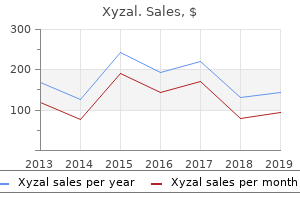
Safe 5 mg xyzal
IgM antibodies frequently acknowledge repetitive epitopes similar to those expressed by bacterial cell-wall polysaccharides, but the binding of particular person sites is commonly of low affinity as a result of|as a outcome of} IgM is made early in immune responses, earlier than somatic hypermutation and affinity maturation. Multisite binding makes up for this, dramatically enhancing the overall functional binding strength. When an immunoglobulin is used as an antigen, it will be to be|will probably be} handled like any other foreign protein and can elicit an antibody response. Anti-immunoglobulin antibodies can be made that acknowledge the amino acids that characterize the isotype of the injected antibody. Such anti-isotypic antibodies acknowledge all immunoglobulins of the identical isotype in all members of the species from which the injected antibody came. It is also be|can be} attainable to raise antibodies that acknowledge variations in immuno-globulins from members of the identical species which might be} the presence of quantity of} alleles of the person C genes within the inhabitants (genetic polymorphism). In contrast to anti-isotypic antibodies, anti-allotypic antibodies will acknowledge immuno-globulin of a selected isotype solely in some members of a species. Finally, as particular person antibodies differ in their V areas, one can raise antibodies towards distinctive sequence variants, which are called idiotypes. A schematic image of the variations between idiotypes, allotypes, and isotypes is given in. Historically, the main features of immunoglobulins had been defined by using isotypic and allotypic genetic markers identified by antisera raised in numerous species or in genetically distinct members of the identical species (see Appendix I, Section A10). The impartial segregation of allotypic and isotypic markers revealed the existence of separate heavy-chain, and genes. The isotypes of immunoglobulins are defined by their heavy-chain C areas, every isotype being encoded by a separate C-region gene. Unlike V(D)J recombination, isotype switching is all the time productive and happens solely in B cells activated by antigen. The immunological features of the varied isotypes differ; thus, isotype switching varies the response to the identical antigen at completely different occasions or underneath completely different situations. In this way, the B-cell antigen receptor has the identical specificity as the antibody that the B cell secretes upon activation. Lymphocyte receptors are remarkably various, and growing B cells and T cells use the identical basic mechanism to achieve this range. In every cell, functional genes for the immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor chains are assembled by somatic recombination from units of separate gene segments that together encode the V area. The substrates for the joining course of, arrays of V, D, and J gene segments, are similar among all the receptor loci, although there are some essential variations within the particulars of their association. As every sort of gene segment is present in quantity of}, slightly completely different, versions, the random choice of gene segments for assembly is the supply of enormous potential range. During the process of assembly, further range is launched at the gene segment junctions by way of imprecise joining mechanisms. The impartial association of the 2 chains of immunoglobulins or T-cell receptors multiplies the overall range of the entire antigen receptor. An essential distinction between immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors is that immunoglobulins exist in each membrane-bound (B-cell receptors) and secreted varieties (antibodies). Heavy-chain C areas contain three or four immunoglobulin domains, whereas the T-cell receptor chains have only one. Antibodies even have a variety of|quite lots of|a big selection of} effector features which might be} mediated by their C areas. Moreover, there are a number of} various heavy-chain C areas for immunoglobulins, every with completely different effector features. The similar V area can be expressed along with completely different C areas by way of a course of identified as|often recognized as} isotype switching. In this way, the progeny of a single B cell can categorical quantity of} completely different isotypes, thus maximizing the attainable effector features of any given antigen-specific antibody. The changes in immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor genes that happen during B-cell and T-cell improvement are summarized in. Changes in immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor genes that happen during B-cell and T-cell improvement and differentiation. The B-cell-specific processes, similar to swap recombination, enable the identical variable (V) area to be attached to a number of} functionally distinct heavy-chain C areas, and thereby create functional range in an irreversible method. By contrast, the expression of IgM versus IgD, and of membrane-bound versus secreted forms of all immunoglobulin sorts, can in precept be reversibly regulated. Evidence for somatic rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes coding for variable and constant areas Proc. The association of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor genes in human lymphoproliferative disorders Adv. Sequence of a mouse germ-line gene for a variable area of an immunoglobulin gentle chain Proc. Mouse variable-region gene households complexity, polymorphism, and use in nonautoimmune responses Immunol. Sequences of 5 potential recombination sites encoded near an immunoglobulin kappa constant area gene Proc. Sequences at the somatic recombination sites of immunoglobulin light-chain genes Nature 1979. Lack of N areas in antigen receptor variable area genes of TdTdeficient lymphocytes [published erratum seems in Science 1993, 262:1957] Science 1993. Rearrangement of genetic information could produce immunoglobulin range Nature 1978. Passenger transgenes reveal intrinsic specificity of the antibody hypermutation mechanism: clustering, polarity, and specific sizzling spots Proc. Monitoring and interpreting the intrinsic features of somatic hypermutation Immunol. TdT-accessible breaks are scattered over the immunoglobulin V area in a constitutively hypermutating B cell line Immunity 1998. The imprint of somatic hypermutation on the repertoire of human germline V genes J. Formation of the hen B-cell repertoire ontogeny, regulation of Ig gene rearrangement, and diversification by gene conversion Adv. Hypermutation generating the sheep immunoglobulin repertoire is an antigen impartial course of Cell 1995. Dependence of antibody somatic diversification on gut-associated lymphoid tissue in rabbits J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition [published erratum seems in Nature 1988, 335:744] Nature 1988. Mapping T-cell receptor-peptide contacts by variant peptide immunization of single-chain transgenics Nature 1992. A new T-cell receptor gene located within the alpha locus and expressed early in T-cell differentiation Nature 1987. Structure, group, and somatic rearrangement of T cell gamma genes Cell 1985. Junctional sequences of T cell receptor gamma delta genes: implications for gamma delta T cell lineages and for a novel intermediate of V-(D)-J joining Cell 1989. Diversity, improvement, ligands, and possible features of gamma delta T cells Adv. Two kinds of somatic recombination are essential for the technology of complete immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes Nature 1980. Recognition sites on human IgG for Fcg receptors the position of glycosylation Immunol. Polymer IgM assembly and secretion in lymphoid and nonlymphoid cell-lines evidence that J chain is required for pentamer IgM synthesis Proc. Structure of antibodies with shared idiotypy: the entire sequence of the heavy chain variable areas of two immunoglobulin M anti-gamma globulins Proc. Antigen Presentation to T Lymphocytes Introduction to Chapter 5 the technology of T-cell receptor ligands the main histocompatibility advanced and its features Summary to Chapter 5 References to Chapter 5 Introduction to Chapter 5 In an adaptive immune response, antigen is recognized by two distinct units of extremely variable receptor molecules the immunoglobulins that function antigen receptors on B cells and the antigen-specific receptors of T cells. As we noticed in Chapter 3, T cells acknowledge solely antigens which might be} displayed on cell surfaces. These antigens could derive from pathogens that replicate within cells, similar to viruses or intracellular bacteria, or from pathogens or their merchandise that cells internalize by endocytosis from the extracellular fluid. The two functional subsets of T cells are thereby activated to initiate the destruction of pathogens resident in these two completely different cellular compartments. The protective operate of T cells depends on by} their ability to acknowledge cells which might be} harboring pathogens or which have internalized pathogens or their merchandise.
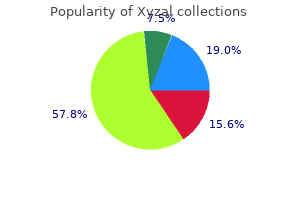
Proven 5mg xyzal
In animals uniparental reproduction has been invented repeatedly, but the asexual clones always turn into extinct after a comparatively brief time. Evolution favors traits that effectively transfer their underlying genes to future generations. Each sexually reproducing mother or father passes on solely one-half of its genes to its offspring. Sex is expensive phrases of|when it comes to|by means of} vitality, time and assets required to find a suitable mate. This applies not solely to dioecious populations, but additionally to hermaphrodites in which self-replication is often restricted. In many organisms, mating requires intimate contact between the two parents, which supplies a possibility for parasites, viruses and micro organism to move from one physique to one other. Bonner (1958) proposed the following widespread definition of sex: Sex is adaptation of oldsters to the potential assembly of their progeny with changed or uncommon circumstances. Different species, capable to asexual nicely as|in addition to} sexual reproduction, are often sexless, and solely underneath sure circumstances swap to sexual reproduction. For example, if there are quantity of} asexual and one sexual era within the life cycle, the final one occurs when two consecutive generations skilled the greatest ecological variations. When asexual and sexual reproduction both occur at the same time, the asexual progeny should develop instantly and near the parents, while progeny from sexual reproduction can have latency or disseminate far away from parents. At the same time they sexually produce seeds, which unfold far away and have lengthy latency. Many parasites are reproduced asexually in one host however sexually when altering hosts. Free residing decrease crops, animals and microorganisms, which frequently are reproduced asexually, and solely often use sexual reproduction, always swap to sexual reproduction in response to environmental adjustments. According to Bell (1982) sex is elicited in populations in which the density of organisms is high. Fisher (1930) was the first to propose that sexual reproduction appeared because of group choice. Moreover, he suggested that sexual reproduction is the only adaptation that appeared end result of|because of|on account of} group choice. He also thought of, that recombination course of could be defined without group choice. The drawback of the selection components liable for the appearance and preservation of sexual reproduction continues to be catching the C H A P T E R 1 W A Y S O F R E P R O D U C T I O N 3 attention of many researchers. Williams (1975) thought that the most important distinction between asexual and sexual offspring is that asexual progeny is standardized (produced end result of|because of|on account of} mitosis), while sexual progeny is diversified (because of meiosis). Because of their bigger size and low mobility, asexual progeny is positioned near the parents. Plants have seeds would possibly be} relatively small and have special features for broad spreadability. The same plant can produce different type of seeds with different latency from a month to many years. High seeds mortality is said to the dimensions (big seeds have more resources) and in addition with latency and broad distribution in space. At a proof of the mechanism of maintenance of sexual duplication with the help of group choice, he accepted, that asexual duplication (parthenogenesis) has a rapidly realized (short-term) benefit, and asserted that this momentary benefit overcomes long-term advantages of sexual reproduction. A short-term benefit of parthenogenesis means its double efficiency related to the absence of male progeny. A double enhance of pace of duplication for parthenogenesis may give advantages in circumstances of a inhabitants growth, when it explores model new} ecological niches. On this foundation Maynard Smith thought of, that new restatement of a question is necessary, namely, Why don`t parthenogenetic versions supersede species utilizing sexual reproduction Most authors nevertheless, continued to ask the question within the type of: "Why are some parthenogenetic species in a position to} exist a protracted time|for a really lengthy time} The same considerations give the answer to all questions related to the coexistence of different forms of reproduction. Williams examined the balanced coexistence of sexual and parthenogenetic methods of reproduction in populations with facultative parthenogenesis, at which people can multiply sexually, nicely as|in addition to} asexually. He got here to a conclusion that because of|as a outcome of} sexual reproduction continues to exist alongside with parthenogenesis, it also has some short-term advantages (Williams, 1975). Another benefit is that gene combinations created end result of|because of|on account of} mutations are transmitted from era to era without change. The disadvantage of asexual reproduction is that mutations are the only supply of diversity. One more disadvantage of asexual reproduction is that it lacks mechanism that prevents accumulation of dangerous mutations. Sexual recombination can remove mutations by crossing-over between chromosomes. Hypotheses and Theories Many shiny scientists have tried to decide the role of sexual reproduction in evolution-Weisman (1889), Goldschmidt (1927), Fisher (1930), M�ller (1932), Crow, Kimura (1965, 1970), Bodmer (1970), Eshel, Feldman (1970). During the previous 25-30 years hypotheses have turn into so numerous that their classification was required. Felsenstein (1988) and later Kondrashov (1993) proposed to divide them into two main teams: immediate benefit and variation and choice hypotheses. Detailed description of these hypotheses could be found in many of} critiques and monographs (Kondrashov, 1993; Michod, Levin, 1987; Ridley, 1994). The Lottery Principle was first suggested by Williams (1975) and makes use of a lottery analogy to illustrate diversity created end result of|because of|on account of} sexual reproduction. The other strategy could be to purchase a small number of tickets, however giving every of them a unique number. The Lottery C H A P T E R 1 W A Y S O F R E P R O D U C T I O N 5 Principle suggests that sex could be favored by a variable surroundings. However, in steady environments (such as within the tropics) sexual reproduction is most typical. Contrary, within the areas where circumstances are unstable (such as at high altitudes or in small ponds), asexual reproduction is rife. According to this principle sex accelerates evolution by combining beneficial mutations (Fisher, 1930; M�ller, 1932). In asexual populations beneficial mutations will compete with each other and only one would win. The chance that two beneficial mutations will appear in the same asexual particular person is very small. In sexual populations, nevertheless, different advantageous mutations can enhance at the same time if two organisms of the other sex with mutations A and B will produce offspring. With asexual reproduction, as soon as} an advantageous combination is achieved it will be to be|will probably be} saved and handed to the progeny. In small populations mutations occur much less often, so the time between beneficial mutations is longer. These mutations are unlikely to be current in the same inhabitants at the same time. For this cause sex has little impact on the rate of evolution in small populations. On the opposite, in large populations different beneficial mutations are likely to to|prone to} be current in vital numbers, so some of them probably be} brought together by mating. Therefore, in accordance with the idea, the benefit of sex should work better in large populations. However, the idea also assumes inhabitants level choice between sexual and asexual populations. Some scientists think that main function of sex is to create selection, so animals can defend themselves from parasites. Parasites are often adapted to assault probably the most widespread genotype and gene combinations confuse them. Carroll`s novel Through the Looking Glass who took Alice on a lengthy run that really went nowhere.
Diseases
- Hypospadias mental retardation Goldblatt type
- Progeroid syndrome De Barsy type
- Trisomy 6
- Craniometaphyseal dysplasia recessive type
- Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia
- Mental retardation macrocephaly coarse facies hypotonia
- Interstitial cystitis
- Glucose-6-phosphate translocase deficiency
- Plague, pharyngeal
- Cholestasis pigmentary retinopathy cleft palate
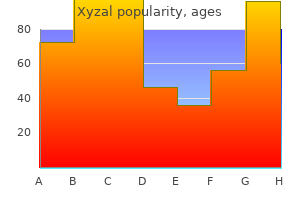
Cheap xyzal 5 mg
Antigens are outlined as any overseas substances that induce an immune system response. They embrace pathogenic microorganisms similar to bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, and most cancers cells. The immune system consists of organs, the innate (or nonspecific) immune system, and the adaptive immune system, which acknowledges and remembers antigens. The organs and cells concerned within the immune system kind a complex system during which antigens and immune system cells are constantly moving via the lymphatic and circulatory system and associated immune organs. Mechanisms of Defense There are two forms of immunity: innate (also called nonspecific) and adaptive. These embrace: Intact skin and epithelial surfaces that act as mechanical limitations Presence of regular microflora on the skin that compete with pathogens for vitamins and inhibit pathogen growth via lactic acid production Normal flora of the throat, colon, and vagina occupy receptors that forestall colonization by pathogens Secretions, all of which. The nose incorporates hairs that filter the upper airway, and the nasal passages, sinuses, trachea, and bigger bronchi are lined with cilia that elevate mucous-containing trapped organisms and sweep microorganisms upward from the lower airways. Second Line of Defense/Nonspecific or Innate Defenses When the first line of protection fails, the innate immune system consists of different components, which act as a second line of protection that limits growth of microorganisms within the physique. This is a system of plasma proteins (complement) that set off a cascade of reactions ensuing within the coating of pathogens and attacking of cell membranes, inflicting the pathogens to rupture. Complement also indicators basophils to launch the chemical histamine, which prompts irritation. Tertiary Defenses/Adaptive or Specific Immunity Adaptive immunity develops after exposure to an antigen, improves on repeated exposures, and is specific (Levinson, 2012). Adaptive immunity is mediated by antibodies may be} produced by B lymphocytes and two forms of T lymphocytes: helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells. Active immunity is resistance after contact with a overseas antigen similar to a microorganism. Passive immunity is resistance primarily based on antibodies that were "preformed" in one other host. Examples embrace the immunoglobulins handed from mom to fetus during being pregnant and the preformed antibodies given to treat a illness in the course of the incubation period. Risks and disadvantages embrace potential hypersensitivity reactions to the antibodies and short life span of such antibodies. The sorts and features of the leukocytes are listed in Table 2-2. Lymphocytes and Adaptive Immunity As talked about earlier, the B and T lymphocytes are concerned in adaptive immunity. There are two major branches of the adaptive immune response: humoral (antibody-mediated) immunity and cell-mediated immunity. Humoral immunity consists of the production of antibody molecules in response to an antigen. Mature B cells are present in bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, some areas of the intestine, and to a smaller extent within the bloodstream (Vizcarra, 2010). When stimulated by an antigen, they mature into plasma cells, which produce antibodies. The major features of those antibodies are to neutralize toxins and viruses and to make bacteria simpler to phagocytize (Levinson, 2012). There are 5 lessons of immunoglobulins: IgG: the most important immunoglobulin within the bloodstream; can enter the tissue areas and coat microorganisms to expedite their destruction by different immune cells; the one immunoglobulin that crosses the placenta and passes immunity on to the toddler. The absence of one or more of} of those substances has been linked to infection or illness processes. The cytotoxic T cells instantly destroy antigens; in addition they reply to overseas tissues within the physique, similar to a transplanted organ. They take away particles and worn out cells, and so they secrete monokines, which are an necessary chemical sign to the immune response. Cytokines embrace interferons, interleukins, and growth elements, which enhance the immune system, restore harm, and defend in opposition to infection (Vizcarra, 2010). Persons who purchase an infection due to a deficiency in any of their multifaceted host defenses are referred to as compromised hosts. Patients with immune dysfunction will typically exhibit the following characteristics: 1. Patients have incomplete response to remedy with out full elimination of the infecting agent. Immune System Disorders Disorders within the immune system consist of both an extreme immune response or a deficiency in response. In such instances, organic agents similar to monoclonal antibodies administered to suppress the immune system. Primary immune deficiencies outcome from an inborn defect within the cells of the immune system. Deficiencies within the immune response a congenital, acquired, or inherited immune dysfunction. Secondary immunodeficiencies come up from illness processes or therapies that decrease immune system organ or cell function. Proliferation and invasion of organisms lead to medical indicators and symptoms similar to irritation, drainage, or fever. Colonization is the presence of a microorganism on or inside physique websites without a a|with no} detectable host immune response, cellular harm, or medical symptoms (McGoldrick, 2010). A service (or colonized person) is an individual colonized with a selected microorganism and from whom the organism can be recovered however who reveals no indicators or symptoms of the presence of the microorganism. The service state transient (short term), intermediate (on occasion), or persistent (long time period, everlasting, or persistent). Dissemination is the shedding of microorganisms into the immediate environment from an individual carrying the microorganisms. Cultures of air samples, surfaces, and objects reveal dissemination or shedding of microorganisms. The threat of dissemination is generally higher from people with illness caused by that organism than from people with subclinical infection or those that are colonized with the organism. Chain of Infection Infections outcome from interaction between infectious agents and prone hosts. The chain of infection refers to six links that make up the chain: the causative agent or microorganism; the place where the organism naturally resides (reservoir); a portal of exit from the reservoir; a way (mode) of transmission; a portal of entry into a host; and the susceptibility of the host. To management infection, the chain of infection must be attacked at its weakest link (Figure 2-1). First Link: Causative Agent the first link within the chain of infection is the microbial agent or source, which can be a bacterium, fungus, virus, or parasite. The capability of an organism to induce illness recognized as} its virulence or invasiveness. The capability of microorganisms to induce illness is referred to as pathogenicity, and it could be assessed by way of disease/colonization ratios. Second Link: Reservoir All organisms have a reservoir, or source of microorganisms. The reservoir is where the organism maintains its presence, metabolizes, and replicates. Viruses survive better in human reservoirs, whereas the gram-negative bacteria may have human, animal, or inanimate reservoirs. Third Link: Portal of Exit from Reservoir the exit site is necessary in transmission of infection. Organisms from humans normally have a single portal of exit, however quantity of} portals of exit are potential. Fourth Link: Method (Mode) of Transmission After a microorganism leaves its source or reservoir, it requires a way of transmission to attain one other person or host via a receptive portal of entry. The first, direct switch of organisms, entails physique surface-to-body surface contact and physical switch of microorganisms between a prone host and an infected or colonized person. The second subgroup, indirect-contact transmission, entails contact of a prone host with a contaminated intermediate object, normally inanimate. Examples of organisms transmitted by way of contact are Staphylococcus and Enterococcus (Siegel, Rhinehart, Jackson, & Chiarello, 2007). The mechanism of switch of the pathogen to the host is completely different from that of contact transmission. Transmission by way of largeparticle droplets (>5 mm in size) requires shut contact between the source and recipient, normally three to 6 ft. Examples of pathogens transmitted by the droplet route are Bordetella pertussis and Neisseria meningitides (Siegel, Rhinehart, Jackson, & Chiarello, 2007). Airborne transmission: Airborne transmission occurs by dissemination of airborne droplet nuclei (small-particle residues, <5 �m) of evaporated droplets containing microorganisms that remain suspended within the air for long periods of time.
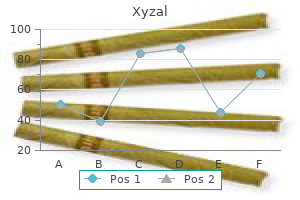
Order xyzal 5mg
Armed effector T cells differ in many ways from their naive precursors, and these changes equip them to respond rapidly and effectively when they encounter particular antigen on target cells. We will go away the activation of B cells by helper T cells till Chapter 9, where the humoral, or antibody-mediated, immune response is mentioned. That requires the simultaneous supply of a co-stimulatory signal by a specialized antigen-presenting cell. The most potent activators of naive T cells are mature dendritic cells and these are thought to provoke most, perhaps all, T-cell responses in vivo. Here they mature into cells that express excessive ranges of co-stimulatory molecules and the adhesion molecules that mediate interactions with the naive T cells frequently recirculating via these tissues. The activation and clonal enlargement of a naive T cell on initial encounter with antigen on the floor of an antigen-presenting cell is often known as priming, to distinguish it from the responses of armed effector T cells to antigen on their goal cells, and the responses of primed reminiscence T cells. T-cell responses are initiated in peripheral lymphoid organs by activated antigen-presenting cells. They occur in the organized peripheral lymphoid tissues via which naive T cells are frequently migrating. Pathogens or their merchandise are transported to lymphoid tissue in the lymph that drains the infected tissue, or, more not often, by the blood. All these lymphoid organs comprise cells specialized for capturing antigen and presenting it to T cells. The most important of those are the dendritic cells, which capture antigen on the website of an infection and then migrate to the downstream lymph node. The supply of antigen from a website of an infection to downstream lymphoid tissue and its subsequent presentation to naive T cells is actively aided by the innate immune response to an infection. As mentioned in Chapter 2, that is rapidly triggered on the website of an infection by nonclonotypic receptors that recognize molecular patterns would possibly be} related to pathogens however not host cells. One of the induced responses of innate immunity is an inflammatory reaction that increases the entry of plasma into the infected tissues and the consequent drainage of tissue fluids into the lymph. Another is the induced maturation of tissue dendritic cells which have been taking on particulate and soluble antigens on the website of an infection. These cells are activated via receptors that signal the presence of pathogen components sure by dendritic cell receptors, or by cytokines produced during the inflammatory response. The dendritic cells respond by migrating to the lymph node and expressing the co-stimulatory molecules would possibly be} required, along with antigen, for the activation of naive T cells. Macrophages, which are phagocytic cells discovered in the tissues and scattered all through lymphoid tissue, and B cells, which bind pathogen components, additionally be} similarly induced via nonspecific receptors to express co-stimulatory molecules and act as antigen-presenting cells. Thus the innate immune response to an infection hastens the transport of antigens to the local lymphoid tissue, and enables these cells which have taken up antigen to current it successfully to the naive T cells that migrate via this tissue. These immature cells are activated and go away the tissues to migrate via the lymphatics to secondary lymphoid tissues. Turley, reprinted with permission from Nature 388:787-792, �1997 Macmillan Magazines Limited. Dendritic cells are discovered all through the cortex of the lymph node in the T-cell areas. Macrophages are distributed all through however are primarily discovered in the marginal sinus, where the afferent lymph collects before percolating via the lymphoid tissue, and likewise in the medullary cords, where the efferent lymph collects before passing through the efferent lymphatics into the blood. The three forms of antigen-presenting cell are thought to be tailored to current sorts of|several sorts of|various kinds of} pathogen or merchandise of pathogens, however mature dendritic cells are by far the strongest activators of naive T cells. The distribution of dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells in a lymph node is proven in. These cells are named after their fingerlike processes, which form a community of branches among the many T cells. By the time they arrive in the lymph nodes, dendritic cells have lost their ability to capture new antigen. Macrophages are discovered in lots of} areas of the lymph node, particularly in the marginal sinus, where the afferent lymph enters the lymphoid tissue, and in the medullary cords, where the efferent lymph collects before flowing into the blood. As most pathogens are particulate, macrophages in the T-cell areas might stimulate immune responses to many sources of an infection. Finally, the B cells, which recirculate via the lymphoid tissues and focus in the lymphoid follicles, are notably environment friendly at taking on soluble antigens corresponding to bacterial toxins by the particular binding of antigen to the Bcell floor immunoglobulin. This is end result of|as a outcome of} only these with the appropriate receptor specificity can internalize and current a specific antigen at excessive frequency, and these might be very scarce. Thus, the likelihood of their encountering a naive T cell particular for a similar antigen may be very low. The antigen-presenting perform of dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells might be mentioned in more element in Sections 8-5 to 8-7. Only these three cell sorts express the specialized co-stimulatory molecules required to activate naive T cells; moreover, all of those cell sorts express these molecules only when suitably activated in the context of a response to an infection. Thus, as naive T cells migrate via peripheral lymphoid tissue, they receive survival indicators via their interactions with dendritic cells. This is essential for the initiation of an adaptive immune response, as only one naive T cell in 104-106 is doubtless to|prone to} be particular for a specific antigen, and adaptive immunity is dependent upon by} the activation and enlargement of such uncommon antigen-specific T cells. Naive T cells that recognize their antigen on the floor of a dendritic cell stop to migrate, and embark on the steps that generate armed effector cells. At the tip of this era, the armed effector T cells go away the lymphoid organ and reenter the bloodstream to migrate to websites of an infection. Naive T cells encounter antigen during their recirculation via peripheral lymphoid organs. Naive T cells recirculate via peripheral lymphoid organs, such as the lymph node proven here, entering via specialized areas of vascular endothelium known as excessive endothelial venules. On leaving the blood vessel, the T cells enter the deep cortex of the lymph node, where they encounter mature dendritic cells. T cells proven in blue encounter their particular antigen on the floor of an antigen-presenting cell and are activated to proliferate and to differentiate into armed effector T cells. These antigen-specific armed effector T cells, now increased a hundred-fold to a thousandfold in number, additionally go away the lymph node through the efferent lymphatics and enter the circulation. Lymphocyte migration, activation, and effector perform depend on cell-cell interactions mediated by celladhesion molecules. Similar interactions ultimately information the effector T cells into the peripheral tissues and play an important half of their interaction with goal cells. Binding of T cells to different cells is controlled by an array of adhesion molecules on the floor of the T lymphocyte that recognize a complementary array of adhesion molecules on the floor of the interacting cell. The major classes of adhesion molecule involved in lymphocyte interactions are the selectins, the integrins, members of the immunoglobulin superfamily, and a few mucinlike molecules. We have already encountered members of the first three classes in the recruitment of neutrophils and monocytes to websites of an infection during an innate immune response (see Section 2-22). Most adhesion molecules play pretty broad roles in the technology of immune responses. Many would possibly be} involved in lymphocyte migration and the interactions of armed effector T cells with their targets are additionally involved in interactions between different leukocytes. P-Selectin and E-selectin are expressed on the vascular endothelium at websites of an infection and serve to recruit effector cells into the tissues at these websites (see Sections 2-21 and 2-22). Selectins are cell-surface molecules with a standard core construction, distinguished from each other by the presence of various lectinlike domains of their extracellular portion (see. The lectin domains bind to particular sugar groups, and each selectin binds to a cell-surface carbohydrate. L-Selectin binds to the carbohydrate moiety, sulfated sialyl-Lewisx, of mucinlike molecules known as vascular addressins, which are expressed on the floor of vascular endothelial cells. L-Selectin and the mucinlike vascular addressins direct naive lymphocyte homing to lymphoid tissues. The members of the family proven limited to people who take part in inflammation and different innate immune mechanisms. The nomenclature of the totally different molecules in these families is complicated end result of|as a outcome of} it usually displays finest way|the way in which} in which the molecules have been first recognized somewhat than their related structural characteristics. For this, proteins from two different families the integrins and the immunoglobulin superfamily are required. These proteins additionally play a critical half in the subsequent interactions of lymphocytes with antigen-presenting cells and later with their goal cells. The integrins comprise a large household of cell-surface proteins that mediate adhesion between cells, and between cells and the extracellular matrix, in regular development nicely as|in addition to} in immune and inflammatory responses.
Safe xyzal 5mg
As we lack the power to specifically suppress the response to the graft with out compromising host protection, most transplants require generalized immunosuppression of the recipient. Tolerance to the fetus would possibly maintain the important thing} to inducing particular tolerance to grafted tissues, or it may be a particular case not applicable to organ alternative remedy. Tolerance to self is acquired by clonal deletion or inactivation of creating lymphocytes. Tolerance to antigens expressed by grafted tissues could be induced artificially, however it is rather troublesome to establish quickly as} a full repertoire of functional B and T lymphocytes has been produced, which happens throughout fetal life in people and around the time of delivery in mice. We have already discussed the 2 important mechanisms of self-tolerance clonal deletion by ubiquitous self antigens and clonal inactivation by tissue-specific antigens presented within the absence of co-stimulatory alerts (see Chapters 7-8). These processes have been first discovered by learning tolerance to nonself, where the absence of tolerance probably be} studied within the type of graft rejection. These mechanisms include direct induction of tolerance within the periphery, either by deletion or by anergy. There additionally be|can be} a state referred to as immunological ignorance, in which T cells or B cells coexist with antigen with out being affected by it. Finally, there are mechanisms of tolerance that involve T-cell-T-cell interactions, recognized variously as immune deviation or immune suppression. In an attempt to understand the related phenomena of autoimmunity and graft rejection, we also look at situations where tolerance to self is lost. We saw in Chapter 7 that clonal deletion removes immature T cells that acknowledge ubiquitous self antigens and in Chapter 8 that antigens expressed abundantly within the periphery induce anergy or clonal deletion in lymphocytes that encounter them on tissue cells. This state has been demonstrated experimentally using transgenic animals in which ovalbumin was expressed at high or very low concentrations within the pancreas. The lymphocytes transferred to animals expressing high ranges of ovalbumin proliferated in response to ovalbumin presented by antigen-presenting cells and then died. In the mice expressing high ranges of ovalbumin, these T cells have been proliferating, in distinction to mice expressing low ranges of ovalbumin, in which no proliferation was noticed. After 4 weeks, the spleens have been obtained, the ovalbumin-specific T cells have been enumerated and their spontaneous proliferation and proliferation in response to ovalbumin in vitro was assessed. At this time no ovalbumin-specific T cells have been recovered from the spleens of the mice expressing high ranges of ovalbumin, and there was no proliferative response to ovalbumin in vitro. Thus in these mice the ovalbumin-specific T cells divided early, after encounter with ovalbumin within the periphery, and then died, illustrating the phenomenon of peripheral tolerance by deletion. In distinction, within the mice expressing very low ranges of ovalbumin, the ovalbumin-specific T cells continued with out proliferating within the periphery, have been recovered from the spleen at 4 weeks, and responded normally to ovalbumin presented in vitro. Rather, the lymphocytes that mediate autoimmune responses appear to not be subject to clonal deletion or inactivation. The autoreactive receptor is present on each T cell, but the mice are wholesome until their T cells are activated. It most likely going} that solely a small fraction of proteins will be able to|be succesful of|have the power to} function autoantigens. Many self proteins are expressed at ranges too low to be detected even by effector T cells. It has been estimated that ready to} make approximately a hundred and five proteins of average size 300 amino acids, able to producing about three � 107 distinct self peptides. Thus, most peptides might be presented at ranges insufficient to have interaction effector T cells, whereas most of the peptides that may be} detected by T cells might be presented at a high sufficient level to induce clonal deletion or anergy. Autoreactivity most likely arises most frequently when the antigen is expressed selectively in a tissue, as is the case of insulin within the pancreas, quite than ubiquitously, as a result of|as a outcome of} tissue-specific antigens are less likely to to|prone to} induce clonal deletion of creating T cells within the thymus. Some ailments show a major bias within the intercourse ratio; this is taken to imply that intercourse hormones are concerned in pathogenesis. Consistent with this, the difference within the intercourse ratio in these ailments is best between the menarche and the menopause, when ranges of such hormones are highest. The induction of a tissue-specific response requires the presentation of antigen by antigenpresenting cells with co-stimulatory activity. As we realized in Chapter 8, solely antigen-presenting cells that specific co-stimulatory activity can provoke clonal expansion of T cells an important step in all adaptive immune responses, together with graft rejection and, presumably, autoimmunity. Antigenpresenting cells bearing both graft antigens and co-stimulatory activity travel to regional lymph nodes. Grafts depleted of antigen-presenting cells are tolerated for long periods, however are finally rejected. The initiation of graft rejection normally involves migration of donor antigen-presenting cells from the graft to local lymph nodes. After traveling to a lymph node, these antigen-presenting cells encounter recirculating naive T cells particular for graft antigens, and stimulate these T cells to divide. The resulting activated effector T cells migrate by way of the thoracic duct to the blood and residential to the grafted tissue, which they quickly destroy. Indirect recognition of the graft (bottom right panel) is mediated by T cells whose receptors are particular for allogeneic peptides derived from the grafted organ. To induce a response to tissue antigens, the antigen-presenting cell should specific co-stimulatory activity. As we saw in Chapters 2 and 8, the expression of co-stimulatory molecules in antigen-presenting cells is regulated to happen in response to infection. Experiments with transgenes show that the expression of overseas antigens in peripheral tissues can in some instances induce tolerance, whereas in different instances the overseas antigen appears to not be presented to naive T cells at a adequate level and is ignored (see. As discussed in Section 13-25, antigens unable to induce clonal anergy or deletion, however that can nonetheless act as targets for effector T cells, can function autoantigens; these antigens are likely to to|prone to} be tissue-specific and comparatively few. Transgenic mice have been developed that expressed ovalbumin within the pancreas at high or very low ranges. This silent persistence within the presence of low ranges of autoantigen illustrates the phenomenon of T-cell ignorance. Once an autoantigen is expressed on a cell with co-stimulatory potential, naive ignorant T cells particular for the autoantigen can turn into activated and might residence to the tissues, where they work together with their target antigens. At this stage, the absence of co-stimulatory molecules on tissue cells that present the autoantigen can once more limit the response. Armed effector T cells kill solely a restricted variety of antigen-expressing tissue cells if these lack co-stimulatory activity; after killing quantity of} targets, the effector cell dies. Therefore, in addition to the question of how autoimmunity is averted, we should ask: Why does it ever happen Dominant immune suppression could be demonstrated in fashions of tolerance and might affect on} the course of autoimmune disease. In some fashions of tolerance, could be} shown that particular T cells actively suppress the actions of different T cells that can trigger tissue damage. Tolerance in these instances is dominant in that could be} transferred by T cells, that are usually called suppressor T cells or regulatory T cells. Furthermore, depletion of the suppressor T cells leads to aggravated responses to self or graft antigens. Neonatal rats could be rendered tolerant to allogeneic skin grafts by prior injection of allogeneic bone marrow. This tolerance is very particular and could be transferred to normal adult recipient rats. This shows that tolerance on this mannequin is dominant and energetic, as the transferred cells prevent the lymphocytes of the recipient from mediating graft rejection. In order to switch this tolerance, cells of both the allogeneic graft donor and the neonatal tolerized host have to be transferred. Tolerance probably be} broken solely by alloreactive cells from an animal that had been immunized with cells from the allogeneic donor before switch; such cells most likely break tolerance by killing the allogeneic donor cells. The tolerance is specific for cells of the original donor, and so the suppression should even be particular. The observation that, when the background inhabitants of various T cells is lost, the mice develop an autoimmune disease means that this inhabitants contains cells normally able to suppressing the autoimmune disease. Such cells have been shown in an growing variety of autoimmune ailments, and their isolation as cloned T-cell traces is a major objective for individuals who research the induction of autoimmunity. The reason for this renewed curiosity in T cell-mediated regulation is that the intentional induction of such cells probably be} a major advance within the prevention of autoimmune disease. Depletion of those cells from the peripheral immune system of normal mice leads to the event of insulin-dependent diabetes, thyroiditis, and gastritis. This means that the insulin-specific T cells can suppress the activity of different autoaggressive T cells in an antigen-dependent manner. They do that by homing to the islet, where they react with insulin peptides presented on the macrophages or dendritic cells. This means that, within the normal course of the disease, particular T cells defend the -cells from attack by effector T cells and the disease subsequently progresses slowly.
Renshen (Ginseng, Panax). Xyzal.
- Thinking and memory.
- Dosing considerations for Ginseng, Panax.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Premature ejaculation when a cream containing ginseng and other ingredients is applied directly to the skin of the penis.
- Improving athletic performance.
- What other names is Ginseng, Panax known by?
- How does Ginseng, Panax work?
- Depression, anemia, fluid retention, stomach inflammation and other digestive problems, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), fibromyalgia, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, skin cancer, fever, bronchitis, cancer, common cold, influenza, and other conditions.
- Improving mood and sense of well-being.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96961
Order xyzal 5 mg
The effect of early nutritional supplementation with a mix of probiotic, prebiotic, fiber and micronutrients in infants with acute diarrhea in Indonesia. Effect of a lactose-containing sweetener on root dentine demineralization in situ. Clinical trial of residence available, blended diets versus a lactose-free, soy-protein method for the dietary management of acute childhood diarrhea. Diagnostic worth of a lymphocyte stimulation take a look at in cow milk protein intolerance. Nutrient consumption and haematological status of vegetarians and age-sex matched omnivores. One hundred cases of recurrent belly pain in children: diagnostic procedures and standards for a psychosomatic prognosis. A double-blind managed medical trial of mastic and placebo in the treatment of duodenal ulcer. The effect of inositol supplements on the psoriasis of patients taking lithium: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Effect of fermentation on lactose, glucose, and galactose content material in milk and suitability of fermented milk products for lactose illiberal people. Lactose malabsorption in the aged: function of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Results from two repeated 5 day dietary information with a 1 y interval among patients with colorectal polyps. Effects of caffeine and tryptophan on rectal temperature, metabolism, total train time, rate of perceived exertion and heart rate. Brazilian journal of medical and organic analysis = Revista brasileira de pesquisas m�dicas e biol�gicas / Sociedade Brasileira de Biof�sica. A quantitative model for prediction of iron bioavailability from Indian meals: an experimental examine. Four cases of long-standing diarrhoea and colic pains cured by fructose-free diet-a pathogenetic discussion. Cows milk consumption in constipation and anal fissure in infants and young children. Low birth-weight infants fed a brand new} carbohydrate-free method with different sugars. Minimization of gastric injury with enteric-coated aspirin granules in comparison with} buffered aspirin. Suppression of histamine-induced pruritus by hydroxyzine and various neuroleptics. Glucose and insulin responses to meals containing milk, lactose, glucose or fructose in topics with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Tolerance and absorption of lactose from milk and yogurt during short-bowel syndrome in people. The exercise of three different small-intestinal galactosidases in adults with and with out lactase deficiency. Contribution of each enzyme to the total lactase exercise in regular and lactose-intolerant patients. Intestinal beta-galactosidases in adult low lactase exercise and in congenital lactase deficiency. Perspectives on consumption of calcium-rich foods among Asian, Hispanic, and white preadolescent and adolescent females. Dietary zinc consumption of vegetarian and nonvegetarian patients with anorexia nervosa. Letter: Intestinal lactase deficiency as a factor in the diarrhea of light-treated jaundiced infants. The application of the "Lojda" method for intestinal lactase in intestinal biopsies from jaundiced new child infants. Intestinal lactase deficiency in newborns with cystic fibrosis- dietary consequences. Blood and urine acid-base status of premenopausal omnivorous and vegetarian women. Consumption of animal foods and endometrial cancer danger: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Effective discount of lactose maldigestion in preschool children by direct addition of beta-galactosidases to milk at mealtime. Test-retest reproducibility of hydrogen breath take a look at for lactose maldigestion in preschool children. A randomised trial of oral gammaglobulin in lowbirth-weight infants infected with rotavirus. Breath hydrogen excretion in regular new child infants in response to usual feeding patterns: evidence for "practical lactase insufficiency" past the first month of life. Roentgenographic observation of gas-fluid levels in the colon of kids with belly pain and malabsorption of lactose. Mucosal operate and breath hydrogen excretion: comparative research in the medical evaluation of kids with nonspecific belly complaints. Effects of method change on intestinal hydrogen manufacturing and crying and fussing habits. A new method for the detection of hydrogen in breath and its application to acquired and inborn sugar malabsorption. Inhaled lactose-free sodium cromoglycate powder in the treatment of recurrent asthma. Effects of oral administration of androstenedione on plasma androgens in young women utilizing hormonal contraception. Biochemical indices and neuromuscular operate exams in rural Gambian schoolchildren given a riboflavin, or multivitamin plus iron, supplement. Recurrent belly pain outcome of} milk and lactose intolerance in school-aged children. Sugar absorption by small bowel biopsy samples from patients with main lactase deficiency and with adult celiac disease. Vegetarian food plan components, protein and blood stress: which nutrients are essential Clinical and experimental allergy: journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology Vol 26; 1996: 96-103. Km defect in neuraminidase of dysmorphic sort sialidosis with and with out beta-galactosidase deficiency. Hydrogen focus in expired air analyzed with a brand new} hydrogen sensor, plasma glucose rise, and symptoms of lactose intolerance after oral administration of 100 gram lactose. Experience from a prospective investigation of suspected malabsorption in children 1968 1976 in Malmo. A boy with severe childish gastrogen lactose intolerance and purchased lactase deficiency. Milk, dairy fat, dietary calcium, and weight acquire: a longitudinal examine of adolescents. The effect of preemptive and/or postoperative ibuprofen therapy for orthodontic pain. American journal of orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics: official publication of the American Association of Orthodontists, its constituent societies, and the American Board of Orthodontics Vol one hundred twenty; 2001: 20-7. A cross-sectional survey of sensitization to Aspergillus oryzae-derived lactase in pharmaceutical employees. Quantitative evaluation of complete physique galactose metabolism in galactosemic patients. Dietary intakes of urban and rural pregnant, lactating and non-pregnant, non-lactating vegetarian women of Varanasi. Efficacy of milk-based diets in persistent diarrhea: a randomized, managed trial. Reference values of urinary electrolyte excretion in respect of a vegetarian food plan. Lactose intolerance in persistent diarrhoea during childhood: the function of a conventional rice-lentil (Khitchri) and yogurt food plan in nutritional management. The tolerability of quantity of} oral doses of Pulsincapregistered trade mark capsules in wholesome volunteers.
Best 5mg xyzal
Natural energetic (choice D) immunity would end result after a recovery from an an infection. The child receives preformed antibodies (IgG across the placenta and IgA in milk), which serve to defend the kid until a pure energetic immune response may be mounted. Their expression is genetically decided, and variations can be used as evidence in favor of paternity in some instances. Allotypic markers are most regularly utilized in studies of inhabitants genetics, as sure ethnic teams are doubtless to|prone to} have similar allotypic markers on their immunoglobulins. The term "idiotype" (choice B) describes the 3-dimensional form of the antigen-combining site of an antibody or T-cell receptor molecule. Because all normal human beings produce some quantity of this immunoglobulin, it will not be useful in paternity instances. An isotype (choice E) is discovered within the heavy- or light-chain fixed domains of an immunoglobulin. Thus, there are 5 heavy-chain isotypes (A, E, G, M, and D) and two light-chain isotypes (and). Because all human beings produce heavy- and light-chain isotypes, is ready to|this may} not be useful in paternity testing. Although this vaccine is no longer in use because of the potential unwanted side effects} of Bordetella pertussis inoculation, in this case the whole, killed micro organism served as an adjuvant. They elevated local inflammation, thus calling inflammatory cells to the location and prolonging publicity to the immunogen, the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus. The mitogens most commonly utilized in medical laboratory medication are lipopolysaccharide, concanavalin A, and pokeweed mitogen. This is a case of DiGeorge syndrome, which is a congenital failure within the formation of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches. As a end result, people with this defect have aplastic thymus and parathyroids and facial, esophageal, and cardiac malformations. Immunologically, the absence of the thymus will finally have world effects on the event of all T-cell�mediated immune responses. At delivery, the kid will have IgG antibodies which have been transplacentally transferred from the mom, but by 9 months or so after delivery, these will be gone and IgM would be the solely isotype of immunoglobulin current. Phagocytic killing will be normal until that time, although after all of the maternal IgG is gone, opsonization of micro organism will no longer be potential. Cellularity of splenic periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths (choice B) will be decreased in this child these are T-cell�dependent areas of the spleen. The proliferative response to concanavalin A (choice E) will be depressed in this child concanavalin A is a T-cell mitogen. It is caused by a mutation in a tyrosine kinase gene, which is essential in B-cell maturation. Persons with this situation are unable to mount a standard antibody response; due to this fact, symptoms seem after the disappearance of maternal antibodies. Common variable hypogammaglobulinemia (choice B) is a situation that usually seems within the late teens or early twenties. It is believed to be an autoimmune illness and is associated with the disappearance of immunoglobulin isotypes over time. These infants have facial abnormalities, failure of formation of the parathyroids, and cardiac defects, nicely as|in addition to} absence of T-lymphocyte growth. Selective IgA deficiency is commonest of those and would manifest as elevated susceptibility to mucosal-surface pathogens. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (choice E) is a fancy immune deficiency with a triad of symptoms: eczema, thrombocytopenia, and immunodeficiency. These patients are susceptible to growth of malignant lymphomas and have lack of ability to respond to polysaccharide antigens. Unusual frequency or severity of Neisseria infections ought to all the time result in a suspicion of a terminal complement part deficiency (C5, C6, C7, or C8). Neisseria seems to be extremely susceptible to complement-mediated lysis, so any failure of production of the membrane assault advanced predisposes the affected person to recurrent bacteremias with these organisms. Common variable immunodeficiency (choice A) is a situation that usually seems within the late teens or early twenties. It is believed to be an 166 Immunology Practice Questions autoimmune illness and is associated with the disappearance of immunoglobulin isotypes over time. Diagnosed in infancy, these people have facial abnormalities, failure of formation of the parathyroids, and cardiac defects, nicely as|in addition to} an absence of T-lymphocyte growth. Selective IgA deficiency (choice D) would be expected to end in respiratory and gastrointestinal tract infections, autoimmune illness, and allergy symptoms. Severe mixed immunodeficiency (choice E) usually presents with early susceptibility to viral and fungal brokers. It is most regularly identified in infancy, after the disappearance of maternally derived IgG antibodies. The description of painful belly edema and edema within the oral mucosa are typical of hereditary angioedema. Abnormal superoxide anion production by neutrophils (choice A) would end in predisposition to infections with extracellular pathogens. Abnormal T-cell operate (choice B) would end in predisposition to infections with viral and fungal pathogens, not edema of the mucosal surfaces. Abnormal T-cell numbers (choice C) would end in predisposition to infections with viral and fungal pathogens, not edema of the mucosal surfaces. Defective neutrophil chemotaxis (choice D) would end in neutrophilia and failure to produce pus and abscesses in response to extracellular bacterial invasion. Adenosine deaminase deficiency (choice A) produces a severe mixed immunodeficiency. The infections seen are doubtless to|prone to} be T-cell deficiency (viral and fungal agents). In the absence of adenosine deaminase, deoxyadenosine phosphate builds up in T cells and is poisonous to them. It is absent within the situation known as as|often recognized as} hereditary angioedema, represented by recurrent, painful bouts of mucosal edema. The normal counterpart of the mutant gene encodes a protein tyrosine kinase (Bruton tyrosine kinase, Btk), which is essential in B-cell signaling. Thus, the bone marrow becomes hypercellular, whereas the peripheral blood is lacking mature B lymphocytes. Persons with this situation are unable to mount a standard antibody response; due to this fact, symptoms seem after the disappearance of maternal antibodies, and susceptibility to extracellular, encapsulated pathogens such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae is profound. When this enzyme is absent, poisonous metabolites build up in B and T lymphocytes and cause a basic failure of the immune response. It would have medical manifestations of each B- and T-lymphocyte defects, and not solely B lymphocytes, as described in this case historical past. Patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome show a triad of signs: thrombocytopenia, eczema, and immunodeficiency. It is often identified by the finding of depressed ranges of complement part C4 within the blood. Other descriptions that might apply would be that it has two chains of similar size, is produced with an invariant chain, and is designed to current overseas peptides to Th cells. It has an chain with 3 domains, and a smaller chain, 2 microglobulin, becomes associated with the chain. Because the response to poison ivy is a delayed-type hypersensitivity response and due to this fact is mediated by Th1 cells and macrophages, inhibiting their activity would reduce the severity of the response. It inhibits the proliferation of Th2 cells and due to this fact would skew the immune response towards a more potent cell-mediated arm. Atopic allergy (choice B) is a sort I hypersensitivity, mediated by IgE antibodies and mast cells. In these instances, antibody binds to cells or tissues of the physique and elicits complement activation in these areas. The description within the vignette is a sort I hypersensitivity response the only kind of hypersensitivity could be} manifested in minutes.

Proven 5 mg xyzal
In common, all hemolytic anemias may be categorized into considered one of two teams (Figure 4�5). The frequent medical and laboratory characteristics of these problems are given in Table 4�5. These subtypes are Type A and Type B, depending on their electrophoretic mobility. These people have clinically gentle circumstances but may be affected by oxidants to produce a hemolytic crisis. These sufferers are more susceptible to extreme oxidant hemolysis than are Type A people. Acute posthemorrhagic anemia, caused by a sudden blood loss, first results in early hypovolemia with none signs of anemia. With reticulocytosis, the anemia could also be} macrocytic with polychromasia caused by shift reticulocytosis. Cell constructions that take up acid stains are identified as|often recognized as} acidophilic or eosinophilic. Acidophilia may end up} from the following errors in method: (a) Insufficient staining time (b) Prolonged washing time (c) Excessive acidity of the stain or buffer B. Promyelocytes are the second stage following one or more of} mitotic divisions of myeloblasts. The myelocyte stage of maturation begins with the looks of a brand new} type of granulocyte-specific granule. These granules (secondary granules) give the mature granulocyte its attribute look and functional future. Therefore, the maturation of the myelocyte, which is predicated on granule type, provides rise to neutrophils, eosinophils, or basophils. Phagocytic perform includes the following common steps: (1) Increase in cell numbers at the infected website (2) Cell attachment to the overseas or dead materials (3) Engulfment of overseas or dead materials (4) Dissolving of overseas or dead materials (5) Disposition of catabolic elements b. Well-known chemotactic factors are activated complement C3b and C5a, lymphocyte secretions, and bacterial products, such as endotoxins or bradykinin. Engulfed materials is roofed by internalized surface membrane, which types a phagosome. Degranulation is the process by which Table 4�8 Morphology of Monocyte Maturation Nucleus Shape Chromatin Nucleoli Normal Range in Cytoplasm Peripheral Staining Granules Blood Stage Cell Size N�C Ratio Monoblast 12�20 m four:1 Promonocyte 15�20 m three:1 Round with Smooth folding and clefting Oval, Delicate indented, or folded Slightly condensed 1�2 obvious Deeply basophilic Faint None None Monocyte 14�20 m 2:1�1:1 Variable Obscure Basophilic Few with a frosted look Few Blue-gray with a frosted look; typically vacuolated None 3%�7% or 120�800/ mm3 148 A Concise Review of Clinical Laboratory Science Figure 4�6 the process of peroxidation. Granulopoiesis is controlled by glycoproteins isolated from lymphocytes and monocytes. Tissue destruction or damage Figure 4�7 Algorithm demonstrating the differential prognosis of the nonmalignant granulocytic problems. Granulocytopenia occurs with a reduction of absolutely the rely to lower than 3000/mm3. Neutropenia outcomes from the following physiologic mechanisms: (1) Decreased flow of neutrophils from marrow caused by decreased or ineffective production (Figure 4�7) (2) Increased removal of neutrophils from the blood. Granulocytosis refers to an absolute enhance within the concentration of circulating leukocytes higher than normal for a sure age. Myeloid development factors are also launched to stimulate the marrow to enhance production. This results in a neutrophilia, a shift to the left, and a decrease in eosinophils. The complete number of granulocytes decreases, and the total number of monocytes increases. Disorders and circumstances that show eosinophilia embody the following: (a) Allergic illnesses (b) Skin problems (c) Parasitic infections. Monocytosis is commonly noticed in the course of the recovery section of infections and in various myeloproliferative illnesses. Congenital and acquired qualitative problems of neutrophils can have an effect on} both the cytoplasm or the nucleus. This dysfunction must be differentiated from the hypersegmentation of megaloblastic anemia. Monocyte-macrophage qualitative abnormalities are uncommon, autosomal recessive lipid-storage illnesses. This leads to the production of lipid-heavy and blocked foamy macrophages, which stimulate further macrophage production and lead to an growth of the monocyte-macrophage system. Leukemia is a relatively frequent dysfunction with roughly seven new cases per a hundred,000 inhabitants reported annually within the United States. Leukemia may be defined as a generalized abnormal neoplastic proliferation or accumulation of hemopoietic cells within the bone marrow, organs, and the peripheral blood. Clinical classifications (1) Acute leukemias are refractory to remission, often fatal inside three months, and show a bone marrow full of primitive cells. The common precept of most cytochemical stains is to incubate cells on a blood smear with a substrate that reacts with an intracellular marker. In enzymatic procedures, the reaction product is coupled with a diazonium salt. As the cell matures from the promyelocyte stage to the mature segmented neutrophil, every stage is generally more optimistic. Esterase cytochemical stains embody both particular or nonspecific esterase pro- cedures. The addition of sodium fluoride to the incubation answer inhibits the staining reaction in monocytes but not in granulocytes. Acid phosphatase cytochemical staining is helpful for confirming a prognosis of hairy-cell leukemia and for differentiating a T-lymphocytic leukemia from a Blymphocytic leukemia. A complete of a hundred mature neutrophils are scored from 0 (negative) to four (strongly positive), primarily based upon the depth of the staining reaction. Reference values are often within the vary of 20 to 200, although every hospital often establishes its own normal vary. Myeloproliferative problems are a group of closely related illnesses characterized by the spontaneous proliferation of erythroid, granulocyte, monocyte, or megakaryocyte precursors within the marrow. Myeloproliferative problems are clonal in origin, having arisen from a single pluripotential hemapoietic stem cell. Cytogenetic abnormalities are frequent to most myeloproliferative problems (Table 4�10). Chronic myeloproliferative problems embody a group of leukemias that share a standard stem cell lesion and are gradual of their medical course. However, this group is characterized by the following: a bigger proportion of children, not nearly as good as good} a response to remedy, and a shorter survival. It is characterized by a predominance of megakaryocytic proliferation within the marrow. Thrombocythemia has a stable course a couple of of} years}, but may develop into different myeloproliferative problems. Mutations have been generally discovered on chromosome 5, but also have been noted on chromosomes 7, 8, 12, and 20. The blood has a better percentage of monocytes than the marrow, and the commonest type of cell is the promonocyte. Mainly, solely the erythroblast stage of maturation is seen within the erythroid marrow. This type differs from chloroma solely within the absence of the inexperienced pigment discovered within the tumor. Other immature myeloid precursor cells are often involved, and their ranges are elevated within the blood and marrow. This dysfunction must be distinguished from hypereosinophilic syndrome seen with parasitic an infection. The identification of immature types within the blood and a rise of eosinophils within the marrow of >5% assist diagnose eosinophilic leukemia. The pool of undifferentiated stem cells is situated within the bursa-equivalent tissue of the bone marrow, the place proliferation and maturation occurs. Secondary lymphoid tissues contain mixed T-cell and B-cell populations; these tissues are discovered within the spleen, lymph nodes, and gut-associated lymphoid tissue. From a morphologic basis, lymphocyte growth consists of three recognized stages.
Quality 5mg xyzal
These persons could make solely IgM, and this affected person clearly has efficiently produced IgA. It due to this fact not directly reduces cytokine production by Th1 cells and dampens the activation of the cell-mediated arm of the immune response. It acts on inflammatory cells to a hundred and sixty Immunology Practice Questions induce cytokine secretion and causes the cachexia associated with persistent inflammation. The class I molecule is a two-chain construction, with one long chain that passes by way of the mobile membrane and a shorter chain known as 2 microglobulin that becomes associated with the chain. It is composed of an and a chain of comparable lengths, each of which have transmembrane domains. Other parameters that could be be} depressed embody immune responses to intracellular pathogens and secondary antibody responses. Therefore, following thymic irradiation, decreased cellularity of these areas would occur. This is a cell-mediated reaction brought on by sensitization of Th1 cells and demonstrated by the inflow and activation of macrophages in response to the cytokines that they elaborate. Neutrophils are the necessary cells in abscess formation, not granuloma formation. The objective of this therapy is to present an elevated inhabitants of activated antigen-presenting cells primed with tumor cell antigens so that these can be offered to the Th cells involved in stimulation of cell-mediated immunity. The Th1 cell is the first cell listed which would be activated by such a remedy. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (choice B) would be not directly stimulated by this remedy. Cytokines secreted by the activated Th1 cells would have the impact of accelerating the quantity and cytotoxic activity of killer cells. The protecting response to the tetanus toxoid depends on by} production of antibodies that stop the binding of the toxin. After repeated immunizations, the inhabitants of memory B cells is stimulated, which is the objective of such prophylaxis. Memory B cells might have IgG, IgA, or often IgE on their surfaces serving as antigen receptors. This is because of|as a result of} IgM, which is the immunoglobulin of the primary immune response and is the receptor on mature naive B lymphocytes, is replaced in secondary and subsequent responses by isotype switching to different isotypes similar to IgG or IgA or IgE. The secondary and subsequent responses ought to have elevated affinity (goodness-of-fit of idiotype for epitope), however decreased avidity. As quickly as the primary response begins, isotype switching to different lessons of immunoglobulin is directed by Th cells. Because rabies antitoxin is a pooled, human immunoglobulin product, repeated inoculation will trigger a affected person to produce anti-allotype antibodies. Allotypes are minor amino-acid sequence variations within the constant domains of heavy and lightweight immunoglobulin chains. Their expression is genetically decided, and repeated exposure to molecules of international allotype could cause antibodies to be produced which acknowledge these sequence variations. Anti-epitope antibodies (choice B) would be produced by repeated inoculation of an immunogen. The epitope of the antigen has a three-dimensional complementarity with the idiotype of the antibody molecule. In this case, anti-epitope antibodies would be generated by rabies vaccination, however the question asks what repeated exposure to immunoglobulins would be. Anti-idiotype antibodies (choice C) would be generated in a human if a monoclonal antibody preparation were repeatedly inoculated. The idiotype of an antibody is the three-dimensional shape of its antigen-combining site. Because the material mentioned on this case is a pooled human immunoglobulin, it would contain many alternative idiotypes and would be unlikely to elicit any one specific anti-idiotype antibody. For example, to produce anti-human IgG, IgG pooled from many humans is repeatedly injected into rabbits, goats, or sheep. These animals will acknowledge the human determinants within the constant domains of the heavy and lightweight chains (the isotypes) and can produce antibodies that specifically acknowledge these determinants. When the killed virus is run, the affected person makes an lively, artificial response to the immunogen and produces immunoglobulins, which is able to} shield against virus attachment. This type of immunization causes the event of memory within the affected person that will shield for the entire season, but it requires approximately two weeks for growth of protection. Artificial passive (choice C) immunity is achieved when preformed immunologic merchandise (immune cells or antibodies) are given to a affected person. Natural lively (choice D) immunity would result following recovery from an an infection. Natural passive (choice E) immunity is acquired throughout the placenta and within the colostrum and breast milk, from mom to youngster. The youngster receives preformed antibodies (IgG throughout the placenta and IgA in milk) that shield the kid until a natural lively immune response can be mounted. In this case, an attempt at postexposure prophylaxis against tetanus is made by inoculating antitetanus immunoglobulin into the affected person. Adaptive (choice A) immunity describes all immune responses which have specificity and memory. Because this affected person is being given a product of the adaptive immune response (antibodies), there shall be no elicitation of an adaptive immune response on this particular person. Artificial lively (choice B) immunity is produced during the process of vaccination. These are IgE-mediated responses and are an necessary protecting response against helminth parasites that migrate by way of the tissues. After the sensitizing exposure, symptoms of kind of|this kind of|this type of} hypersensitivity will occur in forty eight to seventy two hours (not minutes, as described here). These hypersensitivities develop when antigen is added to pre-existing antibody and immune complexes are filtered out of the circulation within the small vasculature. In this vignette, the killing is occurring within the pores and skin and is related within minutes with stinging, itching, and urticaria. This is the one form of transplantation that will succeed without immunosuppression. The lowest stimulation index (and the lowest quantity of proliferation) is proven between sibling 1 and the potential recipient, each when the donor cells are used as stimulators and as responders. This means (most importantly) that the recipient will make little response to the graft and (less importantly, except in graft-versus-host disease) that the donor will make little response against the recipient. The endogenous pyrogen is responsible for alteration of the hypothalamic temperature set point throughout acute inflammatory occasions. It is produced by Th cells and causes proliferation of many lessons of lymphocytes. It is a product of Th2 cells and inhibits Th1 cells; thus, it inhibits the cellmediated arm of the immune response. It might act instantly on tumor cells to trigger their necrosis and decrease angiogenesis. It is a product of Th1 cells that stimulates the effector cells of cellmediated immunity. Serum from the take a look at subjects is added, adopted by antihuman-immunoglobulin, which is labeled with an enzyme. When the substrate for the enzyme is added, if the antibodies listed have certain in sequence, there shall be a colour change in that microtiter properly. If the kid is developing hemolytic disease of the new child, then his erythrocytes will already be coated with maternal antiRh antibodies. If the mom is sensitized, she is making IgG antibodies of the identical specificity. This is a take a look at used to determine if the mom is making IgG anti-Rh antibodies, which could cross the placenta and hurt a fetus. It is critical within the direct and oblique Coombs tests because of|as a result of} in these cases, one is in search of IgG antibodies that could be be} transported throughout the placenta to hurt an unborn youngster. It will bind to the Fc portion of any human IgG molecule, regardless of its antigenic specificity.
Trusted xyzal 5mg
Carbohydrates are polyhydroxyl aldehydes or ketones that, on hydrolysis, yield certainly one of these compounds. Carbohydrates are a significant supply of energy for the body, and starch is the most important supply of carbohydrate. Monosaccharides are easy sugars that contain four to eight carbons and only one aldehyde or ketone group. Oligosaccharides are formed by the interplay of two monosaccharides with the lack of a water molecule and are generally referred to as disaccharides. Salivary amylase breaks down ingested starches into disaccharides, and these are further broken down into monosaccharides by disaccharides and absorbed into intestinal cells. Some glucose is released into the blood, and the remaining is stored as glycogen within the liver and skeletal muscle. Glycogenesis is the method of glycogen formation by enzyme motion on glucose to ultimately type glycogen. Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen, with the eventual formation of glucose-6-phosphate or free glucose that can be utilized for energy production. Gluconeogenesis is the formation of glucose from amino acids and lipids that happens when carbohydrate consumption decreases. Insulin, which is a pancreatic hormone that decreases glucose levels by growing mobile uptake of glucose and selling glycogenesis and lipogenesis (formation of fats from carbohydrates) b. Glucagon, which is a pancreatic hormone that will increase glucose levels by stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis c. Thyroid hormones, which stimulate glycogenolysis and increase blood glucose levels 22 A Concise Review of Clinical Laboratory Science 4. Hyperglycemia happens when the fasting blood sugar degree rises larger than a hundred and ten mg/dL because of of} a pathologic dysfunction, corresponding to diabetes mellitus or liver failure. This usually happens as a result of|because of|on account of} hormone deficiency, drug reaction, insulin excess (as in insulinoma), or a genetic dysfunction. Glycosuria (sugar within the urine) happens when the renal threshold for glucose is exceeded (160�180 mg/dL) throughout hyperglycemia. Diabetes mellitus is a genetic dysfunction of glucose metabolism that ends in insulin deficiency and lack of carbohydrate tolerance. There are two classifications: (1) Type 1, previously insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. This sort is brought on by an autoimmune destruction of pancreatic cells and is normally juvenile onset. This is a multifactorial disease with potential causes together with genetics, environment (lifestyle), and autoimmunity. One reason for onset is believed to be mobile resistance to insulin or decreased insulin receptors on cell surfaces. Most individuals with this dysfunction are obese or obese, and onset is often throughout adulthood. Glucose is oxidized to gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide to ultimately type a coloured product. Falsely low results are brought on by high serum levels of uric acid, bilirubin, or ascorbic acid. Falsely elevated glucose values are obtained by interference of mannose and galactose, whereas bilirubin induces a false decrease in glucose values. Glycated hemoglobins are formed when a glucose is hooked up to the N-terminal valine residue of both chain of the hemoglobin A molecule. Hemoglobin A1 (made up of a number of} minor hemoglobins) is termed a fast hemoglobin based on its electrophoretic migration. Glycated hemoglobin is separated from nonglycated hemoglobin by affinity chromatography. Interferences embody the presence of hemoglobin S and hemoglobin F and will produce increased or decreased glycated hemoglobin values depending on the precise methodology used. It is useful in evaluating pregnancy-induced diabetes and involves drawing a fasting blood specimen, followed by affected person ingestion of a 75-g oral dose of glucose in liquid within a 5-minute period. Blood samples are then taken at 30-, 60-, 120-, and 180-minute intervals and examined for glucose. Lipids are substances which might be} insoluble in water and could be extracted from cells solely by organic solvents. Fats are carboxylic esters derived from glycerol and are recognized as|also called|also referred to as} glycerides. Triglycerides comprise 98% of fats found in meals and are made up of 95% fatty acid and 5% glycerol. Fatty acids are lengthy carbon chains joined by single (saturated) or double bonds (unsaturated) and a terminal carboxyl group. The remaining 2% of fats in meals consists of ldl cholesterol, phospholipids, diglycerides, fat-soluble nutritional vitamins, steroids, and terpenes. Triglycerides are digested by lipase, other enzymes, bile salts, and acid within the intestine to type monoglycerides and diglycerides. Absorptive part happens within the small intestine as triglycerides and ldl cholesterol within the micelles are absorbed and broken down into fatty acids. Transport part happens as lengthy fatty acids reassemble into chylomicrons (watersoluble macromolecules) and enter the lymphatic system. Short fatty acids enter the blood sure to albumin, and these head to all tissues, together with adipose tissue. Cholesterol is a sterol (steroid with lengthy aspect chains), which is a four-ringed structure made in liver hepatocytes from two acetate models. Cholesterol is a vital constituent of cell membranes and a precursor of many hormones. Triglyceride is made up of fatty acids and glycerol and is partly synthesized within the liver hepatocyte. Phospholipids make up the bilayer of cell membranes and also type a coating that surrounds ldl cholesterol and triglyceride and "glues" them to the lipoprotein core. Sphingolipids are necessary in cell membrane composition and in nerve transmission. Lipoproteins are transport automobiles for lipids that contain varying quantities of particular lipid, phospholipid, and apoprotein. They originate within the intestinal tract and travel by way of the blood and lymph to numerous tissues. They are taken into cells through a particular cell-surface receptor- the apoprotein B (apoB) receptor-and are degraded into part parts. Lipid problems normally result in abnormal lipid deposits on partitions of vasculature (atherosclerosis) and skin (xanthomas). Hyperlipidemia (1) Triglyceride levels are most affected by food regimen, but high triglyceride levels are sometimes brought on by diabetes or pancreatitis. Hyperlipoproteinemia involves an increase in sure lipoproteins due to improper synthesis or breakdown of lipoprotein fractions. Total ldl cholesterol evaluation involves both: (1) Formation of free ldl cholesterol, which is oxidized to type hydrogen peroxide, which then reacts with a dye to type a coloured product (2) Selective oxygen electrode, which measures the speed of oxygen consumption when an enzyme particular for ldl cholesterol is added to serum b. Vitamins are organic molecules required by the body in small quantities for regular metabolism. Most are obtained from the food regimen; some are formed endogenously; others are produced by the intestine. The best understood physiology of vitamin A is within the visual system; a scarcity of vitamin A leads to night blindness. Vitamin D is crucial for bone mineralization and neuromuscular exercise, and some types act to regulate uptake of calcium and phosphate. A lack of vitamin D leads to rickets (failure of bones to calcify) or osteomalacia (abnormal bone synthesis). Vitamin E (-tocopherol) is on the market solely from dietary consumption and accumulates within the liver, adipose tissue, and muscle. Vitamin E is critical for regular neurologic structure and function, and also features as an antioxidant by stopping formation of free radicals. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is absorbed within the stomach and distributed to all tissues. It is a potent lowering agent, features within the synthesis of collagen, and aids within the biosynthesis of some neurotransmitters.
References:
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/018829s022lbl.pdf
- http://www.cdpho.org/files/CHAPTER%2010%20-%20Respiratory%20with%20Answers.pdf
- https://www.fulltextarchive.com/pdfs/Roget-s-Thesaurus-of-English-Words-and.pdf
- https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/82379379.pdf
.png)