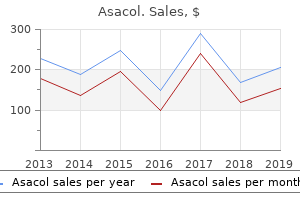
400 mg asacol
Agglutination is the clumping collectively of particles, usually by antibody molecules binding to antigens on the surfaces of adjoining particles. When the particles are red blood cells, the phenomenon identified as} hemagglutination. Agonist peptides are peptide antigens that activate their particular T cells, inducing them to make cytokines and to proliferate. They are thought to differ from antagonist peptides by their ability to induce T-cell receptor dimerization. Allelic exclusion refers to reality that|the fact that} in a heterozygous individual, only one of the different C-region alleles of the heavy or mild chain is expressed in a single B cell and in an immunoglobulin molecule. The time period has come to be used more generally to describe the expression of a single receptor specificity in cells with the potential to categorical two or more receptors. Allergic bronchial asthma is constriction of the bronchial tree because of of} an allergic response to inhaled antigen. The lining of the eye, called the conjunctiva, manifests allergic conjunctivitis in sensitized individuals exposed to allergens. An allergic response is a response to innocuous environmental antigens, or allergens, because of of} preexisting antibody or primed T cells. There are varied immune mechanisms of allergic reactions, but the commonest is the binding of allergen to IgE antibody on mast cells, which causes bronchial asthma, hay fever, and other frequent allergic reactions. Allergic rhinitis is an allergic response in the nasal mucosa, recognized as|also called|also referred to as} hay fever, that causes runny nose, sneezing, and tears. It results from the interaction between the antigen and antibody or primed T cells produced by earlier publicity to the same antigen. An allograft is a graft of tissue from an allogeneic or nonself donor of the same species; such grafts are invariably rejected unless the recipient is immunosuppressed. Allotypes are allelic polymorphisms that can be be} detected by antibodies particular for the polymorphic gene products; in immunology, allotypic variations in immunoglobulin molecules were important in deciphering the genetics of antibodies. An altered peptide ligand, or partial agonist, is a peptide, usually carefully associated to an agonist peptide in amino acid sequence, that induces only a partial response from T cells particular for the agonist peptide. The different pathway additionally amplifies the classical pathway of complement activation. Anaphylactic shock or systemic anaphylaxis is an allergic response to systemically administered antigen that causes circulatory collapse and suffocation because of of} tracheal swelling. It results from binding of antigen to IgE antibody on connective tissue mast cells throughout the body, leading to the disseminated launch of inflammatory mediators. Anaphylatoxins are small fragments of complement proteins, launched by cleavage during complement activation. These small fragments are recognized by particular receptors, and so they recruit fluid and inflammatory cells to websites of their launch. The fragments C5a, C3a, and C4a are all anaphylatoxins, listed in order of reducing potency in vivo. Antagonist peptides are peptides, usually carefully associated in sequence to an agonist peptide, that inhibit the response of a cloned T-cell line particular for the agonist peptide. An antibody is a protein that binds specifically to a selected substanceits antigen. Each antibody molecule has a unique structure that enables it to bind specifically to its corresponding antigen, but all antibodies have the same total structure and are identified collectively as immunoglobulins or Igs. Antibodies are produced by plasma cells in response to infection or immunization, and bind to and neutralize pathogens or prepare them for uptake and destruction by phagocytes. The antibody repertoire or immunoglobulin repertoire describes the entire number of antibodies in the body of a person. The antigen-binding web site of an antibody, or antibody combining web site, is found on the surface of the antibody molecule that makes physical contact with the antigen. Antigen-binding websites are made up of six hypervariable loops, three from the light-chain V region and three from the heavy-chain V region. In an antigen-capture assay, the antigen binds to a selected antibody, and its presence is detected by a second antibody that should be labeled and directed at a unique epitope. Influenza virus varies from 12 months to 12 months by a means of antigenic drift during which level mutations of viral genes cause small variations in the structure of viral surface antigens. Periodically, influenza viruses undergo an antigenic shift by way of reassortment of their segmented genome with another influenza virus, changing their surface antigens radically. The primary antigen-presenting cells for T cells are dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells. T and B lymphocytes collectively bear on their surface highly various antigen receptors capable of recognizing a wide variety of antigens. Anti-immunoglobulin antibodies are antibodies against immunoglobulin constant domains, helpful for detecting sure antibody molecules in immunoassays and other purposes. These can be divided into anti-isotype antibodies made in a unique species, anti-allotype antibodies made in the same species against allotypic variants, and anti-idiotype antibodies, made against unique determinants to a single antibody. Anti-lymphocyte globulin is antibody raised in another species against human T cells. An antiserum: antisera is the fluid part of clotted blood from an immune individual that contains antibodies against the molecule used for immunization. Antisera comprise heterogeneous collections of antibodies, which bind the antigen used for immunization, but each has its own structure, its own epitope on the antigen, and its own set of cross-reactions. Aplastic anemia is a failure of bone marrow stem cells in order that formation of all mobile elements of the blood ceases; it may be} treated by bone marrow transplantation. Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a type of cell death during which the cell activates an inside death program. Proliferating cells frequently undergo apoptosis, which is a pure process in growth, and proliferating lymphocytes undergo high charges of apoptosis in growth and through immune responses. Apoptosis contrasts with necrosis, death from without, which happens in conditions similar to poisoning and anoxia. The appendix is a gut-associated lymphoid tissue located at the beginning of the colon. The Arthus response is a pores and skin response during which antigen is injected into the dermis and reacts with IgG antibodies in the extracellular areas, activating complement and phagocytic cells to produce an area inflammatory response. Atopic allergy, or atopy, is the elevated tendency seen in some people to produce instant hypersensitivity reactions (usually mediated by IgE antibodies) against innocuous substances. Pathogens are mentioned to be attenuated once they can develop in their host and induce immunity without producing critical medical disease. A graft of tissue from one web site to another on the same individual identified as} an autograft. Diseases during which the pathology is brought on by adaptive immune responses to self antigens are called autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is a pathological situation with low ranges of red blood cells (anemia), which is brought on by autoantibodies that bind red blood cell surface antigens and goal the red blood cell for destruction. An adaptive immune response directed at self antigens identified as} an autoimmune response; likewise, adaptive immunity particular for self antigens identified as} autoimmunity. Avidity is the sum whole of the energy of binding of two molecules or cells to one another at a number of} websites. It is distinct from affinity, which is the energy of binding of one web site on a molecule to its ligand. The antigen receptor on B lymphocytes, usually called the B-cell receptor, is a cell-surface immunoglobulin. On activation by antigen, B cells differentiate into cells producing antibody molecules of the same antigen specificity as this receptor. They have a far less various repertoire of receptors than do B-2 cells, recognized as|also called|also referred to as} typical B cells, which are generated in the bone marrow throughout life, rising to populate the blood and lymphoid tissues. A sheet considered one of the|is among the|is doubtless certainly one of the} basic structural constructing blocks of proteins, consisting of adjoining, extended strands of amino acids (strands) which might be} bonded collectively by interactions between spine amide and carbonyl groups. A barrel or a sandwich is another means of describing the structure of the immunoglobulin domain. Many infectious diseases are brought on by bacteria, which are prokaryotic microorganisms that exist as many alternative species and strains.
Proven asacol 800mg
Antibodies directed towards the type-specific capsular polysaccharides defend towards illness brought on by immunologically related strains, so capsular switching allows a pressure to keep away from immune clearance. The capsular polysaccharides are soluble and have been referred to as particular soluble substances. Free polysaccharides can defend viable organisms from phagocytosis by binding with opsonic antibodies. Pneumococcal illness is most commonly related to an antecedent viral respiratory illness, corresponding to influenza, or with different situations that intrude with bacterial clearance, corresponding to chronic pulmonary illness, alcoholism, congestive heart failure, diabetes mellitus, chronic renal illness, and splenic dysfunction or splenectomy. Clinical Diseases Pneumonia (Clinical Case 19-3) Pneumococcal pneumonia develops when the bacteria multiply within the alveolar spaces. Erythrocytes leaking from congested capillaries accumulate within the alveoli, adopted by the neutrophils, and then the alveolar macrophages. Resolution happens when particular anticapsular antibodies develop, facilitating phagocytosis of the organism and microbial killing. The onset of the scientific manifestations of pneumococcal pneumonia is abrupt, consisting of a severe shaking chill and sustained fever of 39� C to 41� C. The affected person usually has signs of a viral respiratory tract an infection 1 to three days before the onset. Most sufferers have a productive cough with blood-tinged sputum, and they generally have chest ache (pleurisy). Patients often recuperate quickly after the initiation of acceptable antimicrobial remedy, with full radiologic resolution in 2 to three weeks. The total mortality price is 5%, although the chance of death is influenced by the serotype of the organism and the age and underlying illness of the affected person. The mortality price is significantly larger in sufferers with illness brought on by Epidemiology S. Subsequently, the kid is transiently colonized with different serotypes of the organism. The duration of carriage decreases with each successive serotype carried, partially due to the event of serotype-specific immunity. Although new serotypes are acquired 12 months long}, the incidence of carriage and related illness is highest through the cool months. The strains of pneumococci that cause illness are the identical as those related to carriage. Pneumococcal illness happens when organisms colonizing the nasopharynx and oropharynx unfold to the lungs (pneumonia), paranasal sinuses (sinusitis), ears (otitis media), or meninges (meningitis). It is acknowledged that some serotypes have the next predilection for invasive pneumococcal illness. Although the introduction of vaccines for pediatric and grownup populations has decreased the incidence of illness brought on by S. Disease is most common in youngsters and the elderly with low ranges of protecting antibodies directed towards the pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides. Pneumonia happens when the endogenous oral organisms are aspirated into the lower airways. Although strains can Clinical Case 19-3 Streptococcus pneumoniae Pneumonia Costa and associates (Am J Hematol 77:277�281, 2004) described a 68-year-old lady who was in good health till three days before hospitalization. She developed fever, chills, elevated weak point, and a productive cough with pleuritic chest ache. On admission, she was febrile, had an elevated pulse and respiration price, and was in reasonable respiratory misery. Chest radiograph demonstrated infiltrates in the best and left lower lobes, with pleural effusions. Therapy with a fluoroquinolone was initiated, and blood and respiratory cultures were optimistic for S. Additional exams (serum and urine protein electrophoresis) revealed the affected person had a number of} myeloma. This affected person illustrates the everyday picture of pneumococcal lobar pneumonia and the elevated susceptibility to an infection in sufferers with defects in their capacity to clear encapsulated organisms. In distinction, bacteria are generally not present within the blood of sufferers with sinusitis or otitis media. Endocarditis can happen in sufferers with normal or beforehand broken heart valves. Laboratory Diagnosis Microscopy Gram stain of sputum specimens is a rapid method to diagnose pneumococcal pneumonia and meningitis. The organisms characteristically seem as elongated pairs of gram-positive cocci surrounded by an unstained capsule; nonetheless, they might also seem to be gram unfavorable outcome of|as a result of} they have a tendency not to stain properly (particularly in older cultures). In addition, their morphology distorted in a affected person receiving antibiotic remedy. In this test, polyvalent anticapsular antibodies are mixed with the bacteria, and then the combination is examined microscopically. Patients with splenic dysfunction or splenectomy can also have severe pneumococcal illness due to decreased bacterial clearance from the blood and the defective production of early antibodies. In these sufferers, illness could be related to a fulminant course and high mortality price. Pleural effusions are seen in roughly 25% of sufferers with pneumococcal pneumonia, and empyema (purulent effusion) is a uncommon complication. Antigen Detection Pneumococcal C polysaccharide is excreted in urine and could be detected using a commercially prepared immunoassay. Sensitivity has been reported to be 70% in sufferers with bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia; nonetheless, specificity could be low, particularly in pediatric sufferers. Middle ear an infection (otitis media) is primarily seen in young youngsters, but bacterial sinusitis can happen in sufferers of all ages. Culture Sputum specimens should be inoculated onto an enriched nutrient medium supplemented with blood. Selective media have been used with some success to isolate the organism from sputum specimens, however it takes some technical ability to distinguish S. An aspirate must be obtained from the sinus or center ear for the organism responsible for sinusitis or otitis to be recognized definitively. Mortality and severe neurologic deficits are four to 20 times extra common in sufferers with meningitis brought on by S. Thus the organism could be identified by inserting a drop of bile on an isolated colony. The isolate is streaked onto a blood agar plate and a disk saturated with optochin is positioned in the middle of|in the midst of|in the course of} the inoculum. A zone of inhibited bacterial progress is seen around the disk after overnight incubation. Additional biochemical, serologic, or molecular diagnostic exams could be carried out for a definitive identification. The cocci develop both aerobically and anaerobically in a broad temperature range (10� C to 45� C), in a large pH range (4. Thus there are very few scientific situations that inhibit the growth of enterococci. Glucose is fermented with l-lactic acid because the predominant finish product (enterococci are generally referred to as lactic acid bacteria). After 24 hours of incubation, colonies on enriched sheep blood agar are large and might seem nonhemolytic, -hemolytic, or, hardly ever, -hemolytic. Treatment, Prevention, and Control Historically penicillin was the therapy of choice for pneumococcal illness; nonetheless, in 1977, researchers in South Africa reported isolates of S. Now resistance to penicillin is noticed for as many as half of the strains isolated within the United States and in different countries. Resistance to penicillins is related to a decreased affinity of the antibiotic for the penicillinbinding proteins present within the bacterial cell wall, and sufferers contaminated with resistant bacteria have an elevated threat of an antagonistic consequence. Thus, for serious pneumococcal infections, therapy with a combination of antibiotics is beneficial till in vitro susceptibility outcomes are available. Vancomycin combined with ceftriaxone is used generally for empirical therapy, adopted by monotherapy with an efficient cephalosporin, fluoroquinolone, or vancomycin. Efforts to forestall or management the illness have focused on the event of effective anticapsular vaccines. A 23valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (with 23 completely different capsular polysaccharides) is beneficial for children older than 2 years and adults.
Diseases
- Rectal neoplasm
- Ulna metaphyseal dysplasia syndrome
- Dyserythropoietic anemia, congenital type 3
- Scoliosis as part of NF
- Craniostenosis cataract
- Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita neurogenic type
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis
- Spastic paraplegia familial autosomal recessive form
- Prognathism dominant
Order 800mg asacol
The nonlymphoid area of the spleen during which red blood cells are damaged down is known as} the red pulp. When neutrophils and macrophages take up opsonized particles, this triggers a metabolic change within the cell called the respiratory burst. The Rhesus (Rh) blood group antigen is a red cell membrane antigen that additionally be|can be} detectable on the red blood cells of rhesus monkeys. Rheumatic fever is brought on by antibodies elicited by an infection with some Streptococcus species. The disease is accompanied by the production of rheumatoid issue, an IgM anti-IgG antibody that can also be|may additionally be|can be} produced in regular immune responses. Scatchard evaluation is a mathematical evaluation of equilibrium binding that allows the affinity and valence of a receptorligand interplay to be decided. Scavenger receptors on macrophages and different cells bind to quite a few ligands and remove them from the blood. This approach is extensively used to characterize proteins, particularly after labeling and immunoprecipitation. A secondary antibody response is the antibody response induced by a second or booster injection of antigena secondary immunization. The secondary response begins sooner after antigen injection, reaches larger ranges, is of higher affinity than the first response, and is dominated by IgG antibodies. Therefore, the response to every immunization is more and more intense, so the secondary, tertiary, and subsequent responses are of accelerating magnitude. When the recipient of a first tissue or organ graft has rejected that graft, a second graft from the identical donor is rejected more quickly and vigorously in what is known as} a second set rejection. The co-stimulatory sign required for lymphocyte activation is commonly called a second sign, with the primary sign coming from the binding of antigen by the antigen receptor. The secretory part attached to IgA antibodies in physique secretions is a fragment of the poly-Ig receptor left attached to the IgA after transport across epithelial cells. If the cell begins to proliferate in consequence, this is called clonal choice, and the cell founds a clone; if the cell is killed outcome of|because of|on account of} binding antigen, this is called adverse choice or clonal deletion. Selectins are a household of cell-surface adhesion molecules of leukocytes and endothelial cells that bind to sugar moieties on specific glycoproteins with mucinlike options. Lymphocytes are screened throughout their immature stages for reactivity with self antigens, and those who do reply bear apoptosis. Tolerance is the failure to reply to an antigen; when that antigen is borne by self tissues, tolerance is known as} self tolerance. Allergic reactions require prior immunization, called sensitization, by the allergen that elicits the acute response. A sequence motif is a pattern of nucleotides or amino acids shared by completely different genes or proteins that usually have related functions. Seroconversion is the part of an an infection when antibodies in opposition to the infecting agent are first detectable within the blood. Serology is the usage of} antibodies to detect and measure antigens using serological assays, so called outcome of|as a outcome of} these assays were initially carried out with serum, the fluid part of clotted blood, from immunized people. Different strains of micro organism and different pathogens can generally be distinguished by their serotype, the power of an immune serum to agglutinate or lyse some strains of micro organism and not others. Serum illness happens when overseas serum or serum proteins are injected into an individual. It is brought on by the formation of immune complexes between the injected protein and the antibodies formed in opposition to it. A sign joint is formed by the exact joining of recognition sign sequences within the process of somatic recombination that generates T-cell receptor and immunoglobulin genes. Signal transduction describes the final process by which cells understand adjustments of their setting. In lymphocytes, the most important adjustments are these occurring throughout an infection that generate antigens that stimulate the cells of the immune system to result in an adaptive immune response. A single-chain Fv fragment, comprising a V area of a heavy chain linked by a stretch of synthetic peptide to a V area of a lightweight chain, can be made by genetic engineering. Sirolimus is the drug name that has been adopted for the chemical rapamycin; the 2 terms are used interchangeably within the literature. Small G proteins are monomeric G proteins corresponding to Ras, that act as intracellular signaling molecules downstream of many transmembrane signaling occasions. Smallpox is an infectious disease, brought on by the virus variola, that once killed at least of|no much less than} 10% of contaminated individuals. When immunologists found that antibodies were variable, they entertained various theories, together with the somatic diversification concept that postulated that the genes for immunoglobulin were fixed, and that they diversified in somatic cells. This turned out to be partly true, as somatic hypermutation is now nicely established. However, different theories were needed to explain different options of antibody range, together with somatic gene rearrangement and isotype switching. During lymphocyte improvement, receptor gene segments bear somatic recombination to generate intact V-region exons that encode the V area of every immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor chain. The specificity of an antibody determines its ability to distinguish the immunogen from different antigens. The spleen is an organ within the higher left facet of the peritoneal cavity containing a red pulp, concerned in removing senescent blood cells, and a white pulp of lymphoid cells that reply to antigens delivered to the spleen by the blood. The improvement of B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes happens in affiliation with stromal cells, which offer various soluble and cell-bound signals to the growing lymphocyte. Antigens can be injected into the subcutaneous layer to induce an adaptive immune response. The membrane-bound immunoglobulin that acts as the antigen receptor on B cells is commonly recognized as|often identified as} floor immunoglobulin (sIg). Together, this chain can pair with an in-frame heavy chain, move to the cell floor, and sign for pre-B-cell growth. Systemic anaphylaxis is probably the most harmful form of instant hypersensitivity response. The activation of these mast cells causes widespread vasodilation, tissue fluid accumulation, epiglottal swelling, and infrequently death. Most T cells have a:b heterodimeric receptors but g:d T cells have a g:d heterodimeric receptor. Tacrolimus and cyclosporin A are probably the most generally used immunosuppressive medicine in organ transplantation. The functions of effector T cells are always assayed by the adjustments that they produce in antigenbearing goal cells. These cells can be B cells, which are activated to produce antibody; macrophages, which are activated to kill micro organism or tumor cells; or labeled cells which are be} killed by cytotoxic T cells. It is produced when latently contaminated cells are activated, and it binds to a transcriptional enhancer within the lengthy terminal repeat of the provirus, rising the transcription of the proviral genome. T-cell hybrids are formed by fusing an antigen-specific, activated T cell with a T-cell lymphoma. The hybrid cells bear the receptor of the specific T-cell mother or father and develop in tradition just like the lymphoma. T-cell strains are cultures of T cells grown by repeated cycles of stimulation, usually with antigen and antigen-presenting cells. When single T cells from these strains are propagated, they can provide rise to T-cell clones or cloned T-cell strains. Both of these receptors are expressed with a disulfide-linked homodimer of z chains. The T-cell zones in lymphoid tissues are enriched in T cells and are distinct from the B-cell zones and the stromal parts. The complement system can be activated immediately or by antibody, but each pathways converge with the activation of the terminal complement elements, which could assemble to form the membraneattack advanced. The enzyme terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) inserts nontemplated or Nnucleotides into the junctions between gene segments in T-cell receptor and immunoglobulin Vregion genes. When the identical antigen is injected a third time, the response elicited is known as} a tertiary response and the injection a tertiary immunization. The lymph from many of the physique, besides the pinnacle, neck, and right arm, is gathered in a large lymphatic vessel, the thoracic duct, which runs parallel to the aorta through the thorax and drains into the left subclavian vein. The thoracic duct thus returns the lymphatic fluid and lymphocytes again into the peripheral blood circulation. The thymic anlage is the tissue from which the thymic stroma develops throughout embryogenesis.
Cheap asacol 400mg
During somatic hypermutation in germinal facilities (depicted in the high panel), B cells with autoreactive B-cell receptors can arise. Ligation of those receptors by soluble autoantigen induces apoptosis of the autoreactive B cell by signaling via the Bcell antigen receptor in the absence of helper T cells. Before an immune response could be initiated want to|they should} obtain efficient assist, the B-cell receptors must be ligated, and their intracellular signaling equipment must be set to respond normally. Human autoimmune diseases often appear gradually, making it tough to find out how the method is initiated. Indeed, many experimental autoimmune diseases are induced by mixing tissue cells with adjuvants that include bacteria. For instance, transgenic mice that express a T-cell receptor specific for myelin primary protein (see Section 13-25) often develop spontaneous autoimmune encephalo-myelitis in the event that they} turn out to be infected. One possible mechanism for this lack of tolerance is that the infectious brokers induce co-stimulatory activity on antigen-presenting cells expressing low ranges of peptides from myelin primary protein, thus activating the autoreactive T cells. Bacterial adjuvants are required for induction of experimental autoimmune illness. Moreover, T cells from these mice can switch protection from illness to naive, syngeneic recipients. It has also been suggested that autoimmunity could be initiated by a mechanism recognized as|often known as} molecular mimicry, by which antibodies or T cells generated in response to an infectious agent cross-react with self antigens. To show that infectious brokers can trigger responses that can destroy tissues, mice were made transgenic for a viral nuclear protein driven by the insulin promoter, in order that the protein was expressed solely in pancreatic cells. As the amount of viral protein expressed was low, the T cells that recognized this protein remained immunologically ignorant. That is, they were neither tolerant to the viral protein nor activated by it, and the animals confirmed no signal of illness. Virus infection can break tolerance to a transgenic viral protein expressed in pancreatic cells. It is believed that infectious brokers can sometimes elicit T-cell responses that cross-react with self peptides (a course of recognized as|often known as} molecular mimicry) and that this might trigger autoimmune illness in an analogous way It has lengthy been known that molecular mimicry can function in antibody-mediated autoimmunity; microbial antigens can elicit antibody responses that react not solely with the antigens on the pathogen but in addition with host antigens of similar construction. These elicit antibodies that cross-react with kidney, joint, and coronary heart antigens to produce rheumatic fever. These and another mechanisms that would allow an infectious agent to break tolerance are summarized in. Because some antigens are sequestered from the circulation, both behind a tissue barrier or inside the cell, an infection that breaks cell and tissue obstacles might expose hidden antigens (first panel). A second chance is that infectious brokers might trigger expression of co-stimulators on antigen-presenting cells which have taken up tissue antigens, thereby inducing an autoimmune response (second panel). Because the infectious agent induces a helper T-cell response, any B cell that recognizes the self protein will also obtain assist (third panel). Such responses must be self-limiting as soon as} the infectious agent is eradicated, end result of|as a result of} at this level the T-cell help will not be provided. Molecular mimicry might end in infectious brokers inducing both T- or B-cell responses that can cross-react with self antigens (fourth panel). Polyclonal T-cell activation by a bacterial superantigen might overcome clonal anergy, allowing an autoimmune course of to begin (last panel). The argument that some autoimmune diseases may be initiated by infection is strengthened by reality that|the truth that} there are quantity of} human autoimmune diseases by which a prior infection with a selected agent or class of brokers leads to a particular illness. Several autoimmune diseases happen after specific infections and are presumably triggered by the infection. The case of post-streptococcal illness is best known but is now rare end result of|as a result of} efficient antibiotic remedy of group A streptococcal infection often prevents postinfection issues. The means of clonal deletion influences the kinds of autoimmune illness that can happen. Autoimmunity to these antigens, similar to insulin, causes organ-specific autoimmune diseases similar to sort I diabetes mellitus. Predisposition to these diseases inherited abnormalities in the regulation of immune responses and in the waste disposal mechanisms for removing dying cells at sites of inflammation. A third mechanism of self-tolerance dominant suppression has been noted in quantity of} experimental techniques of autoimmunity and graft rejection; if this mechanism presumably be} understood, it may be possible to use it to forestall each graft rejection and autoimmunity, that are carefully related issues. The response to noninfectious antigens causes three kinds of medical problem: allergy (the subject of Chapter 12), and autoimmunity and graft rejection, the topics of this chapter. These responses have many options in frequent end result of|as a result of} all use the normal mechanisms of the adaptive immune response to produce signs and pathology. What is unique to these syndromes is their initiation and the character of the antigens recognized, not the underlying nature of the response itself. For each of those undesirable classes of response, the question is control them without adversely affecting protecting immunity to infection. The answer might lie in a extra full understanding of the regulation of the immune response, particularly the suppressive mechanisms that seem to be important in tolerance. The deliberate control of the immune response is examined additional in the subsequent chapter. Balancing immunity and tolerance: deleting and tuning lymphocyte repertoires Proc. A few autoreactive cells in an autoimmune infiltrate control an enormous population of nonspecific cells: a tale of good bombs and the infantry Proc. Immunopathology or organ-specific autoimmunity as a consequence of virus infection Immunol. A full genomic display for a number of} sclerosis underscores a role for the major histocompatibility complicated the Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Group Nat. Discovering the function of the major histocompatibility complicated in the immune response Annu. A mechanism for the major histocompatibility complex-linked resistance to autoimmunity J. Serum amyloid P component controls chromatin degradation and prevents antinuclear autoimmunity Nat. Accelerated development of IgG autoantibodies and autoimmune illness in the absence of secreted IgM Proc. Deficiency in serum immunoglobulin (Ig)M predisposes to development of IgG autoantibodies J. [newline]Significance of autoreactive T cells in diseases similar to a number of} sclerosis utilizing an innovative primate model J. Natural and pathologic human autoimmune responses to carbohydrate antigens on purple blood cells Springer Semin. Role of the complement membrane assault complicated (C5b-9) in mediating experimental mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis Kidney Int. The complement assault phase: control of lysis and non-lethal results of C5b-9 Immunopharmacology 1992. Cytotoxic motion and other metabolic consequences of terminal complement proteins Prog. Mechanism of Graves thyroiditis: implications for ideas and remedy of autoimmunity Int. Uncoupling of immune complicated formation and kidney harm in autoimmune glomerulonephritis Science 1998. Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology Adv. Cigarette smoking and lung haemorrhage in glomerulonephritis brought on by autoantibodies to glomerular basement membrane Lancet 1983. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies: present diagnostic and pathophysiological potential Kidney Int. Association of neonatal myasthenia gravis with antibodies towards the fetal acetylcholine receptor J. Clinical and experimental observations in sufferers with congenital myasthenic syndromes Ann. T-cell clones specific for myelin primary protein induce persistent relapsing paralysis and demyelination Nature 1985. Myasthenia gravis: recognition of a human autoantigen at the molecular stage Immunol. B lymphocytes as autoantigenpresenting cells in the amplification of autoimmunity Ann.
Buy asacol 400mg
Serology (as used in this case) is essentially the most commonly used diagnostic process however is also be|can be} insensitive. Infection occurs by person-to-person unfold through infectious respiratory secretions. He was well until four days earlier than admission, when he developed a fever reaching 40� C, chills, extreme headache, and muscle aches. The patient recalled having had quite a few tick bites 10 days earlier than the onset of symptoms. Rocky Mountain noticed fever was considered in the analysis, and serologic exams for Rickettsia species confirmed this analysis. Although chloramphenicol has in vitro exercise, a high incidence of relapse is related to this antibiotic. Rickettsiae are small and stain poorly with the Gram stain outcome of|as a outcome of} the peptidoglycan layer is minimal. Approximately 1 to three weeks after exposure, patients develop a flulike illness with high fever, headache, malaise, and myalgias. Approximately 5 to eleven days after exposure, a similar flulike illness develops, however a rash is rare. In both diseases, more than half of the infected individuals require hospitalization, and recovery is prolonged. Severe diseases embody pneumonia, hepatitis, or isolated fever; nevertheless, the commonest presentation is subacute endocarditis. A � Rickettsiaceae the family Rickettsiaceae consists of two genera, Rickettsia and Orientia, and the genus Rickettsia is subdivided into the noticed fever group and the typhus group. Many species of Rickettsia in the noticed fever group are related to human disease; nevertheless, only Rickettsia rickettsii (Rocky Mountain noticed fever) and Rickettsia akari (rickettsialpox) are discussed in this chapter. Burnet, who isolated the bacterium from ticks in Montana and patients in Australia, respectively are members of the typhus group: R. A single species is in the genus Orientia, Orientia tsutsugamushi, the organism answerable for the disease scrub typhus. Both groups of organisms are seen finest with Giemsa or Gimenez stains (Figure 34-1). Rickettsia and Orientia are strict intracellular parasites found free in the cytoplasm of infected cells. The micro organism enter eukaryotic cells by attaching to host cell floor receptors and stimulating phagocytosis. Multiplication in the host cell by binary fission is gradual (generation time, 9 to 12 hours). The noticed fever group of Rickettsia and Orientia develop in the cytoplasm and nucleus of infected cells and are regularly released from cells by way of lengthy cytoplasmic projections. In distinction, the typhus group accumulates in the cell cytoplasm until the cell membranes lyse, signaling cell death and bacterial release. It is believed that the elemental distinction is caused by intracellular motility-the noticed fever group is able to|is ready to} polymerize host cell actin, whereas the typhus group lacks the required gene. The micro organism rely upon their host cell for many of} functions: carbohydrate metabolism, lipid biosynthesis, nucleotide synthesis, and amino acid synthesis. The major medical manifestations appear to outcome from the replication of micro organism in endothelial cells, with subsequent harm to the cells and leakage of the blood vessels. Hypovolemia and hypoproteinemia caused by the lack of plasma into tissues can result in lowered perfusion of assorted organs and organ failure. Mites Soft ticks (Lone Star tick Soft ticks (Lone Star tick Soft ticks (Blacklegged tick) Japan, Eastern Asia, Northern Australia, Western and Southwestern Pacific North and South America, Asia North America (uncommon, Missouri) North America (Upper Midwest and Northeast), Europe, Asia Worldwide Ticks incidental (most infections following inhalation) Epidemiology the pathogenic species of Rickettsia and Orientia are maintained in animal and arthropod reservoirs and are transmitted by arthropod vectors. Rickettsiae are maintained in reservoir hosts (primarily rodents) and their arthropod vectors. The distribution of rickettsial diseases is decided by the distribution of the arthropod host/vector. In 2011, more than 2800 cases of Rocky Mountain noticed fever have been reported in the United States. More than 90% of the infections occurred from April to September, corresponding to the period of best tick exercise, with the majority of of} infections reported in 5 states: North Carolina, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Tennessee, and Missouri. The three onerous ticks most commonly related to disease in the United States are the American dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis) in the southeastern states and on the West Coast, brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) in Arizona, and wooden tick (Dermacentor andersoni) in the Rocky Mountain States and southwestern Canada. The dormant avirulent rickettsiae are activated by the nice and cozy} blood meal and then released from the tick salivary glands into the blood of the human host. Culture-confirmed disease has been reported from Ukraine, Croatia, Korea, and the United States, primarily in the New York City area. A cluster of cases was documented in New York City following the release of Bacillus anthracis in 2001, when biopsies of eschars from city residents have been demonstrated to comprise R. Humans are the principal reservoir of this disease, and the vector is the human body louse, Pediculus humanus. Epidemic typhus occurs amongst people residing in crowded, unsanitary situations that favor the unfold of body lice-conditions such as those who come up throughout wars, famines, and natural disasters. Lice die from their infection inside 2 to three weeks, preventing transovarian transmission of R. The disease is current in Central and South America, Africa, and less commonly in the United States. Sporadic disease in the United States is primarily restricted to rural areas of the japanese states. In this area, flying squirrels squirrel fleas and lice are infected with R. In the United States, 50 to 100 cases are reported yearly, with most cases in the Gulf States (especially Texas) and Southern California. Endemic disease continues to be reported in people residing in the temperate and subtropical coastal areas of Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, and South America. Rodents are the first reservoir, and the rat flea (Xen opsylla cheopis) is the principal vector. However, the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), which infests cats, opossums, raccoons, and skunks, is considered an essential vector for disease in the United States. The reservoir is the mite inhabitants, by which the micro organism are transmitted by transovarian means. Infection is also be|can be} current in the rodent inhabitants, which might serve as a reservoir for mite infections. Scrub typhus is current in people residing in japanese Asia, Australia, and Japan and other Western Pacific islands. Clinical Case 34-1 Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Oster and associates (N Engl J Med 297:859�863, 1977) described a collection of patients who acquired Rocky Mountain noticed fever after working with Rickettsia rickettsii in the laboratory. One patient, a 21year old veterinary technician, presented to a clinic with complaints of myalgia and a nonproductive cough. Intramuscular tetracycline was began, however he remained febrile, and the rash evolved to petechiae on his truck, his extremities, and the soles of his feet. Over the following 2 weeks, the effusions resolved and the patient made a gradual however uneventful recovery. This patient illus trates the attribute presentation of Rocky Mountain noticed fever- headache, fever, myalgias, and a macular rash that can evolve into a petechial or noticed rash. Clinical Diseases Symptomatic Rocky Mountain noticed fever (Clinical Case 34-1) develops 7 days (range, 2 to 14 days) after the tick chew (Table 34-3), though the patient might not recall the painless tick chew. The onset of disease is heralded by a high fever and headache related to malaise, myalgias, nausea, vomiting, abdominal ache, and diarrhea. [newline]A macular rash develops in 90% of patients after three days, initially on the wrists, arms, and ankles and then spreading to the trunk. The rash can evolve to the "noticed" or petechial type, which is a harbinger of extra extreme disease. Complications of Rocky Mountain noticed fever embody neurologic manifestations, pulmonary and renal failure, and cardiac abnormalities. The papule appears approximately 1 week after the chew and shortly progresses to ulceration and then eschar formation. After an incubation period of 7 to 24 days (average, 9 to 14 days), the second phase of the disease develops abruptly, with high fever, extreme headache, chills, sweats, myalgias, and photophobia. A poxlike progression of the rash is then seen by which vesicles type and then crust over. Presence of the rash distinguishes this disease from anthrax and, in a patient with a high fever and eschar, should increase suspicion of rickettsialpox. Despite the appearance of the disseminated rash, rickettsialpox is normally gentle and uncomplicated, and complete healing is seen inside 2 to three weeks with out treatment (Clinical Case 34-2). In one study of epidemic typhus in Africa, medical disease developed a mean of 8 days after exposure (range, 2 to 30 days).
Scutellaria Lateriflora (Skullcap). Asacol.
- Dosing considerations for Skullcap.
- What is Skullcap?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Insomnia, anxiety, seizures, stroke, and other conditions.
- How does Skullcap work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96947

Generic asacol 800 mg
This affected person illustrates (1) the danger issue of an unimmunized affected person traveling to an endemic space, (2) the traditional presentation of extreme respiratory diphtheria, (3) delays associated with diagnosis of an unusual illness, and (4) the difficulties most laboratories would now have isolating the organism in culture. The photograph was taken 4 days after the onset of fever, malaise, and sore throat. Hemorrhage brought on by removing of the membrane by swabbing seems as a dark space on the left. Tellurite inhibits the expansion of most upper respiratory tract bacteria and gram-negative rods and is decreased by C. More extensive biochemical exams or nucleic acid sequencing of species-specific genes is required for identification on the species level. Unfortunately, as a result of|as a end result of} diphtheria most likely not|will not be} suspected initially, vital progression of illness can occur earlier than the antitoxin is administered. Bed rest, isolation to prevent secondary unfold, and maintenance of an open airway in sufferers with respiratory diphtheria are all necessary. After the affected person has recovered, immunization with toxoid is required as a result of|as a end result of} most sufferers fail to develop protecting antibodies after a pure infection. Symptomatic diphtheria can be prevented by actively immunizing folks with diphtheria toxoid. After that point, it is strongly recommended that booster vaccinations with diphtheria toxoid mixed with tetanus toxoid be given each 10 years. The effectiveness of immunization is nicely documented, with illness restricted to nonimmune or incompletely immunized individuals. Nasopharyngeal specimens for culture ought to be collected from all shut contacts and antimicrobial prophylaxis with erythromycin or penicillin started instantly. Any contact who has not completed the sequence of diphtheria immunizations or who has not obtained a booster dose throughout the earlier 5 years should receive a booster dose of toxoid. Bibliography Allerberger F, Wagner M: Listeriosis: a resurgent foodborne infection, Clin Microbiol Infect sixteen:16�23, 2010. Freitag N, Port G, Miner M: Listeria monocytogenes-from saprophyte to intracellular pathogen, Nat Rev Microbiol 7:623�628, 2009. Wing E, Gregory S: Listeria monocytogenes: scientific and experimental update, J Infect Dis 185(Suppl 1):S18�S24, 2002. The gold normal for detection of diphtheria toxin is an in vitro immunodiffusion assay (Elek test). This check can detect the tox gene in scientific isolates and immediately in scientific specimens. E1 Case Study and Questions A 35-year-old man was hospitalized because of headache, fever, and confusion. He had obtained a kidney transplant 7 months earlier, after which he had been given immunosuppressive medication to prevent organ rejection. The most typical gram-positive coccobacillus that causes meningitis in immunosuppressed sufferers is Listeria monocytogenes. Streptococcus pneumoniae, the commonest explanation for bacterial meningitis in the United States, should also to|must also} be considered. However, Listeria are motile and produce weak -hemolysis on blood agar media, properties not shared with S. Listeria can multiply in these food merchandise to excessive concentrations, even when saved in a refrigerator. Other sources of this organism embrace contaminated milk and uncooked vegetables such as cabbage. The ability of the organism to grow at chilly temperatures allows small numbers of organisms to multiply to concentrations that can cause illness. Treatment of Listeria infections is difficult by reality that|the reality that} the organism is naturally proof against many commonly used antibiotics, together with the cephalosporins. The treatment of alternative for critical infections is a mix of ampicillin or penicillin with an aminoglycoside. Antimicrobial susceptibility exams have to be carried out as a result of|as a end result of} increased resistance has been famous. Two weeks earlier, the affected person had seen the event of a dry, persistent cough. Five days earlier than admission, the cough became productive and pleuritic chest pain developed. On the day of admission, the affected person was in mild respiratory misery, and chest radiographs revealed a patchy right upper lobe infiltrate. Sputum specimens had been initially despatched for bacterial culture, and the modified acid-fast stain was constructive. The two most typical genera that stain with the modified acid-fast stain are Mycobacterium and Nocardia. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the most effective known pathogen in the genus however is rare in the United States. More probably the affected person has an infection with one other Mycobacterium species or Nocardia. The organism can become energetic as immunity wanes in old age or through illness, initiate replication, and produce illness. Other mycobacteria species are opportunistic pathogens, mostly infecting immunocompromised sufferers but additionally individuals with persistent pulmonary illness, such as bronchiectasis. Myco bacterium fortuitum and the other "quickly rising" mycobacteria are opportunistic pathogens introduced into wounds or contaminating intravenous catheters. The most typical illnesses associated with Nocardia are pulmonary infections and primary or secondary cutaneous infections. All acid-fast organisms are relatively slow-growing bacteria, requiring incubation for 2 to 7 days (Nocardia, Rho dococcus, Gordonia, Tsukamurella) to lengthy as|so long as} 1 month (Mycobacteria). This is especially problematic with sputum specimens during which more quickly rising bacteria from the oropharynx could obscure the colonies of these organisms, so preprocessing of the specimen to get rid of quickly rising bacteria and use of selective media are required for optimum recovery. Only slowgrowing mycobacteria stain uniformly with sturdy acidfast stains, however all genera will stain with weak or modified acid-fast stains. The most typical mycobacterial species will seem as quick, "beaded" rods, whereas Nocardia species type long filamentous rods. The look of weakly acid-fast�staining filamentous rods is enough for a preliminary identification of Nocardia. Colonies can seem pink, however this sometimes develops after incubation for quantity of} days. This staining property is necessary as a result of|as a end result of} solely five genera of acid-fast bacteria are medically necessary (Table 22-1). All acid-fast organisms are relatively slow-growing bacteria, requiring incubation for 2 to 7 days (Nocardia, Rhodococcus, Gordonia, Tsukamurella) to lengthy as|so long as} 1 month or more (Mycobacteria). Currently, greater than 350 species of acid-fast bacteria have been described; nonetheless, the quantity associated commonly with human illness is comparatively limited (Table 22-2). The spectrum of the infections associated with the acid-fast genera is extensive and consists of insignificant colonization, cutaneous infections, pulmonary illness, systemic infections, and opportunistic infections. Mycobacteria and Nocardia will be the emphasis of this chapter as a result of|as a end result of} these are the commonest acid-fast bacteria answerable for human illness. Table 22-2 Classification of Selected Acid-Fast Bacteria Pathogenic for Humans Organism Pathogenicity Frequency in United States Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex M. Growth properties and colonial morphology are used for the preliminary classification of mycobacteria. The colonies of these mycobacteria are either nonpigmented or a light tan colour (Figure 22-1). The pigmented mycobacteria produce intensely yellow carotenoids, which may be stimulated by exposure to mild (photochromogenic organisms, Figure 22-2) or are produced in the absence of sunshine (scotochromogenic organisms). Currently used methods for fast detection and identification of mycobacteria have made this scheme less necessary. Nonetheless, a pigmented or quickly rising Mycobacterium should by no means be mistaken for M. Maintenance of persistent infection without progression to illness involves a delicate steadiness between development of the bacteria and immunologic regulation. At the same time, the phagosome in a position to|is prepared to} fuse with other intracellular vesicles, permitting entry to nutrients and facilitating intravacuole replication. Phagocytized bacteria are also in a position to} evade macrophage killing mediated by reactive nitrogen intermediates formed between nitric oxide and superoxide anions by catalytically catabolizing the oxidants may be} formed. The effectiveness of bacterial elimination is partially associated to the dimensions of the main target|the primary focus} of infection.
Proven 400 mg asacol
There are, nonetheless, many self molecules out there solely in the periphery whose expression is restricted to explicit organs. An example is thyroglobulin (the precursor of thyroxine), which is expressed solely in the thyroid and at extremely low ranges in plasma. When a mature B cell in the periphery encounters self molecules that bind its receptor, four proposed mechanisms might convey in regards to the observed nonreactivity. First, B cells that recognize a self antigen arrest their migration in the T-cell zone of peripheral lymphoid tissues. This lack of interplay prevents the B cells from migrating out of the T-cell zones into the follicles; instead, the trapped self-reactive B cells undergo apoptosis. Those with reactivity for overseas antigens are shown in yellow; autoreactive cells are grey. The autoreactive cells fail to compete with B cells specific for overseas antigens for exit from the T-cell zone and entry into major follicles (center panel). The autoreactive B cells that fail to obtain survival signals more than likely undergo apoptosis in situ in the T-cell zone (bottom panel). A second mechanism is the induction of B-cell anergy, which is associated with downregulation of floor IgM expression and partial inhibition of the linked signaling pathways. B-cell anergy can be induced by publicity to soluble circulating antigen (see Section 7-17); if mice are inoculated intravenously with protein solutions from which all protein aggregates have been rigorously eliminated to remove multivalent complexes, the peripheral B cells that bind these proteins can be inactivated. An autoreactive B cell encounters its soluble autoantigen in the periphery (first panel), which results in|which finally ends up in} the development of B-cell anergy (second panel). This is characterised by a reduction in each the expression of floor IgM and the signaling pathways after ligation of floor immunoglobulin. A additional mechanism for maintaining peripheral B-cell tolerance is shown in the two panels on the proper. If an anergized, self-reactive B cell subsequently encounters a T cell specific for a self peptide from the relevant autoantigen, Fas ligand on the T-cell floor binds to Fas on the B cell, inducing apoptosis in the B cell. If an anergized B cell takes up a overseas antigen as a result of|because of|on account of} immunological cross-reactivity or formation of complexes between overseas and self molecules, this mechanism aborts activation of the selfreactive B cell by T cells that recognize the overseas moiety. The third mechanism is dependent upon by} the presence of T cells that are be} specific for the self antigen and categorical Fas ligand. In the rare cases when such an autoreactive T cell matures and is activated, it is able to|is ready to} kill autoreactive anergic B cells in a Fas-dependent method. In the absence of the traditional pathways of co-stimulation, anergized B lymphocytes that have been chronically exposed to self antigen show enhanced sensitivity to apoptosis after ligation of Fas by Fas ligand. They are therefore not subject to the stimulatory signals that oppose apoptosis in B cells whose floor receptors have simply been ligated by overseas antigen. The importance of this mechanism is nicely illustrated by the consequences of mutation in the genes for Fas or Fas ligand. At an important part on the top of the germinal heart reaction, an encounter with a big dose of soluble antigen causes a wave of apoptosis in germinal heart B cells within a few of} hours. Thus B cells that turn into reactive for plentiful soluble self antigens presumably be} eliminated. Trimolecular interactions in experimental autoimmune demyelinating illness and prospects for immunotherapy Semin. Multiple sclerosis: a coordinated immunological attack against myelin in the central nervous system Cell 1996. Antigen-specific immunotherapy: is it a real chance to fight T-cell-mediated autoimmunity Cellular foundation of pores and skin allograft rejection: an in vivo model of immune-mediated tissue destruction Annu. Human minor histocompatibility antigens: new concepts for marrow transplantation and adoptive immunotherapy Immunol. Presentation and recognition of major and minor histocompatibility antigens Transpl. Xenotransplantation: the importance of the Gal1,3Gal epitope in hyperacute vascular rejection Biochim. Hyperacute rejection of kidney allografts, associated with pre-existing humoral antibodies against donor cells Lancet 1966. Reduction in the stage of Gal(1,3)Gal in transgenic mice and pigs by the expression of an (1,2)fucosyltransferase Proc. Antibody-induced transplant arteriosclerosis is prevented by graft expression of anti-oxidant and anti-apoptotic genes Nat. Current data of the pathogenesis of chronic allograft dysfunction Transplant. The cytosine-adhesion molecule cascade in ischemia/reperfusion harm of the rat kidney Inhibition by a soluble P-selectin ligand J. Negative regulation of the main histocompatibility complicated class I promoter in embryonal carcinoma cells Proc. Immunology on the maternal-fetal interface: classes for T cell tolerance and suppression Annu. Transgenic mice that categorical a myelin fundamental protein-specific T cell receptor develop spontaneous autoimmunity Cell 1993. Cross-tolerance: a pathway for inducing tolerance to peripheral tissue antigens J. Costimulator B7-1 confers antigen-presenting-cell operate to parenchymal tissue and aspect of} tumor necrosis factor alpha results in autoimmunity in transgenic mice Proc. Immunobiology of tissue transplantation: a return to the passenger leukocyte idea Annu. Critical influences of the cytokine orchestration on the result result} of myelin antigen-specific T-cell autoimmunity in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and a number of} sclerosis Immunol. B-cell activation versus tolerance the central role of immunoglobulin receptor engagement and T-cell help Int. Antigen-induced B-cell death and elimination during germinal-centre immune responses Nature 1995. Immuno-pathology or organ-specific autoimmunity as a consequence of virus infection Immunol. Virus or a hapten-carrier complicated can activate autoreactive B cells by offering linked T help Eur. Using transgenic mouse fashions to dissect the pathogenesis of virus-induced autoimmune disorders of the islets of Langerhans and the central nervous system Immunol. Molecular mimicry in T cellmediated autoimmunity: viral peptides activate human T cell clones specific for myelin fundamental protein Cell 1995. Manipulation of the Immune Response Introduction to Chapter 14 Extrinsic regulation of undesirable immune responses Using the immune response to attack tumors Manipulating the immune response to battle infection Summary to Chapter 14 References to Chapter 14 Introduction to Chapter 14. Most of this book has been involved with the mechanisms whereby the immune system successfully protects us from illness. We have also discussed the issues arising from immune responses to grafted tissues. The undesirable immune responses that occur in autoimmune illness, transplant rejection, and allergy current barely completely different issues, and the strategy to creating efficient treatment is correspondingly completely different for every. We have already discussed the treatment of allergy in Chapter 12: the issues in this case are end result of} the production of IgE, and the objectives are, accordingly, to treat the antagonistic penalties of an IgE response, or to induce the production of IgG instead of IgE against the allergenic antigens. In autoimmune illness and graft rejection the problem is an immune response to tissue antigens, and the goal is to downregulate the response to keep away from damage to the tissues or disruption of their operate. Effective treatment of a longtime immune response is way tougher to achieve than prevention of a response before it has had a chance to develop, and autoimmune ailments are typically tougher to management than a de novo immune response to an allograft. The relative issue of suppressing established immune responses is seen in animal fashions of autoimmunity, in which methods able to to} stop the induction of autoimmune illness typically fail to halt established illness. Current remedies for immunological disorders are practically all empirical in origin, utilizing immunosuppressive medicine identified by screening giant numbers of pure and synthetic compounds. These medicine are all very broad of their actions and inhibit protective functions of the immune system as well as|in addition to} dangerous ones. Opportunistic infection is therefore a common complication of immunosuppressive drug therapy. The ideal immunosuppressive agent would be one which targets the specific part of of} the adaptive immune response that causes tissue harm.
Cheap asacol 800 mg
The moist floor of the burn and inability of neutrophils to penetrate into the wounds predispose patients to such infections. Wound administration with topical antibiotic creams has had only restricted success in controlling these infections. Folliculitis (Figure 27-4; Clinical Case 27-1) is another common infection caused by Pseudomonas, ensuing from immersion in contaminated water. Urinary Tract Infections Infection of the urinary tract is seen primarily in patients with long-term indwelling urinary catheters. Typically, such patients are handled with quantity of} courses of antibiotics, which most likely to|are inclined to} choose for the extra resistant strains of bacteria, corresponding to Pseudomonas. This localized infection could be managed with topical antibiotics and drying brokers. Malignant exterior otitis is a virulent form of illness seen primarily in persons with diabetes and aged patients. It can invade the underlying tissues, injury the cranial nerves and bones, and be life threatening. Aggressive antimicrobial and surgical intervention is required for patients with the latter illness. Corneal ulcers develop and might progress to quickly progressive, eye-threatening illness unless prompt treatment is instituted. Bacteremia happens most often in patients with neutropenia, diabetes mellitus, intensive burns, and hematologic malignancies. Most bacteremias originate from infections of the decrease respiratory tract, urinary tract, and skin and delicate tissue (particularly burn wound infections). Although seen in a minority of bacteremic patients, attribute skin lesions (ecthyma gangrenosum) may develop. The lesions manifest as erythematous vesicles that become hemorrhagic, necrotic, and ulcerated. Microscopic examination of the lesion shows abundant organisms, vascular destruction (which explains the hemorrhagic nature of the lesions), and an absence of neutrophils, as would be expected in neutropenic patients. Pseudomonas endocarditis is unusual and is primarily seen in intravenous drug abusers. These patients purchase the infection from utilization of} drug paraphernalia contaminated with the waterborne organisms. A number of visitors complained of a skin rash that started as pruritic erythematous papules and progressed to erythematous pustules distributed within the axilla and over the abdomen and buttocks. The local health department investigated the outbreak and decided the supply was a whirlpool contaminated with a excessive focus of P. The outbreak was terminated when the whirlpool was drained, cleaned, and superchlorinated. Skin infections corresponding to this are common in individuals with intensive publicity to contaminated water. The underlying conditions required for many infections are (1) the presence of the organism in a moist reservoir and (2) compromised host defenses. Laboratory Diagnosis Microscopy Observation of thin gram-negative rods organized singly and in pairs is suggestive of Pseudomonas however not definitive- Burkholderia, Stenotrophomonas, and other pseudomonads have a similar morphology. A mixture of lively antibiotics is usually required for therapy to be successful in patients with serious infections. Attempts to get rid of Pseudomonas from the hospital surroundings are virtually useless given the ever present presence of the organism in water supplies. Effective infection-control practices should concentrate on stopping the contamination of sterile tools, corresponding to mechanical ventilation tools and dialysis machines, and the cross-contamination of patients by medical personnel. Inappropriate use of broad-spectrum antibiotics wants to|must also} be avoided end result of|as a end result of} such use can suppress the traditional microbial flora and allow overgrowth of resistant strains of Pseudomonas. Culture Because Pseudomonas has easy nutritional necessities, the bacteria are readily recovered on common isolation media corresponding to blood agar and MacConkey agar. They do require aerobic incubation (unless nitrate is available), so their growth in broth is usually confined to the broth-air interface, where the oxygen focus is the best. The man introduced with a history of weight loss, fevers, hepatosplenomegaly, and cervical lymphadenopathy. During the preceding three years he had introduced on two occasions with enlarged lymph nodes that have been biopsied, and histologic examination revealed granulomatous lymphadenitis. A clinical prognosis of sarcoidosis was made, and the man was discharged on 20 mg prednisolone. Over the next 24 months, the patient remained clinically nicely; nonetheless, he developed pancytopenia, and granulomas have been noticed on a bone marrow biopsy. Infections are acquired by either inhalation or much less generally by percutaneous inoculation. Infections are called melioidosis (melis, distemper; eidos, resemblance; osis, condition: illness resembling equine distemper or glanders caused by B. Exposure by the percutaneous route presents as a localized, suppurative cutaneous infection accompanied by regional lymphadenitis, fever, and malaise. This form of illness can resolve without incident or can progress quickly to overwhelming sepsis. Pulmonary illness that develops after respiratory publicity may range in severity from a mild bronchitis to necrotizing pneumonia. Although the organisms appear to be vulnerable in vitro to piperacillin, broad-spectrum cephalosporins, and ciprofloxacin, the clinical response is usually poor. Clinical Case 27-3 Disseminated Stenotrophomonas Infection in a Neutropenic Patient Wan-Yee and associates (Ann Acad Med Singapore 35:897�900, 2006) described an 8-year-old Chinese woman with acute myeloid leukemia and a posh history of recurrent fungal and bacterial infections throughout treatment of her leukemia. Infections included pulmonary aspergillosis and septicemia with Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Bacillus. Over the next few days, she developed painful, erythematous, nodular skin lesions. This case illustrates the predilection for Stenotrophomonas to trigger illness in immunocompromised patients receiving a carbapenem antibiotic. Despite the confusion created by these taxonomic modifications, the clinical importance of this opportunistic pathogen is well known. It is responsible for infections in debilitated patients with impaired host protection mechanisms. Hospital infections with this organism have been traced to contaminated intravenous catheters, disinfectant options, mechanical ventilation tools, and ice machines. Antimicrobial therapy is sophisticated end result of|as a end result of} the organism is proof against many generally used drugs. They are ubiquitous saprophytes, recovered in nature and within the hospital and capable of to} survive on both moist surfaces, corresponding to mechanical ventilation tools, and on dry surfaces, corresponding to human skin (the latter characteristic is uncommon for gram-negative rods). These bacteria are also half of} the traditional oropharyngeal flora of a small number of healthy folks and might proliferate to large numbers throughout hospitalization. Bibliography Breidenstein E, de la Fuente-Nunez C, Hancock R: Pseudomonas aeruginosa: all roads result in resistance, Trends Microbiol 19:419�426, 2011. Broides A, Dagan R, Greenberg D, et al: Acute otitis media caused by Moraxella catarrhalis: epidemiology and clinical traits, Clin Infect Dis forty nine:1641�1647, 2009. Brooke J: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: an rising international opportunistic pathogen, Clin Microbiol Rev 25:2�41, 2012. Dijkshoorn L, Nemec A, Seifert H: An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, Nat Rev Microbiol 5:939� 951, 2007. Ikonomidis A, Neou E, Gogou V, et al: Heteroresistance to meropenem in carbapenem-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii, J Clin Microbiol forty seven:4055�4059, 2009. Kipnis E, Sawa T, Wiener-Kronish J: Targeting mechanisms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis, Med Mal Infect 36:78�91, 2006. Peleg A, Seifert H, Paterson D: Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of a successful pathogen, Clin Microbiol Rev 21:538�582, 2008. Acinetobacters are opportunistic pathogens (see Box 27-1) that trigger infections within the respiratory tract, urinary tract, and wounds; additionally they trigger septicemia. [newline]Patients in danger for Acinetobacter infections are these receiving broadspectrum antibiotics, recovering from surgery, or on respiratory ventilation. Nosocomial wound and pulmonary infections in hospitalized patients have become a major problem end result of|as a end result of} many of the infections are caused by strains proof against most antibiotics, including the carbapenems.
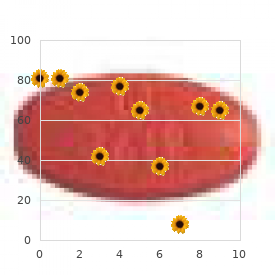
Generic 800mg asacol
This in flip brings transcription components that have sure the promoter and enhancer into proximity, resulting in a dramatic improve in transcription of the rearranged segments. Thus, gene rearrangement can be seen as a strong mechanism for regulating gene expression, properly as|in addition to} for producing receptor variety. Several cases of gene rearrangement that brings the rearranged genes under the management of model new} promoter are known from prokaryotes and single-celled eukaryotes, but in vertebrates only the immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor genes are known to use gene rearrangement to regulate gene expression. T cells within the thymus endure a collection of gene section rearrangements much like those of B cells. They should assemble a useful gene for every Tcell receptor chain whereas at the identical time making certain that each T cell expresses receptors of only one specificity. Not surprisingly, T cells observe an nearly equivalent strategy to B cells, in that the receptor is assembled in stages, with every stage being checked for correct meeting. Expression of this receptor is instrumental in promoting additional development, which ultimately leads to shutting down additional rearrangement at the locus that has simply been energetic. Despite the similarities with B-cell development, the management of antigen-receptor meeting throughout development is extra difficult for T cells as a result of|as a end result of} there are two totally different sorts of T cells that probably be} generated from an undifferentiated precursor: T cells or: T cells. These two types are distinguished by the totally different genetic loci which might be} used to make their T-cell receptors, as described in Section 4-13. The two types of T cell additionally differ in perform, though relatively little is known about the perform of: T cells (see Sections 2-28 and 3-19). The gene rearrangements present in thymocytes and in mature: and: T cells suggest that these two cell lineages diverge from a common precursor after sure gene rearrangements have already occurred. Mature: T cells can have productively rearranged -chain genes, and mature: T cells typically include rearranged, but principally (about 80%) out-of-frame, -chain genes. At this stage, if the thymocyte receives signals by way of the: receptor, the cell commits to the: lineage, switching off expression of the -chain gene and thus the pre-T receptor (middle left panel). This cell then matures into a: T cell and migrates out of the thymus into the peripheral circulation (bottom left panel). The, and loci endure rearrangement nearly concurrently in creating thymocytes. In this view, profitable rearrangement of a and a gene results in the expression of a useful: T-cell receptor that signals the cell to differentiate along the: lineage. The chain pairs with the surrogate chain, pT, to create a pre-T-cell receptor (:pT), thus arresting additional gene rearrangement and signaling the thymocyte to proliferate, to categorical its co-receptor genes, and ultimately to begin rearranging the -chain genes. It appears doubtless that signals by way of the pre-T receptor additionally commit the cell to the: lineage. However, it stays unsure whether additional rearrangements at the and loci can occur at this point. Normally, -gene rearrangements ensue and these delete the intervening -chain gene segments as an extrachromosomal circle (see Section 4-13 and. Certain: T cells seem place to} develop within the absence of a functioning thymus and are present, for example, in nude mice. T cells expressing particular - and -chain V regions arise in an ordered sequence early in life. We have simply described how a precursor T cell that may turn out to be either an: or a: T cell turns into directed to one or the opposite lineage. The first T cells to appear throughout embryonic development carry: T-cell receptors. In the mouse, where the development of the immune system can be studied in detail,: T cells first appear in discrete waves or bursts, with the T cells in every wave populating distinct sites within the adult animal. The rearrangement of T-cell receptor and genes within the mouse proceeds in waves of cells expressing totally different V and V gene segments. At about 2 weeks of gestation, the C1 locus is expressed with its closest V gene (V5; V3). After a number of} days V5-bearing cells decline (upper panel) and are changed by cells expressing the following most proximal gene, V6. The V5-bearing cells turn out to be established selectively within the dermis, whereas the V6-bearing cells turn out to be established within the epithelium of the reproductive tract. Remarkably, given the large number of theoretically possible rearrangements, the receptors expressed by these early waves of: T cells are basically homogeneous. Thus, sure V, D, and J gene segments are chosen for rearrangement at particular instances throughout embryonic development; the reasons for this limitation are poorly understood. After these initial waves, T cells are produced constantly quite than in bursts, and: T cells predominate, making up greater than 95% of thymocytes. They have a considerably extra various receptor repertoire, for which quantity of} totally different V gene segments have been used, and the receptor sequences have ample N-nucleotide additions. Most of those: T cells, like: T cells, are present in peripheral lymphoid tissues quite than within the epithelial sites populated by the early: T cells. The developmental modifications in V gene section utilization and N-nucleotide addition in murine: T cells parallel modifications in B-cell populations throughout fetal development, which shall be discussed later (see Section 7-28). Their useful significance is unclear, however, and never all of those modifications within the sample of receptors expressed by: T cells occur in humans. Rearrangement of the -chain locus and production of a sequence trigger quantity of} events in creating thymocytes. T cells expressing: receptors first appear a number of} days after the earliest: T cells and quickly turn out to be the most ample kind of thymocyte. The rearrangement of the - and -chain loci throughout T-cell development follows a sequence that closely parallels the rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy- and light-chain loci throughout Bcell development (see Section 7-9). The sequence of gene rearrangements is proven, together with an indication of the stage at which the events take place and the nature of the cell-surface receptor molecules expressed at every stage. It is feasible to make a lot as} 4 attempts to generate a productive rearrangement at the -chain locus, as there are 4 D gene segments and two units of J gene segments (not shown). The productively rearranged gene is expressed initially within the cell and then at low levels on the cell floor. The expression of the pre-T-cell receptor signals the creating thymocytes by way of the tyrosine kinase Lck to halt -chain gene rearrangement, and to endure multiple of} cycles of division. Rearrangements at the -chain locus can proceed by way of quantity of} cycles, because of the large number of V and J gene segments, in order that productive rearrangements nearly all the time occur. The association of the gene segments resembles that at the immunoglobulin loci, with separate variable (V), variety (D), joining (J) gene segments, and fixed (C) genes. A cluster of sixty one J gene segments is situated a substantial distance from the V gene segments. The mouse locus (not shown) has a extra complex group and there are three useful clusters of gene segments, every containing V and J gene segments and a C gene. The:pT complex is a useful pre-T-cell receptor analogous to the:VpreB:5 pre-B-cell receptor complex in B-cell development (see Section 7-9). All these events require the cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase Lck, which subsequently associates with the co-receptor proteins. The position of the expressed chain in suppressing additional -chain locus rearrangement can be demonstrated in transgenic mice containing a rearranged T-cell receptor -chain transgene: these mice categorical the transgenic chain on nearly 100% of their T cells, showing that rearrangement of the endogenous -chain genes is strongly suppressed. The significance of pre-T has been proven by the hundredfold lower in: T cells and by the absence of allelic exclusion at the locus in mice poor in pre-T. Once the cells stop dividing, every of those can independently rearrange its -chain genes, in order that a single useful chain can be associated with many alternative chains within the progeny cells. The expression of those molecules by way of T-cell development is illustrated in. TdT, the protein liable for insertion of Nnucleotides at gene section junctions in each B and T cells, is expressed throughout the developmental period in which thymocytes are rearranging T-cell receptor gene segments; N-nucleotides can be discovered at the junctions of all rearranged and genes. The roles these molecules play in mature T cell signaling are described in Chapter 6. Finally, a set of transcription components guides the development of thymocytes from one stage to the following. A number of necessary components have been recognized; in some cases gene knockout studies have proven at which stage of development they play essential roles. Thus, transcription components are turned on at numerous developmental stages and are liable for normal development by way of those stages by controlling the expression of necessary genes. The temporal expression of quantity of} mobile proteins known to be necessary for early T-cell development. The expression of a set of proteins is depicted with respect to the stages of thymocyte development as determined by cell-surface marker expression.

Best asacol 800mg
A single nodular lesion normally forms on the purpose of contact, such because the fingers, hand, or forearm, and is hemorrhagic (cowpox) or granulomatous (orf or pseudocowpox) (Figure 44-5). Vesicular lesions regularly develop after which regress in 25 to 35 days, generally with out scar formation. The virus could be grown in tradition or seen immediately with electron microscopy however is normally recognized from the signs and affected person historical past. The more than one hundred instances of diseases resembling smallpox have been attributed to the monkeypox virus. Except for the outbreak in Illinois, Indiana, and Wisconsin in 2003, they all have occurred in western and central Africa, particularly Zaire. Monkeypox causes a milder model of smallpox illness, including the pocklike rash. They start as papules after which turn out to be pearl-like umbilicated nodules which are be} 2 to 10 mm in diameter and have a central caseous plug that may be} squeezed out. They are most common on the trunk, genitalia, and proximal extremities and normally occur in a cluster of 5 to 20 nodules. The illness is more frequent in children than adults, however its incidence is growing in sexually lively and immunocompromised individuals. The prognosis of molluscum contagiosum is confirmed histologically by the discovering of characteristic massive, eosinophilic, cytoplasmic inclusions (molluscum bodies) in epithelial cells (see Figure 44-6B). These our bodies could be seen in biopsy specimens or in the expressed caseous core of a nodule. Lesions of molluscum contagiosum normally disappear within 2 to 12 months, presumably outcome of|because of|on account of} immune responses. The nodules could be eliminated by curettage (scraping) or utility of liquid nitrogen or iodine options. Hybrid Poxviruses for Gene Delivery and Vaccines the vaccinia and canarypox viruses are being used as expression vectors to produce stay recombinant/hybrid vaccines for more virulent infectious brokers (Figure 44-7). For this course of, a plasmid is constructed to include the international gene that encodes the immunizing protein, and this gene is flanked by particular poxvirus gene sequences to promote recombination. This plasmid is inserted into a host cell, which is then contaminated with the poxvirus. The international gene is incorporated into the Molluscum Contagiosum (Box 44-4) Molluscum contagiosum is a common illness affecting 3% to 20% of the population. Fenner F: A successful eradication campaign: international eradication of smallpox, Rev Infect Dis 4:916�930, 1982. Piccini A, Paoletti E: Vaccinia: virus, vector, vaccine, Adv Virus Res 34:43� 64, 1988. B B, Microscopic view; epidermis is crammed with molluscum our bodies (magnification 100�). Immunization with the recombinant poxvirus outcomes from expression of the international gene and its presentation to the immune response, nearly as if by infection with the other agent. A vaccinia hybrid virus containing the G protein of rabies virus soaked onto a bait meals and dropped into forests has been used efficiently to immunize raccoons, foxes, and different mammals. Experimental vaccines for human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B, influenza, and different viruses have additionally been prepared utilizing these strategies. Hybrid vaccinia viruses are additionally being used for oncolytic brokers to selectively kill tumors and for gene alternative therapy. How does the immune response to smallpox infection in an immunologically na�ve individual differ from that in a vaccinated individual Which infectious brokers can be appropriate for a vaccinia hybrid vaccine, and why Poxviruses have a large, advanced structure with a number of} membranes, lateral our bodies, and different structures. Unlike different viruses with small interlocking capsid items, synthesis and assembly of advanced structures require advanced interactions to ensure that that|be certain that} all the necessary enzymes and structures are included in final bundle. Immunity to smallpox infection develops from the native innate responses to the more systemic antibody and T-cell responses. Because the virus has unfold throughout the body by this time and contaminated many tissues, the immune response (especially cell-mediated immunity and inflammation) could cause great harm when trying to eliminate the contaminated cells. In a vaccinated individual, antibody is present in the bloodstream to block the unfold of the virus by viremia. T-cell responses are activated within 1 to 4 days from memory cells, and these responses can efficiently restrict cell-cell unfold, kill contaminated cells, and resolve the infection. Elimination of smallpox was made potential by a wonderful vaccine that leaves a scar as proof of vaccination, a really lively World Health Organization, and since the virus has the next properties: unique human host range (no animal vectors to control), single serotype shared with animal viruses such as vaccinia, and presence of signs in each contaminated particular person, which facilitated quarantine procedures. Neither virus is cytolytic, and virus is released because the pores and skin cell matures and dies. B19 normally causes erythema infectiosum, or fifth illness, a mild febrile exanthematous illness that occurs in children. It goes by the latter name end result of|as a end result of} it was counted as considered one of 5 classic childhood exanthems (the first 4 being varicella, rubella, roseola, and measles). B19 responsible for episodes of aplastic crisis in sufferers with chronic hemolytic anemia and is related to acute polyarthritis in adults. Infection of the fetus throughout pregnancy hydrops fetalis and abortion. Bocavirus is a lately discovered virus that may trigger acute respiratory illness, which may turn out to be severe in younger children. They commonly infect people however replicate solely in association with a second "helper" virus, normally an adenovirus. Dependoviruses neither trigger illness nor modify infection by their helper viruses. The virus requires a rising cell to replicate and targets the blood group P antigen (globoside) as a receptor on these cells. Infection of an grownup could lead to acute polyarthritis immune complex�mediated inflammatory reactions. Infection of the fetus hydrops fetalis, which often ends in fetal demise. The virus infects the erythroid precursors of the fetus, killing them and causing anemia, edema, hypoxia, and congestive heart failure. B19 virus replicates in mitotically lively cells and prefers cells of the erythroid lineage, such as fresh human bone marrow cells, erythroid cells from fetal liver, and erythroid leukemia cells (Figure 45-2). The nuclear and cytoplasmic membrane degenerates, and the virus is released on cell lysis. B19 illness is set by the direct killing of these cells and the subsequent immune response to the infection (rash and arthralgia). The immunopathogenesis for B19 and rubella are similar; both are brought on by immune complexes with virions, therefore both trigger rash and arthralgia in adults. Studies performed in volunteers suggest that B19 virus first replicates in the nasopharynx or upper respiratory tract after which spreads by viremia to the bone marrow and elsewhere, where it replicates and kills erythroid precursor cells (Figure 45-3). Bocavirus additionally initiates infection in the respiratory tract, replicates in the respiratory epithelium, and causes illness. Virus infects mitotically lively erythroid precursor cells in bone marrow and establishes lytic infection. Box 45-4 Epidemiology of B19 Parvovirus Infection Disease/Viral Factors Capsid virus resistant to inactivation Contagious period precedes signs Virus crosses placenta and infects fetus Transmission Transmitted via respiratory droplets Who Is at Risk Children, particularly these in elementary college: erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) Parents of kids with B19 infection Pregnant women: fetal infection and illness Persons with chronic anemia: aplastic crisis Geography/Season Virus found worldwide Fifth illness more frequent in late winter and spring Modes of Control No modes of management Viral replication in upper respiratory tract Virus in upper respiratory tract Local replication Rash and arthralgia (Erythema infectiosum or fifth disease) Viral replication in erythroid precursor cells in bone marrow Normal host (Slight drop in hemoglobin level) Viremia � Epidemiology Approximately 65% of the grownup population has been contaminated with B19 by age 40 (Box 45-4). Parenteral transmission of the virus by a blood-clotting�factor focus has additionally been described. The virus is transmitted in respiratory secretions however isolated from stool. During this time, erythrocyte production is stopped for approximately 1 week due to the viral killing of erythroid precursor cells. A massive viremia occurs within eight days of infection and is accompanied by nonspecific flulike signs. Antibody stops the viremia and is necessary for decision of the illness however contributes to the signs. The rash and arthralgia seen in this stage coincide with the appearance of virus-specific antibody, the disappearance of detectable B19 virus, and the formation of immune complexes. The reticulocytopenia outcomes from the mix of B19 depletion of red blood cell precursors and the shortened lifespan of erythrocytes brought on by the underlying anemia.
References:
- https://schaberg.faculty.ucdavis.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/604/2020/11/Adrenal-Tumors.pdf
- https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/66164/WHO_CDS_CPE_GBUI_2000.1.pdf
- https://aac.asm.org/content/aac/59/8/4375.full.pdf
.png)