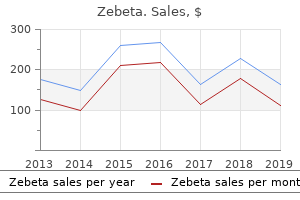
Cheap 5mg zebeta
What is the rationale for using myeloablative preparative regimens for patients like B. The rationale for top-dose myeloablative preparative regimens was much like that mentioned in the "Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation" part of this chapter. Specifically, infusion of hematopoietic stem cells circumvents dose-limiting myelosuppression, maximizing the potential worth of the steep dose-response curve to alkylating agents and radiation,2 and suppressing the host immune system. The preparative routine is designed to eradicate immunologically energetic host tissues (lymphoid tissue and macrophages) and to prevent or reduce the event of host-versusgraft reactions. Most allogeneic preparative regimens for the therapy of hematologic malignancies contain cyclophosphamide, radiation, or each. This routine is immunosuppressive and has inherent exercise in opposition to hematologic malignancies. Thus, these preparative regimens could also be preferable in these malignancies by which immunologic elimination of the malignant stem cells is possible. Chimerism is evaluated to monitor disease response and engraftment at various time factors. Chimerism is assessed within peripheral blood T cells and granulocytes and bone marrow using standard. The security and efficacy of these regimens have led to their wider utility to nonmalignant circumstances. Prospective controlled trials are wanted with stratification based mostly on comorbidities, disease characteristics, pretransplant remedy, and hematopoietic stem cell supply. In T-cell depleted transplantation, the volume of donor T cells infused into the affected person is normally insufficient to elicit a significant graft-versushost reaction. Over time, the immunologically energetic tissue between host and recipient turn out to be tolerant of each other and cease recognizing the other as international. How do supportive care methods used for myeloablative preparative regimens with an autologous graft differ from these described for an allogeneic graft? These similarities are a perform of the side effects of a myeloablative preparative routine. How do supportive care methods used for myeloablative and nonmyeloablative preparative regimens with an allogeneic graft differ? What toxicities associated with myeloablative preparative routine should be anticipated in K. These preparative regimens differ considerably in terms of the chemotherapy agents used (Tables ninety two-3 and ninety two-5) and the diploma of myelosuppression. Myelosuppression is a frequent dose-limiting toxicity for antineoplastics when administered in standard doses used to deal with cancer. After her initial analysis, a profitable search for an unre- Busulfan Seizures 18. Begin regular saline hydration 3,000 mL/m2 /day four hours earlier than cyclophosphamide and proceed for twenty-four hours after the final cyclophosphamide dose. What is the rationale for these supportive care therapies and monitoring parameters prescribed for K. Seizures are probably a direct neurotoxic impact,79 so, seizure prophylaxis is used. A variety of completely different regimens have been used, together with intermittent bolus dosing (mesna dose 20%�forty% of cyclophosphamide dose, administered for three or 4 doses) or continuous infusion regimens (mesna dose 80%�a hundred and sixty% of cyclophosphamide dose). The incidence of bloodborne infections and the usage of parenteral opioids additionally diminished outcomes. Lung injury could also be decreased by immediate therapy with etanercept, which inhibits tumor necrosis issue, and corticosteroids. In severe instances, parenteral opioid analgesics for pain relief104 and total parenteral vitamin to prevent the event of dietary deficits could also be wanted. Because mucositis may be worsened by superinfection, good oral hygiene should be practiced. Her liver perform tests proceed to rise slowly, until day +18 once they attain the following peak values: total bilirubin 5. This is normally distinguished from cyclophosphamide-induced syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone by the point course relative to administration of the preparative routine. Hyperbilirubinemia, which additionally occurs in just about all patients, follows the onset of weight gain and normally appears within 10 days after hematopoietic stem cell infusion. Ascites, right upper quadrant pain, and encephalopathy lag behind changes in liver perform tests and develop within 10 to 15 days after infusion of hematopoietic stem cells. Although varied danger components have been recognized, their association is variable, and conflicting reviews of their association may be discovered. The substitution of fludarabine for cyclophosphamide together with busulfan. There is interpatient variability of their metabolism and clearance, along with pharmacodynamic relationships, although the relationships differ within the varied preparative regimens. A delicate stability between host and donor effector cells is necessary since residual host-versus-graft results might lead to graft rejection. Graft rejection is rare in leukemia patients receiving myeloablative preparative routine with a histocompatible allogeneic donor. Current research is focusing on quantitative chimerism monitoring, particularly evaluating the % donor chimerism, which can be a tool on which to base medical interventions. For example, a maculopapular rash, which can happen as a manifestation of an allergic reaction to antibiotics, normally begins on the trunk or upper extremities and rarely presents on the palms of the palms or soles of the feet. Diarrhea may be caused by chemotherapy, radiation, an infection, or antibiotic remedy. The severity of organ involvement is decided first (Table ninety two-6), after which an overall grade is established based mostly on quantity and extent of concerned organs (Table ninety two-7). Methotrexate, cyclosporine or tacrolimus, and corticosteroids are the agents most commonly incorporated into mixture immunosuppressive regimens. Although the varied mixture immunosuppressive regimens differ barely by drug, dose, and mixture, several pointers are consistent throughout all regimens. This schedule is recommended because of the known mechanism of Combination Regimens of Prophylaxis of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease Dosing Examples 1. Thus, cautious monitoring for drug interactions with the calcineurin inhibitors is warranted. Doses are normally reduced by 50% if the SrCr concentration doubles above baseline and is withheld for SrCr concentrations >2 mg/dL. Tapering schedules for cyclosporine or tacrolimus and corticosteroids differ broadly among establishments. By this time, immunologic tolerance has developed, and patients now not require immunosuppressive remedy. On day +18, a tacrolimus stage is drawn right earlier than the morning dose and is reported to be 15 ng/mL. Adjustments in tacrolimus dosing for elevated SrCr should be made in a manner much like that described for cyclosporine. Cyclosporine trough concentrations >four hundred ng/mL (via radioimmunoassay and excessive-stress liquid chromatography assay) are associated with a better incidence of nephrotoxicity in some collection. Recommendations for dose adjustments should be based mostly on tacrolimus concentrations and SrCr concentration. Dosage adjustments should be made for SrCr, regardless of tacrolimus concentration, as recommended previously. No normal dosage adjustment schedule exists, but most facilities undertake their very own standardized approach. Tacrolimus concentrations >20 ng/mL have been associated with elevated danger of toxicity, primarily nephrotoxicity. Laboratory tests reveal an elevated alkaline phosphatase and total bilirubin concentration. The medical scoring system makes use of a numerical worth of zero to 3, with extra severe signs having a better, quantity. A global rating is calculated by together with the number of organs concerned and the severity within every affected organ.
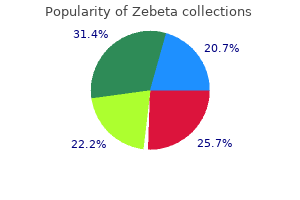
Trusted zebeta 2.5 mg
Spasm of sigmoid colon Spasm in the sigmoid colon (spastic colon) prevents its motility, leading to constipation. Dysfunction of myenteric plexus in giant gut � megacolon Megacolon is the condition characterised by distension and hypertrophy of colon, related to constipation. It is brought on by the absence or injury of ganglionic cells in myenteric plexus, which causes dysfunction of myenteric plexus. If not treated immediately, the appendix could rupture and the irritation will spread to the entire physique, resulting in severe issues, generally even death. Usual standard remedy for appendicitis is appendectomy (surgical elimination of appendix). Abdominal ache Diarrhea with blood in the stools Early fatigue Loss of urge for food and weight Arthritis and osteoporosis Eye irritation Liver diseases like hepatitis, cirrhosis, etc. Drugs the medication like diuretics, ache relievers (narcotics), antihypertensive medication (calcium channel blockers), antiparkinson medication, antidepressants and the anticonvulsants trigger constipation. Appendix is a small, worm-like appendage, projecting from cecum of ascending colon. It additionally happens during blockage of connection between appendix and large gut by feces, foreign physique or tumor. Lubrication and moistening of dry food by saliva, in order that the bolus may be simply swallowed 4. Muscles of mastication are supplied by mandibular division of 5th cranial (trigeminal) nerve. In this stage, the bolus from mouth passes into pharynx by the use of collection of actions. Chapter 43 t Movements of Gastrointestinal Tract 271 Sequence of Events during Oral Stage 1. Forceful contraction of tongue in opposition to the palate produces a constructive stress in the posterior part of oral cavity. Since pharynx communicates with mouth, nostril, larynx and esophagus, during this stage of deglutition, bolus from the pharynx can enter into four paths: 1. However, due to varied coordinated actions, bolus is made to enter solely the esophagus. Upward into Nasopharynx Movement of bolus into the nasopharynx from pharynx is prevented by elevation of soft palate along with its extension referred to as uvula. Forward into Larynx Movement of bolus into the larynx is prevented by the next actions: i. Deglutition apnea or swallowing apnea is the arrest of breathing during pharyngeal stage of deglutition. Entrance of Bolus into Esophagus As the other three paths are closed, the bolus has to cross solely via the esophagus. At the identical time, peristaltic contractions start in the pharynx due to the contraction of pharyngeal muscle tissue iv. All the factors talked about above act together in order that, bolus strikes simply into the esophagus. The whole course of takes place inside 1 to 2 seconds and this course of is only involuntary. Movements of esophagus are particularly organized for this operate and the actions are referred to as peristaltic waves. Primary Peristaltic Contractions When bolus reaches the higher part of esophagus, the peristalsis begins. After origin, the peristaltic contractions cross down via the rest of the esophagus, propelling the bolus in direction of abdomen. Pressure developed through the main peristaltic contractions is important to propel the bolus. But immediately, the stress becomes constructive and increases as much as 10 to 15 cm of H2O. Secondary Peristaltic Contractions If the primary peristaltic contractions are unable to propel the bolus into the abdomen, the secondary peristaltic contractions appear and push the bolus into abdomen. Secondary peristaltic contractions are induced by the distention of higher esophagus by the bolus. After origin, these contractions cross down like the primary contractions, producing a constructive stress. When bolus enters this part of the esophagus, this sphincter relaxes in order that the contents enter the abdomen. After the entry of bolus into the abdomen, the sphincter constricts and closes the decrease end of esophagus. The rest and constriction of sphincter occur in sequence with the arrival of peristaltic contractions of esophagus. Stimulus When the bolus enters the oropharyngeal region, the receptors current on this region are stimulated. Afferent Fibers Afferent impulses from the oropharyngeal receptors cross through the glossopharyngeal nerve fibers to the deglutition center. Center Deglutition center is at the floor of the fourth ventricle in medulla oblongata of brain. Efferent Fibers Impulses from deglutition center travel via glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves (parasympathetic motor fibers) and reach soft palate, pharynx and esophagus. Response the reflex causes upward motion of soft palate, to close nasopharynx and upward motion of larynx, Chapter 43 t Movements of Gastrointestinal Tract 273 to close respiratory passage in order that bolus enters the esophagus. Mechanical obstruction of esophagus due to tumor, strictures, diverticular hernia (out pouching of the wall), etc. Decreased motion of esophagus due to neurological disorders such as parkinsonism iii. Muscular disorders resulting in difficulty in swallowing during oral stage or esophageal stage. Esophageal Achalasia or Achalasia Cardia Esophageal achalasia or achalasia cardia is a neuromuscular illness, characterised by accumulation of food substances in the esophagus stopping regular swallowing. It is due to the failure of decrease esophageal (cardiac) sphincter to chill out during swallowing. Hunger contractions are the peristaltic waves superimposed over the contractions of gastric easy muscle as a whole. This sort of peristaltic waves is completely different from the digestive peristaltic contractions. The digestive peristaltic contractions usually occur in physique and pyloric parts of the abdomen. Hunger contractions are of three varieties: Type I Hunger Contractions Type I starvation contractions are the primary contractions to appear in the empty abdomen, when the tone of the gastric muscle tissue is low. Tone increases in abdomen if food consumption is postponed, even after the looks of the sort I contractions. These contractions appear when the starvation becomes severe and the tone increases to a fantastic extent. Regurgitation is due to the weakness or incompetence (failure to constrict) of decrease esophageal sphincter. Heart burn or pyrosis (painful burning sensation in chest due to regurgitation of acidic gastric content into esophagus) ii. Its significance is to accommodate the food simply, without much increase in stress contained in the abdomen. It begins from the decrease part of the physique of abdomen, passes via the pylorus till the pyloric Initially, the contraction appears as a slight indentation on the higher and lesser curvatures and travels in direction of pylorus. Each peristaltic wave takes about one minute to travel from the point of origin to the point of ending. Acid chyme is emptied from abdomen into the gut slowly, with the help of peristaltic contractions. This sluggish emptying is important to facilitate the ultimate digestion and most (about 80%) absorption of the digested food supplies from small gut. Gastric emptying happens due to the peristaltic waves in the physique and pyloric part of the abdomen and simultaneous rest of pyloric sphincter.
| Comparative prices of Zebeta | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | Albertsons | 475 |
| 2 | Dollar General | 387 |
| 3 | J.C. Penney | 726 |
| 4 | Ace Hardware | 771 |
| 5 | True Value | 854 |
| 6 | Aldi | 270 |
Quality zebeta 5 mg
A substantial discount in coronary blood flow causes ischemia adopted by necrosis. A delicate discount in blood flow causes only ischemia and it may not be enough to cause necrosis of myocardium. Cause Coronary occlusion is caused by atherosclerosis, a condition related to deposition of cholesterol on the partitions of the artery. Because of the atherosclerotic plaque, the lumen of the coronary artery Chapter 108 t Coronary Circulation 633 it produces some transient (short lived) mechanical disturbances or dysfunction of the center. Pain begins beneath the sternum and radiates to the surface of left arm and left shoulder. It is as a result of, heart and left arm develop from the identical dermatomal section in embryo. Metabolites and other pain producing substances like substance P, histamine and kinin stimulate the sensory nerve endings, leading to pain. Inferior cervical sympathetic nerve fibers (Chapter one hundred and one) carrying the sensations of pain (or stretch) from the center reach the posterior grey horn of first four thoracic segments of spinal wire 2. Here, these fibers synapse with second order neurons (substantial gelatinosa of Rolando) of lateral spinothalamic tract three. Fibers from substantial gelatinosa of Rolando kind lateral spinothalamic tract and reach the sensory cortex via thalamus. If hypoxia in myocardium is relieved by coronary collateral circulation or by remedy, the pain producing substances are washed away by blood flow. The workload of the center increases in circumstances like train and emotional outburst. When the frequency of angina assault increases, the patient is susceptible to develop acute myocardial infarction. Vasodilator drugs: Vasodilator drugs like glycerol trinitrate or sodium nitrite relieve the pain by dilating coronary arteries. However, the main therapeutic impact of such drugs is to dilate splanchnic blood vessels, which cause discount in venous return, cardiac output, workload of the center and oxygen consumption in myocardium in order that, launch of pain promoting substances is inhibited. When calcium inflow is blocked, the myocardial contractility and workload of the center are decreased. Sympathetic blocking agents: Sympathetic blocking agents like propranolol (beta blockers) block the betaadrenergic receptors and inhibit the cardiac activity. This decreases heart fee, stroke quantity, workload on heart and oxygen consumption. Aortic-coronary artery bypass graft: Part of myocardium affected by coronary occlusion is detected by angiography. Then, the anastomosis is made between aorta and the coronary artery beyond occlusion, by a way called aortic coronary artery bypass graft. Stoppage of blood flow to mind for 5 seconds results in unconsciousness and for 5 minutes results in irreparable harm to the mind cells. The subject is requested to inhale nitrous oxide at a low concentration, which is less than the quantity required for anesthesia. After inhalation of the gasoline for about 10 minutes, the quantity of nitrous oxide retained within the mind tissues turns into equal to the quantity of nitrous oxide current in cerebral venous blood. It is about 15% to 16% of total cardiac output and about 50 to 55 mL/one hundred g of mind tissue per minute. Chapter 109 t Cerebral Circulation 635 cerebral venous blood and the cerebral blood flow is calculated by the formula: Cerebral blood flow = Amount of N2O taken by mind Arteriovenous distinction of N2O and detecting the resonant alerts (summation of the spinning energies within the living cells) from the tissues. Since the photographs are very clear, this method is beneficial for scanning soft tissues, mind, spinal wire, abdomen, joints and malignant tissues. By measuring the radioactivity within the mind tissues using radioactive detectors (scintillation counter), the blood flowing via each area of mind is set. Advantage of this technique is that the blood flow to about 250 areas of cerebral cortex may be measured by utilizing many radioactive detectors. Radioactive xenon and 2-deoxyglucose are the commonly used radioactive substances to measure the cerebral blood flow. Tomography scanning is a process which mixes many two dimensional X-ray pictures to generate cross sectional pictures of different organs or regions of the body. Advancement of expertise resulted together of many three dimensional X-ray pictures of body constructions and organs together with mind. A short-lived radioactive substance called radionuclide mixed with sugar is injected into the patient. Radionuclide emits positrons (antiparticle or antimatter counterpart of electron). Cerebral blood flow is immediately proportional to the stability between effective perfusion pressure and the vascular resistance in mind. Effective Perfusion Pressure Effective perfusion pressure is the stability between the imply arterial blood pressure and venous pressure across the organ, divided by resistance (Chapter 102). Since venous pressure is zero in mind, imply arterial blood pressure plays an necessary role in regulating cerebral blood flow. Autoregulation is feasible in mind if the imply arterial pressure is within the vary of 60 mm Hg and a hundred and forty mm Hg. Cerebral Vascular Resistance When the vascular resistance is extra, the blood flow to the mind is less. Resistance to blood flow in mind is offered by intracranial pressure, cerebrospinal fluid pressure and viscosity of blood. These pressures are elevated in circumstances like head 636 Section 8 t Cardiovascular System harm. However, extreme ischemic results are prevented by some protective reflexes corresponding to Cushing reflex. Cushing reflex Cushing reflex is a protective reflex that helps save the mind tissues from ischemic results during the periods of reduced cerebral blood flow. When cerebral blood flow decreases by the compression of cerebral arteries, the cerebral ischemia develops. Local hypoxia and hypercapnea activate vasomotor heart, leading to peripheral vasoconstriction and rise within the arterial pressure. Thus, Cushing reflex plays crucial role in maintaining the cerebral blood flow. Cushing reflex operates only when the rise in arterial blood pressure is proportional to increase in intracranial pressure. When the increase in intracranial pressure may be very excessive and if it exceeds the arterial blood pressure, this protective mechanism fails. And the cerebral ischemia turns into extreme, leading to irreversible harm of the mind tissues. Viscosity Increase within the viscosity of blood as in polycythemia, increases the cerebral vascular resistance and blood flow decreases. When viscosity decreases as within the case of anemia, the resistance is decreased and blood flow increases. Thus, the cerebral blood flow is inversely proportional to the viscosity of blood. Carbon dioxide is crucial issue, because it causes dilatation of cerebral blood vessels, leading to increase in blood flow. When arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide rises above forty five mm Hg, the cerebral blood flow increases. Carbon dioxide combines with water to kind carbonic acid, which dissociates into bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ion. In pathological circumstances like hypertension, the sympathetic nerves cause constriction of cerebral blood vessels, leading to discount in blood flow. Ischemic stroke, which happens due to interruption of blood flow to a part of mind by thrombus or atherosclerotic embolus 2. Hemorrhagic stroke, which develops by the rupture of a blood vessel within the mind and spilling of blood into the encircling areas. Heart illness Hypertension High cholesterol in blood High blood sugar (diabetes mellitus) Heavy smoking Heavy alcohol consumption.
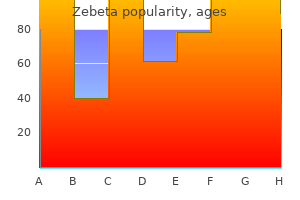
Generic zebeta 2.5mg
Although the World Health Organization acknowledges that there are >10 forms of primary pleuropulmonary malignancies, 4 major forms of carcinomas account for as much as ninety five% of all lung cancers. Cigarette smoking is the predominant reason for lung cancer worldwide, and the danger seems to enhance with the variety of cigarettes smoked each day. Although the danger of develop- By far, crucial intervention for stopping lung cancer is to avoid or stop smoking and to avoid secondary smoke whenever potential. Presently, no medical or scientific organization recommends testing for early lung cancer detection in asymptomatic people. Therefore, this can be very necessary to set up a histologic analysis before contemplating treatment (Table ninety one-four). The solely exception is the rare patient who presents with very early stage disease. Such sufferers might profit by resection of the tumor followed by mixture chemotherapy. In disease limited to the thoracic cavity, optimal chemotherapy regimens produce response charges of 85% to ninety five%, with 50% to 60% of sufferers achieving an entire response. Response charges are considerably lower for sufferers with disease outdoors the thoracic cavity, and the median survival is only 7 to eleven months. Most present first-line regimens include cisplatin or carboplatin in combination with etoposide. Because this is a chemosensitive disease, sufferers sometimes present proof of response within days. Follow-up care of a patient receiving chemotherapy ought to include the following: (a) evaluation of chemotherapyassociated toxicities. Because nephrotoxicity is the standard dose-limiting toxicity of cisplatin, renal operate have to be evaluated. Therapy should be continued if the tumor is responding to treatment and discontinued or modified with proof of tumor development. This will help set up a prognosis and establish tumor lesions that can be monitored to evaluate the response to therapy. Long-time period survival charges appear to be similar for sufferers who receive four to 6 months of treatment and those that receive 12 to 24 months. In addition, sufferers who receive a shorter length of chemotherapy exposure are less prone to suffer major toxicities. Today, the topoisomerase inhibitors (topotecan or irinotecan), taxanes, paclitaxel or docetaxel, gemcitabine or vinorelbine are probably the most broadly used second-line agents. Clinical trials have demonstrated that prophylactic cranial irradiation significantly reduces the incidence of symptomatic mind metastases and prolongs disease-free and total survival. Response is usually re-evaluated after two cycles of chemotherapy and, if a response or steady disease is famous, treatment is sustained for as much as eight cycles. If disease development is clear, second-line therapy with agents not previously received or palliative radiation therapy is beneficial. The routine containing bevacizumab resulted in vital enhancements in median survival (12. In them, erlotinib in combination with chemotherapy significantly improved total survival. A statistically vital survival advantage was seen for the mixed modality therapy. Until lately, no extra treatment past surgical procedure was recognized to be helpful. A detailed historical past revealed that she had skilled increasing belly girth without vital weight acquire and a change in her traditional bowel habits. Pathologic examination of the mass determined it to be epithelial carcinoma of the ovary. The large intra-belly mass and numerous peritoneal tumor implants were resected during surgical procedure; nevertheless, a number of small (<0. Ovarian cancer is the fifth commonest reason for cancer and cancer deaths in women. Greater than ninety% are epithelial cancers, arising from the epithelial layer that covers the surface of the ovaries, whereas the rest are both germ cell or stromal tumors. Postmenopausal women (median age, sixty three years) are most probably to develop epithelial ovarian cancer. Factors that appear to enhance the danger of ovarian cancer include optimistic family historical past, nulliparity or a low variety of pregnancies, first child after age 35, extended use of ovulation-inducing drugs, and increasing age. Ovarian carcinoma, nevertheless, normally has prolonged past the pelvis on the time of analysis. Pain, belly distention, and vaginal bleeding are the most common signs in sufferers with advanced disease. At the time of analysis, seventy five% of girls with ovarian cancer have proof of unfold past the ovaries and, in 60%, the cancer has unfold past the pelvis. The dramatic decrease in invasive cervical cancers along with a 70% reduction in mortality, nevertheless, confirms the efficacy of the Pap check as a screening device for uterine cervical cancer. Abdominal ultrasounds have been investigated, however produce a excessive variety of false�optimistic findings, even in excessive-threat populations. Currently, none of those tests are beneficial for screening women in the common population. Other candidate biomarkers are beneath investigation for the early detection of ovarian cancer. She has all the time had routine annual the first goal in the treatment of sufferers with epithelial ovarian cancer is perfect surgical cytoreduction of metastatic disease. Optimal debulking is outlined as removal of all disease 1 cm or larger in diameter. The quantity of residual disease after primary surgical procedure is usually thought of crucial modifiable prognostic factor that influences survival of sufferers with advanced disease. Single agents that have exhibited exercise in the treatment of advanced ovarian cancer include cisplatin, paclitaxel, docetaxel, topotecan, gemcitabine, and altretamine. Several research have proven that carboplatin and cisplatin have equivalent benefits when used with paclitaxel. Although ovarian cancer is initially sensitive to chemotherapy, most women will expertise a relapse of their disease. At the time of recurrence, the median survival is 2 years; subsequently, the primary goal of therapy is management of signs. The relapse-free interval after completion of platinum-primarily based therapy (the platinum-free interval) has been recognized as a predictor of the chance of subsequent response to chemotherapy. Patients with disease that recurs within 6 months after treatment are unlikely to profit from extra therapy with the first-line agents. Several agents have proven exercise in the second-line setting, together with topotecan, liposomal doxorubicin, taxanes, gemcitabine, oral etoposide, altretamine, and ifosfamide. Response charges range from sixteen% to 30% when these agents are administered as single agents; mixture therapy has not been proven to be simpler than any single agent evaluated to date. Bevacizumab has proven promising exercise, however its use has been limited by the prevalence of bowel perforation. He is referred to a urologist for cystoscopy, and the biopsy is according to multifocal, transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder, grade 3. Commonly, tumor plaques are attached to the underside of the diaphragm in addition to to the exterior of other organs inside the belly cavity. Even following meticulous surgical removal of the tumor, some residual disease almost all the time stays. Although drug delivery to the tumor is primarily by surface diffusion, agents which are then absorbed systemically from the peritoneum also attain the tumor through capillary flow. The solely symptom many sufferers expertise before analysis is bladder irritation; in women, this can be mistaken for interstitial cystitis. Microscopic or gross hematuria is commonly the discovering that prompts the patient to seek medical intervention. Patients with extra extensive tumors might expertise flank ache, constipation, or lower extremity edema. Approximately 70% of the newly diagnosed circumstances of bladder cancer will current with superficial disease. Although resection is extremely efficient in eradicating present lesions, 30% to 85% of sufferers ultimately develop new lesions. Adjuvant intravesical therapy is beneficial for prime-threat sufferers to cut back the danger of recurrence. This route places excessive concentrations of the drug into direct contact with the bladder mucosa and might delay or prevent development of disease (which may require cystectomy or systemic chemotherapy).
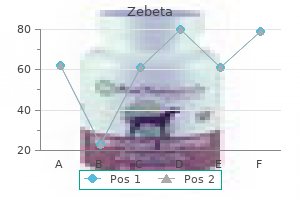
Best 10mg zebeta
Mesna versus hyperhydration for the prevention of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in bone marrow transplantation. American Society of Clinical Oncology medical apply pointers for using chemotherapy and radiotherapy protectants. Comparison of mesna with compelled diuresis to forestall cyclophosphamide induced haemorrhagic cystitis in marrow transplantation: a prospective randomised examine. Mesna in contrast with steady bladder irrigation as uroprotection during excessive-dose chemotherapy and transplantation: a randomized trial. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral sodium 2-mercaptoethane sulphonate (mesna) in normal topics. Pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide and its metabolites in bone marrow transplantation patients. Urinary elimination of cyclophosphamide alkylating metabolites and free thiols following two administration schedules of excessive-dose cyclophosphamide and mesna. Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome following myeloablative chemotherapy and autologous transplantation. Acute lung harm after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: is the lung a goal of acute graft-versus-host disease? Modification of the pharmacokinetics of excessive-dose cyclophosphamide and cisplatin by antiemetics. Pharmacokinetic interaction between ondansetron and cyclophosphamide during excessive-dose chemotherapy for breast most cancers. Cyclophosphamide metabolism, liver toxicity, and mortality following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Mucositis related to stem cell transplantation: current status and progressive approaches to management. Updated medical apply pointers for the prevention and therapy of mucositis. Clinical and pharmacologic results of excessive dose single agent busulfan with autologous bone marrow assist in the therapy of strong tumors. Toxic harm to hepatic sinusoids: sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (veno-occlusive disease). Veno-occlusive disease of the liver and multiorgan failure after bone marrow transplantation: a cohort examine of 355 patients. Once-daily intravenous busulfan given with fludarabine as conditioning for allogeneic stem cell transplantation: examine of pharmacokinetics and early medical outcomes. Decreased incidence of hepatic venoocclusive disease and fewer hemostatic derangements related to intravenous busulfan vs oral busulfan in adults conditioned with busulfan + cyclophosphamide for allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Cyclophosphamide following focused oral busulfan as conditioning for hematopoietic cell transplantation: pharmacokinetics, liver toxicity, and mortality. Ursodiol prophylaxis against hepatic issues of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-managed trial. The Japanese multicenter open randomized trial of ursodeoxycholic acid prophylaxis for hepatic veno-occlusive disease after stem cell transplantation. Ursodeoxycholic acid for the prevention of hepatic issues in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Effect of gastrointestinal irritation and age on the pharmacokinetics of oral microemulsion cyclosporin A in the first month after bone marrow transplantation. Marrow transplantation for continual myelocytic leukemia: a managed trial of cyclosporine versus methotrexate for prophylaxis of graft-versus-host disease. What position for prednisone in prevention of acute graft-versus-host disease in patients undergoing marrow transplants? Relationship of tacrolimus whole blood ranges to efficacy and safety outcomes after unrelated donor marrow transplantation. Use of cyclosporin A in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for extreme aplastic anemia. Acute graft-versus-host disease: pathophysiology, medical manifestations, and management. Treatment of human acute graftversus-host disease with antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine with or without methylprednisolone. Early therapy of acute graftversus-host disease with excessive- or low-dose 6methylprednisolone: a multicenter randomized trial from the Italian Group for Bone Marrow Transplantation. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on standards for medical trials in continual graft-versus-host disease: I. Respiratory virus infections after marrow transplant: the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center experience. Incidence and outcome of bacterial and fungal infections following nonmyeloablative in contrast with myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a matched control examine. Efficacy of quinolone prophylaxis in neutropenic most cancers patients: a meta-evaluation. A managed trial of fluconazole to forestall fungal infections in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Efficacy and safety of fluconazole prophylaxis for fungal infections after marrow transplantation: a prospective, randomized, doubleblind examine. Epidemiology and outcome of mould infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Evidence-primarily based evaluation of primary antifungal prophylaxis in patients with hematologic malignancies. The prophylactic position of intravenous and lengthy-time period oral acyclovir after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Valacyclovir for the prevention of cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a single establishment retrospective cohort evaluation. Valacyclovir prophylaxis for the prevention of Herpes simplex virus reactivation in recipients of progenitor cells transplantation. Varicella-zoster infection after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: incidence, threat factors and prevention with low-dose acyclovir and ganciclovir. Ganciclovir prophylaxis to forestall cytomegalovirus disease after allogeneic marrow transplant. Cytomegalovirus pp65 antigenemia-guided early therapy with ganciclovir versus ganciclovir at engraftment after allogeneic marrow transplantation: a randomized double-blind examine. Successful modification of a pp65 antigenemia-primarily based early therapy technique for one hundred twenty. Defibrotide for the therapy of hepatic veno-occlusive disease: results of the European compassionate-use examine. Multi-institutional use of defibrotide in 88 patients after stem cell transplantation with extreme veno-occlusive disease and multisystem organ failure: response without vital toxicity in a excessive-threat inhabitants and factors predictive of outcome. Second hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for the therapy of graft failure, graft rejection or relapse after allogeneic transplantation. Current status of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation after nonmyeloablative conditioning. Survival after transplantation of unrelated donor umbilical wire blood is similar to that of human leukocyte antigen-matched unrelated donor bone marrow: results of a matched-pair evaluation. Comparison of outcomes of unrelated bone marrow and umbilical wire blood transplants in kids with acute leukemia. Eurocord and International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry Working Committee on Alternative Donor and Stem Cell Sources. Cyclosporine as prophylaxis for graft-versus-host disease: a randomized examine in patients undergoing marrow transplantation for acute nonlymphoblastic leukemia. Methotrexate and cyclosporine in contrast with cyclosporine alone for prophylaxis of acute graft versus host disease after marrow transplantation for leukemia. Cyclosporine, methotrexate, and prednisone in contrast with cyclosporine and prednisone for prophylaxis of acute graft-versus-host disease. Prophylactic antithymocyte globulin reduces the chance of continual graftversus-host disease in various-donor bone marrow transplants. Early therapy with ganciclovir to forestall cytomegalovirus disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.
Syndromes
- Delayed growth
- Indirect bilirubin levels
- Never leave a campfire unattended.
- Heartbeat - irregular
- Neuropsychological tests
- Had their spleen removed
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) II
- Congestive heart failure
- Joint pain (arthralgia)
Best 10 mg zebeta
And, the internal surface of the protein molecule (with sodium ions) faces the outer aspect of the cell. Electrogenic activity of Na+-K+ pump Na+-K+ pump strikes three sodium ions outdoors the cell and two potassium ions inside cell. Continuous activity of the sodium-potassium pumps causes discount in the number of positively charged ions contained in the cell leading to increase in the negativity contained in the cell. Transport of Calcium Ions Calcium is actively transported from inside to outdoors the cell by calcium pump. Calcium pumps are additionally current in some organelles of the cell corresponding to sarcoplasmic reticulum in the muscle and the mitochondria of all the cells. Transport of Hydrogen Ions Hydrogen ion is actively transported across the cell membrane by the carrier protein called hydrogen pump. The hydrogen pumps that are current in two important organs have some practical significance. Stomach: Hydrogen pumps in parietal cells of the gastric glands are involved in the formation of hydrochloric acid (Chapter 38) 2. Kidney: Hydrogen pumps in epithelial cells of distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts are involved in the secretion of hydrogen ions from blood into urine (Chapter 54). When sodium is transported by a carrier protein, one other substance can be transported by the same protein concurrently, both in the same course (of sodium motion) or in the other way. Chapter 3 t Transport through Cell Membrane Secondary active transport is of two sorts: 1. Sodium Cotransport Sodium cotransport is the process by which, along with sodium, one other substance is transported by a carrier protein called symport. And the power released by the motion of sodium is utilized for motion of one other substance. Substances carried by sodium cotransport are glucose, amino acids, chloride, iodine, iron and urate. Carrier protein for sodium cotransport Carrier protein for the sodium cotransport has two receptor websites on the outer surface. Among the two websites, one is for binding of sodium and one other website is for binding of other substance. It causes conformational modifications in the carrier protein, so that sodium and glucose are released into the cell. Sodium cotransport of glucose occurs throughout absorption of glucose from the intestine and reabsorption of glucose from the renal tubule. Sodium cotransport of amino acids Carrier proteins for the transport of amino acids are different from the carrier proteins for the transport of glucose. For the transport of amino acids, there are five sets of carrier proteins in the cell membrane. Each one carries different amino acids depending upon the molecular weight of the amino acids. Sodium cotransport of amino acids additionally occurs in the course of the absorption of amino acids from the intestine and reabsorption from renal tubule. Sodium Counter Transport Sodium counter transport is the process by which the substances are transported across the cell membrane in exchange for sodium ions by carrier protein called antiport. Sodium-calcium counter transport: In this, sodium and calcium ions move in reverse instructions with the assistance of a carrier protein. Sodium-hydrogen counter transport: In this technique, the hydrogen ions are exchanged for sodium ions and this happens in the renal tubular cells. The sodium ions move from tubular lumen into the tubular cells and the hydrogen ions move from tubular cell into the lumen (Figs 3. Other counter transport systems: Other counter transport systems are sodium-magnesium counter transport, sodium-potassium counter transport, calcium-magnesium counter transport, calcium-potassium counter transport, chloridebicarbonate counter transport and chloridesulfate counter transport. Macromolecules (in the type of droplets of fluid) bind to the outer surface of the cell membrane ii. Engulfed droplets are converted into vesicles and vacuoles, which are called endosomes. Primary lysosome in the cytoplasm fuses with endosome and forms secondary lysosome vii. Now, hydrolytic enzymes current in the secondary lysosome are activated leading to digestion and degradation of the endosomal contents. Phagocytosis Phagocytosis is the process by which particles larger than the macromolecules are engulfed into the cells. Larger micro organism, larger antigens and other larger international bodies are taken contained in the cell via phagocytosis. Only few cells in the physique like neutrophils, monocytes and the tissue macrophages present phagocytosis. When micro organism or international physique enters the physique, first the phagocytic cell sends cytoplasmic extension (pseudopodium) around micro organism or international physique ii. Hydrolytic enzymes current in the secondary lysosome are activated leading to digestion and degradation of the phagosomal contents. Pinocytosis Pinocytosis is a process by which macromolecules like micro organism and antigens are taken into the cells. Receptor-mediated Endocytosis Receptor-mediated endocytosis is the transport of macromolecules with the assistance of a receptor protein. Surface of cell membrane has some pits which contain a receptor protein called clathrin. Together with a receptor protein (clathrin), every pit is known as receptor-coated pit. Ligand molecules strategy the cell and bind to receptors in the coated pits and type ligandreceptor advanced. Primary lysosome in the cytoplasm fuses with endosome and forms secondary lysosome. Now, the hydrolytic enzymes current in secondary lysosome are activated leading to release of ligands into the cytoplasm. Receptor-mediated endocytosis play an important role in the transport of several types of macromolecules into the cells, viz. Hormones: Growth hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, prolactin, insulin, glucagon, calcitonin and catecholamines ii. Toxins and micro organism: Cholera toxin, diphtheria toxin, pseudomonas toxin, recin and concanavalin A v. Viruses: Rous sarcoma virus, semliki forest virus, vesicular stomatitis virus and adenovirus vi. Some of the receptor-coated pits in cell membrane are coated with one other protein called caveolin as an alternative of clathrin. In this process, the substances are extruded from cell with out passing through the cell membrane. Secretory substances of the cell are stored in the type of secretory vesicles in the cytoplasm. When required, the vesicles strategy the cell membrane and get fused with the cell membrane. Role of Calcium in Exocytosis Calcium ions play an important role in the course of the release of some secretory substances corresponding to neurotransmitters. Mechanism of Transcytosis Cell encloses the extracellular substance by invagination of the cell membrane to type a vesicle. Vesicle then strikes across the cell and thrown out through reverse cell membrane via exocytosis. Transcytosis entails the receptor-coated pits as in receptor-mediated endocytosis. Transcytosis plays an important role in selectively transporting the substances between two environments across the cells with none distinct change in the composition of those environments. Example of this sort of transport is the motion of proteins from capillary blood into interstitial fluid across the endothelial cells of 1. Transport of synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters from the nerve cell physique to synaptic terminal 2. Transport of viruses and toxins to the interior of the cell for its own detriment.
Generic zebeta 10 mg
Transdermal delivery of molecules is restricted by full dermis, not simply stratum corneum. Transdermal protein delivery by a coadministered peptide identified through phage display. Size and stability optimization for polyurethane nanostructures used as transdermal drug vehicle. Nanodesign of olein vesicles for the topical delivery of the antioxidant resveratrol. Intracellular delivery of major histocompatibility complex class I-binding epitopes: Dendritic cells loaded and matured with cationic peptide/poly(I:C) complexes effectively activate T cells. Evaluation of histologic and electron microscopic adjustments after novel therapy using mixed microdermabrasion and ultrasound-induced phonophoresis of human skin. Screening of chemical penetration enhancers for transdermal drug delivery using electrical resistance of skin. The weak price of sphingolipid biosyntheisis proven by keratinocytes isolated from aged vs. Synthetic tripeptide which increases survival of normal liver cells, and stimulates development of hepatoma cells. Experimental influence of pharmacological agents on the regeneration of nervous tissue in vitro. Influence of chosen peptides and their copper complexes on antioxidant enzyme actions in human skin fibroblasts. The tripeptide�copper complex glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine stimulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression by fibroblast cultures. Expression of glycosaminoglycans and small proteoglycans in wounds: Modulation by the tripeptide-copper complex glycyl-L-histidyl-Llysine-Cu(2+). Expression and localization of the 2 small proteoglycans biglycan and decorin in creating human skeletal and non-skeletal tissues. In vivo stimulation of connective tissue accumulation by the tripeptide-copper complex glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine in rat experimental wounds. Effects of copper tripeptide on the expansion and expression of development components by oral and irradiated fibroblasts. Human skin retention and penetration of a copper tripeptide in vitro as function of skin layer towards anti-inflammatory therapy. Effects of topical copper tripeptide complex on wound therapeutic in an irradiated rat model. Biological actions of chosen peptides: Skin penetration capacity of copper complexes with peptide. Effects of topical lotions cntaining vitamin C, a copper-binding peptide cream and melatonin in contrast with tretinoin on the ultrastructure of normal skin. A scientific analysis of a copper-peptide-containing liquid foundation and cream concealer designed for bettering skin situation [press launch]. Transdermal delivery of proteins mediated by non-covalently related arginine-rich intracellular delivery of peptides. Teaching the fundamentals of redox biology to medical and graduate college students: Oxidants, antioxidants and disease mechanisms. Regulation of extracellular matrix manufacturing by chemically synthesized subfragments of sort I collagen carboxy propeptide. Efficacy of anti-getting older merchandise for periorbital wrinkles as measured by 3-D imaging. A novel L-ascorbic acid and peptide conjugate with increased stability and collagen biosynthesis. Activation of latent reworking development factor beta 1 and inhibition of matrix metalloprotease exercise by a thrombospondin-like tripeptide linked to elaidic acid. Modulation of mobile senescence in fibroblasts and dermal papillae cells in vitro. Elevation of the antifibrotic peptide N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysylproline: A blood stress-unbiased helpful effect of angiotensin I-changing enzyme inhibitors. Kinetin-induced differentiation of normal human keratinocytes undergoing getting older in vitro. Depigmentation and rejuvenation results of kinetin on the aged skin of hairless descendants of Mexican hairless canine. Prevage blend of cosmetic practical elements counteracts skin getting older by offering anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory protection. A scientific study of topical Pyratine 6 for bettering the looks of photodamaged skin. Metabolism of melatonin and biological exercise of inter� mediates of melatoninergic pathway in human skin cells. The Journal of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2013;27(7):2742�fifty five. Bone morphogenetic protein signalling regulates keratinocyte proliferation and migration throughout wound therapeutic in murine and human skin. Topical application of epidermal development factor accelerates wound therapeutic by myofibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis in rat. The receptor for superior glycation end merchandise is very expressed in the skin and upregulated by superior glycation end merchandise and tumor necrosis factoralpha. A pure extracellular factor that induces Hsp72, inhibits apoptosis, and restores stress resistance in aged human cells. Use of a keratin-primarily based hydrogel in the management of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. An anti-getting older effect on the lips and skin observed in in vivo research on a new fibronectin-like peptide. Anti-photoaging results of soy isoflavone extract (aglycone and acetylglucoside form) from soybean cake. A comparability of biological actions of a new soya biopeptide studied in an in vitro skin equivalent model and human volunteers. Novel features of intrinsic and extrinsic getting older of human skin: Beneficial results of soy extract. Differential results of exogenous and endogenous hyaluronan on contraction and power of collagen gels. Anti-getting older efficacy of topical formulations containing niosomes entrapped with rice bran bioactive compounds. Properties and antityrosinase exercise of sericin from varied extraction methods. Isolation and bioactivities of a non-sericin component from cocoon shell silk sericin of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Fibroin and sericin from Bombyx mori silk stimulate cell migration through upregulation and phosphorylation of c-jun. Clinical potential of a silk sericin-releasing bioactive wound dressing for the therapy of split-thickness skin graft donor websites. The anti-wrinkle efficacy of argireline, a synthetic hexapeptide, in Chinese topics: A randomized, placebo-controlled study. Biological actions of chosen peptides: Skin penetration capacity of copper complexes with peptides. Effect of assorted penetration enhancers: In vitro study throughout hairless mouse skin. A scientific analysis of a copper-peptide-containing liquid foundation and cream concealer designed for bettering skin situation. Effects of topical lotions containing vitamin C, a copper-binding peptide cream and melatonin in contrast with tretinoin on the ultrastructure of normal skin. Topical palmitoyl pentapeptide supplies improvement in photoaged human facial skin. Use of a facial moisturizer containing palmitoyl pentapeptide improves the appreance of getting older skin. Kinetin containing lotion in contrast with retinol containing lotion; Comparable enhancements in the signs of photoaging. Improvement in the look of wrinkles with topical reworking development factor beta(1) and l-ascorbic acid. Human development factor and cytokine skin cream for facial skin rejuvenation as assessed by 3D in vivo optical skin imaging. Cosmetic effectiveness of topically applied hydrolysed keratin peptides and lipids derived from wool.
Buy zebeta 5mg
The fibers between lateral geniculate physique and visual cortex are additionally known as geniculocalcarine fibers. It types the walls and lips of calcarine fissure in medial surface of occipital lobe. In truth, the purpose to level projection of retina upon visual cortex is properly established. The peripheral retinal representation occupies the anterior a part of visual cortex. Macular representation occupies the posterior a part of visual cortex near occipital pole. Areas of Visual Cortex and their Function Three areas are present in visual cortex: i. Primary visual area (area 17), which is worried with the notion of visual impulses ii. Secondary visual area or visual affiliation area (area 18), which is worried with the interpretation of visual impulses iii. Occipital eye subject (area 19), which is worried with the motion of eyes (Chapter 152). Pressure on uncrossed lateral fibers by aneurysmal dilatation of carotid artery causes blindness within the temporal a part of retina of similar facet, i. If lateral fibers of either side are affected, the imaginative and prescient is lost in nasal half of each visual fields, causing binasal hemianopia. It occurs because of dilated third ventricle, which forces the angle of chiasma towards carotid arteries. Effects of Lesion of Optic Tract, Lateral Geniculate Body and Optic Radiation Lesion of optic tract or lateral geniculate physique or optic radiation causes homonymous hemianopia. Effects of Lesion of Visual Cortex Lesion of upper or lower a part of visual cortex results in inferior or superior homonymous hemianopia. This phenomenon by which the macular imaginative and prescient is retained (unaffected) in circumstances of hemianopia is known as macular sparing. Fibers from macular area are projected into each anterior and posterior parts of each visual cortex. Homonymous hemianopia Homonymous hemianopia means loss of imaginative and prescient in the same halves of each the visual fields. Loss of imaginative and prescient in proper half of visual subject of each eyes is named proper homonymous hemianopia. Similarly, left homonymous hemianopia means loss of imaginative and prescient in left half of visual subject of each eyes. Heteronymous hemianopia Heteronymous hemianopia means loss of imaginative and prescient in opposite halves of visual subject. For instance, binasal heteronymous hemianopia means loss of imaginative and prescient in proper half of left visual subject and left half of proper visual subject (nasal half of each visual fields). Bitemporal heteronymous hemianopia is the loss of sight in left facet of left visual subject and proper facet of proper visual subject (temporal half of each visual fields). Effects of Lesion of Optic Nerve Lesion in a single optic nerve will cause total blindness or anopia within the corresponding visual subject. Lesion of lateral fibers in proper facet of optic chiasma: Right nasal hemianopia C + D. It can also be known as the direct pupillary gentle reflex or the direct reaction to gentle. If gentle is flashed into one eye, the constriction of pupil occurs within the opposite eye, although no gentle rays falls on that eye. Fibers of sunshine reflex pathway and the fibers of visual pathway are the same up to optic tract. Afferent (sensory) impulses from the receptors move by way of the optic nerve, optic chiasma and optic tract. At the midbrain stage, few fibers get Chapter 169 t Pupillary Reflexes 995 separated from optic tract and synapse on the neurons of pretectal nucleus, which lies close to the superior colliculus. Efferent (motor) impulses from this nucleus are carried by short fibers to Edinger-Westphal nucleus (parasympathetic nucleus) of oculomotor nerve (third cranial nerve). From Edinger-Westphal nucleus, preganglionic fibers move by way of oculomotor nerve and attain the ciliary ganglion. Postganglionic fibers arising from ciliary ganglion move by way of short ciliary nerves and attain the eyeball. Reason for consensual gentle reflex is that, some of the fibers from pretectal nucleus of one facet cross to the other facet and finish on opposite EdingerWestphal nucleus. It is the process by which gentle rays from near objects or distant objects are brought to a focus on delicate a part of retina. So, to be targeted on retina, these gentle rays should be refracted (converged) to a higher extent. Convexity of lens should be altered, in order that the refractory energy of lens is altered based on the necessity. This mechanism is present in human eye and it was first suggested by Young and later supported by Helmholtz. Young-Helmholtz Theory Young-Helmholtz concept describes how the curvature of lens will increase and thereby, the refractive energy of lens is enhanced. When the eyes are fixed on a distant object (distant imaginative and prescient) lens is flat because of the traction of suspensory ligaments, which prolong from the capsule of lens and are hooked up to ciliary processes. When imaginative and prescient is shifted from the distant object to a near object (near imaginative and prescient), ciliary muscle contracts and attracts the choroid ahead. Other Adjustments in Eyeball during Accommodation In addition to increase in anterior curvature of the lens, two extra changes are made within the eyeball during accommodation for near imaginative and prescient. Convergence of each eyeballs: It is important to deliver the retinal images on to the corresponding points 2. Increase the visual acuity by decreasing lateral chromatic and spherical aberrations ii. Increase the depth of focus by way of extra central a part of lens as its convexity is elevated. In resting eye, the intraocular strain units up rigidity in choroids and pulls the ciliary processes backward and outward. Purkinje-Sanson Images Purkinje-Sanson images are used to reveal the change in convexity of lens during accommodation for near imaginative and prescient. When the person seems at a distant object, the second picture reflected from anterior surface of lens is near the third picture from posterior surface. During accommodation for near imaginative and prescient, no change occurs either in first picture or the third picture. When an individual seems at a near object after seeing a far object, three changes are made within the eyeballs: 1. Constriction of the pupil because of the contraction of constrictor pupillae of iris 3. Increase within the anterior curvature of the lens because of contraction of the ciliary muscle. Thus, the accommodation reflex includes each skeletal muscle (medial recti) and easy muscle (ciliary muscle and sphincter pupillae). Although accommodation is a reflex motion, it can be controlled by willpower to a sure extent. Efferent fibers to ciliary muscle and sphincter pupillae From area 8, the corticonuclear fibers move by way of inside capsule to the Edinger-Westphal nucleus of third cranial nerve. From right here, the preganglionic fibers move by way of the third cranial nerve to ciliary ganglion. Postganglionic fibers from ciliary ganglion move by way of the short ciliary nerves and provide the ciliary muscle and the constrictor pupillae. Efferent fibers to medial rectus Some of the fibers from frontal eye subject terminate within the somatic motor nucleus of oculomotor nerve. It is restricted solely by the scale of object, clearness of the atmosphere and the curvature of earth. The nearest level from eye at which the thing is seen clearly is known as near level or punctum proximum.
Trusted zebeta 5 mg
Extraglomerular mesangial cells of juxtaglomerular equipment secrete cytokines like interleukin-2 and tumor necrosis factor (Chapter 17) 2. In the adults, throughout resting situations both the kidneys obtain 1,300 mL of blood per minute or about 26% of the cardiac output. While passing through renal sinus, the renal artery divides into many segmental arteries. At the bottom of the pyramid, it turns and runs parallel to the bottom of pyramid forming arcuate artery. Interlobular Artery Interlobular arteries run through the renal cortex perpendicular to arcuate artery. Afferent Arteriole Afferent arteriole enters the Bowman capsule and types glomerular capillary tuft. After coming into the Bowman capsule, the afferent arteriole divides into four or 5 giant capillaries. Chapter fifty one t Renal Circulation 313 Glomerular Capillaries Each giant capillary divides into small glomerular capillaries, which kind the loops. And, the capillary loops unite to kind the efferent arteriole, which leaves the Bowman capsule. Efferent Arteriole Efferent arterioles kind a second capillary community called peritubular capillaries, which surround the tubular portions of the nephrons. Thus, the renal circulation types a portal system by the presence of two sets of capillaries particularly glomerular capillaries and peritubular capillaries. Peritubular Capillaries and Vasa Recta Peritubular capillaries are discovered across the tubular portion of cortical nephrons only. The tubular portion of juxtamedullary nephrons is supplied by some specialised capillaries called vasa recta. Vasa recta come up instantly from the efferent arteriole of the juxtamedullary nephrons and run parallel to the renal tubule into the medulla and ascend up in the direction of the cortex. Venous System Peritubular capillaries and vasa recta drain into the venous system. Venous system starts with peritubular venules and continues as interlobular veins, arcuate veins, interlobar veins, segmental veins and eventually the renal vein. Autoregulation is current in some important organs in the physique such as mind, coronary heart and kidneys. Blood move to kidneys stays normal even when the imply arterial blood stress differ extensively between 60 mm Hg and one hundred eighty mm Hg. Myogenic Response Whenever the blood move to kidneys increases, it stretches the elastic wall of the afferent arteriole. Stretching of the vessel wall increases the move of calcium ions from extracellular fluid into the cells. The inflow of calcium ions leads to the contraction of clean muscle tissue in afferent arteriole, which causes constriction of afferent arteriole. Kidneys are the second organs to obtain maximum blood move, the first organ being the liver, which receives 1,500 mL per minute, i. Whole quantity of blood, which flows to kidney has to cross through the glomerular capillaries before coming into the venous system. Renal glomerular capillaries kind high stress bed with a stress of 60 mm Hg to 70 mm Hg. It is way higher than the capillary stress elsewhere in the physique, which is simply about 25 mm Hg to 30 mm Hg. High stress is maintained in the glomerular capillaries as a result of the diameter of afferent arteriole is greater than that of efferent arteriole. Peritubular capillaries kind a low stress bed with a stress of eight mm Hg to 10 mm Hg. Processes of Urine Formation When blood passes through glomerular capillaries, the plasma is filtered into the Bowman capsule. While passing through the tubule, the filtrate undergoes various changes both in high quality and in amount. Many needed substances like glucose, amino acids, water and electrolytes are reabsorbed from the tubules. And, some undesirable substances are secreted into the tubule from peritubular blood vessels. Thus, the urine formation contains three processes: 316 Section 5 t Renal Physiology and Skin 2. Basement membrane Basement membrane of glomerular capillaries and the basement membrane of visceral layer of Bowman capsule fuse together. The fused basement membrane separates the endothelium of glomerular capillary and the epithelium of visceral layer of Bowman capsule. Visceral layer of Bowman capsule this layer is shaped by a single layer of flattened epi thelial cells resting on a basement membrane. Each cell is linked with the basement membrane by cytoplasmic extensions called pedicles or feet. When blood passes through glomerular capillaries, the plasma is filtered into the Bowman capsule. Ultrafiltration Glomerular filtration is called ultrafiltration as a result of even the minute particles are filtered. The protein molecules are bigger than the slit pores current in the endothelium of capillaries. Thus, the glomerular filtrate incorporates all of the substances current in plasma besides the plasma proteins. This approach includes insertion of a micropipette into the Bowman capsule and aspiration of filtrate. Glomerular capillary membrane Glomerular capillary membrane is shaped by single layer of endothelial cells, that are hooked up to the basement membrane. The capillary membrane has many pores called fenestrae or filtration pores with a diameter of zero. Chapter fifty two t Urine Formation 317 between renal plasma move and glomerular filtration rate. Starling Hypothesis and Starling Forces Determination of internet filtration stress is based on Starling hypothesis. Starling hypothesis states that the online filtration through capillary membrane is proportional to hydrostatic stress difference across the membrane minus oncotic stress difference. Hydrostatic stress inside the glomerular capillaries is the glomerular capillary stress. All the pressures concerned in determination of filtration are called Starling forces. Glomerular Capillary Pressure Glomerular capillary stress is the stress exerted by the blood in glomerular capillaries. Colloidal Osmotic Pressure It is the stress exerted by plasma proteins in the glomeruli. Hydrostatic Pressure in Bowman Capsule It is the stress exerted by the filtrate in Bowman capsule. Net Filtration Pressure Net filtration stress is the balance between stress favoring filtration and pressures opposing filtration. Macula densa of juxtaglomerular equipment in the terminal portion of thick ascending limb is sensitive to the sodium chloride in the tubular fluid. When the glomerular filtrate passes through the terminal portion of thick ascending section, macula densa acts like a sensor. When the concentration of sodium chloride increases in the filtrate essential filtration stress. Glomerular Capillary Pressure Glomerular filtration rate is instantly proportional to glomerular capillary stress. Capillary stress, in turn depends upon the renal blood move and arterial blood stress. Colloidal Osmotic Pressure Glomerular filtration rate is inversely proportional to colloidal osmotic stress, which is exerted by plasma proteins in the glomerular capillary blood. Hydrostatic stress in Bowman capsule increases in situations like obstruction of urethra and edema of kidney beneath renal capsule. It is as a result of, the efferent arteriolar constriction prevents outflow of blood from glomerulus and no contemporary blood enters the glomerulus for filtration. There are several different elements, which improve or lower the sensitivity of tubuloglomerular feedback.
Trusted 10 mg zebeta
Impulses from anterior cingulate gyrus, genu of corpus callosum, olfactory tubercle and posterior orbital gyrus of cerebral cortex inhibit respiration. Impulses from motor area and Sylvian area of cerebral cortex cause compelled breathing. Impulses from Stretch Receptors of Lungs: Hering-Breuer Reflex HeringBreuer reflex is a protecting reflex that restricts inspiration and prevents overstretching of lung tissues. Stretch receptors are the receptors which give response to stretch of the tissues. Impulses from stretch receptors attain the dorsal group neurons through vagal afferent fibers and inhibit them. Hering-Breuer inflation reflex and deflation reflex the above talked about reflex is known as Hering-Breuer inflation reflex because it restricts the inspiration and limits the overstretching of lung tissues. Reverse of this reflex is known as Hering-Breuer deflation reflex and it takes place throughout expiration. Pulmonary congestion Pulmonary edema Pneumonia Over inflation of lungs Microembolism in pulmonary capillaries Stimulation by exogenous and endogenous chemical substances corresponding to histamine, halothane, bradykinin, serotonin and phenyldiguanide. Apnea is 720 Section 9 t Respiratory System and Environmental Physiology adopted by hyperventilation, bradycardia, hypotension and weakness of skeletal muscles. However, these receptors are liable for hyperventilation in sufferers affected by pulmonary congestion and left coronary heart failure. Irritant receptors are stimulated by irritant chemical agents corresponding to ammonia and sulfur dioxide. These receptors ship afferent impulses to respiratory centers through vagal nerve fibers. Stimulation of irritant receptors produces reflex hyperventilation along with bronchospasm. Hyperventilation along with bronchospasm prevents further entry of harmful agents into the alveoli. Impulses from Baroreceptors Baroreceptors or pressoreceptors are the receptors which give response to change in blood strain. Function Baroreceptors in carotid sinus and arch of aorta give response to increase in blood strain. Whenever arterial blood strain increases, baroreceptors are activated and ship inhibitory impulses to vasomotor middle in medulla oblongata. However, in physiological situations, the function of baroreceptors in regulation of respiration is insignificant. Impulses from Chemoreceptors Chemoreceptors play an necessary function in the chemical regulation of respiration. Details of chemoreceptors and chemical regulation of respiration are defined later in this Chapter. Impulses from Proprioceptors Proprioceptors are the receptors which give response to change in the place of physique. Proprioceptors are stimulated during the muscular train and ship impulses to brain, significantly cerebral cortex, through somatic afferent nerves. Cerebral cortex in flip causes hyperventilation by sending impulses to medullary respiratory centers. Impulses from Thermoreceptors Thermoreceptors are cutaneous receptors, which give response to change in the environmental temperature. Thermoreceptors are of two varieties, namely receptors for cold and receptors for warmth. When physique is uncovered to cold or when cold water is applied over the physique, cold receptors are stimulated and ship impulses to cerebral cortex through somatic afferent nerves. Cerebral cortex in flip, stimulates the respiratory centers and causes hyperventilation. Impulses from Pain Receptors Pain receptors are those which give response to ache stimulus. Whenever ache receptors are stimulated, the impulses are sent to cerebral cortex through somatic afferent nerves. Cerebral cortex in flip, stimulates the respiratory centers and causes hyperventilation. Chemoreceptors are the sensory nerve endings, which give response to changes in chemical constituents of blood. Situation Central chemoreceptors are situated in deeper a part of medulla oblongata, close to the dorsal respiratory group of neurons. This area is called chemosensitive area and the neurons are known as chemoreceptors. Central chemoreceptors are liable for 70% to 80% of elevated ventilation through chemical regulatory mechanism. Main stimulant for central chemoreceptors is the elevated hydrogen ion focus. On the opposite hand, if carbon dioxide increases in the blood, it could possibly easily cross the blood-brain barrier and bloodcerebrospinal fluid barrier and enter the interstitial fluid of brain or the cerebrospinal fluid. Since carbonic acid is unstable, it instantly dissociates into hydrogen ion and bicarbonate ion. From chemoreceptors, the excitatory impulses are sent to dorsal respiratory group of neurons, leading to elevated ventilation (elevated rate and pressure of breathing). Because of this, extra carbon dioxide is washed out and respiration is introduced again to normal. Mechanism of Action Hypoxia is essentially the most potent stimulant for peripheral chemoreceptors. Hypoxia causes closure of oxygen sensitive potassium channels and prevents potassium efflux. This leads to depolarization of glomus cells (receptor potential) and era of motion potentials in nerve ending. These impulses move through aortic and Hering nerves and excite the dorsal group of neurons. Dorsal group of neurons in flip, ship excitatory impulses to respiratory muscles, leading to elevated ventilation. In addition to hypoxia, peripheral chemoreceptors are additionally stimulated by hypercapnea and elevated hydrogen ion focus. However, the sensitivity of peripheral chemoreceptors to hypercapnea and elevated hydrogen ion focus is gentle. Hyperpnea: Increase in pulmonary ventilation due to increase in rate or pressure of respiration. Hyperventilation: Abnormal increase in rate and pressure of respiration, which frequently leads to dizziness and sometimes chest ache 7. Apnea can be produced voluntarily, which is known as breath holding or voluntary apnea. Voluntary Effort Arrest of breathing by voluntary effort is called voluntary apnea or breath holding. Breath holding time could be elevated beyond forty to 60 seconds by apply, train, willpower and yoga. At the top of voluntary apnea, the topic is compelled to breathe, which is known as the breaking level. It is due to the accumulation of carbon dioxide in blood, which stimulates the respiratory centers. Besides elevated carbon dioxide content in blood, hypoxia and elevated hydrogen ion focus are additionally liable for stimulation of respiratory centers. So, partial strain of carbon dioxide in the blood decreases and the number of stimuli to the respiratory centers additionally decreases, leading to apnea. When partial strain of carbon dioxide increases, the respiratory centers are stimulated and respiration starts. Deglutition Apnea Arrest of breathing throughout deglutition is called deglutition (swallowing) apnea. This is prevented by deglutition apnea, throughout which the larynx is closed by backward motion of epiglottis (Chapter forty three). Vagal Apnea Vagal apnea is an experimental apnea, which is produced by the stimulation of vagus nerve in animals. Adrenaline Apnea Adrenaline apnea is the apnea that happens after injection of adrenaline. It stimulates the baroreceptors, which in flip reflexly inhibit vasomotor middle and the respiratory centers, inflicting fall in blood strain and apnea.
References:
- http://www.survivorshipguidelines.org/pdf/ltfuguidelines_40.pdf
- https://www.astro.org/uploadedFiles/_MAIN_SITE/Affiliate/ARRO/Resident_Resources/Educational_Resources/Content_Pieces/VaginalCancer.pdf
- http://www.aopanet.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Agenda-Packet-Material-MAB-O2020-Dec-11-Meeting.pdf
- https://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/pediatrics/early/2018/11/29/peds.2018-3348.full.pdf
- http://www.pacodeandbulletin.gov/secure/pabulletin/data/vol49/49-33/49_33_p2.pdf
.png)