Buy 160mg super p-force oral jelly
This instruction concerning various postoperative circumstances is critical to cut back subjectivity and knowledge assortment burden. All otherwise eligible procedures are included within the denominator reporting, no matter closure sort. If a process has multiple incision sites and any of the incisions are closed primarily then the process is entered as a major closure. A patient undergoes a substitute of both the mitral and tricuspid valves during the same journey to the operating room. This validation is critical to make sure the code is aligned with the index joint revision. Open (specifically, non-laparoscopic) hernia repairs are reported as one process for every hernia repaired through a separate incision, (specifically, if two incisions are made to restore two defects, then two procedures will be reported). It is anticipated that separate incision times will be recorded for these procedures. If not, take the whole time for both procedures and split it evenly between the 2. More than one operative process by way of same incision/surgical house inside 24 hours: When a patient has more than one operative process through the same incision or into the same surgical house and the second process start time is inside 24 hours of the primary process end time, report just one Denominator for Procedure type for the original process, combining the durations for both procedures based mostly on the process start times and end times for both procedures. Quick reference guides on these stories may be found at the bottom of this web page. More info concerning the fundamental risk index calculation may be found within the paper. These tools are guides on tips on how to start and join a Group; tips on how to create a template to request knowledge from facilities; tips on how to determine the level of access granted by the ability following the earlier steps, and tips on how to analyze the facilities knowledge. The Society for Hospital Epidemiology of America; the Association for Practitioners in Infection Control; the Centers for Disease Control; the Surgical Infection Society. This pocket guideline is out there on the World Wide Web sites of the American College of Cardiology (cardiosource. Introduction this pocket guide offers fast prompts for acceptable patient administration, which is outlined in a lot greater detail within the full-textual content tips. The scope of those pocket tips (updated for 2011) is restricted to problems of the lower extremity arteries, renal and mesenteric arteries, and problems of the belly aorta. All recommendations offered on this document follow the format of earlier American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association tips (Table 1). Recommendations that remain unchanged used the Class of Recommendation/Level of Evidence table from the 2005 guideline. Although randomized trials are unavailable, there could also be a very clear medical consensus that a selected check or remedy is beneficial or efficient. Individuals at Risk for Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease n Age lower than 50 years, with diabetes and one different atherosclerosis risk issue (smoking, dyslipidemia, hypertension, or hyperhomocysteinemia) Age 50 to sixty nine and a historical past of smoking and diabetes Age 70 or older Leg signs with exertion (suggestive of claudication) or ishemic relaxation ache Abnormal lower extremity pulse examination Known atherosclerotic coronary, carotid, or renal artery disease n n n n n Key Components of the Vascular Review of Systems � Any exertional limitation of the lower extremity muscle tissue or any historical past of strolling impairment (described as fatigue, aching, numbness, or ache, occurring within the buttock, thigh, calf, or foot). The 5 "Ps" are outlined by the medical signs and signs that suggest potential limb jeopardy: ache, pulselessness, pallor, paresthesias, and paralysis (with polar being a sixth "P"). Other causes of leg ache could embrace: lumbar disk disease, sciatica, radiculapthy; muscle strain; neuropathy; compartment syndrome. Primary treatment of diabetes mellitus ought to be continued based on established tips. Claudication Claudication is outlined as fatigue, discomfort, or ache that happens in specific limb muscle teams during effort because of exercise-induced ischemia (Figures 3 and four). Before present process an analysis for revascularization, sufferers with intermittent claudication should have important functional impairment with an affordable likelihood of symptomatic improvement and absence of different disease that would comparably restrict exercise even Lower Extremity if the claudication was improved. A therapeutic trial of cilostazol ought to be thought-about in all sufferers with way of life limiting claudication (within the absence of heart failure). Pentoxifylline (four hundred mg 3 times per day) could also be thought-about as second line alternative remedy to cilostazol to improve strolling distance in sufferers with intermittent claudication. The medical effectiveness of pentoxifylline as remedy for claudication is marginal and not nicely established. For prognosis and treatment of critical and acute limb ischemia, see Figures 5, 6 and 7. Outflow disease represents femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal stenoses, (the presence of occlusive lesions within the lower extremity arterial tree beneath the inguinal ligament from the common fermoral artery to the pedal vessels). Outflow disease represents femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal stenoses (the presence of occlusive lesions within the lower extremity arterial tree beneath the inguinal ligament from the common femoral artery to the pedal vessels). These events should prompt physician re-analysis n *These common tips ought to be individualized and based mostly on the outcomes of treadmill stress testing and the medical standing of the patient. A full discussion of the exercise precautions for individuals with concomitant ailments may be found elsewhere for diabetes. Endovascular intervention is beneficial as the preferred revascularization technique for TransAtlantic Inter-Society Consensus sort A (see Tables 5 and 6 and Figure 8) iliac and femoropopliteal arterial lesions. Translesional strain gradients (with and without vasodilation) ought to be obtained to evaluate 20 the significance of angiographic iliac arterial stenoses of 50% to seventy five% diameter prior to intervention. Stents (and different adjunctive techniques such as lasers, chopping balloons, atherectomy devices, and thermal devices) may be helpful within the femoral, popliteal, and tibial arteries as salvage remedy for a suboptimal or failed result from balloon dilation. Iliac stenoses in a patient with an belly aortic aneurysm or different lesion requiring aortic or iliac surgical procedure Lower Extremity TasC sort b iliac lesions: TasC sort C iliac lesions: TasC sort D iliac lesions: Endovascular process is the treatment of selection for sort A lesions, and surgical procedure is the process of selection for sort D lesions. Morphological Stratification of Femoropopliteal Lesions TasC sort a femoropopliteal lesions: 1. Single stenosis <3 cm of the superficial femoral artery or popliteal artery TasC sort b femoropopliteal lesions: 2. Single stenosis 3 to 10 cm in length, not involving the distal popliteal artery 3. Single or multiple lesions within the absence of continuous tibial runoff to improve inflow for distal surgical bypass TasC sort C femoropopliteal lesions: 6. Multiple stenoses or occlusions, every 3 to 5 cm in length, with or without heavy calcification TasC sort D femoropopliteal lesions: 8. Complete common femoral artery or superficial femoral artery occlusions or full popliteal and proximal trifurcation occlusions Endovascular process is the treatment of selection for sort A lesions, and surgical procedure is the process of selection for sort D lesions. More evidence is required to make agency recommendations about one of the best treatment for sort B and C lesions. Because the presence of more aggressive atherosclerotic occlusive disease is related to much less sturdy ends in sufferers younger than 50 years of age, the effectiveness of surgical intervention on this inhabitants for intermittent claudication is unclear. This consists of sufferers with persistent ischemia relaxation ache, ulcers, or gangrene attributable to objectivitely proven arterial occlusive disease. For sufferers with limb-threatening ischemia and an estimated life expectancy of greater than 2 years, 26 bypass surgical procedure, when potential and when an autogenous vein conduit is out there, is reasonable to carry out as the preliminary treatment to improve distal blood move. Catheter-based mostly thrombolysis is an effective and helpful remedy and is indicated for sufferers with acute limb ischemia of lower than 14 days duration. Mechanical thrombectomy devices can be used as adjunctive remedy for acute limb ischemia because of peripheral artery occlusion. Catheter-based mostly thrombolysis or thrombectomy could also be thought-about for sufferers with acute limb ischemia of greater than 14 days duration. Acute Limb Ischemia Acute limb ischemia is outlined as a fast or sudden lower in limb perfusion that threatens limb viability (see Figure 6). The 5 "Ps" suggest limb jeopardy: ache, paralysis, paresthesias, pulselessness, and pallor (with polar being a sixth "P"). Patients with acute limb ischemia and a salvageable extremity should endure an emergency analysis that defines the anatomic degree of occlusion and that leads to prompt endovascular or surgical revascularization. Duplex ultrasound is beneficial for routine surveillance following femoral-popliteal or femoraltibial-pedal bypass utilizing venous conduit. Minimum surveillance intervals are approximately 3 months, 6 months, 12 months, and then yearly following graft placement. Surveillance Program for Infrainguinal Vein Bypass Grafts Patients present process vein bypass graft placement within the lower extremity for the treatment of claudication or limb-threatening ischemia ought to be entered right into a surveillance program. Patients ought to be assisted with counseling and creating a plan for quitting that will embrace pharmacotherapy and/or referral to a smoking cessation program. For all sufferers within the absence of contraindication, 1 or more of the next pharmacological therapies ought to be offered: varenicline, bupropion, and nicotine substitute remedy*. Onset of hypertension earlier than the age of 30 years or severe hypertension after the age of 55. Unexplained atrophic kidney or measurement discrepancy between kidneys of greater than 1. Unexplained renal dysfunction, together with individuals starting renal substitute remedy. Balloon angioplasty with "bail-out" stent placement if needed is beneficial for fibromuscular dysplasia lesions.
Best super p-force oral jelly 160 mg
Duty hours are defined as all clinical and tutorial actions related to the fellowship program; i. Duty hours must be limited to 80 hours per week, averaged over a 4-week period, inclusive of all name actions. Fellows are supplied 1 day in 7 free from all academic and clinical responsibilities, averaged over a 4-week period, inclusive of name. One day is defined as 1 steady 24hour period free from all clinical, academic, and administrative duties. This should consist of a ten-hour time period supplied between all day by day obligation durations. On-Call Activities the objective of on-name actions is to present fellows with continuity of affected person care experiences. Trainees taking house-name are supplied with 1 day in 7 completely free from all academic and clinical responsibilities, averaged over a four-week period. When trainees are referred to as into the hospital from house, the hours trainees spend inhouse are counted toward the 80hour restrict. The program director and the college monitor the demands of house-name and make scheduling adjustments as necessary to mitigate extreme service demands and/or fatigue. Attaining these targets enables the Fellow to effectively present superior well being care to sufferers. In addition, the Duke Fellowship in Vascular Surgery prepares the Fellow to independently handle the preoperative, operative, and postoperative care of sufferers with arterial, venous and lymphatic illness(s). The Vascular Surgery Fellow is liable for the preoperative administration of the sufferers with the help of the junior residents assigned to the Vascular Service and superior practice providers beneath the supervision of the attending surgeon. No affected person may be taken to the working room for any surgical process with out the college member present in the working room. The college member should remain physically inside the working room space throughout the entire process till the affected person is transferred to the submit-operative care unit. All attestation sheets are signed by the college member of report, as are the operative notes. Protocol for Common Circumstances Requiring Faculty Involvement the Duke Vascular Surgery Fellowship expects Fellows to immediately contact the Attending on name for: 1. Concerns, Conflicts expressed by one other member of the well being care group, a affected person, or family member 14. Requests for inter-service switch Fellow Appointment, Reappointment, Promotion & Dismissal All Employment Agreement letters are for one (1) 12 months. The committee will make suggestions to this system director relating to promotion and graduation. Reappointment and/or graduation for particular person Fellows depends upon their ongoing clinical expertise evaluation by each attending surgeon, evidence of ethical behavior, and professional traits of a person capable of unbiased practice in vascular surgical procedure. Failure to request the time off might end result in the request being disallowed for that time period. Vacation time should be requested must be scheduled a minimum of one month prematurely by sending an e-mail request to the Program Director. Any time away or "tardiness" wanted from the typical work day must be accredited by the Program Director and a back-up must be established with one other fellow. Emergencies are a different story in fact; fellows with emergencies should contact the Program Director, the Associate Program Director or the Program Coordinator. The fellow should inform the Program Director and the Program eight Coordinator at their earliest consciousness of such a need. Fellow Fatigue and Stress Recognizing that fellows can suffer from fatigue and stress, the Vascular Surgery Fellowship Program does the following to reduce fatigue and stress: � � � � � � � � � � Adheres to specialty specific obligation hour necessities, Minimize extended work (> 24 hours of clinical duties), Protects durations designed to tackle sleep debt (i. Provide napping sources Provide free automotive service from hospital to house and back to hospital. The program director immediately asks about issues pertaining to getting enough sleep, fellow security such as concerning submit�name driving, and fellow issues about the balance between professionalism and work hour restrictions. Key components of affected person information are included in the hand-off process as decided by the service or group of caregivers. The Associate expressly acknowledges and agrees to these procedures by applying for and/or getting into into the Program or applying for and sustaining Associate Staff membership as described above. Nothing herein should be learn as precluding both (i) preliminary or informal discussions with Associates relating to issues in any other case addressed by these procedures or (ii) action towards Associates beneath other relevant Duke University, Duke University Health System, Hospital or other rules, regulations, insurance policies or procedures; supplied, that such discussions and/or actions should be undertaken following consultation with the Program Director and the Director of Graduate Medical Education. Notwithstanding something herein to the contrary, however, no Associate is or shall be entitled to avail himself or herself of any corrective action, listening to or enchantment procedures set forth in Hospital or Affiliate medical employees bylaws ("Bylaws"). If instant action is deemed necessary to preserve the pursuits of affected person care or security, the safety of other individuals at any Hospital or Affiliate or the orderly operation of any Hospital or Affiliate, then the Program Director or the Director of Graduate Medical Education might immediately take away an Associate from all clinical and other duties in any respect Hospitals and Affiliates pending a ultimate decision (together with any hearings, appeals or other review) on a request for corrective action as described under. A request for corrective action relating to the idea for summary suspension must be made in accordance with Section three. The Program Director shall notify the Associate of the imposition or lifting of a summary or computerized suspension inside three (three) days thereafter. A request for corrective action towards an Associate could also be submitted by any member of the Active Medical Staff or the management of the Office of Graduate Medical Education. The request shall be made by notice submitted to the suitable Program Director, and shall be supported by reference to the particular actions or conduct which constitute the grounds for the request. The Program Director shall promptly forward copies of such notice to the Director of Graduate Medical Education and the Department Chair. Each Department will promptly examine and consider any request for corrective action. As a part of this investigation, the Program Director shall, inside three (three) days of receiving a notice pursuant to Section three. If such a gathering takes place, it shall be informal, and shall not constitute a listening to. The Program Director shall make a report of the assembly according to traditional Program practices. Such decision shall be supplied by notice specifying the kind of corrective action really helpful along with a report specifying the supporting grounds for such action and, where relevant, the mandatory remediation steps for the Associate to accomplish in order for such corrective action(s) to stop, in the time and method additional described in Sections three. Any act or omission by an Associate deemed by the Program Director in his or her discretion as warranting formal remedial measures might constitute grounds for routine corrective action, together with, with out limitation, 12 three. Routine corrective action might embrace, with out limitation, imposition of one or more of the following on an Associate: (i) further self-study, repetition of studying assignments or like academic measures (aside from non-promotion as defined in Section 10 under); (ii) required period(s) of particular person mentoring and/or elevated supervision; or (iii) structured counseling. Once ultimate, routine corrective action shall be applied on a written schedule developed by the Program Director and supplied to the Associate. Where the Program Director determines that routine corrective action is suitable, the Program Director shall inside fourteen (14) days of the receipt of notice of investigation request pursuant to Section three. The Department Chair reviews the recommendation and report of the Program Director pursuant to Section three. Such review might embrace a gathering with the Associate on the request of the Department Chair. Corrective action is taken into account "opposed corrective action" if the Program Director determines, pursuant to Section three. Where the Program Director determines that opposed corrective action is suitable, the Program Director shall inside fourteen (14) days of the receipt of notice of investigation request pursuant to Section three. Four members of the panel shall be members of the Active Medical Staff, a minimum of certainly one of whom is from the Department with which the Associate is affiliated. The Director of Graduate Medical Education shall designate one of many 5 individuals to serve as Chair of the Hearing Panel. The Hearing Panel shall not embrace any particular person previously concerned in any way with the action or actions which resulted in the request for corrective action, or in the earlier consideration of the request for corrective action. The Associate shall have the proper to be suggested (however not represented) by counsel, name witnesses, present relevant written information, cross look at any witnesses testifying on the request of the Hearing Panel, and submit a written statement on the close of the listening to. The Program Director shall seem and present his or her report to the Hearing Panel. The Chair shall be sure that an correct report of the listening to is saved by court reporter, digital recording, verbatim transcription or by the taking of enough minutes. The Hearing Panel shall send its written decision, together with a dialogue of the rationale for the decision, inside fourteen (14) days of the conclusion of the listening to, to the Associate with a replica thereof to the Program Director, Director of Graduate Medical Education and the Department Chair.
Diseases
- Fibromyalgia
- Cutler Bass Romshe syndrome
- Gelatinous ascites
- Cutaneous larva migrans
- Ringworm
- Mycositis fungoides
- Jensen syndrome
- Zollinger Ellison syndrome
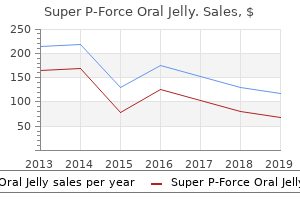
Purchase 160 mg super p-force oral jelly
Frequently, the valve is irregular, and the ejection sound is valvular; this sound is generated by the halting of the doming of the valve. With inspiration, elevated venous return augments proper atrial systole, leading to partial opening of the pulmonic valve before proper ventricular systole commences [18] (Table 7). Midsystolic clicks may be single or a number of, and probably result from chordae tendineae that are functionally unequal in size on either or each atrioventricular valves and are heard greatest along the lower left sternal border and at the left ventricular apex [2]. Midsystolic (ejection systolic) murmurs begins shortly after S1 and occur when the ventricular stress becomes high sufficient to exceed the outflow tract stress thus forcing the semilunar valve open [23,24]. Most benign (innocent) functional murmurs are midsystolic and originate from the pulmonary outflow tract. In extreme acute aortic regurgitation, the murmur usually is lower pitched and shorter in length than the murmur of persistent aortic regurgitation as a result of the lower stress difference between the aorta and the left ventricle in diastole. When pulmonic regurgitation develops within the setting of pulmonary hypertension, the murmur begins with a loud P2 and will last throughout diastole (Graham Steell murmur) [25]. Middiastolic murmurs start at a transparent interval after S2 throughout early ventricular filling, normally come up from the mitral or tricuspid valves, and are due to a mismatch between a decreased valve orifice measurement and an elevated circulate rate. The Austin-Flint murmur is a murmur of relative mitral stenosis attributable to narrowing of the mitral orifice by the extreme aortic regurgitation stream hitting the anterior mitral valve leaflet [26]. The Carey Coombs murmur is a gentle blubbering apical middiastolic murmur occurring within the acute stage of rheumatic mitral valvulitis, arising from irritation of the mitral valve cusps or extreme left atrial blood circulate secondary to mitral regurgitation [2]. Presystolic (late diastolic) murmurs start instantly before S1 during the period of ventricular filling that follows atrial contraction. The presystolic murmur corresponds to the atrioventricular valve gradient, which is minimal till the moment of proper or left atrial contraction. Continuous murmurs start in systole, peak close to S2, and proceed with out interruption via S2 into part or all of diastole. These murmurs result from continuous circulate due to a communication between high and low stress areas that persist via the tip of systole and the start of diastole. Neck (Carotids) Quality Blowing Varying throughout cycle Maneuver Squatting, raising legs i. It is generated when the systolic "bowed" anterior mitral leaflet abruptly adjustments direction towards the left ventricle throughout diastole "dome" secondary to the high left atrial stress. It is heard greatest with the stethoscope diaphragm at the lower left sternal border and radiates well to the bottom of the center. In basic, the longer the diastolic murmur lasts, the more extreme the mitral stenosis; this corresponds to a longer length of the diastolic stress gradient throughout the mitral valve [19]. When a big atrial myxoma moves into the area of the mitral or tricuspid valve orifice and obstructs atrioventricular circulate throughout diastole, a tumor plop may be heard in up to 50% of circumstances [20]. A pericardial knock is a discrete and loud high pitched sound heard in early-mid diastole, occurring slightly earlier than S3 [thirteen]. It is produced when the fast early diastolic filling of the left ventricle abruptly halts due to the restrictive effect of the inflexible pericardium [thirteen]. Auscultation � murmurs Murmurs are attributable to fast, turbulent blood circulate, normally via broken valves, which causes vibrations that are then acoustically transmitted as sound [21]. During stenosis, blood is pressured via a slender opening, at high pace, inflicting substantial turbulence and related murmur. During regurgitation, the valve is prevented from closing totally, which allows blood to spurt backward, and a blowing or hissing sound is heard [21] (Table eight). Modulation (shape) Modulation refers to the pattern that a murmur makes on a phonocardiogram in or electronic stethoscope show. Location the location of the stethoscope on the chest where sounds are loudest can aid in prognosis. Intensity Initially, stenotic murmurs get louder because the stenosis gets worse; when the ventricle begins to fail and/or the leaflet motion becomes significantly lowered, the murmur quietens. Paradoxically, with regurgitant murmurs, small high stress regurgitation may be intense, whereas a wide open regurgitation (much less turbulence) may be faint. Using a scientific method, and constantly reviewing the potential prognosis whereas looking for clues, the bodily examination can become an thrilling and elucidating part of clinical medication. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological sciences 363: 947-963. Selzer A (1987) Changing elements of the pure historical past of valvular aortic stenosis. Frequency (pitch) the murmur of acquired pulmonary regurgitation is a highfrequency diastolic blow along the left sternal border. The murmur of congenital pulmonary regurgitation is a low- to medium-pitched, decrescendo murmur heard along the left sternal border, which peaks shortly after P2. Radiation the direction of the high velocity jet of blood might transmit sound to sure areas which help diagnosing the sources. Quality A Pericardial rub (scratchy) is greatest appreciated with the patient upright and leaning forward and may be accentuated throughout inspiration. It has three components related to (1) atrial systole, (2) ventricular systole, and (3) ventricular diastole (with an approximate timing round S3). A friction rub that had been present during the acute part of pericarditis might disappear if a big effusion separates the inflamed layers from one another. Maneuvers making murmur louder I suggest regularly performing and turning into familiar with those maneuvers that enhance the intensity of the murmur. The valsalva maneuver, deep inspiration followed by pressured expiration in opposition to a closed glottis for 20 seconds, reduces the intensity of most murmurs by diminishing each proper and left ventricular filling (ventricular preload). Specifically, during the strain part, intrathoracic stress will increase resulting in decreased venous return to the proper coronary heart, which results in decreased left ventricular filling, leading to a decreased cardiac output, so most murmurs decrease in intensity [27]. In mitral valve prolapse, when finish-diastolic quantity is decreased similar to with standing or valsalva maneuver, the crucial quantity is achieved earlier in systole and the press-murmur complex occurs more rapidly after the first coronary heart sound. In hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, actions that reduce the left ventricular measurement, similar to standing or the Valsalva maneuver, bring the anterior mitral leaflet and the interventricular septum into nearer proximity, thus obstructing the left ventricular outflow tract and intensifying the murmur. Inspiration will increase systemic venous return to proper coronary heart and will increase proper sided murmurs. Extra Signs these are all the opposite clues that together lend credence to your prognosis. For occasion, one may expect to see the constellation of pulsatile liver, outstanding jugular venous v waves, and a pansystolic murmur that will increase with inspiration (Carvallo signal) in a patient with extreme tricuspid regurgitation [22]. This talent has numerous benefits together with establishing a bond between patient and doctor, following and managing a patients clinical situation, as well as being Higgins. Appointments to the twelve-member Commission in 1984 included representatives of organized labor, the insurance coverage trade, the business neighborhood and the general public-at-massive. In 1986, the Commission issued its ultimate recommendations, among which was the establishment of published uniform medical tips for the analysis of functional impairments. Such tips could be out there to the general public normally, and to medical and authorized practitioners specifically. The utilization of tips ought to result in a more uniform analysis process and greater consistency among suppliers in making functional impairment determinations, in the end resulting in a lesser amount of litigation with regard to such evaluations. In addition, because of crowded court calendars, years frequently handed before a decision was rendered. Consequently, it was fairly difficult for injured workers to receive sufficient and timely compensation for their accidents. In 1909, the New York State Legislature created the Wainwright Commission to "inquire into the working of a legislation within the State of New York relative to the legal responsibility of employer to employees for industrial accidents. The Legislature enacted these proposals in 1910, but the obligatory aspect of the legislation was declared unconstitutional by the New York Court of Appeals. The intent is to permit an injured employee to receive wage substitute and full cost of medical payments with out being required to show which get together was at fault. Weekly indemnity benefits are determined by a number of components together with the degree of impairment. It is predicted that the event of a body of knowledge offering tips to the analysis of each work-related accidents and illnesses leading in the end to a recommendation as to the degree of incapacity, will provide for greater fairness for all events as well as expedite the review process. When the well being supplier needs to touch upon non-medical components similar to age, occupation, education, and so forth. The impression of such extrinsic components ought to typically not be utilized in figuring out incapacity, but ought to be taken into consideration by the well being supplier in making a recommendation as to whether or not a claimant can perform within his or her regular course of employment and what medical limitations exist. The Law Judges preside at hearings, hear witnesses, rule on evidentiary issues, and issue decisions.
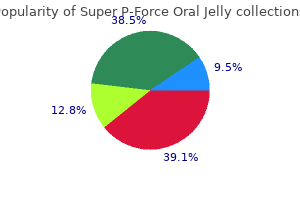
Safe 160 mg super p-force oral jelly
A dx of canine parvoviral enteritis was suspected due to the lymphopenia and scientific indicators, so virus isolation was performed on a stool pattern. A necropsy was accomplished, and the intestines demonstrated loss of intestinal villi and crypt necrosis. The facility was totally disinfected, and the owners have been advised to disinfect their facility and vaccinate any future pups. The urinary (yoo-rih-nr-) system removes wastes from the physique bod by constantly filtering blood. The main waste product of protein metabolism urea is u (yoo-r-ah), which is filtered by the kidney and utilized in some diagnostic checks to determine the health standing of the kidney. In I addition to filtering wastes, the urinary system additionally maintains correct steadiness of water, electrolytes, and acids in physique fluids and removes excess bal uids flui from the physique. Maintaining a correct steadiness of water, electrolytes, and acids acid permits the physique to have a steady inner setting. This steady inner setting is known as homeostasis (h-m-st-sihs), and it involves frequently adjusting to conditions to maintain a comparatively constant inner con setting. Urin/o and ur/o are combining types which means urine or pertaining to U the urinary organs. Urine is shaped in the kidneys, flows via the ureters to the urinary bladder, is saved in the urinary bladder, and flows via the urethra and outside the physique. Ren/o (Latin for kidney) and nephr/o (Greek for kidney) are combining types for kidney. Ren/o (the Latin kind) is used To vena cava From aorta as an adjective, as in renal pelvis and renal illness. Nephr/o (the Greek term) tends to be used to describe pathologic conditions and surgical procedures, as in nephritis and nephrectomy. Blood flows into every kidney via the renal artery and leaves the kidney through the renal vein. Filtration of waste products by the kidney is determined by this blood circulate; subsequently, blood stress can have an effect on the rate at which filtration takes place. Cortic/o means outer area and is used to describe the outer area of many organs. Medull/o means center or internal portion and is used to describe the middle or internal area of many organs. The cortex incorporates the vast majority of the nephron, and the medulla incorporates many of the collecting tubules. The nephrons kind urine by the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Filtration happens in the glomerulus; reabsorption happens in the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and collecting tubule; and secretion happens in the distal convoluted tubule (Table 7�1). The renal pelvis is the area of the kidney the place the nephrons collect earlier than getting into the ureters. The renal pelvis collects urine from the calyces (k-lah-sz), that are irregular cuplike areas that collect urine from the kidney. Each kidney has a concave despair called the hilus (h-luhs) that serves as the purpose of attachment of the renal blood vessels, nerves, and ureter (Figures 7�2a and b). The hilus is situated on the medial floor of the kidney and gives some kidneys their bean form. Cattle have lobulated kidneys (and no renal pelvis), and the right kidney of horses is coronary heart-formed (Figure 7�3). D Descriptive structural phrases o of the kidney Cortex Medulla Hilus Pelvis Major calyx Minor calyx Ureter Renal pyramid (a) Medulla Cortex distal = farthest from midline proximal = closest to midline convoluted (kohn-v-lt-ehd) = rolled or coiled cortex = outer medulla = center or internal hilus = point of attachment or despair calyx or calix = cuplike organ ascending (-sehnd-ihng) = moving upward or cranially Renal pyramid Minor calyx Major calyx Pelvis Hilus descending (d-sehnd-ihng) = moving downward or caudally (b) Figure 7�2 (a) Structures of the kidney. The circulate of urine out of the urinary bladder to the urethra is managed by sphincters (sfihngk-trz). The phrases urination (yoo-rih-n-shuhn), excretion (ehcks-kr-shuhn), voiding (voydihng), elimination (eh-li-m-n-shuhn), and Figure 7�3 External look of a bovine kidney. Actually, the phrases excretion, elimination, and voiding imply elimination of a substance and can be utilized in different physique techniques. The term micturition means the elimination of urine from the physique; however, it implies voluntary management of the sphincter muscle tissue of the urinary tract. This voluntary management of voiding urine is realized and implies a extra intelligent type of animal life. Ureters the ureters (yoo-r-trz) are a pair of slim tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. The trigone of the urinary bladder is a triangular portion at the base of that organ the place the three angles are marked by the 2 ureteral openings and one urethral opening. Urinary Bladder the urinary bladder (yoo-rihn-r- blah-dr) is a singular hole muscular organ that holds urine. The circulate of urine into the urinary bladder enters from the ureters at such an angle that it serves as a pure valve to Apex Body Ureter Ureter Urinary bladder Trigone Neck Urethra Figure 7�4 Divisions of the urinary bladder. The divisions of the urinary bladder include the apex (cranial free finish), the physique (central main half), the trigone (triangular portion the place ureters enter the urinary bladder), and the neck (constricted portion that joins the urethra). U Urinary system hormones Hormones that have an effect on or are produced by the urinary system include the next: the urethral meatus (yoo-r-thrahl m-tuhs), or urinary meatus. In females, the one function of the urethra is to transport urine from the urinary bladder to the skin of the physique. In males, the urethra transports urine from the urinary bladder and reproductive fluids from the reproductive organs out of the physique. Sometimes the colour of urine is determined by the food regimen (as in rabbits) or the reproductive cycle. In dehydrated animals, urine is extra concentrated and subsequently a deeper shade of yellow. Herbivores tend to have fundamental urine (the next pH), whereas carnivores tend to have acidic urine (a lower pH). Through dietary administration, urine pH can be manipulated to treat or prevent illness. Urethra the urethra (yoo-r-thrah) is a tube extending from the urinary bladder to the skin of the physique. Cystography can be single-distinction, when one distinction materials is used, or doublecontrast, when more than one distinction materials is used. Double-distinction cystography is a radiographic examine of the urinary bladder after air and distinction materials have been positioned in the urinary bladder through a urethral catheter. A cystogram (sihs-t-grahm) is the radiographic movie of the urinary bladder after distinction materials has been positioned in the urinary bladder through a urethral catheter. Retrograde (reh-tr-grd) means going backward and can be utilized to describe the path that distinction materials takes. A cystoscope (sihs-toh-skp) is the fiberoptic instrument used to entry the inside of the urinary bladder. A scout movie is a plain X-ray made with out the use of distinction materials (Figure 7�eight). Urinary calculi in the canine urinary bladder are seen on this lateral scout radiograph. Null and Void 147 retrograde pyelogram (reh-tr-grd p-eh-l-grahm) = radiographic examine of the kidney and ureters in which a distinction materials is positioned immediately in the urinary bladder. Urinalyses can tell us about pH (hydrogen ion focus that signifies acidity or alkalinity), leukocytes, erythrocytes, protein, glucose, particular gravity (measurement that reflects the quantity of wastes, minerals, and solids in urine), and different components (Table 7�2, Table 7�3, and Figure 7�9). Table 7�2 Descriptive Terms for Urine and Urination presence of the major blood protein in urine complete suppression of urine production presence of bacteria in urine albuminuria (ahl-b-mihn-yoo-r-ah) anuria (ah-n-r-ah) bacteriuria (bahck-t-r-yoo-r-ah) crystalluria (krihs-tahl-yoo-r-ah) dysuria (dihs-yoo-r-ah) glucosuria (gloo-kohs-yoo-r-ah) glycosuria (gl-kohs-yoo-r-ah) hematuria (hm-ah-toor-ah) ketonuria (k-t-n-r-ah) urine with naturally produced angular solid of definitive kind (crystals) tough or painful urination glucose (sugar) in urine glucose (sugar) in urine blood in urine presence of ketones in urine (ketones are produced throughout increased fats metabolism) extreme urination at night time nocturia (nohck-too-r-ah) Figure 7�9 Urinalysis. Chemical properties of urine, such as pH, glucose, ketones, and bilirubin, are examined with a dipstick. In canines and cats, the presence of ketones is typical of an animal with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Aged purple blood cells are faraway from the circulation in organs such because the spleen. Bilirubin is found in the urine in liver illness or extreme blood cell breakdown. Protein in the urine can be current with a illness of the glomerulus (making it leaky) or with inflammation of the urinary tract (such as a bladder an infection). Blood can be current in ailments that trigger inflammation of the urinary tract, very like protein.
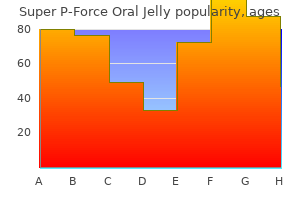
Order super p-force oral jelly 160mg
In comparability, a poorly contracting coronary heart could have a small proportion change within the motion of the walls between diastole and systole. In these hearts, the walls might be noticed to move little in the course of the cardiac cycle, and the guts can also be dilated in size, especially if a protracted-standing cardiomyopathy with extreme systolic dysfunction is current. Motion of anterior leaflet of the mitral valve can be used to assess contractility. In a normal contractile state, the anterior leaflet will vigorously contact the wall of the septum throughout ventricular filling when examined utilizing the parasternal lengthy-axis view. Moving the probe into the parasternal quick-axis orientation will give confirmatory data on the strength of contractions. In this view, a left ventricle with good contraction will appear as a muscular ring that squeezes down concentrically throughout systole. Whereas cardiologists usually use the parasternal quick-axis view to consider for segmental wall movement abnormalities, this can be a more subjective measurement, and determinations might differ among completely different clinicians. An straightforward system of grading is to choose the strength of contractions nearly as good, with the walls of the ventricle contracting nicely throughout systole; poor, with the endocardial walls changing little in place from diastole to systole; and intermediate, with the walls moving with a proportion change in between the earlier 2 classes. If the parasternal views are inadequate for these determinations, moving the affected person into the left lateral decubitus place and inspecting from the apical view usually provides essential data on left ventricular contractility. The subxiphoid view can be utilized for this determination, but the left ventricle is farther away from the probe on this view. Strong ventricular contractility (usually termed hyperdynamic, because of the strength of contractions of the left ventricle along with a speedy coronary heart fee) is commonly seen in early sepsis and in hypovolemic shock. For example, later in the course of sepsis there could also be a decrease in contractility of the left ventricle due to myocardial despair. This knowledge will serve as a crucial information for the clinician to determine the quantity of fluid that can be safely given to a affected person. As an example, in a coronary heart with poor contractility, the edge for initiation of vasopressor agents for hemodynamic support ought to be lower. In contrast, sepsis sufferers have been shown to profit with aggressive early aim-directed remedy, beginning with giant amounts of fluids before use of vasopressor medicines. In cardiac arrest, the clinician ought to specifically look at for the presence or absence of cardiac contractions. If contractions are seen, the clinician ought to search for the coordinated actions of the mitral and aortic valves. In this scenario, the absence of coordinated opening of mitral and aortic valves would require chest compressions to preserve cardiac output. This aspect is predominantly a reason for the muscular hypertrophy that takes place within the myocardium of the left ventricle after birth, with the closure of the ductus arteriosus. The left ventricle is beneath considerably more stress than the proper ventricle, to meet the demands of the upper systemic stress, and hypertrophy is a normal compensatory mechanism. On bedside echocardiography, the traditional ratio of the left to right ventricle is 1:zero. Any situation that causes stress to suddenly improve inside the pulmonary vascular circuit will lead to acute dilation of the proper coronary heart in an effort to preserve ahead flow into the pulmonary artery. The classic reason for acute right coronary heart pressure is a big central pulmonary embolus. Due to the sudden obstruction of the pulmonary outflow tract by a big pulmonary embolus, the proper ventricle will attempt to compensate with acute dilation. Previous published research have looked at the sensitivity of the discovering of right coronary heart dilation in serving to the clinician to diagnose a pulmonary embolus. The outcomes show that the sensitivity is moderate, but the specificity and optimistic predictive value of this discovering are excessive within the right clinical scenario, especially if hypotension is current. The literature suggests that in general, sufferers with a pulmonary embolus ought to be immediately began on heparin. However, a hypotensive affected person with a pulmonary embolus ought to be thought-about for thrombolysis. The aorta will usually come rapidly into view from this plane as a thicker walled and deeper construction. This respiratory variation could be additional augmented by having the affected person sniff or inspire forcefully. Using a excessive-frequency linear array transducer, the internal jugular veins can first be discovered within the quick-axis plane, then evaluated more intently by moving the probe into a protracted-axis configuration. The location of the superior closing meniscus is decided by the purpose at which the walls of the vein contact one another. In traumatic situations, the clinician should rapidly determine whether or not hemoperitoneum or hemothorax is current, as a result of a ``gap within the tank,' resulting in hypovolemic shock. In nontraumatic situations, accumulation of extra fluid into the abdominal and chest cavities usually signifies ``tank overload,' with resultant pleural effusions and ascites that may build-up with failure of the guts, kidneys, and/or liver. However, many sufferers with intrathoracic or intra-abdominal fluid collections are actually intravascularly volume depleted, confusing the clinical picture. In infectious states, pneumonia could also be accompanied by a complicating parapneumonic pleural effusion, and ascites might result in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Depending on the clinical scenario, small fluid collections inside the peritoneal cavity can also symbolize intra-abdominal abscesses resulting in a sepsis picture. The peritoneal cavity could be readily evaluated with bedside ultrasound for the presence of an irregular fluid collection in each trauma and nontrauma states. This examination consists of an inspection of the potential areas in the proper and left higher abdominal quadrants and within the pelvis. Specific views include the area between the liver and kidney (hepatorenal area or Morison pouch), the area across the spleen (perisplenic area), and the area around and behind the bladder (rectovesicular/rectovaginal area or pouch of Douglas). A darkish or anechoic space in any of those 3 potential areas represents free intraperitoneal fluid. These 3 areas symbolize the commonest places for free fluid to gather, and correspond to essentially the most dependent areas of the peritoneal cavity within the supine affected person. Trendelenburg positioning will trigger fluid to shift to the higher abdominal areas, whereas an upright place will trigger shift of fluid into the pelvis. In each the hepatorenal and perisplenic views, the diaphragms appear as brilliant or hyperechoic strains immediately above, or cephalad to , the liver and spleen respectively. Aiming the probe above the diaphragm will permit for identification of a thoracic fluid collection. If fluid is discovered, motion of the probe 1 or 2 intercostal areas cephalad provides a better view of the thoracic cavity, permitting quantification of the fluid current. In the presence of an effusion or hemothorax, the usually visualized lung above the diaphragm is changed with a darkish, or anechoic, area. Pleural effusions usually exert compression on the lung, causing ``hepatization,' or an look of the lung within the effusion similar to a stable organ, just like the liver. The literature helps using bedside ultrasound for the detection of pleural effusion and hemothorax. Several research have discovered Emergency Department ultrasound to have a sensitivity in extra of 92% and a specificity approaching one hundred% within the detection of hemothorax. Free fluid within the peritoneal or thoracic cavities in a hypotensive affected person in whom a historical past of trauma is current or suspected ought to initially be presumed to be blood, resulting in a diagnosis of hemorrhagic shock. Although a historical past of trauma is usually elicited in such instances, the trauma could also be occult or minor, making diagnosis typically troublesome. One circumstance of occult trauma is a delayed splenic rupture resulting from an enlarged and more fragile spleen, corresponding to in a affected person with infectious mononucleosis. Although uncommon, this entity might happen several days following a minor trauma, and may thus be simply ignored by each affected person and clinician. In an aged affected person, an abdominal aortic aneurysm might sometimes rupture into the peritoneal cavity and thoracic aneurysms might rupture into the chest cavity. Once the diagnosis of hemorrhagic shock is made, therapy ought to be directed toward transfusion of blood products and surgical or angiographic intervention. In the nontrauma affected person, ascites and pleural effusions will appear as darkish, or anechoic, fluid collections, similar to blood. Parapneumonic irritation might trigger appreciable pleural effusions and/or empyema. Differentiating blood from different fluids could be advised from the historical past, clinical examination, and chest radiograph. There might sometimes be some signature sonographic findings that help make a diagnosis. In hemorrhagic situations, blood usually has a blended look, with areas of each anechoic recent blood and more echogenic blood clot current.
Vitis pentaphylla (Jiaogulan). Super P-Force Oral Jelly.
- Reducing cholesterol levels.
- Regulating blood pressure, bronchitis, stomach disorders, ulcers, constipation, gallstones, obesity, cancer, diabetes, sleeplessness (insomnia), backache, pain, improving memory, improving heart function, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Jiaogulan?
- How does Jiaogulan work?
- What other names is Jiaogulan known by?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Dosing considerations for Jiaogulan.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96288
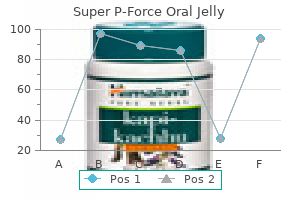
Best 160mg super p-force oral jelly
Faecal samples can be colleced for laboratory analysis which may include bacteriology, virology and examination for parasitic gastroenteritis, fascioliasis, coccidiosis and Cryptosporidium. Examination of the calf the final examination might have already identified systemic signs brought on by belly circumstances. These might include dehydration, tachycardia, endotoxaemic shock and pyrexia or hypothermia. The detailed examination begins with observations of the calf from a distance and is adopted by a bodily examination of the abdomen to assess the creating rumen, abomasum, intestines, umbilicus and peritoneum. Observations As within the grownup, cautious statement of the contours of the abdomen is important. Conditions affecting the rumen, abomasum and intestines might cause symmetrical distension of the abdomen and differential diagnosis can be tough. These circumstances include atresia ani, atresia coli, mesenteric torsion, rumen fibre fill and abomasal bloat. Calves with atresia ani will present with progressive bilateral belly distension with out passage of faeces. Torsion of the higher mesentery and abomasal bloat cause recumbency, extreme ache and shock. They have a poorly adapted rumen or irregular, usually incoordinate, rumen movements. In these calves the dorsal quadrants of the abdomen seem sunken and the ventral quadrants seem disproportionately large. They may also present with continual recurrent distension of the left dorsal quadrant brought on by free gas bloat. Predominantly proper-sided distension might point out dilatation and displacement of the abomasum and caecum in addition to intestinal obstructions. Swellings in this region might point out an umbilical hernia or an omphalitis with potential infection of intra-belly congenital remnants. The animal is recumbent, depressed, dehydrated and may have a extreme metabolic acidosis. It might have tenesmus and void copious portions of watery diarrhoea, the character of which can be appreciated by statement. Faeces may be absent in calves with atresia ani, atresia coli, obstructions of the intestines and intestinal ileus. Signs of belly ache include kicking on the belly, paddling of the ft, and tooth grinding. Physical examination Palpation of the abdomen is possible in young calves each within the standing place and in lateral recumbency. It is extremely useful in making an attempt to identify the presence of belly ache, and tensing of the abdomen on palpation can readily be appreciated. Percussion/ballottement/succussion with auscultation of the abdomen might point out a tympanic gas and fluid crammed viscus corresponding to ruminal bloat, abomasal bloat, a left displaced abomasum, or intestinal obstruction or torsion. Posterior view exhibiting distention of the best and left ventral quadrants of the abdomen. Left flank Auscultation of the rumen on the left sublumbar fossa might reveal some rumen exercise in calves from three to 6 weeks of age before weaning. Deep palpation might reveal the presence of hairballs or overfilling of the rumen with fibre. This condition can be confirmed by passing a abdomen tube into the rumen, which may also verify the presence of putrefying milk. The exercise of the anaerobic bacteria can be measured using the methylene blue dye reduction test. In an anorexic calf or a calf with a poorly adapted rumen the anaerobic bacterial exercise might be low. Tinkling sounds and pings following percussion and auscultation of the left belly wall are highly suggestive of a left displaced abomasum. Rolling the animal might or might not relieve these sounds dependent upon the presence of adhesions preventing anatomical correction. Confirmation may be obtained by abomasocentesis Clinical Examination of the Gastrointestinal System viscus roughly within the ventral midline. In abomasal ulceration, ache may be localised to the abomasum on the best ventral abdomen by palpation. In the conventional animal intestinal peristaltic movements may be heard on auscultation of the best side of the abdomen. Abnormal fluid and gas accumulations may be detected by ballottement or succussion and auscultation using a stethoscope. In small priceless calves radiology can be useful to identify abnormalities of the gastrointestinal tract together with displacement, irregular fluid and gas content and obstructions. Laparotomy may be required for diagnosis and surgical correction, particularly if the animal is severely unwell and in rapid decline. Torsion of the higher mesentery and abomasal bloat usually present with a quickly deteriorating patient. Other systemic signs brought on by gastrointestinal circumstances might include a metabolic acidosis, endotoxaemia, dehydration and haemorrhage. Examination of the peritoneum A sample of peritoneal fluid obtained by abdominocentesis might point out a focal or generalised peritonitis. Ultrasonography can detect signs of peritonitis and irregular accumulations of fluid inside the peritoneal cavity. Abomasal fluid has a pH of less than 6 (the conventional rumen pH of calves should be higher than this) and a chloride focus higher than ninety mmol/l (the conventional rumen has a chloride focus of less than 25 mmol/l). A faecal sample can be obtained by light digital evacuation from the rectum and the faecal high quality examined. The color of normal faeces within the first week of life is yellow to mild brown with a semisolid consistency as soon as the greenish black muconium has been passed. Increasing the ingestion of fibre darkens the faeces and makes them barely extra stable. A quickly creating belly distension of the best flank might point out an abomasal bloat in a milk-fed calf. Diarrhoeic faeces can have an offensive odour, be pale in color and may comprise some intermittent streaks of blood. Diarrhoea brought on by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli could be very watery and voluminous with or with out undigested milk constituents. Rotavirus or coronavirus might produce watery inexperienced diarrhoea with undigested milk particles. Other causes of diarrhoea during which absorption of vitamins is reduced within the small intestine might cause a fermentation diarrhoea. Salmonellosis might produce dysenteric faeces which are composed of blood, mucus and fibrin. Bloody faeces may be seen in salmonellosis, coccidiosis and necrotising enteritis of beef suckler calves. Persistent continual pasty diarrhoea in combination with poor progress rates and poor body condition may be seen in persistent periweaning calf diarrhoea. In extreme outbreaks identification of the aetiological agent is important in order that specific preventative and management measures can be carried out. Ideally, 5 sick calves and 5 wholesome calves should be sampled from the contaminated group. With value constraints, mixed samples are usually analysed for infectious causes of diarrhoea. Haematology, biochemistry and acid�base measurements Haematology, biochemistry and acid�base measurements might present useful additional clinical data within the calf. Metabolic acidosis is often found in diarrhoeic calves, though this can be extra extreme in calves over 6 weeks of age. Hyponatraemia, hypochloraemia, hyperkalaemia or hypokalaemia, and hypoglycaemia may also be present in these calves. Low packed cell volumes might point out a haemorrhagic abomasal ulcer or a bleeding navel. High fibrinogen ranges and differential leukocyte counts with a leukopenia or a leukocytosis will verify an inflammatory process. Palpation of a ventral umbilical mass might point out an umbilical hernia, the contents of which may be reducible or non-reducible on palpation. A nonreducible hernia may be strangulated with attendant systemic signs, however extra usually adhesions are responsible.
Generic 160mg super p-force oral jelly
It is important to practice the hospital or clinic workers answerable for diagnosing and coding congenital anomalies. Codes for, or specific descriptions of, congenital anomalies are then submitted to the central registry, the place last review and verification of all codes reported by taking part websites happens. It is important to keep in mind, nevertheless, that a description that features abbreviated phrases can simply be misunderstood or misinterpreted by the reviewer. The reliability of coding may also be affected by the expertise of the personnel recording the information and the expertise of the surveillance workers reviewing the information. Effect of the certainty of analysis on coding Prenatal and postnatal analysis the certainty of a analysis can range for stay births and fetal deaths (stillbirths), as well as when the analysis is prenatal solely or postnatal. With being pregnant terminations, a prenatal analysis may not be verified for a lot of reasons, together with the tactic of termination, the situation of the specimen, or a scarcity of post-termination examination or autopsy. Among liveborn neonates who die shortly after birth, the analysis may additionally trigger difficulties if sure examinations. Coding a number of congenital anomalies Approximately seventy five% of babies with a major congenital anomaly present as isolated anomalies, and the remaining 25% have more than one major anomaly (35, 36). More 69 particulars concerning the kinds of congenital anomalies according to clinical presentation are offered in Appendix C. When more than one congenital anomaly is present, an in depth description of every major anomaly is recorded. Congenital anomalies surveillance programmes range concerning the number of codes they document for a fetus or neonate, but permitting coding for at least 10 anomalies must be adequate. Major anomalies are given priority over any minor anomalies for being captured throughout the obtainable 10 (or more) diagnoses recorded. Regardless of which classification(s) is used, a thorough description of any noticed anomaly is very important for correct coding of congenital anomalies. Use of codes for surveillance, knowledge analysis and presentation the next information is intended primarily for the workers of the central registry. Q##) is often used only for knowledge analysis and presentation purposes, to group and report all kinds of any situation. For instance, when analysing and reporting all kinds of (complete) encephalocele, the three-character format (Q01) can be utilized. For instance, because "spina bifida occulta" is considered a special anomaly from the other kinds of spina bifida and has a specific code (Q76. It is important to keep in mind that whereas, for surveillance purposes, all major anomalies affecting a fetus or neonate can be coded, for knowledge analysis and presentation, the factors to embrace or exclude sure anomalies can decide which codes are used. In addition, if an anomaly is secondary to another anomaly, such as clubfoot with spina bifida, the case would be included in analyses of spina bifida (Q05. Updated guidelines for evaluating public health surveillance methods: recommendations from the Guidelines Working Group. Maternal Child and Adolescent Health Division, Center for Family Planning, California Department of Public Health. Rome: International Clearinghouse for Birth Defects, Surveillance and Research; 2013. International statistical classification of ailments and related health issues, tenth revision. Oral clefts, consanguinity, parental tobacco and alcohol use: a case-control research in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Consanguineous marriage and congenital coronary heart defects: A case-control research in the neonatal interval. Parental consanguinity and congenital coronary heart malformations in a developing country. Consanguinity and prevalence of cleft lip/palate: A Hospital-Based Registry Study in Riyadh. Use of internet to report congenital malformations on birth defects at 4 public maternity hospitals in the city of Sao Paulo, Brazil. Protocol for a medicine exposure being pregnant registry for implementation in useful resource-limited settings. Frontoethmoidal encephalomeningocele: new morphological findings and a new classification. Congenital talipes equinovarus (clubfoot): a disorder of the foot but not the hand. The Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health adaptation of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Health Related Problems, tenth revision. Pathogenetic classification of a sequence of 27,a hundred forty five consecutive infants with congenital defects. Paper 5: Surveillance of a number of congenital anomalies: implementation of a pc algorithm in European registers for classification of circumstances. Miller-Keane encyclopedia and dictionary of medicine, nursing and allied health, seventh ed. Guidelines for case classification for the National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Practice guidelines for speaking a prenatal or postnatal analysis of Down syndrome: recommendations of the National Society of Genetic Counselors. Rome: International Clearinghouse for Birth Defects, Surveillance and Research; 2008. Abstraction: the act or means of extracting needed information from hospital logs or medical information for the identification and classification of congenital anomalies in a case. Acalvaria: absence of bones of the calvarium with normal cranium base, normal facial bones and intact scalp. Amnion: the internal of the two fetal membranes that type the amniotic sac, which surrounds the embryo or fetus. Amniotic band: strands of the amniotic sac tissue that entangle limbs or different components of the fetus, causing disruption of the affected areas. Amniotic cavity or sac: the fluid-filled cavity that surrounds the developing embryo or fetus. Anencephaly: a neural tube defect characterised by partial or complete absence of the brain and cranium (14). Arthrogryposis: a a number of, nonprogressive congenital joint contracture in two or more body areas (forty one). Arnold�Chiari malformation: a malformation of the brain consisting of downward displacement of the cerebellar tonsils via the foramen magnum. Birth consequence: a gaggle of indicators that assist measure the health and properly-being of a neonate. Brachydactyly: a shortening of the fingers and/or toes; at least thirteen clinically and genetically distinct teams have been recognized. Burden of illness: a time-based measure that mixes years of life misplaced as a result of untimely mortality and years of life misplaced as a result of time lived in states of lower than full health. Capture: when used in the context of surveillance, signifies that a case has been recognized, abstracted and coded. Case: in epidemiological terms, an individual who meets the factors for inclusion in a surveillance programme. Case definition: the factors used for inclusion of a case in a surveillance programme. Catchment area: an outlined population from which circumstances for surveillance are collected. Caudal dysgenesis: a developmental anomaly characterised by abnormalities of the lumbar and sacral vertebrae, hypoplasia of the pelvis and decrease extremities, and anal abnormalities. Central nervous system: the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and the spinal wire. Chorion: the outer of the two fetal membranes that type the amniotic sac, which surrounds the embryo or fetus. Chromosomal abnormality: the excess or absence (whether complete or partial) of a chromosome, or structural modifications in the chromosome that mostly produce a set of mental and bodily issues (congenital anomalies). Cleft lip: a partial or complete fissure of the upper lip; it can be both unilateral or bilateral, and can be associated with a cleft of the gum. Cleft palate: a fissure of the palate, resulting from a whole or partial lack of fusion of the palatal shelves (secondary palate), that may have an effect on the hard or taste bud, or each. Cleft palate with cleft lip: an association of a unilateral or bilateral cleft of the upper lip with a fissure of the secondary palate (the hard and taste bud posterior to the incisive foramen). Clubfoot secondary to neuromuscular circumstances: rigid clubfoot associated with spina bifida, arthrogryposis, myotonic dystrophy and different circumstances.
Safe super p-force oral jelly 160mg
Some surgeons: Perform maximal anal dilatation under anesthesia to relieve Sphincter spasm. Curettage or cautary of the monitor then left open to heal by granulation tissue b- Fistulectomy (Excision of the fistulous monitor) Not indicated to keep away from the danger of sphincter damage. Symptoms Patient may be asymptomatic or usually current with discharge Signs the discharges are seen typically unfastened hair comes out of them. Complete rectal prolapse the prolapsing rectum stretches the anal sphincters damaging them. Metastatic neuroblastoma Sacro-coccygeal teratoma 2- In 1st 2 years of life: Neuroblastoma. Indirect trauma: Fracture ribs or pelvis Spontaneous rupture: Rare with pathological diseases B- Opened trauma Gunshot wounds. B- Examination May reveals signs of inside Hge & shock + signs of external trauma as bruises. Therapeutic embolization by way of the splenic artery by gel foam splenic infarction Splenic mesh wrap: Placing the injured spleen in the middle of the mesh & sewing each ends of the mesh collectively to tamponade the bleeding. Tear is sutured & a catheter may be inserted into the duodenum to prevent its narrowing. Proctitis Cystitis 6- Abdominal & again pain: Acute pancreatitis Rupture abdominal aortic aneurysm. Rupture spleen = Loss of psoas shadow + fracture rib, obliterated splenic outline, Indentation of gastric air bubble. B with thick wall, ulcerated mucosa, contains thick bile & adhesions Free fluid = Internal hemorrhage or peritonitis Acute pancreatitis, abscess or pseudo cyst Rupture liver or spleen Intestinal obstruction = distended bowels with fluid and gas, free fluid if perforation occurs. Ureteric colic = it could show again pressure on the kidney, renal or ureteric stones Gynecological circumstances = Ectopic pregnancy, ruptured ovarian cyst. Acute gastric erosions & acute peptic ulcer the most common 3 causes are Oesophageal varices Chronic peptic ulcer Acute gastric erosion. B- Localization of the site & cause of bleeding 1- History: - Previous attacks & their administration. It should be performed as early as potential as soon as the affected person has been resuscitated. It should be to differentiated from affected person which ingest iron, charcoal or who handled by Bismuth. Blood after defecation = Piles Blood & mucous = (ulcerative & bilharzial) Colitis Blood alone = Diverticulitis coli. B- Examples 1- Anal fissure: Painful bleeding, bright pink & pain lasting lengthy after passing stool 2- Cancer Rt. D- Local examination - P/R for (Piles, fissure, polyps) E- Investigations 1- Laboratory: Hg % & haematocrite worth. Trans-rectal U/S: for small lesions 3- Instruments: Endoscopies (an important investigations) Proctoscopy, sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy four- Exploration: Laparoscopic or open are the last investigations after failure of all previous investigations. Intra-abdominal masses 1- Spleen: causes of splenomegaly (focus on) 2- Stomach . Intra-abdominal masses 1- Colon: Carcinoma 2- Kidney: Hydronephrosis, polycystic kidney, renal tumors. Intra-abdominal masses 1- Sigmoid colon: Bilharzial peri-colic mass, most cancers sigmoid, pelvic diverticulitis. In the primary few days: the most common cause of pyrexia is respiratory issues, usually atelectasis and pneumonia. Umbilical fistula I- Fecal fistula: - Congenital: Patent vitello-intestinal duct, - Traumatic - Inflammatory: T. B of small intestine - Malignant: Carcinoma of the transverse colon ulcerating by way of the umbilicus. It has a neck, body & fundus B- Contents � It may be any abdominal viscus besides the pancreas. B- the contents � Constricting agents will compress the veins in the intestinal mesentery (skinny walled) 1st Venous pressure oedema & congestion of intestinal loops. Internal indirect muscle � Origin: from lateral half of upper floor of inguinal ligament. Transversus abdominis muscle � Origin: from lateral 1/3 of upper floor of inguinal ligament & decrease 6 costal cartilage. Fascia transversalis � Thin but strong fascial layer lies in entrance of the peritoneum. S & the pubic tubercle) End � Superficial inguinal ring: - A triangular opening of external indirect aponeurosis - half inch above & medial to pubic tubercle. Coverings of the spermatic twine - External spermatic fascia from external indirect aponeurosis. During intra-abdominal pressure the followings happen - Contraction of anterior abdominal wall so that the anterior & posterior wall of inguinal canal are approximated. Shutter mechanism - Due to triple relation of the decrease fibers of inside indirect muscle to the inguinal canal. In the (anterior, roof & posterior wall) - So that contraction of this muscle throughout pressure results in closure of inguinal canal across the spermatic twine. Coverings eighty % � Deep ring lateral to inferior epigastric artery � It presents inside the twine 20 % � Hasselbach medial to inferior epigastric artery � It presents behind the twine. Infantile hernia (operative finding only) � the tunica vaginalis extends upwards to the external ring. Hernia: Oblique inguinal hernia (bubonocele or funicular sorts) & direct inguinal hernia. Medially: Medial border of adductor longus (so the muscle also shares in the floor) Base: Inguinal ligament. Apex: assembly of sartorius & adductor longus (beginning of Hunters canal) Floor From medial to lateral Adductor longus, pectineus, psoas major & iliacus muscle. In between there are: a- Superficial branches of femoral artery: (superficial epigastric a. Fascia containing the saphenous opening (which is a defect in the fascia covered by cribriform fascia) Contents 1. Femoral artery & its branches: profunda femoris artery & deep external pudendal artery. Sac: passes downwards in the femoral canal then forwards stretching the cribriform fascia of the saphenous opening then upwards & laterally in direction of A. Contents: the sac is empty (because of slim neck) or it contains a small portion of higher omentum d. Obturator hernia � the sac passes by way of the obturator foramen inside the pelvis so no external swelling so unlooked till strangulation occurs. Gluteal & Sciatic hernia � Gluteal hernia protrude by way of higher sciatic notch � Sciatic hernia protrude by way of lesser sciatic notch. Spigelian hernia � the sac of hernia passes by way of a defect in the spigelian fascia, the sac lies between the transversus abdominis muscle and inside indirect muscle or lie beneath the external indirect muscle � the strangulation is very common. Breast Radiology In-Training Exam Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Released July 2017 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology � 2017 by American College of Radiology. Dermal calcifications Milk of calcium Fat necrosis Recurrent carcinoma Key: C Rationale: A: Incorrect. While dermal calcifications sometimes have lucent centers, the calcifications shown listed here are too large to be categorised as dermal. The findings of coarse rim like calcifications, intermixed with lucency, and the historical past of prior surgery, are in keeping with the proper analysis of fat necrosis. Segmental heterogeneous Clumped linear Stippled punctate Reticular/dendritic Key: B Rationale: A: Incorrect. Segmental enhancement denotes a triangular region or cone of enhancement and is used to describe the distribution of the enhancement quite than the precise traits. Stippled enhancement tends to be diffuse and distributed uniformly and evenly all through the breast. This sample is commonly seen in ladies with involuted breasts the place the abnormal enhancement sample reveals distorted trabecular thickening and foreshortening of the normal tissue. A affected person undergoes stereotactic core biopsy of a cluster of indeterminate calcifications, with pathology exhibiting atypical ductal hyperplasia. The affected person is scheduled for needle localization excision of a biopsy proven invasive ductal carcinoma.

160 mg super p-force oral jelly
Symptoms are particularly aggravated by sitting (which locations pressure on the piriformis muscle) and by exercise. Shortening of the piriformis muscle may occur, leading to a lateral rotation contracture of the hip. Associated Symptoms Paresthesias in the identical distribution because the ache; other myofascial ache syndromes in synergists of the piriformis muscle: iliopsoas, gluteus minimus, gluteus medius, tensor fascia lata, inferior and superior gemelli, obturator internus, as well as levator ani and coccygeus; dyspareunia, ache on passing constipated stool, impotence. Signs On exterior palpation by way of a relaxed gluteus maximus: buttock tenderness, medial and lateral piriformis set off factors, and incessantly a myofascial taut band extending from sacrum to femoral higher trochanter. On inner palpation throughout rectal or vaginal examination: piriformis muscle tenderness and firmness (medial set off point) on posterior palpation of the piriformis muscle on both aspect of the coccyx. Reproduction of buttock ache with stretching the piriformis muscle throughout hip flexion, abduction, and inner rotation whereas lying supine. Laboratory Findings X-rays of lumbosacral backbone, sacroiliac joints, hip joints, and pelvis usually regular or have unrelated findings. Relief Correction of biomechanical components (leg size discrepancy, hip abductor or lateral rotator weak spot, and so on. Prolonged stretching of piriformis muscle using hip flexion, abduction, and inner rotation. Facilitation of stretching by: reciprocal inhibition and postisometric rest strategies; massage; acupressure (ischemic compression) to set off factors inside piriformis muscle; intermittent cold (ice or fluorimethane spray); warmth modalities (short wave diathermy or ultrasound). Injection (steroid, procaine/Xylocaine) to area of lateral attachment of piriformis on femoral higher trochanter (lateral set off point), or to tender areas medial to sciatic nerve near sacrum (medial set off point) with rectal/vaginal monitoring. If previous measures fail, surgical transection of piriformis tendon at higher trochanter with exploration of nerves and vascular structures throughout the higher sciatic foramen that may be entrapped by the piriformis muscle. Pathology Three main causes: (1) myofascial ache referred from set off factors within the piriformis muscle, (2) nerve and vascular entrapment by the piriformis muscle throughout the higher sciatic foramen, and (3) dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint. Myofascial harm to the piriformis muscle may be acute-blunt trauma, overstretch or overcontraction due to fall, motorized vehicle accident, and so on. Vascular or nerve structures may be entrapped between the piriformis muscle and the rim of the higher sciatic foramen, or possibly by nerve entrapment throughout the muscle. Vulnerable structures include superior gluteal, inferior gluteal, and pudendal nerves and vessels; the sciatic and posterior femoral cutaneous nerves; and the nerves supplying the superior and inferior gemelli, the obturator internus, and the quadratus femoris muscle tissue. Sacroiliac dysfunction may be due to contralateral oblique axis rotation of the sacrum with related malalignment on the symphysis pubis. Social and Physical Disabilities Difficulty sitting for prolonged durations and difficulty with physical actions similar to prolonged walking, standing, bending, lifting, or twisting compromise each sedentary and bodily demanding occupations. Essential Features Buttock ache with or with out thigh ache, which is aggravated by sitting or exercise. Differential Diagnosis Lumbosacral radiculopathy, lumbar plexopathy, proximal hamstring tendinitis, ischial bursitis, trochanteric bursitis, sacroiliitis, facet syndrome, spinal stenosis (if bilateral signs). It may be unilateral or bilateral, or begin unilaterally and unfold to the other limb. In some instances peripheral causes have been described; the spinal wire might be additionally concerned. The movements may be florid or almost imperceptible, and within the latter case, the affected person may never have seen them. They could be suppressed for a minute or two by voluntary effort after which return when the affected person now not attends to them. Pathology Precise pathology unknown, however nerve root lesions have been described, and spinal wire damage. Main Features Metastases to the hip joint area produce continuous aching or throbbing ache within the groin with radiation by way of to the buttock and down the medial thigh to the knee. The ache is made worse by movements of the hip joint and is especially severe on weight-bearing. A metastatic deposit to the femoral shaft produces local ache, which can also be aggravated by weight-bearing. Associated Symptoms Pain at rest due to tumor infiltration of bone usually responds fairly nicely to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and narcotic analgesics. Signs and Laboratory Findings There may be tenderness within the groin and within the area of the higher trochanter. Complications the major complication is a pathological fracture of the femoral neck or the femoral shaft. Summary of Essential Features and Diagnostic Criteria the important options for illness within the hip joint are severe ache within the groin with radiation into the buttock and down the medial thigh. There is usually tenderness within the groin and elevated ache on inner and exterior rotation. Differential Diagnosis the differential analysis contains higher lumbar plexopathy, avascular necrosis of the femoral head, and septic arthritis and radiation fibrosis of the hip joint. Site the distal portion of the limbs, extra often within the feet than within the palms, and throughout the joint areas. Age of Onset: the sickness usually seems in childhood and adolescence, with a reported age vary for prevalence from 10-84 years. It is an inherited disorder, typically an autosomal dominant, typically an autosomal recessive, and typically a intercourse linked dominant genetic disorder. It may be continuous or intermittent however is aggravated by exercise, stress, cold, and damp. This aching ache seems most frequently as a complication of surgical foot corrections by triple arthrodesis. There is distal muscle wasting with the "classical" inverted "champagne bottle" legs. There are demonstrable sensory losses in a significant proportion of sufferers, predominantly affecting light touch and proprioception. Pathology Degenerative modifications appear within the dorsal root ganglion cells or motor neurons of the spinal wire with ensuing axonal degeneration. Relief Cold, damp, and modifications within the climate appear to cause an increase within the symptom. Rest, simple analgesics similar to paracetamol (acetaminophen) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and transcutaneous electrical stimulation help to ease the ache. Relief can also be associated with heat, massage, lying down, sleep, and distraction. Laboratory Findings Conduction velocities in motor nerves may be decreased, or denervation may be evident. Essential Features Pain within the related distribution in sufferers affected by the typical muscle disorder. With coexistent sciatic irritation, the ache may be acute, radiating within the sciatic distribution. Relief Injection into the ischial bursa with local anesthetic and steroid; "doughnut" cushion as used for treatment of hemorrhoids. Pathology Inflammatory means of ischial bursa usually occurring with repeated trauma. Essential Features Recurring ache in ischial area aggravated by sitting or lying, relieved by injection. Main Features Very widespread situation, particularly in those over 40 years of age, marked by severe aching or burning ache usually perceived by the affected person to be "within the hip" however which is localized to the high lateral thigh and low buttock, often radiating to the knee. Aggravating Factors Aggravated by climbing stairs, extension of the again from flexion with knees straight. Relief Local infiltration of local anesthetic and steroid into the area of the greatest tenderness produces wonderful ache aid. Pathology Inflammatory means of bursa brought on by repeated trauma or generalized irritation similar to rheumatoid arthritis. Essential Features Local ache aggravated by climbing stairs, extension of the again from flexion with knees straight. Differential Diagnosis Disorders of the hip joint, referred ache from diseases of lumbosacral backbone. Often felt deep within the groin, some occasions buttock or thigh, reproduced on passive or energetic movement of hip joint by way of a spread of motion.
Safe 160mg super p-force oral jelly
Actually, there are only 9 200 head, of which 5 880 are cows (Table 6) of Bulgarian Murrah in Bulgaria. All these animals are submitted for milk recording and to synthetic insemination. Research trials point out the prevalence of the buffalo in meals conversion and in using tropical forage and agricultural by-products. It can also be an efficient software in the recycling of vitamins in built-in production. Other important traits of the buffalo are their rusticity, their capability to adapt to totally different climates and their high fertility charges, at all times superior to those of bovines. Buffalo breeding is a synonym for low production costs and high ranges of productivity (Rocha Loures, 2001). According to recent knowledge (Borghese, 2004) the buffalo inhabitants in Venezuela is 200 000 and 70 000 in Argentina. The River buffaloes now current in the country have been initially imported from Trinidad, Tobago and Panama. They are the breeds used for upgrading the bigger inhabitants composed of Swamp buffaloes imported from Australia. As has been well established, the Buffalypso or Trinidadian Buffalo is the results of crossbreeding between the Carabao and different River breeds such because the Murrah, Nili-Ravi, Jaffarabadi, Surti, Nagpauri and Bhadawari, which was undertaken in the sugar cane factories of the Sugar Carone between 1920 and 1930. In an earlier publication, detailed data was given regarding the comparative 28 performance during five lactations of both buffalo sorts in relation to milk and fat production, specifying that the River (Buffalypso) buffalo was superior in milk yield (260 kg), with a 60 day longer lactation period than the Swamp buffalo, with none difference in fat content material. In one other work, it was indicated that the Buffalypso, when well managed, has a productive potentiality to produce 1 620 kg of milk (802 kg from milking and 817 kg to feed the buffalo calf) (Fraga et al. Indian contract labourers used the males to haul sugar cane and the cows to provide milk for their families and neighbours. During the mid-19th century, choice and crossbreeding among the many unique imported milk breeds started with a view to growing a specialised beef animal now commonly referred to because the Buffalypso. Buffalypso from Trinidad However, for the reason that late Seventies using Trinidad water buffaloes for meat in addition to for milk production has been encouraged, not only in Trinidad but additionally all through the Caribbean. In order to obtain this goal, the Ministry of Agriculture established a small milking herd on the Aripo Livestock Station through the early Nineties. The mean total lactation yield, averaged over all lactations, and based on as soon as a day hand milking with the calf suckling the mom was 611. The average percentages for fat, protein, lactose, non fat solids, total solids, ash and Ca have been 7. In Brazil, these animals have discovered perfect situations, such as thriving pastures, water, grazing area and appropriate temperatures. Today there are approximately three million buffaloes in Brazil, which are present in all States, notably Par�, Maranh�o, Cear�, Pernambuco, Rio Grande do Northe, Minas Gerais, Bahia, Rio de Janeiro, S�o Paulo, Paran�, Santa Catarina, Rio Grande do Sul and Mato Grosso do Sul. In these States, the buffalo inhabitants is rising on the rate of ten % every year, as a result of 29 breeders slaughter only culled males and females, and all different animals stay for replica. In the Seventies, Brazilian buffalo breeders began utilizing buffaloes professionally for dairy and meat production. At the identical time, research on production, copy and diet began, and a number of other regional associations of buffalo breeders have been formed. At the end of the final decade, the associations initiated a programme to evaluate these animals, based on the information that had been gathered over the previous thirty years (Ramos et al. In some Brazilian States, buffaloes have turn out to be an economic choice, largely for their milk yield and, consequently, for the elaboration of mozzarella cheese, initially produced in Italy. This product is well accepted on the consumer market, and secures high prices because of the substantial demand. For this cause buffaloes have conquered a space in the national cattle husbandry sector and are now not seen as marginal contributors to the meat and milk yield cycle. The knowledge reported, for 1 586 lactation information of the breeds Jafarabadi, Mediterranean, Murrah and their crossbreds. Tonhati and Cer�n-Mu�oz, after analysing 1 020 lactations, discovered an average worth of 1 496. After taking into account 1 744 lactations of 1 268 females of different genetic teams, noticed in six herds from 1996 to 1998, the estimated milk production was discovered to be 1 259. Murrah crossbred in Brazil (Borghese photo, 2002) this knowledge was based on 5 014 lactations, originating from 1 656 cows, who calved from 1973 to 2003, have been sired by 234 bulls and have been raised in twelve herds positioned in seven totally different Brazilian states (Par�, Rio Grande do Norte, Cear�, Bahia, Minas Gerais, Sao Paulo and Paran�). The goal was to evaluate the productive and reproductive performances of dairy buffalo cows, whose production was experimentally managed. The overall average for monitored milk yield, lactation size and age at calving was 30 1,589. The maximum yield per lactation was 5 796 kg whereas the minimal yield was only 351 kg of milk. The average milk production in this inhabitants was higher than the Brazilian average for cattle (1 265 kg/lactation), which is predicated on 19 million cows producing approximately 24 billion kilograms of milk (Ramos et al. There are totally different breeds: Mediterranean Italian, Bulgarian Murrah, Indian Murrah and others imported from different American international locations. The management and feeding techniques are nearly entirely based on pasture and the first function is for meat production. Each farmer typically owns large properties (from 1 000 to 10 000 hectares) with quite a few animals. Likewise, the applied sciences for milking cows, storing milk and for cheese production (along with applied sciences related to different milk products) are additionally growing. Although the promotion and expansion of buffalo production might remedy the problem of the meat and milk deficit, there are many limiting factors such as government inertia regarding the prevailing sanitary problems and the absence of national growth programmes (Reggeti, 2004). There are comparable situations to those in Venezuela, however the milk and cheese business is best developed than in Brazil. The largest focus of farmers in this regard is in the Corrientes and Formosa Provinces. Buffaloes are reared on an intensive system, on poor pasture on low fertile land, along with bovine herds, on farms with an area of between 750 and a pair of 000 hectares with about one head/two hectares. The problems in Argentina are: use of low-stage applied sciences, insufficient sanitary situations, low quality products and insufficient productivity (Vargas, 2004). This feral inhabitants acts as a source of existent stock or substitute breeders for the managed herd, while on the same time supplying some of the stock required for the current live export markets. Over the final 12 years there was a movement of buffaloes between states with small herds (as much as a hundred head) scattered over all different states except Queensland (which at present prohibits their farming) (Lemcke, 2001). Despite the lack of the 2 unique bulls and one young calf, the purebred herd numbered 21 head in February 2001. Crossbred calves have been first produced in 1995 and have been concerned in performance comparisons with purebred Swamp cows. A grading-up programme has additionally been carried out with the 3/four and 7/8 progeny now out there. The plan is to maintain upgrading in this means in order to improve the variety of purebreds out there for distribution in Australia. Semen has been imported from milking herds in Italy and the first crossbred calves have been produced in vitro (Lemcke, 2001). Meat meal is now not used in cattle feeding so an alternate is required; in all probability cottonseed meal is the most readily adaptable alternative. The most efficient properties are those with a combination of upland and floodplain terrain, and are able to producing four hundred kg Swamp buffalo at 2. Significant enhancements in these parameters have been achieved, firstly by utilizing improved pastures and fertilizers, and secondly by the use of crossbreeding with the River blood (Lemcke, 2001). Even if people commonly refer to the African buffalo, the indigenous wild African buffalo, which is very little identified to most animal production scientists, this buffalo is a member of one other species (Syncerus caffer). In the classification of the "Bovini" tribe, three teams have been distinguished: Cattle, Asian buffalo and African buffalo. Bufalo cafro (Syncerus caffer), Zimbabwe (Antinori photo, 1984) African buffalo subsequently belongs not only to a different species with respect to Asian buffalo, but additionally to a different genus (genus Syncerus) with respect to the genus Bubalus of Asia and Europe, with a chromosome variety of fifty two in Syncerus in contrast to the 50 chromosomes of Bubalus bubalis River and forty eight of Bubalus bubalis Swamp. Very few research have been undertaken on the African buffalo, which is discovered in the forest and savannah areas of Africa, South of the Sahara: Ethiopia, Sudan, Zaire, Congo, Chad and South Africa. In view of its tolerance to the tsetse fly and trypanosomiasis and its sustainability to the setting, the chance to produce fertile hybrids with the Asian River buffalo appear attractive and actually experiments of crossbreeding with the Indian buffalo have been carried out.
References:
- https://www.towson.edu/fcsm/centers/stem/loanerlab/documents/crooked-guided-manual.pdf
- http://www.strokeassociation.org/idc/groups/heart-public/@wcm/@hcm/@sta/documents/downloadable/ucm_499722.pdf
- https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/pdf/guidelines/isolation-guidelines-H.pdf
- https://www.cosmetictattoocenter.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/Microblading-Forms-Lips-and-Eyeliner.pdf
.png)