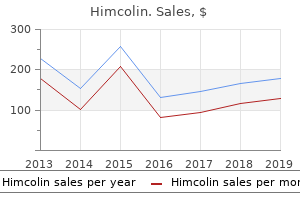
Quality himcolin 30gm
In 2006, the Agency consulted with the Science Advisory Board, describing its approach to the revision and summarizing feedback obtained from Agency scientists, the scientific community and the public public}. This revised doc, Guidelines for Human Exposure Assessment, advantages from many further years of expertise with exposure assessments across the Agency, conversations with the broader scientific community and merchandise from the Science Advisory Board and the National Research Council of the National Academy of Sciences. This Guidelines for Human Exposure Assessment is designed to help exposure scientists in getting ready exposure assessments, analyzing standing and developments, developing mitigation strategies, making regulatory decisions and conducting epidemiological research. This revision focuses on human exposure to chemical agents and presents the final ideas of exposure science (including evaluation and monitoring). This Guidelines for Human Exposure Assessment is intended principally for exposure and threat assessors in the Agency and consultants, contractors or others who perform kind of|this type of|this kind of} work under Agency contract or sponsorship. The technical materials cited and hyperlinked throughout this doc present particular info for particular person exposure evaluation situations. At the time of publication, all cited materials and hyperlinks had been correct and useful. This mission is, in part, achieved by understanding, characterizing and managing health dangers related to exposure to environmental contaminants and different agents. Exposure science characterizes, estimates and predicts exposures; it additionally supplies info for getting ready exposure assessments and for developing effective strategies to reduce exposure and manage threat. This Guidelines for Human Exposure Assessment supplies an updated resource on assessing human exposure for exposure and threat assessors in the Agency, and for consultants, contractors or others who perform kind of|this type of|this kind of} work under Agency contract or sponsorship. This doc builds on and supersedes the 1992 Guidelines for Exposure Assessment (U. It briefly describes the ideas of exposure science and evaluation, supplies steerage on the varied approaches for conducting an exposure evaluation and presents references for extra detailed info. Aspects of these advances that have been published in the peer-reviewed literature, nonetheless, are included. Finally, this Guidelines supplies hyperlinks to exposure evaluation instruments and technical documents that tackle specific exposure evaluation needs. The focus of this Guidelines for Human Exposure Assessment is on human exposure to chemical agents in the non-occupational environment. This doc is organized in chapters, each of which explores a component of the exposure evaluation course of. Chapter 1 introduces this Guidelines for Human Exposure Assessment and discusses the purpose and scope of the doc. Chapter 2 supplies a basic review of exposure science concepts and ideas, together with approaches and instruments for consideration when planning and conducting exposure assessments. Topics include an outline of exposure science, the function of exposure evaluation in the threat evaluation course of, concepts and kinds of exposure assessments, equations and enter variables for estimating exposure, presentation of exposure evaluation findings and a quick historical past of exposure science. Page xiv Exposure characterization is a crucial step in all exposure assessments, and the chapter presents steerage relating to the synthesis of exposure info. Chapter three describes a course of for the planning and scoping and drawback formulation steps for an exposure evaluation. It emphasizes the significance of establishing targets and objectives; constructing an interdisciplinary staff; developing a conceptual model; figuring out evaluation options, out there assets and knowledge needs; producing an general evaluation plan; partaking and involving acceptable stakeholders; partaking and involving the community; establishing knowledge high quality objectives; and conducting peer review. Chapter 4 discusses potential increased threat of antagonistic health effects from environmental contaminants for different lifestages, susceptible teams and populations of concern due to disproportionate exposure or varied responses to exposure. These components can include age, sex, genetic susceptibility, cultural traits, behaviors, occupation, socioeconomic standing, entry to a nutritious diet, race/ethnicity and geographic location. This chapter assembles different current Agency steerage, along with examples of case research, to focus on where strategies and issues related to lifestages, susceptible teams and populations of concern could be utilized in exposure assessments. Understanding knowledge availability, applicability, traits, high quality issues and limitations is critical to conducting a scientifically-sound exposure evaluation. This chapter presents steerage on the evaluation of data uncertainty and variability. It additionally emphasizes the significance of transparency and communication of findings to the chance manager/decision maker and stakeholders. Chapter 6 highlights primary concepts in modeling, together with the ideas of the modeling course of. It supplies an outline of modeling for exposure evaluation, outlines the criteria for choosing acceptable fashions primarily based on the targets and knowledge high quality objectives and describes how to to|tips on how to} consider a model that may be helpful for an exposure evaluation. Chapter 6 includes info on modeling inventories and clearinghouses and describes assets that support the use of of} fashions of various levels of complexity, together with probabilistic fashions. Chapter 7 supplies particulars on planning an observational human exposure measurement examine. The research contain measurements of chemical, bodily or organic agents in environmental media; collection of details about examine members and their homes, work environments and actions; and collection of personal Page xv exposure and organic samples. This chapter discusses the features of planning an observational human exposure measurement examine, together with price range and logistical planning, establishing a examine design, planning and executing a pilot examine and a full area examine and the significance of conducting peer review. It additionally addresses ethical issues that exposure assessors need to think about when interacting with examine members and the community. Chapter 8 discusses the compounded effects of uncertainty and variability in exposure assessments, accounting for uncertainty and variability in planning and scoping and drawback formulation (Chapter 3), and uncertainty and variability throughout the knowledge used for exposure assessments (Chapter 5). Chapter 6 highlights how an assessor makes use of these concepts in the application of fashions in an exposure evaluation. Chapter 9 synthesizes the concepts introduced in the previous eight chapters into a communication plan and supplements them with extra particular info. Chapter 9 emphasizes the significance of figuring out the supposed audience, the kinds of communication merchandise, communication plans that may be acceptable for different exposure assessments and associated ethical issues. Assessors need to assistance of} with their programs for particular commonplace working procedures or guidelines. As acceptable, the Risk Assessment Forum will consider the need to|the necessity to} update this doc and make acceptable changes as the sector of exposure science evolves. Exposure science characterizes and predicts the intersection of an agent and receptor in area and time. It supplies info to develop exposure assessments and the simplest strategies to reduce human health threat by way of mitigating exposure. The increasing quantity and complexity of threat assessments the Agency conducts, and the attendant threat management decisions, present new challenges. Purpose and Scope of the Guidelines this doc builds on and supersedes the Guidelines for Exposure Assessment (U. Planning and Scoping (1997a) General Principles for Performing Aggregate Exposure and Risk Assessments (2001f) Exploration of Perinatal Pharmacokinetic Issues (2001e) Example Exposure Scenarios (2003c) Guidance on Selecting Age Groups for Monitoring and Assessing Childhood Exposures to Environmental Contaminants (2005c) Supplemental Guidance for Assessing Susceptibility from Early-Life Exposure to Carcinogens (2005h) A Framework for Assessing Health Risk of Environmental Exposures to Children (2006d) Concepts, Methods and Data Sources for Cumulative Health Risk Assessment of Multiple Chemicals, Exposures, and Effects: A Resource Document (2007c) Scientific and Ethical Approaches for Observational Exposure Studies (2008c) Exposure Factors Handbook: 2011 Edition (2011d) and Highlights of the Exposure Factors Handbook (2011e) Recommended Use of Body Weight 3/4 as the Default Method in Derivation of the Oral Reference Dose (2011h) Benchmark Dose Technical Guidance (2012b) Microbial Risk Assessment Guideline: Pathogenic Microorganisms with Focus on Food and Water (2012e) Page 1 Framework for Human Health Risk Assessment to Inform Decision Making (2014f) Peer Review Handbook, 4th Edition (2015c) Superfund Community Involvement Handbook (2016e). This Guidelines describes the ideas of exposure science and exposure evaluation, offers steerage to the reader on numerous approaches to be used in conducting an exposure evaluation and supplies references for extra detailed info, together with exposure evaluation instruments and technical documents that tackle specific exposure evaluation needs. Aspects of these programs published in the peer-reviewed literature, nonetheless, are included. Agency exposure and threat assessors are encouraged to assistance of} with their programs to acquire particular procedures and guidelines. This Guidelines for Human Exposure Assessment focuses on human exposure to chemical agents under non-occupational scenarios. This doc focuses on the information and knowledge utilized in exposure assessments carried out across the Agency. The type and function of an exposure evaluation determine the information and knowledge requirements. Screening-level exposure assessments require few assets and infrequently use out there knowledge, whereas complicated exposure assessments tackle probably the most demanding exposure questions and can include observational human exposure measurement research. Many different assets are available from the Agency and exterior sources to be used with this Guidelines for Human Exposure Assessment. Organization of Guidelines for Human Exposure Assessment the order by which the contents of this doc are introduced is identical as the order of the steps that assessors generally absorb getting ready exposure assessments: Chapter 2 Chapter three � � an outline of the fundamental concepts and ideas of exposure science planning and scoping and drawback formulation for exposure assessments 1 We use the time period "agent" throughout this doc to indicate any entity that an exposure assessor may measure or analyze. Chapter 2 makes use of the time period "stressor" instead of "agent" for consistency with National Research Council documents. Page 2 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 � � � � � Chapter 9 � Chapter 10 � lifestages, susceptible teams and populations of concern in exposure assessments collection and use of data for exposure evaluation modeling for exposure evaluation planning for an observational human exposure measurement examine info on evaluating uncertainty and variability in exposure evaluation the presentation and communication of outcomes of exposure assessments full references for all cited documents. Describing the fundamental ideas of exposure science and exposure evaluation, it presents info for taking numerous approaches to exposure evaluation, supplemented by detailed info published in the literature. Exposure Science Human exposure science is the examine of human contact with chemical, bodily or organic agents occurring in their environments. It is intended to advance the information of the mechanisms and dynamics of occasions leading to antagonistic health outcomes, both to perceive their cause(s) or to prevent them (Barr et al.
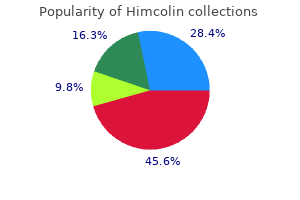
Effective himcolin 30gm
Probabilistic Techniques in Exposure Assessment: A Handbook for Dealing with Variability and Uncertainty in Models and Inputs. A Framework for Assessing Risks to Children From Exposure to Environmental Agents. Risk Communication: Proceedings of the National Conference on Risk Communication, held in Washington, D. Communicating their Individual Results to Participants in an Environmental Exposure Study: Insights from Clinical Ethics. Vulnerability as a Function of Individual and Group Resources in Cumulative Risk Assessment. Representing Uncertainty in Silvicultural Decisions: An Application of the Dempster-Shafer Theory of Evidence. Integration of Life-Stage Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models with Adverse Outcome Pathways and Environmental Exposure Models to Screen for Environmental Hazards. Exposures of Children to Organophosphate Pesticides and Their Potential Adverse Health Effects. Federal Actions to Address Environmental Justice in Minority Populations and Low-Income Populations. The Benefits of Probabilistic Exposure Assessment: Three Case Studies Involving Contaminated Air, Water, and Soil. Environmental Health Disparities: A Framework Integrating Psychosocial and Environmental Concepts. Reconstructing Population Exposures to Environmental Chemicals from Biomarkers: Challenges and Opportunities. Sensitivity Analysis, Monte Carlo Risk Analysis, and Bayesian Uncertainty Assessment. Improving Human and Ecological Exposure Assessments: A Bayesian Network Modeling Approach. Use of Probabilistic Techniques (Including Monte Carlo Analysis) in Risk Assessment, and Guiding Principles for Monte Carlo Analysis. Traditional Tribal Subsistence Exposure Scenario and Risk Assessment Guidance Manual. Biomonitoring Equivalents: A Screening Approach for Interpreting Biomonitoring Results from a Public Health Risk Perspective. Development of a Source-to-Outcome Model for Dietary Exposures to Insecticide Residues: An Example Using Chlorpyrifos. Concentrations of Environmental Phenols and Parabens in Milk, Urine and Serum of Lactating North Carolina Women. Developmental Expression of Drug Metabolizing Enzymes: Impact on Disposition in Neonates and Young Children. Practising Science Communication within the Information Age: Theorising Professional Practices. Disparities in Exposure to Automobile and Truck Traffic and Vehicle Emissions close to the Los Angeles-Long Beach Port Complex. Are Societal Judgments Being Incorporated into the Uncertainty Factors Used in Toxicological Risk Assessment Combining Regional- and Local-Scale Air Quality Models with Exposure Models for Use in Environmental Health Studies. Scientific Uncertainty: How Do We Know When to Communicate Research Findings to the Public Presenting Uncertainty in Health Risk Assessment: Initial Studies of Its Effects on Risk Perception and Trust. Plant Foods versus Compounds in Carcinogenesis; Observational versus Experimental Human Studies. Six Propositions on Public Participation and their Relevance for Risk Communication. Caution Regarding the Use of Pilot Studies to Guide Power Calculations for Study Proposals. Benchmark Data and Power Calculations for Evaluating Disease Outbreak Detection Methods. Human Milk Biomonitoring of Phthalates: Expanding our Understanding of Infant Exposure is Compatible with Supporting Breastfeeding. Population-Based Exposure Measurements in Arizona: A Phase I Field Study in Support of the National Human Exposure Assessment Survey. Improving the Risk Assessment of Lipophilic Persistent Environmental Chemicals in Breast Milk. Associations between Maternal Phthalate Exposure and Cord Sex Hormones in Human Infants. Lioy, P; Lebret, E; Spengler, J; Brauer, M; Buckley, T; Freeman, N; Jantunen, M; Kissel, J; Lebowitz, M; Maroni, M; Moschandreas, D; Nieuwenhuijsen, M; Seifert, B; ZmirouNavier, D. Numeric, Verbal, and Visual Formats of Conveying Health Risks: Suggested Best Practices and Future Recommendations. Feasibility of Assessing Public Health Impacts of Air Pollution Reduction Programs on a Local Scale: New Haven Case Study. A Simple Pharmacokinetic Model to Characterize Exposure of Americans to Di-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate. Evaluation of Background Exposures of Americans to Dioxin-Like Compounds within the 1990s and the 2000s. Computational Toxicology of Chloroform: Reverse Dosimetry Using Bayesian Inference, Markov Chain Monte Carlo Simulation, and Human Biomonitoring Data. Practice Periodical of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste Management eight: 181-198. A Biomonitoring Study of Lead, Cadmium, and Mercury within the Blood of New York City Adults. Evaluation and Recommendation of Sensitivity Analysis Methods for Application to Stochastic Human Exposure and Dose Simulation Models. Separate and Unequal: Residential Segregation and Estimated Cancer Risks Associated with Ambient Air Toxics in U. Environmental Justice and Regional Inequality in Southern California: Implications for Future Research. Uncertainty: A Guide to Dealing with Uncertainty in Quantitative Risk and Policy Analysis. Exposures of Preschool Children to Chlorpyrifos and Its Degradation Product 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-pyridinol in their Everyday Environments. Ensuring Risk Reduction in Communities with Multiple Stressors: Environmental Justice and Cumulative Risks/Impacts. Ethical Considerations for Research on Housing-Related Health Hazards Involving Children. Workshop to Develop a Framework for Assessing Risks to Children from Exposure to Environmental Agents. Characterizing Variability and Uncertainty in Exposure Assessments Improves Links to Environmental Decision Making. The 2nd International Conference on Risk Assessment, January 26-28, Brussels, Belgium. Communications with Research Participants and Communities: Foundations for Best Practices. Closing the Research Loop: A Risk-Based Approach for Communicating Results of Air Pollution Exposure Studies. Pellizzari, E; Lioy, P; Quackenboss, J; Whitmore, R; Clayton, A; Freeman, N; Waldman, J; Thomas, K; Rodes, C; Wilcosky, T. Effect of Prenatal Exposure to Airborne Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons on Neurodevelopment within the First 3 Years of Life among InnerCity Children. A New Method for Generating Distributions of Biomonitoring Equivalents to Support Exposure Assessment and Prioritization. Adapting Concepts from Systems Biology to Develop Systems Exposure Event Networks for Exposure Science Research. Epigenetic Regulation of Neurodevelopmental Genes in Response to In Utero Exposure to Phthalate Plastic Chemicals: How Can We Delineate Causal Effects Monte Carlo Modeling of Time-Dependent Exposures Using a Microexposure Event Approach.
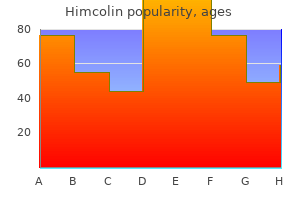
Best himcolin 30 gm
Soundness of Assumptions, Methods and Conclusions, Appropriateness Peer enter offers an independent evaluation and evaluate of models utilized in an publicity assessment. The objective of mannequin peer enter is to consider the assumptions and whether or not sound scientific principles underlie the methods and conclusions derived from models and to check the scientific appropriateness of a mannequin for informing a specific regulatory or risk management choice (U. The latter objective is especially essential for functions of present models for purposes aside from those supposed of their initial design. Researchers and Page 125 practitioners in academia, consulting, personal business and state and native governments-both nationally and internationally-frequently use models and typically collaborate of their growth. A crucial consideration in using models is transparency, together with providing rigorous mannequin documentation and selling unfettered communication amongst an publicity assessor, modeler and risk manager/decision maker in the software of the mannequin to a specific problem. Attainment of Quality Assurance Objectives For a selected mannequin, an publicity assessor determines whether or not the inputs the mannequin requires can be found and all parameters the mannequin requires are obtainable or cheap default values are accessible. After running the mannequin, an publicity assessor needs to consider whether or not the mannequin outputs meet the publicity assessment goal(s) and information quality objectives. Qualitative and Quantitative Model Calibration As a standard follow, an publicity assessor verifies mannequin operation and results. Calibration is the process of adjusting chosen mannequin parameters inside an expected vary till the variations between mannequin predictions and field observations are inside chosen standards (U. Model Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analyses An publicity assessor acknowledges and characterizes essential sources of uncertainty in modeled estimates, either qualitatively, quantitatively or each. Uncertainty is the lack of exact information, either qualitative or quantitative, and may refer to the restricted information about the factors affecting publicity and adequacy of mannequin outputs for choice making. An publicity assessor characterizes the quality of the enter information and the resulting limitations on the makes use of of the mannequin results. Chapter eight presents a broader dialogue of issues on uncertainty in publicity assessment. Models are mathematical representations of processes that quantify how a system behaves in response to modifications in its inputs. Exposure mannequin growth entails a number of} choices concerning what to include and at what level of detail. Important sources of uncertainty are measurement error, statistical sampling error, nonrepresentativeness of information and structural uncertainties in scenarios and formulations of models. Page 126 Scenarios are assumptions concerning the factors that outline the scope of the assessment, such as the averaging time, geographic and temporal scales and the exposed population of curiosity (�zkaynak et al. Omitting any elements of the situation of curiosity from the modeling strategy can bias the estimates. Uncertainty additionally would possibly stem from extrapolating past circumstances for which the mannequin was constructed or calibrated. The extent of verification and validation, whether or not the mannequin is extrapolated past the vary of its evaluation and whether or not various theories exist upon which various modeling approaches could be be} developed all influence mannequin uncertainty (Cullen and Frey 1999). Assessments of enter and parameter uncertainty can use advanced statistical methods. Such assessments iterate mannequin simulations using various units of variability distributions for key inputs and parameters. Most Monte Carlo functions performed for predicting exposures seize the combined variability and uncertainty associated with every enter and variable in the mannequin runs. In models that are extra refined, using two-dimensional Monte Carlo methods distinguishes variability from uncertainty. These correlations can be captured, nevertheless, by the use of of} bootstrap-based uncertainty analysis techniques utilized in Xue et al. Some of the fate and transport, human publicity and built-in fate/transport-exposure models can simulate stochastic processes, which allows assessment of the variability and uncertainty in modeled estimates and enter parameters. Variability refers to the heterogeneity or range of potential exposures in a population. The models, which might simulate stochastic processes, most likely to|are inclined to} be higher tier publicity models and a few of the the} built-in fate/transport-exposure models. For these models, such assessments often contain performing univariate or multivariate Monte Carlo analyses, sensitivity analyses or publicity pathway contribution analyses. The most typical mannequin enter parameters diversified to tackle variability or uncertainty are publicity factors and chemical residue values in several environmental media. A key problem for built-in fate/transport-exposure models is the quantification of coupled mannequin uncertainties resulting from propagation of errors from the completely different mannequin parts, linked throughout an built-in analysis. In other words, for understanding and addressing information uncertainty, the sensitivity analysis is a means of figuring out which parameter(s) in an publicity assessment drive the outcomes. An publicity assessor makes use of these analyses to decide when to cease amassing information or Page 127 performing extra time-consuming probabilistic analyses. Sensitivity analyses can vary from simple to extra complicated analyses, together with modeling and regression analysis. Simpler analysis sometimes entails a one-at-a-time fixed or percentile scaling strategy. Fixed approaches, as an example, would possibly take a look at the variation of results by various every enter up and down by a factor of 2. For every run and simulated particular person, modelers determine the mean outputs for every decrease and higher percentile simulation and evaluate them to the reference or base case results. These ratios or ranges present assessors with the influence and significance of every influential variable on the publicity modeling predictions. The modeler then makes use of this info in stepwise regression models to examine the connection between inputs and outputs of the mannequin to determine the influence of necessary thing} variables in the presence of others that influence the outcomes. The kind of sensitivity analysis wanted for every state of affairs is dependent upon by} the complexity of the publicity assessment query (U. The essence of the analysis, nevertheless, remains the identical: evaluating how modifications in the enter parameters change the output. Several methodological instruments and approaches can be found for conducting sensitivity and uncertainty analysis (Cullen and Frey 1999; Mokhtari et al. This section has targeted on sensitivity and uncertainty analyses inside a particular mannequin. Performing sensitivity analyses throughout completely different models appropriate to determine whether or not some models are much less sensitive to sure crucial parameters. Uncertainty throughout models Page 128 appropriate, for instance, to quantify ranges of outputs that mirror the uncertainties of mannequin assumptions for a given set of inputs (Cullen and Frey 1999; Young et al. The assessor determines whether or not a mannequin to meet those wants is on the market or if a brand new} mannequin needs to be developed. Models vary in complexity from deterministic to probabilistic to advanced probabilistic modeling. The scenarios incorporate environmental measurement information and publicity factor info. The consequence of the situation evaluation is an publicity estimate that results from combining concentrations with publicity factors. Forward and reverse dosimetry are two approaches for using biomonitoring information to present quantitative estimates of human publicity to chemical substances. Model evaluation is the process that generates info throughout mannequin software to determine whether or not the mannequin and its analytical results are of enough quality to function the idea for a decision. Sensitivity analysis is "any systematic, frequent sense approach used to perceive how risk estimates and, particularly, risk-based choices, are depending on variability and uncertainty in the factors contributing to risk. Overview Observational human publicity measurement research allow publicity scientists and risk assessors to determine agents to which persons are exposed; publicity concentrations; essential sources, routes and pathways of publicity; and factors that have the best influence on publicity. Observational human publicity measurement research additionally can be conducted throughout the context of an epidemiological investigation. Results from observational human publicity measurement research assist the regulatory work of Agency programs and contribute considerably to our understanding of human exposures and dangers from environmental agents. In addition, results from these research have recognized major stressors and determined whether or not mitigation measures have been profitable and whether or not exposures exceeded regulatory standards. Data from an observational human publicity measurement study additionally can be used to consider and refine publicity and dose models. The information collected in the study, nevertheless, have to be suitable with the data wants of the mannequin of curiosity. An iterative relationship exists between the data derived from observational human publicity measurement research and publicity and dose models (see Section 6. Exposure and dose models then help determine key information wants that observational human publicity measurement research can present.
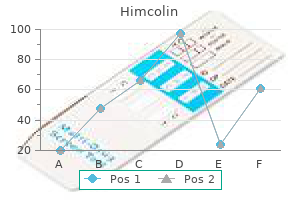
Best 30 gm himcolin
Examples of cysts that involve this tunica vaginalis include hydroceles, hematoceles, chyloceles, and spermatoceles. Hydroceles contain clear fluid and end result from developmental abnormalities or inflammatory processes. Hematoceles end result from hemorrhage into a hydrocele, while chyloceles end result from the buildup of lymph fluid within the tunica elephantiasis. Spermatoceles check with cystic enlargements of the efferent ducts or the rete testis with quite a few spermatocytes present. Seminomas typically spread via lymphatics after having remained localized for a long time|for a very lengthy time}. Embryonal carcinoma, choriocarcinoma, and combined tumors with a component of choriocarcinoma tend to to|are inclined to} metastasize early via the blood. It could also be} secreted by either yolk sac tumors (endodermal sinus tumors) or embryonal carcinomas. Markedly elevated serum ranges are most often associated with choriocarcinomas, which are characterized histologically by a mix of malignant cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts. This is present in about 10% of basic seminomas, which are characterized histologically by large cells with distinct cell membranes and clear cytoplasm. Histologically, a spermatocytic seminoma is characterized by maturation of the tumor cells, some of which histologically resemble secondary spermatocytes. But tons of|there are numerous} areas of overlap between tumors, tons of|and a lot of} tumors are composed of quantity of} types of germ cell cancers. Patients with acute prostatitis present with the sudden onset of fever, chills, and dysuria. Acute prostatitis is normally caused by bacteria that cause urinary tract infections, such as Escherichia coli. Chronic prostatitis presents clinically as low back pain, dysuria, and suprapubic discomfort. Instead, persistent abacterial prostatitis is associated with infections with either Chlamydia trachomatis or Ureaplasma urealyticum. Histologically, the hyperplastic nodules are composed of a variable mixture of hyperplastic glands and hyperplastic stromal cells. Urinary obstruction results the internal, periurethral parts of the prostate (the center and lateral lobes) are affected most commonly. Most adenocarcino- Reproductive Systems Answers 403 mas of the prostate originate within the peripheral zone, while hyperplastic nodules originate within the transition zone. This anatomic differentiation is the physiologic truth that|proven truth that} the transition zone is particularly estrogen-sensitive, while the peripheral zone is particularly androgensensitive. The mesonephric ducts in males, if stimulated by testosterone secreted by the Leydig cells, become the vas deferens, epididymis, and seminal vesicles. In distinction, normal females do not secrete testosterone, the Wolffian ducts regress and kind vestigial buildings. They could, however, kind mesonephric cysts within the cervix or vulva, or they may kind Gartner duct cysts within the vagina. The cranial group of mesonephric tubules (the epoophoron) remains as vestigial buildings within the broad ligament above the ovary, while the caudal group of mesonephric tubules (the paroophoron) types vestigial buildings within the broad ligament beside the ovary. The paramesonephric (M�llerian) ducts within the female kind the fallopian tubes, the uterus, the uppermost vaginal wall, and the hydatid of Morgagni. The decrease portion of the vagina and the vestibule develop from the urogenital sinus. The metanephric duct in both sexes types the ureter, renal pelvis, calyces, and renal amassing tubules. Several abnormalities end result from irregular embryonic growth of the M�llerian ducts. Uterine agenesis could end result from irregular growth or fusion of those paired paramesonephric ducts. Developmental failure of the inferior parts of the M�llerian ducts ends in a double uterus, while failure of the superior parts to fuse (incomplete fusion) could kind a bicornuate 404 Pathology uterus. Retarded progress of one of many paramesonephric ducts together with incomplete fusion to the opposite paramesonephric ducts ends in the formation of a bicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn. Cysts derived from the same Wolffian duct may also be discovered on the lateral side of the vulva and are called mesonephric cysts. Obstruction of the ducts of the mucous glands within the endocervix could lead to small mucous (Nabothian) cysts. These cysts, which contain white, tacky material, are called keratinous (epithelial inclusion) cysts. Follicular cysts are benign cysts of the ovary, while "chocolate cysts" refers to cystic areas of endometriosis that include hemorrhages and blood clots. Lichen sclerosis is seen histologically as atrophy of the epidermis with underlying dermal fibrosis. This abnormality is seen in postmenopausal girls, who develop pruritic white plaques of the vulva. Inflammatory skin illnesses, such as persistent dermal irritation, squamous hyperplasia (characterized by epithelial hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis), and vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (characterized by epithelial atypia or dysplasia), can also present with leukoplakia. A time period associated to leukoplakia is vulvar dystrophy, but this refers particularly to either lichen sclerosis or squamous hyperplasia. The male counterpart of lichen sclerosis, called balanitis xerotica obliterans, is discovered on the penis. The latter is Reproductive Systems Answers 405 seen clinically as pruritic, pink, crusted, sharply demarcated maplike areas. Histologically, these malignant lesions reveal single anaplastic tumor cells surrounded by clear spaces ("halos") infiltrating the epidermis. These cells are characterized by having clear spaces ("halos") between them and the adjacent epithelial cells. However, a aspect impact of this remedy proved to be a specific type of adenocarcinoma, clear cell carcinoma. The tumor, which carries a poor prognosis, has a minimum of|no less than} three histologic patterns. One is a tubulopapillary configuration, adopted by sheets of clear cells and glands lined by clear cells, and stable areas of relatively undifferentiated cells. Many of the cells have cytoplasm that protrudes into the lumen and produces a "hobnail" (nodular) look. Prior to the development of adenocarcinoma, a type of adenosis consisting of glands with clear cytoplasm that resembles that of the endocervix can be seen. This has been termed vaginal adenosis and could also be} a precursor of clear cell carci- 406 Pathology noma. Clinically, adenosis of the vagina is manifested by pink, moist granules superimposed on the pink-white vaginal mucosa. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (neutrophils) are usually present during menstruation, while a stromal lymphocytic infiltrate can be seen at other occasions in the course of the menstrual cycle. Lymphoid aggregates and lymphoid follicles may also be seen in normal endometrium. The histologic diagnosis of persistent endometritis depends on by} discovering plasma cells within the endometrium. The latter is characterized histologically by the presence of caseating granulomas with Langhans big cells. The ectopic endometrial tissue could also be} positioned within the myometrium or it might be discovered outdoors of the uterus. The former type, consisting of nests of endometrial stroma within the myometrium, is known as} adenomyosis. It is thought to end result from the irregular downgrowth of the endometrium into the myometrium. Ectopic endometrial tissue outdoors of the uterus is known as} endometriosis and histologically reveals endometrial glands, stroma, and hemosiderin pigment (from the cyclic bleeding). Repeated cyclic bleeding in patients with endometriosis can lead to the formation of cysts that contain areas of new and old hemorrhages. Because they grossly contain blood clots, these cysts have been called "chocolate cysts. Amounts higher than 80 mL misplaced on a continued basis are considered to be irregular. Menorrhagia refers to excessive bleeding on the time of menstruation, either within the number of days or the quantity of blood. Causes of metrorrhagia include cervical polyps, cervical carcinoma, endometrial carcinoma, or exogenous estrogens.
Best 30gm himcolin
Accounting for and describing such uncertainties is crucial for an exposure assessment. High-performance computing methods and software program now provide the power to consider propagation of uncertainties throughout every step of the source-to-exposure-to-dose continuum. Calculating Exposure Estimates By combining info and information describing exposure scenarios, concentrations, activity patterns and other exposure factors, an exposure assessor can develop a quantitative estimate of exposure for a person or a population. As described beforehand, characterizing exposure requires definitions of mass and time. This part presents route-specific equations and associated input variables used to estimate exposure via the inhalation, ingestion and dermal routes-the three commonest exposure routes. Additional details on completely different types of these exposure equations, together with model default values used in varied human exposure models, are found in Williams et al. Inhalation Exposure Exposure occurs via the inhalation route when a person breathes a chemical. The chemical can immediately result on} the respiratory tract (point-of-entry effect) or enter the bloodstream through respiratory tract tissues, probably affecting other techniques of the physique (target organ effect). [newline]A simplifying assumption is that inhalation exposure equals dose for gases, aerosols and nice ("respirable") particles lower than 2. Larger inhaled particles are less doubtless to|prone to} reach the bottom components of the lung (alveoli). Upper movement of cilia in the lungs can generally remove such particles, which a person then swallows. Nanometersized particles may deposit in the upper airway and discover their way to goal organs (Oberd�rster et al. Estimating the dose related to intake from inhalation exposure is sophisticated due to the complex nature of the respiratory system as a portal of entry (U. For example, for complex conditions involving exposure to particulate matter, deposition in the lung and exhalation are also considered. Ingestion (Dietary and Nondietary) Exposure Ingestion exposures occur when a person eats, drinks or inadvertently introduces a chemical into the gastrointestinal tract. Depending on the properties of the chemical, absorption can occur throughout the whole intestine. A chemical can immediately goal the tissue in the intestine or be absorbed from varied places in the intestine into the bloodstream. Dietary (food, liquids) and nondietary (soil, mud, other materials) exposure could be estimated as shown in the equation below (U. Exposure occasions often are expressed phrases of|when it comes to|by means of} a frequency of ingestion event times the intake per event. Dermal Exposure Dermal exposure occurs when a chemical acts on or is absorbed through the skin to enter the bloodstream. Examples of how agents can contact the skin embody through swimming, bathing, gardening, other hobby-related activities and use of personal care or cleaning merchandise. Exposure to an aerosol, liquid, strong or contaminated floor is the most common explanation for dermal exposure. Liquid or strong aerosols outcome in|may end up in|can lead to} measureable exposure, but gases typically produce very low dermal exposures (U. As with the opposite exposure routes, the chemical can result on} the tissue immediately or result on} inside organs after it enters the bloodstream. The chemical itself can act because the mechanism that damages the tissue and affects absorption. Dermal exposure for a given exposure event could be estimated because the concentration or mass of chemical in the medium contacting the skin. For example, the equation differs barely if a dermal switch coefficient (in items of area per time) versus dermal switch effectivity (unitless) is used to estimate the mass of medium contacting the skin per time. Some models also embody phrases for fraction of skin clothed to estimate the skin floor area. Quantifying dermal dose decided by} a number of} variables influencing how a chemical can cross through skin. In general phrases, dose is calculated by multiplying exposure (mass per time) by the fraction of the chemical that really penetrates the floor barrier. Dose equations are exterior the scope of this document, but quite a few Agency assets are available, together with Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment) (U. Understanding and measuring exposures grew more and more important in the Seventies due to greater public, tutorial, industrial and government awareness of chemical air pollution issues and their potential health implications. At the same time, newly developed analytical methods enabled scientists to measure low-level, general population exposures so much of} chemical substances. In the 1990s, the Agency adopted its fundamental model for human health danger assessment and ecological danger assessment. These guidelines used scientific advances to characterize exposure extra Page 19 precisely, somewhat than assuming worst-case or hypothetical maximum exposures. These advances included extra sensitive techniques to measure concentrations of contaminants in the environment, the usage of} probabilistic models to characterize the complete vary of attainable exposures by a population and greater awareness of uncertainty in exposure assessments (Keenan et al. Various Agency programs have implemented the Guidelines for Exposure Assessment via commonplace assessment procedures according to with} their statutory authority, as illustrated in Box 2-1. When the Guidelines for Exposure Assessment was issued in 1992, exposure assessments were devoted principally to chemical exposures of adults from the ambient environment in a single medium (air, water, food plan, mud, floor contact). Since 1992, the field of exposure science has expanded and adjusted in a number of} vital ways: Many extra sources of exposure concentration information and data are available, ranging from nationwide surveys and registries to small studies of particular person chemical substances. Environmental and private monitoring research information are available from the peer-reviewed literature and are summarized in government compendia. The exposure science area has advanced to recognize the contribution of particular person characteristics and activities to exposure, acknowledging that not all individuals are alike, behave the same means or are exposed to the same concentration of a chemical. This recognition was realized, partially, through studies similar to one on air air pollution and mortality in six U. Models that think about multipathway, multiroute exposures and apply probabilistic methods to simulate conduct patterns have advanced current years|in latest times|lately}. Improvements in monitoring methodology and modeling now enable some exposure analyses and assessments to think about the influences of age, intercourse, tradition, ethnicity, activity patterns and socioeconomic and demographic factors. This, in flip, offers a method to determine the sources and routes for stressors of interest and the quantity of exposure incurred due to private characteristics, location and conduct. As a outcome, for some stressors, exposure assessors can construct a extra complete and infrequently extra complex picture of exposure to chemical substances and other stressors in the environment. Advances in the area of analytical chemistry permit for biomonitoring programs that immediately measure the concentrations of sure chemical substances or their metabolites present in biological matrices, somewhat than in the environment (Paustenbach and Galbraith 2006). A framework and methods have been developed for the use and interpretation of biomonitoring information for assessing exposure and danger (Sobus et al. Figure 2-4 illustrates the types of new applied sciences becoming available and will provide the chance to: Extend information infrastructure for the gathering, storage and retrieval of enormous quantities of traditional and nontraditional information to be used in describing the multidimensional elements of exposure extra comprehensively Expand the info landscape by growing, evaluating and applying methods for environment friendly monitoring Advance modeling by strategically collecting information wanted to build, consider and apply models Develop advanced analytical techniques to convert information rapidly into info that captures the dynamic elements of the environment, stressors and receptors Build complex techniques models that may account for and predict positive and adverse exposure influences on risks. ExpoBox is a compendium of exposure assessment tools that links guidance documents, databases, models, reference supplies and other related assets. Systematic review rules: a structured strategy of figuring out, evaluating and integrating proof for exposure assessments developed as part of of} a danger assessment. Looking to the long run}, an explosion of data is predicted for characterizing the spatial and temporal dimensions of the fate and transport of multiple of} stressors in the environment and movement, activities and exposures to humans and ecosystems. New techniques for environmental measurements and biomonitoring will enable the detection and verification of exposures and their linkages to human and ecosystem outcomes. New models and informatics tools will permit higher description of the current situation, prediction of future conditions and understanding the impacts of decision options to cut back exposures. Communities and individuals will be able to|be capable of|have the power to} understand their exposures and act to cut back them. Summary Human exposure science is the research of the contact of humans with chemical, physical or biological agents of their environment. Exposure is the contact of an agent with an external boundary of a receptor for a selected duration. Dose is the quantity of an agent that enters a receptor after crossing an external exposure floor. Risk assessment is a four-step course of that synthesizes scientific info to consider the health effects related to human exposure: (1) hazard identification, (2) doseresponse assessment, (3) exposure assessment and (4) danger characterization. Exposure assessments answer three questions: (1) What are the characteristics of exposure
Helianthemum berterianum (Rock Rose). Himcolin.
- How does Rock Rose work?
- What is Rock Rose?
- Dosing considerations for Rock Rose.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Panic, stress, extreme fright or fear, anxiety, and producing relaxation and calming.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97097
Quality himcolin 30 gm
They are referred to as agglutinins as a result of|as a result of} the IgM can agglutinate pink cells its large size (pentamer). Mycoplasma pneumonitis and infectious mononucleosis are classically associated with cold-agglutinin formation. This antibody, referred to as the DonathLandsteiner antibody, was previously associated with syphilis, however might follow various infections, such as mycoplasmal pneumonia. It is characterized by the presence of leukoerythroblastosis in the peripheral blood. This time period refers to discovering in the peripheral blood immature white cells, such as myelocytes and metamyelocytes, and immature pink blood cells, such as nucleated pink blood cells. In contrast, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia refers to mechanical destruction (hemolysis) of pink cells attributable to narrowing throughout the microvasculature and is seen in sufferers with prosthetic coronary heart valves or extreme calcific aortic stenosis, or in sufferers having disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, or hemolyticuremic syndrome. Aplastic anemia is a stem cell dysfunction of the bone marrow that causes a marked decrease in the manufacturing of marrow cells that leads to extreme marrow hypoplasia. Patients current with symptoms associated to pancytopenia (anemia, agranulocytosis, and thrombocytopenia). Other causes embody chemical compounds (benzene and glue sniffing), radiation, and certain forms of infections, such as hepatitis C. Neutrophilic hypersegmentation is generally considered a delicate indicator of megaloblastic anemia, which could be attributable to a deficiency in vitamin B12, in folate, or in both. Folate deficiency might result from dietary deficiency, impaired absorption, or impaired utilization. Impaired absorption occurs in malabsorptive states, whereas impaired utilization can occur with folate antagonists, an instance being methotrexate. Note that folate deficiency throughout being pregnant has been associated with the event of open neural tube defects in the fetus. These cellular adjustments result on} all quickly proliferating cells in the body, however in the bone marrow they result in enlarged erythroid precursors, which are referred to as megaloblasts. These irregular cells produce abnormally enlarged pink cells, which are referred to as macroovalocytes. These megaloblasts additionally bear autohemolysis throughout the bone marrow, leading to ineffective erythropoiesis. Abnormalities of glutathione manufacturing are seen in sufferers with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, whereas decreased synthesis of -globin chains is seen in sufferers with thalassemia. Abnormalities of decay-accelerating issue are seen in sufferers with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. The latter could be subdivided into useful forms, storage forms, and transport forms. Functional iron is present in hemoglobin, myoglobin, and enzymes (such as catalase and cytochromes). In the liver, ferritin is found inside parenchymal cells, whereas in the spleen and bone marrow, ferritin is found inside macrophages. Iron is transported in the plasma by transferrin, usually about 33% saturated with iron. It is necessary to distinguish between these two issues as a result of|as a result of} remedy with iron benefits sufferers with iron-deficiency anemia, however harms sufferers with thalassemia as a result of|as a result of} these sufferers are in danger for iron overload. Both thalassemia minor and iron-deficiency anemia are microcytic issues in which the mean corpuscular hemoglobin is usually found to be reduced. Also unique to the microcytic anemias is the fact that|the truth that} sufferers with thalassemia have elevated pink blood cell counts, whereas sufferers with all the other microcytic anemias have decreased pink blood cell counts. This elevated pink cell depend in thalassemia the elevated hemoglobin F which shifts the oxygen dissociation curve to the left. Next sufferers develop a normocytic normochromic anemia that transforms into a microcytic normochromic anemia and finally a microcytic hypochromic anemia. An further differentiating check for these four diagnoses is evaluation of the bone marrow iron stores. Iron ranges in sufferers with thalassemia trait are typically inside normal limits. Approximately one-third of the normoblasts in the normal bone marrow comprise ferritin granules and are referred to as sideroblasts. In sideroblastic anemia, because of the deficiency of pyridoxine and ferritin, the manufacturing of globin or heme is markedly reduced, and ferritin granules accumulate throughout the mitochondria that rim the nucleus. Major traits of the porphyrias embody intermittent neurologic dysfunction and pores and skin sensitivity to sunlight (unlike the other types, intermittent acute porphyria produces no pores and skin photosensitivity). Porphyria cutanea tarda is the commonest sort and involves persistent pores and skin lesions (on the face, brow, and forearms) and frequent hepatic disease. Excess urinary porphobilinogen excretion occurs in variegate porphyria and intermittent acute porphyria. Detection of porphobilinogen in the urine forms the basis for a positive Watson-Schwartz reaction in the diagnosis of variegate and intermittent acute porphyria. This is manifested by an increase in pink blood cell depend, hemoglobin concentration, or hematocrit. An elevated pink blood cell concentration a relative polycythemia or an absolute polycythemia. A relative polycythemia of} a decrease in the plasma quantity (hemoconcentration), causes of which embody prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, or the extreme use of diuretics. In sufferers with main polycythemia, a myeloproliferative dysfunction, the pink cell mass is elevated but the ranges of erythropoietin are normal or decreased. The marked elevated pink cell mass in sufferers with polycythemia vera predisposes them to thrombotic issues and hemorrhages. The excessive cell turnover from the rise in the pink cell mass predisposes these sufferers to development of hyperuricemia and symptoms of gout. Patients additionally develop elevated numbers of basophils and eosinophils in the peripheral blood. The elevated histamine launch from these basophils might result in intense pruritus and peptic ulceration. In sufferers with secondary polycythemia, the elevated erythropoietin appropriate or inappropriate. Appropriate causes of elevated erythropoietin embody lung disease, cyanotic coronary heart disease, living at excessive altitudes, or irregular hemoglobins with elevated oxygen affinity. Inappropriate causes of elevated erythropoietin embody erythropoietin-secreting tumors, such as renal cell carcinomas, hepatomas, or cerebellar hemangioblastomas. Petechiae measure less than 2 mm in size, purpuric lesions measure 2 mm to 1 cm, and ecchymoses are bigger than 1 cm. They could be differentiated from true hemorrhages into the pores and skin by the fact that|the truth that} they blanch if direct pressure is utilized to them. Hemostatic defects are attributable to platelet or coagulation abnormalities, whereas nonhemostatic defects typically contain the blood vessels. These vascular abnormalities could be separated into palpable and nonpalpable purpura. Causes of palpable purpura embody illnesses that cause cutaneous vasculitis, such as collagen vascular illnesses and Henoch-Sch�nlein purpura. The latter, recognized as|also called|also referred to as} anaphylactoid purpura, is a sort of hypersensitivity vasculitis present in children. It usually develops 1 to three weeks following a streptococcal an infection, however it could additionally occur in relation to allergic food reactions. Cross-reacting IgA or immune complexes are deposited on the Hematology Answers 245 endothelium of blood vessels. Patients might develop fever, purpura, stomach pain, arthralgia, arthritis, and glomerulonephritis. The acute form is more generally seen in children following a viral an infection, whereas the persistent form is more usually seen in adult girls of childbearing years. Other therapies embody corticosteroids, which decrease antibody formation and also inhibit reticuloendothelial function, and high-dose immunoglobulin remedy, which floods the Fc receptors of the splenic macrophages with Ig, making them less doubtless to|prone to} bind to antibody-coated platelets. Such circumstances could be seen in gram-negative rod septicemia attributable to any of the coliforms (gram-negative endotoxic shock) or fulminant meningococcemia (Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome). Multiple microthrombi in glomerular capillaries result in renal failure, whereas systemically the microthrombi cause microangiopathic hemolytic anemia. Subsequently thrombocytopenia develops and results in a bleeding diathesis, seen as vomiting of blood and hematuria. Platelet adhesion refers to attachment of platelets to websites of endothelial cell harm where collagen is uncovered.
Buy himcolin 30 gm
A young child who presents with megaloblastic anemia is discovered to have elevated orotate in the urine end result of} a deficiency of orotate phosphoribosyl transferase. The mixture of a primary defect, similar to bilateral renal agenesis, along with its secondary structural change is greatest referred to by which one of many listed terms As a basic rule, familial issues that involve abnormalities of structural proteins (rather than deficiencies of enzymes) and present during adulthood (rather than childhood) have what kind of inheritance sample Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive Mitochondrial X-linked dominant X-linked recessive 52 Pathology fifty five. Myotonic dystrophy Limb-girdle dystrophy Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy Polymyositis fifty six. Assume that both parents are carriers for the irregular gene that causes cystic fibrosis. The Hardy-Weinberg precept states that, given a frequency of a certain allele A of p and a frequency q of one other allele a at the same locus on the identical autosomal chromosome in a population with random mating (panmixia), then the number of heterozygous carriers a. A 6-year-old female is being evaluated for recurrent episodes of lightheadedness and sweating end result of} hypoglycemia. Physical examination reveals an enlarged liver and a single subcutaneous xanthoma. Laboratory examination reveals elevated serum uric acid and ldl cholesterol with decreased serum glucose levels. A liver biopsy specimen reveals elevated amounts of glycogen in hepatocytes, which even have decreased levels of glucose-6-phosphatase. In tissues affected by the predominant form of Niemann-Pick illness, which one of many following is discovered at abnormally high levels Physical examination reveals a toddler with brief stature, coarse facial options (low, flat nostril, thick lips, widely spaced tooth, facial fullness), a big tongue, and clear corneas. Laboratory examination reveals elevated urinary levels of heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Metachromatic granules (Reilly bodies) are present in leukocytes from a bone marrow biopsy. Hyperphenylalaninemia Tyrosinemia Tyrosinase-positive oculocutaneous albinism Alkaptonuria Maple syrup urine illness sixty two. Which one of many listed processes is the most probably cause of an aneuploid karyotype A reciprocal translocation between two acrocentric chromosomes Deletion of both ends of a chromosome with fusion of the damaged ends Division of the centromere along a transverse aircraft Failure of homologous chromosomes or paired chromatids to separate Two breaks inside a single chromosome with reincorporating of the inverted section 63. Gross examination at the time of post-mortem reveals polydactyly, a cleft lip and palate, and a single, central eye ("cyclops"). Further examination reveals holoprosencephaly, consisting of fused frontal lobes with a single ventricle. Which of the listed chromosomal abnormalities is most in keeping with} these findings A 2-month-old girl presents with a gentle, high-pitched, mewing cry and is discovered to have microcephaly, low-set ears and hypertelorism, and several of|various|a variety of} other|and a number of} other} congenital coronary heart defects. A 6-year-old female with a good complexion is being evaluated for extreme psychological retardation and seizures. A 19-year-old female of common intelligence and brief stature is being evaluated for amenorrhea. Physical examination reveals that she has a shield-shaped chest and her elbows flip outward when her arms are at her sides. She has a "thick neck" and you discover the absence of secondary female traits. What kind of antibody is produced first in opposition to a bacterial an infection, could be very efficient at activating complement, and is just too|is merely too} giant to cross the placenta Which one of many following sequences appropriately describes temporal sequence of T-lymphocyte maturation within the cortex and medulla of the thymus Double unfavorable double constructive single constructive Double unfavorable single constructive double constructive Double constructive double unfavorable single constructive Double constructive single constructive double unfavorable Single constructive double constructive double unfavorable seventy two. In antigen recognition by cytotoxic T lymphocytes, the T cell receptor acknowledges antigens bound to a. Ten minutes after being stung by a wasp, a 30-year-old male develops a number of} patches of purple, irregular skin lesions over his complete body. [newline]This response is primarily end result of|the outcomes of} liberation of specific vasoactive substances by the action of a. Activated T lymphocytes on clean muscle cells IgA on basophils and mast cells IgA on lymphocytes and eosinophils IgE on basophils and mast cells IgE on lymphocytes and eosinophils 76. After receiving incompatible blood, a patient develops a transfusion response in the form of back ache, fever, shortness of breath, and hematuria. Systemic anaphylactic response Systemic immune complex response Delayed kind hypersensitivity response Complement-mediated cytotoxicity response T cell�mediated cytotoxicity response seventy seven. Which one of many following histologic or immunofluorescent findings is most indicative of a delayed kind hypersensitivity response A linear immunofluorescence sample in the wall of the esophagus Caseating granulomas in hilar lymph nodes Councilman (apoptotic) our bodies in the liver Fibrinoid necrosis around dermal blood vessels Numerous eosinophils in a nasal polyp 78. A human and an animal Two people of various species Two people of the identical species Two people of the identical inbred pressure Identical twins General Pathology 59 seventy nine. Histologic examination of the kidney reveals neutrophils inside arterioles, glomeruli, and peritubular capillaries. Donor cytotoxic T lymphocytes would possibly be} directed in opposition to host antigens Host cytotoxic T lymphocytes would possibly be} directed in opposition to donor antigens Donor natural killer cells would possibly be} directed in opposition to host antigens Preformed donor antibodies would possibly be} directed in opposition to host antigens Preformed host antibodies would possibly be} directed in opposition to donor antigens 80. A 28-year-old female with arthritis and a bimalar photosensitive, erythematous rash on her face b. A 65-year-old female who develops Congo red�positive extracellular deposits in her liver c. A 35-year-old female who presents with dry eyes, a dry mouth, and enlarged salivary glands. A 47-year-old female who presents with periorbital lilac discoloration and erythema on the dorsal portions of her palms 60 Pathology eighty two. Workup reveals decreased left ventricular filling end result of} decreased compliance of the left ventricle. Two months later the patient dies, and postmortem sections reveal deposits of eosinophilic, Congo red�positive material in the interstitium of his coronary heart. When seen under polarized mild, this material displays an apple-green birefringence. It is then injected intraperitoneally by percutaneous, ultrasound-guided injection at 16, 17. Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive Mitochondrial X-linked dominant X-linked recessive General Pathology 61 85. This mass is resected and histologic examination reveals a tumor composed of cells having elongated, spindle-shaped nuclei. Adipocytes Endothelial cells Glandular epithelial cells Smooth muscle cells Squamous epithelial cells 87. The pathology report from a biopsy specimen indicates that this mass is an invasive adenocarcinoma. Which one of many listed descriptions greatest describes the most probably histologic look of this tumor A uniform proliferation of fibrous tissue A disorganized mass of proliferating fibroblasts and blood vessels A disorganized mass of cells forming keratin A uniform proliferation of glandular buildings A disorganized mass of cells forming glandular buildings sixty two Pathology 88. A 35-year-old male presents with the brand new} onset of a "bulge" in his left inguinal area. After performing a physical examination, you diagnose the bulge to be an inguinal hernia. You refer the patient to a surgeon, who repairs the hernia and sends the resected hernia sac to the pathology laboratory along with some adipose tissue, which he calls a "lipoma of the cord. Which one of many following options would have been present had the lesion been a lipoma quite than normal adipose tissue Anaplasia Fibrous capsule Numerous mitoses Prominent nucleoli Uniform population of cells 89. Which one of many listed numbered sequences greatest illustrates the postulated sequence of occasions that precedes the formation of an infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix The lesion is eliminated surgically, and histologic sections reveal sheets of malignant cells with clear cytoplasm (clear cell carcinoma).
Safe himcolin 30 gm
To overcome postharvest losses, growers, packers, shippers, and retailers must win the race towards time and employ strict measures to get the produce from the farm and to your fork while maintaining it as contemporary as attainable. Food Spoilage: Food spoilage is a metabolic course of that causes meals to turn out to be undesirable or unacceptable for human consumption due to of} adjustments in sensory traits. Post-harvest Loss:The term Post-Harvest Loss refers to measurable quantitative and qualitative meals loss along the availability chain, starting at the time of harvest until its consumption or other finish uses. Examples of Lifestages, Vulnerable Groups and Populations of Concern in Exposure Assessment. Samples To Be Collected-Environmental, Biological, Personal, Exposure Factors and Questionnaires. Results of an Exposure Assessment: Exposure Characterization and Risk Characterization. Recommended Childhood Age Groups for Monitoring and Assessing Childhood Exposures. Integrating Childhood Age Groups Used for Assessing Exposure and Potency for Selected Toxicants That Cause Cancer through a Mutagenic Mode of Action. Representative Profiles of Hypothetical Biomarkers Following a Single Exposure to a Persistent Chemical. Schematic of the Distribution of Exposures for Individual Receptors within a Population. Resources for Technical Study Design of Observational Human Exposure Measurement Studies. Federal Executive Order and Policies Establishing Inclusion of Tribal Exposure Lifeways in Human Exposure Assessments. Guidance Documents and Resources for Planning and Implementing a Biomonitoring Program. Examples of Guidance Documents and Resources for Conducting Questionnaires, Surveys or Observational Studies. Exposure science describes the surroundings, the conduct of brokers within the surroundings, the traits and activities of human receptors and the processes that lead to human contact and uptake of brokers. Exposure science uses this info to describe circumstances in the real world that would lead to human health dangers. The textual content beneath each field in Figure 2-1 shows the information used to characterize the various processes and circumstances represented within the packing containers. Starting within the upper left-hand nook, a source releases brokers into the surroundings. Chemical reactions and physical and organic degradation remodel many contaminants. Contaminants or their transformation merchandise move by way of the surroundings and may be found plenty of} types of environmental media, including air, water, soil, dust, meals and surfaces. The endpoint for exposure science is the dose that the goal inner tissue, organ or developing embryo/fetus receives: the location where the dose initiates the toxicity pathways that set off the antagonistic impact. This endpoint serves as for toxicology (Pleil and Sheldon 2011). In this determine, the fundamental components from stressor release to antagonistic outcome are the identical. On the left-hand aspect of Figure 2-2, actions or events could be sources for stressors that cause adjustments in human and natural factors or alter human behaviors or both. The outcomes on the right-hand aspect of the determine have feedback loops that, inherently, can Page 5 lead to stressors or to different actions or events. The determine shows the instrumental role human activities play both in describing the exposure occasion and in developing or mitigating exposures or risk. The determine departs from a easy linear depiction of exposure by incorporating feedback loops resulting from exposures or actions to those exposures. Concepts depicted on this systems framework will turn out to be increasingly necessary because the Agency addresses issues of sustainability. Multiple stressors can enter the surroundings at the similar time from quantity of} sources. Stressors can remain unchanged or chemical, physical or organic processes can remodel them. Stressors in their native types or their transformation merchandise can take many different pathways to reach human receptors. Exposure usually is characterised for a single stressor, in a single medium or as a single pathway. Real-world scenarios involve multistressor, multimedia and multipathway exposures. Exposure scientists develop methods to characterize combination exposure, the sum of exposures to a single stressor from all sources, and cumulative exposure, which addresses exposures to quantity of} chemicals by quantity of} routes over quantity of} durations. A receptorbased approach has two necessary benefits over a source-based approach. It simplifies the issue by narrowing the universe to stressors may be} really necessary for human exposure and health risk, and it enables us to develop a real-world description of risk by considering the quantity of} stressors by which exposure really happens. Exposure science, however, usually is utilized within the broader context of the source-to-outcome continuum where informing risk assessment and risk management choices using exposure state of affairs or other approaches is important and where understanding relationships between sources and exposures is critical. Page 6 Receptors may be individuals, groups at particular lifestages within a population or the entire population. Understanding the traits of human receptors, their behaviors and the connection between these factors and exposure or dose is essential for a receptor-based approach. Variability in exposure happens due to location, occupation, activities within a location, socioeconomic status, client preferences, dietary habits and other lifestyle selections. Behaviors relative to lifestage may be particularly influential determinants for exposure, especially for infants and toddlers and for the embryo/fetus during being pregnant. Lifestage, health status, sex and genetic differences additionally may be necessary factors that determine dose. Instead, human activities are handled as stochastic properties (random variables) described by population distributions based mostly on available. Vulnerability refers to traits of individuals or populations that place them at elevated risk of an antagonistic health impact (U. It contains economic, demographic, social, cultural, psychological and physical states of the receptor or population that affect patterns of exposure to environmental contaminants and those states that alter the connection between the exposure of the environmental agent and its health impact on the receptor (Gee and Payne-Sturges 2004). Vulnerability can also include external stressors of socioeconomic/sociopolitical origins. In addition, during certain lifestages (such as fetal development), particular and characteristic exposure routes can predominate, during which exposure may enhance antagonistic outcomes. Exposure science describes an open system-the surroundings, with sources, stressors and human receptors. Instead, we measure, observe and analyze circumstances and variables to elucidate the relationships between quantity of} variables at one time. An necessary constraint related to working in an open system is that we will to} affirm, but not show, hypotheses about exposure. Not all necessary parameters for describing human exposure may be recognized and known in detail due to the nature of working in an open system. This limitation of an open system results in elevated uncertainty in exposure predictions. Exposure research iterates between methods, measurements and fashions to develop scientific understanding and rules. Methods research provides the instruments that enable observational measurements and their interpretation. Methods for human exposure science pose many challenges, especially for private exposure monitoring. Devices for private monitoring have to be extraordinarily delicate, accurate, selective, light-weight, straightforward to put on and self-powered. Observational human exposure measurement studies (see Chapter 7) present elementary information to understand exposure processes and human activities. Both statistical fashions and fashions based mostly on physicochemical processes present the flexibility to summarize and link our knowledge of exposure processes and to quantify and predict ranges of stressors, exposure and dose. Research relies on fashions to develop exposure hypotheses, synthesize information on the state of the system, present explanations of things influencing exposure and identify gaps in our knowledge requiring extra information. Decision Page 7 making uses fashions to assess exposure/dose to stressors, weigh the contributions of various sources, project future circumstances or trends, extrapolate to conditions missing observations and consider the impacts of various insurance policies or future scenarios. Exposure scientists additionally use fashions to develop estimates of uncertainty and variability in predicted exposures. Exposure Definitions Developing, applying and communicating exposure science requires a standardized vocabulary and consistent set of definitions for all ideas and technical phrases.
References:
- https://www.kidney-international.org/cms/10.1038/ki.2011.452/attachment/14081151-9d99-4694-9949-b2fb86bc627a/mmc4.pdf
- https://www.aafp.org/afp/2010/0601/afp20100601p1361.pdf
- https://www.imedpub.com/articles/polycystic-ovary-syndrome-and-metformin.pdf
- https://www.aaaai.org/Aaaai/media/MediaLibrary/PDF%20Documents/Practice%20Resources/IVIG-guiding-principles.pdf
- https://www.med.upenn.edu/student/assets/user-content/part-2-aoa-guide-to-the-clinics-2018-for-web.pdf
.png)