Buy oxybutynin 5mg
Deficiencies of both vitamin could cause megaloblastic anemia; nonetheless, inappropriate therapy of B12 deficiency with folate could cause irreversible nerve degeneration. Data are largely based on surveys of subjects with florid manifestations or from retrospective analyses of beforehand identified disease. However, drug remedy, adopted by alcohol, liver disease, and reticulocytosis, is the commonest reason for macrocytosis (imply corpuscular volume greater than one hundred fl) in a sample of 300 hospitalized subjects. On the other hand, a imply corpuscular volume greater than 120 fl was usually caused by B12 deficiency. Atrophic gastritis leads to a low acid�pepsin secretion by the gastric mucosa, which in flip leads to a reduced launch of free vitamin B12 from food proteins. In addition, hypochlorhydria in atrophic gastritis leads to bacterial overgrowth of the stomach and small intestine, and these micro organism could bind vitamin B12. The capacity to take in crystalline vitamin B12 stays intact in older folks with atrophic gastritis. Because the American food provide is now fortified with folic acid, concern is rising about neurologic exacerbation in individuals with marginal vitamin B12 status and high-dose folate consumption. A more delicate method of screening for vitamin B12 deficiency is measurement of serum methylmalonic acid and homocysteine ranges, which are increased early in vitamin B12 deficiency. A homocysteine stage will be elevated in both vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies, but a methylmalonic acid stage will be elevated solely in vitamin B12 deficiency (Figure 31. Renal failure is the one different confounding reason for an elevated methylmalonic acid focus. Although elderly folks with low vitamin B12 status frequently lack the classical indicators and signs of vitamin B12 deficiency. Low folate/cobalamin ranges have been linked to delirium, confusion, psychosis, melancholy, and dementia (Alzheimer-related dementia in addition to the vascular kind). In addition, folate and vitamin B12 deficiency and the compensatory enhance in homocysteine are vital risk components for cardiovascular disease. The main trigger of those anemias appears to be interference by medicine with vitamin metabolism, notably within the case of pyridoxine. In renal dialysis sufferers maintained on recombinant human erythropoietin, a significant enhance in erythrocyte vitamin B2 and vital decrease in erythrocyte vitamin B6 was observed. Supplementation with 20 mg/day of pyridoxine led to a significant enhance in vitamin B6 on the end of the 9 months. The examine means that erythrocyte vitamin B6 is consumed by the hemoglobin synthesis throughout erythropoietin remedy. Whatever the chosen dose, a reticulocyte rely ought to be obtained 1 week after starting iron. Some controversy exists in regards to the needed quantity of iron and the frequency of dosing. Dosing iron as soon as a day could have an identical impact to three-instances-a-day dosing if absorption is normal. Hemoglobin and ferritin ranges have been comparable in each group after 60 days, but antagonistic results, including stomach discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and adjustments in bowel actions, have been greater with the upper iron doses. The duration of iron remedy may be longer when as soon as-a-day dosing is used (Table 31. Anemia as a result of vitamin B12 or folate deficiency is treated by alternative of the vitamin. Folate (1 mg) ought to be used to deal with folate deficiency in addition to during the first few weeks of vitamin B12 deficiency. In 18 subjects with newly identified B12 deficiency, cyanocobalamin was given both as 1 mg intramuscularly on days 1, 3, 7, 10, 14, 21, 30, 60, and 90 or as 2 mg orally daily for 120 days. There was no distinction in correction of hematologic and neurologic abnormalities between the 2 groups. Significantly greater ranges of serum cobalamin and decrease serum methylmalonic acid ranges have been discovered within the oral group than within the parenteral group 4 months after therapy. Anemia in older persons is a risk factor for increased mortality and decline in physical activity performance of daily living actions. The positive scientific outcomes for treating anemia, such as improved quality of life, decreased hospitalization, and decreased mortality, demand that a hemoglobin focus of less than 12 g/dl be investigated and treated every time possible. Looking on the relationship between hemoglobin focus and previous mobility issue in older women: ought to the criteria used to define anemia in older folks be modified? The prevention of falls in later life: a report of the Kellogg International Work Group on the Prevention of Falls by the Elderly. Chronic medical conditions and risk of fall harm events at residence in older adults. Prevalent left ventricular hypertrophy within the predialysis population: figuring out alternatives for intervention. The impact of correction of mild anemia in severe, resistant congestive coronary heart failure using subcutaneous erythropoietin and intravenous iron: a randomized managed examine. World Health Stat Q Rapport Trimestriel Statistiques Sanitaires Mondiales 1985;38:302�316. Erythropoietin regulation of hematopoiesis is preserved in wholesome elderly folks. Anemia and hemoglobin ranges in older persons: relationship with age, gender, and well being status. Incidence of anemia in older folks: an epidemiologic examine in a nicely defined population. Effect of reversible androgen deprivation on hemoglobin and serum immunoreactive erythropoietin in males. Combined androgen blockadeinduced anemia in prostate most cancers sufferers with out bone involvement. The ratio of serum transferrin receptor and serum ferritin within the analysis of iron status. Discriminating between iron deficiency anemia and anemia of persistent disease using conventional indices of iron status vs transferrin receptor focus. Assessment of the diagnostic utility and price-benefit evaluation of methylmalonic acid willpower in relation to present diagnostic methods. Vitamin B12 and folate status in acute geropsychiatric inpatients: affective and cognitive characteristics of a vitamin nondeficient population. Cobalamin and folate evaluation: measurement of methylmalonic acid and homocysteine vs. The molecular biology and pyridoxine responsiveness of X-linked sideroblastic anaemia. Severe protein-calorie undernutrition in people alters tissue regeneration, the inflammatory response, and immune function. When stress was 497 498 Geriatric Nutrition applied for 4 hours to the skin of nicely-nourished animals and malnourished animals, stress ulcers occurred equally in both groups. However, the degree of ischemic skin destruction was more severe within the malnourished animals. Epithelialization of the stress lesions occurred in normal animals at 3 days postinjury, whereas necrosis of the dermis was still present within the malnourished animals. Further indication of a relationship between nutrition and tissue harm is suggested by the discovering that mitotic activity in normal dermis is severely depressed in mice whose food consumption was reduced to 70% of normal. For example, collagen deposition is completed in 42 days in animal wounds in comparison with 88 days in human wounds. Undernutrition, defined by an index of biochemical and anthropometric variables, including hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte rely, historical past of weight reduction, physique weight, triceps skinfold thickness, and mid-arm circumference, was present in 29% of sufferers at hospital admission in a potential examine of highrisk sufferers. At 4 weeks, 17% of the undernourished sufferers had developed a stress ulcer, in comparison with 9% of the nonundernourished sufferers. No stress ulcers developed within the mild to reasonably undernourished or nicely-nourished groups. In a long-termcare setting, the estimated p.c consumption of dietary protein, but not total caloric consumption, predicted improvement of stress ulcers. Patients with stress ulcers ingested 93% of the really helpful daily consumption of protein in comparison with an consumption of 119% of the really helpful protein within the non-stress ulcer group. Decreases in serum albumin could replicate the presence of inflammatory cytokine manufacturing or comorbidity somewhat than nutritional status. Thus, serum albumin has not constantly been an unbiased predictor of stress ulcers. Despite an epidemiological affiliation, outcomes of trials of nutritional intervention in prevention of stress ulcers have been disappointing.
Purchase 5 mg oxybutynin
The elaborate and tortuous architecture of those components explains why this a part of the vestibular system is known as the labyrinth. The utricle and saccule are specialized primarily to reply to linear accelerations of the pinnacle and static head position relative to the graviational axis, whereas the semicircular canals, as their shapes counsel, are specialized for responding to rotational accelerations of the pinnacle. The vestibular and auditory parts of the eighth nerve are proven; the small connection from the vestibular nerve to the cochlea incorporates auditory efferent fibers. The membranous sacs inside the bone are full of fluid (endolymph) and are collectively referred to as the membranous labyrinth. Between the bony partitions (the osseous labyrinth) and the membranous labyrinth is another fluid, the perilymph, which is analogous in composition to cerebrospinal fluid. The vestibular hair cells are located in the utricle and saccule and in three juglike swellings referred to as ampullae, located on the base of the semicircular canals next to the utricle. Within every ampulla, the vestibular hair cells lengthen their hair bundles into the endolymph of the membranous labyrinth. As in the cochlea, tight junctions seal the apical surfaces of the vestibular hair cells, ensuring that endolymph selectively bathes the hair cell bundle whereas remaining separate from the perilymph surrounding the basal portion of the hair cell. Vestibular Hair Cells the vestibular hair cells, which like cochlear hair cells transduce minute displacements into behaviorally relevant receptor potentials, present the basis for vestibular perform. Vestibular and auditory hair cells are fairly related; an in depth description of hair cell construction and performance has already been given in Chapter 12. As in the case of auditory hair cells, motion of the stereocilia towards the kinocilium in the vestibular finish organs opens mechanically gated transduction channels located on the suggestions of the stereocilia, depolarizing the hair cell and causing neurotransmitter release onto (and excitation of) the vestibular nerve fibers. Movement of the stereocilia in the direction away from the kinocilium closes the channels, hyperpolarizing the hair cell and thus lowering vestibular nerve exercise. The biphasic nature of the receptor potential means that some transduction channels are open in the absence of stimulation, with the end result that hair cells tonically release the Vestibular System 317 transmitter, thereby generating appreciable spontaneous exercise in vestibular nerve fibers (see Figure 13. One consequence of those spontaneous action potentials is that the firing rates of vestibular fibers can enhance or lower in a way that faithfully mimics the receptor potentials produced by the hair cells (Box B). Importantly, the hair cell bundles in every vestibular organ have particular orientations (Figure 13. As a end result, the organ as a whole is responsive to displacements in all instructions. In a given semicircular canal, the hair cells in the ampulla are all polarized in the identical direction. In the utricle and saccule, a specialized area referred to as the striola divides the hair cells into two populations with opposing polarities (Figure 13. The directional polarization of the receptor surfaces is a primary principle of group in the vestibular system, as will turn into apparent in the following descriptions of the person vestibular organs. The Otolith Organs: the Utricle and Saccule Displacements and linear accelerations of the pinnacle, corresponding to those induced by tilting or translational movements (see Box A), are detected by the 2 otolith organs: the saccule and the utricle. In the sacculus and utricle, the striola divides the hair cells into populations with opposing hair bundle polarities. All our bodies moving in a three-dimensional framework have six degrees of freedom: three of those are translational and three are rotational. The translational elements discuss with linear movements in the x, y, and z axes (the horizontal and vertical planes). Translational motion in these planes (linear acceleration and static displacement of the pinnacle) is the first concern of the otolith organs. The semicircular canals are primarily liable for sensing rotational accelerations round these three axes. Yaw: Rotation round z axis z Roll: Rotation round x axis x y Pitch: Rotation round y axis Figure 13. Overlying the hair cells and their hair bundles is a gelatinous layer; above this layer is a fibrous construction, the otolithic membrane, by which are embedded crystals of calcium carbonate referred to as otoconia (Figures 13. The crystals give the otolith organs their name (otolith is Greek for "ear stones"). The otoconia make the otolithic membrane significantly heavier than the structures and fluids surrounding it; thus, when the pinnacle tilts, gravity causes the membrane to shift relative to the sensory epithelium (Figure 13. The resulting shearing motion between the otolithic membrane and the macula displaces the hair bundles, which are embedded in the lower, gelatinous floor of the membrane. This displacement of the hair bundles generates a receptor potential in the hair cells. A shearing motion between the macula and the otolithic membrane additionally occurs when the pinnacle undergoes linear accelerations (see Figure 13. The related results exerted on otolithic hair cells by certain head tilts and linear accelerations would be expected to render these totally different stimuli perceptually equal when visual suggestions is absent, as occurs in the dead of night or when the eyes are closed. Nevertheless, evidence suggests that subjects can discriminate between these two stimulus classes, apparently by way of mixed exercise of the otolith organs and the semicircular canals. As already talked about, the orientation of the hair cell bundles is organized relative to the striola, which demarcates the overlying layer of otoco- the Vestibular System 319 (A) Striola Otoconia Otolithic membrane, gelatinous layer Reticular membrane Supporting cells Hair cells (B) Static tilt Gravitational drive (C) Utricular macula Anter ior Striola Lat era l Superior Saccular macula Anterior Utricular macula Saccular macula Figure 13. The saccules on both facet are oriented more or less vertically, and the utricles more or less horizontally. The striola is a structural landmark consisting of small otoconia organized in a narrow trench that divides every otolith organ. The striola forms an axis of mirror symmetry such that hair cells on opposite sides of the striola have opposing morphological polarizations. Thus, a tilt along the axis of the striola will excite the hair cells on one facet whereas inhibiting the hair cells on the opposite facet. Despite its great sensitivity, the hair cell can adapt shortly and repeatedly to static displacements of the hair bundle attributable to massive movements. Such adjustments are especially useful in the otolith organs, where adaptation permits hair cells to keep sensitivity to small linear and angular accelerations of the pinnacle despite the fixed input from gravitational forces which are over 1,000,000 instances larger. In different receptor cells, corresponding to photoreceptors, adaptation is accomplished by regulating the second messenger cascade induced by the initial transduction event. Adaptation occurs in each instructions by which the hair bundle displacement generates a receptor potential, albeit at totally different rates for every direction. When the hair bundle is pushed towards the kinocilium, tension is initially increased in the gating spring. During adaptation, tension decreases again to the resting degree, maybe as a result of one finish of the gating spring repositions itself along the shank of the stereocilium. When the hair bundle is displaced in the other way, away from the kinocilium, tension in the spring initially decreases; adaptation then entails an increase in spring tension. During sustained depolarization, some Ca2+ enters by way of the transduction channel, together with K+. Ca2+ then causes the motor to spend a larger fraction of its time unbound from the actin, leading to slippage of the spring down the facet of the stereocilium. During sustained hyperpolarization (Figure A), Ca2+ levels drop below normal resting levels and the motor spends extra of its time certain to the actin, thus climbing up the actin filaments and growing the spring tension. In support of this model, when inside Ca2+ is decreased artificially, spring tension increases. This model of hair cell adaptation presents a chic molecular solution to the regulation of a mechanical process. Electrical Tuning Although mechanical tuning plays an necessary role in generating frequency selectivity in the cochlea, there are different mechanisms that contribute to this process in vestibular and auditory nerve cells. Movement of the insertion level up or down the shank of the stereocilium, maybe pushed by a Ca2+-dependent protein motor, can regularly adjust the resting tension of the tip hyperlink. One such mechanism is an electrical resonance displayed by hair cells in response to depolarization: the membrane potential of a hair cell undergoes damped sinusoidal oscillations at a particular frequency in response to the injection of depolarizing current pulses (Figure B). The ionic mechanism of this process entails two main forms of ion channels located in the membrane of the hair cell soma. The first of those is a voltage-activated Ca2+ conductance, which lets Ca2+ into the cell soma in response to depolarization, corresponding to that generated by the transduction current. The second is a Ca2+-activated K+ conductance, which is triggered by the rise in inside Ca2+ focus. These two currents produce an interplay of depolarization and repolarization that ends in electrical resonance (Figure C).
Diseases
- Generalized torsion dystonia
- Vasculitis hypersensitivity
- Paget disease extramammary
- Horn Kolb syndrome
- Mitochondrial disease
- Osteochondritis deformans juvenile
- Familial hypertension
- Deletion 6q16 q21
- Endometriosis
- Scotoma
Best oxybutynin 5mg
Vitamin C facilitates absorption of iron in the duodenum and the conversion of methemoglobin to hemoglobin by lowering ferric iron (Fe3+) to the ferrous form (Fe2+). Decreased formation of mutagenic nitrosamines possibly confers protection against gastric most cancers. Decreased wound therapeutic and weakened blood vessels cause hemostasis abnormalities. Clinical manifestations include painful subperiosteal hemorrhages, hemarthrosis, hemorrhagic perifolliculitis, gingival bleeding, and petechia or ecchymoses. Some of these findings are common in the elderly and may be attributed to age-related physiologic modifications, drugs, or comorbidities, somewhat than vitamin deficiency (Joshi and Morley 2006). Another consequence of structurally irregular collagen is structurally irregular bone. Scurvy, the complete-blown deficiency syndrome, develops with vitamin C intake of less than 10 mg/day for as little as 3 months. In addition to the previously talked about bodily findings, scurvy includes the development of corkscrew hairs, glossitis, gingival hyperplasia and bleeding, and poor dentition or loss of teeth because of periodontal illness. Terminal options include icterus, 166 Geriatric Nutrition edema, hypotension, convulsions, and dying. Being water soluble, vitamin C has few poisonous results, and antagonistic results are related to intake dose (Levine et al. Ingestion of more than 2000 mg day by day, the Tolerable Upper Limit, can cause gastrointestinal signs similar to nausea, belly cramps, and diarrhea (Miller and Hays 1982). Abnormal vitamin B12 absorption and increased blood ranges of estrogen substitute hormone also can occur. Excess vitamin C could interfere with numerous laboratory exams and will cause false-adverse results on stool guaiac exams and on urine dipstick analysis for blood, glucose, bilirubin, nitrites, and leukocyte esterase. Because vitamin C enhances iron absorption, patients suffering from hemochromatosis, thalassemia major, sideroblastic anemia, or different situations requiring multiple red blood cell transfusion ought to monitor their vitamin C intake (Levine et al. High-dose vitamin C supplementation has been proposed as a treatment for the common chilly (Pauling 1970), and quite a few placebo-managed trials have been performed to handle this question. A meta-analysis of 30 trials performed over the previous 35 years found that supplementing vitamin C in doses as much as 2000 mg/day had no perceptible effect on lowering the incidence of colds except in choose circumstances of topics uncovered to extreme train or chilly (Douglas et al. Megadose vitamin C supplementation continues to be recommended by some consultants for the prevention of cardiovascular disease and most cancers in the elderly despite limited proof to help such claims. The protective function of vitamin C in delaying age-related lens opacities is supported in most studies (Hankinson et al. Since megadose vitamin C given chronically appears to have little extra profit in delaying the growing older process and might have antagonistic results, it seems prudent to ingest enough vitamin C to maintain tissue shops saturated. Diets wealthy in vitamin C (200 mg or extra) from pure sources are related to decrease most cancers risk and can easily be attained with five day by day servings of fruit and veggies. The potential advantages of vitamin C and different antioxidants in prevention of cardiovascular disease and most cancers are briefly discussed subsequent. These investigations include epidemiological studies and medical trials of nutritional vitamins in their pure in addition to supplemental varieties. The ensuing physique of literature is too intensive to comprehensively evaluate on this chapter; key trials have been reviewed elsewhere (Thomas 2004, Asplund 2002, Pearce et al. A massive physique of proof means that diets wealthy in antioxidant nutritional vitamins shield against the development of various age-related diseases. Based on epidemiological studies, the inverse relationship between fruit/vegetable consumption and the chance of creating atherosclerotic vascular illness has been sturdy and consistent, and appears evident, albeit somewhat less vigorous, for most cancers prevention (Gillman et al. In a examine of over forty,000 topics adopted for 18 years, day by day intake of inexperienced-yellow greens was related to a statistically important 26% discount in the risk of mortality from all strokes, compared with intake of as soon as or less per week (Sauvaget et al. Furthermore, the incidence of stroke in day by day customers of fruits was lowered by 35% in men and 25% in women. In another 14-12 months potential cohort examine that combined over a hundred,000 members, fruit and vegetable consumption was related to a modest, although not statistically important, discount in cardiovascular disease, but not most cancers (Hung et al. In a smaller trial, dependence in self-care had a strong adverse affiliation with lycopene, but was not clearly related to different carotenoids in elderly nuns dwelling in a managed setting (Snowdon et al. By the character of these trials, confounding components are ill managed for and particular person elements of a healthy diet are troublesome to identify. Despite these limitations, the clear inverse affiliation between fruit and vegetable intake and the chance of cardiovascular disease and a few forms of most cancers is firmly established. The sturdy affiliation between dietary vitamin intake and illness prevention seen in epidemiologic studies has not been borne out in medical trials (Thomas 2004). Vitamin E supplementation in human managed trials showed a reduction in mortality and morbidity from atherosclerotic illness in the Cambridge Heart Antioxidant Study (Ness and Smith 1999) but not in the Primary Prevention Project (Collaborative Group of the Primary Prevention Project 2001), the Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study (Yusuf et al. Despite the tremendous zeal for the therapeutic properties of vitamin C in pharmacological doses, no interventional examine has demonstrated any major helpful effect against most cancers or atherosclerotic illness (Hercberg et al. In reality, excessive doses of vitamin C could exhibit pro-oxidant results, as ranges of 8-oxoadenine are increased (Podmore et al. Fresh fruit and veggies could include but unidentified elements answerable for the improved health consequence in those that devour them. Finally, risk discount could not solely be because of the nutritional vitamins themselves, but partially to decreased intake of harmful compounds, ensuing from the substitution of dietary meat and fats with fruit and veggies (Jha et al. Failure to diligently screen and treat at-risk populations is a failure to provide optimal care and preserve function in an already frail inhabitants. As vitamin supplementation moved from the realm of stopping deficiency situations to administration of chronic illness, a big selection of age-related situations, and indeed the growing older process itself, have been thought to be influenced by vitamin use. The promise of avoiding illness with nutritional vitamins has led to their widespread use, typically in megadoses. While these health advantages continue to be studied, current consensus is for obtaining nutritional vitamins in their pure somewhat than synthetic form, because the latter have proven less promising in stopping illness up to now. Many diseasespecific exceptions exist, such because the clear benefit of vitamin supplements in slowing the progression of osteoporosis and macular degeneration, and the administration of pernicious anemia with massive doses orally of vitamin B12. American Cancer Society Advisory Committee on Diet, Nutrition and Cancer Prevention. Guidelines on food regimen, diet and most cancers prevention: lowering the chance of most cancers with healthy meals selections and bodily exercise. Effect of vitamin D and calcium supplementation on falls: a randomized managed trial. Effect of cholecalciferol plus calcium on falling on ambulatory older men and women: a 3-12 months randomized managed trial. Fracture prevention with vitamin D supplementation: a meta-analysis of randomized managed trials. Beneficial results of combined colestipol-niacin remedy on coronary atherosclerosis and coronary venous bypass grafts. Dietary vitamin K intakes are related to hip fracture but not with bone mineral density in elderly men and women. A quantitative evaluation of plasma homocysteine as a risk issue for vascular illness. Simvastatin and niacin, antioxidant nutritional vitamins, or the combination for the prevention of coronary illness. Regression of coronary artery illness as a result of intensive lipid-lowering remedy in men with excessive ranges of apolipoprotein B. Short-term folate, vitamin B-12 or vitamin B-6 supplementation barely impacts memory efficiency but not temper in women of various ages. Reduction of mortality in the Stockholm Ischaemic Heart Disease Secondary Prevention Study by combined therapy with clofibrate and nicotinic acid. Fifteen 12 months mortality in coronary drug project patients: long-term profit with niacin. Effect of calcium and cholecalciferol therapy for 3 years on hip fractures in elderly women. Folate, vitamin B12, and serum whole homocysteine ranges in confirmed Alzheimer illness. Low-dose aspirin and vitamin E in individuals at cardiovascular risk: a randomised trial generally follow. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on wintertime and total bone loss in healthy post menopausal women. Effects of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on bone density in men and women 65 years or age or older. Vitamin B-6 supplementation in elderly men: results on temper, memory, efficiency and mental effort.
Cheap 5mg oxybutynin
It has been the usual drug for treating all forms of leprosy, however irregular and inadequate duration of treatment as a single agent has produced resistance. Dapsone is used to treat dermatitis herpetiformis, in addition to leprosy, pneumocystis and, combined with pyrimethamine, for malaria prophylaxis. Mechanism of motion Dapsone is a competitive inhibitor of dihydropteroate (folate) synthase, thereby impairing manufacturing of dihydrofolic acid. Control and prevention of tuberculosis in the United Kingdom: code of apply 2000. Management of opportunist mycobacterial infections: Subcommittee of the Joint Tuberculosis Committee of the British Thoracic Society. Chemotherapy and management of tuberculosis in the United Kingdom: suggestions 1998. Pharmacokinetics Dapsone is properly absorbed (90%) from the gastro-intestinal tract. It is extensively metabolized in the liver, partly by N-acetylation, with solely 10�20% of the father or mother drug being excreted in the urine. Drug interactions the metabolism of dapsone is increased by hepatic enzyme inducers. The very success of antibacterial remedy has created ecological situations by which opportunistic fungal infections can flourish. In addition, potent immunosuppressive and cytotoxic therapies produce patients with critically impaired immune defences, in whom fungi that are nonpathogenic to healthy individuals turn out to be pathogenic and trigger illness. Itraconazole or voriconazole oral Caspofungin if failing azole remedy Aspergillus Amphotericin B i. Its spectrum is broad and contains Aspergillus and Candida species, Blastomyces dermatitidis (which causes North American blastomycosis), Histoplasma capsulatum (which causes histoplasmosis), Cryptococcus neoformans (which causes cryptococcosis), Coccidioides immitis (which causes coccidioidomycosis) and Sporotrichum schenckii (which causes sporotrichosis). Amphotericin is insoluble in water, however could be complexed to bile salts to give an unstable colloid which could be administered intravenously. Amphotericin B is often given as an intravenous infusion given over four to six hours. Several liposomal or lipid/colloidal advanced amphotericin preparations have now been formulated, and are less poisonous (significantly less nephrotoxic), however costlier than the usual formulation. Liposomal amphotericin is reserved for patients who expertise unacceptable antagonistic results from regular amphotericin or in whom nephrotoxicity must be minimized. Topical amphotericin lozenges or suspension are used for oral or pharyngeal candidiasis. Nystatin works in the identical means as amphotericin B, however its higher toxicity precludes systemic use. Its indications are restricted to cutaneous/mucocutaneous and intestinal infections, especially those attributable to Candida species. Cutaneous infections are treated with ointment and vaginitis is treated by suppositories. Adverse results Nystatin could cause nausea and diarrhoea when giant doses are administered orally. Available for topical (nystatin and amphotericin) treatment of widespread mucocutaneous fungal infections. Amphotericin is used intravenously for deep-seated and severe fungal infections. Intravenous amphotericin is poisonous, causing fever, chills, hypotension during infusion, nephrotoxicity, electrolyte abnormalities and transient bone marrow suppression. Systemic toxicity (especially nephrotoxicity) of amphotericin is reduced by using the liposomal/ lipid/micellar formulations. Amphotericin combined with 5-flucytosine may be used in severe infections and immunosuppressed patients. Mechanism of motion Amphotericin is a polyene macrolide with a hydroxylated hydrophilic surface on one side of the molecule and an unsaturated conjugated lipophilic surface on the opposite. Adverse results these embrace: � fever, chills, headache, nausea, vomiting, and hypotension during intravenous infusion. It outcomes from vasoconstriction and tubular injury resulting in acute renal impairment and sometimes renal tubular acidosis. Mechanism of motion of azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Imidazoles competitively inhibit lanosterol 14-demethylase (a fungal cytochrome-haem P450 enzyme), which is a major enzyme in the pathway that synthesizes ergosterol from squalene. This disrupts the acyl chains of fungal membrane phospholipids, growing membrane fluidity and causing membrane leakage and dysfunction of membrane-certain enzymes. The imidazoles have appreciable specificity/affinity for fungal cytochrome-haem P450 enzymes. Pharmacokinetics Poor gastro-intestinal absorption necessitates intravenous administration for systemic infections. It remains to be used to treat metastatic prostate cancer and adrenocortical carcinoma (see Chapter 48). Pharmacokinetics Fluconazole is properly absorbed after oral administration and is widely distributed throughout the body. About 80% is excreted by the kidney and dose discount is required in renal failure. The fluconazole mean elimination t1/2 is 30 hours in patients with regular renal operate. It is energetic against many Candida species, Cryptococcus neoformans and Histoplasma capsulatum. However, Aspergillus species are resistant and resistant Candida species are problematic in immunocompromised patients. Fluconazole is used clinically to treat superficial Candida infections and oesophageal Candida, for the acute remedy of disseminated Candida, systemic remedy for blastomycosis and histoplasmosis, for dermatophytic fungal infections and, in low doses, for prophylaxis in neutropenic and immunocompromised patients. The plasma concentrations and toxicity of these medication will enhance during concomitant treatment with fluconazole. Oral bioavailability is good for both agents, however intravenous use is indicated for severe fungal infections. For intraconazole, once every day Adverse results Adverse results embrace: � nausea, abdominal distension, diarrhoea and flatulence; � rashes, together with erythema multiforme; � hepatitis (rarely, hepatic failure). Induces its own metabolism Miconazole Oral Candida (topical remedy for ringworm, Candida and pityriasis Oral gel, four times every day 2% cream or powder applied twice every day Nausea and vomiting, rashes. Local irritation Systemic absorption is very poor, undergoes intensive hepatic metabolism Tiaconazole Topical treatment for nail infections with dermatophytes and yeasts Apply 28% resolution to nails and native skin twice every day for six months Minor local irritation Systemic absorption is negligible a Other medication on this group that are used topically embrace butoconazole, econazole, fenticonazole, isoconazole and sulconazole (see additionally Chapter 50). Adverse results embrace gastro-intestinal upsets, rashes and hepatitis with uncommon case of hepatic failure. Posaconazole is a novel agent with appreciable potential due to its prolonged antifungal spectrum. They are used primarily for fungal infections that are immune to azoles or the place patients are illiberal of azoles and are administered by intravenous infusion, normally once every day. Mechanism of motion Key points Azole antifungal medication Relatively wide spectrum of antifungal activity, fungistatic, however fungicidal with larger concentrations. The mechanism of motion of echinocandins is unique and medicines of this class are doubtlessly additive or synergistic with polyenes and azoles. Adverse results Adverse results (normally delicate and rarely problematic) embrace: � infusion phlebitis and fever, histamine-like infusion reactions, if infused rapidly; � infrequently nausea, diarrhoea, hyperbilirubinaemia; � rarely hepatitis, leukopenia. It is given once every day for two to six weeks (longer in infections of the nailbed, as an alternative choice to griseofulvin, see beneath). It acts by inhibiting the enzyme squalene epoxidase, which is involved in fungal ergosterol biosynthesis. It is properly absorbed, strongly certain to plasma proteins and concentrated in the stratum corneum. Its major unwanted effects are nausea, abdominal discomfort, anorexia, diarrhoea and rashes (together with urticaria). Both agents are eradicated by hydrolysis and N-acetylation to inactive metabolites. The mean elimination t1/2 for caspofungin is 9�eleven hours and for micafungin is eleven�17 hours. The dose of caspofungin ought to, nonetheless, be reduced in important hepatic dysfunction. They inhibit 1,three-beta D glucan synthase involved in the formation of glucan polysaccharide in sure fungal cell walls. It is excreted unchanged by glomerular filtration (10% of a dose is metabolized). Antiviral remedy is tougher than antibacterial remedy because viruses are intimately incorporated in host cells and the therapeutic targets are often much like the equal enzymes/structures in human cells.
Quality 2.5 mg oxybutynin
While thyroglobulin is being synthesized, thyroperoxidase is assembled in the granular endoplasmic reticulum and then passes by way of the Golgi complex and is released by small vesicles on the apical floor of the cells. Follicular cells have a novel capacity to take up iodide from the blood utilizing a Na+-I- cotransporter and concentrate it. The iodide subsequently is oxidized to iodine by this intracellular peroxidase and used in the iodination of tyrosine groups in thyroglobulin. Formation of monoiodotyrosine and diiodotyrosine is thought to happen in the follicle, instantly adjacent to the microvillus border of the follicular cells. When one molecule of monoiodotyrosine is linked to one of diiodotyrosine, a molecule of triiodothyronine is fashioned. Coupling of two molecules of diiodotyrosine results in the formation of tetraiodothyronine (thyroxin). The thyronines make up a small a part of the thyroglobulin complex but symbolize the one constituents with hormonal exercise. Thyroglobulin and the thyronines are stored in the lumen of the follicle as colloid till wanted. Lysosomes coalesce with the resorption droplets and hydrolyze the contained thyroglobulin, liberating monoiodotyrosine, diiodotyrosine, triiodothyronine, and tetraiodothyronine into the cytoplasmic matrix. The mono- and diiodotyrosines are deiodinated by the enzyme deiodinase, and the iodine is reused by the follicular cell. Thyroxin (tetraiodothyronine) molecules constitute what is called thyroid hormone and are released with triiodothyronine on the base of the cell into blood and lymphatic capillaries (Fig. Thyroxin is transported in the blood plasma complexed to a binding protein known as thyroxine binding globulin. Most of the secreted thyroid hormone (ninety%) is thyroxine but is converted to the extra active kind, triiodothyronine, by peripheral target tissues. The kidney and liver are important deiodinators of thyroxin and convert it to the functionally stronger triiodothyronine. Triiodothyronine then bids to a nuclear receptor in cells of the target organ the net results of which is a rise in oxygen consumption and metabolic price. Thyroid hormone has general results on the metabolic price of most tissues, and among its features are increased carbohydrate metabolism, increased price of intestinal absorption, increased kidney function, increased coronary heart price, increased ventilation, regular body progress and growth, and increased psychological actions. The thyroid also contains a smaller number of cells variously known as parafollicular, gentle, or C cells, that are present adjacent to the follicular epithelium and in the delicate connective tissue between follicles. The C cells adjacent to the follicular epithelium seem to be sandwiched between the bases of follicular cells and lie instantly adjacent to the basal lamina; parafollicular cells by no means directly border on the lumen of the follicle. In electron micrographs, the parafollicular cells show numerous reasonably dense, membrane-sure secretory granules that measure 10 to 50 nm in diameter. The cytoplasm also contains occasional profiles of granular endoplasmic reticulum, scattered mitochondria, and poorly developed Golgi complexes. Parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin (thyrocalcitonin), another polypeptide hormone that regulates blood calcium levels. Calcitonin lowers blood calcium by acting on osteocytes and osteoclasts to suppress resorption of calcium from bone and its launch into the blood. Thus, calcitonin has an effect reverse that of parathyroid hormone, serves to control the action of parathyroid hormone, and helps regulate the higher levels of calcium concentration in the blood. Adrenal Gland the adrenal glands in humans are a pair of flattened, triangular buildings with a combined weight of 14 to sixteen gm. The adrenal gland is a fancy organ consisting of a cortex and medulla, each differing in structure, function, and embryonic origin. The capsule contains a wealthy plexus of blood vessels - mainly small arteries - and numerous nerve fibers. Some blood vessels and nerves enter the substance of the gland in the trabeculae that extend inward from the capsule and then depart the trabeculae to enter the cortex. The parenchyma of the adrenal cortex consists of steady cords of secretory cells that extend from the capsule to the medulla, separated by blood sinusoids. The cortex is subdivided into three layers according to the arrangement of the cells inside the cords. These cortical layers include an outer zona glomerulosa (10%), a middle zona fasciculata (seventy five%), and an inner zona reticularis (15%). The columnar cells are arranged into ovoid groups or arcades and have centrally placed spherical nuclei. In electron micrographs, the cells show a properly-developed smooth endoplasmic reticulum and numerous mitochondria which are evenly distributed all through the cytoplasm. Occasional lipid droplets and scattered profiles of granular endoplasmic reticulum are also present. Zona fasciculata varieties the widest zone of the cortex and consists of long cords that usually are one or two cells thick. The cords run parallel to one another, separated by sinusoids which are lined by an attenuated endothelium. The cytoplasm contains numerous rounded mitochondria with tubular cristae, plentiful smooth endoplasmic reticulum, and properly-developed granular endoplasmic reticulum. Many lipid droplets are also present and contain neutral fat, fatty acids, and fatty acyl esters of cholesterol; these symbolize stored precursors for the synthesis of the steroid hormones secreted by the zona fasciculata. Zona reticularis varieties the innermost zone and is made up of a community of irregular, anastomosing cords that are also separated by sinusoids. The adrenal cortex synthesizes and secretes in excess of twenty-four steroid hormones, which typically could be placed in three broad categories: mineralocorticoids that control water and electrolyte balance, glucocorticoids that have an effect on carbohydrate metabolism, and intercourse steroids (androgens). Enzymes for the synthesis of those steroid hormones are situated mainly in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of the adrenal cortical cells. The pathway involves transfer of precursor molecules and intermediate products forwards and backwards between these two organelles. Adjacent lipid droplets provide the substrates wanted for the biosynthetic processes. Aldosterone performs a serious function in the regulation of extracellular fluid and blood volumes as well as maintaining potassium balance. It acts on the distal and accumulating tubules of the kidney to improve the speed of sodium chloride and water reabsorption from the glomerular filtrate and, on the identical time, to improve potassium secretion. It also lowers the concentration of sodium chloride in the secretions of sweat and salivary glands and intestinal mucosa. Aldosterone secretion is controlled primarily by the renin-angiotensin system, which is delicate to modifications in blood strain and to the concentration of sodium chloride and potassium in the blood plasma and extracellular fluid. It has been advised that the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidney receives alerts created by decreased arterial renal blood strain (which reduces the diploma of stretch on the juxtaglomerular cells) and/or by a decrease in the quantity of sodium chloride and potassium detected by the macula densa. In response to this sign, juxtaglomerular cells launch renin, which acts enzymatically on a circulating protein known as angiotensinogen altering it to angiotensin I. Glucocorticoids (cortisol, cortisone, and corticosterone) are secreted by cells of the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. These steroid hormones act mainly on the metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, resulting in an increase in blood glucose and amino acid levels and in the motion of lipid into and out of fat cells. Cortisol also suppresses the inflammatory response and a few allergic reactions by inhibiting the enzyme phospholipase A2. Adrenal androgens, dehydroepiandrosterone and androstenedione, are also secreted by cells of the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis, although cells of the reticularis are stated to be the extra active in androgen secretion. In women adrenal androgens contribute to the event of secondary sexual characteristics such as progress of axillary and pubic hair, and sebaceous gland hypertrophy at puberty. Abnormally high levels of adrenal androgens may have masculinizing results on women and in boys induce precocious puberty. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone stimulates the synthesis and launch of steroids, will increase blood move by way of the cortex, and promotes progress of the two inner zones of the adrenal cortex. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are metabolized by the liver and have a half lifetime of about 2 to 3 minutes. Blood Supply the wealthy plexus of small arteries in the capsule of the adrenal offers cortical arterioles that enter the parenchyma of the adrenal to empty into the vast community of cortical sinusoids that separates the cords of epithelial cells making up the cortex. The attenuated endothelium of the sinusoids has numerous fenestrations and is supported only by a thin basal lamina and a delicate community of reticular fibers. The sinusoids move by way of all three layers of the cortex and near the corticomedullary junction start to merge to kind massive accumulating veins. These drain towards the central medulla and at last gather right into a single, massive suprarenal vein that drains the entire adrenal gland.
Safe oxybutynin 2.5 mg
However, in contrast to menopause, the place complete estrogen deficiency with known scientific consequences happens, the decline in androgens in growing older men varies from modest to severe and has unclear scientific consequences. Low testosterone ranges have been related to minimal hip fracture in older men in nursing houses. Sperm manufacturing is steady from quickly after the completion of puberty to about age 70 years, after which it declines progressively by about 50% by age 90 years. The vasopressin response to osmotic stimulation might or will not be increased in older subjects, whereas the vasopressin response to volume depletion, a response mediated via baroreceptors, is increased. As a result of the decreases in thirst and renal responsiveness to vasopressin, older subjects can turn into more simply dehydrated, even when vasopressin secretion rises. Nutrition and the Endocrine System 485 Aging additionally produces gentle carbohydrate intolerance and a minimal improve in fasting serum glucose in healthy, nonobese aged individuals, primarily because of lowering postreceptor responsiveness to insulin (see Chapter 26). The doubtless reason for this improve is a fall in serum calcium concentration because of gentle vitamin D deficiency and likewise phosphate retention attributable to declining renal perform. Melatonin secretion is lower in older subjects than in youthful subjects, notably the surge in melatonin secretion that occurs throughout sleep at night. Leptin, a hormone produced by adipose tissue in proportion to body fats mass, decreases appetite. The modest fall in serum leptin concentrations with age might contribute to rising adiposity in older individuals. It reduces insulin resistance, is related to lower risk of atherosclerosis, and has anti-inflammatory properties. The greater ranges of adiponectin noticed in older men could reflect a longitudinal growing older change or simply enhanced survival of men with more of this adipokine hormone. In the established population database, 9% of men and women age 71 to 74 years were anemic. The proportion of anemic individuals increased differentially with age, reaching forty one% for men and 21% for ladies age 90 years or older, respectively. The corrected annual incidence of anemia was greater in men older than 65 years (90. Hypogonadism in older males (andropause) is usually related to roughly a 1 g/dl fall in hemoglobin concentration. The causes of anemia may be grouped into failure of the bone marrow to manufacture sufficient blood parts, gradual or speedy blood loss from hemorrhage, or a speedy breakdown of blood parts (hemolysis) in the marrow or peripherally. The bone marrow might fail to produce sufficient blood parts because of inadequate vitamins (vitamin B12, folate, pyridoxine, or iron) essential for blood manufacturing, altered maturation of blood cells (myelodysplastic syndromes), or main impairment of hemoglobin synthesis (hemoglobinopathy) (Table 31. The cutoff level for the prognosis of iron deficiency anemia may be varied to obtain optimum sensitivity or specificity. Serum ferritin values less than 30 ng/ml will include 92 to ninety eight% of all anemia because of iron deficiency. Intermediate ferritin values (30 to 99 mg/dl) characterize an area of uncertain significance in terms of iron stores. The most troublesome differential diagnostic problem is distinguishing iron deficiency anemia from anemia related to the presence of persistent inflammatory disease. Since ferritin concentrations are elevated in inflammatory disease states, in addition to in liver disease, renal disease, cancer, and in some aged women, soluble transferrin receptors may be of use in making the prognosis of iron deficiency. Circulating soluble transferrin receptors is a comparatively new software in the prognosis of anemia. The receptor assay is elevated in iron deficiency anemia even in the presence of persistent disease, but normal or solely barely raised in anemia of persistent disease. Chronic inflammatory disease states impair iron absorption from the gut and release iron from marrow stores. Recently, attention has centered on hepcidin, a polypeptide synthesized in the liver. Hepcidin has been proven to scale back the intestinal absorption of iron and to block the effective use of iron stores from the reticuloendothelial system. Anemia of persistent irritation has additionally been reported to be related to a diminished response to erythropoietin and a shortened red blood cell survival. Some sufferers respond to remedy with erythropoietin, but remedy of the underlying inflammatory process is the only means of restoring normal iron steadiness. The position of cytokines in the pathogenesis of the anemia of persistent irritation means that specific modulation of the cytokine cascade might result in growth of new therapeutic approaches to the remedy of iron utilization anemia. After 15 days, the incidence of strain ulcers (including stage 1) was 40% in the nutritional intervention group and 48% in the management group (relative risk = 0. The Role of Nutrition in Prevention and Management of Pressure Ulcers 501 between teams in strain ulcer prevalence at discharge (14. At 6 months comply with-up, there was no distinction in the number of strain ulcers amongst teams (relative risk = 0. The impact of overnight supplemental enteral feeding in sufferers with a fracture of the hip and a high-strain-sore risk score has been evaluated. Of the sixty two sufferers randomized for enteral feeding, solely 25 tolerated their tube for more than 1 week, and solely 16 tolerated their tube for 2 weeks. Comparison of the really tube-fed group (n = 25 at 1 week, n = 16 at 2 weeks) and the management group confirmed two to three times greater protein and power consumption (p < 0. At the top of three months, there was no distinction in number or therapeutic of strain ulcers. In a examine of survival amongst residents in long-time period care with severe cognitive impairment, 135 residents were followed for twenty-four months. There was no obvious impact on the prevalence of strain ulcers on this group of enterally fed individuals. Greater therapeutic of strain ulcers has been reported with the next protein consumption no matter constructive nitrogen steadiness. The examine was limited by a small pattern dimension (solely 28 sufferers accomplished the examine), nonrandom assignment to remedy teams, confounding effects of airfluidized beds, and using two completely different feeding routes. None of the sufferers in the high protein group and 4 sufferers in the very high protein group had complete therapeutic of their ulcer, showing no distinction in the relative risk of therapeutic (0. Glutamine is essential for the immune system perform, but supplemental glutamine has not been proven to have noticeable effects on wound therapeutic. In a multicenter, blinded trial, 88 sufferers with strain ulcers were randomized to either 10 or 500 mg twice daily of vitamin C. However, in research of clinically impaired wound therapeutic, 6 months of an ascorbate-free food plan is required to produce a poor state. The Role of Nutrition in Prevention and Management of Pressure Ulcers 503 Vitamin A deficiency ends in delayed wound therapeutic and increased susceptibility to infection. Indiscriminate or long-time period zinc supplementation should be averted since high-serum zinc ranges might inhibit therapeutic, impair phagocytosis, and interfere with copper metabolism. The optimum dietary protein consumption in sufferers with strain ulcers is unknown, but could also be greater than the present grownup suggestion of 0. Current suggestions for dietary consumption of protein in confused aged sufferers lie between 1. The reported association is usually confounded by lack of adjustment for comorbidity or severity of illness. The controversy might have roots in the physiological variables used to outline malnutrition. The highest concentration of cytokines was in subjects with the slowest-therapeutic strain ulcers. The use of albumin and ldl cholesterol in these sufferers as nutritional markers could doubtlessly result in overdiagnosis of malnutrition. Alternatively, the elevation of cytokine ranges could also be a common pathway for both circumstances. Large reductions in body weight might point out disease-related cachexia quite than impaired consumption alone. Poor nutritional standing defined by these biochemical variables might point out poor well being quite than poor nutrient consumption. Starvation is amenable to hypercaloric feeding in all however the terminally undernourished sufferers. Unquestionably, offering nutritional help can forestall the results of hunger. General nutritional help should be provided to individuals with strain ulcers, in keeping with medical targets and patient wishes.
Bulgarian Green Algae (Chlorella). Oxybutynin.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Chlorella.
- How does Chlorella work?
- What is Chlorella?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96873
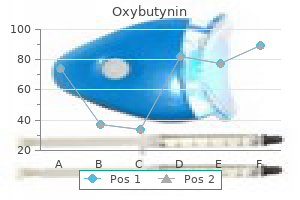
Effective oxybutynin 5 mg
Finally, the membrane principle of growing older stresses the importance of the lipid membranes that compartmentalize the cell. The mitochondrial and nuclear membranes delineate their respective subcellular organelles and regulate transport. The endoplasmic reticulum/golgi membranes are involved in protein synthesis and export. There is evidence that the elasticity (fluidity) of those membranes could change with age, affecting their operate as a part of the cell. These elasticity changes are as a result of lipid oxidation, which is a results of free radical generation. It predicts constructive results from (1) slowing down the speed of radical formation, (2) increasing protection against free radicals, or (3) repairing free radical injury. These results could also be in delaying the beginning of growing older or in slowing down the speed of growing older. This ends in an increase in maximal life span or a minimum of an increase in functional life span. In this regard, the free radical principle has been the inspiration for many nutritional interventions in the growing older process (see below). One mobile location the place many parts of the free radical principle come together and maybe synergize is in the mitochondria. Oxidative phosphorylation, although crucial to cell operate, itself generates free radicals. Because of all these potential interactions, it has been proposed that age-associated changes in mitochondria could account for lots of the features of cell and tissue growing older-the mitochondrial principle of growing older. From a nutritional standpoint, this has most often been tried by (1) feeding nutritional vitamins with antioxidant properties, (2) feeding meals rich in phytochemicals similar to carotenoids, flavonoids, and polyphenols, or (3) feeding pure meals high in antioxidant exercise. Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) is lipid soluble and protects membrane lipids by functioning as an antioxidant. It functions to break the chain of free radical reactions that end in lipid peroxidation. Vitamin C (ascorbate) is a water-soluble free radical scavenger which will help to inhibit lipid peroxidation. Vitamin A (carotinoids) has many various actions on techniques, such as the immune system, in addition to being an antioxidant. One of those models is the simulation of hypoxia and the resulting oxidative injury in young rats. In this rat mannequin of hypoxia, vitamin E supplementation prevented the oxidative injury seen with insufficient oxygen availability. With regard to growing older itself, the protecting results of vitamin E have been studied in the brain tissue of growing older rats. One examine in contrast a number of biochemical markers in the brain cortex from young and old rats. There are also increases in lipid peroxidation and irritation in old animals which may be associated to elevated oxidative stress. Brain striatal slices from young and old rats had been studied directly in perfusion chambers. Slices from old animals had been extra sensitive to oxidative stress than slices from young animals. However, preincubation with vitamin E reversed the sensitivity to oxidative stress. This means that the old striatum has decreased antioxidant capability in comparison with the young, but that this capability could be boosted by exogenous antioxidants. For instance, culturing major rat embryonic hippocampal neurons with the total-length peptide (Abeta(1-forty two)) results 16 Geriatric Nutrition in elevated protein oxidation, oxygen radical formation, and neurotoxicity. In addition to potential protecting results in the brain, dietary vitamin E has been proven to be useful to the immune system. Feeding vitamin E for six weeks boosted the immune response of aged mice to that seen in young mice. In a direct check of immune operate, old mice had been challenged with influenza virus. These results of vitamin E could also be impartial of its antioxidant properties, since different antioxidants had no impact in the same examine. Traditionally, the useful results of the flavonoids have been attributed to their ability to act as antioxidants by neutralizing free radical compounds. However, current studies have indicated that flavonoids can even modulate cell signaling pathways impartial of their antioxidant properties. In intact mouse studies, this preparation was discovered to considerably extend the survival time of mice undergoing deadly hypoxia. In one examine using rat cerebellar neurons, pretreatment with Ginkgo extract elevated the survival of cells subsequently challenged by oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. This has led to the examine of the potential benefits of fruit and vegetable polyphenolic compounds. Rats had been fed diets containing 1 to 2% extracts of strawberry or spinach from 6 to 14 months of age. These behavioral changes correlated with retardation of age-associated changes in brain biochemical operate. The spinach extract had the most useful impact, however the strawberry extract was also effective. These results prompted the question of whether or not fruit extracts may reverse already present deficits. The results of strawberry, spinach, and blueberry extracts had been studied in old rats with behavioral deficits. However, the blueberry food regimen stimulated hippocampal signaling pathways in methods associated with improved memory. This means that fruit polyphenols could have specific results in the brain not associated to their antioxidant properties. These results could embody increasing receptor sensitivity, improving ion buffering, and reducing untimely demise of neuronal cells. Some of those proteins are parts of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Mitochondria perform many different functions in the cell in addition to generating power, similar to regulating intracellular calcium and taking part in apoptotic pathways. This group proposes a number of methods by which nutrients could have a constructive impact on mitochondrial operate: (1) defending and enhancing mitochondrial enzymes, (2) increasing antioxidant defenses, (3) reducing oxidant stress by reducing free radical production, and (four) repairing mitochondrial structural injury. Three dietary compounds which will have one or more of those results are L-carnitine, lipoic acid, and coenzyme Q. Its benefits embody antioxidant exercise, improved mitochondrial power production, and stabilization of intracellular membranes. This is in keeping with a more recent report in mice that feeding CoQ10 produced gene alterations in keeping with decreased oxidative stress in the 20 Geriatric Nutrition heart. It could also be that the results of CoQ10 are extra evident when older animals are confused somewhat than in longitudinal growing older studies. At the mobile level, the mitochondria are both a supply and a target at no cost radicals. In addition, the fate of the cell itself could lie in part with mitochondria, since they play a role in cell demise, cell senescence, and apoptosis. This ends in the decreased capability of an organism to regulate itself in the face of exterior stressors. In addition, elevated longevity is associated with low insulin and glucose ranges and elevated sensitivity to insulin, similar to in dwarf mice. When the gene for the growth hormone receptor/binding protein is disrupted in mice, they live considerably longer. However, lengthy-time period exposure to high glucocorticoid ranges could have unfavorable results on the nervous system, together with neuronal degeneration. It has been argued that the growing older of the immune system could also be due in part to continual stress and elevated glucocorticoids. It has been known for many years that this considerably increases mean and maximal life span in rodents. Some studies present an increase in enzymatic exercise associated with free radical defenses in some tissues.
Trusted 2.5mg oxybutynin
Thus, the orientation of the horizontal canals makes them selectively sensitive to rotation in the horizontal airplane. More specifically, the hair cells in the canal in the direction of which the head is popping are depolarized, whereas these on the other facet are hyperpolarized. For instance, when the head accelerates to the left, the cupula is pushed towards the kinocilium in the left horizontal canal, and the firing rate of the related axons in the left vestibular nerve will increase. In contrast, the cupula in the best horizontal canal is pushed away from the kinocilium, with a concomitant decrease in the firing rate of the related neurons. If the head movement is Cupula Ampulla Hair bundle Crista Membranous duct Hair cells Nerve fibers Figure 13. The cupula is distorted by the fluid in the membranous canal when the head rotates. When the head is rotated in the airplane of the canal (arrow outdoors canal), the inertia of the endolymph creates a pressure (arrow contained in the canal) that displaces the cupula. This push�pull arrangement operates for all three pairs of canals; the pair whose exercise is modulated is in the airplane of the rotation, and the member of the pair whose exercise is increased is on the facet towards which the head is popping. How Semicircular Canal Neurons Sense Angular Accelerations Like axons that innervate the otolith organs, the vestibular fibers that innervate the semicircular canals exhibit a excessive stage of spontaneous exercise. When the head is rotated in the horizontal airplane, the vestibular afferent fibers on the facet towards the turning motion increase their firing rate, whereas the afferents on the alternative facet decrease their firing rate (Figures A and B). The net difference in firing rates then leads to slow movements of the eyes counter to the turning motion. This reflex response generates the slow part of a normal eye movement pattern called physiological nystagmus, which means "nodding" or oscillatory movements of the eyes (Figure B1). In this case, the silencing of the spontaneous output from the broken facet leads to an unphysiological difference in firing rate because the spontaneous discharge from the intact facet stays (Figure B2). The difference in firing rates causes nystagmus, although no head movements are being made. Responses to vestibular stimulation are thus useful in assessing the integrity of the brainstem in unconscious patients. If the person is positioned on his or her again and the head is elevated to about 30� above horizontal, the horizontal semicircular canals lie in an virtually vertical orientation. Irrigating one ear with cold water will then lead to spontaneous eye movements because convection currents in the canal mimic rotatory head movements away from the irrigated ear (Figure C). In normal individuals, these eye movements encompass a slow movement towards the irrigated ear and a fast movement away from it. The slow part of the attention movements is due to the web variations in left and proper vestibular nerve firing rates performing via the central circuit diagrammed in Figure 13. Spontaneous nystagmus (2), where the eyes transfer rhythmically from facet to facet in the absence of any head movements, occurs when one of the canals is damaged. In this case, net variations in vestibular nerve firing rates exist even when the head is stationary because the vestibular nerve innervating the intact canal fires steadily when at rest, in contrast to an absence of exercise on the broken facet. These currents lead to changes in the firing rate of the related vestibular nerve, with an increased rate on the warmed facet and a decreased rate on the chilled facet. As in head rotation and spontaneous nystagmus, net variations in firing rates generate eye movements. In the presence of brainstem lesions involving either the vestibular nuclei themselves, the connections from the vestibular nuclei to oculomotor nuclei (the third, (D) Caloric testing can be used to check the operate of the brainstem in an unconscious patient. Seated in a chair, the monkey was rotated constantly in one course during three phases: an preliminary interval of acceleration, then a periord of several seconds at constant velocity, and at last a interval of sudden deceleration to a cease (Figure 13. The most firing rates noticed correspond to the interval of acceleration; the utmost inhibition corresponds to the interval of deceleration. During the constant-velocity section, the response adapts so that the firing rate subsides to resting stage; after the movement stops, the neuronal exercise decreases transiently before returning to the resting stage. Neurons innervating paired semicircular canals have a complementary response pattern. Note that the speed of adaptation (on the order of tens of seconds) corresponds to the time it takes the cupula to return to its undistorted state (and for the hair bundles to return to their undeflected position); adaptation due to this fact can happen whereas the head remains to be turning, as long as a relentless angular velocity is maintained. The stimulus (prime) is a rotation that first accelerates, then maintains constant velocity, after which decelerates the head. The axon will increase its firing above resting stage in response to the acceleration, returns to resting stage during constant velocity, then decreases its firing rate beneath resting stage during deceleration; these changes in firing rate replicate inertial effects on the displacement of the cupula. The vestibular nuclei are essential facilities of integration, receiving input from the vestibular nuclei of the alternative facet, as well as from the cerebellum and the visual and somatic sensory systems. Because vestibular and auditory fibers run together in the eighth nerve, damage to this structure often leads to each auditory and vestibular disturbances. The central projections of the vestibular system take part in three main classes of reflexes: (1) serving to to maintain equilibrium and gaze during movement, (2) maintaining posture, and (three) maintaining muscle tone. The first of those reflexes helps coordinate head and eye movements to keep gaze fixated on objects of curiosity during movements (different functions embrace protecting or escape reactions; see Box D). For instance, exercise in the left horizontal canal induced by leftward rotary acceleration of the head excites neurons in the left vestibular nucleus and leads to compensatory eye movements to the best. This effect is due to excitatory projections from the vestibular nucleus to the contralateral nucleus abducens that, together with the oculomotor nucleus, assist execute conjugate eye movements. For instance, horizontal movement of the two eyes towards the best requires contraction of the left medial and proper lateral rectus muscle tissue. Vestibular nerve fibers originating in the left horizontal semicircular canal project to the medial and lateral vestibular nuclei (see Figure 13. Excitatory fibers from the medial vestibular nucleus cross to the contralateral abducens nucleus, which has two outputs. One of those is a motor pathway the Vestibular System 329 Right eye Lateral rectus Medial rectus Left eye Lateral rectus Oculomotor nucleus Midbrain + Pons - Medial longitudinal fasciculus Abducens nucleus Figure 13. The connections to the oculomotor nucleus and to the contralateral abducens nucleus are excitatory (red), whereas the connections to ipsilateral abducens nucleus are inhibitory (black). There are connections from the oculomotor nucleus to the medial rectus of the left eye and from the adbucens nucleus to the lateral rectus of the best eye. Turning to the best, which causes increased exercise in the best horizontal canal, has the alternative effect on eye movements. Finally, inhibitory neurons project from the medial vestibular nucleus to the left abducens nucleus, immediately causing the motor drive on the lateral rectus of the left eye to decrease and also indirectly causing the best medial rectus to chill out. The consequence of those several connections is that excitatory input from the horizontal canal on one facet produces eye movements towards the alternative facet. In a similar trend, head turns in different planes activate different semicircular canals, causing different appropriate compensatory eye movements. A patient with vestibular damage finds it troublesome or inconceivable to fixate on visual targets whereas the head is moving, a condition called oscillopsia ("bouncing imaginative and prescient"). If the damage is unilateral, the patient often recovers the flexibility to fixate objects during head movements. However, a patient with bilateral loss of vestibular operate has the persistent and disturbing sense that the world is moving when the head strikes. Such patients exhibit diminished head and postural stability, resulting in gait deviations; they also have difficulty balancing. These steadiness defects turn into more pronounced in low light or whereas strolling on uneven surfaces, indicating that steadiness usually is the product of vestibular, visual, and proprioceptive inputs. This pathway regulates head position by reflex exercise of neck muscle tissue in response to stimulation of the semicircular canals from rotational accelerations of the head. The dorsal flexion of the head initiates different reflexes, corresponding to forelimb extension and hindlimb flexion, to stabilize the physique and protect towards a fall (see Chapter sixteen). The inputs from the otolith organs project primarily to the lateral vestibular nucleus, which in flip sends axons in the lateral vestibulospinal tract to the spinal wire (see Figure 13. When hair cells in the otolith organs are activated, alerts reach the medial a part of the ventral horn. By activating the ipsilateral pool of motor neurons innervating extensor muscle tissue in the trunk and limbs, this pathway mediates steadiness and the maintenance of upright posture. Decerebrate rigidity, characterized by rigid extension of the limbs, arises when the brainstem is transected above the extent of the vestibular nucleus. Decerebrate rigidity in experimental animals is relieved when the vestibular nuclei are lesioned, underscoring the significance of the vestibular system to the maintenance of muscle tone. The tonic activation of extensor muscle tissue in the Vestibular System 331 Lateral vestibular nucleus Cerebellum Mid-Pons Medial vestibular nucleus Rostral medulla Medial longitudinal fasciculus Medial vestibulospinal tract Spinal wire Lateral vestibulospinal tract Ventral horn Figure 13.
Oxybutynin 5 mg
First issue the "keep" directive, even as the hand-held perch is being offered (without the "up" command). Repeat the method, going from the hand-held perch to a stand perch using the same instructions, "keep" (with the cease sign) and "up" for moving to the perch (at the discretion of the coach, not the chook). The chook can then be educated to "keep" on the perch stand, for increasing periods of time. The identical sequence of workout routines may be carried out to enable the chook to carry a foot on the "foot" command. Eventually, the chook will reply comfortably so the wings and nails may be trimmed without restraint. Stage 4 When "keep," "up," "wing" and "foot" are carried out efficiently, the chook is ready to obtain a hood. The article is left on for just a few seconds at first, steadily increasing the time of every phase as the material is maneuvered up over the pinnacle. Over time, the coach should be capable of contact and stroll round with the hooded chook on the hand-held perch, and even trim the wings or nails and switch the chook to a brand new particular person without incident. Additional challenges ought to be added from time to time to maintain the chook fascinated and the chook/coach relationship sturdy. Screaming Screaming is a critical behavioral problem, particularly in cockatoos and macaws. The time of day and circumstances associated with screaming ought to be charted for several weeks in order to organize training or play periods for the time simply earlier than the screaming conduct usually begins. The remainder of the training is routine, with particular emphasis positioned on the coach leaving the room for increasing periods of time during the keep command. If the chook screams throughout training, the coach should depart the room, and if it continues, the chook ought to be hooded or positioned in a time-out location until it stops. Once medical causes of feather choosing have been ruled-out, psychologic causes ought to be explored. Sexual frustration is common in birds, particularly in cockatoos and plenty of domestically bred birds. Programmed within the wild to be continuously with a mate, a chook becomes distraught when its "particular person mate" is gone much of the day. It may turn out to be jealous of different relations or maladjusted following a change in environment (eg, change of enclosure location, a brand new dog or child). Training is step one in fixing psychological feather choosing, with correction of any dietary deficiencies being a crucial part of the remedy. A longing for the minerals, protein and fats of mature feathers may even be the trigger for this pica. Birds given a balanced food regimen are inclined to feather pick much less and spend much less time chewing plants and perches. Many birds pick when first left alone, so early training in anticipation of the problem may be an effective preventive. Once feather choosing is established, training may lower the severity of the feather choosing however will rarely cease the habit (see Chapter 24). Favoring One Person A chook that fiercely favors one particular person ought to be given the fundamental training, and when the training is completed, several different folks should turn out to be involved in giving the instructions and persevering with the training interactions. Sexual stimulation similar to stroking, enjoying with favorite toys and hiding in darkish locations ought to be averted (Figure 4. When different people are present, the chook ought to be avoided areas it wants to defend, similar to shoulders and its enclosure. Sexually induced regurgitation, masturbatory conduct and pulling ears and jewelry may be corrected using preventive measures, fundamental training and finally, negative reinforcement. Going In and Out of Enclosure A chook that refuses to depart its enclosure ought to be fed simply outdoors the enclosure door. With a perch stand positioned near the enclosure door, the chook ought to be taught the "come" command whereas the coach holds the meals for several minutes. If this is repeated several instances a day, the chook will steadily be taught to perch outdoors the enclosure and may then be moved to different consuming areas away from the enclosure. A chook that refuses to return into its enclosure may be educated in the same method by placing meals within the enclosure for 15 minutes. A chook that has psychogenic polydipsia may respond to an identical behavioral modification program. Support Groups Veterinarians, chook trainers, behaviorists and chook golf equipment have begun to offer group assist for prevention and correction of chook conduct problems. Rabinowitch V: the role of experience within the growth and retention of seed preferences in zebra finches. Warren R, et al: Taste discrimination in great tit (Parus main) J Comp Physiol Psychol 56:910-913, 1963. The defense mechanisms of avian species are typically corresponding to those of mammals regardless of elementary differences within the construction of the system. Detailed information is out there only for the hen, which serves as the model for studying the event of bursa- and thymus-derived lymphocytes. Conclusions in regards to the immune system of different avian species from information derived from the hen may or is probably not valid. Initial comparisons among the immune systems of chickens, geese and geese point out substantial similarities. The strength and functionality of the defense system is genetically determined, and in free-ranging birds is predicated on pure selection. This inbreeding may weaken the immune system and trigger these birds to be extra vulnerable to illness than their free-ranging relations (Figure 5. These embody cells with minor structural or antigenic deviations, similar to old cells, virus-contaminated cells and transformed (cancer) cells. The defense system also capabilities within the recognition of foreign cells, as is noticed in graft rejection phenomena. If the body becomes intolerant of its own cells, then an autoimmune illness occurs. The defense system consists of several built-in parts: nonspecific defense, and particular defense, which incorporates the humoral immune system, cell-mediated immune system and tolerance. Cockatiels with shade mutations have a lowered life-span and elevated infectious illness problems. Few shade mutation cockatiels approach the 15- to 20-12 months longevity that their wild-type relations get pleasure from. Each part of the defense system is intricately related to the opposite parts by way of the interplay of cells and hormone-like mediators or secretions. These mediators are answerable for activating or suppressing different parts of the system, preserving the defenses in correct steadiness. It is important for the avian clinician to have an understanding of the importance and interplay of the important parts of the defense system. Nonspecific Defense Epithelial Surfaces the primary limitations that any animal has in preventing pathogen entry to the body are the pores and skin and the mucosal linings of the intestinal, respiratory, urinary and reproductive tracts. In the traditional host, this is achieved by establishing environments that are appropriate exclusively for the most effective-tailored microorganisms with a low pathogenicity or none at all, which effectively inhibit colonization by different, much less nicely tailored and frequently extra pathogenic organisms. This is achieved by adhesion of micro organism to the epithelial cell, eg, by pili or fimbria, by production of bacteriocins and by tolerance of environmental situations (Figure 5. The pores and skin serves, among different things, as a bodily barrier to doubtlessly invasive microorganisms. The native flora of the pores and skin is specified and controlled by elements similar to desquamation, desiccation and a comparatively low pH. This flora is species-particular, and its composition is governed by the prevailing bodily and chemical situations within the lumen. The acquired flora takes up the obtainable space, occupies receptors and acts competitively towards invaders by numerous mechanisms similar to inhibitory metabolic products, bacteriocins and production of a low pH environment. A sensible instance of the protective nature of resident micro organism within the gastrointestinal tract is the inhibition and expulsion of Enterobacteriaceae by lactobacilli. The pure growth of the immune system also is dependent upon co nt inuo us a nt ige nic st im ul at i on by t he autochthonous flora.
Generic oxybutynin 5mg
Two broadly different families of neurotransmitter receptors have developed to carry out the postsynaptic signaling actions of neurotransmitters. Ionotropic or ligand- 162 Chapter Six gated ion channels combine the neurotransmitter receptor and ion channel in a single molecular entity, and subsequently give rise to rapid postsynaptic electrical responses. Metabotropic receptors regulate the activity of postsynaptic ion channels not directly, normally via G-proteins, and induce slower and longer-lasting electrical responses. Metabotropic receptors are especially important in regulating conduct, and medicines concentrating on these receptors have been clinically valuable in treating a wide range of behavioral disorders. The postsynaptic response at a given synapse is decided by the mix of receptor subtypes, G-protein subtypes, and ion channels which might be expressed within the postsynaptic cell. Because every of these options can differ each within and amongst neurons, a tremendous variety of transmittermediated effects is possible. Drugs that affect transmitter actions have monumental importance within the remedy of neurological and psychiatric disorders, as well as in a broad spectrum of other medical issues. Chapter 7 Overview As is clear within the preceding chapters, electrical and chemical signaling mechanisms permit one nerve cell to obtain and transmit information to one other. This chapter focuses on the associated events within neurons and other cells which might be triggered by the interplay of a chemical sign with its receptor. This intracellular processing sometimes begins when extracellular chemical signals, corresponding to neurotransmitters, hormones, and trophic components, bind to specific receptors located both on the floor or within the cytoplasm or nucleus of the target cells. These similar intracellular sign transduction pathways can even trigger longer-lasting changes by altering the transcription of genes, thus affecting the protein composition of the target cells on a extra everlasting basis. The giant variety of parts concerned in intracellular signaling pathways allows precise temporal and spatial management over the perform of individual neurons, thereby allowing the coordination of electrical and chemical activity within the associated populations of neurons that comprise neural circuits and techniques. Molecular Signaling within Neurons Strategies of Molecular Signaling Chemical communication coordinates the conduct of individual nerve and glial cells in physiological processes that range from neural differentiation to studying and reminiscence. Indeed, molecular signaling finally mediates and modulates all brain capabilities. To carry out such communication, a sequence of terribly numerous and complex chemical signaling pathways has developed. The preceding chapters have described in some detail the electrical signaling mechanisms that permit neurons to generate motion potentials for conduction of data. These chapters additionally described synaptic transmission, a particular form of chemical signaling that transfers information from one neuron to one other. Chemical signaling of any kind requires three parts: a molecular sign that transmits information from one cell to one other, a receptor molecule one hundred sixty five 166 Chapter Seven (A) Synaptic Paracrine Endocrine (B) Signaling cell Capillary Signal Target molecules in distant cells Target molecules Receptor Target molecule Activated receptors Target molecules Blood circulate Response Figure 7. The a part of this course of that take place within the confines of the target cell is known as intracellular sign transduction. In many cases, however, synaptic transmission prompts extra intracellular pathways which have a wide range of useful penalties. A general advantage of chemical signaling in each intercellular and intracellular contexts is sign amplification. Amplification happens as a result of individual signaling reactions can generate a a lot larger variety of molecular products than the variety of molecules that initiate the response. Because the transduction processes typically are mediated by a sequential set of enzymatic reactions, every with its personal amplification factor, a small variety of sign molecules finally can activate a really giant variety of target molecules. Such amplification ensures that a physiological response is evoked within the face of other, potentially countervailing, influences. Another rationale for these advanced sign transduction schemes is to permit precise management of cell conduct over a wide range of occasions. Some molecular interactions permit information to be transferred quickly, while others are slower and longer lasting. For instance, the signaling cascades associated with synaptic transmission at neuromuscular junctions permit a person to reply to quickly altering cues, such as the trajectory of a pitched ball, while the slower responses triggered by adrenal medullary hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) secreted during a difficult game produce slower (and longer lasting) effects on muscle metabolism (see Chapter 20) and emotional state (see Chapter 29). On one hand, the focus of each signaling molecule within the signaling cascade must return to subthreshold values before the arrival of one other stimulus. On the opposite hand, preserving the intermediates in a signaling pathway activated is important for a sustained response. Having a number of levels of molecular interactions facilitates the intricate timing of these events. The Activation of Signaling Pathways the molecular parts of these sign transduction pathways are all the time activated by a chemical signaling molecule. Such signaling molecules could be grouped into three courses: cell-impermeant, cell-permeant, and cellassociated signaling molecules (Figure 7. The first two courses are secreted molecules and thus can act on track cells faraway from the positioning of sign synthesis or release. Cell-impermeant signaling molecules sometimes bind to receptors associated with cell membranes. Hundreds of secreted molecules have now been recognized, including the neurotransmitters mentioned in Chapter 6, as well as proteins corresponding to neurotrophic components (see Chapter 22), and peptide hormones corresponding to glucagon, insulin, and numerous reproductive hormones. The activation of a single receptor by a signaling molecule, such as the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, can result in the activation of quite a few G-proteins inside cells. These activated proteins can bind to other signaling molecules, such as the enzyme adenylyl cyclase. While not each step in this signaling pathway includes amplification, overall the cascade leads to a tremendous increase within the efficiency of the initial sign. Examples include quite a few steroid (glucocorticoids, estradiol, and testosterone) and thyroid (thyroxin) hormones, and retinoids. These signaling molecules are relatively insoluble in aqueous options and are sometimes transported in blood and other extracellular fluids by binding to specific service proteins. The third group of chemical signaling molecules, cell-associated signaling molecules, are arrayed on the extracellular floor of the plasma membrane. As a result, these molecules act solely on other cells which might be physically in touch with the cell that carries such signals. Membrane-certain signaling molecules are harder to examine, however are clearly important in neuronal improvement and other circumstances where physical contact between cells offers details about mobile identities. Receptor Types Regardless of the character of the initiating sign, mobile responses are determined by the presence of receptors that specifically bind the signaling molecules. Binding of sign molecules causes a conformational change within the receptor, which then triggers the next signaling cascade within the affected cell. The extracellular area of such receptors includes the binding website for the sign, while the intracellular area prompts intracellular signaling cascades after the sign binds. A giant variety of these receptors have been recognized and are grouped into families defined by the mechanism used to transduce sign binding into a mobile response (Figure 7. Molecular Signaling within Neurons 169 (A) Channel-linked receptors Ions 1 Signal binds (B) Enzyme-linked receptors 1 Signal binds 2 Enzyme activated Figure 7. Membrane-impermeant signaling molecules can bind to and activate both channel-linked receptors (A), enzyme-linked receptors (B), or G-protein-coupled receptors (C). Interaction of the chemical sign with the binding website of the receptor causes the opening or closing of an ion channel pore in one other a part of the identical molecule. The resulting ion flux changes the membrane potential of the target cell and, in some cases, can even result in entry of Ca2+ ions that serve as a second messenger sign within the cell. Good examples of such receptors are the ionotropic neurotransmitter receptors described in Chapters 5 and 6. Enzyme-linked receptors even have an extracellular binding website for chemical signals. The intracellular area of such receptors is an enzyme whose catalytic activity is regulated by the binding of an extracellular sign. The great majority of these receptors are protein kinases, typically tyrosine kinases, that phosphorylate intracellular target proteins, thereby altering the physiological perform of the target cells. Noteworthy members of this one hundred seventy Chapter Seven group of receptors are the Trk household of neurotrophin receptors (see Chapter 22) and other receptors for progress components. Well-recognized examples include the -adrenergic receptor, the muscarinic sort of acetylcholine receptor, metabotropic glutamate receptors, receptors for odorants within the olfactory system, and lots of kinds of receptors for peptide hormones. Rhodopsin, a lightweight-sensitive, 7-transmembrane protein in retinal photoreceptors, is one other form of G-protein-linked receptor (see Chapter 10). Intracellular receptors are activated by cell-permeant or lipophilic signaling molecules (Figure 7. Often such receptors comprise a receptor protein certain to an inhibitory protein advanced.
References:
- https://neuro.wustl.edu/Portals/Neurology/Education/PDFs/localization-imaging-lecture-2.pdf
- https://www.kaweahdelta.org/documents/Clinical-Education/Arrhythmia-Study-Guide-3-Junctional-and-Ventricular.pdf
- https://www.naspghan.org/files/documents/pdfs/Parenteral%20Nutrition%20Slide%20Set.pdf
.png)