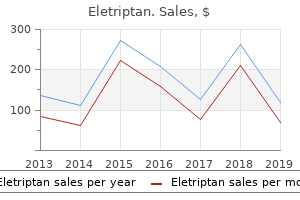
Quality 40mg eletriptan
When the fetus is in the breech place, fetal heart tones are best heard at or above the extent of the umbilicus. Attitude refers to the connection of the fetal components (such as the chest, chin, or arms) to one another in the course of the passage by way of the start canal. The fetal head could also be} in a flexed (chin-to-chest) or prolonged (headto-back) place. Pressure exerted by the maternal pelvis and start canal during labor and delivery causes the sutures of the cranium to permit the cranial bones to shift, leading to molding of the fetal head. Power refers to uterine contractions, which trigger full cervical effacement (thinning) and dilation (expansion). Components of labor the three major elements of labor are the passage, the passenger, and the power. Long and winding road Passage refers to the maternal pelvis and soft tissues, the passageway by way of which the fetus exits the body. This space is affected by the shape of the inlet, the structure of the pelvis, and pelvic diameters. They embrace: · lightening, or fetal descent into the pelvis, which often happens 2 to 3 weeks before term in a primiparous client and later or during labor in a multiparous client · Braxton Hicks contractions, which may occur irregularly and intermittently throughout pregnancy and might turn out to be uncomfortable and produce false labor (Text continues on page 523. This capability is affected by such fetal features as: · the cranium · the lie (relationship of the lengthy axis [spine] of the fetus to the lengthy axis of the mother) · presentation (portion of the fetus that enters the pelvic passageway first) · place (relationship of the presenting half of} the fetus to the entrance, back, and sides of the maternal pelvis). Power, the passenger, and the passage make up the three major elements of labor. Key check outcomes · Electronic fetal monitor reveals fetal distress (during the intrapartum period). For uterine rupture · Ultrasonography might reveal the absence of the amniotic cavity inside the uterus. Key remedies · Supplemental oxygen by face mask, typically at 6 to eight L /minute · I. Key remedies · Hospitalization to monitor for maternal fever and leukocytosis and fetal tachycardia if pregnancy is between 28 and 34 weeks. Determine the extent of descent of the pinnacle by greedy the decrease portion of the stomach above the symphysis pubis to establish the fetal half presenting over the inlet; an unengaged head may be rocked from facet to facet. The thick and thin of it Observe effacement, cervical thinning and shortening, which is measured from 0% (thick) to 100 percent (paper thin). Determine head flexion by transferring fingers down both sides of the uterus to assess the descent of the presenting half into the pelvis; larger resistance is met as the fingers transfer downward on the cephalic prominence (brow) facet. Measuring contractions Phases of uterine contractions embrace increment (buildup and longest phase), acme (peak of the contraction), and decrement (letting-down phase). When assessing intensity by palpation, the contraction is taken into account mild, reasonable, or sturdy. Check the station, the connection of the presenting half to the pelvic ischial spines: · the presenting half is even with the ischial spines at zero station. Monitor the client for signs of dehydration, corresponding to poor pores and skin turgor, decreased urine output, and dry mucous membranes. I want slightly rest Use an exterior stress transducer to monitor the client for tetanic contractions, sustained extended contractions with little rest in between that reduce oxygen provide to the fetus. This is getting thrilling During the latent part, the cervix is dilated zero to 3 cm, contractions are irregular, and the client might experience anticipation, excitement, or apprehension. Contractions are about 5 to eight minutes aside and last forty five to 60 seconds with reasonable to sturdy intensity. During this part, the client turns into severe and concerned concerning the progress of labor; she might ask for ache treatment or use breathing strategies. Pressure verify Contraction frequency and intensity is monitored externally with a tocotransducer. From the within out Internal digital fetal monitoring can consider fetal standing during labor extra accurately than exterior strategies. Contractions are about 1 to 2 minutes aside and last 60 to ninety seconds with sturdy intensity. This stage lasts a mean of forty minutes (20 contractions) for the primiparous client and 20 minutes (10 contractions) for the multiparous client. The client might turn out to be exhausted and dehydrated as she moves from coping with contractions to actively pushing. During this stage, the fetus is moved alongside the start canal by the mechanisms of labor described right here. Intense data to decide the true intensity of contractions, a pressure-sensitive catheter is inserted into the uterine cavity alongside the fetus. Stages of labor the labor process is split into 4 phases, starting from the onset of true labor by way of delivery of the fetus and placenta to the primary hour after delivery. Going down the movement of the presenting half by way of the pelvis recognized as} descent. Nursing care during labor and delivery Nursing actions embrace interventions that correspond to all phases of labor properly as|in addition to} those who apply solely to sure phases. Flex that chin During flexion, the pinnacle flexes in order that the chin moves nearer to the chest. The client might experience discomfort from uterine contractions before expelling the placenta. Head rotation I Internal rotation is the rotation of the pinnacle to be able to} cross by way of the ischial spines. For a review of nursing actions in the course of the delivery process, see Nursing care during labor and delivery. Stretch as you go by Extension is when the pinnacle extends because it passes beneath the symphysis pubis. Pain reduction during labor and delivery Pain reduction is a vital component of client care during labor and delivery. Pain reduction during labor includes nonpharmacologic strategies, analgesics, and common or regional anesthetics. Keep abreast of diagnostic exams 527 Just loosen up Relaxation strategies could also be} effective. Delivery reduction Local infiltration includes an injection of anesthetic into the perineal nerves. It provides no reduction from discomfort during labor however relieves ache during delivery. Just rub it Effleurage, a light belly stroking with the fingertips in a round movement, is effective for mild to reasonable discomfort. Hey, look over right here Distraction can divert consideration from mild discomfort early in labor. Breathing, breathing, breathing Three patterns of managed chest breathing, called Lamaze breathing, are used primarily in the course of the lively and transitional phases of labor. Ancient ache reduction the stimulation of key set off factors with needles (acupuncture) or finger stress (acupressure) can reduce ache and improve vitality circulate. General anesthetics must be used only if regional anesthetics are contraindicated or in a quickly creating emergency. Pain reduction however not with out danger Opioids, corresponding to nalbuphine, can be used to relieve ache. If an opioid is given within 2 hours of delivery, it can possibly} trigger neonatal respiratory melancholy, hypotonia, and lethargy. Less ache however nonetheless awake Lumbar epidural anesthesia requires an injection of treatment into the epidural house in the lumbar region, leaving the client awake and cooperative. An epidural offers analgesia for the primary and second phases of labor and anesthesia for delivery with out antagonistic fetal results. Keep abreast of diagnostic exams necessary thing} diagnostic check in the intrapartum interval is fetal blood sampling. The blood sample is often taken from the scalp however may also be taken from the presenting half if the fetus Urgent cases Spinal anesthesia includes an injection of treatment into the cerebrospinal fluid in the spinal canal. Because of its speedy onset, spinal anesthesia is useful for urgent cesarean deliveries. Fetal blood sampling requires that: · membranes be ruptured · the cervix be dilated 2 to 3 cm · the presenting half be no larger than 2 station.
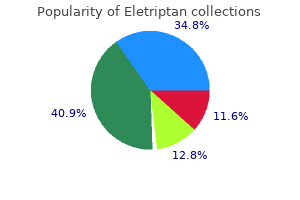
Eletriptan 20mg
Occasionally the onset is more gradual, but features could develop acutely within the immunocompromised patient. Clinical features arise from: Toxicity pyrexia, malaise (although systemic indicators often absent). Antibiotics are selected on an empirical foundation relying on the probably supply of the infection and their capability to cross the bloodbrain barrier and to achieve therapeutic concentrations in intracranial pus. Later determination of the organism and its sensitivities permits alteration to more specific drugs. Intravenous antibiotics ought to proceed for 23 weeks followed by oral medication for an extra 34 weeks. Abscess drainage Various methods exist: Burrhole aspiration of pus, aided by picture guidance using neuronavigation or ultrasound, with repeated aspiration if required. Evacuation of the abscess contents under direct imaginative and prescient, leaving the capsule remnants. Primary excision of the entire abscess including the capsule (standard remedy of cerebellar abscess) Burr gap aspiration is straightforward and comparatively protected. Persistent reaccumulation of pus regardless of repeated aspiration requires secondary excision. Primary excision removes the abscess in a single process, but carries the danger of damage to surrounding mind tissue. Open evacuation of the abscess contents requires a craniotomy, but minimises injury to surrounding mind. Treatment of the infection web site Mastoiditis or sinusitis requires prompt operative remedy, in any other case this acts as a persistent supply of infection. Steroids assist scale back associated oedema but they could additionally scale back antibiotic penetration and impede formation of the abscess capsule. Conservative management: In some conditions the dangers of operative intervention outweigh its advantages. Infection often spreads from contaminated sinuses or mastoids, but could arise from any of the aforementioned sources. Clinical features match these of intracerebral abscess but since speedy extension occurs across the subdural space, overwhelming signs often develop all of a sudden. Management: Intravenous antibiotic remedy is combined with evacuation of pus both through quantity of} burr holes or a craniotomy flap. Clinical features are these of any intracranial mass; alternatively tuberculoma could current in conjunction with of} tuberculous meningitis. Management: When tuberculoma is suspected, a trial of antituberculous therapy is worth it}. Other patients require an exploratory operation and biopsy followed by long-term drug remedy. When sarcoid infiltrates the central nervous system it often includes the meninges. In some patients mass lesions could arise from the dura, but more generally indicators and signs relate to an adhesive arachnoiditis involving the skull base, cranial nerves and pituitary stalk. Mass lesions could sometimes arise within the mind and spinal cord with out apparent meningeal involvement. A definitive analysis is based on clinical and radiological evidence of multisystem disease confirmed by characteristic histology. The analysis is commonly elusive and advised by clinical presentation supported by a number of the} following. Management: Immunosuppression with corticosteroids is often indicated and long-term therapy required. Success in resistant instances is reported with each of the following azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, cyclosporin or irradiation. The extrapyramidal system consists of paired subcortical plenty or nuclei of gray matter basal ganglia. The caudate nucleus and putamen are collectively referred to because the Interconnections of the deep nuclei the connections between parts of the extrapyramidal system and other components of the mind are complicated. When launched by an acceptable stimulus they cross the synaptic gap and mix with specific receptors of the postsynaptic cell. Neuromodulator substances diminish or enhance the effects of neurotransmitters within the basal ganglia. Dopamine Synthesised by cells of substantia nigra (pars compacta) and nigral projections in striatum. Drugs could produce movement problems by interfering with neurotransmission within the following methods: 1. Positive features Involuntary movements: tremor chorea (irregular, repetitive, jerking movements). These problems often share features of slowness and rigidity (akinetic inflexible syndromes). Radiolabelled ligand research have identified two dopamine receptors on striatal cell membranes D1 D2 receptors. It begins unilaterally within the upper limbs and finally spreads to all 4 limbs. Dysarthria, dysphagia and a slow deliberate gait with little associated movement. Rising from a chair becomes laborious with progressive issue in initiating decrease limb movement from a stationary place. As the disease progresses the frequency of drug-induced confusional states and dementia increases, with 80% developing dementia after 20 years of disease (if they survive). Juvenile presentation can happen, when presentation and disease development is commonly atypical; a genetic foundation is more often found. Post-mortem data from the London Brain Bank reveals this to be incorrect in 25% of these recognized in life. New tremor in middle age causes explicit issue senile/essential & metabolic tremor is generally absent at relaxation and worsened by voluntary movement. The diagnostic use of a L-dopa or dopamine agonist (apomorphine) challenge has declined because of of} concerns that it could enhance the danger of subsequent drug induced dyskinesia. Vascular Parkinsonism often presents with gait disturbance with step wise deterioration. It tends to predominantly contain the decrease limbs and have a partial response to L-dopa. Dopamine agonist which mimics dopamine on the postsynaptic striatal receptor web site Postsynaptic receptor Exogenous dopa Levodopa is given with a decarboxylase inhibitor, which prevents peripheral breakdown within the liver (as in 1) allowing a higher focus of dopa to attain the bloodbrain barrier (as in 2) and reduces the peripheral side effects effects} (nausea, vomiting, hypotension). Rapid onset or longer action can be achieved using dispersible or controlled-release preparations. Exogenous dopa improves bradykinesia, rigidity and, to a lesser extent, tremor, but in 20% the response is poor. A new preparation of dopa is on the market for continuous infusion via jejunostomy in severe disease. Dopamine agonists: Now used earlier in disease management, they act directly on the dopamine receptor unbiased of degenerating dopaminergic neurons. There are two forms of dopamine agonists, ergot derived, including pergolide, cabergoline, apomorphine, and non-ergot derived, corresponding to ropinerole, pramipexole, rotigotine (available as a transdermal patch). Ergot agonists are now are|are actually} prevented because of the high price of fibrotic reactions, with up to as} 25% of patients developing cardiac valve fibrosis. Apomorphine is given by continuous infusion or intermittent injection and is helpful late within the disease. Side effects: postural hypotension, hallucinations & psychosis, sedation and agonist specific complications (erythromelalgia/pulmonary fibrosis). Tolcapone is an alternate that can trigger hepatic toxicity; it requires close monitoring. Deep mind stimulation: for patients with regular cognitive operate who stay aware of medication but have important on/off phenomenon regardless of optimum medical therapy, the insertion of deep mind electrodes into the subthalamic nucleus can provide useful clinical advantages. Pathology: Neuronal loss within the striatum is related to a reduction in projections to other basal ganglia buildings. In addition, cells of the deep layers of the frontal and parietal cortex are lost (corticostriatal projections).
Generic 40 mg eletriptan
A combination of maximal protected surgery adopted by mixed chemoradiotherapy is now the standard of take care of good efficiency patients with glioblastoma. Carmustine impregnated wafers (Gliadel) may be thought of each as a primary treatment or for tumour recurrence (see below). Patients with anaplastic oligodendrogliomas and oligoastrocytoma with lack of heterozygosity on chromosomes 1p and 19q have a good prognosis and respond properly to each radiation and to alkylating agent primarily based chemotherapy (nitrosoureas, Temozolomide). Chemotherapy may be be} used either at initial prognosis or at relapse in these patients. Traditionally, chemotherapy has had a lesser function in low grade glial tumours however present research are inspecting its use in each astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas as different to|an alternative choice to|a substitute for} radiation in newly diagnosed patients. Problems of drug administration Toxicity: the ideal cytotoxic drug selectively kills tumour cells; however tumour cell response relates on to the dose. High drug dosage incessantly causes bone marrow suppression which can limit cytotoxic activity earlier than an adequate therapeutic dose is reached. Intrinsic resistance: Some tumour cells appear to have an inbuilt resistance to certain medicine. The vast array of accessible cytotoxic medicine and the infinite permutations of mixed remedy creates difficulties in drug choice. Others are now are|are actually} in trial either as single agents or together with different focused agents or conventional remedy. Male:female = 2:1 Primary websites: Found in equal incidence all through the frontal, temporal, parietal and thalamic areas, however less often in the occipital lobe. They are diffuse and slowly rising, and composed of properly differentiated astrocytic cells subdivided into fibrillary, protoplasmic and gemistocytic types. Although benign, these tumours extensively infiltrate surrounding brain and lack a definitive edge or capsule. Symptoms normally develop progressively, progressing over several of} weeks, months or years, the rate relying on the diploma of malignancy. No clear plane exists between tumour and brain Central, low density areas characterize necrotic areas or cystic cavities; neither enhances with distinction Low grade astrocytoma A low density area, normally unenhancing with distinction suggests a low grade infiltrative lesion; detection is usually difficult in early stages. If not continuing to an open operation, failure to verify the character of the lesion risks omitting treatment in benign situations such as abscess, tuberculoma or sarcoidosis. Identification of tumour sort and grade offers a prognostic guide and aids further management. Prior selection of the needle path avoids vessels and necessary constructions, thus minimising the risks. Since the diploma of malignancy varies from area to area inside a single lesion, several of} samples are taken from different websites to increase accuracy. If findings range, then the area Ultrasound probe Controlled of best malignancy dictates the tumour grade. Provided patients obtain preoperative a change in steroid cover the risks are small, however sometimes consistency may biopsy produces or will increase a focal deficit be detected on or causes a fatal haemorrhage. Ultrasound guided a brain cannula inserted into the irregular area permits aspiration of a small amount of tissue for immediate (smear and frozen section) and later (paraffin section) examination. The issue lies in the absence of a plane of cleavage between tumour tissue and brain. Alternatively performing the procedure in an awake patient and observing the direct effect of electrical stimulation may minimise the danger of inflicting an irreversible neurological deficit (see web page 313). Large resections are most safely performed in the frontal, occipital or nondominant temporal lobes. Studies show a doseeffect relationship the greater the dose to the tumour space, the longer the survival. The worth of mixed remedy in anaplastic astrocytoma and oligodendroglioma is beneath investigation. Malignant astrocytoma/glioblastoma multiforme: Modern methods have extended survival, however these tumours nonetheless carry a grave prognosis. Median survival (months) Burr gap biopsy Tumour resection Burr gap biopsy + radiotherapy 34 6 68 Tumour resection + radiotherapy 1214 Tumour resection + radiotherapy 1418 + concomitant chemotherapy In patients present process surgery, intensive tumour resection extends common survival by solely 2 months, however when mixed with radiotherapy and concomitant chemotherapy features an extra 12 months. Management insurance policies range extensively, however normally, maximal tumour resection with radiotherapy and chemotherapy is taken into account in most patients except: patients over 70 years of age (older patients tolerate radiotherapy less well) patients with intensive, deep lesions. Tumour recurrence may warrant an extra resective procedure, perhaps mixed with carmustine wafer implantation or different chemotherapy, significantly in youthful patients who responded properly to the initial treatment. The dilemma in such patients who often current with epilepsy and no different signs, whether or not or not} to proceed with radical surgery or to wait and watch. The argument for intervention is that sooner or later the tumour will turn into malignant; many therefore opt for resecting as much tumour as is safely attainable at an early stage in the hope that this defers malignant change. There is however no proof that energetic intervention with operation and/or radiotherapy or chemotherapy modifications end result. If continuing to surgery, the operative methods used to avoid damaging eloquent areas apply (page 313). They occur in a slightly youthful age group 3050 years, and normally contain the frontal lobes. Genetic evaluation of anaplastic oligodendrogliomas has revealed that almost about} 80% have 1p and 19q allelic losses. For patients with anaplastic oligodendrogliomas, resection adopted by chemotherapy is mixed with either immediate or delayed radiotherapy. Those patients with lack of 1p and 19q alleles respond properly to chemotherapy and survive over 10 years. The 27% with a genetic profile much like primary glioblastoma (page 316) seldom reply to chemotherapy and survive on common about sixteen months. Mixed oligoastrocytoma: these with a blended form of astrocytoma/oligodendroglioma have a prognosis lying between that for every sort. Eventually an anabolic phase results in weight problems accompanied by diabetes insipidus and delayed puberty. Upward tumour extension may impede the foramen of Munro and cause hydrocephalus. Involvement of the tuberal area may end result in the rare presentation of precocious puberty with secondary sexual traits growing in children perhaps just a few years old. Management: A stereotactic biopsy may assist tumour identification, however the website of the lesion makes tried removing hazardous. If hydrocephalus is current, a bilateral ventriculoperitoneal shunt relieves pressure signs. Malignant bronchus melanomas show the highest frequency (of these with metastasis, breast 66% are in the brain); this contrasts with tumours of the cervix and kidney uterus the place < 3% develop intracranial metastasis. The most thyroid commonly encountered metastatic intracranial tumours arise from stomach the bronchus and the breast; of patients with carcinomas at these websites, prostate 25% develop intracranial metastasis. Occasionally a metastasis to the cranium vault may lead to a nodule or plaque forming over the dural surface from direct unfold. Intracranial websites 3/ 4 1/ 4 cerebral hemispheres In the cerebral hemispheres, metastases often occur on the grey/white matter cerebellum (see web page 329) interface in center cerebral artery territory. Necrotic areas may break right down to down to} kind cystic cavities containing a pus-like fluid. Clinical features Patients with supratentorial metastatic tumours may current with epilepsy, or with indicators and signs occurring from focal damage or raised intracranial pressure. About 10% of diagnosed intracranial metastases are asymptomatic, detected on screening patients with recognized malignancy. A ring-like look may resemble an abscess however the wall is irregular and thickened. The search for a primary lesion if not already established should embrace a radical scientific examination and a chest X-ray. Management and prognosis: Corticosteriods (dexamethasone) have a dramatic, speedy effect, producing scientific improvement in most patients. Stereotactic radiosurgery supplies a valuable alternative, significantly for lesions lower than 3 cm in diameter and for deep-seated lesions. Provided little question exists concerning the prognosis (abscesses or tuberculomata may resemble metastasis) radiosurgery may be be} administered to two and even three lesions. Prognosis: Patients < 65 years, with a good efficiency status and no proof of systemic metastasis have the most effective prognosis. In the absence of proof of systemic cancer, the median survival interval approaches 2 years. In these with systemic disease, outcomes are less good with a median survival of eight months.
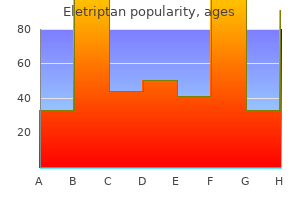
Quality 40 mg eletriptan
The identical idea can theoretically be utilized to a variety of|quite a lot of|a wide range of} other testing procedures the place isolation of glenohumeral movement is desired. In this topic, the scapula began to rotate at approximately 100° of humeral abduction. Therefore, movement above this point is taken into account combined glenohumeral and scapulothoracic movement whereas movement below this point is taken into account isolated glenohumeral movement. In many circumstances, the same impact can be achieved by performing sure examination maneuvers with the affected person placed supine on the examination table. Gagey and Gagey [32] discovered an identical result during which ninety five % of their topics with normal shoulders transitioned to combined scapulothoracic movement between 85° and 90° of glenohumeral elevation. Due to these conflicting outcomes, the reliability of this technique within the measurement of isolated glenohumeral movement came into question. In addition, the clinicians had been somewhat unfamiliar with the digital inclinometers that had been used within the examine, doubtlessly blurring the interpretability of their outcomes. Several biomechanical research have instructed that although the majority of of} scapular movement happens above 90° of glenohumeral elevation, there does exist some scapular movement below this stage. This fact calls into question the ability of an examiner to fully isolate glenohumeral elevation. However, when the angle of glenohumeral elevation is lower than 90°, the degree and high quality of glenohumeral movement can be reliably estimated. The above discussion solely considers the ability of an examiner to isolate glenohumeral movement throughout arm elevation. No revealed research have examined the ability of an examiner to isolate glenohumeral rotation. With vary of movement testing, the idea of finish feel is extraordinarily necessary on several of} levels. In 1947, Cyriax and Cyriax [38] described a basic classification system during which normal finish feel was characterized as bony, capsular or softtissue approximation and abnormal finish feel was characterized as spasm, springy block, and empty (Table 2. These sensations occurred near the extremes of shoulder movement bony structure, muscle contraction, and/or softtissue stretching. A bony finish feel happens when an abrupt finish point is reached as two onerous surfaces come into contact. Capsular finish feel happens because the joint approaches an excessive movement plane-further movement turns into 2. Motion ends in a fashion suggesting that movement would continue if not prevented by one other construction. Motion ends in a "vibrant twang," or when movement is counteracted by muscle contraction. Cyriax and Cyriax [38] instructed that capsular feel was analogous to a thick leather-based band being stretched. Soft-tissue approximation happens when soft tissues prevent additional movement, similar to within the occasion of cross-body adduction or excessive elbow flexion. Muscle spasm can usually have a tough finish feel and was characterized as a "vibrant twang" in the direction of|in direction of} the extremes of movement. This can particularly occur within the evaluation of a affected person with instability who demonstrates a constructive apprehension signal (the apprehension signal is discussed in Chap. A springy block is felt when an intraarticular block prevents movement, followed by an episode of rebound. In 2001, Hayes and Petersen [39] examined the inter- and intra-rater reliability of finish feel in sufferers with painful shoulders and knees. Two physical therapists evaluated each affected person twice, measuring two knee motions and five shoulder motions. The examiners famous the character and high quality of the end feel on the extremes of vary of movement while sufferers vocalized the precise moment of ache copy. However, their examine additionally demonstrated giant variations in finish feel when the shoulder was kidnapped. The authors instructed that this discrepancy was related to the scapulae of the topics had been variably stabilized which may have produced differences in finish feel in these sufferers. The clinical applicability or validity of the various finish feel traits has not been evaluated within the literature. Therefore, regardless of its widespread application in clinical practice, additional examine is required to validate this technique of examination earlier than it may be} formally advocated. Because most main joints within the physique obtain angular (or rotational) movements, vary of movement is often measured in degrees relative to some normative airplane. Shoulder vary of movement is often quantified using considered one of 4 basic strategies; these include estimation by way of visual inspection, the use of of} an inclinometer, the use of of} a goniometer, the use of of} a gyroscope or, extra just lately, digital images using a excessive resolution digicam or smart cellphone. Although several of} 20 2 Range of Motion research have discovered that experienced practitioners can estimate vary of movement with an identical accuracy to standardized measurement units [41, 42], the dearth of instructing concerning the fundamentals of vary of movement testing is disappointing. This ends in inaccurate measurement estimations by the novice examiner who was by no means correctly taught to use goniometers or inclinometers. In a busy clinical practice, nonetheless, the experienced clinician can usually make speedy vary of movement estimations without sacrificing accuracy or precision. Visual inspection and estimation of vary of movement is due to this fact a standard of practice typically, however formal measurements are required when a examine involving vary of movement knowledge is being performed. Both mechanical and digital inclinometers have been described as reliable and valid tools for the measurement of shoulder vary of movement. Mechanical inclinometers, or hygrometers, use gravity and a fluid-level indicator to measure the inclination of the humerus relative to the horizontal airplane in degrees. The first reported use of a mechanical inclinometer to measure vary of movement was in 1975 by Clarke et al. In an adjunct examine [47], the same group discovered that the ability of the inclinometer to detect modifications in joint proprioception was additionally pronounced. In that examine, they calculated inter- and intra-observer reliabilities starting from 0. Currently, digital inclinometers are extra generally used to assess shoulder vary of movement [4857] and performance by calculating the angle of inclination relative to the horizontal airplane using an implanted gravity sensor. Scibek and Carcia [54] studied 13 healthy collegiate topics in an try to quantify scapulohumeral rhythm using a digital inclinometer. One other examine [61] demonstrated the potential of smart phones to measure cervical vary of movement. This technique of measurement eliminates price of|the worth of} commonplace digital inclinometers, a factor that has limited their widespread use. Nevertheless, these research show the utility and practicality of digital inclinometers within the accurate measurement of scapulohumeral rhythm along with glenohumeral vary of movement capability. [newline]The degree of angulation between the two arms of the system represents the whole vary of movement achieved by the joint. It is necessary to preserve stabilization of the limb proximal to the middle of rotation of the joint to keep away from measurement errors. Goniometric mastery requires in depth practice and anatomic data which is able to} finally end in measurement consistency and reproducibility. It is due to this fact recommended for the novice examiner to learn the proper vary of movement measurement strategies early of their orthopaedic career. Goniometers are available in} numerous styles and sizes; nonetheless, the final setup has two movable arms the place one arm is place in line inside a normalized vertical or horizontal airplane (or the "zero place" as defined by Clarke et al. To use a goniometer, the fulcrum of the system is aligned over the middle of rotation of the joint to be measured. The stationary arm of the goniometer is aligned with the limb being measured, typically over proximal muscle origins. The goniometer is held in place while the joint is moved by way of its A gyroscope is essentially a spinning wheel that modifications in three-dimensional orientation with modifications in angular momentum. Gyroscopes have numerous potential purposes similar to inertial navigation techniques. With regard to the shoulder, gyroscopes used to exactly measure vary of movement as shown in a number of} preliminary research [63, 64]. They additionally discovered that use of the gyroscope was a reproducible technique to measure shoulder vary of movement; nonetheless, they recommended repeating the measurements for improved accuracy. Further research are wanted to define how and when gyroscopes ought to be used for accurate vary of movement evaluation. Third, standardized vary of movement images of any given affected person can be in contrast and reviewed over a time period to determine the progress of rehabilitation or physical therapy. In addition to these affected person advantages, taking digital images or video allows for the routine documentation of uncommon pathologies which may facilitate inter-clinician communication and education. Shoulder elevation contains an important shoulder motions would possibly be} needed for actions of day by day dwelling, occupations, sports, and leisure actions.
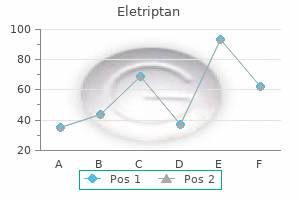
Buy eletriptan 40mg
Ventricular depolarization proceeds inferiorly to superiorly and customarily leftwards. Often biventricular enlargement/hypertrophy is current; the left ventricular hypertrophy indicates extra volume within the left ventricle, and right ventricular 4 Anomalies with a left-to-right shunt in kids 141 enlargement/hypertrophy arises from combinations of extra right ventricular volume and increased pulmonary arterial pressure. Despite the abnormal ventricular conduction sequence, the precordial leads accurately predict ventricular hypertrophy. The final three features reflect the cardiac hemodynamics and vary based on the relative volume and the pressure masses on the respective ventricles. They are therefore useful in assessing the hemodynamic characteristics of the particular anomaly. Chest X-ray In addition to the increase in pulmonary vascularity, varying degrees of cardiomegaly are observed. Cardiac measurement will increase due to each the left-to-right shunt and the mitral regurgitation leading to left ventricular enlargement. Summary of medical findings Although the medical and laboratory findings vary considerably, the electrocardiographic features are probably the most diagnostic for endocardial cushion defect. The auscultatory, electrocardiographic, and chest X-ray findings reflect the three potential hemodynamic abnormalities: mitral regurgitation, pulmonary hypertension, and left-to-right atrial shunt. Natural historical past Patients with full atrioventricular septal defect develop intractable cardiac failure in infancy, which prompts medical management in preparation for an operation. Patients with an ostium primum defect and gentle mitral regurgitation are asymptomatic into 142 Pediatric cardiology Figure 4. Associated lesions, such as persistent left superior vena cava or patent ductus arteriosus, may be ruled out in this view. Partial atrioventricular septal defects vary in severity from a large "primum" defect to a solitary cleft of the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve, which may produce mitral regurgitation. Occasionally, an additional increase is discovered at the ventricular degree, but the atrial increase is commonly so giant that it obscures the ventricular part of the shunt. A slight right-to-left shunt may be be} detectable, either at the atrial degree or at the intrapulmonary degree (because of pulmonary overcirculation and edema). A giant right-to-left shunt suggests pulmonary resistance exceeding systemic resistance or an related anomaly. The pulmonary arterial pressure ranges from regular to systemic levels, the latter suggesting a whole atrioventricular septal defect. Left ventriculography reveals a characteristic abnormality of the left ventricle termed "gooseneck deformity. In a left anterior oblique projection or four-chamber view of a left ventriculogram, the widespread atrioventricular valve may be outlined. The defect is closed; and the cleft of the mitral valve is sutured, which tremendously reduces the degree of mitral regurgitation. In patients with full atrioventricular septal defect, corrective operation may be indicated in very younger symptomatic infants who usually reply poorly to medical management. The authors routinely send infants for a corrective operation at 23 months of age. The danger of pulmonary vascular disease developing inside the first 69 months of life is high, particularly in patients with Down syndrome. The operative results are good in almost all instances, though some infants have such deficient mitral valve anatomy that prosthetic substitute is required. The medical and laboratory findings reflect the atrial left-to-right shunt and the mitral regurgitation. The electrocardiogram displaying left axis deviation, atrial and ventricular hypertrophy, and incomplete right bundle department block kind of|is sort of} diagnostic. Summary of left-to-right shunts Certain generalizations may be made in regards to the cardiac circumstances with a left-to-right shunt that assist in understanding their hemodynamics and that can be be} applied to different lesions, such as these with admixture discussed in a later chapter. The circulate through the defect decided by} either the size of the defect or the relative resistances of the pulmonary and systemic vascular techniques. Volume load is positioned on the left facet of the heart and can lead to congestive cardiac failure. Left atrial enlargement, apical diastolic murmur, and left ventricular hypertrophy are different manifestations of the surplus volume within the left facet of the heart. The shunt decided by} the relative compliance of the ventricles and therefore is influenced predominantly by diastolic occasions. Congestive heart failure is rare in uncomplicated cardiac anomalies because of|as a result of} the amount load is positioned on the right ventricle. The electrocardiogram exhibits a pattern of right ventricular volume overload, and a tricuspid diastolic murmur may be be} current. The features and traditional findings of the 4 major acyanotic circumstances associated with increased pulmonary blood circulate are offered in Table 4. Chapter 5 Conditions obstructing blood circulate in kids Coarctation of the aorta History Physical examination Electrocardiogram Chest X-ray Echocardiogram Cardiac catheterization and angiography Treatment Natural historical past Aortic stenosis Aortic valvar stenosis Discrete membranous subaortic stenosis Supravalvar aortic stenosis Pulmonary stenosis Valvar pulmonary stenosis Pulmonary stenosis secondary to dysplastic pulmonary valve Peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis a hundred and fifty 151 152 153 154 156 156 156 158 159 161 168 a hundred and seventy 173 174 179 181 Although circumstances leading to obstruction of blood circulate from the heart are widespread in kids, these inflicting influx obstruction, such as mitral stenosis, are rare in comparison. In this chapter, therefore, the emphasis is on coarctation of aorta, aortic stenosis, and pulmonary stenosis. The smaller the orifice measurement of the obstruction, the larger is the level of systolic pressure required to eject the cardiac output through the obstruction. This principle is represented by the next equation: Orifice measurement = Constant Ч Cardiac output Pressure distinction throughout obstruction the primary response to the obstruction is myocardial hypertrophy, not ventricular dilation. During childhood, the heart usually maintains the elevated ventricular systolic pressure with out dilation. Eventually, ventricular enlargement might seem because of|as a result of} myocardial fibrosis develops. The fibrotic ventricular modifications occur from an imbalance between the myocardial oxygen calls for and supply. In most youngsters, coronary arterial blood circulate is regular, however with ventricular hypertrophy, myocardial oxygen requirements are increased. Myocardial oxygen requirements are largely devoted to the development of myocardial tension and therefore are associated directly to the level of ventricular systolic pressure and the variety of instances per minute the heart must develop that degree of pressure. Thus, elevated ventricular systolic pressure and tachycardia increase myocardial oxygen consumption considerably. With train, myocardial oxygen requirements increase even more in an obstructive lesion for 2 reasons: (1) cardiac output will increase; so based on the relationship proven earlier, ventricular systolic pressure also will increase; (2) with train, the heart rate will increase. With the development of adequate fibrosis, the contractile properties of the ventricle are affected in order that ventricular dilation and cardiac enlargement develop. Children with obstructive lesions usually present few symptoms, however extreme degrees of obstruction lead to congestive cardiac failure in neonates and younger infants. Aortic coarctation has historically been outlined by its relationship to the ductus arteriosus, whether or not patent or ligamentous. Coarctation might occur either as a localized constriction of the aorta or as tubular hypoplasia of the aortic arch and proximal descending aorta. In basic, patients with tubular hypoplasia of the aortic arch develop cardiac failure within the neonatal period or early infancy. The coarctation in older kids is usually discrete and is located distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery. Preoperative treatment and correction depend extra on the related lesions, such as arch hypoplasia, than on the exact relationship of the coarctation to the ductus. Coarctation of the aorta presents mechanical obstruction to left ventricular output. The pressure proximal to the coarctation is elevated, whereas that past the obstruction is either regular or decrease than regular; this blood pressure distinction is the most important diagnostic feature of coarctation. In response to the pressure distinction between the proximal and distal compartments of the aorta, collateral arteries develop between the high-pressure ascending and the low-pressure descending aorta. Collateral vessels develop in any vascular system when a pressure distinction exists. These vessels symbolize enlargement of naturally occurring small arteries bridging the high- and low-pressure parts. Blood flows through these bridging vessels, and the amount of circulate slowly will increase, leading to the eventual dilation of the vessels. The inside mammary and intercostal arteries are probably the most incessantly occurring collateral vessels in coarctation of the aorta. Left ventricular hypertrophy develops in response to the elevated systolic pressure proximal to the coarctation.
Safe eletriptan 20 mg
Microscopically, myelin is misplaced, oligodendrocytes degenerate but neurons and axons are spared. Clinically, an acute or subacute pontine lesion is suspected, evolving over a few of} days, with bulbar weak spot and tetraparesis (locked-in syndrome). With progression of the lesion, eye signs turn out to be evident and conscious degree becomes depressed coma demise. Vigorous supportive remedy with correction of metabolic abnormalities and vitamin supplementation is suggested. In sufferers with extreme hyponatraemia (< one hundred ten mmol/l), especially alcoholics, sluggish correction is important. The medical picture is that of personality change with signs of frontal lobe illness. Brain, spinal wire, peripheral nerve and muscle could be affected, either separately or in combination. Small cell carcinoma of the lung, gynaecological malignancy and lymphoma are the most common related disorders. These are directed in the direction of|in course of} antigens in the nervous system and the tumour and should explain the pattern toward larger life expectancy in those with, rather than those without, such non-metastatic disorders. Cingulate gyrus Neuropathy Encephalitis Cerebellar degeneration Myelopathy Myopathy Pathology the encephalitic course of selectively impacts the limbic system with neuronal loss, astrocytic proliferation and perivascular inflammatory modifications. Neuromuscular junction disturbance Myasthenic syndrome Uncus Limbic system Parahippocampal gyrus Clinical features Disturbance in behaviour precedes the event of advanced partial (temporal lobe) seizures and memory impairment. Pathology: Characterised by Purkinje cell loss with some involvement of the dentate muscle tissue. Subacute cerebellar degeneration Clinical features: the affected person presents with a quickly growing ataxia. Rarely an acute neuropathy indistinguishable from postinfectious polyneuropathy happens. Proximal myopathy: A slowly progressive syndrome with weak spot of proximal limb muscle tissue. Inflammatory myopathy (polymyositis/dermatomyositis) (see web page 474): the general incidence of related neoplasm in inflammatory myopathy is 15%. Myopathy with endocrine disturbance: Ectopic hormone production (by malignant cells) could induce a myopathy characterised by chronic progressive proximal weak spot. Investigation and therapy of non-metastatic syndromes Successful therapy of the underlying tumour provides the only hope of improvement. Clinical features the affected person develops weak spot of decrease then upper limbs with a bent to fatigue. Following brief exercise, energy could paradoxically suddenly improve second wind phenomenon. Examination reveals a proximal sample of losing and weak spot with diminished tendon reflexes. Up to 50% of sufferers expertise symptoms of autonomic (cholinergic) dysfunction impotence, dry mouth and visible disturbance. Characteristically these disorders: are progressively progressive are symmetrical (bilateral symptoms and signs) could affect on} one or quantity of} particular methods of the nervous system could demonstrate a specific pathology or simply present neuronal atrophy and eventual loss without different features. Classification Degenerative disoders are categorized in accordance with the specific part or parts of the central/ peripheral nervous system affected and in accordance with the following medical manifestations. These degenerative disorders could also be} alternatively termed the system degenerations due to their propensity to affect on} solely the nervous system. Sensorineural deafness + different neurological features Progressive movement dysfunction. Motor neuron illness Spinal muscular atrophy Most of these circumstances are discussed in different chapters. The layers of Light supply Pathology the retina Loss of ganglion cells in the retina Demyelination and axonal loss in the optic nerve (papillomacular bundle) Ganglion cells Clinical features Bipolar cells Onset of visible loss in late teens/early twenties. Characteristically, blue/yellow color discrimination is affected earlier than red/green. The optic disc initially appears pink and swollen with an increase in small Cone vessels, eventually turning into pale and atrophic. The mom of an affected male has the mitochondrial mutation and should or could not have symptoms. Quinone analogues (ubiquinone and idebenone) could assist during periods of speedy visible worsening. Pigment migrates to superficial layers the optic nerve could present some gliosis, but usually is remarkably regular. The retina across the macular space is first affected resulting in a characteristic ring scotoma. The fundal appearance is diagnostic outcome of|because of|on account of} the superficial migration of pigment. The electroretinogram recording the electrical activity of the retina is eventually misplaced. These could also be} categorized by age of onset, presence of related features, but increasingly by mode of inheritance. Patients are eventually confined to a wheelchair and, due to related low serum immunoglobulin levels are prone to repetitive infections. Death happens in second or third decade from an infection or malignancy (often lymphoma). Peripheral nerves present lack of large myelinated axons and segmental demyelination. Onset of symptoms is generally around puberty, and always earlier than 25 years of age; most sufferers turn out to be wheelchair sure by their late twenties. Disturbance of stability is the preliminary symptom, usually related to the event of scoliosis. Corticospinal tract involvement results in limb weak spot with absent stomach reflexes and extensor plantar responses. Posterior column involvement results in lack of vibration and proprioception in the extremities. Dorsal root and peripheral nerve involvement results in absent decrease limb reflexes. Involvement of myocardial muscle (cardiomyopathy) is widespread and results in cardiac failure or dysrhythmias. Pes cavus (club foot) with extension of metatarsophalangeal and flexion of interphalangeal joints. Investigation Identification of the gene and availability of diagnostic testing has restricted the worth of different ancillary investigations such as imaging and neurophysiology. Orthopaedic intervention can alleviate scoliosis, and orthopaedic home equipment and bodily remedy assist preserve ambulation. Cardiac issues could be successfully handled pharmacologically and insulin remedy could also be} essential to management diabetes mellitus. Other causes of areflexic ataxia Abetalipoproteinaemia (Bassen Kornzweig disease) · Malabsorption syndrome · Acanthocytes (thorn-shaped red blood cells) · Low serum ldl cholesterol, triglycerides and fatty acids · Low vitamin E. Xeroderma pigmentatosum · Sensitive to ultraviolet gentle · Keratosis and pores and skin cancer. Commonly different neurological features co-exist: ophthalmoplegia, optic atrophy, retinal pigmentation, deafness, dysarthria, dysphagia, dementia, additional pyramidal and pyramidal signs and peripheral neuropathy. For analysis all different causes of acquired ataxia inflammatory, infective, nutritional, metabolic, endocrine and non-metastatic must be excluded by acceptable investigations. Two types could be distinguished on the premise of the length of the assaults, the presence of myokymia (facial twitching), precipitating elements, response to acetazolamide and the nature of the genetic defect. Type 1, assaults are precipitated by sudden movements, emotional stress, fatigue, exercise, or hunger. Type 2, myokymia is absent, the distinguished symptoms being ataxia of gait and limbs, dysarthria, and gaze-evoked nystagmus. The assaults start abruptly and last from quarter-hour to a few of} hours although generally days. The carbonic anhydrase inhibitor acetazolamide may be very efficient in preventing assaults. Superoxide dismutase is necessary in eradicating toxic superoxide radicals and changing them into non-harmful substances. The last widespread pathway of anterior horn cell demise, regardless of what truly triggers the process, is a fancy interaction of genetic elements, oxidative stress and glutamate excess (excitatory injury). Abnormal clumps of proteins (neurofilaments) could be found in motor neurons that will themselves be toxic or by-products of overwhelming cell harm.
Diseases
- Tracheobronchomegaly
- Digoxin toxicity
- Otofaciocervical syndrome
- Super mesozoic-dysentery complex
- Transient global amnesia
- Ceroid lipofuscinois, neuronal 5, late infantile
Generic 20 mg eletriptan
Through specialised neuronal "osmoreceptors" that sense modifications in plasma osmolality, vasopressin launch and thirst are titrated to be able to} obtain water balance. Fine-tuning of water absorption occurs alongside the collecting duct, and is dependent upon by} distinctive structural modifications of renal tubular epithelium that confer broad range|a variety} of water permeability. In this article, we evaluate the mechanisms that ensure water homeostasis nicely as|in addition to} the fundamentals of problems of water balance. Instead of discarding their now unnecessary strain filters and redesigning their kidneys as environment friendly secretory organs, the terrestrial vertebrates modified and amplified their existing methods to salvage the valuable water of the filtrate. Marine animals survive in the excessive tonicity of seawater (5001000 mOsm/kg) via selection of|quite so much of|a wide range of} mechanisms. The shark maintains a excessive tonicity in its physique fluids (2,3), whereas dolphins absorb water from foodstuffs while producing a extremely concentrated urine via advanced multilobed reniculate kidneys (4). Water is probably the most abundant part of the human physique, constituting roughly 50%60% of physique weight. Cell membranes, which define the intracellular compartment, and the vascular endothelium, which defines the intravascular part, are each water permeable. Because the intracellular area constitutes the most important physique compartment, holding roughly two thirds of physique fluid, modifications in water homeostasis predominantly result on} cells; water extra leads to mobile swelling, and water deficit leads to mobile shrinkage. For each 1 liter of water change, roughly 666 ml result on} the mobile area, with solely about one hundred ten ml affecting the vascular area. Although cells have an innate capability to reply to modifications in cell quantity when extracellular osmolality modifications, the physique protects cells primarily by tightly 852 Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology regulating extracellular osmolality. The amount of physique water remains remarkably steady despite an enormous range of water consumption and a large number} of routes for water loss, together with the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract, skin, and the kidneys. Maintaining Brain Cell Size With a plethora of capillaries descending via the subarachnoid area into the parenchyma, the mind is remarkably vascular. Astrocytes, star-shaped neuronal cells, encapsulate the capillaries, forming a "blood-brain barrier" and controlling many necessary neurologic functions. Because the quantity of intracellular water affects the concentration of intracellular contents and cell measurement, modifications in osmolality can disturb the advanced signaling community that orchestrates cell operate. Given the complexity of mind operate, even minor modifications in neuron ionic composition and measurement can have profound results on the processing and transmission of neuronal alerts. Consequently, the mind has developed advanced osmoregulatory mechanisms to defend in opposition to modifications in plasma osmolality. Penetrating capillaries descend via the subarachnoid area into the parenchyma, and are encased by astrocytes, which along with controlling necessary neurologic functions, type the blood-brain barrier. In the setting of hypotonicity, as shown in Figure 2, the speedy swelling of the cell prompts quiescent cell membrane channels and leads to quick Cl2, K1, and attendant water loss, a process termed regulatory quantity decrease. Over the following 24 hours, the cells lose further organic solutes, such as myo-inositol, and amino acids, such as glutamine, glutamate, and taurine. With hyperosmolar-induced cell shrinkage, mind cells respond with quick uptake of surrounding Na1, K1, and Cl2, correcting cell quantity in a process termed regulatory quantity increase (12). With more extended exposure, organic solute concentrations inside the cells rise, replacing the excessive levels of ions. Despite these necessary cell protective mechanisms, alterations in plasma osmolality can have disastrous consequences. The classic neurologic signs of hypo-osmolality, together with headache, nausea, vomiting, and if severe enough, seizures, are usually thought to happen at a serum sodium 854 Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology Figure 2. In this figure, a traditional cell is challenged by both a hyperosmolar (left) or hypo-osmolar (right) milieu. In the setting of hyperosmolar stress, whereby the cell shrinks with water egress, neurons then respond by quickly accumulating Na1, K1, and Cl2 ions, adopted by the production of intracellular organic solutes. The increase of intracellular solute content material then draws water in to normalize the concentrations across the cell membrane, thereby restoring cell measurement. In the setting of hypo-osmolarinduced swelling, activation of K1 and Cl2 channels, nicely as|in addition to} the K1-Cl2 cotransporter, result in solute and consequent water loss, thereby restoring cell quantity. More gentle modifications of plasma osmolality are additionally associated with neurologic signs, together with gait instability, reminiscence impairment, and cognitive decline. Children are considered at elevated risk of hypo-osmolar encephalopathy, presumably because of the comparatively bigger mind to intracranial quantity compared with adults (13). Conversely, because of|as a end result of} the mind begins to atrophy in the sixth decade, aged people at a lower risk of severe problems from acute hyponatremia. In addition to age, intercourse considered an necessary determinant of neurologic sensitivity. The vast majority of reported cases of postoperative hyponatremia leading to deadly outcomes have been in women (14), together with postpartum and postmenopausal women (15). Unlike the mind swelling associated with hypo-osmolality, the mind shrinks in hypertonic situations. The protective reflex of intense thirst could disappear as hypertonicity worsens, replaced by somnolence, confusion, and muscle weakness (16). If severe enough, the shrinking mind will draw back from the calvarium, tearing the wealthy capillary plexus, and causing subarachnoid hemorrhage, cerebral bleeding, and dying. The highest reported serum sodium in the grownup literature remains 255 mEq/L, a consequence of consuming salty water as a part of} a deadly exorcism ritual (17). Presumably utilization of} table salt as a typical antiemetic, deadly salt ingestion, both by chance or voluntarily, is properly reported (18), as is unintentional iatrogenic administration (19). In summary, despite internal mobile mechanisms to protect cell quantity, cells stay at risk with alterations of water balance; consequently, stopping significant modifications in plasma osmolality is crucial for survival. Sensing Changes in Body Concentration: the Osmoreceptor the ability to internally sense plasma osmolality is prime to the method of water homeostasis. Much progress in explaining the mechanisms of the "osmoreceptor" has been made, as reviewed by Sharif-Naeini et al. Electrophysiologic recordings from supraoptic nuclei of the hypothalamus in rats show an rising rate of mobile depolarization in response to water deprivation (26), and a lowering rate with water administration (27). More recent studies have shown that hyperosmolality causes osmoreceptor membrane depolarization through activation of nonselective calcium-permeable cation channels. It remains somewhat unresolved whether or not the precise stimulus is change of specific intracellular solutes associated with cell dehydration or a mechanical effect linked to cell membrane shrinkage. The osmoreceptor, doubtless because of its position in orchestrating the pathways of water retention, has a blunted regulatory quantity decrease response, whereby its own shrinkage hyperosmolality is maintained, allowing sustained stimulation of thirst and vasopressin launch till the plasma osmolality may be corrected (30). In the next sections, we focus on how the osmoreceptor regulates thirst and vasopressin (synonymously known as as|often known as} antidiuretic hormone) launch. Thirst the sensation of thirst is the experiential part of the advanced physiologic drive to drink. Neuroimaging studies have localized the anatomic origin of thirst, with hyperosmolality stimulating activity in the anterior wall of the third ventricle, the anterior cingulate, parahippocampal gyrus, insula, and the cerebellum (31). These mind areas are additionally associated with advanced functions, together with emotional behavior and thought, perhaps explaining why the perception of thirst, along with its physiologic basis, is so linked to social and behavioral mores. The osmolar threshold for thirst has historically been considered to be roughly 5 mOsm/kg above the edge for vasopressin launch, though some recommend similar set factors (32). A larger thirst threshold allows vasopressin titration of urinary water excretion with out the need to|the necessity to} be continually consuming. Upon consuming, the sensation of thirst is quenched nearly immediately, suggesting that a direct satiating effect of water on the tongue and buccal membrane nicely as|in addition to} cognitive consciousness of fluid consumption may clarify the resolution of thirst. In addition, the recent recognition of peripheral osmoreceptors located inside the gastrointestinal tract and portal venous system recommend a local mechanism that instantly senses gastric water absorption (34). Whether these peripheral osmoreceptors may contribute to the problems of osmolality regularly seen in sufferers with cirrhosis remains unknown. Thirst on the battlefield is famous, with exsanguinating soldiers asking for water. Conversely, hypo-osmolar cell swelling deactivates these channels, resulting in cell hyperpolarization, extinguishing thirst and vasopressin launch. Thirst is a typical criticism for sufferers with congestive heart failure (43,44), regularly plagues dialysis sufferers, and certain contributes to the prevalence of hyponatremia in these populations. In addition to problems of fluid quantity, thirst regularly encountered in sufferers with psychiatric problems, reported in up to as} 25% of hospitalized sufferers with schizophrenia.
Purchase eletriptan 40mg
Malunited fractures of the glenoid neck, proximal humerus, glenoid or coracoid can impinge upon the subscapularis muscle, thus resulting in anterior shoulder pain [85]. Iatrogenic causes can include any kind of anterior shoulder surgery, potentially inflicting the formation of subcoracoid adhesions and a functionally narrowed coracohumeral interval. Idiopathic causes might include ganglion cysts, congenitally malformed coracoid processes or subscapularis calcifications. Recently, quantity of} research have described the various morphologic traits of the coracoid and their potential roles within the development 4. The doubleheaded pink arrow lies perpendicular to the white line and travels to essentially the most lateral tip of the coracoid course of. The double-headed white arrow represents the distance between the lesser tuberosity and essentially the most posterior aspect of the coracoid course of. When the humerus is internally rotated, the coracoid induces a "curler wringer" effect on the subscapularis tendon which induces stretching and tearing of the tendon when the coracohumeral interval is narrowed [87]. More specifically, these patients with out subscapularis pathology had a coracohumeral interval of 10 ± 1. Despite this evidence, the instigating issue concerned within the development of anterosuperior cuff pathology in patients with a narrowed coracohumeral interval has yet to be utterly elucidated. This pain might radiate distally along the brachium if the long head of the biceps tendon is concerned. Because this entity has not been studied extensively, it stays a prognosis of exclusion when all other causes of anterior shoulder pain have been dominated out. Despite the lack of literature on the subject, it is important to|it is very important|you will need to} thoughts that|do not neglect that} subcoracoid impingement additionally be} end result of|the results of} disordered scapular mechanics. In the setting of a standard scapular exam, the subcoracoid impingement check additionally be} an essential tool within the prognosis of subcoracoid impingement. As the arm is adducted and internally rotated, the affected person with subcoracoid impingement will complain of a boring anterior shoulder pain. Because the subscapularis muscle makes a big contribution to the bicipital sheath, testing for pathology of the long head of the biceps tendon additionally be|can be} indicated when subcoracoid impingement is suspected (physical examination of the long head of the biceps tendon is mentioned in Chap. The examiner passively abducts to humerus to 90°, maximally internally rotates the humerus and flexes the elbow to 90°. The check is optimistic for subcoracoid impingement when a boring anterior shoulder pain is elicited. The term "internal impingement" refers to a standard physiologic prevalence where the larger tuberosity makes contact with the posterosuperior glenoid labrum when the humerus is kidnapped and externally rotated. Although its major perform might contain the prevention of hyperexternal rotation and upkeep of stability, repeated episodes of this impingement (which usually happens with repeated overhead actions similar to throwing) might lead to posterosuperior labral tears and posterosuperior rotator cuff tears which finally turn into symptomatic. In essence, the posterosuperior labrum and rotator cuff turn into pinched between the larger tuberosity and the bony glenoid rim resulting in posterior shoulder pain (due to pathology of the posterosuperior labrum and rotator cuff) especially when the humerus is kidnapped and externally rotated. Hyperabduction and external rotation might pinch the posterosuperior cuff between the larger tuberosity and the glenoid, probably resulting in articular-sided posterosuperior rotator cuff tears and tearing of the posterosuperior glenoid labrum. In acute accidents, patients will usually recall the specific occasions resulting in their shoulder pain, weak point, and dysfunction. Although every kind of impingement involves a continual course of, many patients are asymptomatic till the tear has reached adequate dimension and/or has resulted in altered glenohumeral kinematics. Without treatment, small tears with intact glenohumeral mechanics can progress to bigger tears, resulting in weak point and unbalanced force couples and, subsequently, elevated shoulder pain and dysfunction [102, 103]. As mentioned above, subacromial impingement involves a mixture of intrinsic components. As the cuff tear develops and increases in dimension, pain and weak point turn into the predominant options. Pain and weak point turn into worse because the tear extends to contain other tendons, similar to these of the infraspinatus (posterosuperior tear) or subscapularis (anterosuperior tear). Left untreated, pain will usually diminish and the affected person will complain of weak point as the first symptom [104]. Subcoracoid impingement (also mentioned above) is believed to result from a narrowed coracohumeral interval and presents with an insidious onset of dull pain over the anterior aspect of the shoulder in positions of adduction and internal rotation [8386]. Similar to subacromial impingement, the progression of small, structural lesions of the subscapularis can lead to massive, full-thickness tears resulting in progressive pain, dysfunction and, in some cases, anterior instability [10]. Symptomatic internal impingement happens repetitive hyperabduction and external rotation posterosuperior articularsided rotator cuff tears and labral lesions. These patients may also report a gradual decrease in throwing performance similar to a decline in throwing accuracy and 94 4 Rotator Cuff Disorders velocity. Specifically, energy deficits in internal or external rotation (with the arm each at the facet and at 90° of abduction) and/or abduction should direct the clinician to specifically consider rotator cuff energy. Although the presence of pain can lead to guarding and the impression of weak point, the sources of pain and weak point have to be ascertained to arrive at the appropriate prognosis. Furthermore, since painful impingement of the rotator cuff might progress to partial- or fullthickness tears, optimistic impingement indicators may also be current in patients with weak point related to a rotator cuff tear. Rent Test the lease check is a technique of trans-deltoid palpation first described by Codman [105] in 1934 which will have some utility within the detection of supraspinatus tendon defects. When carried out accurately, Codman instructed that clinicians may find a degree of tenderness and detect a sensation "crepitus" beneath their fingers which might therefore counsel the presence of a rotator cuff tear. Specifically, a spot (or "sulcus" [101]) felt between the perimeters of the torn tendon because the humerus was internally and externally rotated throughout palpation. With the arms initially at the facet, the examiner palpates the world just beneath the anterolateral acromion and lateral to the coracoacromial ligament which also corresponds to an anatomically skinny space of the deltoid, probably facilitating the detection of a tendon defect [106]. At roughly 10° of internal rotation, the examiner can determine the bicipital sheath and the lesser tuberosity, thus providing info regarding spatial orientation [17, 106]. Extension of the shoulder might permit extra palpation of the anterior infraspinatus. Although a few years have handed since its unique description, only some research have evaluated the diagnostic utility of this check for the 4. Jobe Test the Jobe check [19] is commonly carried out to elicit weak point supraspinatus tearing. To perform the check, the arms are passively positioned in 90° of abduction within the scapular aircraft with the thumbs pointed downward. Although this check isolates the supraspinatus muscle-tendon unit, scientific weak point can be simulated by the presence of serious pain. To alleviate a few of this pain and to more immediately consider supraspinatus energy, the check can be repeated with the thumbs pointed upward. This maneuver is believed to position the larger tuberosity away from the coracoacromial arch and may therefore decrease the pain related to mechanical cuff impingement. This identified as} "drop arm signal" (not to be confused with the "drop signal," as mentioned below) and is indicative of a big supraspinatus/infraspinatus tear. Although sensitivity and specificity knowledge for the Jobe check and drop arm signal are modest, the mixture of each maneuvers is believed to improve diagnostic accuracy (Table 4. A optimistic check happens when a sulcus is felt by the examiner whatever the presence of pain. Lyons and Tomlinson [107] calculated a sensitivity of 91 % and a specificity of seventy five % after performing the check throughout energy testing in a collection of forty five patients. Their results counsel that the lease check was more priceless within the detection of full-thickness tears when in comparison with} any of the partial-thickness tears. In this check, each arms are positioned in roughly 90° of abduction inside the scapular aircraft and maximally internally rotated (thumbs pointed downward). A optimistic check happens when uneven weak point happens involving the affected shoulder. Both arms are positioned in roughly 90° of abduction inside the scapular aircraft and externally rotated (thumbs pointed upward). The affected person then attempts to additional abduct the humerus towards resistance applied by the examiner. This variation of the Jobe check is believed to reduce the pain related to supraspinatus impingement and additionally be} more delicate to precise weak point rather than guarding impingement. The external rotation lag signal is an effective various that eliminates the effect of pain on external rotation perform. From this position, the humerus is passively positioned in 2030° of external rotation. A optimistic external rotation lag signal happens when the affected person is unable to hold this externally rotated position (estimate the amount of internal rotation that occurs, corresponding to degrees of lag;.
Best eletriptan 40 mg
It contains a number of} essential reflex centers that help management posture and steadiness, listening to, movement of the head and eyes in a coordinated method, visible reflexes and responses to auditory stimuli. Superior and Inferior Colliculi the tectum is the dorsal roof of the midbrain, and controls visible and auditory reflexes. It is divided into the corpora quadrigemina, which consists of two superior and two inferior colliculi. They relay information to the thalamus, which sends the information on to the cerebral cortex. The superior colliculi are situated beneath the thalamus, and are the visible reflex centers, coordinating head and eye actions throughout monitoring of a transferring object. The inferior colliculi are the auditory relay areas, and assist in sound localization. The tectum and the 4 colliculi are step one of the neural pathway that determines how individuals react to what they see and hear. Substantia Nigrae and Red Nuclei the region beneath the colliculi known as as} the tegmentum, which forms the ground of the midbrain. The tegmentum surrounds the cerebral aqueduct, which connects the third and fourth ventricles. The tegmentum additionally regulates autonomic capabilities, which are these acts that the physique carries out with out aware thought. Within the tegmentum are discovered the substantia nigrae, red nuclei, and nuclei of the reticular formation. The substantia nigrae are functionally linked to the basal ganglia, and have been reviewed in the basal ganglia section of this seminar. The substantia nigrae are situated behind the cerebral peduncles, which are fiber tracts in the midbrain. They are involved in motions such as the crawling of babies, arm swinging in typical walking, and have minimal management over hand motion. Reticular formation nuclei are scattered in the tegmentum, and are additionally discovered in the brainstem. They have a job in stereotypical conduct patterns, nicely as|in addition to} wakefulness, degree of arousal, and sleep patterns. Fiber Tracts Two massive fiber tracts traverse the midbrain, which are the cerebral peduncles and the superior cerebellar peduncles. The cerebral peduncles are situated on the ventral or anterior aspect of the midbrain. They divide the mind into two halves, with every half further divided into anterior and posterior elements by the substantia nigra. The cerebral peduncles are separated from the tectum by the cerebral aqueduct, identified as|also called|also referred to as} the aqueduct of Sylvius. The superior cerebellar peduncles are situated posteriorly, and join the midbrain to the cerebellum. These nerve cells are essential in regulating motor function and emotion, and their death results in signs such as tremors, physical instability, and emotional modifications. Researchers have famous that dopamine manufacturing is often abnormally high in individuals with sure psychological diseases, such as schizophrenia. The best medicines for the therapy of psychosis are those that scale back dopamine activity. In addition, the substantia nigra, the place most dopamine is produced, has been seen to bear structural and mobile modifications in an individual with schizophrenia. Hindbrain the hindbrain is situated at the rear of the cranium, and is the bottom portion of the mind. The pons and medulla of the hindbrain be a part of the midbrain to type the brainstem, which extends from the higher cervical spinal cord to the diencephalon of the cerebrum. The brainstem is involved in alertness and in monitoring basic survival capabilities such as respiratory, heartbeat, blood pressure, consciousness, cardiac function, involuntary muscle actions, swallowing, movement of the eyes and mouth, relaying sensory messages (pain, warmth, noise, and so forth. Messages from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord and nerves that branch from the spinal cord are despatched by way of the pons and brainstem. The cerebellum is very involved in maintaining equilibrium and the coordination of muscle actions and movement. The fourth ventricle situated in the hindbrain, posterior to the pons and the higher portion of the medulla oblongata. It is situated in the higher hindbrain, serving as a bridge to join the brainstem and the cerebellum, and relaying information between the medulla oblongata, cerebrum, and cerebellum. Fiber tracts referred to as the middle cerebellar peduncles cross the fourth ventricle and the pons to reach the cerebellum. The pons contains centers that impact the speed and depth of respirations, and is involved with coordinating facial actions, facial sensation, listening to and steadiness. It receives information from visible areas to management eye and physique actions, and performs a job in controlling patterns of sleep and arousal. The pons relays information to the cerebellum to management coordination of muscular actions and keep equilibrium. Damage to the pons end result in|may end up in|can lead to} an incapability to close the mouth, chewing issue, atrophy of the muscular tissues involved in chewing, visible issues, a serious lack of coordination in motor capabilities of the head, neck and face, and/or listening to issues. Medulla Oblongata the medulla oblongata, or just medulla, is inferior to the pons, and is joined to the spinal cord. It serves as the connection between the brainstem and relaxation of|the the rest of} the mind, nicely as|in addition to} connecting the mind to the spinal cord to allow communication between the mind and relaxation of|the the rest of} the physique. The inferior cerebellar peduncles carry fiber tracts from the spinal cord and vestibular centers in the medulla. The medulla is house to many life-sustaining management centers- a respiratory middle to regulate respiratory, a cardiac middle that can increase or lower coronary heart fee, and a vasomotor middle that regulates how blood vessels dilate and constrict, thereby affecting blood pressure. It additionally has a job in regulating reflexes, and maintaining muscle tone and upright posture. Cerebellum the cerebellum is situated again of|behind|in the again of} the mind, beneath the occipital lobes and posterior to the brainstem. The peduncles are paired bundles of nerves that carry impulses from one area of the mind to one other. The superior cerebellar peduncles join the cerebellum to the midbrain, the middle pair join with the pons, and the inferior cerebellar peduncles join the cerebellum with the medulla oblongata. The vermis, a word which suggests "wormlike structure", is midline and connects the two hemispheres of the cerebellum. The cerebellum is separated from the inferior parts of the occipital lobes of the cerebrum by the tentorium cerebelli, which is an extension or fold of dura mater. The tentorium is clinically significant as mind tumors are often characterized as to their location with reference to the tentorium- supratentorial (above the tentorium) or infratentorial (below the tentorium). In addition, most childhood major mind tumors are infratentorial, whereas most grownup major mind tumors are supratentorial. The cerebellum has a cortex of gray matter on its floor, with finely spaced parallel grooves that stand in distinction to the broad, irregular convolutions of the cerebral cortex. The cerebellar cortex is tightly folded in the type of an accordion, and divided into smaller "lobules". Underneath the grey matter of the cortex are bands of white matter, made up largely of myelinated nerve fibers working to and from the cortex. Embedded in the white matter are 4 deep cerebellar nuclei composed of gray matter, which are motor-related. The cerebellum contains more nerve cells than both cerebral hemispheres combined, but takes up solely about ten % of the total mind volume. Unlike the cerebrum, the best aspect of the cerebellum controls the best aspect of the physique, with the left aspect controlling the left. It fantastic tunes motor activity or movement, helping one to keep posture and a way of steadiness or equilibrium by controlling the tone of muscular tissues and position of limbs. The cerebellum is critical for the coordinated actions required for normal gait in walking or working. It is very involved in position sense, which is the innate capability to know the place your arms and legs are in area with out having to see them. It additionally coordinates sensory input from the inside ear and muscular tissues to provide correct management of position and movement.
Best 40 mg eletriptan
There is good proof prednisolone given in high dosage within the acute stage (50 mg per day for 10 days) improves recovery. The position of antiviral remedy is less clear as conflicting outcomes have been present in current massive trials. Eye care (shielding and synthetic tears) is necessary in stopping corneal abrasion. In patients with complete paralysis, electrical absence of denervation on electromyography is an optimistic sign. Occasionally aberrant reinnervation occurs motion of the angle of the mouth on closing the eyes (jaw winking) or lacrimation when facial muscle tissue contract (crocodile tears). The stapedius muscle can be affected producing a subjective ipsilateral clicking sound. Contractions are irregular, intermittent and worsened by emotional stress and fatigue. Most circumstances come up from vascular compression of the facial nerve at the root entry zone (in the same means as trigeminal neuralgia). Treatment Drugs Local infiltration with botulinum toxin of involved muscle tissue is useful. Flickering of facial muscle tissue outcomes from spontaneous discharge within the facial motor nucleus. Sound waves are transmitted by the tympanic membrane and the ossicles to the oval window, setting up waves within the perilymph of the cochlea. Vestibular function: the vestibular system responds to rotational and linear acceleration (including gravity) and along with a visual and proprioceptive enter maintains equilibrium and physique orientation in area. Linear acceleration ends in displacement of the otoliths within the utricle or saccule. The cochlear (acoustic) and vestibular divisions journey together by way of the petrous bone to the interior auditory meatus the place they emerge to pass by way of the subarachnoid area within the cerebellopontine angle, each getting into the brain stem separately at the pontomedullary junction. Third order neurons from the inferior colliculus on each side run to the medial geniculate physique on both sides. Fourth order neurons pass by way of the interior capsule and auditory radiation to the auditory cortex. Second order neurons come up within the vestibular nucleus and descend within the ipsilateral vestibulospinal tract. Sensorineural deafness: failure of motion potential production or transmission end result of} disease of the cochlea, cochlear nerve or cochlear central connections. Further subdivision into cochlear and retrocochlear deafness helps set up the causative lesion. Pure word or cortical deafness: a bilateral or dominant posterior temporal lobe (auditory cortex) lesion produces a failure to perceive spoken language despite preserved listening to. Tinnitus may be be} (i) continuous or intermittent, (ii) unilateral or bilateral, (iii) high or low pitch. Vertigo may end result from disease of the labyrinth, vestibular nerve or their central connections. Causes of deafness Conductive Cochlear Wax Infection Trauma otitis media* cholesteatoma tympanic membrane rupture ossicular disruption Sensorineural Retrocochlear Cerebellopontine angle tumour acoustic neuroma meningioma epidermoid/dermoid Brain stem disease (associated with different brain stem symptoms and signs) demyelination syringobulbia herpes zoster vascular insufficiency tumours astrocytoma Otosclerosis Tumours carcinoma glomus jugulare Congenital* . Cerebellopontine angle tumours acoustic schwannoma meningioma epidermoid/dermoid Central (associated with different brain stem symptoms and signs) Demyelination Vertebrobasilar insufficiency Tumour astrocytoma Syringobulbia Causes of tinnitus Any lesion causing deafness may also trigger tinnitus. Occasionally patients understand a vibratory noise inside the top, transmitted from an arteriovenous malformation or carotid stenosis. Preganglionic parasympathetic fibres come up within the Medulla inferior salivatory nucleus and pass to the otic ganglion. General somatic sensory fibres innervate the realm of pores and skin behind the ear, pass to the superior ganglion and finish within the nucleus and tract of the trigeminal Olivary nerve. Sensory fibres innervate the posterior third of the tongue (taste), pharynx, eustachian tube and carotid Corticospinal body/sinus and terminate centrally within the nucleus solitarius. Within the neck the nerve lies in close proximity to the interior carotid artery and inner jugular vein. The superior and inferior ganglia lie within the jugular foramen, the otic ganglion within the neck below the foramen ovale. Reflex bradycardia and syncope happen end result of} stimulation of vagal nuclei by discharges from glossopharyngeal. The central connections are complicated although just like these of the glossopharyngeal nerve. Motor fibres supplying the pharynx, soft palate and larynx come up within the nucleus ambiguus. Afferent fibres from the pharynx, larynx and exterior auditory meatus have cell our bodies within the jugular ganglion and finish within the nucleus and tract of the trigeminal nerve. Afferent fibres from abdominal and thoracic viscera have cell our bodies within the nodose ganglion and finish within the nucleus solitarius. Extracranial branches: Motor and sensory supply to the pharynx Superior laryngeal branch to the laryngeal muscle tissue Recurrent laryngeal branch Supply to thoracic and abdominal viscera Disorders of the vagus nerve trigger: Palatal weakness Unilateral minimal symptoms. Pharyngeal weakness Pharyngeal muscle tissue are represented by the center part of of} the nucleus ambiguus. Fibres to adductors and abductors of the vocal cords are provided by the laryngeal nerves. Pharyngeal and palatal involvement trigger marked dysphagia and nasal regurgitation. Bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve lesions trigger stridor and breathlessness on exertion. The cranial portion of the accent nerve arises from the bottom part of of} the nucleus ambiguus within the medulla. The spinal part arises within the ventral gray matter of the higher five cervical segments, ascends alongside the spinal wire and passes by way of the foramen magnum. After joining with the cranial portion it exits because the accent nerve by way of the jugular foramen. The supranuclear connections act on the ipsilateral sternomastoid (turning the top to the contralateral side) and on the contralateral trapezius. This ends in: head turning away from the relevant hemisphere during the seizure head turning path of|in path of} the relevant hemisphere with cerebral infarction. Unilateral lower motor neuron weakness produces a lower shoulder on the affected facet (trapezius) and weakness in turning the top to the alternative facet (sternomastoid). Skull base/intracranial Basal skull tumours meningioma, neurofibroma, metastasis, epidermoid, nasopharyngeal carcinoma Bone lesions osteomyelitis (in diabetics, consider pseudomonas), chordoma Basal meningitis (especially tuberculous) Carcinomatous meningitis Glomous jugulare tumour (chemodectoma) Brain stem Infarction Demyelination Motor neuron disease Syringobulbia Poliomyelitis Intrinsic tumours. Polyneuritis cranialis Multiple cranial nerve palsies of unknown aetiology which spontaneously remit. Myasthenia gravis may current with a weakness of the bulbar musculature (see page 482). The cerebellum consists of two laterally positioned hemispheres and the midline structure the vermis. Tentorium cerebelli Midbrain Pons Medulla Occipital bone Cerebellum Cerebellar tonsil Inferior floor Cerebellar tonsil Vermis Midbrain Superior floor Primary fissure Superior vermis Medulla Flocculus Vagus nerve and Glossopharyngeal nerve roots Three main phylogenetic subdivisions of the cerebellum are recognised. The anterior lobe (paleocerebellum) Receives afferent fibres from (spinocerebellar pathways) within the spinal wire. Receives afferent fibres and initiatives efferent fibres from and to motor cortex/vestibular nuclei, basal ganglia and pons. Deep within the cerebellar hemispheres within the roof of the 4th ventricle, lie 4 paired nuclei separated by white matter from the cortex. These pass either to the deep nuclei of the cerebellum and thence to the brain stem, or to the vestibular nuclei of the brain stem. From there fibres relay again to the cerebral cortex and thalamus, or project into the spinal wire, influencing motor management. Second order neurons come up right here (L1L5) and decussate Ventral spinocerebellar tract the cerebellar peduncles: Three peduncles join the cerebellum to the brain stem: Superior peduncle afferent and efferent fibres. Damage to midline buildings vermis (and flocculonodular lobe) Results in: disturbance of equilibrium with unsteadiness on standing, strolling and even sitting (truncal ataxia). Damage to hemisphere buildings always produces signs ipsilateral to the facet of the lesion.
References:
- https://www.ijcmas.com/8-7-2019/Tripti%20Gurjar,%20et%20al.pdf
- https://www.binghamandhowarth.com/wp-content/uploads/bingham-comprehensive-dentistry-infographic.pdf
- https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.06.20020974v1.full.pdf
.png)