Quality 100 mg carbamazepine
Sensory Whole limb anaesthesia, hemisensory loss for all modalities to the midline. It is rare for a useful analysis to be subsequently revised to a somatic condition. Probably the most problematic areas relate to unwitnessed seizures (video footage or direct statement are often extremely helpful), and weird postures that might turn out to be dystonia. Such emotions are rapidly sensed by families and have a tendency to exacerbate and perpetuate symptoms. In the case of useful seizures, hold open the likelihood that a (small) proportion of occasions additionally be} as a result of} epilepsy. In some situations nevertheless it may be extra appropriate to hand over ongoing management to different services. Be significantly careful to respect confidentiality in discussions with the college. Perceptions of the illness by different professionals involved with the kid have to be addressed. A multidisciplinary physical-psychosocial-schooling rehabilitation approach as utilized in children with acquired mind injuries additionally be} useful for complex situations. Many activists and patient groups resent any suggestion of psychological contributions to causation or prolongation of symptoms for whom an organic. The controversy amongst some help groups about graded exercise pertains to comprehensible worry of over-exhaustion and setback. In apply these fears can be explictly addressed and evaluation arrangements agreed. Common neurological symptoms include reported seizures, collapse, drowsiness, and developmental delay. Verbal fabrications are far more common than induced physical indicators of illness: this poses specific problems in the context of reported seizures, which by their nature are sometimes unobserved. Repeated presentations to multiple of} specialties, the reporting of recent symptoms following decision of the earlier ones and specific reported symptoms (stopping respiration, lack of consciousness, seizures, choking, or collapse) are concerning. Working together to safeguard children: a guide to inter-agency working to safeguard and promote the welfare of kids. Specific investigations Suspected hypoglycaemia · If hypoglycaemia is suspected or documented, measure true blood glucose (fluoride oxalate) and draw 2 mL of blood (in lithium heparin or serum) for C peptide and insulin. The most popular pattern (blood, urine) and handling requirements depend upon the substance of curiosity. Arrange for their correct labelling and careful freezing and storage to enable retrospective evaluation if issues concerning a selected intoxicant come up. Seizures · Prolactin ranges sometimes rise after important tonicclonic seizures but might not, in order that the worth of normal ranges is limited. Sample must be collected within 15 min (which severely limits their usefulness) and compared with a management pattern taken precisely 24 h later (to permit for the conventional circadian rhythm in the levels). Migraine Epidemiology Getting a minimum of|no much less than} one migraine per year: · 3% of all children 710 yrs. Previous vascular hypotheses of vasoconstriction and dilation have been discredited. Genetic components 5080% of kids may have a mother or father with a migraine variant (which might have waned by the point a mother or father is interviewed, so a scarcity of a present headache history additionally be} misleading). Migraine without aura most likely multifactorial with genetic and environmental components. These and different findings counsel a channelopathy might compromise neurotransmitter homeostasis inflicting aura and different neurological manifestations of childhood headache. The trigeminal innervation Large cerebral vessels, pial vessels, venous sinuses and dura mater are innervated by small diameter myelinated and unmyelinated neurons serving nociception. Cortical spreading melancholy might activate trigeminal neurons (especially ophthalmic division) to launch substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide, leading to sterile neurogenic irritation, and plasma extravasation with mast cell degranulation and platelet aggregation. This causes trigeminal space allodynia (perceived pain from a usually non-painful stimulus), sensitization of thalamic neurons and a disordered central nervous system response. Involvement of the trigeminal nucleus with the dorsal horns of C1 and C2 (remember how long the nucleus is! Episodes lasting minutes to days; the pain sometimes bilateral and mild/moderate intensity; no nausea but photo-/phonophobia additionally be} present. Aura is often visible, flashing, glowing or shimmering lights; fortification spectra (zigzags); black dots, and/or scotomata (field defects). Clinically, these syndromes resemble transient ischaemic attacks: creating reversible focal neurological deficits lasting tens of minutes to quantity of} hours. As such, migraine enters into the differential analysis of a wide range|a variety} of episodic neurological symptoms and indicators. Prominent autonomic indicators (nausea, vomiting, sweating, vasomotor changes in skin) are additionally suggestive. Otherwise migraine turns into a analysis of exclusion of different, extra severe pathologies: see sections concerning investigation of kids with arterial ischaemic stroke (see b p. Triggers Migraine episodes additionally be} triggered by a variety of|quite so much of|a wide range of} components including stress, relaxing after stress. Food triggers (chocolate, scorching dogs, smoked and spiced meats, Chinese food containing monosodium glutamate, cheese, cola drinks, bananas, yeast and beef extract, and wine) are much less common in children than adults. The childhood periodic syndromes Recurrent problems considered migrainous in that they generally precede the establishment of a extra standard migraine image. The child is properly in between episodes: · Cyclical vomiting describes recurrent stereotyped episodes of vomiting and intense nausea associated with pallor and lethargy. Between episodes, normal neurological examination, audiometric, and vestibular operate tests. Where symptoms were being experienced a minimum of|no much less than} 15 days a month averaging two hours per day for greater than three mths. To assist the latter explore whether or not the kid is in a predicament of some kind, both at residence or college. Chronic analgesia over-use headache additionally be} an important issue contributing to and perpetuating headache symptoms in these situations. Explain the character of the issue and the need to|the necessity to} change the sample of analgesia use. Children should be inspired to reserve use for severe incapactitating attacks only. Conjunctival injection, lacrimation, nasal congestion, rhinorrhoea, brow and facial sweating, myosis, ptosis, or eyelid oedema. Methysergide should only be used for periods of up to as} 6 mths due to the chance of retroperitoneal fibrosis. Other causes of recurrent headache · Refractive errors are an unusual reason for headaches, but visible acuity should be checked. Migraine, tension-type and mixture headache · Education is extremely important in the management of headache. The underlying reason for the headache should be defined to the kid in addition to the mother and father. Common negative effects: increased appetite and weight achieve, drowsiness dry mouth, constipation. Teenage ladies want advice about concurrent use of oral contraceptive pill (see b p. Behavioural and cognitive approaches Once a extra persistent sample has established, non-pharmacological approaches be efficient. It additionally be} extra practical to counsel avoiding triggers during a known vulnerable period. In long-term follow-up of 9000 Swedish college children with migraine: · One-third had been migraine-free for >1 yr at 6-yr follow-up. Developmental problems that includes ventriculomegaly/hydrocephalus · Neural tube defects: significantly myelomeningocoele and encephalocoele. Acquired causes of obstructive hydrocephalus · Intraventricular haemorrhage: 80% of untimely infants with grade 3 and grade four haemorrhages develop progressive ventricular dilatation. Later childhood · Macrocephaly, additionally be} an isolated discovering in arrested hydrocephalus. Shunts · Ventriculo-peritoneal shunts: a proximal catheter in the lateral or 4th ventricle, a distal catheter in the peritoneal cavity. A long size of tube can be placed in the hope of avoiding re-operation between infancy and maturity, although shunts placed in the neonatal period often fail (typically at about 56 yrs age) as a result of} displacement of both the proximal or extra generally the distal catheter tip with progress. Endoscopic 3rd ventriculostomy · For obstructive hydrocephalus significantly as a result of} aqueductal stenosis.
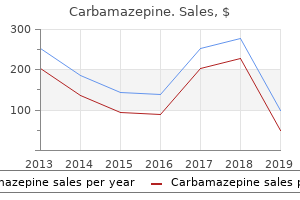
Carbamazepine 400mg
Always administered with cilastatin (inhibitor of renal dehydropeptidase I) to inactivation of drug in renal tubules. Wide spectrum, but significant unwanted effects effects} restrict use to life-threatening infections or after other drugs have failed. Nephrotoxicity, Ototoxicity, Thrombophlebitis, diffuse flushing-red man syndrome A (largely preventable by pretreatment with antihistamines and slow infusion rate). Bactericidal; irreversible inhibition of initiation complex by way of binding of the 30S subunit. Nephrotoxicity, Neuromuscular blockade, Ototoxicity (especially when used with loop diuretics). Bacterial transferase enzymes inactivate the drug by acetylation, phosphorylation, or adenylation. Meningitis (Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae) and Rocky Mountain spotted fever (Rickettsia rickettsii). Limited use owing to toxicities but often nonetheless used in creating nations because of low value. Treats anaerobic infections above the diaphragm vs metronidazole (anaerobic infections beneath diaphragm). Inhibit protein synthesis by binding to 50S subunit and preventing formation of the initiation complex. Bone marrow suppression (especially thrombocytopenia), peripheral neuropathy, serotonin syndrome. Contraindicated in pregnant women, nursing mothers, and youngsters < 18 years old because of of} attainable harm to cartilage. May cause tendonitis or tendon rupture in folks > 60 years old and in sufferers taking prednisone. Gardnerella vaginalis, Anaerobes (Bacteroides, Treats anaerobic infection beneath the diaphragm C difficile). Can be used instead of amoxicillin vs clindamycin (anaerobic infections above in H pylori "triple remedy" in case of penicillin diaphragm). Disulfiram-like response (severe flushing, tachycardia, hypotension) with alcohol; headache, metallic style. Used for meningococcal prophylaxis and chemoprophylaxis in contacts of children with Haemophilus influenzae type B. Minor hepatotoxicity and drug interactions (cytochrome P-450); orange physique fluids (nonhazardous facet effect). Multidrug-resistant P aeruginosa, multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: polymyxins B and E (colistin). Cryptococcus (amphotericin B with/without flucytosine for cryptococcal meningitis), Blastomyces, Coccidioides, Histoplasma, Candida, Mucor. Systemic fungal infections (especially meningitis caused by Cryptococcus) in combination with amphotericin B. Inhibit fungal sterol (ergosterol) synthesis by inhibiting the cytochrome P-450 enzyme that converts lanosterol to ergosterol. Testosterone synthesis inhibition (gynecomastia, particularly with ketoconazole), liver dysfunction (inhibits cytochrome P-450). Dermatophytoses (especially onychomycosis-fungal infection of finger or toe nails). Oral treatment of superficial infections; inhibits progress of dermatophytes (tinea, ringworm). Teratogenic, carcinogenic, confusion, headaches, disulfiram-like response, cytochrome P-450 and warfarin metabolism. Treatment of plasmodial species other than P falciparum (frequency of resistance in P falciparum is just too|is simply too} high). Beginning remedy inside forty eight hours of symptom onset may shorten period of sickness. Obstructive crystalline nephropathy and acute renal failure if not adequately hydrated. Bone marrow suppression (leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia), renal toxicity. Nephrotoxicity, electrolyte abnormalities (hypo- or hypercalcemia, hypo- or hyperphosphatemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia) can result in seizures. Disinfection and sterilization Autoclave Alcohols Chlorhexidine Hydrogen peroxide Iodine and iodophors Goals embody the discount of pathogenic organism counts to safe ranges (disinfection) and the inactivation of self-propagating biological entities (sterilization). Major topics corresponding to inflammation and neoplasia appear regularly in questions throughout totally different organ methods, and such topics are undoubtedly high yield. For instance, the ideas of cell injury and inflammation are key to understanding the inflammatory response that follows myocardial infarction, a very common topic of board questions. Similarly, a familiarity with the early mobile changes that culminate within the growth of neoplasias-for instance, esophageal or colon cancer-is critical. Finally, certain you|ensure you|be sure to} acknowledge the main tumor-associated genes and are snug with key cancer ideas corresponding to tumor staging and metastasis. Intrinsic and extrinsic pathways; both pathways activate caspases (cytosolic proteases) mobile breakdown together with cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, membrane blebbing, and formation of apoptotic our bodies, that are then phagocytosed. Characterized by deeply eosinophilic cytoplasm and basophilic nucleus, pyknosis (nuclear shrinkage), and karyorrhexis (fragmentation caused by endonuclease-mediated cleavage). Cell membrane typically stays intact without significant inflammation (unlike necrosis). Bcl-2 retains the mitochondrial outer membrane impermeable and therefore prevents cytochrome c launch from the internal mitochondrial matrix. Bcl-2 overexpression (eg, follicular lymphoma t[14;18]) caspase activation tumorigenesis. Mutations in Fas numbers of circulating self-reacting lymphocytes because of of} failure of clonal deletion. Pale infarct B Pale (anemic) infarcts B happen in strong organs with a single (end-arterial) blood provide, corresponding to heart, kidney, and spleen. Inflammation Vascular part Cellular part Acute Characterized by rubor (redness), dolor (pain), calor (heat), tumor (swelling), and functio laesa (loss of function). Neutrophils extravasate from circulation to injured tissue to participate in inflammation by way of phagocytosis, degranulation, and inflammatory mediator launch. Neutrophil, eosinophil, antibody (pre-existing), mast cell, and basophil mediated. Acute inflammation is fast onset (seconds to minutes) and of short period (minutes to days). Outcomes embody complete decision, abscess formation, or development to chronic inflammation. Mononuclear cell (monocytes/macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells) and fibroblast mediated. Free radicals may be eradicated by scavenging enzymes (eg, catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase), spontaneous decay, antioxidants (eg, nutritional vitamins A, C, E), and certain steel carrier proteins (eg, transferrin, ceruloplasmin). Pleural effusion is exudative if 1 of the next criteria is met: Pleural effusion protein/serum protein ratio > 0. Amyloid deposits visualized by Congo red stain A, polarized mild (apple inexperienced birefringence) B, and H&E stain (C reveals deposits in glomerular mesangial areas [white arrows], tubular basement membranes [black arrows]). Heterogeneous group of disorders, together with familial amyloid polyneuropathies because of of} transthyretin gene mutation. Isolated atrial amyloidosis because of of} atrial natriuretic peptide is widespread in regular getting older and might predispose to elevated risk of atrial fibrillation. Autopsy of elderly individual will reveal deposits in heart, colon, liver, kidney, eye, and other organs. May be a risk factor for future malignancy (eg, endometrial hyperplasia) but not thought of premalignant. Causes embody disuse, denervation, loss of blood provide, loss of hormonal stimulation, poor vitamin. Mild dysplasia is usually reversible; extreme dysplasia usually progresses to carcinoma in situ. Reversible if the irritant is eliminated but may undergo malignant transformation with persistent insult (eg, Barrett esophagus esophageal adenocarcinoma). The degree to which a malignant tumor resembles its tissue of origin: Well-differentiated tumors (often less aggressive) closely resemble their tissue of origin. Poorly differentiated tumors (often more aggressive) look nearly nothing like their tissue of origin. See cervical instance A, which reveals regular cells and spectrum of dysplasia, as discussed beneath.
Best carbamazepine 200mg
In the presence of a big carotid stenosis, endarterectomy additionally be} very efficient if the current stroke occurred within the territory distal to the stenosis, but of restricted effectiveness if one other territory is concerned. The greater difficulty in using it has been improved by a recently printed laptop algorithm. Anterior circulation syndromes the anterior circulation refers to the part of of} the brain perfused by the carotid arteries. The artery is subdivided into the M1 segment, from which begin the deep perforating lenticulostriate arteries, the M2 segment, corresponding to the segment after the bifurcation into superior and inferior divisions, and the M3 segment, together with the insular half. The M4 segments, the leptomeningeal arteries, come up from the M3 segments and are named orbitofrontal, prefrontal, precentral, central sulcus, anterior parietal, posterior parietal, angular and temporal arteries, with necessary variations in their territories. As collateral networks are highly variable, an occlusion of the same artery on the identical place could result in fairly variable severity of the stroke and of prognosis. The affected person is often awake or presents gentle drowsiness or agitation, significantly with a right infarct. Cognitive indicators are all the time current: within the case of a left lesion, aphasia, and typically than not} world, ideomotor apraxia. This image suggests an M1 occlusion with or without carotid occlusion and is associated with a rather unfavorable prognosis. Particularly in younger people, malignant stroke with brain edema could develop, resulting in excessive intracranial pressure and subsequent subfacial, uncal and transtentorial herniation. The scientific deterioration occurs usually inside 4872 hours, when vigilance decreases and preliminary indicators worsen. Early recognition of patients at risk allows the medical team to suggest a hemicraniectomy for selected patients, a therapy which has proved highly efficient if carried out inside 48 hours and earlier than these indicators occur [6]. Motor and sensitive features of the lower limbs are much less concerned than the face and arms. The visible field deficit additionally be} a contralateral homonymous hemianopia or a quadrantanopsia. The deviation of the pinnacle and the eyes is extra transitory and the sensitive deficit is much less severe. Cognitive deficits are much like an M1 occlusion but usually much less pronounced or rapidly bettering. Involvement of one of the leptomeningeal branches (M3 or M4) can produce highly circumscribed infarcts accompanied by particular neurological deficits and is typically than not} related to embolism. The lenticulostriate arteries vascularize the basal ganglia and components of the interior capsule. Ischemia in their territory can therefore produce severe deficits with a really small-volume lesion. Cortical indicators are absent or minor, except within the case of deafferentation of the cortex by interruption of subcortical cortical pathways. Clinical indicators include proportional hemiparesis, hemihypesthesia, dysarthria, hypophonia, and infrequently irregular actions within the case of involvement of basal ganglia. The centrum ovale receives its blood supply from medullary perforating arteries coming principally from leptomeningeal arteries. Both small and bigger lesions could occur within the border-zone space between the deep (leptomeningeal) and superficial (meningeal) arteries from hemodynamic mechanisms (see below). Malignant stroke with brain edema could develop, resulting in excessive intracranial pressure and subsequent herniation. Infarctions of the lower arterial segments show comparable symptoms, but not the complete image. The A1 segment has deep perforating arteries, named the medial lenticulostriate arteries, and provides rise to the recurrent artery of Heubner (raH), which supplies the caudate head, the genu and anterior arm of the interior capsule and the supero-anterior putamen. Sphincter dysfunction, mutism, anterograde amnesia, greedy, and behavioral disturbances are significantly frequent in ischemia of the deep perforating arteries and the raH. Involvement of the corpus callosum can produce the callosal disconnection syndrome, secondary to interruption of the connection of bodily information from the proper hemisphere to cognitive heart within the left hemisphere. The artery vascularizes to a variable diploma the inferior posterior and retrolenticular part of of} the interior capsule, the tail of the caudate nucleus, part of of} the lenticular nucleus, the posterior corona radiata, the lateral geniculate body and the beginning of the optic radiations. Clinically much less necessary are 123 Section 3: Diagnostics and syndromes variable contributions to the vascular supply of the uncus, amygdala, hippocampus, optic tract, components of midbrain (substantia nigra, cerebral peduncle), subthalamic area, and choroid plexus. In overwhelming majority of} patients, the presentation is a lacunar syndrome: pure motor or sensorimotor hemiparesis and fewer frequently a pure sensory deficit or an ataxic hemiparesis syndrome. A uncommon but particular visible field defect is a homonymous defect within the higher and lower quadrants with sparing of a horizontal sector [8]. It usually occurs when an orthostatic stress leads to a hypoperfusion of the brain [9] secondary to carotid severe stenosis. A progressive atherosclerotic occlusion is often much less severe, with a basic subacute two-phase presentation and even asymptomatic. Retinal ischemia from carotid emboli additionally be} transient (amaurosis fugax) or persistent. Posterior circulation syndromes the posterior circulation additionally be|can be} called the vertebrobasilar circulation. In contrast, a progressive atherosclerotic occlusion is often much less severe, with a basic subacute twophase presentation. Clinical clues to differentiate posterior from anterior circulation strokes Important scientific symptoms and indicators point to a posterior circulation stroke and must be acknowledged. Similarly, headache is extra frequent within the posterior circulation, is typically ipsilateral to the infarct, and may have features of major complications corresponding to migraine [10]. Past diplopia, tilt of the imaginative and prescient, true rotatory or linear vertigo, drunken-type gait, hiccup, bilateral or crossed motor or sensory symptoms, preliminary decreased level of consciousness and amnesia must be actively searched for within the historical past of stroke patients. It could occur as onerous and fast|a set} misalignment of the ocular axis, corresponding to in vertical skew deviation of the eyes as part of of} the ocular tilt reaction. A lateral medullary lesion (Wallenberg syndrome) leads to an ipsilateral deviation of the eyes, nonetheless, and is often accompanied by a marked horizontal or horizonto-rotatory nystagmus. A vertical gaze paresis (upwards, downwards, or both) points to a dorsal mesencephalic lesion and additionally be} associated with a caudal paramedian thalamic infarct, particularly if downgaze palsy additionally be|can be} current. A nystagmus of central origin additionally be} acknowledged by its path (vertical, multidirectional gaze-evoked or pendular), the absence of nausea despite clear-cut nystagmus with major gaze, and its lack of improvement with fixation. An ocular tilt reaction is characterized by the triad of skew deviation (downward displacement of the axis of the globe ipsilateral to the lesion), conjugate ocular torsion the aspect of the lesion and head tilt to the aspect of the lesion. Visual tilt of the surroundings the aspect of the lesion is frequently related and may result in "upside-down imaginative and prescient". It occurs with an ipsilateral dorsolateral brainstem, higher cervical, or thalamic lesion, but can also occur due to of} a carotid dissection, the peripheral sympathetic fibers surrounding the carotid artery. Motor, cerebellar and sensitive indicators are much less particular in brainstem lesions, however the presence of bilateral or crossed indicators is suggestive. The latter is brought on by ischemia of cranial nerves and fascicles that produce ipsilateral indicators and simultaneous harm to the long sensory and motor tracts that cross within the caudal components of the brainstem. If somnolence, early anisocoria or vertical gaze palsy are current, posterior circulation stroke is extra possible than carotid territory stroke. The latter structure can also 125 Section 3: Diagnostics and syndromes 126 receive direct (long circumferential) branches from the vertebral artery. Three basic scientific syndromes are acknowledged in their territory: the medial medullary stroke (or Dйjerine syndrome); the dorsolateral medullary stroke (or Wallenberg syndrome); and the hemimedullary stroke (or Babinski-Nageotte syndrome). The medial medullary stroke is a uncommon stroke syndrome and classically contains contralateral hemiparesis sparing the face (corticospinal tract), contralateral lemniscal sensory loss (medial lemniscus) and ipsilateral tongue paresis (nucleus of hypoglossal nerve and tract). The laterodorsal medullary stroke is the most common of these three syndromes and is known as|is called} the Wallenberg syndrome, after Adolf Wallenberg (18621946), a German neurologist. Wallenberg syndrome and an infarct within the inferior cerebellum stroke could be seen in isolation or collectively, the latter being often the case if the vertebral artery is occluded. One clue which can help to make the correct diagnosis is the presence of an uncommon nystagmus, which might be purely horizontal or direction-changing, and preservation of the vestibulo-ocular reflex with the pinnacle thrust (Halmagyi) maneuver. With transtentorial herniation, lethargy and coma are accompanied by central hyperventilation, upward gaze paralysis, unreactive, midposition pupils and decerebration. Dorsolateral medullary stroke (or Wallenberg syndrome) is the most common brainstem syndrome of vertebral artery involvement. It is frequently misdiagnosed as Wallenberg syndrome, but the principle scientific distinctions are the listening to loss and the peripheral-type facial palsy. Other indicators have been described, corresponding to ipsilateral choreiform irregular actions or palatal myoclonus (superior cerebellar peduncle interrupting the dentatorubral pathway), sleep abnormalities, and partial contralateral deafness (lateral lemniscus). The anteromedial territory receives its blood supply from the paramedian arteries, the anterolateral territory from the quick circumferential arteries (or anterolateral arteries) and the dorsolateral territory from the long circumferential arteries (or posterolateral arteries) nicely as|in addition to} from the cerebellar arteries. In anterolateral lesions, the motor deficit is gentle and might predominate within the leg (crural dominant hemiparesis), reflecting the topographical orientation of the fibers (leg lateral, arm medial) [12].
Purchase carbamazepine 100 mg
Pyelonephritis is an infection of the kidneys brought on by an ascending infection from the lower urinary tract, most often brought on by E coli from the periurethral/ perianal space. The traditional signs are fever, chills, flank pain, and costovertebral angle tenderness, all of that are demonstrated by this affected person. E coli is the main cause of pyelonephritis in uncomplicated cases, accounting for 82% of cases in ladies and 73% of cases in males. K pneumoniae accounts for about 3% of cases in Renal Chapter 15: Renal · Answers 395 ladies and 6% of cases in males. However, it could possibly} cause emphysematous urinary tract infections, particularly in diabetics. It is a gramnegative bacterium could be} identified due to its swarming motility and optimistic urease activity. S saprophyticus is a causative agent of pyelonephritis in approximately 3% of cases. U urealyticum can cause recurrent episodes of pyelonephritis, however is unusual in uncomplicated episodes corresponding to in this affected person. This affected person is most likely affected by bilateral renal artery stenosis, indicated on physical exam by renal bruits. The underperfused kidneys respond by upregulating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Angioplasty is a minimally invasive process that entails inserting intravascular stents within the renal artery, thereby restoring blood move to the kidney. This type of therapy is the first remedy for renal stenosis in symptomatic sufferers. Patency rates after angioplasty are strongly dependent on the size of the vessel handled and the standard of inflow and outflow via the vessel. In sufferers with hypertension brought on by bilateral renal artery stenosis, each kidneys might be underperfused, so each will retain sodium and water by activating the renin-angiotensin/aldosterone system. Smoking is a risk issue for development of atherosclerotic plaques that may occlude vessels such because the renal arteries. The existence of a single kidney that has not migrated from the pelvis suggests a horseshoe kidney. A horseshoe kidney types when the inferior poles of two kidneys fuse throughout development. The history of being began on chemotherapy for leukemia is strongly suggestive of tumor lysis syndrome. Tumor lysis syndrome occurs when leukemic cells die and launch potassium, phosphate, and uric acid. Kidney failure outcome of|because of|on account of} glomerular dysfunction presents with a prerenal azotemia. There is an effective lower in glomerular filtration fee, and sodium and water are retained by the kidney. In an acute setting, it presents with an intrinsic renal picture as is seen in this affected person. In the setting of an infection, urine cultures are usually optimistic; within the setting of an allergic reaction, eosinophilia is common. Kidney failure outcome of|because of|on account of} tubular dysfunction presents with an intrinsic renal picture. Patchy necrosis leads to debris obstructing the tubules and fluid backflow, resulting in a drop in glomerular filtration fee. However, the presentation of extreme intermittent pelvic pain within the context of leukemia therapy is more doubtless to|prone to} be brought on by a kidney stone. The spleen could be involved in leukemia, however the presence of acute renal failure in this case makes a urethral obstruction more doubtless. The affected person could have underlying renal illness outcome of|because of|on account of} her hypertension and diabetes. These channels are permeable solely to water and end in a reabsorption of water, concentration of urine, and dilution of physique fluids. Activation of the V1 receptor found within the vascular easy muscles leads to activation of Gq protein second-messenger cascade and contraction of vascular easy muscle, resulting in a rise in complete peripheral resistance. This causes hyponatremia and decreased serum osmolality without potassium or acid-base disturbances. It additionally be|may additionally be|can be} secreted by pituitary tumors or small cell lung carcinomas, however would current with Cushing syndrome (hypertension, weight acquire, buffalo hump, truncal weight problems, striae, hyperglycemia, and osteoporosis) quite than hyponatremia. V2 receptors are coupled to the insertion of aquaporins; V1 recep- tors are coupled to the contraction of vascular easy muscle. Renin is secreted by easy muscle cells within the afferent arteriole and acts to cleave angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. This prompts the renin-angiotensinaldosterone axis, resulting in elevated salt and water retention. A affected person with persistent activation of this axis would current primarily with hypertension and edema with relatively low urine sodium levels. This affected person has drug-induced acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, which manifests histologically as edema and inflammation of the renal tubules and interstitium with sparing of the glomeruli. Tubulointerstitial nephritis could be brought on by infections and autoimmune phenomena, however is associated most commonly with drug toxicity. Patients classically current with the triad of low-grade fever, rash, and arthralgias, though some studies point out <10% of sufferers report all three signs. Other signs embrace those associated with acute renal failure, corresponding to oliguria, malaise, anorexia, and vomiting. Common findings on urinalysis are sterile pyuria, microscopic hematuria, and eosinophiluria. Drugs that have been associated with tubulointerstitial nephritis embrace sulfonamides (including thiazide diuretics and most loop diuretics), methicillin, ciprofloxacin, cephalosporins, allopurinol, proton pump inhibitors, rifampin, cimetidine, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Withdrawal of the causative agent is commonly the most effective remedy, however it could take months for a affected person to fully get well renal function. Adverse results of hydrochlorothiazide embrace electrolyte disturbances corresponding to hypokalemia and hypercalcemia. It is used as an anti-neoplastic agent or as an immunosuppressant in transplant recipients and sufferers with autoimmune illness. Common opposed results embrace alopecia, myelosuppression, nausea and vomiting, and hemorrhagic cystitis. Membranous glomerulonephritis is the most typical cause of adultonset nephrotic syndrome. Patients with this illness usually current with a nephrotic picture of generalized edema end result of} large loss of albumin and other proteins. This is a finding of membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, an unusual autoimmune renal disorder that usually impacts young people (8-30 years of age). The diagnosis relies on a histologic presentation that includes mesangial proliferation and a tram-track appearance on light microscopy. This is an outline of the findings in acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, an autoimmune illness most frequently seen in kids. It usually presents a number of} weeks after a streptococcal infection (throat or skin) with peripheral and periorbital edema, dark, tea-colored urine, and proteinuria. These signs are brought on by circulating anti-streptococcal antibody-antigen complexes that deposit within the glomerular basement membrane, resulting in complement activation and glomerular injury. As the affected person has been otherwise healthy and is 50 years old, this diagnosis is unlikely. This illness presents within several of} days of an infection (as opposed to poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, which presents weeks after infection) with a nephritic picture end result of} IgA deposition within the mesangium. Diphenhydramine is a first-generation H1-antagonist used to treat allergic reactions, motion illness, and dystonic reactions. It is associated with neurotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, a lupus-like syndrome, and hemolysis in sufferers with glucose-6phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Lithium has been associated with continual tubulointerstitial nephritis, which presents after years of continual lithium therapy.
200 mg carbamazepine
Patient had excess femoral anteversion as manifested by her patellas pointing inward. Despite the inward place of the patella, her foot remains to be pointing forward as a result of} her external tibial torsion Treatment · A extended interval of remark is beneficial before considering surgical excision. Intoeing Three Main Causes of Intoeing · Excess femoral anteversion · Internal tibial torsion · Metatarsus adductus Orthopedics Disorders and Sport Injuries. Diagnosis · With the child lying prone flexing his knee, the foot might be pointing inward in relation to his thigh (thigh foot angle). Metatarsus Adductus Background · Adduction and inward place of the forefoot. Treatment · Most of the infants with metatarsus adductus will improve with out interference. Examination exhibits increase hip inner rotation (b) compared to with} external rotation (c) A. Abdou Clubfoot (Talipes Equinovarus) Background · Complex inflexible deformity of the ankle and the foot. Treatment · Orthopedic referral: Two treatment choices are presently utilized: - Serial casting: weekly change of forged - Physical therapy and stretching. Four year old with average metatarsus adductus on the left side and extreme on the right side (patient is prone with flexed knee). Notice the curved lateral border of the foot Orthopedics Disorders and Sport Injuries. Notice the deformity of the left foot (equinus, varus, forefoot adduction and cavus). No treatment required because the situation is self-limiting · After correction of the foot deformity, a brace (corrective shoes with a bar in-between the shoes to flip the toes outward) must be used for 23 years to prevent the recurrence Cavus Foot Background · High-arched foot. Calcaneovalgus Foot Background · A situation within the newborn in which the foot is in excessive dorsiflexion and valgus. Diagnosis · the foot is in excess dorsiflexion and valgus to the diploma that the dorsum of the foot is touching the entrance of the tibia. Diagnosis · Loss of the arch of the foot (the heel might be in valgus) when the affected person stands. Rarely, the situation may cause ache on the medial facet of the foot over the tarsal head. Treatment · Flexible flat foot: - Reassurance (the situation is a variation of regular development). Tarsal Coalition Background · Abnormal connection (bridging) between two of the tarsal bone. An 11-year-old boy with left flat foot and valgus heel (a; dotted line) and foot ache for six months. Lateral standing radiograph (b) exhibits flat foot with no arch and bony promi- nence of the calcaneus (white arrow; ant eater sign). Oblique radiograph (c) exhibits the calcaneonavicular coalition (black arrow) · Most common coalition is calcaneonavicular and subtalar (talo-calcaneal) fusion. Treatment · If found accidentally during foot radiographs taken for other reasons: No treatment is needed. If no improvement after 6 months of therapy: orthopedic referral for Botox injection of the calf muscle or Achilles tendon lengthening or serial casting. Tip Toe Walking Background · Pattern of walking in which the child walks on his toes with ankle plantar flexion. Upper extremities movement during gait is regular in idiopathic toe walking and restricted in gentle cerebral palsy. Adolescent Hallux Valgus Background · Bunion deformity of the foot that develops in adolescence. Weight bearing radiographs (b) present 28 diploma the primary metatarso-phalangeal angle and 18 diploma first metatarsal-second metatarsal angle A. Ingrowing Toenail Background · the penetration of the border of the nail plate into the nail fold inflicting ache and irritation within the surrounding tissue. Diagnosis · Significant ache and discomfort of the toe with irritation of tissue surrounding the nail bed. Treatment · Proper care of the nail (a snug broad toe box or open-toed shoes, the nail must be cut straight across and avoid chopping back the lateral margins, the nail edge ought to prolong past the nail fold). Orthopedics Disorders and Sport Injuries 521 Madelung Deformity Background · A physeal development arrest involving the ulnar-volar portion of the distal radius development plate. This arrest leads to a attribute look of the distal radius and ulna and gross deformity of the wrist joint. Diagnosis · Patients offered with a deformed wrist, shorten forearm, lack of supination of the forearm, lack of ulnar deviation, and lack of extension of the wrist. Meniscal Injury of the Knee Background · Anatomy of the menisci: Two cartilaginous crescentshaped constructions that act like a cushion contained in the knee. Treatment · Most meniscal tears in adolescent are longitudinal peripheral tear which have good healing potential (in contrary to adults in which most tears have minimal healing potentials). Diagnosis · the child will describe damage adopted by "popping" of the knee and immediate swelling with inability to bear weight. Also assess the integrity of menisci, collateral ligaments, and chondral surfaces. Management · Initial conservative management: rest, ice, activity modification, bracing, and bodily therapy. Abdou Cannot bear weight immediately after damage Bony tenderness/crepitation Palplate, medial and lateral malleolus, base of the fifth metatarsal, midfoot bone Maximal point of tenderness is the bone Painful and swollen Ankle Sprain Background · A twisting damage of the foot and ankle adopted by ache and swelling. Any tenderness, bony deformity or crepitus, in a type of|a sort of} areas suggests the possible presence of a fracture. Radiographs must be obtained in these cases or if the affected person is unable to bear weight on the affected extremity immediately after the damage and within the emergency division (Table 2). It occurs mainly in adolescent with high-energy accidents (motor automobile collisions). Diagnosis · Patient could have extreme hip ache, deformity of the extremity, and possible sciatic nerve palsy after high-energy damage. Treatment · Urgent orthopedic session: Hip dislocation is an orthopedic emergency as it can possibly} lead to disruption of the blood supply to the top of femur. Orthopedics Disorders and Sport Injuries 525 · Posterior glenohumeral dislocation is lower than 10 % of all traumatic shoulder dislocations generally occurs outcome of|because of|on account of} seizures. Diagnosis · Most generally occurs after fall on outstretched hand with arm abducted and externally rotated. Treatment · Closed discount must be achieved as quickly as possible before important muscle spasm and ache improvement. Radiograph of the pelvis exhibits proper hip dislocation (notice the empty proper acetabulum (arrows) compared to with} left hip). Diagnosis · Child with no apparent historical past of trauma all of a sudden refuses to use his/her arm. Treatment · Reduction maneuvers: one hand supporting the elbow and the other hand applies axial compression on the wrist whereas absolutely supinating the forearm then flexing the elbow. Acromioclavicular Dislocation Background · Separation of the joint between the lateral finish of the clavicle and acromion. Abdou · Marked displacement: orthopedic referral for possible surgical intervention SalterHarris Injuries Background · Injuries of the bone that undergo the growth plate (physis) · Classification: kind I through kind V. Physeal accidents heal quicker than other fractures outcome of|as a outcome of} they happen through rapidly dividing cells; they need to be decreased as quickly as possible. Compartment Syndrome Background · Elevation of the interstitial strain in a closed osteofascial compartment that leads to microvascular compromise. Diagnosis · Pain, deformity, and swelling over the clavicle after falling on the outstretched hand. Proximal Humeral Fracture Diagnosis · Pain and swelling of the proximal arm · Radiographs will present the fracture. The radiograph exhibits a mid-shaft clavicle fracture Humerus Fracture Diagnosis · Pain, swelling, and deformity of the arm. Please notice the displacement of the fracture ends · Can be related to wrist drop as a result of} radial nerve palsy.
Purchase 100mg carbamazepine
Dermatoscopy of the free finish of the nail plate normally allows the melanin within the nail plate to be localized. Pigment in the entire nail thickness indicates lively melanocytes in the entire size of the matrix. New subtle and costly strategies like optical coherence microscopy and reflectance confocal laser scanning microscopy permit the melanin to be exactly localized in the nail plate. Confocal laser microscopy allows the examiner additionally to discern single melanocytes and nevus cell nests in the nail. Melanonychia 173 Histopathology Depending on the fabric out there for histopathological examination, totally different alterations are seen. Melanin is commonly seen in H&E sections of melanonychias due to of} lentigines and nevi, and sometimes, the latter may also present an intraungual nevus cell nest. Depending on the width of the brown band, a punch with a maximal diameter of three mm, a transversely oriented fusiform, or a slightly crescentic matrix biopsy, and in the case of lateral localization a lateral longitudinal nail biopsy or, notably for wider melanonychias, a tangential excisional biopsy is most popular. In most cases, it is recommended to gently separate the nail plate from the matrix before taking the biopsy. This nail laid back after the biopsy and stuck with a suture strip or one or two stitches, which facilitates wound therapeutic. The specimen ought to be marked to enable it to be oriented in the histopathology laboratory. It has to be stressed that the staining of serial sections of the same specimen very often yields totally different staining intensity and patterns with the assorted melanocyte markers and is thus useful in doubtful cases. Functional melanonychia exhibits just an increase of melanin granules with a traditional melanocyte rely, which is about 6. The discrepancy between a traditional H&E stain and regular immunohistochemistry on one side and the increased pigmentation seen in the argentaffin reaction of FontanaMasson allows the prognosis of functional melanonychia to be made. A matrix lentigo is characterised by a numerical increase of melanocytes with marked pigmentation (Figure thirteen. In distinction to regular matrix melanocytes would possibly be} incessantly localized above the basal row of matrix keratinocytes, melanocytes in lentigines usually mainly occupy the basal layer. Immunohistochemically and with particular melanin stains, lengthy however slender dendrites could be identified (Figure thirteen. The melanocyte nests of a nevus are normally oval and should sometimes be taken up with the maturing cells of the keratogenous zone to finally be included in the nail plate (Figure thirteen. The variety of matrix melanocytes is both regular or increased in the LaugierHunzikerBaran syndrome,1618 which is characterised by lenticular brown spots of the oral mucosa, sometimes additionally the genito-anal mucosa and brown streaks in some nails (Figure thirteen. PeutzJeghers syndrome, outlined by quantity of} colon polyps and periorificial lentigines, was additionally noticed to trigger nail involvement with longitudinal melanonychia. They are normally a lot bigger and darker than acquired ones and the entire nail plus periungual tissue concerned, occasionally resulting in nail deformation. However, a very giant congenital blue nevus involving the entire massive toenail and periungual tissue was noticed with the so-called benign lymph node metastasis. A explicit cut-off age, which a brown band could be thought-about to be benign, is yet to be established. Since the underlying cause of melanonychia-simple hypermelanosis, lentigo, nevus, or melanoma-cannot be identified with certainty on medical grounds and nail plate histopathology alone, one has to be notably prudent in light-skinned individuals. Dermatoscopy gives little more accuracy, although standards like background colour, evenness of striation, common distance of striae within the band, and micro-Hutchinson signal are more simply evaluated. On the other hand, long-standing melanonychias in youngsters have been noticed to steadily lighten and eventually disappear. More than 35 years ago, it was stated that an acquired longitudinal melanonychia in a fair-skinned adult should somewhat be seen as malignant than benign,38 which contrasts with melanonychia in youngsters. Since approximately two-thirds to three-quarters of all nail melanomas begin as a longitudinal melanonychia,39 they theoretically provide an excellent chance|a nice opportunity|a good chance} for early prognosis. A brown background and common brown traces have been linked with nevus, whereas melanoma shows a brown background and irregular brown traces. Depending on the width of the melanonychia, totally different strategies similar to punch, fusiform, crescentic, or lateral longitudinal biopsies are available. The superficial tangential biopsy allows giant areas of the matrix to be biopsied just about without the chance of postbiopsy nail dystrophy. Fumagoid our bodies (Medlar bodies) have been quickly as} seen to trigger longitudinal melanonychia. Staining from enterobacteria is normally on the nail floor and could be scraped off as can many different exogenous discolorations. Nail clippings might contain nests of nevus cells however intraungual single melanocytes are thought-about to be melanoma cells. Furthermore, the fabric is scraped out and differentiated utilizing the benzidine reaction: the clotted blood is collected in a tiny check tube, a drop of water is added, and a check stripe for the prognosis of blood in urine or feces is dipped into the check tube after a couple of minutes; in the case of blood, the check stripe turns constructive. This is a very safe check for blood, however it has to be saved in thoughts that a bleeding melanoma may also be constructive. Note the increased pigmentation of the proximal nail fold (false Hutchinson sign), which was not related together with his onychomycosis. The staining grows out with its proximal margin being parallel to the free margin of the nail fold, which is proof of the exogenous nature of the darkish nail stain. Downloaded by [Chulalongkorn University (Faculty of Engineering)] at Natural Course the pure course of longitudinal melanonychias has not been systematically studied. Parents presenting their child with a brown streak in the nail are both worried about the prognosis or embarrassed due to the weird cosmetic appearance. A few giant studies have noticed the youngsters over a interval of 10 years and more. Even when a lightweight brown streak reoccurs, the histopathologic prognosis has been made with certainty. Outlook-Future Developments Although fairly widespread, notably in more deeply pigmented individuals, melanonychias are still usually ignored or incorrectly identified. Certainly, more precise standards for the prognosis of matrix lentigines and nevi shall be developed and the 178 Pediatric Nail Disorders refinement of confocal laser scanning microscopy standards will enable us to differentiate, at least of|no much less than} in lots of} cases, lentigines from nevi and above all from subungual melanoma. Mosaicism in Human Skin: Understanding Nevi, Nevoid Skin Disorders, and Cutaneous Neoplasia. Tangential excision of pigmented nail matrix lesions answerable for longitudinal melanonychia: Evaluation of the approach on a collection of 30 patients. A quickly rising pigmented nail streak leading to diffuse melanosis of the nail. Downloaded by [Chulalongkorn University (Faculty of Engineering)] at Melanonychia 179 27. Subungual melanoma in situ in a Hispanic lady handled with functional resection and reconstruction with onychocutaneous toe free flap. Longitudinal melanonychia in youngsters: A medical and histopathologic examine of 40 cases. Consenso sobre dermatoscopia da placa ungueal em melanonнquias [Consensus on melanonychia nail plate dermoscopy]. Early malignant melanoma manifested as longitudinal melanonychia: Subungual melanoma might come up from suprabasal melanocytes. Patterns of nail matrix and mattress of longitudinal melanonychia by intraoperative dermatoscopy. Proposed classification of longitudinal melanonychia based mostly on medical and dermoscopic standards. Understanding the progression of melanocytic neoplasia utilizing genomic evaluation: From fields to most cancers. Two cases of bizarre acral melanocytic tumors: Illustration of molecular cytogenetics as a diagnostic device. Downloaded by [Chulalongkorn University (Faculty of Engineering)] at a hundred and eighty Pediatric Nail Disorders 53. Longitudinal melanonychia of the toenails with presence of Medlar our bodies on biopsy. Downloaded by [Chulalongkorn University (Faculty of Engineering)] at 14 Dermoscopy in Pediatric Longitudinal Nail Pigmentation Luc Thomas Nowadays, dermoscopy is considered as a mandatory step in the medical evaluation of pores and skin pigmented lesions.
Best 400 mg carbamazepine
This factor is required Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia (Familial Benign Hypercalcemia) Background · Autosomal dominant situation of benign hypercalcemia · Asymptomatic · Usually found incidentally on routine labs 420 K. Failure of osteoid to calcify in adults is known as} osteomalacia · Vitamin D deficiency rickets happens when the metabolites of vitamin D are deficient. After the parathyroid response, the calcium concentration normally returns to the reference vary, although phosphorus levels stay low. A excessive index of suspicion for vitamin D deficiency should be maintained for these infants and kids. Clinical presentation in males · 21-hydroxylase deficiency Generally not recognized within the neonatal interval end result of|as a result of} the genitalia are regular. Hyperaldosteronism Background · Rare in kids · Primary hyperaldosteronism normally adrenal tumor · Secondary hyperaldosteronism. Management · Surgical elimination of adenoma · Prednisone for glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism 426 K. Management · Treatment of pheochromocytoma is with surgical elimination and pretreatment with alpha-blockade. Management · Insulin remedy All kids with sort 1 diabetes mellitus require insulin remedy. The preprandial insulin is both rapid-acting (lispro, aspart, or glulisine) or short-acting (regular). Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Background · Type 2 diabetes mellitus characterised by: Hyperglycemia Insulin resistance Family historical past of sort 2 diabetes in first- or seconddegree relative · Obesity strongly related to sort 2 in kids and adolescents Clinical presentation · Slow and insidious onset · Signs of insulin resistance. Insulin · Time of insulin initiation is controversial · Insulin is administered as a continuous intravenous infusion of regular insulin at a fee of zero. Management · Diabetes training and lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, and weight control) · Pharmacologic remedy with metformin (drug of choice) · Insulin is normally required in instances not managed by pharmacologic brokers alone. Management · Multidisciplinary approach · Weight reduction · Diet and exercise · Management of weight problems related circumstances · Treatment of the cause if relevant Suggested Readings 1. Prolactinomas immune to normal dopamine agonists reply to continual cabergoline treatment. Urine free cortisol within the high-dose dexamethasone suppression test for the differential diagnosis of the Cushing syndrome. Single-day remedy for dietary vitamin D-deficiency rickets: a preferred methodology. Consensus development for the supplementation of vitamin D in childhood and adolescence. Hartonian () Department of Pediatrics, White Memorial Pediatric Medical Group, 1700 Cesar E. Night Terrors · · · · · · Non-rapid eye motion disorder A sort of parasomnia Most generally happen in first third of night time Clinically can see facial flushing and agitation Child will have amnesia for the occasion Night terrors can happen throughout first decade of life and normally will spontaneously remit Epilepsy Mimics Breath Holding Spells · Typical age of onset is between 6 and 18 months · Cyanotic breath holding episodes often triggered by emotional stimuli (anger, frustration); the breath holding happens in expiration · Pallid breath holding episodes often provoked by sudden concern (after harm, surprise) · With both spells, there may be loss of consciousness followed by limpness and actions that can look similar to tonic posturing or myoclonic jerks · By age 4, about half of the kids will now not have episodes Movement Disorders · the actions related to various motion issues may be perceived as epileptic in nature · Examples include tic disorder, sleep myoclonus, paroxysmal dyskinesia Headache Epidemiology · Prevalence of headache in kids up to as} the age of 20 years is roughly 58 %. During adolescence or grownup life may cause recurrent complications, urinary frequency, neck pain, and progressive decrease extremity spasticity. Polymicrogyria Definition · Presence of huge number of small gyral convolutions separated by shallow sulci. Cerebellar tonsillar and decrease medullary herniation by way of the foramen magnum into the higher cervical canal. Symptoms · Some can present in infancy with dysphagia, stridor, apnea, and weak cry. Agenesis of Corpus Callosum Definition · Complete or partial relying on the stage of development at which progress was arrested. DandyWalker Malformation Definition · Cystic expansion of the fourth ventricle within the posterior fossa. Pediatric Neurology 445 Symptoms/Diagnosis · Wide vary of neurodevelopmental outcomes. Can even be related to orofacial deformities, and congenital abnormalities of the cerebrovascular, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary systems. Inheritance is mostly from mother and symptoms turn into extra extreme with each successive era (genetic anticipation). Symptoms/Exam · Hypotonia within the newborn "floppy toddler," hollowing of temporal bones, tenting of higher lip, feeding issues, respiratory misery intercostal and diaphragmatic weak point, arthrogryposis, and a few sufferers have cataracts. Primary Muscle Disease (Myopathies) Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Genetics · X-linked recessive disorder (only affects males) leading to an absence of dystrophin. Occurs in wholesome individuals, days to weeks after an antecedent illness · Miller Fisher Variant presents with facial weak point, ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and areflexia Causes · Strongest affiliation with bacteria Campylobacter jejuni, additionally related to Mycoplasma pneumoniae · Autoimmune circumstances, surgery, and vaccinations Clinical presentation · Weakness Refusal to stroll, walking on a wide base, or issue with working or climbing stairs. Deep tendon reflexes are markedly diminished or absent, vibration sense and proprioception are significantly decreased. Onset in childhood and related to extreme losing of calf muscular tissues with pes cavus and losing of dorsal interossei of hands, foot drop, ankle-foot orthosis to help with the foot drop. Pediatric stroke: the importance of cerebral arteriopathy and vascular malformations. Preclinical analysis in Rett syndrome: setting the inspiration for translational success. Primary versus secondary headache in kids: a frequent diagnostic problem in scientific routine. Tethered cord syndrome in childhood: particular emphasis on the surgical technique and review of the literature with our experience. Clinical practice guidelines- febrile seizures: guideline for the neurodiagnostic analysis of the child with a simple febrile seizure. Naga Management · Treatment of the cause Acute Hemorrhagic Conjunctivitis Causes · Coxsackievirus A24 · Enterovirus 70. Clinical presentation · Highly contagious disease · Large subconjunctival hemorrhage · Patients additionally may present with fever and headache. Parasitic Conjunctivitis Background · Pediculosis may cause a follicular conjunctivitis in adults with pubic lice. Clinical presentation · Itching · Conjunctival chemosis, which manifests as pale edema; eyelid edema · Watery or mucoid discharge · Giant papillae assume a flat top appearance, which often is described as "cobblestone papillae". Naga Preseptal Cellulitis Background · Infection of periorbital soft tissues anterior to the orbital septum · Usually result from extension of external ocular an infection such as: Hordeolum (stye) Dacryocystitis/dacryoadenitis Rhinosinusitis Dental abscess Insect bite Post Traumatic puncture, laceration, or abrasion of the eyelid pores and skin. Direct penetrating harm to the orbit; and hematogenous seeding Severe conjunctivitis Skin infections: impetigo or herpes zoster Causes · Staphylococcus and streptococcus have turn into the 2 commonest pathogens liable for pediatric orbital cellulitis seventy five % Clinical presentation · Erythema · Swelling with no limitation of eye motion Diagnosis · Clinical · No imaging study is important Management · the selection of the antibiotic relying on the source of an infection. Orbital Cellulitis Background · Infection of orbital soft tissue posterior to orbital septum. Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction (Congenital Dacryostenosis) Background · Tearing and mucoid or mucopurulent discharge · Normal conjunctiva, however they might develop acute irritation · Digital strain leads to retrograde discharge of mucopurulent supplies · Congenital glaucoma should be ruled out by historical past and bodily examination 462 V. Congenital Glaucoma Definition · Elevated intraocular strain Clinical presentation · Corneal cloudiness. Management · Referral to ophthalmologist Conditions related to glaucoma · SturgeWeber syndrome · Intraocular hemorrhage · Inflammation or tumor · Aniridia · Lowe syndrome · Aphakia · Marfan Syndrome Acquired Ptosis Causes · Horner syndrome; ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis · Myasthenia gravis Eye Disorders 463 · Homocystinuria · Steroid treatment Congenital Cataract Background · Cataracts may happen at any age Causes · Approximately 50 % of congenital cataracts are idiopathic · Hereditary: autosomal dominant are always bilateral. Clinical presentation · Leukocoria and strabismus are the most common presenting discovering. Management · All kids with a new new} leukocoria should be referred to an ophthalmologist. Naga · Intra-arterial chemotherapy is a new new} modality of treatment in sure instances. Papilledema Background · Papilledema is a swelling of optic disc secondary to elevated intracranial strain. Clinical presentation · Bilateral imaginative and prescient loss · Painful eye actions · Disc edema Management · Intravenous steroids should be considered if imaginative and prescient loss is bilateral find a way to} hasten visual recovery. Causes · First epidemic Nineteen Forties and 1950s Primary cause: oxygen unmonitored Few small (7501000 g) infants survived (< 8 %) · Second epidemic Seventies to present Oxygen carefully monitored Primary cause: many small (5001000 g) infants survived (> eighty %) · Third epidemic 2000s to present. Optic Neuritis Background · Optic neuritis implies an inflammatory process involving the optic nerve. Causes · Presents often after systemic infections, such as measles, mumps, chickenpox, and viral sicknesses. Orbital Fracture Background · Blunt trauma to the face or directly to eye Clinical presentation · Periorbital ecchymosis · Eye/face pain 466 V. Diagnosis · Topical fluorescein, which is on the market in paper strips · May apply topical anesthetic in resolution to facilitate the attention exam · Fluorescein available in topical eye drops together with an anesthetics · the area of abrasion will fluoresce under a cobalt blue filter gentle Management · Topical eye antibiotic ointment, for example, erythromycin, bacitracin ophthalmic should be utilized each 4 h to forestall an infection Important to know · Corneal abrasions heal quickly, often within 24 h for smaller accidents. Causes · Strabismus (the commonest cause) · Anisometropia (unequal refractive errors) or excessive refractive errors · Stimulus deprivation: cataracts, corneal opacities, vitreous hemorrhage, lid hemangiomas Diagnosis · Vision screening Management · Patients who failed imaginative and prescient screening need to be referred to ophthalmologist. Congenital esotropia · Onset within first 6 months of age · Associated with giant angle strabismus · Amblyopia 50 % of sufferers · Bad depth perception · Treatment: early surgery within first 12 months.
Buy carbamazepine 400mg
Simple and efficient non-invasive treatment strategies for ingrown nail and pincer nail together with acrylic affixed gutter splint, anchor taping, sculptured nails, shape reminiscence alloy and plastic nail braces as well as|in addition to} 40% urea paste. Anchor taping technique for the treatment of ingrown nail, nail trauma and different nail problems. Surgical pearl: Nail splinting by versatile tube-A new noninvasive treatment for ingrown toenails. Sodium bicarbonate attenuates pain on skin infiltration with lidocaine, with or without epinephrine. Pain tolerance, especially in the course of the native anesthesia, is the cornerstone of any surgical process. Fortunately, the indications of a nail biopsy in a child are very limited and must be carried out only for particular functions. Indeed, the scope of nail conditions in youngsters is totally different from the one in adults and hopefully, many pediatric nail ailments are clinically recognizable. The latter is aggressive and must be recognized as quickly as possible to avoid any permanent scarring. Nail psoriasis is far less typically biopsied as there are in most cases clues to assist the prognosis, such as plaques on the body or scalp or a familial historical past of psoriasis. The lesion is biopsied because of|as a result of} it has an unusual location or an unusual presentation5 (Figure 19. In some rare cases of dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, the nail abnormalities will be the only signal of the condition over several of} generations. One ought to thoughts that|do not overlook that} the stress of the dad and mom may be very easily transmitted to the child. Older youngsters must be included within the dialogue and a simple, clear, and reassuring rationalization must be given to them. Several studies compared totally different regimens: these with midazolam, chloral hydrate, hydroxyzine, and mepiridine, respectively. It is amazing to discover how dad and mom are unable to perform this kind of|this type of|this type of} dressing. A demonstration on means to|tips on how to} carry out an enough occlusion (with any cream) in the course of the preoperative session is of great assist. Time of occlusion must be respected, too, minimal of|no less than} 2 hours previous to the process for fingers or toes. It is a cost-effective and efficacious alternative to conscious sedation or basic anesthesia for minor pediatric surgical procedures. Managing the Child in the course of the Biopsy Pain from the Needle As previously mentioned, youngsters largely fear the needle. The mother (or the nurse) additionally be} requested to firmly press on the purpose of injection for minimal of|no less than} 5 minutes earlier than the needle prick. Another option is to use a vibrating tool for several of} minutes, at the location of the long run} injection, till the child finds that the world is becoming numb (Figure 19. This was demonstrated as an efficient technique to lower pain throughout native anesthesia. Downloaded by [Chulalongkorn University (Faculty of Engineering)] at Pain from Dilation Once the needle is inserted painlessly, the infusion of the anesthetic might begin. The subungual house may be very limited, and excessive pressure on the Vater-Pacini corpuscules inside the distal soft tissue will trigger pain. The injection must be extraordinarily slow, thus performing a really slowly progressive swelling. If the child moves a little bit, displaying some discomfort from the infusion, the surgeon ought to cease injecting for quantity of} seconds, then begin once more. Buffering it (1 volume of bicarbonate for 9 volumes of lidocaine) dramatically reduces pain throughout infusion. Keeping the anesthetic out of the fridge or at body temperature in a water tub will render the infusion less painful. The best approach to scale back pain from infusion is to inject warmed, buffered lidocaine. Distraction is a really commonly used trick, known as talkesthesia, which was identified to work well with youngsters. There is inadequate evidence of the analgesic results of sweet-tasting options or substances throughout painful procedures. Dealing with Postoperative Pain Once the process is done, the first two questions of the dad and mom might be "When will the anesthetic effect stop? This might be painless due to the earlier lidocaine block and this will also act as a volumetric tourniquet by urgent on the digital proper arteries, thus limiting the danger of postoperative bleeding. The very first thing to clarify to the dad and mom is that the limb must be stored elevated for the next 2 days. The type and power of painkiller will depend upon the process performed, the age of the patient, and his/her tolerance to pain. This is why the immediate postoperative dressing must be adapted to nail surgical procedure. Applying large amounts of ointment coated with nonadherent dressing, such as petrolatum-coated gauze (Tulle gras, Bactigras, Adaptic, Jelonet) will protect the wound from drying and can permit a simple and painless removing. Mepitel is a porous, semitransparent, low-adherent, versatile polyamide internet coated with soft silicone. Sometimes, early removing is necessary after 24 hours if bleeding is severe, because of|as a result of} the impregnated gauze of the cumbersome dressing dries and turns into stiff, and will cause disagreeable or painful compression. If left in place for too lengthy, such dry and hard dressings might induce superficial erosion on the skin of the proximal and/or lateral nail folds. Hydrogen peroxide additionally be|can be} a very good option, however the youngster must be knowledgeable that some mild warmth would possibly occur. Anesthesia procedures are equivalent to the ones performed in adults (distal digital block and wing block). The various biopsy methods performed for prognosis in youngsters are listed within the following sections. The fragile specimen must be harvested delicately with sharp, curved scissors and never pulled out with forceps. In psoriatic onycholysis, the nail bed biopsy has virtually at all times a nonspecific picture under the microscope, even if performed at the most proximal edge of the onycholysis. In order to collect relevant microscopic info, this biopsy must be performed on a nail exhibiting a lateral involvement with marked clinical signs (Figure 19. Pathologists favor this technique because it permits the study of the whole nail equipment: proximal nail fold, matrix, nail bed, nail plate and hyponychium. Its major disadvantage, although, is the permanent narrowing of the nail the partial amputation of the lateral horn of the matrix (Figure 19. Postoperative dangers embody lateral deviation if the specimen exceeds three mm49 and nail spicule formation if some nail matrix tissue is left after incomplete detachment of the matrix from the bone at the proximal tip of the biopsy. Two lateral incisions are performed in order to to} permit retraction of the proximal nail fold. Most of the time, nail pigmentation originates from the distal matrix (95% of cases) and in this case postoperative sequelae might be a thinned nail plate. If the pigment location is within the proximal matrix, a postoperative dystrophy with longitudinal fissure is expected50 (Figure 19. If the form of the pigment is longitudinally oriented, a slim ellipse is performed and delicate lateral undermining permits suturing of the defect with 5/0 sutures (Figure 19. In all cases, the pigmented space have to be removed fully, as this must be an excisional biopsy, allowing the pathologist to absolutely study the lesion. It consists of a tangential excision of the matrix dermis and a small layer of dermis (Figure 19. Note the proximal curve of the incision to guarantee removing of the lateral horn of the matrix. As the condition was monodactylic a biopsy was required earlier than embarking with intramuscular systemic steroids. One can see the scar from the lateral longitudinal biopsy on the medial aspect of the left thumb (arrow). Though the margins are difficult to assess, the pathologist in a position to|is prepared to} study the complete lesion.
References:
- https://www.depts.ttu.edu/education/our-people/Faculty/additional_pages/duemer/epsy_5310_class_materials/evolutionary-universals-in-society.pdf
- https://scottalexander.me/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Fundamental-of-Joint-Injection-AJR-Sept-2016.pdf
- https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/STATUTE-108/pdf/STATUTE-108-Pg1796.pdf
- https://www.aafp.org/afp/2012/1201/afp20121201p1027.pdf
.png)