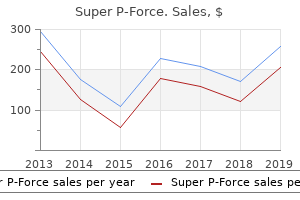
Order super p-force 160mg
The cell is normally bigger than the resting lymphocyte and has an irregular form. The nucleus is commonly elongated and irregular with a finer chromatin pattern than that of the resting lymphocyte. Often this cell is increased in viral infections; additionally referred to as a virocyte, or stimulated, transformed, atypical, activated, or leukocytoid lymphocyte. Measurement of absorbance due to reagent alone; eliminates false enhance in pattern absorbance due to reagent colour. Thrombus composed largely of purple blood cells; so named due to its purple coloration. Refractive Index the degree to which a transparent object will deflect a lightweight ray from a straight path. There are normally cytopenias and signs of dyspoiesis within the peripheral blood with <5% blasts. The bone marrow is normally hypercellular with dyspoiesis in all hematopoietic cell lineages. Normally reticulocytes represent approximately 1% of the circulating erythrocyte population. The calculation corrects the reticulocyte rely for the presence of marrow reticulocytes within the peripheral blood. Ribosomes seem singly or in reversibly dissociable models and may be free within the cytoplasm or hooked up to endoplasmic reticulum. The cytoplasm of blood cells that contain a excessive concentration of ribosomes stains bluish purple with Romanowsky stains. Ringed sideroblasts Erythroblasts with abnormal deposition of extra iron inside mitochondria leading to a ring formation around the nucleus. Romanowsky-kind stain Any stain consisting of methylene blue and its oxidation products and eosin Y or eosin B. A globule crammed with immunoglobulin found in pathologic plasma cells referred to as Mott cells (see Mott cell). Schistocyte Fragment of an erythrocyte; a schistocyte might have a variety of shapes together with triangle, helmet, and comma. Secondary aggregation Irreversible aggregation of platelets that occurs over time. Secondary fibrinolysis A scientific condition characterised by excessive fibrinolytic exercise in response to disseminated intravascular clotting. Secondary hemostasis the formation of fibrin that stabilizes a primary platelet plug. Secondary hemostatic A primary platelet mixture that has been plug stabilized by fibrin formation throughout secondary hemostasis. They selectively hydrolyze arginine- or lysinecontaining peptide bonds of different zymogens changing them to serine proteases. Each serine protease involved within the coagulation cascade is very specific for its substrate. The time period for which a reagent or control is stable given applicable storage conditions. Shelf life will change once the reagent or control is reconsitituted if lypholyzed or opened if liquid. The appearance of increased numbers of immature leukocytes within the peripheral blood. Sickle cell (drepanocyte) Elongated crescent shaped erythrocyte with pointed ends. Sickle cell formation may be observed in wet preparations or in stained blood smears from patients with sickle-cell anemia. Sickle-cell anemia Sickle-cell trait A genetically determined dysfunction in which hemoglobin S is inherited within the homozygous state. A genetically determined dysfunction in which hemoglobin S is inherited within the heterozygous state. The two problems seem to belong to one disease entity with differing scientific manifestations. Increased numbers of smudge cells are observed in lymphoproliferative problems like persistent lymphocytic leukemia. Stab 530 Hematology Stage the stage of a neoplasm is the extent and distribution of disease. Determining the stage of disease normally involves radiologic research, peripheral blood examination, and bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. Starry sky Morphologic appearance characteristic of highgrade lymphoma produced by numerous tingible physique macrophages (stars) and a diffuse sheet of neoplastic cells (sky). Stomatocyte An abnormal erythrocyte form characterised by a slit-like area of central pallor. Streptokinase A bacterial enzyme derived from group C-beta hemolytic steptococci that prompts plasminogen to plasmin and is used as a thrombolytic agent within the treatment of thrombosis. Stroma Extracellular matrix or microenvironment that supports hematopoietic cell proliferation within the bone marrow. Stromal cells Cellular elements of the hematopoietic microenvironment within the purple portion of bone marrow. Submetacentric Chromosome that has the centromere positioned off-heart in order that the quick arm is shorter than the lengthy arm. Sucrose hemolysis take a look at A screening take a look at to establish erythrocytes which are abnormally delicate to complement lysis. Supernatant Clear liquid remaining on high of an answer after centrifugation of the particulate matter. Teardrop might type after erythrocytes with mobile inclusions have transversed the spleen. Heterozygotes may be asymptomatic but homozygotes usually have a extreme, usually fatal, disease. Thalassemia occurs most incessantly in populations from the Mediterranean area and Southeast Asia. A decrease within the number of platelets within the peripheral blood beneath the reference vary for an individual laboratory (normally beneath a hundred and fifty X 109/L). An enhance within the number of platelets within the peripheral blood above the reference vary for an individual laboratory (normally over 440 X 109/ L). Blockage of a small blood vessel by a blood clot that was fashioned within the coronary heart, arteries, or veins, dislodged and moved through blood vessels until reaching a smaller vessel and blocking further blood move. A humoral issue that regulates the maturation of megakaryocytes and the production of platelets. Formation of a blood clot or thrombus, normally considered to be under abnormal conditions inside a blood vessel. Characterized by microangiopathic anemia, decreased number of platelets, and renal failure as well as neurological signs. They are found in areas of extensive apoptosis (reactive germinal centers and highgrade lymphoma). Large, dark blue-black primary granules within the cytoplasm of neutrophils which are present in sure infectious states. Toxoplasmosis Trabecula Transferrin A condition that results from infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Acquired infection may be asymptomatic, or signs might resemble infectious mononucleosis. There is a leukocytosis with relative lymphocytosis or hardly ever an absolute lymphocytosis and the presence of reactive lymphocytes. Projection of calcified bone extending from cortical bone into the marrow area; provides support for marrow cells. A plasma 1-globulin answerable for the binding of iron and its transport within the bloodstream. It catalyzes the formation of isopeptide bonds between glutamine and lysine residues on fibrin, forming stable covalent cross-hyperlinks. A temporary suppression of erythropoiesis that incessantly occurs after a viral infection in infants and kids. More mature than the sort I myeloblasts, these cells can contain Auer rods, phi our bodies, and/or primary granules.
Indian Podophyllum (Podophyllum). Super P-Force.
- Raised areas on the tongue and mouth in people with immune system diseases (hairy leukoplakia), liver problems, cancer, and other conditions.
- How does Podophyllum work?
- Treating human papilloma virus (genital and anal warts).
- What is Podophyllum?
- Dosing considerations for Podophyllum.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96783
Super p-force 160mg
Histogenesis of mucinous tumours, according to that of serous tumours, is by metaplasia from the coelomic epithelium that differentiates alongside endocervical kind or intestinal kind of mucosa. They are smooth-surfaced cysts with characteristic multiloculations containing thick and viscid gelatinous fluid. Benign tumours generally have thin wall and septa dividing the loculi are also thin and infrequently translucent, but malignant varieties usually have thickened areas. Mucinous cystadenoma is lined by a single layer of these cells having basal nuclei and apical mucinous vacuoles. Borderline (atypical proliferating) mucinous tumour is identified by the identical histologic standards as for borderline serous tumour i. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma likewise is characterised by piling up of malignant epithelium, at places forming strong sheets, papillary formation, adenomatous sample and infiltration into stroma with or with out swimming pools of mucin. They are known as endometrioid carcinomas because of the shut resemblance of histologic sample to that of uterine endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Histogenesis of these tumours in majority of cases is believed to be from ovarian coelomic epithelium differentiating in the direction of endometrial kind of epithelium. G/A these tumours are partly strong and partly cystic and will have foci of haemorrhages, particularly in benign variety. M/E the endometrioid adenocarcinoma is distinguished from serous and mucinous carcinomas by typical glandular sample that closely resembles that of uterine endometrioid adenocarcinoma. They are termed clear cell or mesonephroid carcinomas because of the shut histologic resemblance to renal adenocarcinoma. M/E Clear cell or mesonephroid carcinoma is characterised by tubules, glands, papillae, cysts and strong sheets of tumour cells resembling cells of renal adenocarcinoma. Rarely, borderline form is encountered known as proliferating Brenner tumour whereas the one with carcinomatous change is termed malignant Brenner tumour. Histogenesis of the tumour is from coelomic epithelium by metaplastic transformation into transitional epithelium (urothelium). M/E Brenner tumour consists of nests, lots and columns of epithelial cells, scattered in fibrous stroma of the ovary. Nearly 95% of them are benign and happen chiefly in younger females, overwhelming majority of them being benign cystic teratomas (dermoid cysts). For occasion, benign cystic teratoma or dermoid cyst so widespread in ovaries is extremely uncommon within the testis. Cytogenetic research have revealed that these tumours arise from a single germ cell (ovum) after its first meiotic division. Infrequently, mature teratoma could also be strong and benign and has to be distinguished from immature or malignant teratoma. Benign cystic teratomas are extra frequent in younger girls throughout their active reproductive life. G/A Benign cystic teratoma or dermoid cyst is characteristically a unilocular cyst, 10-15 cm in diameter, usually lined by the pores and skin and hence its name. On sectioning, the cyst is crammed with paste-like sebaceous secretions and desquamated keratin admixed with lots of hair. M/E the most distinguished characteristic is the liner of the cyst wall by stratified squamous epithelium and its adnexal buildings such as sebaceous glands, sweat glands and hair follicles. Though ectodermal derivatives are most distinguished features, tissues of mesodermal and endodermal origin are also commonly present. They are extra widespread in prepubertal adolescents and younger girls underneath 20 years of age. G/A Malignant teratoma is a unilateral strong mass which on cut part reveals characteristic variegated appearance revealing areas of haemorrhages, necrosis, tiny cysts and heterogeneous admixture of varied tissue components. Immature tissue components could differentiate in the direction of cartilage, bone, glandular buildings, neural tissue and so forth, and are distributed in spindle-formed myxoid or undifferentiated sarcoma cells. An necessary think about grading and determining the prognosis of immature teratoma is the relative amount of immature neural tissue. Struma ovarii It is a teratoma composed completely of thyroid tissue, recognisable grossly in addition to microscopically. Carcinoid tumour this is an ovarian teratoma arising from argentaffin cells of intestinal epithelium within the teratoma. Struma-carcinoid this is a uncommon mixture of struma ovarii and ovarian carcinoid. Cut part of the tumour is grey-white to pink, lobulated, soft and fleshy with foci of haemorrhages and necrosis. The tumour cells are arranged in diffuse sheets, islands and cords separated by scanty fibrous stroma. The tumour cells are uniform in appearance and huge, with vesicular nuclei and clear cytoplasm rich in glycogen. The fibrous stroma generally contains lymphocytic infiltrate and typically could have sarcoidlike granulomas. More usually, endodermal sinus tumour is discovered in combination with other germ cell tumours somewhat than in pure form. M/E Like its testicular counterpart, the endodermal sinus tumour is characterised by the presence of papillary projections having a central blood vessel with perivascular layer of anaplastic embryonal germ cells. Such buildings resemble the endodermal sinuses of the rat placenta (SchillerDuval physique) from which the tumour derives its name. Ovarian choriocarcinoma is extra malignant than that of placental origin and disseminates extensively via bloodstream to the lungs, liver, bone, brain and kidneys. The group contains: pure granulosa cell tumours, pure thecomas, mixture of granulosa-theca cell tumours and fibromas. These tumours invade domestically but often could have extra aggressive and malignant behaviour. G/A Granulosa cell tumour is a small, strong, partly cystic and usually unilateral tumour. M/E the granulosa cells are arranged in a variety of patterns including micro- and macrofollicular, trabecular, bands and diffuse sheets. The microfollicular sample is characterised by the presence of characteristic rosettelike buildings, Call-Exner bodies, having central rounded pink mass surrounded by a round row of granulosa cells. M/E Thecoma consists of spindle-formed theca cells of the ovary admixed with variable amount of hyalinised collagen. The cytoplasm of theca cells is lipid-rich and vacuolated which reacts with lipid stains. Well-differentiated androblastoma composed virtually entirely of Sertoli cells or Leydig cells forming properly-defined tubules. Tumours with intermediate differentiation have a biphasic sample with formation of strong sheets by which abortive tubules are present. Poorly-differentiated or sarcomatoid variety is composed of spindle cells resembling sarcoma with interspersed scanty Leydig cells. The time period gynandroblastoma stands for mixture of female (gyn) and male (andro). The examples of these tumours are: hilus cell tumours, adrenal rest tumours and luteomas. Metastasis could happen by lymphatic or haematogenous route but direct extension from adjoining organs. Bilaterality of the tumour is the most helpful clue to prognosis of metastatic tumour. Most widespread major websites from where metastases to the ovaries are encountered are: carcinomas of the breast, genital tract, gastrointestinal tract. The tumour is usually secondary to a gastric carcinoma but other major websites where signet ring carcinomas happen. G/A Krukenberg tumour varieties moderately large, rounded or kidneyshaped, firm, multinodular lots in each ovaries. Cut part reveals greywhite to yellow, firm, fleshy tumour and will have areas of haemorrhage and necrosis. M/E It is characterised by the presence of mucin-filled signet ring cells which can lie singly or in clusters. It is accompanied by cellular proliferation of ovarian stroma in a storiform sample. The umbilical cord is about 50 cm long and contains two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein hooked up on the foetal floor. The maternal portion of the placenta has irregular grooves dividing it into cotyledons that are composed of sheets of decidua basalis and remnants of blood vessels. The foetal portion of the placenta is composed of quite a few useful models known as chorionic villi and comprise the major part of placenta at time period.
Trusted super p-force 160 mg
Dentin has a radially striated appearance as a result of quite a few minute canals referred to as dentinal tubules that pursue an S-shaped course as they lengthen from the pulp chamber to the dentinoenamel junction. The cell body of the odontoblast lies within the pulp cavity adjoining to the dentin. Teeth In humans, the enamel appear as two distinct sets: major (deciduous) and everlasting. Primary enamel erupt 6 to 8 months after start and type a whole set of 20 by 2 years of age. They are shed between the sixth and thirteenth 12 months and progressively are replaced by the everlasting set of 32. Sensation is assumed to be perceived by the processes of odontoblasts, which in flip transmit the sensory stimulation to adjoining nerves in the pulp chamber. It incorporates quite a few thin, collagenous fibers embedded in an abundant gelatinous ground substance. Stellate fibroblasts are probably the most prominent cells of the pulp, though mesenchymal cells, macrophages, and lymphocytes are found in limited numbers. The cell bodies of the odontoblasts are also found in the pulp, lining the perimeter of the pulp cavity immediately adjoining to the dentin. Blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves enter and exit the pulp cavity through the apical foramen. It is acellular and consists primarily of calcium salts in the type of apatite crystals. Enamel consists of thin rods referred to as enamel prisms that lie perpendicular to the surface of the dentin and lengthen from the dentinoenamel junction to the surface of the tooth. Each prism, 6 to 8 �m in diameter, follows a spiraling, irregular course to the surface of the tooth. A small quantity of natural matrix surrounds every enamel prism and is called the prismatic rod sheath. The natural matrix of enamel consists primarily of proteins referred to as enamelins that bind to crystallites of the enamel prisms. Between the enamel prisms is the interprismatic substance, which additionally consists of apatite crystals in a small quantity of natural matrix. Each enamel prism is the product of a single ameloblast, the enamelproducing cells which are misplaced throughout eruption of the tooth. The orientation of the fibers in the periodontal membrane varies at completely different levels in the alveolar socket. In addition to typical connective tissue cells, osteoblasts and osteoclasts may be found the place the periodontal membrane enters the alveolar bone. The periodontal membrane has a wealthy vascular provide and is sensitive to strain modifications. Nearest the neck of the tooth, the cementum is thin and lacks cells, forming the acellular cementum. The remainder, which covers the apex of the tooth root, incorporates cells, the cementocytes, that lie in lacunae and are surrounded by a calcified matrix much like that of bone. Proximally, the elastic layer blends with the connective tissue between the muscle bundles of the pharyngeal wall. A submucosa is current solely the place the pharynx is steady with the esophagus and in the lateral walls of the nasopharynx. The muscularis of the pharyngeal wall consists of the skeletal muscle of the three pharyngeal constrictor muscle tissue, which, in flip, are lined by connective tissue of the adventitia. Near the tooth, collagenous fibers of the gingival lamina propria mix with the uppermost fibers of the periodontal membrane. Some collagenous fibers lengthen from the lamina propria into the cervical (upper) cementum and constitute the gingival ligament, which provides a firm attachment to the tooth. The keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of the gingiva also is connected to the surface of the tooth and at this point varieties the epithelial attachment cuff. Attachment of the cuff to the tooth is maintained by a thickened basal lamina and hemidesmosomes that seal off the dentogingival junction. Tubular Digestive Tract the tubular digestive tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, small gut, colon, and rectum. Each area of the digestive tube consists of the 4 basic layers, however the parts of those layers range according to the capabilities of the area. It is steady above with the oropharynx at the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage and beneath becomes steady with the cardia of the stomach. Antigen-presenting (Langerhans) cells have been recognized in the esophageal epithelium. The digestive and respiratory techniques merge briefly in the pharynx, which is subdivided into nasal, oral, and laryngeal components. The pharyngeal walls principally consist of three strata: a mucosa, a muscularis, and an adventitia. The lamina propria is a loose areolar connective tissue with diffuse and nodular lymphatic tissue scattered all through its size. The muscularis mucosae consists of longitudinally arranged clean muscle cells in a fine, elastic network. The muscularis mucosae is steady with the elastic layer of the pharynx at the degree of the cricoid cartilage. Within it are larger blood vessels, lymphatics, nerve fibers, occasional autonomic ganglia, and glands. Extensive longitudinal folds of the submucosa give the mucosa of the nondistended esophagus a characteristic pleated appearance. During swallowing the bolus of meals smoothes out these folds and permits the lumen to enhance in dimension quickly to accommodate the material swallowed. A chemically induced continual esophagitis outcomes, and the esophageal epithelium undergoes metaplasia, changing from wet stratified squamous to a simple columnar epithelium much like gastric lining epithelium. The upper esophageal sphincter capabilities to keep air from coming into the proximal esophagus. The hormone gastrin acts to stimulate the constriction of the lower esophageal sphincter. Adventitia A layer of loosely arranged connective tissue, the adventitia, covers the outer surface of the esophagus and binds it to surrounding buildings. Two groups of esophageal cardiac glands are current: one group located in the proximal esophagus close to the pharynx, the opposite in the distal esophagus close to the cardia of the stomach. Both are compound tubuloacinar glands of mucous sort and occur solely in the lamina propria. The esophageal glands proper are also mucous producing compound tubuloacinar glands however are confined to the submucosa and scattered all through the remaining size of the esophagus. Lysozyme and pepsinogen have been recognized in some however not the entire secretory cells. Myoepithelial cells are related to the secretory units of human esophageal glands. From the lower border of the inferior constrictor muscle of the pharynx, the muscle progressively becomes extra frequently arranged into internal circular and outer longitudinal layers. In the second quarter of the esophagus, mixed skeletal and clean muscle is found, while in the distal one-half, solely clean muscle is current. Both are physiologic quite than 177 Stomach the stomach varieties an expanded portion of the tubular digestive tract between the esophagus and small gut. In humans, the stomach is divided into the cardia, a brief area the place the esophagus joins the stomach; the fundus, a dome-shaped elevation of the stomach wall above the esophagogastric junction; the corpus, the large central half; and the pylorus, a slim area just above the gastrointestinal junction. The digestive capabilities of the stomach contain mechanical and chemical breakdown of ingested supplies. A scanning electron micrograph of the luminal surface of a human fundic stomach illustrates quite a few gastric pits. The gastric lining epithelium is simple columnar and begins abruptly at the junction with the wet stratified squamous epithelium of the esophagus and ends just as abruptly at its junction with intestinal epithelium. The lining epithelium has a similar structure all through the stomach and consists of secretory columnar cells that collectively type a secretory sheet. The impartial mucin produced by the surface epithelium is secreted repeatedly and varieties a mucous movie that helps defend the mucosa from the acid/pepsin in the gastric lumen and lubricates the surface. The apices of the columnar cells are held in shut apposition by tight junctions, and the lateral cell membranes present quite a few desmosomes. Scattered, stubby microvilli are current on the apical surfaces, and quite a few discrete mucin granules fill the apical cytoplasm. Granular endoplasmic reticulum is current in the basal cytoplasm, and well-developed Golgi complexes occupy the supranuclear area.
Quality 160 mg super p-force
If "danger factors" (Table 35-2) are absent, initial treatment is symptomatic and no diagnostic tests essential. Patients with no danger factors and no improvement over four weeks are subdivided by the presence/absence of leg symptoms and managed accordingly. Possible advantages of early exercise- cardiovascular conditioning, disk and cartilage vitamin, bone and muscle power, elevated endorphin levels. Proof missing to support acupuncture, ultrasound, diathermy, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, therapeutic massage, biofeedback, or electrical stimulation. Self-application of ice or warmth or use of shoe insoles is optionally available given low value and danger; good thing about exercises unsure. A brief course of spinal manipulation or physical remedy may reduce ache and improve perform. Temporary suspension of actions recognized to improve mechanical stress on the backbone (heavy lifting, straining at stool, extended sitting/bending/twisting) may relieve symptoms. Muscle relaxants (cyclobenzaprine, methocarbanol) provide brief-time period benefit (four� 7 days), however drowsiness limits use. Hydrotherapy may be helpful, and a few pts experience brief-time period ache aid with percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. A Acute low back +/- leg symptoms Medical history and examination Risk factors for serious etiology Yes No See text No diagnostic tests Reassurance Patient education Pain aid essential Yes Evaluate and treat Absent Consult backbone surgeon Algorithm C 1 Appropriate intervention Reconsider symptomatic treatment choices Exercise program optionally available Symptoms enhancing Yes No Spine surgery session to focus on: Surgical procedure Risks/advantages Short-time period and lengthy-time period outcomes Availability of second opinion Does the affected person choose surgery In one research, 18% of pts with whiplash harm had persistent harm-associated symptoms 2 years after the car accident. Cervical Disk Disease Herniation of a lower cervical disk is a common explanation for neck, shoulder, arm, or hand ache. Neck ache (worse with movement), stiffness, and limited range of neck movement are frequent. Cervical Spondylosis Osteoarthritis of the cervical backbone may produce neck ache that radiates into the back of the pinnacle, shoulders, or arms; can also be source of headaches within the posterior occipital region. Neck ache may be referred from the guts with coronary artery ischemia (cervical angina syndrome). Thoracic Outlet An anatomic region containing the primary rib, the subclavian artery and vein, the brachial plexus, the clavicle, and the lung apex. True neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome outcomes from compression of the lower trunk of the brachial plexus by an anomalous band of tissue; treatment consists of surgical division of the band. Disputed thoracic outlet syndrome includes numerous sufferers with continual arm and shoulder ache of unclear trigger; surgery is controversial, and treatment usually unsuccessful. Brachial Plexus and Nerves Pain from harm to the brachial plexus or arm peripheral nerves can mimic ache of cervical backbone origin. Neoplastic infiltration can produce this syndrome, as can postradiation fibrosis (ache much less usually current). Acute brachial neuritis consists of acute onset of severe shoulder or scapular ache adopted over days by weak spot of proximal arm and shoulder girdle muscles innervated by the upper brachial plexus; onset usually preceded by an an infection or immunization. Table 35-four Cervical Radiculopathy- Neurologic Features Examination Findings Motor Pain Distribution Cervical Nerve Roots Reflex Sensory C5 Biceps Over lateral deltoid Lateral arm, medial scapula C6 Biceps Lateral forearm, thumb, index finger Posterior arm, dorsal forearm, lateral hand 4th and 5th fingers, medial forearm Medial arm, axilla C7 Triceps Thumb, index fingers Radial hand/forearm Middle fingers Dorsum forearm C8 Finger flexors Little finger Medial hand and forearm T1 Finger flexors Axilla and medial arm Supraspinatusa (initial arm abduction) Infraspinatusa (arm exterior rotation) Deltoida (arm abduction) Biceps (arm flexion) Biceps (arm flexion) Pronator teres (inside forearm rotation) Tricepsa (arm extension) Wrist extensorsa Extensor digitoruma (finger extension) Abductor pollicis brevis (abduction D1) First dorsal interosseous (abduction D2) Abductor digiti minimi (abduction D5) Abductor pollicis brevis (abduction D1) First dorsal interosseous (abduction D2) Abductor digiti minimi (abduction D5) a these muscles obtain the vast majority of innervation from this root. Mechanical ache is commonly worse at evening, associated with shoulder tenderness, and aggravated by abduction, inside rotation, or extension of the arm. Indications for cervical disk and lumbar disk surgery are related; nevertheless, with cervical illness an aggressive method is indicated if spinal wire harm is threatened. Surgery of cervical herniated disks consists of an anterior method with diskectomy adopted by anterior interbody fusion; a simple posterior partial laminectomy with diskectomy is an appropriate alternative. The cumulative danger of subsequent radiculopathy or myelopathy at cervical segments adjoining to the fusion is three% per 12 months and 26% per decade. Nonprogressive cervical radiculopathy (associated with a focal neurologic deficit) as a result of a herniated cervical disk may be treated conservatively with a excessive fee of success. Cervical spondylosis with bony, compressive cervical radiculopathy is generally treated with surgical decompression to interrupt the development of neurologic indicators; spondylotic myelopathy is managed with anterior decompression and fusion or laminectomy. Fever: An elevation of regular physique temperature in conjunction with a rise within the hypothalamic set point. Urticarial eruptions: Hypersensitivity reactions are normally not associated with fever. Cirrhosis, asplenia, immunosuppressive drug use, or latest unique travel may be acceptable settings for empirical treatment. Treatment of the fever with antipyretics may masks essential medical indicators; examples include a relapsing pattern seen in malaria and a reversal of the usual occasions of peak and trough temperatures in typhoid fever and disseminated tuberculosis. However, treatment of fever is suitable to ameliorate symptoms and scale back oxygen demand in pts with underlying cardiovascular or pulmonary illness or to forestall seizures in youngsters with a history of febrile seizures. Dantrolene is also helpful in neuroleptic malignant syndrome and drug-induced hyperthermia and may be useful in serotonin syndrome and thyrotoxicosis. Pain within the joints have to be evaluated in a uniform, thorough, and logical fashion to ensure one of the best likelihood of accurate diagnosis and to plan acceptable followup testing and remedy. Joint ache and swelling may be manifestations of issues affecting primarily the musculoskeletal system or may replicate systemic illness. Historic Features � Age, intercourse, race, and family history � Symptom onset (abrupt or indolent), evolution (continual fixed, intermit- tent, migratory, additive), and length (acute versus continual) � Number and distribution of concerned structures: monarticular (one joint), oligoarticular (2� three joints), polyarticular (three joints); symmetry � Other articular options: morning stiffness, impact of movement, options that improve/worsen Sx � Extraarticular Sx. Physical Examination Complete examination is crucial: explicit attention to skin, mucous membranes, nails (may reveal characteristic pitting in psoriasis), eyes. Nonarticular condition Consider � Trauma fracture � Fibromyalgia � Polymyalgia rheumatica � Bursitis � Tendinitis Acute No Is it articular Laboratory Investigations Additional evaluation normally indicated for monarticular, traumatic, inflammatory, or continual circumstances or for circumstances accompanied by neurologic changes or systemic manifestations. No Consider noninflammatory articular circumstances � Osteoarthritis � Trauma � Other Consider other inflammatory or septic arthritides � Gram stain, culture mandatory Yes Consider inflammatory or septic arthritis Is the effusion hemorrhagic Special Considerations within the Elderly Patient the evaluation of joint and musculoskeletal issues within the elderly pt presents a particular problem given the regularly insidious onset and chronicity of illness in this age group, the confounding impact of other medical circumstances, and the elevated variability of many diagnostic tests within the geriatric population. Faintness refers to prodromal symptoms that precede the lack of consciousness in syncope. Syncope is more probably if the event was provoked by acute ache or anxiety or occurred immediately after arising from a mendacity or sitting place. Seizures occur either very abruptly and not using a transition or are preceded by premonitory symptoms similar to an epigastric rising sensation, notion of weird odors, or racing thoughts. Etiology Transiently decreased cerebral blood flow is normally as a result of considered one of three basic mechanisms: issues of vascular tone or blood volume together with vasovagal syncope and postural hypotension, cardiovascular issues together with cardiac arrhythmias, or uncommonly cerebrovascular illness (Table 38-1). Neurocardiogenic (Vasovagal and Vasodepressor) Syncope the frequent faint, skilled by regular persons and accounting for roughly half of all episodes of syncope. Frequently recurrent and may be provoked by sizzling or crowded setting, alcohol, fatigue, ache, starvation, extended standing, or annoying situations. Postural (Orthostatic) Hypotension Cause of syncope in 30% of elderly; polypharmacy with antihypertensive or antidepressant medication usually a contributor; physical deconditioning may play a task. Approach to the Patient the cause of syncope may be apparent only at the time of the event, leaving few, if any, clues when the pt is seen by the doctor. First contemplate causes that represent serious underlying etiologies; amongst these are large inside hemorrhage or myocardial infarction, which can be painless, and cardiac arrhythmias. In elderly persons, a sudden faint with out apparent trigger should arouse the suspicion of full heart block or a tachyarrhythmia, even when all findings are adverse when the pt is seen. Symptoms of impotence, bowel and bladder difficulties, or disturbed sweating, or an irregular neurologic exam, recommend a primary neurogenic trigger. Drug-induced (especially antihypertensive or vasodilator medication) Peripheral neuropathy (diabetic, alcoholic, dietary, amyloid) Idiopathic postural hypotension Multisystem atrophies Physical deconditioning Sympathectomy Acute dysautonomia (Guillain-Barre syndrome variant) � Decreased blood volume (adrenal insufficiency, acute blood loss, and so forth. Pts with vasovagal syncope should be instructed to avoid situations or stimuli that provoke attacks. Episodes associated with intravascular volume depletion may be prevented by salt and fluid preloading. Permanent cardiac pacing is effective for pts whose episodes of vasovagal syncope are frequent or associated with extended asystole.
Purchase 160 mg super p-force
Patient History: 69 A 46-yr-old female was admitted to the emergency division with complaints of headache, dizziness, lethargy, nausea, vomiting, and weakness. The patient had a gastrectomy process four months earlier to remove adenocarcinoma of the abdomen. The neurological symptoms in this patient are manifested by headache, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. The presence of schistocytes on the peripheral blood with low platelet counts and low haptoglobin are consistent with microangiopathic hemolytic anemia. The excessive blood urea nitrogen and creatinine ranges are characteristic of renal failure. The platelet depend, carried out on admission, was accomplished on a hematology analyzer and was falsely elevated due to the presence of microcytes or fragmented pink cells. The acute onset of symptoms could also be related to mitomycin used for the therapy of gastric carcinoma in this patient. Patient History A 1-yr-old infant was admitted to the hospital with recurrent epistaxis for the past 5 days. The past medical historical past revealed straightforward bruising and a extreme nosebleed at 3 months of age, necessitating transfusion remedy. The laboratory checks that verify an inherited platelet dysfunction are platelet aggregation studies. Patient History: seventy one A 30-yr-old female was referred to the hospital for analysis for a number of spontaneous abortions and present grievance of pain and swelling in her proper leg. D these clinical manifestations and laboratory results are consistent with lupus anticoagulant. As many as forty eight% of ladies with repeated spontaneous abortions have lupus anticoagulant or/and antibody to phospholipid similar to anticardiolipin antibodies. The unremarkable household historical past in this patient rules out an inherited thrombotic dysfunction. Lupus anticoagulant Hemostasis/Correlate clinical and laboratory information/ Coagulopathies/3 15. The technologist calls the nursing unit to examine whether or not the patient is on heparin remedy. After 6 days of heparin remedy, the patient complained of pain and swelling in her left leg. Several days later, the patient developed a large clot in her left leg that necessitated amputation. There are new anticoagulant medication obtainable for the therapy and prevention of thrombosis. Examples of those medication are hirudin, which inhibits thrombin; and danaparoid, which inhibits factor Xa. The blood sample ought to be examined a minimum of four hours after heparin remedy is discontinued. The patient was bleeding throughout surgical procedure and the postoperative test results revealed an Hgb = 5. The patient had no historical past of extreme bleeding throughout childbirth several years earlier nor throughout a tonsillectomy in childhood. B the shortage of a constructive household historical past in this patient indicates the presence of an acquired coagulopathy. D Immunoglobulin is a selected a part of the adaptive immune system and is shaped solely in response to a selected antigenic stimulation. Complement, lysozyme, and commensal organisms all act nonspecifically as part of the adaptive immune system. Immunoglobulin Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Immune system/1 2. B the bone marrow and thymus are thought-about main lymphoid organs as a result of immunocompetent cells either originate or mature in them. T lymphocytes, after originating within the bone marrow, journey to the thymus to mature and differentiate. Lymph nodes and thoracic duct Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Immune system/Organs/1 stimulation Receptor-activated B cells Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Immune system/Cells/1 3. A Mature B cells exhibit surface immunoglobulin which will cross link a overseas antigen, thus forming the activated B cell and leading to capping and internalization of antigen. The activated B cell provides rise to plasma cells that produce and secrete immunoglobulins and memory cells that reside in lymphoid organs. B Immature T cells journey from the bone marrow to the thymus to mature into practical T cells. Once within the thymus, T cells undergo a variety and maturation sequence that begins within the cortex and moves to the medulla of the thymus. Thymic elements similar to thymosin and thymopoietin and cells inside the thymus similar to macrophages and dendritic cells assist in this sequence. After completion of the maturation cycle, T cells are released to secondary lymphoid organs to await antigen recognition and activation. Bone marrow to the cortex; after thymic schooling, released again to peripheral circulation B. Maturation and selection happen within the cortex; migration to the medulla; launch of mature T cells to secondary lymphoid organs C. Storage in either the cortex or medulla; launch of T cells into the peripheral circulation D. Activation and selection happen within the medulla; mature T cells are stored within the cortex till activated by antigen Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Immune system/Cells/1 seventy seven seventy eight Chapter 3 Immunology 5. C3 Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Complement/Components/1 Answers to Questions 5�11 5. This peculiar characteristic was the premise for the traditional E rosette test as soon as used to enumerate T cells in peripheral blood. Do not bind to infected cells Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Lymphocytes/Functions/1 phagocytic cells are interested in a substance similar to a bacterial peptide Phagotaxis Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Immune system/Cells/1 of complement except: A. Anaphylatoxin formation Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Complement/Functions/1 6. C Chemotaxis is the method by which phagocytic cells are attracted toward an space the place they detect a disturbance within the normal functions of body tissues. Products from micro organism and viruses, complement parts, coagulation proteins, and cytokines from other immune cells could all act as chemotactic elements. D C3 is present in both the traditional and various (alternate) pathways of the complement system. In the traditional pathway, C3b types a posh on the cell with C4b2a that enzymatically cleaves C5. IgG solely Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Complement/Activation/1 17. IgG3 and IgA Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Immunoglobulins/Structures/1 13. C Both IgG and IgM are the immunoglobulins that help to provoke the activation of the traditional complement pathway. Freezing serum at 0�C for twenty-four hours Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Complement/Activation/1 14. A Complement activity in serum in vitro is destroyed by heating the serum at fifty six�C for 30 min. In test procedures the place complement could interfere with the test system, it might be necessary to destroy complement activity within the test sample by heat inactivation. To bind with particular membrane receptors of lymphocytes and trigger launch of cytotoxic substances B. To trigger increased vascular permeability, contraction of easy muscle, and launch of histamine from basophils C. To bind with membrane receptors of macrophages to facilitate phagocytosis and the removing of debris and overseas substances D. To regulate and degrade membrane cofactor protein after activation by C3 convertase Immunology/Apply information of fundamental organic traits/Complement/Anaphylatoxins/1 can bind antigen
Best super p-force 160 mg
Random plasma glucose of 250 mg/dL and presence of symptoms Chemistry/Evaluate laboratory information to recognize health and illness states/Carbohydrates/2 for fasting blood glucose. Administration of seventy five g of glucose is given to an grownup patient following a ten�12-hour quick Chemistry/Apply data to recognize sources of error/Glucose tolerance test/3 Answers to Questions four�7 four. C Type 2, or late-onset diabetes, is related to a defect in the receptor web site for insulin. Patients are often obese and over forty years of age, though the incidence is growing in each kids and younger adults. D the American Diabetes Association recommends the following criteria for diagnosing diabetes mellitus: fasting glucose 126 mg/dL, informal (random) glucose 200 mg/dL in the presence of symptoms (polyuria, increased thirst, weight loss), glucose 200 mg/dL at 2 hours after an oral dose of seventy five g of glucose, and hemoglobin A1c 6. A analysis of diabetes mellitus is indicated if any one or combination of these four criteria is met on greater than a single testing event. The fasting plasma glucose test requires at least eight hours with no food or drink besides water. The 2-hour postloading test should be performed in accordance with the oral glucose tolerance pointers currently recommended by the World Health Organization. Enzymatic strategies particular for glucose have an upper restrict of regular no larger than ninety nine mg/dL. This is the cutoff value for impaired fasting plasma glucose (prediabetes) recommended by the American Diabetes Association. Is defined as glucose intolerance originating during being pregnant Chemistry/Evaluate laboratory information to recognize health and illness states/Glucose tolerance test/2 of all types of medical hypoglycemia Decreased serum C peptide Chemistry/Correlate medical and laboratory information/ Carbohydrates/2 Answers to Questions eight�10 eight. The screening test could be carried out nonfasting and consists of an oral 50-g glucose problem adopted by serum or plasma glucose measurement at 1 hour. A result a hundred and forty mg/dL is adopted by a 2-hour or 3-hour oral glucose tolerance test to confirm gestational diabetes. For the three-hour test, a one hundred-g dose of glucose is used and at least two of the following cutoffs must be exceeded: fasting, ninety five mg/dL or greater; 1 hour, one hundred eighty mg/dL or greater; 2 hour one hundred fifty five mg/dL or greater; 3 hour, a hundred and forty mg/dL or greater. C Clinical hypoglycemia could be brought on by insulinoma, drugs, alcoholism, and reactive hypoglycemia. Reactive hypoglycemia is characterized by delayed or extreme insulin output after eating and could be very uncommon. High fasting insulin levels (often > 6 g/L) are seen in insulinoma, and patients with insulinoma almost all the time display fasting hypoglycemia, especially when the quick is prolonged to 48�72 hours. In hypoglycemia, low levels indicate an exogenous insulin source, whereas excessive levels indicate overproduction of insulin. Reflects the extent of glucose regulation in the eight- to 12-week interval prior to sampling D. Will be irregular within four days following an episode of hyperglycemia Chemistry/Correlate laboratory information with physiological processes/Glycated hemoglobin/2 recommended cutoff value for sufficient management of blood glucose in diabetics as measured by glycated hemoglobin The assay must be done by chromatography Chemistry/Apply data to recognize sources of error/Glycated hemoglobin/2 measurement of hemoglobin A1c by excessive performance liquid chromatography Polystyrene divinylbenzene Chemistry/Apply principles of particular procedures/ Glycated hemoglobin/2 Answers to Questions eleven�14 eleven. C G-Hgb outcomes from the nonenzymatic attachment of a sugar such as glucose to the N-terminal valine of the chain. Hemoglobin A1c makes up about 80% of glycated hemoglobin, and is used to decide the adequacy of insulin remedy. Also, glycated protein assay (called fructosamine) provides similar information for the period between 2 and four weeks before sampling. A Since Hgb A1C represents the average blood glucose 2�3 months prior to blood collection, the dietary status of the patient on the day of the test has no effect upon the outcomes. Normal hemoglobin A has a weak constructive cost at an acidic pH and binds weakly to the resin. Glycated hemoglobin has a good weaker constructive cost and is eluted before hemoglobin A. Abnormal hemoglobin molecules S, D, E, and C have a better constructive cost than hemoglobin A and are retained longer on the column. Evaluate the following chromatogram of a 209 entire-blood hemolysate, and establish the cause and finest plan of action. Labile hemoglobin is shaped initially when the aldehyde of glucose reacts with the N-terminal valine of the globin chain. This Shiff base is reversible however is transformed to Hgb A1c by rearrangement to a ketoamine. A fasting glucose of 126 or greater on two consecutive events signifies diabetes. May be used only to monitor persons with only type 1 diabetes type 2 diabetes Chemistry/Correlate medical and laboratory information/ Glycated hemoglobin/2 210 Chapter 5 Clinical Chemistry 18. What is the recommended cutoff for the early detection of continual kidney illness in diabetics using the test for microalbuminuria Estimated glomerular filtration fee Chemistry/Select methodology/Carbohydrates/2 of level-of-care entire-blood glucose strategies Monitoring diabetics for hyperglycemic episodes only Chemistry/Select methodology/Carbohydrates/2 for measuring serum glucose Glucose dehydrogenase Chemistry/Select methodology/Carbohydrates/2 Answers to Questions 18�21 18. The time period microalbuminuria is defined as albumin excretion 30 mg/g creatinine however 300 mg/g creatinine. The use of the albumin to creatinine ratio is most well-liked to measures of albumin excretory fee (g/min) because the latter is topic to error related to timed specimen collection. While the urinary ketone test is a helpful screening test for diabetic and other types of ketosis, the plasma hydroxybutyrate test should be used to establish and monitor ketosis in diabetic persons. Fructosamine is a helpful adjunct to Hgb A1c to establish poor management of blood glucose prior to now 2�four weeks, however has not been recommended for routine use in all diabetic patients. The analytical measurement range of these devices varies significantly, and entire blood glucose is roughly 10% decrease than serum or plasma glucose. In addition, analytical variance is bigger and accuracy lower than for laboratory instruments. Whole blood glucose meters should be used by diabetics and caregivers to monitor glucose management and may detect each hyper- and hypoglycemic states that result from too little or too much insulin substitute. Therefore, postprandial monitoring with such a tool is recommended for all persons who receive insulin remedy. Polarographic strategies for glucose analysis are 211 based upon which precept of measurement The change in electrical potential as glucose is oxidized Chemistry/Apply principles of basic laboratory procedures/Carbohydrates/2 electrochemical methodology can be used to measure glucose in plasma Amperometry Chemistry/Apply principles of basic laboratory procedures/Carbohydrates/2 -D-glucose. Glucose oxidase Chemistry/Apply data of elementary biological characteristics/Biochemical/1 methodology for glucose. Glucose-6-phosphatase Chemistry/Apply data of basic laboratory procedures/Carbohydrates/1 Answers to Questions 22�26 22. B Polarographic glucose electrodes measure the consumption of O2 as glucose is oxidized. Glucose oxidase in the reagent catalyzes the oxidation of glucose by O2 under first-order circumstances, forming hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). As the dissolved O2 decreases, less is reduced on the cathode, leading to a lower in current proportional to glucose focus. This is prevented by including molybdate and iodide that react with H2O2, forming iodine and water, and by including catalase and ethanol that react with H2O2, forming acetaldehyde and water. The electrons produced are used to scale back oxygen on the cathode, finishing the current path. However, the peroxidase coupling response used in the glucose oxidase methodology is topic to constructive and adverse interference. Polarography Chemistry/Apply data to recognize sources of error/Carbohydrates/2 26.
Syndromes
- Mineral oil
- Tube through the mouth into the stomach to wash out the stomach (gastric lavage)
- Location of tumor
- Straining to urinate
- Rubbing alcohol
- Infections that spread to the fallopian tubes can cause scarring. This can cause problems getting pregnant at a later time.
- Chronic heavy menstrual bleeding
- Exposure to certain gases or fumes in the workplace
- Diabetes
Cheap 160 mg super p-force
Radiation remedy may be given to one particular position infested with leukemia cells or to the whole physique. Bone marrow gets affected in leukemia and the affected bone marrow may be replaced by wholesome one by stem cell transplant or bone marrow transplant. Chemotherapy utilizing a single drug or a combination of medicine is the appropriate treatment modality for leukemia. Other medication like etoposide, fludarabine may be included in remedy to enhance possibilities of remission. The aim of this induction remedy is to reduce the variety of malignant blast cells, which is followed by consolidation remedy and maintenance remedy. Consolidation remedy 5 Leukemia causes, symptoms & treatment comprises of chemotherapy or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. There are other therapeutic options that are yet to acquire much recognition, these are leukapheresis, surgical procedure, or radiation remedy. Prior to introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, use of radiation remedy, busulphan, hydroxyurea, cytarabine had been practised [38]. Phytochemicals as adjuvants Phytochemicals are typically an integral part of our diet and are supposed to be free from toxicity but a couple of could also be potential carcinogens or tumor promoters. This is extremely relevant notably in pharmaceutical industry, in order to develop and improvise therapeutic regimens. The details of concern are whether or not administration of these biomolecules hinders the efficacy of medicine or induce any toxic results because of the reactive metabolite. Therefore, security of these molecules along with conventionally used anticancer medication must be addressed. The treatment modalities followed in most cancers management are typically not full proof. Besides curing the offending development, these therapeutic methods also show extreme toxicity to the normal cells, rendering undesirable impact on the affected person. There are inter-individual variations and the extent of side impact depends on the kind and dose of medicine or radiation and the general health of the affected person. Fast dividing wholesome cells are the main targets of anti neoplastic agents like hematopoietic cells, epithelial cells of the gut and cells of the hair follicles. Chemotherapy usually results in decrease resistance to infection because of suppression of the immune system. Patients regularly suffer from fatigue, hair loss, nausea, and diarrhoea, loss of appetite, sores in mouth, decreased blood cell counts, susceptibility to bleeding and bruising [forty]. People present process stem cell transplantation suffer from graft versus host disorder [42]. Existing therapeutic protocols may lead to fertility problems in men and women [45]. Thus, present day most cancers therapeutic procedures usually lead to compromised life quality of the affected person. Keeping these components in mind, higher, safer and various means must be appeared into. Combination of current remedy with compounds having reduced toxicity may lead to increased therapeutic effectivity and higher prognostic outcome in most cancers. Dietary phytochemicals stud with anti most cancers properties could also be an excellent possibility in this regard. Various research have been carried out to establish the potential of phytochemicals as an adjuvant to leukemia remedy. Flavonoids: Fisetin, a flavonoid abundantly current in strawberries, grapes, apples, onions and so on is wealthy in anti most cancers properties. Thus, this phytochemical has the potential to be used as a therapeutic agent in leukemia, either alone or at the side of other medication, though further trials are warranted [46]. Phytochemicals not solely will increase the efficacy of remedy, nevertheless it has been reported that a combination of various phytochemicals could also be a better possibility in imparting cytotoxicity to most cancers cells. Binding of quercetin or fisetin to particular mobile targets contributes to increased anti-apoptotic 7 Leukemia causes, symptoms & treatment signalling pathways induced by luteolin [forty seven]. Genestein, a soy isoflavone at the side of -irradiation induces death in leukemia cells by sensitizing the cells to radiation [forty eight]. Galangin, a flavonol present in Alpina species exerts anti leukemic activity on each imatinib delicate and imatinib resistant leukemia cells, thus suggesting its function as an adjuvant in leukemia remedy [forty nine]. Quercetin, a flavonol present in vegetables and fruits enhances the activity of busulfan in leukemia. The indispensable part of every Indian delicacies is turmeric, whose lively ingredient curcumin is answerable for its beneficial function in illness management. Curcumin prevents proliferation of main leukemic cells when used at the side of cytarabine [53]. Celastrol is one other phytochemical derived from the roots of Tripterygium wilfordii (Thunder god vine). Resveratrol, a polyphenol present in abundance in grapes could also be used as dietary supplement while treating leukemia patients with proteasome inhibitors. Treatment of myeloid leukemia cells with a combination of arsenic trioxide and resveratrol potentiates the anti leukemic potential of arsenic trioxide [fifty nine]. Terpenoids: Glycyrrhetinic acid, the lively compound in licorice root may serve as adjuvant to chemotherapy in leukemia [60]. Extracts from two vegetation used in traditional drugs specifically Zingiber officinale Roscoe and Nerium oleander L. Use of these compounds in 8 Leukemia causes, symptoms & treatment conjunction with current medication may enhance responses to remedy [sixty one]. Isothiocyanates: Cruciferous vegetables owe their flavour to isothiocyanates, which possess potent most cancers preventing properties. B cell prolymphocytic leukemia is a uncommon form of leukemia with very low survival rates. It has usually been noticed that current medication fail to get rid of most cancers stem cells leading to relapse of the illness. This phytochemical in combination with anthracycline doxorubicin induces apoptosis in leukemia cells and it has been reported that indole three carbinol enhances the cytotoxic results of doxorubicin in leukemia cells [sixty five]. Others: Neutraceuticals like zinc are sometimes given to most cancers patients to relieve them of the unwanted side effects of remedy. Supplementation of Zinc in patients suffering from acute leukemia has been reported to relieve the patients of opposed results of chemotherapy [sixty eight]. Saponins obtained from Panax ginseng potentiate homoharringtonin, cytarabine, adriamycin and so on to leukemic stem cells [70]. Coenzyme Q10 helps to reduce the opposed results of daunorubicin in patients suffering from leukemia [seventy one]. Rocaglamide and silvestrol, two flavglines differentially get rid of leukemia progenitor cells and impart sensitivity to standard therapeutic regimens [73]. Crocetin, a carotenoid and the lively ingredient of Indian spice saffron may serve as an adjuvant to standard medication used in leukemia cells, though intense research is warranted [seventy six]. Conclusion 9 Leukemia causes, symptoms & treatment Phytochemicals are tumor preventing armaments, that are potential candidates for chemoprevention and remedy. Leukemia is a hematopoietic malady involving extreme production of immature blood cells, where several genes are concerned. Alterations on the genetic level perturb the sign transduction pathways concerned in carcinogenesis. The standard treatment methods goal these pathways, thereby halting the three stages of most cancers specifically initiation, promotion and progression. Existing therapeutic regimens pose undesirable opposed results on an individual, as they target not solely the most cancers cells, but in addition the normal cells. Therefore, various means must be explored which might help to combat the unwanted side effects of treatment. Phytochemicals are recognized to be wealthy in anti-most cancers properties and so they have the distinctive property of preferentially appearing on most cancers cells, sparing the normal ones. These plant-derived biomolecules help in combating leukemia by concentrating on various signalling pathways concerned within the process.
Quality super p-force 160 mg
The 25 cm is the C-formed portion of the small intestine into which the abdomen empties. The nice size of the small intestine is important for ; in addition, its surface is shaped into, and, in order that its complete surface space is big - roughly the dimensions of a tennis courtroom! The, and approximately one half of the are found on the best facet of the body. Approximately one half of the is found on the left facet of the body; from there, feces attain the, their last storage place previous to their exit via the. The colon is divided into four areas, the colon on the best facet of the body, the colon which crosses from proper to left, and the colon and colon on the left facet of the body. The chyme, or bolus, enters the massive intestine on the prime of the, and is allowed to fill it and remain there for awhile to decrease the water content material. Entry of chyme into the massive intestine is managed by the, which is found on the juncture of the ileum and large intestine. They cause the formation of puckered pouches called alongside the whole size of the massive intestine. Small, fats-crammed pouches are connected to the massive intestine here and there alongside its size: these are called. The bulk of the liver is on the facet of the body, to the esophagus and vena cava. The area on the surface of the liver at which blood vessels, ducts, and nerves enter the organ is called the. Accumulation of unused bile within the gallbladder is harmful, because as water and electrolytes continue to be eliminated,. The gallbladder can retailer approximately ml (plus or minus 15 ml or so) of concentrated bile. Bile leaves the gallbladder through the duct, which merges with the duct to type the duct. The gallbladder has three layers: the lumen is lined with, which is surrounded by the, and that in flip by. The pancreas is a protracted, roughly triangular organ nestled within the curve of the, lying posterior to the. The head of the pancreas lies in opposition to the, while the tail extends toward (and nearly reaches) the. The secretions of the acini are collected in a community of ducts which feeds into the, which empties into the through two branches, one small and one massive. The larger department of the pancreatic duct joins the to type the, which empties into the duodenum through the. Mastication; mechanical digestion propulsion; deglutition; peristalsis Peristalsis; bolus 5. Smooth muscles within the gastrointestinal tract are responsible for the of meals from mouth to anus through processes called (swallowing) and. Mechanical digestion is continued all through the gastrointestinal tract through a course of called, by which the bolus is rhythmically divided into ever-smaller portions by bidirectional, peristalsis-like contractions of clean muscle. During, complicated molecules are separated and hydrolyzed by enzymes, emulsifiers and corrosive chemical substances. Neural regulation of the digestive system is complicated, and includes over 30, each mediating a slightly completely different response from the cells which receive them as alerts. This allows each area of the digestive system to interact with, even those some distance away. The inner layer of the muscularis consists of clean muscle fibers which the lumen, while within the outer layer the fibers are arranged. Neurons of the enteric plexus within the submucosa are called the plexus; those within the muscularis lie and are called the plexus. The mouth is saved moist between meals primarily by the, that are scattered all through the oral mucosa. The department of the autonomic nervous system inhibits production of serous (watery) saliva, but not of mucin-wealthy saliva, in order that stress leaves the mouth feeling dry and sticky. Saliva incorporates amylase to begin, chemical substances together with lysozyme and immunoglobin starch digestion; inhibit A to , and mucin to . The two main processes which moisten and soften meals within the oral cavity are and. The voluntary portion of deglutition is the part, which occurs within the mouth. During the pharyngeal part of deglutition, the prevents meals from returning to the mouth. During the pharyngeal part of deglutition, the and stop meals from entering the nasopharynx. During the pharyngeal part of deglutition, the prevents meals from entering the larynx. Three rings of muscles within the pharynx called the contract one after the opposite to propel meals into the esophagus. During the third part of deglutition, the part, meals is propelled toward the abdomen by <what kind of muscle movement Since the task of the esophagus is simply to transport meals, its surface is optimized for resisting friction as meals passes by; it consists of. Mixing semi-solid meals with liquid to type completely liquid is likely one of the main capabilities of the. Unlike the esophagus, whose surface is specialised to resist friction, the surface of the abdomen is specialised for, and consists of. Gastric secretions and meals are blended within the abdomen by muscular contractions called. These contractions happen primarily within the, the widest a part of the pyloric area. The abdomen adjusts to the ingestion of meals or drink by and to accommodate to the brand new demand for quantity. While most digestion occurs within the, digestion of begins within the abdomen. Hydrochloric acid proteins and nucleic acids within the abdomen and converts to denatures; pepsinogen; pepsin its active type,. To do away with bicarbonate ions, parietal cells secrete it into the blood, exchanging it for the available. The mucus that coats the abdomen is thick, heavy, and (just as importantly). This is neutral to alkaline; bicarbonate because the mucus producing cells combine their product with. Thus, production of this glycoprotein by the abdomen is absolutely important to survival. Gastrin is launched by enteroendocrine cells within the abdomen mucosa in response to or to alerts from the. Gastrin has a number of results, one of which is to promote within the cells of the abdomen: thus, in the long term, a big urge for food leads to a big. Histamine binds to H2 receptors on cells, and is essentially the most potent acid-producing sign molecule. The part of gastric regulation occurs earlier than meals (or drink) enters the abdomen, and is dependent upon taste, scent, and anticipation. During the part of gastric regulation, alerts from the medulla oblongata are conveyed by the nerve to the enteric ganglia. During the gastric part of gastric regulation, the main alerts are and the presence of within the abdomen. Two chemical substances commonly consumed by students (and academics, to be fair) also trigger the gastric part or gastric reflex: and. In the part, sensations within the abdomen activate cells: these launch gastrin and other hormones into the blood, which finally trigger an increase in. Mixing waves happen within the abdomen three times per minute: less incessantly, stronger waves overwhelm the partially closed sphincter and send a small quantity of into the duodenum. In the gastrointestinal or intestinal part of gastric regulation, the inhibits the activities of the abdomen so as to give itself time to address, or. The duodenum alerts the medulla oblongata when circumstances are such that an extra influx from the abdomen would overwhelm it, and the medulla then alerts the abdomen to decrease gastric exercise: that is the. While the abdomen is designed to shield itself and avoid self-digestion, the duodenum is specialised for and, and its epithelia contains many. The cells of the duodenum are covered with, which improve their surface space and allow them to take in extra vitamins than would otherwise be attainable.
160 mg super p-force
The gastric mucosa incorporates about 3 million minute tubular infoldings of the floor epithelium that form the gastric pits or foveolae, which are lined by the same easy columnar epithelium that covers the floor. New cells are derived from a small inhabitants of relatively undifferentiated cells located in the bottoms of the gastric pits. Cells from this region gradually migrate upward along the partitions of the gastric pit to exchange the cells of the floor epithelium. Three types of glands occur in the gastric mucosa: cardiac, gastric (oxyntic), and pyloric. Here, the tubular glands branch freely and seem to be aggregated into lobule-like complexes by the encompassing connective tissue of the lamina propria. Near the junction with the fundus, the cardiac glands show much less branching, the distinct grouping disappears, and the thickness of the glandular space decreases. For essentially the most half, cardiac glands are easy branched tubular glands that open into the overlying gastric pits. The depth of the gastric pit and the length of the cardiac gland are roughly equal. The secretory models consist mainly of mucous cells, but occasional parietal cells are present and seem to be equivalent to these of gastric glands. The glands run perpendicular to the floor of the mucosa, and one or a number of glands may open into the underside of every gastric pit. Each gland incorporates mucous neck cells, parietal cells, chief (zymogen) cells, and endocrine cells. Mucous neck cells occur primarily in the upper regions of the gastric glands, the place the glands open into the gastric pits. The cells usually seem to be sandwiched between different cell types, and their irregular shape is characteristic. Some have broad apices and slender bases; others show slender apices and extensive bases. The nucleus is confined to the bottom of the cell, surrounded by basophilic cytoplasm. Unlike the mucous cells that line the gastric floor and gastric pits, mucous neck cells produce an acidic mucin. Although most numerous in the central space of the gastric glands, parietal cells are also scattered amongst mucous neck cells in the upper elements of the gland. They are massive, spherical cells whose bases usually seem to bulge from the outer margin of the glands into the lamina propria. In routine sections, parietal cells are distinguished by their acidophilic cytoplasm. Each cell incorporates a big, centrally positioned nucleus and numerous mitochondria and is characterized by intracellular canaliculi. Mitochondria make up almost forty% of the parietal cell quantity and account for the eosinophilia in hematoxylin and eosin stained preparations. The canaliculi are invaginations of the plasmalemma that form channels close to the nucleus and open on the apex of the cell into the lumen of the gland. Numerous microvilli project into the lumina of the intracellular canaliculi, their quantity and length varying according to the secretory activity of the cell. Immediately adjacent to each canaliculus, a sequence of clean cytoplasmic membranes forms small tubules and vesicles that make up a tubulovesicular system. Secretion of hydrochloric acid occurs along the cell membrane that strains the canaliculi. During stimulation of parietal cells, the tubulovesicular membranes diminish, canalicular microvilli turn out to be more abundant, and canaliculi elongate; during acid inhibition, the reverse occurs. Hydrogen ions are actively pumped into the lumen of the canaliculus, and bicarbonate ions cross back into the bloodstream of the gastric mucosa to cause a rise in pH known as the alkaline tide. Ion channels promote the motion of potassium and chloride ions into the canalicular lumen. The internet results of this activity is the formation of hydrochloric acid in the canalicular lumen. The improve in canalicular membrane floor space during parietal cell stimulation makes these events possible. A transmission electron micrograph illustrating the ultrastructural features of a non-stimulated human parietal cell. A transmission electron micrograph illustrating the ultrastructural features of a stimulated human parietal cell sampled 10 minutes following gastrin administration. In addition to hydrochloric acid, parietal cells of the human stomach secrete a glycoprotein, gastric intrinsic factor, which complexes with dietary vitamin B12; the advanced is absorbed in the distal small intestine. A deficiency of intrinsic factor leads to decreased absorption of vitamin Bl2, an important vitamin for the maturation and manufacturing of purple blood cells. Lack of this vitamin leads to pernicious anemia and is a condition usually related to atrophic gastritis. Parietal cell stimulation is initiated and modulated by the vagus nerve during the cephalic phase of digestion in response to taste, scent, sight, chewing or even the considered food. These physiologic agonists (gastrin, histamine, acetylcholine) attach to particular person transmembrane receptors in the parietal cell plasmalemma. Somatostatin from adjacent D cells in the pyloric mucosa acts on neighboring G cells to inhibit gastrin launch and thereby inhibit parietal cell activity. Chief (zymogen) cells are present mainly in the basal half of the gastric glands and in routine sections are distinguished by their basophilia. The cells comprise abundant granular endoplasmic reticulum in the basal cytoplasm, nicely-developed Golgi complexes in the supranuclear cytoplasm, and apical zymogen granules, features that characterize cells involved in protein (enzyme) secretion. Chief cells secrete pepsinogen, a precursor of the enzyme pepsin that reaches its optimal activity at pH 2. Pepsin is important in the gastric digestion of protein, hydrolyzing proteins into peptides. Also scattered within the bases of the gastric glands are endocrine cells, peptide/amineproducing cells that comprise particular granules enclosed by clean membranes. The polarization of those cells means that they secrete into the bloodstream or intercellular area somewhat than into the lumina of gastric glands. Gastric A cells produce glucagon which stimulates hepatic glycogen degradation and will increase blood glucose ranges. Kinetics of the Gastric (Oxyntic) Glands Pluripotent stem cells located in the region the place a gastric gland joins the underside of a gastric pit (the isthmus) divide to preserve themselves in addition to give rise to a number of dedicated cell types: pre-pit, pre-mucous neck, pre-parietal, and pre-endocrine. Mucous neck cells, nonetheless, migrate inward towards the bottom of the gastric glands and in about 2 weeks turn out to be pre-chief (zymogenic) cells. As fully differentiated chief cells form, they migrate to occupy the underside of the gastric glands and remain active for up to 6 months. In contrast, differentiating parietal cells migrate in both directions with about equal numbers migrating towards both the gastric lumen or the bottoms of the gastric glands. They have a turnover rate of about 60 days and, if they turn out to be necrotic, are lost by extrusion into the lumen of the gland. Lamina Propria the lamina propria of the stomach is obscured by the shut approximation of the glands in the gastric mucosa. It consists of a delicate network of collagenous and reticular fibers that surrounds and extends between the glands and gastric pits. Numerous lymphocytes, some plasma cells, eosinophils, and mast cells are found within the lamina propria. Muscularis Mucosae the muscularis mucosae consists of an internal round, an outer longitudinal and, in some locations, an extra outer round layer of clean muscle. Slips of clean muscle extending into the lamina propria form a free network around particular person glands and lengthen to the gastric lining epithelium. The contraction of those clean muscle cells acts to compress the contained gastric glands. They are easy or branched tubular glands composed of mucous cells similar in look to mucous neck cells of the fundic region. The pyloric glands empty into gastric pits that are about the same length as the glands. These unicellular endocrine glands produce gastrin, the peptide hormone that stimulates acid secretion by the parietal cells in the remainder of the stomach. Thus, along with the exocrine operate of mucus manufacturing, pyloric glands have important endocrine features as nicely. The serotonin produced will increase gut motility whereas somatostatin acts to inhibit the secretion of adjacent endocrine cells.
Buy 160 mg super p-force
Chemistry/Apply ideas of special procedures/ Biochemical theory and ideas/2 26. Assay use is restricted to serum Chemistry/Apply ideas of special procedures/ Biochemical theory and ideas/2 27. In such circumstances, the enzyme exercise of the low calibrator (drug concentration equal to U. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration minimal for a positive check) is used because the cutoff. The antibody is covalently linked to the enzyme donor Chemistry/Apply ideas of special procedures/ Biochemical theory and ideas/2 27. The concentration of drug within the pattern is instantly proportional to the quantity of chlorophenol pink shaped. Which statement is true regarding particle-enhanced turbidimetric inhibition immunoassay methods for therapeutic drugs Selective response monitoring Chemistry/Apply ideas of special procedures/ Chromatography/1 Answers to Questions 28�30 28. C Particle-enhanced turbidimetric inhibition immunoassays are homogenous immunoassays regularly used to measure proteins and therapeutic drugs in serum or plasma. Polystyrene-modified latex particles conjugated to the drug (particle-sure drug) compete with drug within the pattern for a limited number of antibodies. If drug concentration is low, extra of the antibody binds to the particle-sure drug, rising the turbidity of the response. These are drawn into the mass analyzer, often a vacuum chamber containing two pairs of charged rods (a positive pair and a unfavorable pair) known as a quadrupole analyzer. By altering the potential and radio frequency utilized to the rods, the travel of ions will range depending upon their mass to charge (m/z) ratio. A whole ion chromatograph displays the retention time of all ions detected and their abundance. Creatinine 5 mg/dL Chemistry/Evaluate laboratory information to detect sources of error/Toxicology/three 30. The majority of those conditions could be detected by figuring out temperature (ninety�F�one hundred�F) pH (4. All of the values listed are throughout the limits of a suitable pattern with the exception of creatinine. Dry reagent strips are available that check for pH, particular gravity, creatinine, nitrite, peroxide, pyridinium, and glutaraldehyde. D Some drugs have an extended half-life, and could be 301 Chemistry/Apply information of basic biological characteristics/Drugs of abuse/1 32. Treatment with alkaline dithionite is used to convert carboxyhemoglobin to oxyhemoglobin B. Bichromatic evaluation is required in order to remove interference by oxyhemoglobin D. Carboxyhemoglobin could be measured by potentiometry Chemistry/Apply ideas of special procedures/ Carboxyhemoglobin/2 alcohol measurement is right The reference method is predicated upon enzymatic oxidation of ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase D. Gas chromatography methods require extraction of ethanol from serum Chemistry/Apply ideas of special procedures/ Ethanol/2 detected for longer periods after use, however the detection window additionally is dependent upon other variables such as dosage, frequency of use, and method sensitivity. In individuals who use marijuana a number of instances per week, cannabinoids could be detected a number of weeks after last use. C the absorbance spectras of oxy- and carboxyhemoglobin pigments overlap, and bichromatic or multichromatic evaluation is required in order to precisely measure carboxyhemoglobin. In bichromatic evaluation, oxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin are converted to deoxyhemoglobin by the addition of alkaline sodium dithionite. The ratio of absorbance at 541:555 nm is instantly proportional to carboxyhemoglobin concentration. Percent carboxyhemoglobin is often determined from simultaneous absorbance measurements at 548, 568, and 578 nm, or other wavelength combos, a process known as oximetry. For this cause, and to keep away from interference with the interpretation of chromatograms for volatiles, blood samples are collected after disinfecting the pores and skin site with benzalkonium chloride or other nonalcohol antiseptic. The low boiling level of ethanol permits direct evaluation on blood or plasma diluted with water containing 1-propanol or other appropriate inside normal. Urine Chemistry/Apply ideas of special procedures/ Lead/1 measure plasma or serum salicylate Greatest sensitivity is obtained through the use of entire blood, which may detect exposure over time. When screening for lead poisoning in kids, the method of choice is graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry or inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy as a result of they provide one of the best analytical sensitivity. Which of the next checks is least important to the operation of an emergency department at a basic hospital Salicylate toxicity causes an preliminary respiratory alkalosis as a result of the drug stimulates the respiratory heart. In the absence of particular checks for abuse substances or a comprehensive drug display screen, the serum osmolality measured by freezing level depression is a sensitive surrogate check for drug and alcohol overdose. Which of the next trace components is 303 thought of a vital micronutrient Selenium Chemistry/Apply information of basic biological characteristics/Trace metals/1 than lead, what sort of tube ought to be used Red high Chemistry/Identify normal operating procedures/ Specimen collection and handling/1 exposure to lead in kids but not adults All others could be thought of important, including arsenic that has been shown necessary for regular methionine metabolism. Most trace components are of medical importance as a result of extreme levels result in toxicity. However, a deficiency of trace components such as selenium, zinc, and copper are commonly brought on by whole parenteral vitamin and are medically important. A In order to keep away from trace contamination by metals present within the stopper lubricants, a tube with a navy blue high is used for measuring trace metals. Blood and urine copper concentration low, ceruloplasmin low Chemistry/Correlate laboratory results/Metals/2 39. B Because lead exposure in kids leads to learning impairment, the cutoff for exposure really helpful by the Centers for Disease Control is 5 g/dL in venous entire blood. Values of 5 g/dL or extra ought to be monitored closely with comply with-up testing, and in the event that they improve, steps ought to be taken to remove lead contamination from the home and setting. Because lead readily enters the pink blood cells, and passes from plasma to urine shortly, entire blood is a extra sensitive measure of exposure than plasma. Because lead from the fingers could contaminate the specimen, a venous pattern is preferred over a capillary pattern collected by finger stick. Copper deposits in tissues, particularly the liver and mind, causing necrosis, and excess is excreted within the urine. A Tumor markers could also be enzymes, hormones, receptors, oncofetal (glycoprotein) antigens, or oncogenes. Nuclear matrix protein Chemistry/Apply information of basic biological characteristics/Tumor markers/1 the evaluation of a tumor marker most helpful A Most tumor markers are expressed at very low levels so that the concentration in early malignancy overlaps that seen in regular people. Most tumor markers are elevated in nonmalignant disease, and this nonspecificity reduces their usefulness for analysis of malignancy. In addition to the three markers mentioned, the hormones insulin (insulinoma), gastrin (gastrinoma), and prolactin (prolactinoma), and the catecholamines (pheochromocytoma) have some diagnostic utility. Some tumor markers are helpful predictors of disease development and response to therapy. Successful therapy reduces the concentration of the marker significantly or leads to an undetectable degree. Which of the next enzymes is elevated in individuals with prostate and small-cell lung cancer Lactate dehydrogenase Chemistry/Correlate medical and laboratory information/ Tumor markers/2 three. It could also be present in individuals with central nervous system damage and another problems but its presence is often associated with varied malignancies, particularly prostate cancer and small-cell carcinoma of the lung. Which of the next is one of the best analyte to 305 monitor for recurrence of ovarian cancer Cathepsin-D Chemistry/Correlate medical and laboratory information/ Tumor markers/2 Answers to Questions 4�6 4.
References:
- https://www.med.upenn.edu/student/assets/user-content/aoa-guide-to-the-clinics-2019-dec-9-2019.pdf
- https://www.pcf.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/2018PCF_PatientGuide.pdf
- https://www.tpadministrator.com/internet/Cssc.nsf/files/partguide-revisions-1a_030205.pdf/$FIle/partguide-revisions-1a_030205.pdf
- https://www.shea-online.org/images/ThePolicyResourceCenter/AntimicrobialResistance/2017.pdf
- http://psychrights.org/Research/Digest/CriticalThinkRxCites/cohen-randomized.pdf
.png)