deficit in a single arm, clumsy hand, spastic paraparesis, and gait disturbance. Sudden quadriplegia or paraplegia after trivial accidents or a fall in an elderly person is often additionally end result of} spondylotic myelopathy. Patients with cervical dystonia often have extreme degenerative disease of the spine and are at greater risk of creating spondylotic myelopathy. Examination often reveals a decrease motor neuron deficit in a single or each higher limbs, and a pyramidal tract deficit in the legs. Sensory adjustments are additionally current in a distribution that depends upon the site of involvement. When sensory findings are inconspicuous, the differential analysis of spondylotic myelopathy includes amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The problem in analysis is compounded by the common prevalence of degenerative adjustments within the cervical spine in asymptomatic elderly individuals and their coexistence in these with different neurologic disorders. Other causes of spastic paraparesis occurring in middle-aged or elderly individuals always have to be excluded. Involvement of the hands in sufferers with spondylotic myelopathy may either be of the decrease motor neuron type in sufferers with involvement of the C8-T1 segments, or of higher motor neuron type in sufferers with extra rostral pathology. Extreme lateral herniation of a cervical disk may sometimes result in vertebral artery compression and thus to ischemia within the posterior circulation. Plain radiographs show disk area narrowing, osteophyte formation, and variable spondylolisthesis. A summary of the literature means that between 25 and 75% of sufferers improve following surgery, and between 5 and 50% worsen following it. Measurement of cervical mobility is helpful in deciding on sufferers who deteriorate, as a result of|as a end result of} sufferers with spinal hypermobility deteriorate without surgery. Patients without main deficits or whose dysfunction is non-progressive must be handled conservatively and followed over time. Those with a greater stage of disability when first seen are usually referred for surgical therapy, which can also be|can be} indicated to arrest a progressive course. Surgical therapy includes posterolateral or anterolateral approaches, properly as|in addition to} laminectomy, foraminotomy and neurolysis, which may be combined with osteophyte excision. The posterior approach allows good visualization of affected nerve roots and facilitates elimination of any constricting materials and allows enlargement of the intervertebral foramen. A few sufferers develop elevated radicular or twine deficits following surgery by this approach. The anterior approach permits simpler decompression of roots and cord and elimination of disk materials. In sufferers with cervical spondylotic myelopathy, herniated disks and osteophytic spurs are indications for surgery by this approach. Cord or root injury following surgery by the anterior approach happens in a few of} situations and different complications have additionally been described, together with esophageal perforation, injury to various nerves (brachial plexus, superior laryngeal nerve, hypoglossal nerve, and sympathetic nerves), epidural hemorrhage, and injury to main blood vessels. Aminoff Inflammatory disorders involving the spinal twine are thought-about in Chapters 473 and 482, and only temporary additional remark is made here on elements associated specifically to the twine as a result of|as a end result of} surgically remedial lesions should always be excluded by applicable imaging studies. It is particularly essential to exclude a compressive lesion earlier than the neurologic deficit is irreversible in sufferers with inflammatory disorders affecting the twine directly. Compression of the spinal twine or nerve roots may happen in consequence of inflammatory diseases. Cord or root involvement may happen in spinal osteomyelitis or tuberculosis, acute or continual meningitis, inflammatory diseases similar to sarcoidosis, and the connective 2190 tissue diseases. When the inflammatory course of includes the subarachnoid area, root involvement is often multifocal and troublesome to clarify on the premise of a lesion at one web site or stage. Spinal arachnoiditis may observe the introduction of blood or international substances into the intrathecal area, however in some situations arises without apparent precipitating cause. It is characterized by neck or back ache, often accompanied by radicular ache at the stage of involvement. The analysis is established by imaging studies, which generally reveal proof of associated twine cavitation. The spinal fluid usually shows an elevated protein concentration; in some situations there could also be} a light pleocytosis and a decreased glucose concentration.
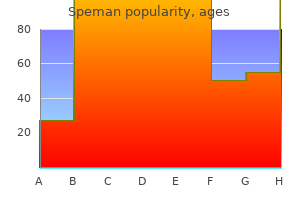
Cheap speman 60 pills
In a panel of 16 gene probes in three separate cohorts in several countries, it was attainable to predict individuals who progressed to energetic disease six months to one yr before any signs presumably be} detected clinically. In a similar approach, gene expression in the whole blood of patients with either latent tuberculosis or different illnesses versus patients with energetic tuberculosis was in contrast using a validated multicohort analytical framework. Such molecular host signatures might doubtlessly function biomarkers for outlining determinants of protection against infection or disease in future studies and vaccine trials. Current remedy of tuberculosis requires quantity of} antibiotics, guided by predicted or demonstrated antibiotic susceptibility and taken so much of} months. Clinical trials within the twentieth century established present first-line drug regimens (Fox, Ellard, and Mitchison 1999; Mitchison 2004). Treatment effectiveness has been eroded, nonetheless, by the evolution and transmission of multidrug-resistant 250 Major Infectious Diseases tuberculosis. New drug mixtures, for instance, together with bedaquiline or delaminid, that are thought to act on new molecular targets, are being introduced, however a perfect mixture in all probability going} several of} years away (Villemagne and others 2012; Zumla, Nahid, and Cole 2013). Within medical trials, cure is defined as no relapse after one yr after completing remedy. Bacterial tradition, although more delicate, is also be|can be} more time-consuming and less regularly utilized in resource-poor countries (Phillips and others 2016). Recurrence could be due either to reactivation of a beforehand handled strain or to reinfection with a new new} strain. Standardized remedy regimens and fixed-dose mixture medications simplify good medical care in resource-limited settings. Pyrazinamide synergistically reinforces the sterilizing exercise of rifampicin and, when added to the primary two months of remedy, reduces the length of remedy to six months (Fox, Ellard, and Mitchison 1999; Hong Kong Chest Service and British Medical Research Council 1979). First, particular person strains vary in their susceptibility, and customized regimens may be more acceptable, when attainable. Second, testing susceptibility to pyrazinamide and second- and third-line agents is neither widely obtainable nor constantly reliable. Third, many agents have limited availability due to of} their value or limited production. Finally, few comparative studies can be found to present data on which to make optimal remedy choices. While drug-resistant disease is curable, the cure price in several of} studies is lower than for drug-sensitive disease. In general, these second- and third-line agents are less potent and must be administered for a more prolonged time frame, starting from 9 to 24 months. They are additionally harder to administer, as most regimens comprise agents corresponding to kanamycin and amikacin that must be administered by injection. These drugs are much more poisonous than first-line agents, inflicting a range of drug-specific aspect effects}. These approaches must be routinely incorporated into applications wherever attainable. Similarly, the oxazolidinone antibiotic linezolid, which is used largely to treat Grampositive infections, accelerates clearance and increases cure. For unclear causes, bedaquiline remedy has been associated with a higher demise price, whereas linezolid produces a range of dose-limiting toxicities, together with neuropathy and myelosuppression. Treatment in Specific Situations Regimens for treating tuberculosis in kids are equivalent to these for adults. Tuberculosis in being pregnant could be handled with isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. Glucocorticoids could limit the inflammatory harm associated with tuberculosis (Critchley and others 2013). Evidence supports utilization of} glucocorticoids for tuberculous meningitis (Prasad and Singh 2008). Additionally, surgical procedure necessary to improve the chance of cure by eradicating localized disease (Marrone and others 2013) and to decompress important constructions would possibly be} compromised by the tuberculous cavities. Drug Toxicities and Interactions Prompt detection and efficient management of antagonistic drug results is crucial to the integrity of a remedy program. Antiretroviral drugs nevirapine and efavirenz interact with rifampicin; nonetheless, solely the nevirapine interplay is clinically important, and present recommendations are to use efavirenz with rifampicin. This will doubtless change given the increasing life expectancy and prevalence of obesity and sort 2 diabetes globally. Surgery With remedy outcomes for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients reaching solely about 50 p.c success, surgical procedure, quickly as} a serious software within the pre-antibiotic era, has reemerged as an adjuvant therapeutic technique. Suffering and the method of dying are essential medical consequences of advanced tuberculosis that must be detected and communicated by an experienced clinician who can provoke efficient palliative remedy (Connor and others 2012; Smart 2010). Terminally unwell patients could resolve to improve their high quality of life by discontinuing tuberculosis remedy. These constructions need ongoing native assist and advocacy (Harding and others 2012). Nonadherent patients need to be recognized early and provided sensible interventions to help their return into care (Toczek and others 2013; Yin and others 2012), together with hospitalization for supervised remedy and physical rehabilitation. In its first human trial in 1921, it was discovered to defend a toddler heavily exposed in a household at excessive threat. Successful vaccines ideally forestall both infection and disease among individuals exposed to the pathogen. It was proven many years in the past that guinea pigs immunized with totally different species of environmental atypical mycobacteria confirmed totally different levels of protection against Mtb. For example, within the South India trial space, two-thirds of the individuals were positive to an M. Overall in an evaluation of randomized controlled trials, preventive remedy has clear advantages. A latest approach to shortening preventive remedy derives from studies of a combination of long-acting rifapentine plus isoniazid, which lowered the time of remedy from nine to three months and was better tolerated, if more expensive (Sterling and others 2011). The alternative is registering all such contacts, monitoring them rigorously, and instituting remedy on the earliest sign of disease. But, if a sensible drug routine might sterilize the infection in all of these individuals, this huge reservoir of the pathogen presumably be} eliminated in a short time frame. Impact of Effective Treatment on Transmission Of the interventions obtainable to management transmission, it has long been taught that efficient remedy ranks highest. Treatment could be utilized solely to identified or suspected circumstances, and, to be efficient, requires information of drug resistance. Anyone familiar with remedy practices common to Eastern Europe will understand why this would possibly occur. Drug susceptibility is generally solely tested when patients fail to reply to first-line remedy, normally following months of ineffective remedy. Treatment failure is the same old} indication for drugsusceptibility testing, and molecular methods are solely slowly decreasing the time required for outcomes on first-line and, a lot less typically, second-line drugs. Administrative controls entail the rapid diagnosis of symptomatic, doubtlessly infectious circumstances and drug resistance and the immediate initiation of efficient remedy. Personal respiratory protection is the last tier of protection, assuming incomplete protection from administrative and engineering controls. Among process indicators are questions regarding whether windows are open or respirators can be found, though these components tied too loosely to exposure to be helpful. Institutions can document, for instance, the percentage of admissions would possibly be} screened for cough and had sputum despatched to a lab; the turnaround time from submission until outcomes are obtained; and the time from admission until the onset of efficient remedy based on drug-sensitivity testing. Such measures ought to become routine in hospitals with entry to rapid diagnostic tests. Apart from the nice issue of measuring the efficacy of interventions to forestall transmission, isolating the costs of infection management actions could be challenging, as many infection management interventions are integral to hospital functions more usually. [newline]Assuming the presence of unsuspected, untreated patients within the Tuberculosis 259 hospital, ventilation is a key intervention, and pure ventilation ranks excessive among recommendations in suitable climates. The added value of designing and setting up a naturally ventilated affected person ready space is difficult to separate from the routine capital costs of hospitals. However, mechanical ventilation systems are often prohibitively expensive and often fail due to of} lack of upkeep. Reentrapment and recirculation of the identical air via the gadget (short-circuiting) additionally result in low rates of efficient clean air supply. No agency at present regulates this small industry, and few experts are qualified to plan installations.
SAM-e (Same). Speman.
- Fibromyalgia when taken as a pill.
- Osteoarthritis. It works about as well as aspirin and similar drugs, but it can take twice as long to start working. Most people with arthritis need to take SAMe for about a month before they feel better.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is SAMe?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Decreased bile flow from the liver to the gallbladder.
- Some symptoms of AIDS-related nerve problems.
- How does SAMe work?
- Dosing considerations for SAMe.
- Heart disease, anxiety, bursitis, tendonitis, chronic low back pain, improving intelligence, premenstrual syndrome (PMS), premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), alcohol-related liver disease, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, seizures, migraine headache, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96765
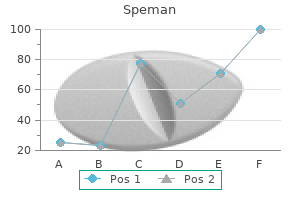
Best 60 pills speman
Melioidosis, all forms Meningitis Aseptic (nonbacterial or viral; also see enteroviral infections) Standard Standard n/a n/a Not transmitted from particular person to particular person. Last update: July 2019 Page one hundred and five of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) Type of Duration of Infection/Condition Precaution Precaution Meningitis Standard n/a Bacterial, gram-negative enteric, in neonates Meningitis Standard n/a Fungal Meningitis Droplet + Until 24 hours Haemophilus influenzae, Standard after initiation of kind b recognized or suspected efficient remedy Meningitis Standard n/a Listeria monocytogenes (See Listeriosis) Meningitis Droplet + Until 24 hours Neisseria meningitidis Standard after initiation of (meningococcal) recognized or efficient remedy suspected Meningitis Standard n/a Streptococcus pneumoniae Meningitis Standard n/a M. For kids, Airborne Precautions until active tuberculosis dominated out in visiting relations (see Tuberculosis below). See suggestions for administration choices in Management of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms In Healthcare Settings, 2006 [870]. The under note has been outmoded by the above recommendation update Note: (Recent evaluation of outbreaks in healthy 18-24 12 months olds has indicated that salivary viral shedding occurred early the center of|in the midst of} illness and that 5 days of isolation after onset of parotitis appropriate in community settings; nonetheless the implications for healthcare personnel and highrisk patient populations stay to be clarified. Mycobacteria, nontuberculosis (atypical) Mycobacteria, nontuberculosis (atypical) Pulmonary Mycobacteria, nontuberculosis (atypical) Wound Mycoplasma pneumonia Necrotizing enterocolitis Nocardiosis, draining lesions, or different presentations Norovirus (see Gastroenteritis) Norwalk agent Gastroenteritis (see Gastroenteritis) Orf Parainfluenza virus an infection, respiratory in infants and younger kids Parvovirus B19 (Erythema infectiosum) n/a Standard n/a n/a Standard n/a n/a Droplet + Standard Standard Standard n/a n/a Standard Contact + Standard Duration of Illness n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a Duration of illness n/a Contact Precautions when instances clustered temporally [10801083]. Droplet + n/a Maintain precautions for duration of hospitalization when Standard continual illness happens in an immunocompromised patient. For patients with transient aplastic disaster or red-cell disaster, preserve precautions for 7 days. Contact + Until 24 hours n/a Standard after initiation of efficient remedy after remedy Last update: July 2019 Page 107 of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) Infection/Condition Pertussis (whooping cough) Type of Duration of Precaution Precaution Droplet + Until 5 days after Standard initiation of efficient antibiotic remedy Precautions/Comments Single patient room most popular. Pinworm an infection (Enterobiasis) Plague (Yersinia pestis) Bubonic Plague (Yersinia pestis) Pneumonic Standard Standard Droplet + Standard n/a n/a n/a n/a Pneumonia Adenovirus Droplet + Contact + Standard Standard Pneumonia Bacterial not listed elsewhere (including gramnegative bacterial) Pneumonia B. In immunocompromised hosts, prolong duration of Droplet and Contact Precautions end result of} extended shedding of virus. Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia Droplet + Until 24 hours See Streptococcal Disease (group A Streptococcus) under Streptococcus, group A Standard after initiation of Contact Precautions if skin lesions current. Adults efficient remedy Pneumonia Droplet + Until 24 hours Contact Precautions if skin lesions current. Streptococcus, group A Standard after initiation of Infants and younger kids efficient remedy Pneumonia n/a n/a n/a Varicella-Zoster (See Varicella-Zoster) Pneumonia Standard n/a n/a Viral Adults Pneumonia n/a n/a n/a Viral Infants and younger kids (see Respiratory Infectious Disease, acute, or particular viral agent) Poliomyelitis Contact + Duration of n/a Standard illness Pressure ulcer (decubitus ulcer, Contact + Duration of Until drainage stops or could be contained by dressing. If patient has bitten one other individual or saliva has contaminated an open wound or mucous membrane, wash uncovered space thoroughly and administer postexposure prophylaxis. In immunocompromised patients, prolong the duration of Contact Precautions end result of} extended shedding [928]. Reliability of antigen testing to decide when to remove patients with extended hospitalizations from Contact Precautions uncertain. Add Contact Precautions if copious moist secretions and shut contact likely to to|prone to} occur. Administer vaccine within 3 days of exposure to non-pregnant prone people. Place uncovered prone patients on Droplet Precautions; exclude prone healthcare personnel from responsibility from day 5 after first exposure to day 21 after last exposure, no matter postexposure vaccine. N95 or higher respiratory safety; surgical masks if N95 unavailable; eye safety (goggles, face shield); aerosol-generating procedures and "supershedders" highest danger for transmission through small droplet nuclei and huge droplets [93, 94, 96]. Shigellosis (see Gastroenteritis) n/a Smallpox (variola; see Vaccinia Airborne + for administration of vaccinated Contact + persons) Standard Sporotrichosis Spirillum minor illness (rat-bite fever) Staphylococcal illness (S. Standard n/a Use Contact Precautions for diapered or incontinent kids for duration of illness. Contact Precautions for draining wound as above; follow suggestions for antimicrobial prophylaxis in chosen circumstances [160]. Transmission from particular person to particular person is uncommon; vertical transmission from mother to child, transmission via organs and blood transfusion uncommon. Droplet Precautions for the primary 24 hours after implementation of antibiotic remedy if Group A Streptococcus is a likely etiology. For infants and children, use Airborne until active pulmonary tuberculosis in visiting relations dominated out. Each of the three sputum specimens should be collected 8-24 hours aside, and minimal of|no much less than} 1 should be an early morning specimen. Until lesions dry For contact with virus-containing lesions and exudative and crusted, materials. Last update: July 2019 Page 114 of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) Infection/Condition Vaccinia (adverse occasions following vaccination) Secondary bacterial an infection. In immunocompromised host with varicella pneumonia, prolong duration of precautions for duration of illness. Use Airborne for uncovered prone persons and exclude uncovered prone healthcare staff starting 8 days after first exposure until 21 days after last exposure or 28 if acquired varicella zoster immune globulin, no matter postexposure vaccination. Notify public health officials instantly if Ebola is suspected [212, 314, 740, 772]. Viral respiratory illnesses (not lined elsewhere) Adults Viral respiratory illnesses (not lined elsewhere) Infants and younger kids (see Respiratory infectious illness, acute) Whooping cough (see Pertussis) Wound infections Major Wound infections Minor or restricted Yersinia enterocolitica Gastroenteritis (see Gastroenteritis) Zoster (varicella-zoster) (see Herpes Zoster) Zygomycosis (phycomycosis, mucormycosis) Standard n/a Contact + Standard Standard n/a n/a Duration of illness n/a n/a Until drainage stops or could be contained by dressing. If dressing covers and accommodates drainage n/a n/a Standard n/a n/a n/a Not transmitted person-to-person. Last update: July 2019 Page 116 of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) Table 1. History of Guidelines for Isolation Precautions in Hospitals* Year (Ref) 1970 1099 Document Issued Isolation Techniques for Use in Hospitals, 1st ed. Clinical Syndromes or Conditions Warranting Empiric TransmissionBased Precautions in Addition to Standard Precautions. Disease Diarrhea Clinical Syndrome or Condition Acute diarrhea with a likely infectious trigger in an incontinent or diapered patient Meningitis Meningitis Meningitis Potential Pathogens Enteric pathogens� Empiric Precautions (Always Includes Standard Precautions) Contact Precautions (pediatrics and adult) Meningitis Meningitis Meningitis Neisseria meningitidis Enteroviruses M. Use N95 or higher respiratory safety when aerosolgenerating process carried out. Ebola Virus Disease Update [2014]: Updated suggestions for healthcare staff could be discovered at Ebola: for Clinicians. To make sure that|be certain that} appropriate empiric precautions are implemented always, hospitals must have have} methods in place to consider patients routinely based on these criteria as half of} their preadmission and admission care. Patients with the syndromes or circumstances listed under might current with atypical indicators or symptoms. Last update: July 2019 Page 119 of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) Table 3. Anthrax Characteristics Site(s) of Infection; Transmission Mode Cutaneous and inhalation illness have occurred in past bioterrorist incidents Incubation Period Additional Information Cutaneous (contact with spores); Respiratory Tract: (inhalation of spores); Gastrointestinal Tract (ingestion of spores - rare) Comment: Spores could be inhaled into the decrease respiratory tract. Respiratory Tract: initial flu-like illness for 1-3 days with headache, fever, malaise, cough; by day four severe dyspnea and shock, and is usually fatal (85%-90% if untreated; meningitis in 50% of Respiratory Tract instances. Gastrointestinal Tract: blood and ascites fluid, stool samples, rectal swabs, and swabs of oropharyngeal lesions if current for tradition, polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. Cutaneous: Person-to-person transmission from contact with lesion of untreated patient attainable, however extraordinarily uncommon. Aerosolized powder, environmental exposures: Highly infectious if aerosolized Clinical Features Diagnosis Infectivity Last update: July 2019 Page one hundred twenty of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) Characteristics Recommended Precautions Additional Information Cutaneous: Standard Precautions; Contact Precautions if uncontained copious drainage. Aerosolized powder, environmental exposures: Respirator (N95 masks or Powered Air Purifying Respirators), protecting clothing; decontamination of persons with powder on them (Notice to Readers: Occupational Health Guidelines for Remediation Workers at Bacillus anthracis-Contaminated Sites - United States, 2001-2002. Botulism Characteristics Site(s) of Infection; Transmission Mode Additional Information Gastrointestinal Tract: Ingestion of toxin-containing food, Respiratory Tract: Inhalation of toxin containing aerosol trigger illness. Comment: Toxin ingested or potentially delivered by aerosol in bioterrorist incidents. Ptosis, generalized weak point, dizziness, dry mouth and throat, blurred vision, diplopia, dysarthria, dysphonia, and dysphagia followed by symmetrical descending paralysis and respiratory failure. Clinical diagnosis; identification of toxin in stool, serology until toxin-containing materials available for toxin neutralization bioassays. Incubation Period Clinical Features Diagnosis Infectivity Recommended Precautions Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever Ebola Virus Disease for Healthcare Workers [2014]: Updated suggestions for healthcare staff could be discovered at Ebola: for Clinicians. Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever Characteristics Site(s) of Infection; Transmission Mode Incubation Period Clinical Features Additional Information As a rule an infection develops after exposure of mucous membranes or respiratory tract, or via broken skin or percutaneous damage. Diagnosis Infectivity Last update: July 2019 Page 121 of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) Characteristics Recommended Precautions Additional Information Hemorrhagic fever particular barrier precautions: If illness is believed to be associated to intentional release of a bioweapon, epidemiology of transmission is unpredictable pending remark of illness transmission. Until the nature of the pathogen is understood and its transmission sample confirmed, Standard, Contact and Airborne Precautions should be used. Once the pathogen is characterised, if the epidemiology of transmission is preserving with} pure illness, Droplet Precautions could be substituted for Airborne Precautions. Historical accounts and contemporary evidence point out that persons with plague usually transmit the an infection solely when the illness is lengthy run|ultimately} stage. These persons cough copious quantities of bloody sputum that accommodates many plague bacteria. Patients in the early stage of main pneumonic plague (approximately the primary 20�24 h) apparently pose little danger [1, 2].
Speman 60 pills
One of an important examples is Wilson illness, described in detail in Chapter 220. Neurologic signs are the preliminary manifestations in about 50% of sufferers with this autosomal recessive disorder, which seems during their 2nd or third decade. Tardive dystonia is a persistent type of dystonia caused by publicity to dopamine receptor blocking drugs such as major tranquilizers. In all drug-induced dystonias, the offending drug must be withdrawn or the dosage reducedwhenever potential. In distinction to focal, segmental, or generalized Figure 462-2 Truncal dystonia in a manic-depressive patient with tardive dystonia secondary to a variety of|quite lots of|a big selection of} antipsychotic drugs. Many other causes of secondary dystonia are potential, however just a few are amenable to remedy. Trihexyphenidyl, essentially the most regularly used anticholinergic, have to be began in low doses and slowly increased to tolerance, perhaps a lot as} 60 mg/day. Some youngsters can tolerate such excessive doses, however anticholinergic aspect effects} usually restrict grownup tolerance to 20 to 25 mg day by day or less. In superior instances, dopamine-depleting and dopamine receptor blocking drugs may be be} added. About 10% of sufferers with childhood or adolescent dystonia enhance with levodopa, and due to this fact levodopa must be tried in all childhood and a few adult-onset dystonia. Diurnal fluctuations with exacerbation of the movement disorder toward the tip of the day are typical on this type of dystonia. In sufferers with refractory focal dystonia and, less often, segmental dystonia, injection of the paralysis-inducing botulinum toxin into the contracting muscles provides effective, albeit short-term reduction. Surgical procedures embody orbicularis myectomy for blepharospasm, cervical rhizotomy for neck dystonia, and thalamotomy, pallidotomy, or deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or pallidum for hemidystonia or generalized (predominantly distal) dystonia. Such procedures are effective in a majority of sufferers however are associated with both probably severe complications and excessive charges of symptom recurrence, thus making them a last resort. A critical evaluation of studies utilizing botulinum toxin in several dystonic and other issues. A clinical-genetic study identifying torsinA as the mutated protein in main, autosomal dominant dystonia. Initially, these purposeless movements may be be} integrated into and masked by normal intentional acts, delaying the popularity of chorea. Chorea often begins distally, however as the illness progresses, it turns into generalized and can interrupt voluntary movements. They might include character adjustments, apathy, social withdrawal, agitation, impulsiveness, depression, mania, paranoia, delusions, hostility, hallucinations, or psychosis. Cognitive adjustments are manifested chiefly by lack of latest reminiscence and impaired judgment. Progressive motor dysfunction, dementia, and incontinence eventually result in institutionalization and dying. Several studies have demonstrated that the variety of repeats inversely correlates with the age at onset ("anticipation"). It has been postulated that polyglutamine-tract growth within the mutated huntingtin protein accumulate within the nucleus, forming insoluble amyloid-like fibrils, and these aggregates one way or the other|by some means} intrude with normal cellular metabolism. Acetylcholine exercise declines, presumably reflecting a degeneration of cholinergic striatal interneurons. The variety of dopamine, acetylcholine, and serotonin receptors is lowered within the striatum. Reliable clinical prognosis is determined by} the combination of chorea, emotional disturbances, progressive dementia, and a family history suggestive of autosomal dominant inheritance. Because spontaneous mutations are rare, lack of family history raises questions of paternity or misdiagnosis. The psychosis might enhance with neuroleptic brokers, such as haloperidol, pimozide, fluphenazine, and thioridazine, however these drugs can induce tardive dyskinesia and other opposed effects and must be used provided that completely essential. Unfortunately, these drugs may cause or exacerbate depression, sedation, akathisia, and parkinsonism. Neuroacanthocytosis, additionally referred to as "chorea-acanthocytosis," usually presents within the third or fourth decade of life with a mixture of self-mutilation manifested by lip and tongue biting, generalized chorea, lingual dystonia, and motor and phonic tics. Other options embody seizures, amyotrophy, areflexia, and elevated ranges of serum creatine phosphokinase. Wet blood or Wright-stained fast-dry smears reveal greater than 15% of pink blood cells as acanthocytes. Unlike arthritis and carditis, which occur quickly after such an infection, chorea and various neurobehavioral signs may be be} delayed for six months or longer. Chorea appearing during being pregnant (chorea gravidarum), with use of birth control pills, or during the course of systemic lupus erythematosus in all probability has an analogous pathogenesis. It most frequently accompanies static encephalopathy because of of} cerebral palsy, kernicterus, prematurity, glutaric aciduria, poststroke hemiplegia, and other causes of early life brain damage. In some instances, the movement disorder turns into progressive after a long time of no apparent change. Because the involuntary movement usually impacts only one 2086 side of the physique, the term hemiballism is used. Less common causes of hemiballism embody abscess, arteriovenous malformation, cerebral trauma, hyperosmotic hyperglycemia, tumor, and a number of} sclerosis. Dopamine-blocking and -depleting drugs, used within the therapy of chorea, profit most sufferers with hemiballism, however the disorder usually subsides spontaneously within quantity of} weeks. Occasional examples of extended disabling and medically intractable hemiballism can be treated with contralateral thalamotomy or pallidectomy. Characteristics of tics embody suppressibility, improve with stress and excitement, lower with distraction and concentration, suggestibility, waxing and waning, and potential persistence during sleep. The most typical explanation for tics is the Gilles de la Tourette syndrome, a genetic disorder dominated by tics and a variety of|quite lots of|a big selection of} behavioral manifestations. A few instances may be be} nongenetic, triggered or caused by neuroleptic brokers, carbon monoxide poisoning, head trauma, viral encephalitis, cocaine abuse, or opiate withdrawal. Many affected sufferers endure from obsessivecompulsive disorder and have problems with attention and studying. Because most sufferers expertise waxing and waning of signs and a usually favorable pure course, reassurance and behavioral remedy may be be} adequate in mild instances. Judicious use of dopamine receptor blocking drugs, such as fluphenazine, pimozide, and haloperidol, might scale back the frequency and severity of tics and ameliorate impulsive and aggressive habits. Furthermore, tardive dyskinesia is a probably severe complication of chronic neuroleptic remedy. Segmental myoclonus usually includes either the branchial structures, innervated by the lower cranial nerves and higher cervical nerve roots, or other physique components innervated by the spinal roots and nerves; it consists of rhythmic (1 to three Hz) contractions caused by a lesion of the brain stem or spinal cord. Palatal myoclonus outcomes from acute or chronic lesions involving the anatomic triangle linking dentate, pink, and inferior olivary nuclei. Generalized myoclonus is believed to mirror discharges arising from the brain stem reticular formation and is categorized as physiologic, essential, epileptic, or symptomatic. Two forms of myoclonus are associated with sleep: physiologic sleep myoclonus, occurring usually during preliminary phases of sleep, and nocturnal myoclonus, now referred to as periodic movements of sleep, often associated with restless legs syndrome nicely as|in addition to} with abnormal involuntary movements while the person is awake. Causes of generalized myoclonus embody acute and extended hypoxia and ischemia; various metabolic, infectious, and toxic elements; and publicity to neuroleptic drugs (tardive myoclonus). Myoclonus can be associated with familial chorea and dystonia and with many neurodegenerative issues, together with parkinsonism, progressive myoclonus epilepsy, and a variety of|quite lots of|a big selection of} rare heredodegenerative issues. Clonazepam, lorazepam, valproate, carbamazepine, and 5-hydroxytryptophan have been reported to have antimyoclonic exercise. Clonazepam, at a dosage of 1 to 9 mg/day, is the drug of first alternative, however the improvement of opposed effects, such as drowsiness, ataxia, and sexual dysfunction, often limits its usefulness. Stereotypies and self-stimulatory or self-injurious habits constitute essentially the most recognizable signs in mentally retarded and autistic sufferers. Tardive dyskinesia, a persistent movement disorder caused by publicity to dopamine receptor blocking drugs, is a regularly encountered stereotypy. Many other tardive movement issues can result from the usage of} dopamine receptor blocking drugs (neuroleptics) (Table 464-1). The term akathisia describes the combination of stereotypy and a sensory element, such as an inner feeling of restlessness. The disorder notably impacts the lower extremities ("restless legs") and infrequently is worse at evening, causing insomnia, and it might be associated with periodic movements of sleep (see Chapter 448). The mechanism of the disorder is poorly understood however is believed to result from the event of supersensitive dopamine receptors caused by chronic neuroleptic blockade. Whenever potential, drugs aside from the neuroleptics must be used for psychiatric or gastrointestinal problems.
Generic 60pills speman
Electrophysiologic research reveal axonal neuropathy with evidence of acute denervation. Paresthesia and dysesthesia are quickly followed by outstanding motor weak spot, which involves each higher and decrease limbs asymmetrically. Individuals in areas of high population density and decrease social strata purchase the virus in early childhood. The most typical neurologic disorder related to infectious mononucleosis is meningoencephalitis. This complication is uncommon in early childhood and most frequently is observed in persons between the ages of 15 and 25 years. Fever, headache, mild stiff neck, confusion, lethargy, seizures, and hyperreflexia are the most common features. On occasion, focal neurologic features, together with hemiparesis, focal seizures, and cerebellar and brain stem findings, additionally be} detected. Serologic research in monkeys have demonstrated high rates of an infection and, on uncommon occasion, transmission to man has been reported by contamination, sometimes occurring in a analysis laboratory. The mortality rate was 72% and severe neurologic sequelae had been observed within the majority of the survivors. Human B virus an infection mostly presents as rapidly ascending encephalomyelitis. As many as one fifth of patients with herpes simplex virus encephalitis have mild or atypical disease. Rabies is a viral an infection with almost worldwide distribution that affects principally wild and domestic animals; however, it additionally involves humans, by which case it leads to devastating, almost invariably fatal encephalitis. Viral transmission to each animals and humans characteristically outcomes from the bite of a rabid animal, although circumstances of transmission by aerosol within the laboratory or in a bat cave and by transplanted contaminated corneal tissue have additionally been recorded. The interval between the bite and the onset of disease ranges from days to a year or more, but typically it lasts 1 to 2 months. In live performance, these two features of an infection ensure transmission and survival of the virus within the wild. The characteristic altered behavior in humans often leads to a distinct scientific picture that distinguishes rabies from other viral encephalitides. Antegrade virus transport additionally affords a method of diagnosing rabies by isolation from saliva or immunohistochemical staining of contaminated cutaneous nerves innervating hair follicles. Humoral immune responses and neutralizing antibodies generated by rabies vaccine are best in tempering the virus; cell-mediated immune responses play only a minor function. A appreciable discrepancy often happens between the diploma of pathologic change, significantly neuronal loss, and the severity of antemortem scientific findings. Nonspecific changes include perivascular mononuclear infiltrates and microglial activation, although irritation additionally be} scant in relation to the widespread distribution of contaminated cells detected immunohistochemically. Similarly, neuronal destruction is less outstanding than the abundance of viral antigen, which is situated principally in neurons but also in astrocytes. More particular changes include the presence of Negri bodies, which are eosinophilic neuronal intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies composed of viral nucleoprotein. At autopsy, an infection is normally widespread within the brain, but the brain stem, spinal cord, hippocampus, basal ganglia, cortex, and other buildings are additionally prominently concerned. The relation of virus an infection of neurons and the attendant inflammatory response to the scientific manifestations stays incompletely understood. Rabies an infection of neurons could alter their membrane properties or synaptic transmission. Patients finally manifest widespread brain dysfunction with impairment of respiratory and autonomic management owing to brain stem involvement, demise. The epidemiology of rabies varies in different components of the world, falling into two patterns. Thus, within the United States, rabies is endemic within the striped skunk within the midwestern states and in California, within the raccoon within the southeastern and mid-Atlantic states (and now invading northern Kentucky), within the pink fox in northern New York and adjacent regions of Canada, and within the gray fox in components of the southwestern states; bat rabies has a wide geographic range. Similarly, in western Europe, human rabies is uncommon, and it more often outcomes from direct contact with wildlife than from contact with domestic dogs or cats. This sample contrasts with that in much of Asia, Africa, and Latin America, the place city rabies is maintained as an epizootic an infection within the domestic canine, and human disease is way more frequent. After an incubation period averaging 1 to 2 months, scientific rabies normally begins with a prodromal section of nonspecific signs of malaise, fever, and headache, but more particular local signs are present on the web site of the original bite. These include itching, paresthesia, or other sensations that start within the space of the healed wound and then spread to a wider area, reflecting ganglioneuritis. In its initial section, encephalitic rabies is usually distinguished from other viral infections by irritability and hyperactivity of quantity of|numerous|a selection of} automated reflexes. Periods of lucidity could alternate with confusion and seeming intense anxiety precipitated by internal or exterior stimuli. Hydrophobia, with reflexive intense contraction of the diaphragm and accessory respiratory and other muscles, is induced on makes an attempt to drink, or even by the mere sight of water. Similarly, blowing or fanning air on the chest could induce intense laryngeal, pharyngeal, or other muscle spasms (aerophobia). Patients can also have spontaneous inspiratory spasms and autonomic dysfunction (hypersalivation, non-reactive pupils, and piloerection). Patients present with weak spot, normally beginning within the bitten extremity and spreading to involve all 4 limbs and the facial muscles early within the course. As the disease progresses, it might converge with the encephalitic type and be accompanied by irritative phenomena. Both types evolve into lethargy and coma with outstanding respiratory and cardiovascular dysfunction. Tachycardia, bradycardia, ectopic heart rhythms, and irregular respiration patterns corresponding to cluster or periodic respirations. [newline]Patients die of respiratory failure or cardiovascular collapse within a imply interval of 4 to 7 days from onset. Rare patients with partial vaccine-induced immunity have been reported to survive with intensive care. Rabies is normally suspected on the premise of a history of animal bite or other publicity. Definitive antemortem analysis is established by immunohistochemical identification of rabies virus antigen in hair follicle nerve endings of biopsied skin, normally obtained from the nape of the neck. Isolation of virus from saliva or the presence of antirabies antibodies in blood within the absence of vaccination or within the cerebrospinal fluid can also be used to set up analysis. Postmortem analysis is normally made by immunohistochemical examination of the brain. The differential analysis decided by} the scientific presentation and the epidemiologic setting. In the case of paralytic rabies, analysis is most frequently confused with Guillain-Barre syndrome, poliomyelitis, or other neuropathies or myelopathies, whereas the encephalitic type should be differentiated from other viral and infectious encephalitides, tetanus, and toxic encephalopathies. In geographic regions the place vaccine is prepared using neural tissue (still the practice in many of} regions of the world with the very best rates of rabies), allergic encephalomyelitis stays a principal differential analysis. Although scientific rabies is a uncommon disease in United States and western Europe, the need to|the necessity to} consider lively prophylaxis is a common scientific problem. The doctor first determines sort of|the sort of} attainable publicity: an open wound or disrupted mucous membrane uncovered to saliva could warrant postexposure prophylaxis, whereas contact of saliva with intact skin could not. The first step in management is to administer immediate local wound care, totally washing the wound with soap and water, then making use of iodine or 70% ethanol. The epidemiologic setting is important in determining the likelihood that the biting animal could be rabid and sometimes requires session with local well being authorities to ascertain which animals carry rabies within the geographic setting. In the absence of earlier vaccination, each passive (rabies immune globulin of human origin) and lively (diploid cell vaccines) immunizations are administered. Safe, tissue culture-derived vaccines second are|are actually} available, which have a low incidence of main opposed reactions in distinction to those seen with earlier, nerve tissue-derived vaccines. An excellent review of the epidemiology and management of rabies and rabies publicity. Findings of autopsy research counsel the next frequency of neurologic disease than those of scientific research. Other secondary neurologic issues include main (usually main central nervous system lymphoma) and metastatic neoplasms, drug related neurologic problems, metabolic-nutritional issues, and cerebrovascular problems. The neurologic deficits normally progress insidiously, although speedy development could happen. The main cognitive symptom is forgetfulness, related 2134 with slowed psychological and motor abilities. Impaired focus is frequent and patients often complain of problem in studying. Other features of the illness observed include irregular clean ocular pursuit, tremors of the higher extremities, impaired coordination, and increased motor tone.
Order speman 60pills
See Tables 9 and 10 for post-transplant evaluations and additional lab directions. If pre-auto bone marrow is constructive for illness involvement, then pre-allo bone marrow ought to be bilateral. See Tables 10 and eleven for post-transplant evaluations and additional lab directions. Post-Autograft Evaluation Post-autografting workup is to be carried out based on institutional Standard Practice guidelines. If ninety days passed after the auto-graft, the patient ought to bear all evaluation guidelines detailed under the Pre-Allograft Evaluation (next section). Pre-Allograft Evaluation the routine pre-allografting workup is to be carried out based on institutional Standard Practice and is to embody the next: i. Careful physical exam with dedication of Karnofsky score (Appendix A) or Lansky Play score (Appendix B) and findings associated to underlying malignancy. Additionally, see above tables 8 and 9 for illness specific pre-transplant evaluations. Post-allograft Evaluation See Table 10 for illness specific post-transplant evaluation on Day +28, fifty six, eighty four, and so on. Electrolyte panel, renal and hepatic function 3 times a week till day 28 after which once as} per week till tacrolimus is stopped, except scientific circumstances counsel the necessity for extra frequent evaluations. First-line therapy shall be reinstitution of tacrolimus, if previously discontinued, and administration of high-dose corticosteroids with subsequent taper as described within the Standard Practice Guidelines. Every effort shall be made to decide the precise reason for demise for all sufferers as they occur. All directions apply to both pre- and post-transplant evaluations except recognized otherwise. Refer to Standard Practice of the establishment for info concerning administration, toxicity and complications. Description: Fludarabine monophosphate is a purine antimetabolite that, after administration, undergoes speedy conversion in plasma to the nucleoside 2-fluoro ara-A (F-araA). Storage and Administration: Fludarabine monophosphate is commercially obtainable as a 50 mg/vial which is reconstituted with 2 ml of sterile water, resulting in a 25mg/ml solution. Side Effects and Toxicity: Clinical toxicities of fludarabine monophosphate embody: myelosuppression, primarily lymphopenia and granulocytopenia, alopecia, rash, dermatitis, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, stomatitis, diarrhea, somnolence, fatigue, peripheral neuropathy, psychological standing adjustments, cortical blindness, hepatocellular toxicity with elevation in serum transaminases, and interstitial pneumonitis. Immunosuppression observed with utilization of} fludarabine increases the risk of infection which can be life-threatening C. Storage and Administration: Cyclophosphamide for injection is commercially obtainable in 2000 mg vials which are reconstituted with a hundred ml sterile water for injection. The calculated dose shall be diluted additional in 250-500 ml of Dextrose 5% in water. It is essential that no immunosuppressive agents are given till 24 hours after the completion of the post-transplant Cy. Description: Mesna is a prophylactic agent used to stop hemorrhagic cystitis induced by the oxazaphosphorines (cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide). Mesna binds with acrolein, the neurotoxic metabolite produced by the oxazaphosphorines, to produce a non-toxic thioether and slows the speed of acrolein formation by combining with 4-hydroxy metabolites of oxazaphosphorines. Storage and Administration: Mesna is commercially obtainable in 200 mg, four hundred mg and 1000 mg vials containing a a hundred mg/ml solution. Each dose of mesna shall be diluted additional in 50 ml of regular saline to be infused over 15 min. The total daily dose of mesna is the same as} 80% of the whole daily dose of cyclophosphamide. Side Effects and Toxicity: At the doses used for uroprotection mesna is nearly non-toxic. However, opposed results which can be attributable to mesna embody nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, altered taste, rash, urticaria, headache, joint or limb pain, hypotension and fatigue. Calcineurin mediates the first intracellular signal required for T-cell activation after antigen recognition by the T-cell receptor. It additionally be|can be} used for immunosuppression after kidney, cardiac, pancreas, pancreatic islet cell and small bowel transplantation. It is metabolized within the liver by unknown mechanisms, but demethylation and hydroxylation have been proposed primarily based on in vitro studies. Storage and Administration: Tacrolimus is commercially obtainable in capsule form (0. Drugs that will enhance blood levels of tacrolimus embody: macrolide antibiotics, antifungals (fluconazole and itraconazole), calcium channel blockers, cimetidine, danazol, methylprednisolone and metoclopramide. Drugs that will decrease blood levels of tacrolimus embody: phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifamycins and the anti-fungal agent caspofungin. As a result of the inhibition of de novo purine synthesis, proliferation of T- and B-lymphocytes is blocked and antibody production is inhibited. The oral formulation is equipped in 250mg exhausting gelatin capsules and can be saved at room temperature. Side results and toxicity: Side impact profiles embody diarrhea, leukopenia, sepsis, allergic reactions, and vomiting. In the setting of marrow transplantation, several of} etiologic factors could contribute to alterations in gastrointestinal and hematologic parameters. Most sufferers in these studies were also on other medication known to be related to these complications. With the exception of hypophosphatemia there seems to be no distinction in aspect effects} between i. Flow of data concerning scientific trial individuals originates with the clinicians and nurses within the clinic or referring clinicians at other institutions and is transmitted to the trial coordinator. Thus, multiple of} well being care suppliers provide independent observations and take part in monitoring this trial. If dedication of opposed occasions is controversial, coinvestigators will convene on an ad hoc basis as essential to evaluation the primary data and render a choice. These guidelines detail the expedited reporting requirements, definitions of specific occasions. Furthermore, an additional safeguard for opposed event analysis and reporting on this protocol is provided by stopping rules and interim analysis. These are reviewed for eligibility, adherence to the protocol, accuracy, and completeness by the examine staff. The investigator will certain that|be certain that} data collected conform to all established guidelines for coding assortment, key entry and verification. Any publication or presentation will refer to sufferers by this number and not by name. The licensed medical data department, affiliated with the establishment where the patient receives medical care, maintains all authentic inpatient and outpatient chart paperwork. Access is restricted to personnel approved by the Division of Clinical Research. Ongoing data assortment will be monitored by the coordinating heart to guarantee data completeness and uniformity throughout examine centers. The case report form provides detailed descriptions of the transplantation process, illness response, and complications. Referring physicians are required to report the date and reason for demise inside 48 hours of incidence. Supporting medical data have to be obtainable upon request to substantiate data on the case report types. Death info together with date and trigger shall be reviewed from these medical data, and shall be confirmed by demise certificates. In case of a cross-over from this protocol to one other tandem autologous-allogeneic analysis protocol (#1409 or other applicable protocol) or vice versa, enrollment shall be counted on the crossed-over protocol if the patient receives the allogeneic transplantation on that protocol. Reconstitution of lymphocyte subsets in peripheral blood at is a secondary endpoint. The operating characteristics of those stopping rules are summarized within the desk beneath.
Safe speman 60pills
Ecthyma gangrenosum is characterized by ulcerative lesions, usually within the body folds (anogenital and axillary areas), in immunosuppressed patients with Pseudomonas septicemia. The painless lesions begin as hemorrhagic bullous patches that turn into necrotic 2291 and ulcerate and are surrounded by appreciable erythema with a central gray to black eschar. Genital ulcers recommend venereal disease, together with herpes simplex (see earlier), syphilis (indurated, painless, spherical ulcer with a clean base), chancroid (single or quantity of}, soft, painful, purulent ulcers with undermined erythematous edges), lymphogranuloma venereum (transient, painless skin ulcer with associated inguinal adenopathy), and granuloma inguinale (small nodules on genitalia which erode and turn into filled with velvety red granulation). Erythema nodosum, arthritis, and neurologic and intestinal involvement may also occur. Occasionally sterile pustules and ulcers occur on the site of minor trauma similar to blood sampling. Geometric, bizarre-shaped, angular ulcers are characteristic of a self-inflicted, factitial trigger. Hyper- and hypomelanoses could be further subdivided into localized or generalized (total-body) alterations of pigmentation (Table 522-12). Freckles (ephelides), that are gentle brown-red macules present in sun-exposed areas, are attributable to increased melanin production in regular numbers of melanocytes. Lentigines are also hyperpigmented macules, but they occur due to increased numbers of melanocytes within the basal layer of the epidermis. Two sorts are acknowledged: lentigos that occur early in life and are congenital and actinic lentigines, that are acquired in middle age and are related to solar harm over the face, arms, and dorsum of the hands. Melasma (chloasma) of the face usually affects women; the melanocytes produce more melanin than regular in response to hormonal elements (occurs during being pregnant or while on birth control pills) in affiliation with ultraviolet radiation. This type of pigmentation happens symmetrically over the malar eminences, brow, and higher lip. The lesions could fade with supply but usually persist and are accentuated when birth control tablets are used. Hydroquinone, a bleaching agent (2 to 4% creams), is controversial and should worsen the situation. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is macular pigmentation following inflammatory skin diseases. Cafe au lait spots are gentle brown (coffee-with-cream hue) macules that occur on the trunk and extremities in neurofibromatosis (Chapter 456). Keratoses, keratoacanthomas, basal and squamous cell cancers, and malignant melanomas evolve and regularly lead to early dying. This disease could be delicate in its preliminary presentation, and whole avoidance of the solar from adolescence could prevent subsequent fatal skin cancers. Other circumstances during which addisonian-like diffuse hyperpigmentation could be seen embody scleroderma, lupus erythematosus, and hyperthyroidism. Hyperpigmentation happens with cyclophosphamide, busulfan, daunorubicin, and doxorubicin. Bleomycin can produce a particular linear "flagellate" pattern of hyperpigmentation, usually seen on the trunk. Antimalarials may cause a patchy slate-gray pigmentary alteration confined to cartilaginous buildings (pseudo-ochronosis), and the pimples treatment minocycline may cause similar pigmentary deposition within the skin, nails, bones, and enamel. In addition, inorganic trivalent arsenicals (found in insecticides and contaminated water) may also produce a generalized brown pigmentation, but on this occasion the hypermelanosis is studded with small, scattered, depigmented macules (likened to rain drops on a dusty road) and punctate keratoses on the palms and soles. Hemochromatosis (Chapter 221) causes a metallic gray-brown generalized hyperpigmentation, and cutaneous adjustments are the presenting sign in 25 to 40% of patients. Similarly, brown generalized hyperpigmentation, which is accentuated in uncovered areas, in affiliation with pruritus, jaundice, and xanthoma, is typical of biliary cirrhosis (Chapter 157). Vitiligo, a circumscribed hypomelanosis of progressively enlarging amelanotic macules in a symmetrical distribution around body orifices and over 2292 bony prominences (knees, elbows, hands), is familial in 36% of cases. In one third of cases, some spontaneous repigmentation happens, significantly in sun-exposed areas. Circulating complement-binding antimelanocyte antibodies have been present in some vitiligo patients. If an inflammatory border rims the patches of pigment loss, topical steroids could prove beneficial in slowing or halting development of disease. Piebaldism is a dominantly inherited situation of localized hypopigmentation that resuts from a mutation within the c- kit proto-oncogene. Patients present with a characteristic white forelock and hypomelanosis on the extremities, anterior thorax, and central scalp, presumably representing mosiac patches of mutated neural crest cells. Tuberous sclerosis is an autosomal dominant neurocutaneous dysfunction that features localized hypopigmentation in nearly all cases. The "ash-leaf macule," a distinctively formed focal patch of pigment diminution sometimes on the trunk, is characteristic of this disease and is the earliest presenting cutaneous manifestation. Although up to as} 4% of the conventional population has one hypopigmented macule, quantity of} lesions strongly recommend tuberous sclerosis (Chapter 456). Pityriasis alba presents as oval hypopigmented macules on the cheeks, trunk, and extremities of kids, significantly those with darker skin sorts, and certain represents a form of post-inflammatory pigment loss. Infectious causes of localized pigment loss embody the non-venereal treponemal an infection pinta, which is endemic in areas of Central and South America. Certain chemicals, significantly phenol derivatives, when applied to the skin, could trigger everlasting depigmentation. Hypomelanosis has been observed on the hands of black-skinned individuals carrying rubber gloves during which hydroquinine is used as an antioxidant. Oculocutaneous albinism, which is an autosomal recessive dysfunction because of of} mutations affecting melanin biosynthesis, generally leads to pigmentary absence or dilution of the hair, skin, and eyes. Mutations on this gene trigger different diseases similar to Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes, as well as|in addition to} autosomal recessive ocular albinism. The proximal nail fold homes the matrix of the nail, the place basal cells rapidly proliferate and differentiate into the nail plate, which grows over the nail bed (Table 522-14). In 10% of lichen planus patients, accentuated longitudinal nail ridging happens with pterygium formation resulting from harmful focal scarring of the matrix. Atopic eczema and different eczematous entities could trigger pitting, transverse striations, and onycholysis. Nail adjustments in psoriasis (see earlier) involve fingernails more regularly than toenails. Onychomycosis, or fungal infections of the nail, attributable to dermatophyte (tinea unguium) or candidal infections. Infection of toenails is more frequent than of fingernails, but all nails concerned. The nail plate is discolored, thickened, crumbly, and onycholytic with accumulation of particles. White superficial onychomycosis appears as white patches within the toenail plate outcome of|because of|on account of} organisms growing on the floor and barely penetrating the nail. An uncommon situation, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, is attributable to widespread Candida albicans an infection leading to diffuse white thickening of all nails. Terbinafine, itraconazole, griseofulvin, and ketoconazole are efficient therapies (see earlier). In older individuals, toenail problems could by no means be completely eradicated because of|as a outcome of} the nails grow so slowly. Residual fungal spores in sneakers and surroundings no doubt trigger frequent recurrences; topical antifungal powders useful in long-term prophylaxis. Paronychia, or painful, red swelling of the nail fold, could be either acute or chronic. This an infection usually happens in hands of those continually uncovered to a moist surroundings (bartenders, janitors). Therapy consists of avoidance of water and use of appropriate antibacterial or antifungal options two or 3 times a day for a month or so. Splinter hemorrhages outcome from the extravasation of blood from longitudinally oriented vessels of the nail bed. Longitudinal pigmented bands occur most frequently in response to trauma or a nevus situated within the matrix. Yellow nail syndrome reveals yellow thickening of the nails with absence of the lunula and variable levels of onycholysis accompanying pulmonary circumstances similar to bronchiectasis, pleural effusion, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clubbing of the nails (increased bilateral curvature of the nails with enlargement of the soft connective tissue of the distal phalanges resulting within the flattening of the obtuse angle formed by the proximal finish of the nail and the digit) happens most frequently with bronchiectasis, lung abscess, and pulmonary neoplasms.
References:
- https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/CRC/PDF/Public/8669.00.pdf
- https://www.stjoes.org/ourpages/auto/2013/12/8/49320261/Genetic%20Disorder%20Research%20Assignment.pdf
- https://www.pdffiller.com/240872-Radar8-3-3-RADAR--Search-into-EH---Archibel-Various-Fillable-Forms
.png)