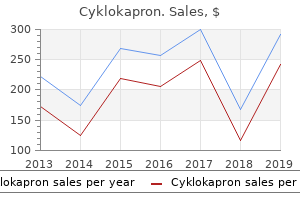
Trusted cyklokapron 500mg
Most folks with thyroiditis recuperate their thyroid operate, but as much as one-fourth of people could have permanent hypothyroidism. Other medicines that may trigger hypothyroidism are amiodarone, interferon alpha, and interleukin-2. All of those drugs are most probably to set off hypothyroidism in people who have a genetic tendency to autoimmune thyroid disease. Newer drugs used within the remedy of most cancers, similar to ipilimumab, pembrolizumab, and nivolumab, can set off the manufacturing of thyroid antibodies and trigger autoimmune hypothyroidism. Iodine comes into the body in meals, primarily dairy products, hen, beef, pork, fish, and iodized salt. Keeping thyroid hormone manufacturing in balance requires the correct quantity of iodine. People who live in undeveloped parts of the world could not get sufficient iodine of their food plan. The major source of an excessive amount of iodine is dietary dietary supplements containing kelp, a sort of seaweed. Most of those dietary supplements are sold with the false promise of serving to folks lose weight. If the pituitary gland is damaged by damage, a tumor, radiation, or surgical procedure, it could no longer be able to give the thyroid the best instructions and the thyroid could cease making sufficient hormone. Diagnosing hypothyroidism early by testing newborn infants, pregnant ladies, and folks with signs or danger elements is the best way to discover hypothyroidism and stop it from worsening. In some circumstances, different exams, similar to free T4, free T4 index and total T4 could also be useful. Most hypothyroid signs are common complaints that many individuals with a normally functioning thyroid can have. These signs might be clues to situations that may or is probably not related to the thyroid. This consists of information about: � Your overall health, especially adjustments in your health. Severe hypothyroidism could be indicated by findings similar to dry skin, swelling, slower reflexes, or sluggish coronary heart rate. For less severe circumstances however, few, if any, physical signs can clearly predict hypothyroidism. The system works like a thermostat and a heater: special cells in your pituitary gland decide the normal T4 vary for your body. An underactive thyroid could seem like a standard thyroid or it could be bigger or smaller. Hypothyroidism is treated by replacing the quantity of hormone that your own thyroid can no longer make. Synthetic thyroxine (additionally known as L-thyroxine or levothyroxine) drugs comprise the hormone T4 like a healthy thyroid makes naturally. Like the T4 that your own thyroid makes, each dose of synthetic thyroxine keeps working in your blood for a few week (Thyroxine takes about four weeks to clear fully from the body). This lets the T4 levels in your blood stay steady so a constant provide of T4 is out there to your body cells. Older folks ought to begin on a low dose and raise it slowly to give their bodies time to adjust, particularly the center. If your hypothyroidism is caused by autoimmune disease and is still making some T4, you could only want a low dose of thyroxine. Your physician could purposely begin you on a low dose to prevent you from getting signs of an excessive amount of thyroxine, like anxiety, restlessness, nervousness, and a racing coronary heart. You will eventually reach a stable dose, and you could stay on that dose for many years. Many folks need to take two thyroxine drugs-sometimes of two different strengths-to get the best dose. If your dose must be 163 mcg, your physician may give you prescriptions for seventy five mcg drugs and for 88 mcg drugs. Getting the best dose for you is just a matter of taking your drugs as prescribed and getting common blood exams. Your physician may prescribe that you simply take the same dose every single day or different doses on different days. The only approach to control your hypothyroidism is to take your tablet every single day for the remainder of your life. For instance, you could keep in mind to take your tablet if you take it before or after brushing your tooth. To keep better observe of your drugs, store them in a container that has a field marked for each day of the week. Do not try to swallow your tablet with out liquid; if it dissolves in your mouth or throat, not sufficient medicine will be absorbed into your blood. If you at all times take your tablet with food, you could want a higher dose than if you at all times take it on an empty abdomen. Or, put the tablet in a small paper cup with simply sufficient water to dissolve the tablet and have the kid drink the solution. Then, put a little more water within the cup to catch any more bits of the tablet and have the kid drink that. Each brand accommodates the same active ingredient, but each is made a little differently, and there could also be small variations within the precise dose quantity from brand to brand. If you alter from one brand to another, even at the identical dose, your body could take up and respond to it differently. The American Thyroid Association recommends that once you get used to one brand or formulation of thyroxine, you continue with that brand. Make certain the pharmacist offers you the same brand (or the same manufacturer for generics) each time you decide up your drugs. This is because your body will react as if are you taking a lower dose than wanted. Just begin over with daily drugs and determine how to best keep in mind to take them. You could need to elevate your thyroxine dose by as much as 30 to 50 % because your body needs more T4 to handle the physical calls for of pregnancy. You and your physician will work closely throughout your pregnancy to ensure the best possible health for your self and your baby. After the infant is born, your body returns to needing the same quantity of T4 as before you had been pregnant. In fact, greater than 80% of the T3 in your blood is produced from T4 that has been changed by the liver and different tissues outdoors the thyroid. Because the failing thyroid nonetheless makes some T3, and because body tissues turn T4 into T3, most hypothyroid sufferers need to be treated only with T4. In these sufferers, having the correct quantity of T4 allows the body to make the correct quantity of T3. However, some researchers have wondered whether or not a mix of T4 and T3 might be better. Some folks argue that drugs produced from animal thyroids are more pure, but these drugs pose a number of dangers. Thyroxine made in a lab is precisely the same hormone that a human thyroid makes, but in a pure kind. People who take too excessive of a thyroxine dose within the hope of speedy weight loss can weaken their muscular tissues and bones and harm the center-all of which might make it tougher to exercise. In fact, taking an excessive amount of iodine can worsen each hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Worse yet, taking these can prevent folks from getting the thyroxine remedy that they actually need. The most common signs of an excessive amount of thyroid hormone are fatigue, the inability to sleep, higher appetite, nervousness, shakiness, feeling scorching when different persons are cold, muscle weak point, shortness of breath, and a racing, skipping coronary heart. For instance, if a lab runs two exams on one blood sample, it could get two slightly different results.
Effective cyklokapron 500mg
Unlike Nedungadi, they discovered persistently, topics falsely recognized the major brand more usually than any of the minor brands (or associates). Taken collectively, these outcomes suggest that brand primes can indirectly shape brand remembering, but just for major brands. Further, influences on brand choice is probably not independent of brand name evaluation, as advised by Nedungadi (1990). These findings present us with the idea for utilizing our stimulus set to assess the relationships between consideration set inclusion, brand evaluation, and selection. This thought as soon as once more assumes a community organization of memory that operates underneath principles of activation and inhibition. Such an inhibition account is dominant in different research displaying a decrement in efficiency, including research on directed forgetting (Bjork, 1989; Bjork, Bjork, & Anderson, 1998), negative priming. Such an inhibitory mechanism has been assumed by many investigators of shopper memory. Rather, based on the interference hypothesis, efficiency in recalling class members might be facilitated to the extent that applicable cues are available for accessing the traces, and might be impeded to the extent that the demands of the duty are difficult. That is, whereas an inhibition account would predict that recall of unpracticed members are inaccessible; an interference account would predict that recall of unpracticed members are accessible, so long as the suitable cues are supplied during the take a look at. We discovered that topics had been less more likely to recall unpracticed objects from the practiced classes than from the non-practiced classes. The stimuli however, had been chosen such that they might be subcategorized by a particular function. Assignment of classes into situations was randomly-determined, and was re-randomized for each topic. According to inhibition accounts, repeated practice of some members of a class requires inhibition of unpracticed members of that class, but not different classes. The outcomes of Kronlund and Hughes (2005a, 2005b) demonstrate that a change in the way that stimuli are construed or characterised within the task can eliminate or enhance observed switch. This level might be further demonstrated by the "mere publicity" research described in the subsequent section. The notion is that differential levels of consciousness are concerned in efficiency, and that an implicit form of memory exists to account for results of prior expertise on present conduct in the absence of acutely aware consciousness. This dichotomy has been increasingly used as a theoretical framework by investigators of shopper memory. Lee (2002) introduced the implicit/ specific dichotomy as a means to evaluate publicity to brand names. She offered topics with a list of brand name names either in the context of a sentence. After completing a distractor task, half of the subjects made a memory-primarily based choice. When offered in a sentence, the chance of brand name choice for that brand was greater for the memory-primarily based task than for the stimulus-primarily based task, and the reverse occurred when the brand was offered in isolation. Lee concluded that such outcomes demonstrate that "the consequences of presentation context on conceptual and perceptual priming present clear assist that the two forms of implicit memory are distinct constructs of memory" (p. She advised that implicit memory tasks are superior to specific tasks for measuring advertising effectiveness. The mere publicity effect is the remark that when pictures of the identical class. The failure of reaching above chance levels in recognition is assumed to be as a result of ineffective encoding of the stimuli caused by the rapid presentation of the objects during the research section. However, a puzzle arises as a result of fluency of processing additionally permits one to infer from the fluency of present efficiency to an earlier, maybe in some circumstances hypothetical, expertise of the stimulus and thus to make an effective remembering choice (Jacoby, Kelley, & Dywan, 1989). In fact, recognition memory outcomes from either of two bases, familiarity, governed by fluent processing. Thus a paradox emerges: why is it that topics are able to utilizing fluency as a basis for choice but not for recognition Whittlesea and Price (2001) attempted to disambiguate why the feeling of familiarity was not highly effective sufficient to trigger recognition ratings to be above chance in any previously examined mere publicity experiment. When topics had been requested to choose which of two objects they preferred, they carried out above chance in a choice judgment for objects proven earlier, but had been at chance on recognition for these objects. They then carried out two more experiments, one during which topics had been requested to choose which of two objects globally resembled an item proven earlier, and one during which topics had been requested to choose which of two objects they preferred and to justify their choice. In the previous, topics carried out above chance at recognition, most likely as a result of the non-analytical processing that they had been required to do, which allowed them to expertise and use fluency in their response. In the latter, topics had been at chance at preferring the old item, doubtless as a result of the now analytical processing that they had been utilizing, which prevented them from experiencing the fluency. This demonstration exhibits the importance of considering of memory not in terms of specific and implicit techniques, each only measurable by direct and indirect exams of efficiency, but somewhat as a unitary system, that makes use of completely different strategies which rely upon the stimulus, task, and context. Memory makes use of the identical set of information and skill to perform quite a lot of tasks, including both remembering (recognition) and non-remembering (choice) tasks, utilizing quite a lot of dimensions. There are but different examples of dissociations that can be explained with the identical precept. This is usually the case with analysis thought to present take a look at contexts that are believed to selectively faucet into specific and implicit memory techniques. Those take a look at contexts merely foster topics in adopting completely different strategies which either facilitate or preclude them from experiencing priming. We submit that this is a vital consideration for shopper researchers, who could merely be creating contexts which facilitate completely different processing strategies. Said one other method, are topics capable of form and use expectations about how fluent one thing should be The thought of fluency as a basis for recognition selections was initially investigated by Jacoby and Dallas (1981). At take a look at, earlier than making their recognition choice, topics had been required to make a tachistoscopic identification of every word; identification was used as an index of fluency of processing. Jacoby and Dallas observed that top-frequency phrases had been processed more fluently than had been low-frequency phrases. More importantly, prior expertise enhanced the fluency of processing for the low-frequency phrases greater than that of the excessive-frequency phrases. Further, they discovered that low-frequency phrases that had been studied had been more more likely to be claimed "old" than excessive-frequency phrases which had been studied. Jacoby and Dallas advised that topics appeared to be impressed not by absolutely the fluency of processing of a target item, but somewhat by the relative fluency of processing: topics had been impressed by the deviation between precise and expected fluency. The fluency-attribution thought has additionally been applied to understanding shopper conduct. There are two major problems with the above-mentioned research as well as quite a few different research investigating fluency. First, in contrast to the procedure used by Jacoby and Dallas, the fluency manipulation in these research was experimental: fluency was enhanced by some type of manipulation. Second, it seems illogical that the feeling of familiarity is created from absolute velocity of processing. During the take a look at section, topics first named each word (to get an index of processing fluency) and then made a recognition choice on old and new stimuli of every class. Whittlesea and Williams (1998) reasoned that when studying the easy to pronounce nonwords shock resulted from an unknown supply that was wrongly attributed to the past. It was the shock related to the mismatch between expectation and outcome which led to the feeling of familiarity. This research was replicated by Menon and Raghubir (2003) utilizing the accessibility/ease of retrieval framework (see additionally Huber, 2004). Whittlesea and Williams (2001a, 2001b) attempted to create and study the perception of discrepancy utilizing a unique paradigm which consisted of probe objects following a predictive sentence stem and a pause. Using this procedure during a take a look at section (targets in isolation during the research section), topics had been more more likely to declare "old" for probes following a predictive stem and pause as opposed to a predictive stem and no pause. In this case, the predictive stem was thought to create an expectation, the pause uncertainty, and the terminal word a surprising validation, similar to what happens when waiting for the other shoe to drop. While topics had been specializing in the salient facet of the duty, they skilled the perception of discrepancy upon seeing the terminal probe. Knowing that they had been in a recognition experiment, topics unconsciously attributed the shock to a prior expertise of the target word, consciously experiencing the feeling of familiarity. The perception of discrepancy happens when outcomes either violate or validate expectations in a surprising method.
Diseases
- Cataract, congenital, with microcornea or slight microphthalmia
- Tropical sprue
- Birnstad syndrome
- Fibromatosis
- Variegate porphyria
- Karandikar Maria Kamble syndrome
- Peanut hypersensitivity
- Heart defects limb shortening
- Prostaglandin antenatal infection
- Chondrodysplasia punctata
Generic 500mg cyklokapron
They discovered that, compared to management individuals, individuals who were in a great temper sampled a larger variety of merchandise similar to crackers, soups, and chips, unless the selection set included items expected to taste poorly. Again, constructive temper appeared to promote threat-seeking in benign settings and threat-avoidance in settings involving potential threat. According to Isen and her colleagues, when the decisions entail low dangers and stakes, constructive temper individuals are inclined to have more optimistic (temper-congruent) expectations concerning the outcomes and, therefore, take larger dangers compared to neutral temper individuals. However, when the stakes are high and the potential for losses vital, constructive temper individuals turn into threat-averse because they want to keep their constructive affective state, which a loss would disrupt. Several studies indicate that unfavorable emotional states accompanied by sturdy arousal improve threat-seeking (Fessler, Pillsworth, & Flamson, 2004; Leith & Baumeister, 1996; Mano, 1992, 1994). For example, Leith and Baumeister (1996) discovered that offended individuals and individuals anticipating impending embarrassment were more likely to select an economically inferior "long-shot" gamble with a low likelihood of obtaining a bigger amount of money and a high complementary likelihood of putting up with some stressful noise, over a superior "protected-bet" gamble with a higher likelihood of obtaining a smaller amount of money with a low likelihood of putting up with the stressful noise. Fessler, Pillsworth, and Flamson (2004) also discovered that anger triggered more riskseeking in playing, especially among males. For example, as mentioned beforehand, in decisions between low-threat/low-reward and highrisk/high-reward options, anxious individuals are inclined to prefer the former, whereas sad individuals are inclined to prefer the latter (Raghunathan & Pham, 1999; Raghunathan, Pham, & Corfman, 2006). In reality, other studies present that, when the level of arousal is held constant, anxiousness reduces threat-seeking (Mano, 1992, 1994). Similarly, Lerner and Keltner (2001) observed that, even though fear and anger are each high-arousal unfavorable emotions, fear tends to trigger threat-aversion, whereas anger tends to trigger threat-seeking. This is apparently because fear is typically related to situations of uncertainty and low management, whereas anger is typically related to situations of certainty and high management. It has also been discovered that disgust, another high arousal emotion, decreases threat-seeking in playing among women (Fessler, Pillsworth, & Flamson, 2004). High emotional arousal seems neither needed, nor sufficient to explain threat-seeking under unfavorable emotions. The results of unfavorable emotions on threat-seeking seem to depend not solely on the level of arousal related to the emotional state, but also on advanced interactions between the targets activated by the emotional state and the nature of the dangers to be taken. This could partly explain why a meta-evaluation of published studies relating continual states of anger, sadness, and anxiousness to dangerous sexual conduct (Crepaz & Marks, 2001) discovered nearly no correlation (r =. A frequent task-related affect is the unpleasant emotions that buyers often experience when they should trade off essential attributes whose values are negatively correlated throughout selection options. Apartment A is way roomier, however is situated in a foul neighborhood; whereas Apartment B is way smaller, however situated in a great neighborhood. This avoidant conduct seems to be a deliberate attempt by the buyer to mitigate the unpleasant emotions by eschewing the trade-offs altogether. This avoidant conduct is attenuated under situations of cognitive load, which reduces the aversiveness of the trade-offs by making them much less apparent (Drolet & Luce, 2004). Another way by which consumers try and deal with the emotional aversiveness of difficult selections is to resort to easier, heuristic choice strategies similar to processing attributeby-attribute (as opposed to various-by-various) and invoking dominance relations (Luce, 1998; Luce, Bettman, & Payne, 1997). It has also been discovered that, when trade-offs are emotional, consumers are inclined to place larger weight on the relative quality of the options, such as the relative security of two automobiles, rather than on their relative useful resource necessities. Task-related affect, within the type of stress, may also be induced by giving choice makers a while pressure and the impression of being monitored in the course of the choice (Stone & Kadous, 1997). Unlike the manipulations primarily based on trade-off issue mentioned above, this technique presents the advantage of holding details about the options constant. Stone and Kadous (1997) discovered that, under task-related stress, choice makers are inclined to use a "scanning" technique of rapidly however indiscriminately inspecting obtainable info, which can improve selection accuracy in straightforward selection environments however lower selection accuracy in tough selection environments. Another frequent sort of task-related affect in choice making is the unpleasant feeling of getting to forego attractive options. Dhar and Wertenbroch (2000) discovered that the emotional discomfort of forgoing an choice is larger when the option is primarily hedonic, similar to a fun sports activities automotive, than when the option is primarily utilitarian, similar to a practical minivan. It has also been discovered that the more consumers deliberate about their decisions, the more they turn into emotionally hooked up to the options, which leads to choice-related discomfort (or cognitive dissonance) as soon as one choice has been chosen (Carmon, Wertenbroch, & Zeelenberg, 2003). A particularly essential consequence of task-related affect is the switch of that affect onto the valuation of the chosen various. Just like incidental affective states, task-related affective responses may be misconstrued as reflecting real integral affective responses to one of the options-a phenomenon again broadly in keeping with the affect-as-info framework (Schwarz, 1990; see also Pham [2004] for a evaluation). For example, Garbarino and Edell (1997) discovered that decreasing the hassle involved in selecting an alternative. The switch of task-related affect onto the valuation of alternatives underlies a rising physique of analysis on the "worth-from-fit" hypothesis (Higgins, 2000). According to this hypothesis, a fit between the manner by which a choice is made and the current orientation of the choice maker can produce pleasant task-related emotions of "being right," which may then be (mis)attributed to a selected object, enhancing its perceived worth. This finding also illustrates the shut connection between affect and motivation, mentioned subsequent. Some researchers argue that affective states operate as a part of a superordinate program that directs motivational priorities and aim selection (Cosmides & Tooby, 2000) and motivates individuals to pursue particular targets. The interplay between motivation and affect is bidirectional: (1) affective states activate targets; and (2) aim pursuit (achievement, blockage, progress rate, and so forth. Although each directions of affect are of substantial theoretical curiosity, in this chapter we concentrate on the affect-to-motivation path because the motivational consequences of affect have been studied more extensively. When requested to assess their life satisfaction, many respondents in this study misattributed their climate-induced emotions to the unrelated judgment at hand. Usually missed within the literature is the fact that the study also requested individuals to assess their "want to change. Strength of the Signal, Approach, and Avoidance When affect deviates from a homeostatic vary, this alerts that one thing has altered the actual or anticipated state of the setting, thus increasing the probability of unanticipated unfavorable or constructive consequences, similar to those related to threats or security. The strength of this signal is a direct operate of how much affect deviates from its regular homeostatic vary. In the absence of such a motivation to explore, organisms would learn little about novel or neutral-appearing environments and their potential reward worth. Ito, Cacioppo, and Lang (1998) analyzed affective responses to hundreds of slides from the International Affective Picture System (Lang, Bradley, & Cuthbert, 1997). In one evaluation, subjective rankings of positivity of the principally pleasant slides, and subjective rankings of negativity of the principally unpleasant slides, were modeled as a operate of the level of arousal elicited by each slide. Not surprisingly, each relationships were constructive: pleasant slides were rated more positively as they arousal ranges elevated; and ugly slides were rated more negatively as they arousal ranges elevated. More importantly, rankings of positivity had a higher intercept than rankings of negativity. When arousal was very low, pleasant slides were rated more positively than unpleasant slides were rated negatively-a finding in keeping with a positivity offset. On the opposite hand, the slope of the negativity rankings was steeper than that of the positivity rankings-a fi nding in keeping with the negativity bias. Therefore, at low ranges of activation, constructive stimuli have a larger influence on affective responses (and presumably conduct) than unfavorable stimuli do. Respondents were uncovered subliminally to each constructive and unfavorable phrases and requested to guess whether the phrases were constructive or unfavorable. Performance was better than likelihood for unfavorable phrases, however not for constructive phrases. Th is finding suggests a decrease threshold for unconscious unfavorable affect to turn into accessible. According to Cacioppo, Gardner, and Bernsten (1999), the positivity offset fosters useful exploratory conduct. This duality of operate could have contributed to distinguishable method and avoidance mechanisms mobilizing the individual toward immediate action. A similar evaluation by Lang and his colleagues (Lang, Bradley, & Cuthbert, 1990, 1992) supports the excellence between an aversive/defensive/withdrawal system and an appetitive/method system, each with distinct patterns of neural exercise. The larger the appetitive enter, the stronger the activation of positivity and method forces; the larger the aversive enter, the stronger the activation of negativity and avoidance forces. However, physical conduct is facilitated by integrating the output of those twin processes and resolving any co-activation of opposing forces to categorical the dominant tendency and inhibit the weaker tendency. This is clear in postural assist reactions, steadiness, and dynamic motor changes and implies a neurological substrate for central bivariate management. Co-activation can also be in keeping with fi ndings indicating that central mechanisms for reward and aversion may be independently manipulated, since this means a elementary dissociability of related mind methods. One essential implication of co-activation is that an increase within the intensity of both constructive or unfavorable valence can transform inaction into action, perhaps main a person to take dangers that had restrained conduct, as when fear of unsafe sex or cigarette dependancy are overcome by both added momentary attractiveness or the notion of decreased probability or severity of consequences (Bolton, Cohen, & Bloom, 2006). Broadly speaking, then, affective alerts direct consideration to each environmental and personal components (specific current actions) that appear likely to alter consequences.
500 mg cyklokapron
Arousal can be linked to another central construct in individual-setting analysis: emotion. Individuals within the aroused state will seek an evidence for his or her arousal (loud music, too many individuals, and so forth), which subsequently affects their attributions about and responses to the setting. This is closely associated to the "scapegoating" principle advocated by Keating (1979) the place people wrongly attribute their arousal induced by other reasons (such as unattained objectives) to probably the most readily visible cause (such as too many individuals). Both over- and underarousal produce stress that may lead to behavioral, psychological and physiological outcomes (Patterson, 1976). Information overload is the second mechanism proposed to explain the inverted-U formed perform encountered in environmental influences. Milgram (1970) defines overload as a situation the place the speed and amount of environmental stimuli exceed the capacity to cope with them. Rapoport (1976) expands the overload principle by proposing that there exists some optimal degree of stimulation, which individuals try to keep. The overload principle provides a solid theoretical foundation for examining client-environmental results in marketing domains. A variety of analysis questions surface after we look at client-setting interactions from the arousal and overload perspectives. The extent of over- or underneath-arousal experienced by the patrons within the store influences their cognitive. Similarly, what are the optimal ranges for certain environmental stimuli (such as music, illumination, and client and merchandise density) which are proven to be influential in industrial domains How do shoppers cope with persistent overload circumstances such as persistent loud music, noise or merchandise and customer density so common in certain industrial domains. What is the relative significance of bodily and social environmental stimuli in industrial domains What impression do particular person traits and cultural variables have in shaping optimum stimulation ranges What role do sociocultural and interpersonal qualities of a setting play in figuring out the optimum stimulation ranges How can the over- and undermanning theories contribute to our understanding of these dynamics Which cognitive and behavioral mechanisms do shoppers use while making an attempt to restore their optimum stimulation ranges within the shopping and service environments Intervening Factors Much like beauty, the standard and amount of environmental impression appear to be within the eyes of its beholder. The perception and interpretation of environmental stimuli differ among individuals, as do their responses to them. Research has to explicitly look at whether or not environmental influences on cognitive, affective and behavioral outcomes are direct or are partially or fully mediated by other variables. Going beyond the direct results will enhance our understanding of the dynamics of environmental influences and enhance predictions about both client and employee reactions to the industrial setting. There are a variety of constructs which may serve as powerful mediators and moderators in this context. Social Climate is one potential intervening factor that can enhance our understanding of environmental results in industrial domains (Moos, 1973). Social climate refers to the interpersonal and socio-cultural qualities of a setting. Environmental psychology literature identifies a variety of dimensions that define the social climate of most organizations. Sirgy, Grewal, and Mangleburg (2000) posited that buyers whose actual, ideal and social self match their picture of a store are more likely to patronize it. Such low system-maintenance stores may have an effect on store evaluations and behaviors of certain customer segments, such because the aged and the harried buyers. The private development dimension concerns the availability of non-public progress and selfenhancement provided within the setting. For example, in-store promotions, both bodily (such as aisle banners and product indicators) and social. The interaction of social climate variables with the environmental stimuli could be higher predictors of client conduct than either of these variables alone. Individual traits constitute another priceless set of intervening variables in this space. Individual distinction traits might help higher explain and define the boundary circumstances for responses to various industrial environments. Despite their consideration as being problematic factors in psychology and client conduct, particular person variables can enhance our understanding and predictions of client-industrial setting interactions. Baker (1998) suggests persona factors, such as sensation in search of, as believable moderating variables. Sensitivity to noise has been found to be predictive of quite a lot of responses including the level of disturbance that postoperative sufferers felt while recovering (Topf, 1985; Weinstein, 1978). Atmospheric responsiveness (Eroglu, Machleit, & Davis, 2003) and tolerance for crowding (Eroglu, Machleit, & Barr, 2005) are also found to have moderating results on environmental influences on buyers. Other potential particular person variables embrace variety-in search of conduct (McAlister & Pessemier, 1982) and client want for uniqueness (Tian, Bearden, & Hunter, 2001), gender, and tradition. For example, one attention-grabbing avenue of analysis is whether or not certain customer segments (such because the aged, children, and women) are extra/much less susceptible to certain environmental cues and the types of coping mechanisms they might or may not have in place to take care of unfavorable environmental circumstances, such because the overload. Coping has been a serious focus of analysis in environmental psychology for many years. For no less than two reasons, coping could be a crucial mediator between the negative store stimuli and client responses. Second, given that emotions and coping processes are inextricably linked (Lazarus, 1991) and that client-setting interactions are mediated by emotions, coping is a conceptually applicable intervening variable in this context. Research on coping is just starting to proliferate in marketing (Duhachek, 2005; Duhachek & Iacobucci, 2005; Luce, 1998). Duhachek (2005) proposes a multi-dimensional model of client dealing with the objective of accounting for the "multitude of methods shoppers enact" (p. Do different bodily and social environmental cues instigate different coping methods by buyers Put in a different way, are they "stimulus-specific" or do shoppers have basic coping methods based on their past experiences in comparable situations Research on client-setting interaction, to date, has focused totally on strategy-avoidance means of dealing with environmental stressors. Perhaps this orientation is just too delimiting to capture the advanced nature of client coping behaviors, as instructed by Duhachek (2005). Studies are needed to explain how various client experiences in irritating retailing domains are associated to coping responses and the way these methods have an effect on store evaluations and patronage behaviors. Uncovering their potential contribution will help us higher assess the underlying dynamics within the space. In this final part, we take a macro view and elaborate on an strategy which may help further the speculation-constructing and principle use within the space. Specifically, we posit that the transactional strategy to client-setting research might help re-shape the prevalent fragmented analysis custom that characterizes this space in marketing and help in creating some theoretical models to combine and explain the empirical proof to date. Our purpose right here is to not declare one "appropriate" strategy to information principle within the client-setting analysis, but rather to introduce the basic tenets of an more and more dominant view in environmental psychology and to explain our vision as to the way it may enhance the theoretical rigor of our own space. Basically it advocates that: (1) Because people and psychological processes are inseparable from their bodily and social context, the phenomena in these contexts must be handled as holistic units rather than mixtures of separate elements; (2) Time and temporal qualities (within the form of change and continuity) are essential features of these phenomena; and (3) Phenomena must be observed and understood from the view of various kinds of observers and members, and the search must be for a formal cause (Altman et al. The emphasis on formal cause (rather than an "efficient" or pressured cause) constitutes one of many guiding ideas of the transactional strategy (Altman et al. Our review has proven that the predominant technique in our subject has been to isolate one or more environmental stimuli with the aim of assessing their particular person and joint results on certain client conduct variables-specifically, a focus on an antecedent-consequent relationship. For example, in store factors (such as music, illumination, crowding, scents, shade, and so forth) are examined for his or her results on selected shopping outcomes (such as the amount of purchase, time spent in store, satisfaction and re-patronage intentions). While this analysis strategy has its advantages, an overarching reliance on such empirical focus comes at the expense of inadequate thought for principle constructing and use within the space. Such fragmented efforts also tend to isolate one or a number of environmental stimuli as the only explanation for outcomes which are far too advanced to be defined by a single category (in this case, bodily environmental) of determinants. If the character of the transactional strategy is known as above, what does it imply for the buyer-setting analysis

Safe cyklokapron 500 mg
The effect of advertising on perspective accessibility, perspective confidence, and the perspective-conduct relationship. Attitude accessibility as a moderator of autonomic reactivity throughout determination making. Is the Implicit Association Test a valid and valuable measure of implicit consumer cognition Rudimentary determinants of attitudes: Classical conditioning is more effective when prior information about the perspective stimulus is low than high. The energy of the subliminal: Subliminal persuasion and different potential functions. On the useful worth of attitudes: the influence of accessible attitudes upon the benefit and quality of determination making. Attitude accessibility, perspective-conduct consistency, and the strength of the item-evaluation association. On the event and strength of class-model associations in reminiscence: the case of mystery ads. Variability in automatic activation as an unobtrusive measure of racial attitudes: A bona fide pipeline Attitude accessibility as a moderator of the perspective-notion and perspective-conduct relations: An investigation of the 1984 presidential election. Measuring associative strength: Category-merchandise associations and their activation from reminiscence. Category-primarily based versus piecemeal-primarily based affective responses: Development in schema-triggered have an effect on. Measuring particular person variations in implicit social cognition: the Implicit Association Test. Biased processing as a perform `of perspective accessibility: Making goal judgments subjectively. An investigation of the mediational mechanisms underlying attitudinal conditioning. Predictive validity of the Implicit Association Test in research of brands, consumer attitudes, and conduct. Effects of forewarning of persuasive intent and involvement on cognitive responses and persuasion. Elaboration as a determinant of perspective strength: Creating attitudes which might be persistent, resistant, and predictive of conduct. The role of contingency awareness, involvement, and want for cognition in perspective formation. A program of classical conditioning experiments testing variations in the conditioned stimulus and context. Why unhappy individuals like sneakers better: the influence of mood on the classical conditioning of consumer attitudes. Attitudes versus actions: the connection of verbal and overt behavioral responses to perspective objects. Introspection, perspective change, and perspective-conduct consistency: the disruptive effects of explaining why we feel the way in which we do. Retrieval of perspective-relevant information from reminiscence: Effects on susceptibility to persuasion and on intrinsic motivation. Susceptibility to persuasive appeals as a perform of source credibility and prior expertise with the perspective object. Despite this increased consideration to nonconscious processes inside tutorial psychology, consumer research has largely neglected this nascent area: critiques of the last fifteen years of consumer conduct research report a give attention to research methodologies that directly tap acutely aware beliefs, but which provide little perception into underlying implicit processes (Cohen & Chakravarti, 1990; Jacoby, Johar, & Morrin, 1998; Simonson Carmon, Dhar, Drolet, & Nowlis, 2001). As an example, research into the structure and function of attitudes has relied nearly solely on express measures, encouraging the event of theories depending on acutely aware evaluation and deliberation. Although these theories are essential to the advancement of the sector, they usually neglect the potential role of nonconscious processes. Following the looks of a class exemplar on the computer display, a respondent categorizes the merchandise as quickly as attainable by urgent the response key that represents its appropriate class. The ease or problem with which a subject is able to assign the identical response to distinct ideas is taken as a measure of strength of the association between them in reminiscence. The remaining two categories are the attributes that could be variably associated with the target ideas. Exemplar items for a target concept or attribute class can include images, model logos, and/or words. Each task serves either to prepare the respondent in the appropriate responses to a given set of stimuli, or to measure the pace with which the topic can categorize ideas and attributes after they share a response key. The initial discrimination task includes distinguishing items of the 2 target concept categories, for instance, images representing Coke versus Pepsi. Often, the number of initial coaching trials varies with the number of stimulus items, such that every stimulus merchandise is considered twice, in random order. The second discrimination task parallels the first, using the attribute class stimulus items. During this task, a target concept class and an attribute class are assigned a shared response key. Whenever a Pepsi class merchandise or an unpleasant attribute merchandise is offered, the topic would press the alternate response key. Stimulus items are offered alternately from the 2 target concept and the 2 attribute categories, with the actual stimulus merchandise being randomly chosen from the obtainable set of exemplars. The last two discrimination tasks reverse the appropriate response for the target ideas and thereby create a task that can be directly in comparison with the initial mixed task. In the fourth discrimination task, the reversed target concept discrimination, topics follow categorizing the Coke and Pepsi target concept items with the response keys previously used for the opposite. If the initial target concept discrimination assigned the Coke class to the "D" key and the Pepsi class to the "K" key, the reversed discrimination task would assign Pepsi to the "D" key and Coke to the "K" key. This reversal serves two purposes: it permits topics to unlearn the class-response key associations acquired through the first and third discrimination tasks, and it units up the fi ft h discrimination task, or reversed mixed task. This last task is equivalent to the initial mixed task, with the target concept categories reversed. This algorithm was chosen over alternative latency-primarily based scoring algorithms because it produced the largest statistical effects sizes. Although effective, the standard algorithm was selected over different latency measure scoring methods primarily based upon the effect sizes it produced rather than any theoretical reasoning (Greenwald & Nosek, 2001). To establish a psychometrically preferable measure, a new scoring algorithm was developed: the D measure (Greenwald, Nosek, & Banaji, 2003). The D measure is computed by dividing the distinction between the congruent and incongruent test blocks by the usual deviation of the aggregate test-block latencies. This was justified because the magnitudes of variations between experimental treatment means are sometimes correlated with the variability of the information from which the means are computed. Using the usual deviation because the devisor adjusts variations between means for this effect of underlying variability (Greenwald, Nosek, & Banaji, 2003). Further, the D measure contains information from each follow and test blocks in addition to the information from the first two trials in test blocks (these information are dropped in the standard scoring procedure because of sometimes lengthened latencies). The inclusion of those further trials improves the steadiness of the measure and increases correlations with express measures. The present authors advocate using the D measure, not solely because it has been shown to be a superior measure to the standard scoring procedure, but in addition because its use will improve the interpretability and comparability of results across disciplines and experiments by providing an effect dimension-like statistic. Surveys of latest developments in consumer research (Cohen & Chakravarti, 1990; Jacoby, Johar, & Morrin, 1998; Simonson et al. These theories present a foundation for fashions of advertising effectiveness, buy selections, and model and product perspective improvement. By incorporating nondeliberative judgment into the process, these theories are the precursors to newer theories that advocate perspective improvement in the absence of overt cognition. The notion that attitudes may develop as a byproduct of nonconscious, automatic, or implicit course of gained momentum in the early Nineties (Bargh, Chaiken, Govender, & Pratto, 1992; Bargh, Chaiken, Raymond, & Hymes, 1996; Bargh, Chen, & Burrows, 1996; Fazio, Powell, & Williams, 1989), spawning the notion of implicit attitudes-"introspectively unidentified (or inaccurately recognized) traces of previous expertise that mediate favorable or unfavorable feeling, thought, or action towards social objects" (Greenwald & Banaji, 1995). Implicit attitudes are thought to be extra strongly influenced by nonconscious processing because of their independence from acutely aware adjustment and evaluation. Constructs which have relied on self-report measures for description corresponding to self-importance (Netemeyer, Burton, & Lichtenstein, 1995), stigmatized behaviors (Mowen & Spears, 1999; Swanson, Rudman, & Greenwald, 2001), or the exploration of "darkish side behaviors" corresponding to drug and alcohol use (Mick, 1996) may be affected by subject unwillingness to precisely report because of social desirability biases. Prior research revealed low correlations between express and implicit measures when the main target of attitudinal measurement is expounded to race, suggesting that express measures are consciously modified on account of self-presentation bias or reluctance to report true feelings (Dasgupta et al. To this end, commercials had been created that paired model information with athletes, and which manipulated the race of the superstar sportsperson. On the opposite hand, Black respondents indicated a preference for commercials with Black spokespersons on self-report measures, but no important implicit preference.
Proven cyklokapron 500 mg
The leisure industry additionally serves to maintain behaviors already established within the inhabitants. This chapter begins with a have a look at the media surroundings and its evolution as a backdrop for examining media channels that would doubtlessly model smoking conduct. The subsequent sections of this chapter describe what is thought about the smoking images contained in films and the way viewing them impacts attitudes and conduct. The textual content begins with the historical relationship between the tobacco and film industries, both of which came of age during the early 1900s within the United States. The chapter additionally summarizes research on portrayal of tobacco in other types of leisure media including television, music, magazines, and the Internet. Finally, efforts to cut back audience publicity to tobacco-related media content are mentioned, and general chapter conclusions are drawn. Entertainment media embrace print media (books and magazines), audio media (radio and music), and audiovisual media (television, films, Web-based media, and video/computer video games). Just two decades ago, choices for media delivery within the house elevated with the introduction of the videocassette. The Web supplies unique leisure choices through Web websites that deliver every little thing from traditional venues, such as news, to choices for enjoying interactive video video games with multiple gamers and downloading podcasts of movies and tv reveals. The increase in house choices for media and the multiplication of media viewing websites throughout the house (60% of U. In addition, most families reported getting access to all kinds of television channels, with about three-quarters of American families having cable/satellite tv for pc television. The percentages with cable/satellite tv for pc television access for these income teams have been seventy one%, 73%, and seventy seven%, respectively. However, the chances with Internet access have been 23%, 42%, and 58%, respectively. Average media publicity is about one hour less for top-income families than for low-income families. Thus, the viewing of television programming and films takes up more than one-half of the 5 to six hours that youngsters use media each day. All of those media have the potential to affect the attitudes and conduct of young customers toward tobacco products. A giant body of research exists on the impact of tobacco use in films on attitudes toward smoking. This medium subsequently serves as a valuable exemplar for further research in how varied mass media would possibly affect the potential for tobacco use. Later sections study research findings relating to publicity to tobacco in other media. Together 359 Media Use the national surveys cited above additionally assessed media use by youngsters and adolescents. These young Americans are thought-about most susceptible to the effects of media messages, and much of the research mentioned right here addresses the effects of media on their use of tobacco. Role of Entertainment Media with the present body of knowledge surrounding the portrayal of tobacco use in films, this chapter varieties a base for future work on the impact of leisure media on tobacco-related well being issues. Historical Perspective: Movies Examination of the function of leisure media in tobacco advertising is more and more turning into an area of lively research. Quantitative studies recommend that youth exposed to on-screen smoking are more likely themselves to initiate smoking. Pierce and Gilpin10 have recognized 4 key periods in a historical analysis of tobacco advertising and smoking initiation among U. Campaigns explicitly targeted women, as exemplified by the Lucky Strike "Reach for a Lucky Instead of a Sweet" print media marketing campaign during that period. However, the cigarette additionally was positioned as a symbol of independence and equality for women. At about the same time, Chesterfield rolled out a marketing campaign geared toward altering social norms relating to smoking, with an emphasis on the social interplay between women and men. Chesterfield advertisements often featured glamour photographs of a Chesterfield "girl of the month," primarily style models and Hollywood starlets. Some endorsers have been actresses, including Joan Bennett, Claudette Colbert, Joan Crawford, Betty Grable, Rita Hayworth, Marion Hutton, and Rosalind Russell. During the late 1940s, the advertisements continued to function glamorous women but in addition included male stars. Star endorsements during this era included Charles Boyer, Perry Como, Bing Crosby, Arthur Godfrey, Bob Hope, Dorothy Lamour, Virginia Mayo, Ethel Merman, Gregory Peck, Basil Rathbone, Ann Sheridan, Jo Stafford, and James Stewart. From 1943 through 1946, advertisements for the Regent model of cigarettes featured drawings of celebrities, including Fred Astaire, Diana Barrymore, Joan Blondell, Bing Crosby, Robert Cummings, Jinx Falkenberg, Arlene Francis, June Havoc, Celeste Holm, Guy Lombardo, Merle Oberon, and Jane Wyatt. The Role of the Media that period have been starting to understand the potential power of celebrities and the media (including movement pictures) as ways to change social norms around smoking. After 1939, and through the mid-Nineteen Sixties, tobacco advertising not centered on any explicit subgroup. Attending movement pictures was a national pastime by 1940, with Americans spending virtually one-quarter of their total recreation dollars on films Chesterfield cigarette commercial featuring actress Joan Crawford Note: from Ladies Home Journal 1949 mutually helpful relationship between the cigarette industry and the film industry. It could be affordable to assume that the stars have been paid for his or her appearances within the advertisements as well as receiving nonmonetary benefits, such as elevated publicity. Role of Entertainment Media Smoking: A Requirement of the Role One case report describes an actor being introduced to smoking on the set of his first film. In a New York Times Op Ed column,a Kirk Douglas states he by no means smoked during his Broadway profession within the early 1940s. But I had spoken just a few traces when the director, Lewis Milestone, stopped the motion and stated, "Kirk, you ought to be smoking a cigarette in this scene. Bette Davis performs a young Boston socialite who has been repressed and dominated by her mom. She smokes surreptitiously until she meets and falls in love with an older man (Paul Henreid) on a cruise. The sequence is captured at the shut of the voyage, when Henreid lights two cigarettes and arms one to his lover simply before a parting embrace. Given the popularity of this film and these stars at the time, this sequence may have influenced the socialization of ladies to take up smoking, in part by teaching men a novel way to supply a cigarette to a lady. Although no direct evidence helps an advertising motive 362 for such scenes, they mirror the romantic themes included in cigarette advertising at the time, as illustrated by the Lucky Strike advertisements from the mid-1930s. The use of stars to endorse cigarettes in advertisements continued into the 1950s, with Chesterfield endorsements from women film celebrities, such as Dorothy Lamour, Virginia Mayo, Ethel Merman, Ann Sheridan, and Jo Stafford. In addition to main ladies, the advertising of the 1950s heralded new young stars, such as James Dean who depicted rebellious adolescent characters and consolidated the image of the "unhealthy boy" smoker. In Rebel Without a Cause, the image of Dean smoking a cigarette was so intertwined together with his character image that smoking was incorporated into publicity posters for his films. Thus, smoking was promoted in another method-through publicity photographs and posters distributed worldwide (as the German rendition of the poster illustrates). As television started to become a mass medium, the tobacco industry started Monograph 19. The Role of the Media Scenes from Now, Voyager (1942) Magazine advertisements for Lucky Strike documenting thematic similarities between cigarette advertising and film depictions of smoking sponsoring television reveals, providing money to this fledgling leisure industry before it had a sizable audience to attract other types of mainstream advertising. Television advertisements produced during the 1950s included endorsements by distinguished film stars. For instance, John Wayne appeared in a variety of Camel commercials during this era. The extent to which the tobacco industry performed a job in tobacco product placement in films was speculative until specific evidence of financial links between the tobacco and film industries emerged upon the release of tobacco company paperwork. Although these paperwork pertain to model placements in films produced during the Seventies and 1980s only, the practice in all probability preceded those many years. Schudson20 argues that the practice of intentionally mentioning or picturing explicit products in movies occurred earlier. Role of Entertainment Media tobacco industry dates again to the inception of the media industry. However, it seems likely that the depiction of smoking in movies contributed to the Promotional posters for Rebel establishment of social norms that Without a Cause (in English encouraged women to smoke as a and German) mark of independence and equality, as a way to set up a dialog De Beers elevated the function of diamonds (break the ice) between women and men, in Hollywood movies, simply as cigarette and in ways that paralleled other cigarette producers saw to it that main actors advertising themes at that time. Early film and actresses smoked cigarettes in films images of male people who smoke as powerful and within the 1920s. In addition, public relations specialists of that period failed the leisure industry was key in to acknowledge the potential power of movement establishing the prototype of the rebellious pictures as a way to change social norms adolescent cigarette smoker. As mentioned below in continues to attract adolescents to smoking "Movie Content," smoking continues to be within the present. Cigarette manufacturers additionally appear, though film scenes displaying actors really using a specific model have declined.
Baccharis cylindrica (Carqueja). Cyklokapron.
- Dosing considerations for Carqueja.
- Protecting the liver, diabetes, heart pain (angina), improving circulation, and other conditions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Carqueja work?
- What is Carqueja?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97071
Effective 500 mg cyklokapron
The remainder of this chapter is organized as follows: We combine a number of extant approaches to studying health danger and suggest a conceptual model of the antecedents and consequences of health danger perceptions. We place the extant analysis within the health area in our proposed framework, with the antecedents, consequences, and elements moderating their hyperlink described in detail. We conclude with open questions for future analysis that emerge from this synthesis. One of the earliest models proposed was the Health Belief Model (Becker, 1974; Rosenstock, 1974) which proposes that increasing danger perceptions ought to result in precautionary conduct. One of the widest used models to examine health danger is the Theory of Reasoned Action (Ajzen & Fishbein, 1975). This concept has the next key options: (a) Behavior is predicted to observe a behavioral intention, which in turn is based on an total attitude. There is, accordingly, a have to establish: (a) antecedents other than cognitive perception primarily based ones; (b) elements that average the cognitive, motivational, and affective antecedents of danger perceptions; and (c) elements that average the judgment-intention-conduct hyperlink. The Theory of Planned Behavior (Ajzen, 1991) means that perceived management is an impartial construct that affects both intentions in addition to future conduct: the higher the perceived controllability of a symptom, the higher the intention to engage in precautionary or preventive conduct, and the higher the likelihood of engaging within the conduct. In fact, current analysis on these theories has instructed that "previous conduct" could also be one other important construct that affects precise conduct, intentions, perceived management, attitudes, norms, in addition to beliefs (Figure 3 in Albarracin et al. A totally different strategy to understanding health danger and the chance-conduct hyperlink is the Cognitive Adaptation concept (Taylor, 1983). The primary argument put ahead is that accepting physiological danger could also be doubtlessly harmful to psychological danger. Therefore, being unrealistically optimistic within the area of a health danger, similar to cancer, might encourage people to search diagnosis, which might assist prevention and early cure (Taylor, 1983). Taylor, Kemeny, Reed, Bower, & Gruenewald (2000) reviewed a decade of analysis on the relationship between optimism and perceived management with psychological and bodily health. They discover that unrealistically optimistic beliefs, that are related to psychological nicely-being, may also be health protecting, as they act as assets which permit customers to cope with negative life events. This concept explicitly recognizes the position that emotions and have an effect on play in assessing danger and deciding on behavioral actions. Newer additions to the idea permit for the positive impact of psychological simulation where people can think about possible positive situations and, therefore, regulate their conduct to work in the direction of bringing them about (Taylor & Schneider, 1989; Taylor, Pham, Rivkin, & Armor. Their physique of labor means that individual variations average the impact of motivational results on danger perceptions. However, their individual scope is proscribed in laying out the growing array of results, elements, and processes being documented within the area of health risks. Our model categorizes the antecedents of health danger perceptions into 5 broad classes: motivational, cognitive, affective, contextual, and individual variations. Individually and interactively, these elements are integrated to kind a judgment of health danger. We further suggest that there are a number of primary behavioral consequences of forming such a judgment. These are categorized as awareness, curiosity, trial, adoption, repeat-conduct, and word-of-mouth, primarily based on the buyer diff usion of product innovations (Rogers, 1962; 1987). Finally, we suggest that four related danger perceptions-financial, efficiency, psycho-social, and physiological danger-average the likelihood that a health danger perception will translate to a behavioral consequence. The key elements of our model that differentiate it from others are: (a) A broader incorporation of cognitive, motivational, and affective elements; (b) Individual elements proposed both as antecedents of health danger perceptions and moderators of the motivational antecedents of danger; (c) Contextual elements proposed both as antecedents of health danger perceptions and moderators of the cognitive antecedents of danger; (d) the consideration of a wide range of behavioral consequences; and (e) the conceptualization of four other perceived risks that average the chance perception-conduct hyperlink that incorporate prior proposed constructs (similar to perceived management and coping), but also suggest new ones. One of the primary contributions of our strategy is to examine the contextual antecedents of danger perceptions, whose direct and moderating impact suggest that eliciting health danger perceptions might serve a persuasive position besides a measurement position. Given that the measurement of danger perceptions are prone to a wide range of context results, one mind-set about this malleable high quality of health danger is to categorize modifications in danger perceptions as measurement errors. Another way to think about the malleability of health danger is as a measurement impact. For instance, Morwitz and her colleagues have examined how the mere measurement of a construct modifications the likelihood that an occasion will happen in the future. Thus, one could leverage the context results to change danger perceptions, and get customers to take motion. Intertwined within the examination of the totally different antecedents of danger perceptions, we also evaluation the different ways by which danger has been measured and the pros and cons of those methods. Elicit relative measures of Goal should be to bring self-perceptions in line danger: self, common with perceptions of the particular person. Make customers feel good and give attention to advantages when health messages might set off mood or picture administration. Some prescriptions for concept Selected prescriptions for apply Some open questions for future analysis What elements affect what kind of objectives are activated And what can be the impact of a change in both on behavioral intentions and actions Antecedents of Risk Key findings Motivational Short-term somewhat than lengthy-term objectives typically result in underestimation of danger. Social Desirability Bias: People underneath- (over-) report the extent they engage in a risky (preventative) conduct. Examine if improving Improve accuracy via use of counter- accuracy would observe via to conduct. Cognitive Greater accessibility of � Negative information � Extreme information � Recent information � Frequent conduct. Negative, extreme, recent, and frequent behaviors are likely to be given more weight in mixture danger judgments, even though they may be no more diagnostic of danger. A conduct will be integrated into danger estimated to the extent to which a conduct is perceived to be diagnostic. The stage of worry follows an inverted-U formed curve, with low and high ranges of worry backfiring. Increase the salience of alternate information that buyers could use to make danger judgments (such because the accessibility of their own conduct). It could also be easier to frame communication when it comes to a "shut other" to cut back defensive tendencies Consider the frame surrounding estimates. Identify roles of worry, hope, remorse and others within the choice calculus that consumer used to commerce off a current affective state over a future affective/ physiological state. Examine the interaction between affective and cognitive and bodily and psychological health. Increase communication about the diagnosticity of various symptoms and behaviors for a illness. Negative Affect Discrete emotions Contextual Alternative information Response options Measure subjective symptoms utilizing subjective response scales. Proxy information Consumers construct somewhat than retrieve judgments utilizing contextual cues making their danger judgments tensile and easily modified. While survey methodologists can use this information to improve response accuracy, social marketers can use this information to improve estimates of danger in order to encourage conduct change. Depressives are much less prone to self-positivity; optimists are much less likely to replace danger estimates. More controllable events are more prone to self-positivity and have a higher likelihood of danger judgments translating into conduct. The more ambiguous the symptom, the much less likely it is going to be integrated into judgments, and the more likely it is going to be prone to context results. Consumers might use the presence of an extreme symptom on an inventory to categorize themselves as "not at risk. Separate analyses by individual difference variables and establish totally different methods to improve compliance in the direction of a desirable conduct for different segments. Some prescriptions for concept Selected prescriptions for apply Some open questions for future analysis Identifying other individual difference variables that average the extent of selfpositivity and those who average the chance perception-conduct hyperlink. These could include contextual cues, advertising, framing results and other methods. Th ree primary phenomena spotlight the motivational elements affecting health danger perceptions: self-positivity (or unrealistic optimism), social desirability, and self-management. Self-Positivity Bias To accommodate a need for psychological nicely-being and self-enhancement, people may be unrealistically optimistic in their own danger perceptions (Taylor & Brown, 1988). This motivationally pushed bias, referred to because the self-positivity bias (Ragubir & Menon, 1998), is extensively documented within the health literature and may have an effect on danger perceptions in a number of methods (for a evaluation see Taylor, 2003; Taylor et al. The self-positivity impact was first examined within the area of health danger perceptions by Perloff and Fetzer (1986) and has since turn into a topic of mainstream curiosity in consumer psychology (Chandran & Menon, 2004; Keller, Lipkus, & Rimer, 2003; Lin, Lin, & Raghubir, 2003b; Luce & Kahn, 1999; Menon, Block, & Ramanathan, 2002; Raghubir & Menon, 1998, 2001). Shepperd, Helweg-Larsen, and Ortega (2003) found that self-positivity manifests regardless of time, in addition to whether or not one has experienced related occasion. Self-positivity leads people to perceive themselves as being much less danger-prone than known or related others in the same danger group.
Best cyklokapron 500mg
First, the airline could sell too many early restricted tickets and not have sufficient seats remaining to accommodate the complete-fare passengers. Second, the airline could not sell sufficient restricted tickets and find yourself with too many full-fare seats out there on the day of the flight. Airplane seats are a perishable good; any seats which are empty when the plane leaves are immediately value nothing. These seats are usually the supply of Web-based offers during which passengers buy on Friday to fly on Saturday. Passengers could fi nd themselves sitting next to somebody who paid significantly much less for a ticket, however are eating the identical peanuts, watching the identical movie, and reaching the identical location at the same time. Thompson bought an unrestricted ticket one week previous to the flight and paid $four hundred greater than Mr. They start chatting and in the midst of the conversation, they evaluate the prices they paid and when they purchased their tickets. Stone would understand the scenario as truthful, and there was no impact of timing or restrictions. Stone purchased his ticket one month in advance, approximately half (54%) of participants thought Mr. Stone purchased his ticket the morning of the flight, there was a powerful consensus. Virtually all respondents (eighty four%) thought he would find the scenario unfair (2(1) = 24. Consistency of the variable pricing strategies with industry norms may be a minimum of one purpose for the distinction within the perceived fairness of the brick question versus the airline questions. Furthermore, two customers who buy the identical number of bricks will be charged the identical quantity. But within the airline industry, the correlation between time of buy and value is way decrease and perhaps even nonexistent. Consumers could be more keen to settle for variable pricing if costs were more predictable. If customers knew they could get reductions for early purchases or reductions for final minute purchases, such costs could be more acceptable. Being reminded of the inequality by sitting next to somebody who obtained a greater deal makes it even worse. Variable Consumer Pricing With variable shopper pricing, firms sell the identical good or service to totally different customers at totally different costs. The firm identifies differences in value sensitivity amongst customers (either teams or individuals) and expenses costs accordingly. Some firms phase customers into teams based on an simply discernable trait (Carroll & Grimes, 1995). Children and senior citizens typically get reductions at the movies, on the subways, or within the amusement parks. Similarly, many hair salons cost women greater than men to cut and style their hair. We explored some situations of variable shopper pricing amongst teams based on age. Most of the 61 participants (sixty three%) thought that Carrie would understand the scenario as truthful (2 (1) = 24. In the dry cleansing industry, the value of cleansing is predicated on the garment and what it costs to give it again to the consumer in a desired state. Alternatively, perceptions of unfairness could have been based on a common dislike for variable shopper pricing with gender as the discriminating variable. The two eventualities above show that variable shopper costs evoke a range of reactions. Many persons are familiar with senior reductions, and they could view this pricing method as a charitable gesture. People are typically much less familiar with gender-based pricing within the dry cleansing industry, and they could view it as a form of sex discrimination. Another essential distinction between the senior citizen question and the dry cleansing question is that costs were described as senior reductions rather than middle-aged premiums. Even when the higher value was the reference value and the lower price was described as a "low cost" value, costs were still considered as unfair. Since individual customers pays totally different quantities for the same good or service, firms phase customers into teams of dimension one and cost costs accordingly. Variable shopper pricing at the individual stage has been using within the airline industry with frequent flyer cards and within the supermarket industry with loyalty cards. But till lately, it has not been possible for most industries (Carroll & Grimes, 1995). Stores can comply with the movements of tourists on-line, keep observe of what products they view, and keep records of their on-line purchases. Based on this information, they offer totally different costs to totally different buyers for the same good or service. It is authorized for on-line shops to cost totally different costs to totally different customers for the same good at the same time of the day. Some retailers now ship out catalogs that include the identical gadgets at totally different costs to totally different individuals. We requested respondents how they perceived variable shopper pricing at the individual stage. Perhaps more fascinating is the truth that, although Marta was the beneficiary of the value distinction, participants believed that Marta would additionally find the scenario unfair (seventy three%, 2 (1) = 22. Do people assume variable shopper pricing amongst individuals is more acceptable if the individuals concerned are conscious that shops engage in such practices To answer this question, we introduced respondents with an identical state of affairs during which the characters knew about variable shopper pricing at the individual stage. They know that corporations keep observe of their actions on Web sites and try to forecast individual value sensitivities. Again, almost everybody (94%) thought Kirstin would understand the scenario as unfair, and the majority (69%) thought Julie would find it unfair (2 (1) = a hundred. Apparently, even when customers are conscious of behavioral concentrating on, they imagine such practices are unfair. The exact conditions beneath which these pricing strategies are optimum are matters of much debate. Our survey results inform us that, in some instances, variable unit pricing is perceived as truthful. Similarly, in some instances, variable shopper pricing amongst teams is considered as truthful. Four factors contribute to perceptions of fairness-industry norms, justification for value differences, consistency of prices, and transparency of the value structure. Industry Norms Industry norms go a long way toward making variable pricing seem truthful. Lower fares for early purchases were perceived as fairer than decrease fares for final minute purchases. One purpose could have been as a result of decrease fares with early purchases are more widespread occurrences. Minnesota has lately began a program during which drivers pays further to drive within the carpool lane. Drivers have accepted this variable pricing throughout rush hours however have loudly objected to the scheme throughout non-rush hours. Arbitrary or not, certain reference factors turn out to be norms, even when those reference factors range. Justification for Price Differences Consumers will settle for value differences when those differences seem cheap and justified. Consumers found in an internet chat room that Amazon had offered totally different costs to totally different prospects. Amazon replied by telling customers that the prices were determined on a random basis.
500mg cyklokapron
This chapter highlights chosen plant, fungal, and animal toxins as examples of potent agents that target important physiological processes, and it offers information that will facilitate recognition of kinds of envenoming or poisoning in an affected patient. This chapter also supports the perception that animal toxins are generally of low relevance to military functions, and contrarily, the relevant-but restricted-nontactical importance of some plant and fungal toxins. This information is intended to improve awareness of the potential hazards posed by animal toxins that can be utilized for offensive functions on a small scale and likewise provide some essential considerations about potential exposures to venomous and poisonous animals, plants, and mushrooms which may occur throughout military deployments. The use in warfare of numerous animal-derived venoms, as well as the venomous animals themselves, has probably been contemplated for many of human history. The well-known legendary account of the second labor of Hercules slaying the malevolent 9-headed serpent, the Lernaean Hydra (Figure 18-1), featured him using venom-coated arrowheads to accomplish the deed. Some folklore students consider this to be the first description of the use of a bioweapon. Circa 200 bce, Hannibal reportedly used pottery containing venomous snakes to "bombard" opposing maritime vessels. Using venoms as a weapon can also be obviously distinct from the weaponization of poisons from micro organism. However, many toxins found in animals, plants, and mushrooms are highly poisonous-even lethal-to people. These toxins, which may kind the basis for developing tailor-made toxin derivatives for specific functions, are the topic of current intense analysis within the pharmaceutical industry. A well-known instance is paclitaxel, a taxane initially derived from bark extract of the Western yew, Taxus brevifolia. Taxanes, similar to paclitaxel, are potent cytotoxins that stabilize micro- Figure 18-1. Toxins From Venoms and Poisons tubule assembly, thereby disrupting physiological assembly/disassembly of microtubules in a guanosine triphosphate-unbiased manner. Several pharmacotherapeutics are derived from venom parts, and some are in numerous levels of scientific trials. Exendin-four is a 39-amino acid peptide isolated from venom of the helodermatid lizard, the Gila monster (Heloderma suspectum), that has greater than 50% structural homology with glucagon-like peptide 1. Exendin-four exhibits useful similarity with glucagon-like peptide 1, but has an extended half-life and organic stability. This peptide will increase insulin secretion, accelerates gut emptying, and stimulates -islet cell proliferation and survival, as well as different actions. The potential menace posed by these toxins and their derivatives (as discussed additional within the section on Relevance to Biological Warfare) relates principally to their practicality for weaponization and supply, quite than their inherent toxicity. Venoms are mixtures-typically complex mixtures-of poisons produced in defined organs (normally venom glands) or organelles (eg, nematocysts/cnidocysts located in specialized cells and nematocytes/cnidocytes in jellyfish) which might be delivered to the target organism normally using an evolved supply system similar to fangs or a stinging apparatus. Therefore, venom is delivered as an lively process, and if adequate (this can be minute in some cases) amounts are introduced into the target organism, it causes envenomation (also called "envenoming"). Venom used offensively may be used to either kill or immobilize the prey, possibly aid digestion of the prey, or mix these functions, which can also be useful when venom is used defensively. The evolution of venom has been positively chosen among a variety of taxa, suggesting that it offers numerous organisms with selective benefits and health. The definition of venom from evolutionary, phylogenetic, and useful perspectives is actively debated. Animal, plant, or fungal toxins include particular person or mixtures of poisons which might be produced by the organism or, in some cases, by symbiotic micro organism (eg, the synthesis of tetrodotoxin by at least 18 microbial taxa, including Vibrio spp12,thirteen and Shewanella putrefaciens14) that colonize the poisonous animal. These toxins are generally delivered in a passive and, in most cases, a defensive approach to an organism attacking or trying to consume the toxin producer. Examples embody tetrodotoxic fish that cause poisoning when eaten, some toads (eg, widespread African toad, Amietophrynus regularis) that exude toxins from parotid pores and skin glands when mouthed by predators, and both poisonous plants and mushrooms when ingested. However, different animals similar to several species of hedgehogs (eg, four-toed, spiny, or Cape hedgehog, Atelerix albiventris pruneri15) anoint their spines with poisonous toad parotid secretions, and thereby can be considered to actively deter predators by exposing them to toad toxins via their spines. When delivered on the typically delivered dose, the toxins in poisoning can typically cause disagreeable but nonlethal effects. Clear exceptions exist when ingestion of solely a tiny quantity of some of these poisonous organisms, due to their excessive lethal efficiency, can be fatal for people. Detailed epidemiology is unavailable for any toxin-induced disease (other than chosen microbial toxin illnesses, and this information is usually incomplete) on the world level, but more epidemiologic knowledge could emerge for some key disease varieties, on account of growing worldwide efforts directed on the improved administration of regionally essential venom illnesses (eg, several snakebite initiatives). An approximate estimate of epidemiology for some principal groups is offered in Table 18-1. Venomous Bites and Stings Venomous animals embody an unlimited array of organisms discovered in lots of phyla, from primitive to highly advanced, but certain groups have a very essential influence on human health. The most dependable knowledge are for snakebite and the annual world fatalities are probably underestimated. Figures for insects embody extreme and fatal allergic reactions to venomous stings, that are liable for the overwhelming majority of medically significant cases. No well-documented fatalities exist, and inadequate proof for any approximations of possibly reliably reported semianecdotal cases. Tetrodotoxin-distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. The estimated world toll from snakebite stays a mixture of some quality proof and projected hypothesis. Despite this influence, snakebite has generally been relegated to minor standing in medical planning. Scorpions, Spiders, and Other Arachnids Scorpion stings are second, after snakebite with regard to medically significant occurrences, and probably affect more than 1 million people each year, but with a low fatality fee (see Chippaux and Goyffon, 2010). Spiderbite can also be widespread, but with a couple of notable exceptions (widow spiders, Latrodectus spp, family Theridiidae [Figure 18-2]; recluse spiders, Loxosceles spp, family Sicariidae [Figure 18-three]; banana spiders, Phoneutria spp, family Ctenidae; Australian funnelweb spiders, Atrax spp [Figure 18-four]; and Hadronyche spp, family Hexathelidae), these are most commonly of minor medical significance (see Tick envenoming causing paralysis is an issue in Australia, North America, and southern Africa, and possibly elsewhere, but reported cases are few, although rare fatalities have occurred (see Meier and White, 1995). A medically essential widow spider (Latrodectus spp) and comparison of the vertically deployed venom supply apparatus of a mygalomorph spider and the horizontally deployed venom supply apparatus of an araenomorph spider. Note the vertical direction of the fang-bearing chelicerae historically termed paraxial, with the spider in an adopted defensive posture. The determine once more illustrates the vertical direction of the fang-bearing chelicerae. The determine illustrates the horizontal deployment of the chelicerae-bearing fangs historically termed diaxial. One of two genera (Sicarius and Loxosceles) belonging to the family Sicaridae, there are roughly 113 recognized taxa of Loxosceles. Several of these, including L reclusa, have inflicted medically significant bites that will sometimes cause a recurrent ulcer. In some components of South America, several species could cause systemic envenoming (viscerocutaneous loxoscelism), an unusual but potentially life threatening venom disease. There is antivenom available in several Latin American countries (eg, Brazil, Chile, Peru, Mexico), but treatment within the United States stays considerably controversial with no quality proof supporting the earlier administration (eg, surgical debridement, and so forth) of verified L reclusa bites. Meticulous wound administration and possibly bariatric oxygen remedies are essentially the most appropriate administration strategies. Recluse spider bites are among the many most misdiagnosed displays to emergency departments and outpatient/urgent care amenities, and analysis should be founded on verified identification of a spider or, in lieu of a specimen, with a well-supported history of a bite occurring throughout the vary of recluse spiders (many suspected bites have occurred well outdoors any natural vary or region in which the species has been accidentally introduced). Retrospective studies have advised that typically forty to a hundred deaths occur each year from hymenopteran sting anaphylaxis within the United States. Some bee venoms (eg, bumblebee, Megabombus pennsylvanicus; honey bee, Apis mellifera; Figure 18-5) include mast cell degranulating peptide, a 22-amino acid cationic peptide that can directly trigger launch of proanaphylactic mediators without prior sensitization. One unusual instance of a medically essential insect venom is the Lepidopteran larvae (caterpillar) of the giant silkworm moth, Lonomia obliqua (family Saturniidae; Figure 18-6), whose spines include several direct and indirect prothrombin activators, as well as several different toxins. Marine Envenoming: Sea Snakes, Cnidarians, and Venomous Fish Marine envenoming, similar to jellyfish stings, are widespread, but few are medically significant. Significant kinds of marine envenoming embody box jellyfish (eg, Chironex fleckeri, family Chirodropidae) stings (typically lethal); Irukandji jellyfish stings (resulting in a syndrome attributable to several taxa of cnidarians, rarely lethal; see under under Excitatory Neurotoxins); and blue bottle (Physalia spp, family Physaliidae) stings (nonlethal envenoming, but occasional cases of probably lethal allergic reactions). Sea snake (family Elapidae) bites may cause lethal envenoming, but are more and more unusual due to modifications in fishing strategies (eg, decreased handbook removal of snakes from purse nets). Painful stings from venomous fish from several totally different households (eg, Scorpaenidae, Trachinidae, and Tetrarogidae), including many popular food and aquarium fishes as well as marine and recent or brackish water stingrays, are widespread but generally unlikely to be lethal.
Quality cyklokapron 500 mg
The disease first seems as a small papule that progresses over a day or two to a vesicle containing serosanguineous fluid with many organisms and a paucity of leukocytes. Histopathology findings include various degrees of ulceration, vasculitis, perivascular irritation, coagulative necrosis, hemorrhage, and edema. The lesion is often painless, and varying degrees of edema may be present round it. The ulcer base develops a attribute black eschar, and after 2 to three weeks the eschar separates, typically leaving a scar and typically requiring surgical reconstruction. Photographs: Courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia. Of latest interest has been the identification of anthrax instances among intravenous drug users in western Europe. These numbers elevated to a total of 119 instances from December 2009 to December 2010. These signs often persist for 2 or three days, and in some instances there may be a short interval of improvement. Then a sudden onset of accelerating respiratory misery with dyspnea, stridor, cyanosis, elevated chest pain, and diaphoresis occurs. Chest radiograph examination often exhibits the attribute widening of the mediastinum from necrosis and hemorrhage of the lymph nodes and surrounding tissues, typically with related pleural effusions (Figure 6-5). In the 2001 bioterrorist event, the pleural effusions had been initially small however quickly progressed and continued despite effective antibiotic therapy. Effusion fluid from deceased patients who had received fewer than 55 hours of antibiotic therapy revealed bacilli. Mortality had been essentially 100% within the absence of acceptable therapy; however, throughout 2001 the mortality fee was forty five%. Heavy metal publicity produces immunosuppression and an elevated susceptibility to infection. Meningitis with subarachnoid hemorrhage in a person from Thailand who died 5 days after consuming undercooked carabao (water buffalo). Gastrointestinal anthrax begins with nonspecific signs of nausea, vomiting, and fever; generally extreme stomach pain follows. The presenting sign may be an acute stomach, which may be related to hematemesis, massive ascites, and bloody diarrhea. Mortality in each forms may be as excessive as 50%, especially within the gastrointestinal form. Cutaneous anthrax must be considered after a painless pruritic papule, vesicle, or ulcer develops-typically with surrounding edema-and then becomes a black eschar. Bacterial culture exams include colony morphology on sheep blood agar plates incubated at 35�C to 37�C for 15 to 24 hours. B anthracis colonies are 2 to 5 mm in diameter, flat or barely convex, irregularly round with potential comma-formed ("Medusa-head") projections with a ground-glass appearance (Figure 6-7). A motility check must be performed both by wet mount or motility media; B anthracis is nonmotile. Gamma bacteriophage lysis and direct fluorescent antibody exams are performed at Level D laboratories as confirmatory exams (Figures 6-7 and 6-eight). The differential analysis ought to include tularemia, staphylococcal or streptococcal disease, and orf (a viral disease of sheep and goats transmissible to people). The analysis of inhalational anthrax is tough, but the disease must be suspected with a historical past of publicity to a B anthracis�containing aerosol. However, the event of respiratory misery in association with radiographic evidence of a widened mediastinum ensuing from hemorrhagic mediastinitis and the presence of hemorrhagic pleural effusion or hemorrhagic meningitis ought to counsel the analysis. Contrast-enhanced computer tomography images reveal diffuse hemorrhagic mediastinal and hilar adenopathy with edema, perihilar infiltrates, bronchial mucosal thickening, and hemorrhagic pleural, and pericardial effusions. Gastrointestinal anthrax is tough to diagnose because of its rarity and nonspecific signs together with nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and fever. As the disease progresses, patients typically develop acute, extreme stomach pain, hematemesis, and bloody diarrhea. Diagnosis is often considered only with a historical past of ingesting contaminated meat within the setting of an outbreak. The analysis of oropharyngeal anthrax can be made from the clinical and physical findings in a patient with the appropriate epidemiological historical past. Sore throat, dysphagia, hoarseness, cervical lymphadenopathy, and edema in addition to fever are sometimes presenting signs. An necessary distinguishing function is that the cerebral spinal fluid is hemorrhagic in as many as 50% of instances. The analysis can be confirmed by figuring out the organism in cerebral spinal fluid by microscopy, culture, or each. A positive skin check to anthraxin (an undefined antigen derived from acid hydrolysis of the bacillus that was developed and evaluated within the former Soviet Union) has additionally been reported212 to assist with the retrospective anthrax analysis. However, if an inhalational publicity can be suspected, ciprofloxacin or doxycycline is recommended as first-line therapy. Treatment must be continued for 7 to 10 days, unless inhalational publicity is suspected; then therapy must be continued for 60 days. However, latest research of the 2001 bioterrorism event have recognized problems related to pro139 Medical Aspects of Biological Warfare longed therapy, mass prophylaxis, and medicine compliance. Tetracycline, erythromycin, and chloramphenicol have additionally been used successfully228 for treating uncommon instances attributable to naturally occurring penicillin-resistant organisms. Additional antibiotics proven to be active in vitro include gentamicin, cefazolin, cephalothin, vancomycin, clindamycin, and imipenem. Experimental infections utilizing the inhalational mouse model have demonstrated vital efficacy utilizing these additional antibiotics. Inhalational, oropharyngeal, and gastrointestinal anthrax must be handled with intravenous therapy utilizing two or more antibiotics. The therapy ought to initially include a fluoroquinolone or doxycycline with one or more of the next antibiotics: clindamycin, rifampin, penicillin, ampicillin, vancomycin, amino-glycosides, chloramphenicol, imipenem, and/ or clarithromycin. Recommendations for therapy throughout being pregnant and for pediatric populations comply with comparable guidelines. This immunologic over-response has prompted the analysis of varied augmentation therapies to mitigate these occasions. When rabbits had been handled with levofloxacin plus raxibacumab verses levofloxacin alone, the absolute difference in survival rates between the teams was not statistically vital; however, clinically there was only an 18% demise fee within the levofloxacin plus raxibacumab group and a 35% demise fee within the levofloxacin only group. Recent analysis has suggested postexposure vaccination may shorten the length of 140 antibiotic prophylaxis, providing the least expensive and best strategy to counter a bioterrorism event. The final product additionally accommodates 100 �g/mL of formaldehyde and 25 �g/mL of benzethonium chloride as preservatives. The vaccine must be given to industrial employees uncovered to potentially contaminated animal products imported from countries in which animal anthrax stays uncontrolled. People in direct contact with potentially infected animals and laboratory employees must also be vaccinated. Vaccination can be indicated for defense against anthrax use in biological warfare. For preexposure safety the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends intramuscular injections starting on day zero adopted by week four, and each 6 months (6, 12, and 18 months) for a total of 5 doses as the initial vaccination series. Since no in vitro correlate of immunity exists for people, annual boosters are recommended if the potential for publicity continues. A live attenuated, unencapsulated spore vaccine is used for people within the former Soviet Union. When examined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, the present serologic check of alternative, greater than 95% of vaccinees seroconvert after the initial three doses. Then they speculated that this observed stochastic variation in humoral immunity was likely a serious contributing issue to the heterogeneity of vaccine response. Although these data counsel enhancing immunologic recognition of specific epitopes can improve vaccine protective response, the present anthrax vaccine adsorbed vaccine has demonstrated vital safety to nonhuman primates when uncovered to inhalational problem with large doses of anthrax spores. The examine inhabitants labored in four mills within the northeastern United States where B anthracis�contaminated imported goat hair was used. The vaccinated group, compared to a placebo-inoculated management group, 141 Medical Aspects of Biological Warfare was afforded ninety two. There had been inadequate inhalational anthrax instances to decide whether or not the vaccine was effective. This same vaccine was previously proven to shield rhesus monkeys and other animal fashions against an aerosol publicity to anthrax spores.
References:
- https://bnssgccg-media.ams3.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/attachments/09_20150213_governing_body_report_cprg_policies.pdf
- https://www.rand.org/content/dam/rand/pubs/monographs/2008/RAND_MG720.pdf
- https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/PDF/ss/ss4404.pdf
- https://ophed.net/system/files/2009/07/tear-film-duanes-ophthalmology-1768-1768.pdf
.png)