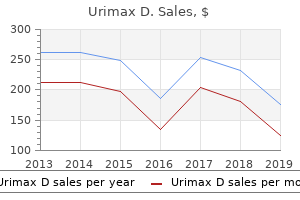
Proven urimax d 0.4mg/0.5mg
This extreme infection is characterised by jaundice, renal failure, and hem orrhagic phenomena. Echinococcus granulosus infestation is brought on by ingestion of tapeworm eggs from the excreta of canine and sheep. It results in hydatid illness of the liver, in which large p arasitic cysts invade the liver. The eggs are highly antigenic and stimulate granuloma formation, with resultant tissue destruction, scarring, and portal hypertension. This group of significant issues is related to the presence of small fats vacuoles in parenchymal liver cells, which differ from the big fats -containing vac uoles characteristic of fatty change. Reye syndrome is related to coma, and aspirin administration to youngsters with acute viral infections. Fatty liver of being pregnant is acute hepatic failure during the third trimester of being pregnant Tetracycline toxicity related to microvesicular fatty liver. Alcoholic liver illness is the constellation of hepatic adjustments related to extreme alco hol consumption; it varies from fatty change to alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis. The most common form of liver illness in the United States, it could be asymptomatic or may be be} asso ciated with mild-to-severe hepatic irritation, cirrhosis, or eBcephalopathy. Destructive chan ges of h e patocytes, fatty change (not shown here), and a ne utro philic inflammatory infi ltrate are different characteris tics. Fatty change (steatosis) is the most frequent morphologic abnormality brought on by alcohol and is reversible. Characteristics embody fatty change, focal liver cell necrosis, infiltrates of neutrophils, and the presence of intracytoplasmic eosinophilic hyaline inclusions (Mallory bodies, 2. Alcoholic hepatitis is commonly related to irreversible fibrosis that characteristically surrounds central veins and has been referred to as perivenular fibrosis, sclerosing hya line necrosis, or central hyaline sclerosis. This fibrosis can lead to central vein obstruc tion and fibrosis surrounding individual liver cells and end result in|may end up in|can lead to} cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is a descriptive term for chronic liver illness characterised by generalized disorganization of hepatic structure with scarring and nodule formation. Classification may be morphologic, on the premise of nodule dimension (micronodular, macro nodular, and mixed macromicronodular forms). Clinical manifestations (1) Findings related to hepatocellular harm and liver failure embody: (a) Jaundice, most frequently mixed conjugated and unconjugated (b) Hypoalbuminemia, brought on by decreased albumin synthesis in damaged hepatocytes (c) Coagulation factor deficiencies, brought on by decreased synthesis; all coagulation (d) (2) factors, aside from von Willebrand factor, are synthesized in the liver. Neurologic manifestations various from slight confusion to deep coma together with asterixis (flapping tremor of hands) are characteristic features. The fibrous bands include proliferating bile ducts and inflammatory cells, most frequently lymphocytes and plasma cells. In late phases, the nodules most likely to|are inclined to} turn out to be larger and irregular; this pattern results in a scarred, shrunken liver termed the hobnail liver. Morphologic traits embody broad fibrous bands dividing the liver into large, irregular nodules, usually containing intact hepatic lobules. Sometimes, may possibly} end result from the development of micro nodular alcoholic cirrhosis. Postnecrotic cirrhosis results in hepatocellular carcinoma extra usually than different forms of cirrhosis. Biliary cirrhosis happens as a major, probably autoimmune, disorder and far more incessantly as a secondary form biliary obstruction. Primary biliary cirrhosis (1) this form of cirrhosis is most probably of autoimmune origin. There is an increased incidence of different autoimmune issues in affected sufferers, and antimitochon drial antibodies are characteristic. Primary sclerosing cholangitis is uncommon besides in affiliation with inflammatory bowel dis ease, particularly ulcerative colitis. Characteristics embody irritation, fibrosis, and stenosis of intrahepatic and further hepatic bile ducts. Although the gene defect is frequent, the penetrance and improvement of clinical illness is low. Secondary biliary cirrhosis (1) the trigger is extrahepatic biliary obstruction, which leads to in|which ends up in} dilation and increased 6. Secondary hemochromatosis is most frequently related to a mix of ineffective erythropoiesis and quantity of} transfusions, such as happens in thalassemia main. Wilson illness (hepatolenticular degeneration) is an autosomal recessive disorder of cop per metabolism. Manifestations embody liver illness that varies from chronic hepatitis to cirrhosis, both micronodular or macronodular in kind. Wilson illness is also be|can be} marked by the Kayser-Fleischer ring circumscribing the periphery of the cornea, representing deposition of copper-containing pigment in Descemet membrane. In addition, there may be be} aminoaciduria and glycosuria renal tubular harm. Wilson illness results in an abnormal main accumulation of copper in parenchymal cells of the liver and kidney and in the brain and cornea. The illness also results in extrapyramidal motor indicators brought on by involvement of the basal ganglia, particularly the putamen of the lenticular nucleus. Cirrhosis inborn errors of metabolism outcomes from a number of} issues, together with: a. Vascular issues of the liver Portal hypertension is characterised by the event of venous collaterals with varices in the submucosal veins of the esophagus, the hemorrhoidal plexus, and different websites. Prehepatic: brought on by portal and splenic vein obstruction, most frequently by thrombosis b. Intrahepatic: brought on by intrahepatic vascular obstruction, most frequently by cirrhosis or metastatic tumor, and extra hardly ever by unique entities such as schistosomiasis c. Posthepatic: brought on by venous congestion in the distal hepatic venous circulation, most frequently constrictive pericarditis, tricuspid insufficiency, congestive coronary heart failure, or hepatic vein occlusion (Budd-Chiari syndrome) 2. Infarction is uncommon, the liver has a double blood provide (mesenteric and hepatic). The trigger is thrombotic occlusion of the main hepatic veins, resulting in stomach b. Budd-Chiari syndrome is most frequently related to polycythemia vera, hepatocel lular carcinoma, and different stomach neoplasms; may happen as a complication of being pregnant. Eventually, centrilobular fibrosis happens, resulting in cardiac cirrhosis (cardiac sclero sis). Similar adjustments may comply with long-standing constrictive pericarditis or tricuspid insufficiency. Hepatocellular carcinoma has been related to aflatoxin B j contamination of nuts and grains; aflatoxin B j is thought to trigger specific point mutations in the p53 gene. Cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct carcinoma) is less frequent than hepatocellular carci noma. Hemangiosarcoma (angiosarcoma) (1) this form of hepatic cancer is a uncommon malignant vascular tumor. Clinical manifestations embody nausea, vomiting, fever, and leukocytosis with right higher quadrant and epigastric ache. Cholelithiasis (gallstones) has a higher incidence in women and is commonly related to obesity and quantity of} pregnancies. Cholesterol stones are often solitary and too large to enter the cystic duct or the com mon bile duct. Pigment stones (1) Precipitation of excess insoluble unconjugated bi liru b i n results in their formation. Common bile duct obstruction results in obstructive jaundice with conjugated hyper c. Ascending cholangitis may result up} from secondary bacterial infection facilitated by obstructed bile flow. Gallstone ileus (intestinal obstruction brought on by passage of a big gallstone by way of g. Mucocele the eroded gallbladder wall into the adjoining small bowel) (distended, mucus-filled gallbladder secondary to chronic cystic duct obstruction) h. Characteristics embody yellow cholesterol-containing flecks in the mucosal floor. Carcinoma of the extrahepatic biliary ducts and the ampulla of Vater is less frequent than carcinoma of the gallbladder. Typical presenting features embody a progressive, relentless obstructive jaundice. Clin ical traits embody the mix of jaundice and a palpably enlarged gall bladder.
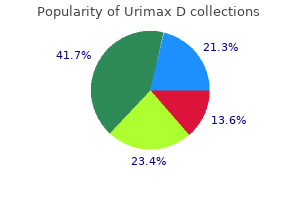
Lactospores (Lactobacillus). Urimax D.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Preventing diarrhea due to traveling.
- Treating and preventing eczema (atopic dermatitis) in infants and children.
- Dosing considerations for Lactobacillus.
- What is Lactobacillus?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs), general digestion problems, yeast infections, high cholesterol, Lyme disease, hives, fever blisters, canker sores, acne, cancer, stimulating the immune system, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96769
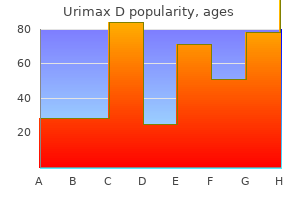
Trusted urimax d 0.4/0.5 mg
The pores and skin in these patients is fragile and hyperextensible, while the joints are hypermobile. These patients have "brittle bones" and also sometimes develop blue scleras and listening to loss. Decreased levels of vitamin D can produce rickets in children or osteomalacia in adults. It could also be} brought on by irritation (inflammatory edema) or it could be due to of} abnormalities involving the Starling forces performing at the capillary degree (noninflammatory edema or hemodynamic edema). Inflammatory edema is brought on by increased capillary permeability, which is the result of|the results of} vasoactive mediators of acute irritation. An exudate is inflammatory edema fluid resulting from increased capillary permeability. It is characterized by a high protein content, much mobile particles, and a selected gravity higher than 1. Pus is an inflammatory exudate containing numerous leukocytes and mobile particles. In distinction, transudates result both from increased intravascular hydrostatic pressure or from decreased osmotic pressure. Noninflammatory edema is the result of|the results of} abnormalities of the hemodynamic (Starling) forces performing at the degree of the capillaries. Increased hydrostatic pressure could also be} brought on by arteriolar dilation, hypervolemia, or increased venous pressure. Hypervolemia could also be} brought on by sodium retention seen in General Pathology Answers 109 renal illness, and increased venous hydrostatic pressure could be seen in venous thrombosis, congestive coronary heart failure, or cirrhosis. Decreased plasma oncotic pressure is brought on by decreased plasma protein, the vast majority of} which is albumin. Decreased albumin levels could also be} brought on by loss of albumin within the urine, which happens within the nephrotic syndrome, or by lowered synthesis, which happens in persistent liver illness. Lymphatic obstruction could also be} brought on by tumors, surgical resection, or infections (for example, an infection with filarial worms and consequent elephantiasis). It could also be} brought on by increased arterial supply (active hyperemia) or impaired venous drainage (passive hyperemia). Examples of energetic hyperemia embody increased blood circulate during train, blushing (such as embarrassment associated with being asked a query during a lecture), or irritation. Examples of passive hyperemia, or congestion, embody the changes produced by persistent coronary heart failure. The lung changes are characterized by intraalveolar, hemosiderinladen macrophages, referred to as "coronary heart failure cells. In distinction to hyperemia, hemorrhage refers to the leakage of blood from a blood vessel. Blood could escape into the tissue, producing a hematoma, or it could escape into areas, producing a hemothorax, hemopericardium, or hemarthrosis. Superficial hemorrhages into the pores and skin or mucosa are categorized as petechiae (small, pinpoint capillary hemorrhages), purpura (diffuse, quantity of} superficial hemorrhages), or ecchymoses (larger, confluent areas of hemorrhages). Their procoagulant activities involve activation of the extrinsic coagulation cascade by their production of tissue factor (thromboplastin) and stimulation of platelet aggregation by their production of von Willebrand factor and platelet-activating factor. The contrasting actions of the arachidonic acid metabolites prostacyclin and thromboxane A2 (TxA2) produce a fine-tuned steadiness one hundred ten Pathology for the regulation of clotting. TxA2, a product of the cyclooxygenase pathway of arachidonic acid metabolism, is synthesized in platelets and is a strong platelet aggregator and vasoconstrictor. Fibrinogen, which is produced by the liver and not endothelial cells, is cleaved by thrombin to form fibrin. When formed inside the coronary heart or the arteries, thrombi could have laminations, referred to as the strains of Zahn, formed by alternating layers of platelets admixed with fibrin, separated by layers with extra cells. Mural thrombi inside the coronary heart are associated with myocardial infarcts and arrhythmias, while thrombi within the aorta are associated with General Pathology Answers 111 atherosclerosis or aneurysmal dilatations. Venous thrombi, that are nearly invariably occlusive, are found most often within the legs, in superficial varicose veins or deep veins. The postmortem clot is often rubbery, gelatinous, and lacks fibrin strands and attachments to the vessel wall. Large postmortem clots could have a "hen fat" appearance overlying a darkish "currant jelly" base. These thromboemboli, most of which originate within the deep veins of the decrease extremities, could embolize to the lungs. Arterial emboli mostly originate inside the coronary heart on irregular valves (vegetations) or mural thrombi following myocardial infarctions. Types of nonthrombotic emboli embody fat emboli, air emboli, and amniotic fluid emboli. Air emboli are seen in decompression illness, referred to as caisson illness or the bends, while amniotic fluid emboli are associated to the rupture of uterine venous sinuses as a complication of childbirth. They could be categorized on the basis of their color into both purple or white infarcts, or by the presence or absence of bacterial contamination into both septic or bland infarcts. White infarcts, additionally referred to as pale or anemic infarcts, are often the 112 Pathology results of arterial occlusion. Red or hemorrhagic infarcts, in distinction, could result from both arterial or venous occlusion. They happen in organs with a dual blood supply, such because the lung, or in organs with intensive collateral circulation, such because the small gut and mind. Hemorrhagic infarcts additionally happen in organs in which the venous outflow is obstructed (venous occlusion). In the latter, twisting of the spermatic wire occludes the venous outflow, but the arterial inflow remains patent these arterial blood vessels have much thicker partitions. Testicular torsion is often the result of|the results of} bodily trauma in a person with a predisposing abnormality, such as irregular growth of the gubernaculum testis. A deficiency of both of those two enzymes leads to a dysfunction referred to as orotic aciduria, which is characterized by orotate within the urine, irregular progress, and megaloblastic anemia. An affiliation is a sample of nonrandom General Pathology Answers 113 anomalies with an unknown mechanism. A deformation is an alteration of a normally formed body part by mechanical forces. A disruption is a defect that results from interference in a normally growing process. A malformation is a morphologic defect that results from an intrinsically irregular developmental process. A sequence is a recognized sample that results from a single preexisting abnormality. Syndrome refers to quantity of} anomalies having a recognizable sample and recognized pathogenesis. Autosomal dominant inheritance characterizes both myotonic dystrophy and the facioscapulohumeral type, while limb-girdle dystrophy is autosomal recessive. In Duchenne muscular dystrophy, males are affected and symptoms start earlier than the age of four. Pelvic girdle muscle tissue are affected, with resultant problem in walking, and this is adopted by shoulder girdle weak point and eventual involvement of respiratory and cardiac muscle tissue with demise from respiratory failure earlier than age 20. Histologic changes embody rounded, atrophic fibers; hypertrophied fibers; degenerative and regenerative changes in adjoining myocytes; and necrotic fibers invaded by histiocytes. To calculate the probability that two or extra occasions would possibly be} unbiased of each other will all happen, you should multiply the probabilities for every of those occasions together. The principle, which assumes random mating, states that given gene frequencies p (for an allele A) and q (for one other allele a), then the aa genotype (homozygous) = q � q and the Aa genotype (heterozygous carriers) = 2pq. Diagnosis requires General Pathology Answers one hundred fifteen biopsy demonstration of excess liver glycogen plus both absent or low liver glucose-6-phosphatase exercise, or a diabetic glucose tolerance curve, or hyperuricemia. Division of this illness into five categories is generally accepted: type A, the acute neuronopathic form, is the one which has the best incidence. The lack of sphingomyelinase in type A is the metabolic defect that forestalls the hydrolytic cleavage of sphingomyelin, which then accumulates within the mind. These patients are prone to growth of subluxation of the spine, which might produce quadriplegia.
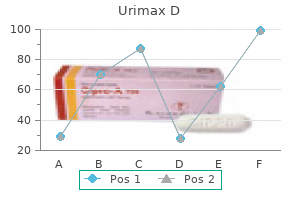
Proven 0.4mg/0.5mg urimax d
Mitosis is split into four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase (see Figure 4. Cytokinesis is the splitting of the cytoplasm and organelles into the daughter cells. The term chromosome additionally be} used to discuss with both the single chromatid or the pair of chromatids hooked up on the centromere. The correct motion of our chromosomes depends on by} specialised subcellular organelles identified as|often identified as} centrioles (see Figure 4. During prophase, the centrioles migrate to reverse poles of the cell and begin to form the spindle fibers, that are created from microtubules. Each of the fibers radiates outward from the centrioles, giving the chromosomes an attachment level for later separation during anaphase. Subsequent shortening of this apparatus ends in separation of sister chromatids. Indeed, we are able to} watch certain types of quickly dividing cells endure the whole mitotic process in about 20 minutes utilizing nothing more than a light-weight microscope. An autosomal cell never has more or fewer than the 2n (46 in human) variety of chromosomes, besides in disease situations. Prophase the chromosomes condense, the centriole pairs separate and move toward reverse poles of the cell, and the spindle apparatus varieties between them. The nuclear membrane dissolves, allowing spindle fibers to enter the nucleus, while the nucleoli become much less distinct or disappear. Kinetochores, with hooked up kinetochore fibers, appear on the chromosome centromere. The kinetochore fibers work together with the fibers of the spindle apparatus to align the chromosomes on the metaphase plate (equatorial plate), which is equidistant to the 2 poles of the spindle fibers. Real World Failure of mitosis or its regulation typically ends in an unequal distribution of genetic material to the daughter cells. However, this kind of unregulated cell division with out regard to genomic stability is a trademark of most cancers. Anaphase the centromeres break up so that each chromatid has its personal distinct centromere, thus allowing the sister chromatids to separate. The sister chromatids are pulled toward the opposite poles of the cell by the shortening of the kinetochore fibers. A nuclear membrane re-forms around each set of chromosomes, and the nucleoli reappear. Each of the 2 new nuclei has obtained a whole copy of the genome identical to the unique genome and to each other. Cancer cells typically divide sooner than normal cells, so most chemotherapeutic brokers work by targeting quickly dividing cells. Cytokinesis At the top of telophase, cytokinesis permits us to separate the cytoplasm and organelles so that each daughter cell has what it must survive on its own. Each cell undergoes a finite variety of divisions earlier than programmed dying; for human somatic cells, this is often between 20 and 50. After that, the cell can not divide with out incorporating errors and will probably die with out being replaced. Some cells never endure division (muscle and nerve), whereas others, corresponding to most cancers cells, escape this cycle and divide constantly. Asexual Reproduction Asexual copy is the manufacturing of offspring from the genetic material of a single father or mother. It is similar to mitosis in eukaryotic cells in that the daughter cells might be genetically identical to their dad and mom (other than random mutations that will come up in the course of the process). We will briefly examine four different types of asexual copy: binary fission, budding, regeneration, and parthenogenesis. The circular chromosome attaches to the cell wall and replicates while the cell continues to develop in dimension. Eventually the plasma membrane and cell wall will start to develop inward alongside the midline of the cell to produce two equal daughter cells (see Figure 4. This process is simple, so may possibly} proceed quickly; certainly, some strains of Escherichia coli can replicate every 20 minutes under perfect development situations. The daughter cell may instantly break off or stay hooked up to the father or mother until it grows to full dimension. Budding takes place in quantity of} organisms, including hydra and yeast (both eukaryotes). Key Concept Binary fission ends in two cells of equal dimension, whereas budding ends in cells of unequal dimension. Lizards that lose their tails when threatened may regrow them, and annelid worms can regenerate anterior head segments. Some animals have intensive capabilities; in fact, sea stars may reproduce their our bodies from just an arm, lengthy as|so long as} an area identified as|often identified as} the central disk is intact. There are at all times exceptions; in people for instance, the liver displays intensive regenerative properties. Both livers (or liver pieces) will develop again to the suitable dimension, no worse for the wear! What does this imply in terms of|when it comes to|by way of} the variety of chromosomes that might be found in each cell They might be haploid in quantity end result of|as a outcome of} just one father or mother contributed genetic material. Remember, the diploid quantity is maintained throughout mitosis, whereas the process of meiosis ends in haploid cells. Mitosis ends in two identical diploid (2n) daughter cells, whereas meiosis yields four different haploid (n) gametes; somatic cells endure mitosis, whereas gametocytes endure meiosis. Whereas mitosis consists of one spherical of replication and division each, meiosis is composed of one spherical of replication followed by two rounds of division. Meiosis I (the first division) ends in homologous chromosomes being separated, generating haploid daughter cells; this the reductional division. Homologous chromosomes code for a similar genes; one is inherited from each father or mother. During prophase, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, the spindle apparatus varieties, and the nucleoli and nuclear membrane disappear. Note that crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes and never between sister chromatids of the identical chromosome. Such genetic recombination can unlink linked genes, thereby growing the variety of genetic combinations produced via gametogenesis. Recombination amongst chromosomes ends in elevated genetic variety inside a species. Real World the rate of gene unlinking is used to map distances between two genes on the identical chromosome. Metaphase I Homologous pairs (tetrads) align on the metaphase plate, and every pair attaches to a separate spindle fiber by its kinetochore. [newline]Metaphase is the best to establish pictorially end result of|as a outcome of} the chromosomes are all neatly lined up on the metaphase plate. Anaphase I Homologous pairs separate and are pulled to reverse poles of the cell. This process disjunction, and it accounts for a basic Mendelian law. During disjunction, each chromosome of paternal origin separates (or disjoins) from its homologue of maternal origin, and both chromosome can end up in both daughter cell. Thus, the distribution of homologous chromosomes to the 2 intermediate daughter cells is random with respect to parental origin. Each daughter cell could have a novel pool of alleles (genes coding for different types of a given trait;. At this level, each chromosome nonetheless consists of sister chromatids joined on the centromere. They are haploid; as soon as} homologous chromosomes separate, solely the n variety of chromosomes is left (23 in humans). Each chromatid inside a pair, nonetheless, has the identical origin (save for genetic recombination).
Best urimax d 0.4/0.5 mg
Common polygenic disorders embody ischemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus, hyperten sion, gout, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and neural tube defects. This uncommon situation is characterized by each ovarian and testicular tissue, with ambigu ous external genitalia and each X and Y chromosomes. One potential mechanism is the parthenogenetic division of a haploid ova into two hap loid ova, adopted by double fertilization and then fusion of the two zygotes in early embryonic improvement. The trigger additionally be} tissue resistance to androgens (testicular feminization), defects in testosterone synthesis, or hormones administered to the mom throughout preg nancy. The situation is most frequently attributable to increased androgenic hormones from congenital adrenal hyperplasia, an androgen-secreting adrenal or ovarian tumor within the mom, or hormones administered to the mom throughout being pregnant. A 1 9-year-old college sophomore is referred by his ophthalmologist due to the discovering of ectopia lentis (dislocation of the lens), which has resulted in visible diffi culties that have interfered together with his per formance on the varsity basketball staff. His chest has a "caved-in" look, and he also has a modest diploma of scoliosis. A midsystolic "click on" is heard, and an echo cardiogram reveals mitral valve prolapse. The most probably diagnosis is (A) Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (8) Dystrophin (e) a- 1 A-Glucosidase (D) a-L-Iduronidase (E) Lysyl hydroxylase four. A newly described neurologic disorder is discovered to result on} multiple of} family members in three generations that were available for examine. In the sec ond technology, the entire kids of the first-generation sisters were affected, but certainly one of the} descendants of the first-gener ation son. In the third technology, the entire kids of the affected second-generation women were affected, but certainly one of the} descendants of the second-generation males. A 20-year-old woman has a robertsonian translocation involving chromosome 2 1 and a second acrocentric chromosome. What is the theoretic probability of a useful tri somy 2 1 if certainly one of her ova is fertilized by a traditional sperm As a part of} a fourth-year elective, a medical student rotating via a medical genetics service is assigned to counsel a affected person who is anxious a couple of family historical past of hypertension. To be properly prepared for the counseling session, the coed evaluations course notes on modes of inheritance of var ious disorders. Knowledge of which of the following modes of inheritance is most per tinent to the upcoming dialogue with the affected person A 2-year-old baby has been adopted for mental retardation and gradual improvement, as well as|in addition to} multiple of} delivery defects. On examina tion, microcephaly, hypertelorism, microg nathia, epicanthal folds, low-set ears, and hypotonia are famous. Karyotypic analysis would be anticipated to present G enetic D isord e rs sixty three (S) a - l,4-Glucosidase (e) Hexosaminidase A (0) a-L-Iduronidase (E) Sphingomyelinase (A) Glucocerebrosidase (A) 5p-. The physician should b e prepared t o focus on which o f the following disorders phrases of|when it comes to|by method of} its association with Down syndrome During a routine physical examination, a four 1 -year-old woman is famous to have blue black pigmented patches within the sclerae and gray-blue discoloration of the ear cartilages. The extensor tendons of the palms exhibit similar discoloration when she is asked to "make a fist. Her only current grievance is slowly rising pain and stiffness of the decrease back, hips, and knees. These findings are attribute of a deficiency of which of the follOwing enzymes The diagnosis was missed at delivery outcome of|as a end result of} (S) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (e) Lymphoblastic leukemia (0) Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid (E) Osteosarcoma (A) Berry aneurysm of the circle of Willis eight. A 1 4-year-old lady with amenorrhea is anxious due to the delayed onset of menses. She has shortened stature and a large, webbed neck; broad chest; and sec ondary sexual characteristics according to with} these of a much younger lady. Which of the following chromosomal changes is most according to with} these findings A 50-year-old woman of Eastern European Jewish ancestry has a historical past of recurrent fractures and simple bruising and is discovered to have hepatosplenomegaly and gentle anemia. Serum assays reveal elevations of chitotriosi dase and angiotensin-converting enzyme. Assay of cultured leukocytes most probably reveals marked deficiency of which of the following enzymes In addition, this disorder has an earlier onset and is more debilitating in successive generations, a phenomenon that could be (B) an increase within the variety of trinucleotide repeats in successive generations. An anterior chest deformity known as as|often identified as} pectus excavatum is usually seen, and vertebral abnormalities embody scoliosis and lordosis. Cardiovascular complications embody mitral valve prolapse and mitral regurgitation. Cystic medial necrosis can result in dilation of the aortic root and aortic regurgitation. Theoretically, a person who carries a robertsonian translocation with chromosome 2 1 and a second acrocentric chromosome has a 1 in three likelihood of getting a baby with trisomy 2 1; nevertheless, the chance of a live delivery of a kid with Down syndrome is definitely much less, presumably due to a high incidence of spontaneous abortion of such fetuses. The necessary level is that a robertsonian translocation predisposes to a hereditable type of Down syndrome. The diagnosis is cystic fibrosis, the commonest lethal genetic disease in Caucasian populations. The disorder of} a defect within the cystic fibrosis transmem brane conductance regulator protein, and about 70% of circumstances have a deletion of pheny lalanine in place 508 (LlF508 mutation). Affected sufferers typically have multiple of} pulmonary infections and p ancreatic insufficiency with steatorrhea and failure to thrive. Death is commonly respiratory failure secondary to repeated pulmonary infections, facilitated by the buildup of thick, tenacious mucus within the airways. Increased concentra tion of chloride in sweat and tears is attribute, and the sweat take a look at is a vital diagnostic adjunct. Abnormalities of mitochondrial inheri tance usually involve genes that code for enzymes of oxidative phosphorylation. Multifactorial disorders are among the most common familial abnor malities and are far more frequent than monogenic disorders. They embody quantity of|numerous|a selection of} frequent entities, corresponding to ischemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, gout, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and neural tube defects. The scientific findings are these of type I Gaucher disease, which is a person ifestation of glucocerebrosidase deficiency. The disorder is most frequently seen in persons of European (Ashkenazic) Jewish lineage. Prominent findings embody bone pain and frac tures, straightforward bruising, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. Bone marrow aspiration reveals quite a few typical Gaucher cells, but specific enzyme assay is required to verify the diagnosis. This lysosomal storage disease is relatively gentle compared to with} quantity of|numerous|a selection of} other such entities, corresponding to Tay-Sachs disease and Niemann-Pick disease, which are not often seen in adults. The disease is very variable in its scientific manifesta tions, and assays of chitotriosidase and angiotensin-converting enzyme, markers of macrophage proliferation, are helpful measures of the extent of disease and of its management. The affected person has homogentisic oxidase deficiency, a uncommon inborn error of metabolism (actually the first such disorder described by Garrod in 1902), clinically mani fest by alkaptonuria and ochronosis. The time period alkaptonuria refers to urinary excretion of unmetabolized homogentisic acid imparting a darkish color to urine on standing. The time period ochronosis refers to pigment deposition in multiple of} tissues, most prominently in cartilage and connective tissue. Most signs end result from joint involvement, which can result in disabling arthritis as sufferers age. Other affected buildings embody the eyes, larynx and bronchi, heart and vessels, prostate, and sweat glands. The focus of phenylalanine in affected infants is often regular at delivery and will increase quickly through the first days of life. False-negative results are com mon immediately after delivery but are uncommon on the second and third days of life. The phenomenon of earlier and more severe manifestations of a disor der in successive generations (anticipation) is a attribute of many trinucleotide repeat disorders, the most effective identified examples of which are fragile X syndrome (discussed on this chapter) and Huntington disease (described on this scientific scenario and further dis cussed in Chapter 23). The diploma of expansion is intently related to the gender of the par ent with the genetic abnormality. They are recognized by cell-surface glycoproteins specific for each cell type and stage of differentiation.
Best urimax d 0.4mg/0.5mg
Oxygen must come from maternal circulation and, therefore, diffuse through placental vessels. The first, called the foramen ovale, connects the best and left atria, with the intent that blood coming into the best atrium from the superior vena cava will flow into the left atrium instead of the best ventricle in order that may possibly} ultimately be pumped out of the aorta into systemic circulation. The proper atrium, end result of|as a result of} blood will travel spontaneously down the stress gradient. This gradient is reversed in adults, so the foramen ovale have to be shut after start for the grownup heart to perform correctly. The ductus arteriosus is current to shunt leftover blood from the pulmonary artery to the aorta. It works for the same reason that the foramen ovale does: the stress in the best fetal heart is greater than that in the left. If blood continues to be shunted from the best facet to the left (as it was in utero), the neonate will turn blue, end result of|as a result of} the deoxygenated venous blood bypasses the lungs and mixes with the oxygenated blood being pumped to the physique through the aorta. Since the placenta is a lot able to pitching in throughout gestation, blood returning from the placenta by way of the umbilical vein is rerouted to the inferior vena cava by way of the ductus venosus. But to stop it from stealing oxygen designated for relaxation of|the remainder of} the physique, the liver has its own reserves from arteries leaving the center. Speaking of shunts and vessels, we ought to be clear on sort of|what kind of} blood the umbilical arteries and veins carry. Just like all other arteries that take blood away from the center, the umbilical arteries carry blood away from the fetus. And similar to all other veins that carry blood toward the center, the umbilical veins carry blood toward the fetus. The best method to bear in mind which type of blood every carries is to recall which method the blood travels in every vessel and to use that pathway to deduce sort of|what kind of} blood is flowing. The fetus would return blood to the placenta only if all of the oxygen in it had been used up. Similarly, the only type of blood that the fetus desires from the placenta is oxygenated blood, so it have to be the case that the umbilical veins carry oxygenated blood. Gestation Human being pregnant lasts an estimated 266 days, which are divided into three trimesters. As a general rule, the larger the animal, the longer the gestational period and the fewer the offspring. For example, elephants usually have one calf and gestate for 22 months (almost two years). Mice have 10 to 12 offspring per litter and gestate for only than|for under} 20 days-quite a difference! The heart begins to beat at roughly 22 days, and soon afterward the eyes, gonads, limbs, and liver start to kind. By 5 weeks, the embryo is 10 mm in size and by week six, it has grown to 15 mm. The cartilaginous skeleton begins to harden into bone by the seventh week (see Chapter 6). By the end of eight weeks, many of the organs have shaped, the mind is pretty developed, and the embryo is referred to as a fetus. It begins to move round in the amniotic fluid, its face seems human, and its toes and fingers elongate. During the ninth month, antibodies are transported by highly selective lively transport from the mom to the fetus for defense towards overseas matter, in preparation for all times outside the womb. The progress fee slows, and the fetus becomes much less lively, as it has much less room to move about. Real World Advances in medicine have allowed infants to be born as early as 24 weeks, which is far want of|wanting} a standard 39. These problems are most obvious in the respiratory system insufficient surfactant production; extra on this in Chapter eight. Birth Vaginal childbirth is accomplished by rhythmic contractions of uterine clean muscle, coordinated by prostaglandins and the peptide hormone oxytocin. First, the cervix thins out, and the amniotic sac ruptures, which is usually identified as|often known as} the water breaking. Conclusion Our chapter has taken us through the fast development of a single-celled zygote to the start of a fullfledged baby. From the first cleavage to the last uterine contraction, we should always|we must always} simply extract the main structures and highlights of embryonic development along with the variations between fetal and grownup physiology. Keep an eye out for Chapters eight and 9 (adult circulatory and respiratory systems), which we can to} use as reference points for learning fetal physiology. Implantation of the embryo into the endometrium is critical for correct and successful progress. Gastrulation is the technology of three primary germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. The development of the nervous system neurulation and occurs throughout gastrulation. Fetal circulation contains three shunts: the ductus venosus, the foramen ovale, and the ductus arteriosus, which serve to bypass blood from the liver and lungs. Gestation consists of three trimesters of three months every; sure key developmental milestones are reached throughout every trimester. Vaginal childbirth is accomplished by coordinated and rhythmic contractions of uterine clean muscle. Which of the next developmental phases has the greatest nuclear-to-cytoplasmic material ratio During which period is a teratogen more than likely to have an effect on} mind development throughout gestation The influence of a specific group of cells on the differentiation of another group of cells is referred to as A. In fetal circulation, the blood delivered by way of the aorta has a better partial stress of oxygen than the blood that was delivered to the lungs. Increased left atrial stress coupled with decreased proper atrial stress causes the foramen ovale to close. The ductus venosus degenerates over time, utterly closing three months after start. C the question is asking us to determine the developmental stage with the best nuclear-tocytoplasmic material ratio. During the series of fast mitotic divisions identified as|often known as} cleavage, the number of cells increases dramatically and not using a|with no} corresponding enhance in the quantity of cytoplasm. As such, a excessive ratio of nuclear-to-cytoplasmic material will be found on the stage with the greatest quantity of cells. From the given decisions, the stage with the greatest number of cells is the blastula. B To reply this question, it could be be} helpful to review quickly the embryonic layers. The ectoderm provides rise to the integument (the epidermis, hair, nails, and epithelium of the nostril, mouth, and anal canal), the lens of the eye, and the nervous system. The endoderm provides rise to the epithelial linings of the digestive and respiratory tracts and components of the liver, pancreas, thyroid, and bladder. Finally, from the mesoderm come up the musculoskeletal system, the circulatory system, the excretory system, and the gonads. Therefore, the only incorrect association could be present in (B), the explanation that} lens of the eye is derived from the ectoderm. D the safest method to reply this question is to review all the reply decisions and eliminate the ones that do happen instantly after start. Because she begins respiratory, resistance in the pulmonary vessels decreases, which causes a rise in blood flow through the lungs. Along with it, as normal blood circulation begins, the foramen ovale snaps closed, the ductus arteriosus and ductus venosus constrict, and the stress in the left atrium increases. However, when blood flow through the umbilical wire stops, the blood stress in the inferior vena cava decreases, causing a decrease in the stress in the best atrium. A the question is mainly asking us when throughout human being pregnant the mind develops. During the first weeks of gestation, the main organs start to develop, amongst them the mind.
Order 0.4/0.5 mg urimax d
A biopsy of a peripheral nerve reveals inflammation and demyelination (radiculoneuropathy). Carpal tunnel syndrome, produced by harm to or pressure on the median nerve deep to the flexor retinaculum, is characterised greatest by which one of the following abnormalities Hyperextension of fingers at metacarpophalangeal joints and flexion at interphalangeal joints (claw hand) b. Weakness of extensors of wrist and fingers (wristdrop) Nervous System Answers 469. Increased intracranial pressure may cause swelling of the optic nerve (papilledema), headaches, vomiting, or herniation of a part of} the brain into the foramen magnum or underneath a free a part of} the dura. Subfalcine herniations are brought on by herniation of the medial facet of the cerebral hemisphere (cingulate gyrus) underneath the falx, which can compress the anterior cerebral artery. Transtentorial herniation, which happens when the medial a part of} the temporal lobe (uncus) herniates over the free edge of the tentorium, may lead to compression of the oculomotor nerve, which results in|which leads to|which finally ends up in} pupillary dilation and ophthalmoplegia (the affected eye factors "down and out"). Tentorial herniation can also compress the cerebral peduncles, within that are the pyramidal tracts. Further caudal displacement of the entire brainstem may trigger tearing of the penetrating arteries of the midbrain (Duret hemorrhages). Masses in the cerebellum may trigger tonsillar herniation, in which the cerebellar tonsils are herniated into the foramen magnum. The Arnold-Chiari malformation 503 504 Pathology consists of herniation of the cerebellum and fourth ventricle into the foramen magnum, flattening of the base of the skull, and spina bifida with meningomyelocele. Newborns with this dysfunction are threat of|susceptible to|vulnerable to} developing hydrocephalus throughout the first few days of supply secondary to stenosis of the cerebral aqueduct. In distinction, extreme hypoplasia or absence of the cerebellar vermis happens in the Dandy-Walker malformation. There is cystic distention of the roof of the fourth ventricle, hydrocephalus, and presumably agenesis of the corpus callosum. Tuberous sclerosis may present attribute agency, white nodules (tubers) in the cortex and subependymal nodules of gliosis protruding into the ventricles ("candle drippings"). Other indicators of tuberous sclerosis embrace the triad of seizures, psychological retardation, and congenital white spots or macules (leukoderma). In von Hippel-Lindau illness, quantity of} benign and malignant neoplasms happen, together with hemangioblastomas of the retina, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata; angiomas of the kidney and liver; and renal cell carcinomas. Patients with Sturge-Weber syndrome, a nonfamilial congenital dysfunction, show angiomas of the brain, leptomeninges, and ipsilateral face, that are referred to as port-wine stains (nevus flammeus). There are quantity of} problems on this group of developmental abnormalities that have various levels of severity. Spina bifida occulta is the mildest form and is characterised by failure of vertebral fusion only. In spina bifida occulta the defect in the closure of the neural tube is roofed by pores and skin and dermis, with only a pinpoint sinus or hair-covered depression marking the site. Bacterial meningitis, or meningomyelitis, is the major potential threat in these sufferers. Because the wire is in its regular location, there are minimal neurologic deficits. Next in severity is spina bifida with a myelomeningocele, which is characterised by herniation of the wire and a meningeal sac through the vertebral defect. This abnormality is often associated with extreme neurologic defects in the decrease extremities, bladder, and rectum. The most extreme form of spina bifida, spina Nervous System Answers 505 bifida aperta or myeloschisis, results from full failure of fusion of the caudal finish of the neural plate, which lies open on the pores and skin floor. This abnormality also ends in extreme neurologic defects in the legs, bladder, and rectum. These hemorrhages outcome from extreme trauma that sometimes causes a skull fracture. The hemorrhage results from rupture of one of the meningeal arteries, as these arteries supply the dura and run between the dura and the skull. The artery concerned is often the center meningeal artery, which is a branch of the maxillary artery, as the skull fracture is often in the temporal space. Bleeding causes elevated intracranial pressure and can result in tentorial herniation and dying. Berry aneurysms are saccular aneurysms that outcome from congenital defects in the media of arteries. Berry aneurysms are mostly discovered in the circle of Willis, sometimes both at the junction of the anterior communicating artery with the anterior cerebral artery or at the junction of the center cerebral artery and the posterior communicating artery. The probability of rupture of berry aneurysms will increase with age (rupture is uncommon in childhood). Rupture causes marked bleeding into the subarachnoid area and produces extreme headaches, sometimes described as the "worst headache ever. Global ischemia results from generalized decreased blood circulate, corresponding to with shock, cardiac arrest, or hypoxic episodes. Global hypoxia ends in watershed (border zone) infarcts, which usually happen at the border of areas supplied by the anterior and center cerebral arteries, and laminar necrosis, which is related to the short, penetrating vessels originating from pial arteries. Atherosclerosis, which predisposes to vascular thrombi and emboli, is related to regional ischemia. Hypertension damages parenchymal arteries and arterioles, producing small ischemic lesions (lacunar infarcts). Fat emboli, related to trauma of lengthy bones, lodge in small capillaries to form petechiae. Venous sinus thrombosis is related to systemic dehydration, phlebitis, and sickle cell illness. This weakens the wall and varieties small Charcot-Bouchard aneurysms, which can finally rupture. Berry aneurysms (small saccular aneurysms) are congenital defects in the media of blood vessels and are positioned at the bifurcations of arteries. Atherosclerotic aneurysms are fusiform (spindle-shaped) aneurysms often positioned in the major cerebral vessels. Mycotic (septic) aneurysms outcome from septic emboli, mostly from subacute bacterial endocarditis. Syphilitic meningitis is characterised by perivascular infiltrates of lymphocytes and plasma cells that trigger obliterative endarteritis and meningeal fibrosis. Tabes dorsalis is degeneration of the posterior columns of the spinal wire. This is brought on by compression atrophy of the posterior spinal sensory nerves, which produces impaired joint place sensation, ataxia, lack of ache sensation (leading to joint harm, i. The virus is transmitted through peripheral nerves to the brain, where it varieties attribute inclusions within neurons (Negri bodies). Symptoms related to destruction of neurons in the brainstem embrace irritability, difficulty in swallowing and spasms of the throat (these two resulting in "hydrophobia"), seizures, and delirium. Poliomyelitis is brought on by an enterovirus that produces a nonspecific gastroenteritis after which secondarily invades the anterior horn motor neurons of the spinal wire, where it causes muscular paralysis. Infection causes acute muscular paralysis (atrophy, fasciculations, fibrillation, and hyporeflexia). Postpolio syndrome happens more than 25 years later, with progressive weak point, decreased muscle mass, and ache. [newline]The arthropod-borne viruses (arboviruses) are transmitted by blood-sucking vectors corresponding to ticks and mosquitoes. These viruses represent a heterogenous group of diseases answerable for most outbreaks of epidemic encephalitis, examples being eastern and western equine encephalitis and St. Disease results from alternate folding (normal helix to irregular pleated sheet) of the usually present PrPc. They are characterised by lengthy incubation periods adopted by slowly progressive ataxia and dementia. It primarily impacts younger adults between 20 and forty years of age, with the onset of symptoms corresponding to abnormalities of vision, tremors, paresthesias, and incoordination. Early findings embrace weak point of the decrease extremities and visual abnormalities with retrobulbar ache. It ends in medial rectus palsy on tried lateral gaze and monocular nystagmus in abducting eye with convergence. Early symptoms embrace weak point and cramping, then muscle atrophy and fasciculations.
Syndromes
- Opening of the surgical cut site
- You have bruising on your breast, but did not experience any injury
- Runny nose
- Syphilis
- Muscular dystrophy - resources
- Dental problems
- Table sugar
- Bronchoscopy -- camera down the throat to see burns in the airways and lungs
- Open heart surgery
- What drugs you are taking, even drugs or herbs you bought without a prescription
Cheap urimax d 0.4/0.5 mg
Initially his wound is full of granulation tissue, which consists of proliferating fibroblasts and proliferating new blood vessels (angiogenesis). Decreased interstitial hydrostatic stress Decreased vascular permeability of capillaries Increased vascular permeability of venules Vasoconstriction of muscular arteries Vasodilation of arterioles 32. During the early stages of the inflammatory response, histamineinduced elevated vascular permeability is most likely to occur in a. Abnormal fusion of phagosomes to main lysosomes Attachment of chemicals to extracellular material to increase phagocytosis Dilation of blood vessels by chemotherapeutic medication Movement of cells toward a sure site or supply Transmigration of cells from blood vessels into tissue 46 Pathology 34. A 3-year-old boy presents with recurrent bacterial and fungal infections primarily involving his skin and respiratory tract. Examination of a peripheral blood smear reveals giant granules inside neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes. Further workup reveals ineffective bactericidal capabilities of neutrophils due to of} defective fusion of phagosomes with lysosomes. Ataxia-telangiectasia Ch�diak-Higashi syndrome Chronic granulomatous disease Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Sturge-Weber syndrome 35. Which of the next laboratory findings is most suggestive of activation of the alternate complement system quite than the classic complement system Serum C2 Decreased Normal Normal Decreased Decreased Serum C3 Normal Decreased Normal Normal Decreased Serum C4 Normal Normal Decreased Decreased Decreased 36. A 19-year-old feminine is being evaluated for recurrent facial edema, particularly around her lips. She additionally has recurrent bouts of intense stomach ache and cramps, generally related to vomiting. Laboratory examination finds decreased C4, whereas levels of C3, decay-accelerating factor, and IgE are inside regular limits. Which one of the listed substances is produced by the action of lipoxygenase on arachidonic acid, is a potent chemotactic factor for neutrophils, and causes aggregation and adhesion of leukocytes During acute inflammation, histamine-induced elevated vascular permeability causes the formation of exudates (inflammatory edema). Which one of the listed cell varieties is the most likely supply of the histamine that causes the elevated vascular permeability What sort of leukocyte actively participates in acute inflammatory processes and accommodates myeloperoxidase inside its main (azurophilic) granules and alkaline phosphatase in its secondary (specific) granules Histologic sections of lung tissue from a 68-year-old feminine with congestive heart failure and progressive breathing issues reveal quite a few hemosiderin-laden cells within the alveoli. Endothelial cells Eosinophils Lymphocytes Macrophages Pneumocytes 48 Pathology forty one. Cholesterol clefts Collagen Endothelial cells and fibroblasts Epithelioid cells Hemosiderin-laden macrophages 42. Endoscopic examination reveals an ulcerated area within the decrease portion of his esophagus. Caseating granulomatous inflammation Dysplastic epithelium Granulation tissue Squamous cell carcinoma Noncaseating granulomatous inflammation forty three. A routine H&E histologic part from an irregular white area within the anterior wall of the center of a 71-year-old male who died secondary to ischemic heart disease reveals the myocytes to be replaced by diffuse red material. It is secreted by fibroblasts and has a excessive content of glycine and hydroxyproline c. It is secreted by hepatocytes and is principally answerable for intravascular oncotic stress d. It is secreted by plasma cells and is important in mediating humoral immunity General Pathology forty nine 44. Examining her eyes reveals the lens of her left eye to be within the anterior chamber. Abnormal copper metabolism Decreased levels of vitamin D Decreased lysyl hydroxylation of collagen Defective synthesis of fibrillin Defective synthesis of sort I collagen 45. Which one of the listed modifications accurately describes the pathophysiology concerned within the production of pulmonary edema in sufferers with congestive heart failure Decreased plasma oncotic stress Endothelial injury Increased hydrostatic stress Increased vascular permeability Lymphatic obstruction 46. Which one of the listed clinical eventualities best illustrates the concept of energetic hyperemia A 22-year-old second-year medical student who develops a red face after being requested a query throughout a lecture b. A 37-year-old male who develops massive swelling of the scrotum due to of} infection with Wucheria bancrofti c. A 69-year-old male who dies secondary to progressive heart failure and at autopsy is discovered to have a "nutmeg" liver d. A 6-year-old boy who develops the sudden onset of intense scrotal ache due to of} testicular torsion. A 71-year-old feminine who develops perifollicular hemorrhages due to of} a deficiency of vitamin C 50 Pathology 47. Grossly show features of recanalization Grossly have lines of Zahn Grossly have the looks of "rooster fats" overlying "currant jelly" Microscopically appear connected to the wall of the blood vessel Microscopically have alternating layers of cells and platelets 50. Deep leg veins Lumen of left ventricle Lumen of proper ventricle Mesenteric veins Superficial leg veins General Pathology 51 51. There his left testis is discovered to be markedly hemorrhagic due to of} testicular torsion. Arterial occlusion Septic infarction the collateral blood provide of the testis the twin blood provide of the testis Venous occlusion 52. A young youngster who presents with megaloblastic anemia is discovered to have elevated orotate within the urine due to of} a deficiency of orotate phosphoribosyl transferase. The mixture of a main defect, such as bilateral renal agenesis, along with its secondary structural change is best referred to by which one of the listed phrases As a common rule, familial problems that involve abnormalities of structural proteins (rather than deficiencies of enzymes) and current throughout adulthood (rather than childhood) have what sort of inheritance pattern Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive Mitochondrial X-linked dominant X-linked recessive 52 Pathology 55. Myotonic dystrophy Limb-girdle dystrophy Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy Polymyositis fifty six. Assume that both dad and mom are carriers for the irregular gene that causes cystic fibrosis. The Hardy-Weinberg precept states that, given a frequency of a sure allele A of p and a frequency q of another allele a at the identical locus on the identical autosomal chromosome in a inhabitants with random mating (panmixia), then the variety of heterozygous carriers a. A 6-year-old feminine is being evaluated for recurrent episodes of lightheadedness and sweating due to of} hypoglycemia. Physical examination reveals an enlarged liver and a single subcutaneous xanthoma. Laboratory examination reveals elevated serum uric acid and ldl cholesterol with decreased serum glucose levels. A liver biopsy specimen reveals elevated amounts of glycogen in hepatocytes, which also have decreased levels of glucose-6-phosphatase. In tissues affected by the predominant type of Niemann-Pick disease, which one of the following is discovered at abnormally excessive levels Physical examination reveals a child with brief stature, coarse facial features (low, flat nostril, thick lips, widely spaced teeth, facial fullness), a large tongue, and clear corneas. Laboratory examination reveals elevated urinary levels of heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Metachromatic granules (Reilly bodies) are present in leukocytes from a bone marrow biopsy. Hyperphenylalaninemia Tyrosinemia Tyrosinase-positive oculocutaneous albinism Alkaptonuria Maple syrup urine disease sixty two. Which one of the listed processes is the most likely cause of an aneuploid karyotype A reciprocal translocation between two acrocentric chromosomes Deletion of both ends of a chromosome with fusion of the broken ends Division of the centromere alongside a transverse airplane Failure of homologous chromosomes or paired chromatids to separate Two breaks inside a single chromosome with reincorporating of the inverted section 63. Gross examination at the time of autopsy reveals polydactyly, a cleft lip and palate, and a single, central eye ("cyclops").
Generic urimax d 0.4mg/0.5mg
Increased lack of protein, for instance, by renal loss in the nephrotic syndrome b. Hydroperitoneum (ascites) is an irregular accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity. This noninflammatory edema fluid results from altered intravascular hydrostatic or osmotic strain. This edema fluid results from increased vascular permeability attributable to irritation. Because the metabolically energetic leukocytes eat glucose, the glucose content material is often significantly lowered. Widespread peripheral vasodilation, as occurs in sepsis or severe trauma, with hypoten sion typically being a distinguished function B. Severe hemorrhage or massive lack of fluid from the pores and skin, from intensive burns, or from severe trauma b. Loss of fluid from the gastrointestinal tract, by way of severe vomiting or diarrhea Cardiogenic shock is circulatory collapse resulting from pump failure of the left ventricle, most often attributable to massive myocardial infarction. Septic shock is most characteristically associated with gram-negative infections, which trigger gram-negative endotoxemia; also occurs with gram-positive and different infections. Initially, vasodilation may result in an overall enhance in blood move; however, signifi cant peripheral pooling of blood from peripheral vasodilation leads to relative hypo volemia and impaired perfusion. Lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin from the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria) and different bacterial products seem to induce a cascade of cytokines. A group of poisonous molecules, the so-called superantigens, produces septic shock-like manifestations. The launch of these molecules occurs in the "poisonous shock syndrome," which is most often associated with Staphylococcus aureus an infection. This constellation of find ings may also be attributable to quantity of|numerous|a variety of} different mechanisms similar to an infection, ischemia, trauma, and so on. Neurogenic shock is most often associated with severe trauma and reactive peripheral vasodilation. This stage is characterised by tissue hypoperfusion and the onset of circulatory and metabolic imbalance, including metabolic acidosis from lactic acidemia. The most necessary of these is acute tubular necrosis of the kidney, which is doubtlessly reversible with acceptable medical administration. A 40-year-old woman dies after a protracted historical past of an illness characterised by dyspnea, orthopnea, hepatomegaly, distended neck veins, and peripheral edema. The reduce surface of the liver because it seems at post-mortem is shown in the first panel. A 70-year-old man seeks medical consideration because of shortness of breath on minimal exertion. A posteroanterior chest radiograph reveals blunting of the proper costophrenic sul cus interpreted as a right-sided pleural effu sion. Microscopic examination reveals an (A) (8) (C) (D) (E) Decreased oncotic strain Left ventricular coronary heart failure Mesothelioma Pneumonia Tuberculosis 3. A 26-year-old woman dies after a brief illness starting in the late levels of labor. The mecha nism of action of this agent is the power to (A) dilate coronary arteries. This was all followed by prolonged hemorrhage from the vagina and generalized bleeding from quantity of} different sites. The changes that have been discovered inside quantity of} blood vessels most probably are (A) bone marrow emboli. Two days following a cholecystectomy, a 32-year-old hospitalized woman has sudden onset of dyspnea, pleural pain, and cough productive of frothy, blood-tinged sputum. If it have been attainable to look at a portion of the affected lung, which of the next would most probably have been discovered A 50-year-old right-handed man with a protracted historical past of rheumatic coronary heart illness with mitral stenosis and atrial fibrillation introduced to|is delivered to|is dropped at} the emergency division after collapsing to the ground at house. He is unable to communicate or stroll and has proper hemiplegia with a proper extensor plantar response. These findings most probably outcome from embolism to which of the next arteries An 86-year-old man with a historical past of recurrent urinary tract an infection presents with fever, tachypnea, tachycardia, mental obtundation, and lowered blood strain. The following day he develops dyspnea, speech difficulties, and a petechial pores and skin rash. A bedridden elderly affected person experiences the sudden onset of pleuritic pain and hemoptysis. The underlying lesion that led to this complication was most probably situated in which of the next sites Fluid is aspirated from the grossly dis tended abdomen of a 47-year-old persistent alcoholic man. The fluid is straw-colored and clear and is discovered to have a protein content material (largely albumin) of 2. Which of the next is a significant contributor to the fluid accumulation in this affected person At post-mortem, the pathologist reviews findings according to with} mitral stenosis and famous the presence of "coronary heart failure cells. During a laboratory exercise on coagula tion testing, a 23-year-old medical scholar is discovered to have a chronic bleeding time. She has had a protracted historical past of "easy bleeding," Hemodyn amic Dysfu n ction 45 with frequent bleeding of the gums, epis taxis, cutaneous bleeding, and menorrhagia. Which of the next thrombogenic processes involving platelets is most instantly impaired A 28-year-old woman is evaluated for attainable thrombophilia since she has had two episodes of deep vein thrombosis, nicely as|in addition to} two pregnancies that terminated in spontaneous abortion. This mixture of findings is most suggestive of (A) antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. The clinical findings described in the query are typical of right-sided coronary heart failure, as are the illustrations, which reveal the nutmeg-like appearance of hepatic persistent passive congestion. The gross morphologic appearance is attributable to congested centrilobular areas alternating with pale portal areas. A clear, straw-colored fluid with low protein and low specific gravity is a transudate, and the time period hydrothorax refers to the accumulation of a significant volume of transudate throughout the pleural cavities (to be detected by chest radiograph, about 200 to four hundred mL of pleural fluid must be present). The commonest explanation for hydrothorax is cardiac failure, which can be either unilateral or bilateral (bilateral is extra common). It is incumbent on the clinician to distinguish pleural transudates from exudates, the causes of each are quite completely different. Nonobstetric causes embody neoplasms or tissue damage from an infection, immunologic mechanisms, or trauma. Tissue damage can result up} from trauma similar to lung surgical procedure, from hemolysis or hemolytic transfusion reactions, and from inflammatory causes, similar to gram-negative sepsis and immune complicated illness. The historical past is that of pulmonary embolism and infarction, a danger of immobilization and the postoperative state. The infarct consists of an area of coagulative necrosis with superimposed hemorrhage, a mix referred to as a hemorrhagic, or pink, infarct. Prominent examples are the lung with its double circulation from the pulmonary and bronchial arteries and the gastrointestinal tract with its mUltiple anastomoses between branches of the mesenteric artery. When a portion of the blood supply is obstructed, different parts remain patent, which might lead to hemorrhage into the infarcted area. The findings are according to with} occlusion of the center cerebral artery, the most common web site of arrest of arterial emboli in branches of the carotid artery. Such emboli usually come up from a mural thrombus in the left atrium or left ventricle. Left atrial mural thrombi are particularly associated with mitral stenosis with atrial fibrillation. Thrombi on the junction of the interior and external carotid arteries are a explanation for thrombotic mind infarcts and a web site of origin of emboli.
Effective 0.4mg/0.5mg urimax d
Real World the excellence between the role of B-cells and T-cells could be appreciated by finding out immunodeficiency states that have an effect on} one lymphocyte class however not the opposite. The lack of B-cells results in the absence of circulating antibodies, resulting in recurrent bacterial infections. Defenses against viral and fungal disorders are regular end result of|as a outcome of} these microorganisms are typically handled by the T-cells. Circulating antibody levels are regular, however these children have impaired defenses against viral and fungal infections. Infection with the poliovirus, for instance, can depart an individual disabled for the remainder of his or her life. The former president of the United States, Franklin Roosevelt, contracted polio in the summertime of 1921 and was paralyzed for relaxation of|the remainder of} his life. So concerned was he that the paralysis can be interpreted as political weak spot, he went to extraordinary lengths to disguise it. In fact, he commissioned a particular train automotive into which the presidential limousine could possibly be} driven and carried from Washington, D. Polio used to be a widespread sickness; nonetheless, right now we hardly hear about it a extremely efficient vaccinization program, which led to the digital eradication of polio in this nation. In lively immunity, the immune system is stimulated to produce antibodies against a specific pathogen. Through pure exposure, antibodies are generated by B-cells once as} an individual becomes contaminated. Artificial vaccination also results in the manufacturing of antibodies; nonetheless, the individual never experiences true an infection. Instead, he receives an injection containing an antigen that can activate B-cells to produce antibodies to struggle the specific an infection. A latest instance is the vaccination against hen pox, which grew to become obtainable in 1995 in the United States. Prior to 1995, immunity was achieved by pure means; individuals grew to become contaminated and had been protected from future bouts of the disease. In fact, some parents had been identified to expose their children deliberately to the virus to guarantee an infection at a younger age (when the virus results in a milder form of illness). After 1995, inoculation began with a live however weakened (attenuated) form of the virus (artificial lively immunization). The immunity is transient as only the antibodies, and never the B-cells that produce them, are given to the immunized particular person. Natural examples are the switch of antibodies across the placenta throughout being pregnant to shield the fetus and the switch of antibodies from a mom to her nursing infant by way of breast milk. Real World Sometimes the organisms that cause different illnesses are so alike in structure that the immune system could be fooled-even for our profit. When Edward Jenner was making an attempt to find a treatment for smallpox, he inoculated his son with infectious particles from a special, however associated disease, cowpox. His expertise with cowpox immunized him to smallpox, thanks to the similarity of the 2 diseases! It is made up of one-way vessels that turn out to be larger as they transfer toward the center of the body (toward the heart). These vessels carry lymphatic fluid and join to comprise a large thoracic duct in the chest, which then delivers the fluid into the left subclavian vein (near the heart). We also saw in Chapter 7 that the smallest lymphatic vessels (lacteals) gather fats in the form of chylomicrons from the villi in the small intestine and ship them into the bloodstream, bypassing the liver. Along the lymphatic vessels are swellings (lymph nodes) that contain immune cells (primarily B-cells). These areas provide a spot for antigens from microbes to first interact with the adaptive immune system and allow its activation. It is sensible that this fluid ought to be checked for pathogens only earlier than being returned to the systemic highway system. In fact, physicians often uncover underlying disease by the presence of enlarged or hardened lymph nodes throughout a bodily exam. Conclusion the ability to fend off microbial invasion is important to our survival. The immune system is housed in many of} locations in the body and entails many various organs and cell types. The adaptive immune system, comprised of Tand B-lymphocytes, permits for our immune system to study from previous exposure. In lively immunization, our immune cells are stimulated in response, resulting in long-term immunity. Passive immunization results from the switch of antibodies alone; subsequently, the protection it provides is transient. They consist of granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and agranulocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes). Humoral immunity is simpler at combating bacterial infections, whereas cell-mediated immunity fights viral and fungal infections. Antibodies struggle an infection by binding to foreign antigens, thereby permitting other immune cells. The three major courses are helper T-cells, suppressor T-cells, and killer (cytotoxic) T-cells. Active immunization results in a sustained immune response mediated by B-cells, whereas the effects of passive immunization are short-lived. Natural immunization is exposure to the antigen in nature or switch of antibodies from mom to fetus. Artificial lively immunization makes use of weakened or dead types of microbes to generate an immune response without causing lively an infection. The lymphatic system is a secondary circulation system that removes extra fluid from the interstitial space. It also transports fats molecules from the intestinal epithelial cells to the bloodstream and serves as a conduit for the movement of immune cells. Active immunity requires weeks to construct, whereas passive immunity is acquired immediately. Therefore, a affected person who lacks T-cells can be prone to viral and fungal infections, as alternative (A) indicates. B the lymphocytes concerned in cell-mediated immunity are the T-lymphocytes, or T-cells. There are 4 forms of T-cells, every enjoying in} a special role in cell-mediated immunity: cytotoxic Tcells, helper T-cells, reminiscence T-cells, and suppressor T-cells. Thus, from the answer choices, the only cells not concerned in cell-mediated immunity are the plasma cells, which are differentiated immunoglobulin-secreting B-lymphocytes concerned in humoral immunity. B the primary perform of the lymphatic system is to gather extra interstitial fluid and return it to the circulatory system, maintaining the stability of body fluids. In addition, the lymphatic system absorbs chylomicrons from the small intestine and delivers them to the cardiovascular circulation. A Humoral immunity is concerned in the manufacturing of antibodies following exposure to an antigen. Antibodies acknowledge and bind to particular antigens, marking them enable them to} be recognized by particular cells referred to as phagocytes. Antibodies may cause the antigens to agglutinate and form insoluble complexes, facilitating their elimination. A Active immunity refers to the manufacturing of antibodies throughout an immune response. Active immunity conferred by vaccination, similar to when an individual is injected with a weakened, inactive, or associated form of a specific antigen, which stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies. Passive immunity, , entails the switch of antibodies either passively or by injection. An instance can be throughout being pregnant, when some maternal antibodies cross the placenta and enter fetal circulation, conferring passive immunity upon the fetus. Although passive immunity is acquired immediately, it is extremely short-lived, lasting only as long as|so long as} the antibodies flow into in blood. D the body employs quantity of|numerous|a variety of} nonspecific defense mechanisms against foreign invasion. Certain passages, such as the respiratory tract, are lined with ciliated mucus-coated epithelia, which filter and lure foreign particles. Many folks use it as a cure-all for aches and pains all through the body, and when used in moderation, it appears to work simply fantastic.
Proven urimax d 0.4/0.5 mg
The decrease finish of the uterus generally known as|often known as} the cervix connects to the vaginal canal, the place sperm is deposited throughout intercourse. As we mentioned earlier, distinction to|not like} males, females have separate excretory and reproductive tracts. Although gametocytes endure the same meiotic process in both females and males, there are some test-worthy variations to hold track of. These cells are 2n (like primary spermatocytes) and are actually frozen in prophase I. Once a girl reaches menarche, one primary oocyte per thirty days will complete meiosis I, producing a secondary oocyte and a polar physique. The division is characterized by unequal cytokinesis, which doles ample cytoplasm to one daughter (the secondary oocyte) and practically none to the other (polar body). Key Concept Remember that spermatogenesis in males is a 1:four division, whereas in females, oogenesis is 1:1. The secondary oocyte undergoes the second division to split into a mature ovum and one other polar physique, is in a position to} finally die. With respect to the scheme of meiosis we learned earlier, are 4 haploid daughter cells fashioned via oogenesis Although the ovum is the only useful gamete, all 4 would carry the haploid genetic materials prescribed by theoretical meiosis. A mature ovum is a really giant cell consisting of enormous quantities of cytoplasm and organelles. Key Concept 1 � oocyte (2n) meiosis l 2 � oocyte (n) fertilization meiosis ll ovum (n) Until menopause (usually between ages 45 and 55), women ovulate one secondary oocyte roughly every 28 days. Sperm will often survive for one to two days after ejaculation if the setting (uterine, in this case) is appropriate. The fusion of these haploid cells, often within the widest part of of} the fallopian tube, ends in restoration of the diploid chromosome quantity and a cell generally known as|often known as} a zygote. Sperm cells secrete acrosomal enzymes to digest the corona radiata and penetrate the zona pellucida (see Figure four. Ca2+ ions are launched into the cytoplasm, which in turn results in the formation of the fertilization membrane. The launch of Ca 2+ also significantly increases the metabolic fee of the ovum and soon-to-be zygote. Real World Identical twins are commonly used to study the interplay between genes and the setting. Because they share the same genetic complement, they are often studied to see how a lot of an impact the setting has in contributing to a certain condition. Multiple Births Monozygotic (Identical) Twins Monozygotic twins develop when a single zygote splits into two. If division is incomplete, conjoined twins may end result during which the two offspring are physically attached . Dizygotic (Fraternal Twins) If two eggs are launched in the same cycle, they might both be fertilized. Each zygote will implant within the uterine wall individually and develop a separate placenta, chorion, and amnion (although the placentas may fuse if the zygotes implant near one another). Conclusion We have taken a a glance at|have a look at} how cells produce extra of themselves: one of many key tenets of the Cell Theory from Chapter 1. We then moved on to asexual replica, which equally ends in genetically similar offspring. A number of processes exist for asexual replica, together with binary fission, budding, parthenogenesis, and regeneration. Sexual replica gives rise to genetically unique offspring and requires specialized cells generally known as|often known as} gametes. Their fusion ends in a zygote, whose development will be mentioned in Chapter 5. The era of these cells requires a process generally known as|often known as} meiosis, which is similar to mitosis but has test-worthy variations. We will revisit these subjects when we talk about the endocrine system, nicely as|in addition to} within the next chapter, when we talk about fetal development. Asexual replica ends in organisms which might be} genetically similar, thus severely limiting variety within the species. Asexual replica is primarily utilized by decrease organisms, such as prokaryotes, yeasts, and hydra, and in certain circumstances by some animals. Sexual replica provides for the mix of two genomes, leading to genetically unique offspring. The era of specialized intercourse cells for sexual replica gametogenesis. Meiosis is a process similar to mitosis but consists of one round of replication followed by two rounds of division. Twinning can occur and result in monozygotic (genetically identical) or dizygotic (fraternal; genetically distinct) twins. Which of the following is the right sequence of the event of a mature sperm cell Which of the following correctly pairs the stage of development of an egg cell with the totally different periods in its life cycle According to the endosymbiont speculation, mitochondria are bacterial descendants they fashioned a eukaryotic cell engulfing a prokaryotic cell. If a cure have been found that would target only most cancers cells with out affecting normal cells, at which point within the cell cycle would the treatment effectively prevent most cancers cell division During which section of the meiotic cycle does the cell have a diploid number of chromosomes Which of the following statements correctly identifies a key difference between mitosis and meiosis In metaphase of mitosis and metaphase of meiosis I, replicated chromosomes line up in single file. During anaphase of mitosis and anaphase of meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate, but sister chromatids stay attached. At the end of telophase of mitosis and the end of telophase of meiosis I, the daughter cells are similar to the mother or father cell. During metaphase of meiosis I, homologous pairs of replicated chromosomes line up. Interstitial cells-produce testosterone and other androgens Small Group Questions 1. Colchicine binds to tubulin and prevents its meeting into microtubules, while cytochalasins bind to the ends of actin filaments and forestall their elongation. B Diploid cells referred to as spermatogonia differentiate into primary spermatocytes, which endure the first meiotic division to yield two haploid secondary spermatocytes. The spermatids then endure a sequence of modifications leading to the manufacturing of mature sperm, or spermatozoa. The only answer that correctly identifies the sequence of development of a mature sperm cell is seen in (B). B From the time of start until hours before ovulation, all egg cells are arrested on the prophase stage of meiosis I. At ovulation, the egg cell has completed meiosis I and is now a haploid cell referred to as a secondary oocyte. B the spindle equipment interacts with the kinetochore fibers in order to to} align the chromosomes on the equatorial plate throughout metaphase. As such, when every chromosome is replicated, one of many chromatids will include the labeled nucleotide. When the cell undergoes mitosis, only one of many daughter cells will comprise the labeled adenine. The chromosomes are replicated in the course of the S stage, the place the S stands for synthesis. After replication, the chromosomes include two similar sister chromatids held together at a central area referred to as the centromere.
References:
- https://icesaht.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Sexual-Assault-e-book-1.pdf
- https://www.caymanchem.com/pdfs/10009172.pdf
- https://www.nwcg.gov/sites/default/files/publications/pms461.pdf
- http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/MedEd/surgery/Goals&Objectives/PediatricSurgeryMS3.pdf
.png)