Best 5ml zaditor
This entails transferring away from a preoccupation with staff,Дф rights in employment and instead prioritising the need to|the necessity to} cut back unemployment (Gill et al. This shift displays the affect of those who see certain features of the present framework of employment rights and social protections within the member states as contributing to unemployment and hindering the creation of jobs (see European Commission, 1999b: 20). Thus, when discussing the need for member states to create,Дтthe conditions during which the flexible agency can exist,Дф, it advocates,Дтreforming, the place needed, the foundations governing contractual relationships,Дф between employer and worker. This offers the prospect of regulations to positive that|be positive that},Дтflexible staff,Дф share the same rights in employment as,Дтstandard,Дф staff. In the sunshine of this, some analysts have suggested that ought to always|we should always} not interpret the adjustments as a easy transfer path of|in direction of} deregulation of labour markets and society. Rather than a straightforward transfer to deregulation, analysts have noticed an attempt at reregulation of labour markets and society (Gill et al. Indeed, there additionally be} extra state intervention in some areas, similar to coaching, to improve financial performance and compensate for market failure. Social safety and employment rights are beneath strain from European competitors law and from the perceived have to cut back costs so as to to} maintain international competitiveness (Barnard and Deakin, 1998). Such pressures appear to be reflected within the bias of most National Action Plans path of|in direction of} the,Дтemployability,Дф and,Дтentrepreneurship,Дф pillars, with much less being carried out to address issues of,Дтadaptability,Дф and,Дтgender equality,Дф (Goetschy, 2002: 408). Thirdly, the technique has been seen as redefining European social coverage increasingly in terms of|when it comes to|by way of} employment coverage. This redefinition has been described as a shift away from the standard view of the welfare state during which social coverage and welfare may be seen as independent of the economy (Pierson et al. In the standard view, social rights and social safety are seen to be desirable in themselves and have a tendency to be based on a redistributive ethic. That is, taxation of the higher off should finance social advantages for off as well as|in addition to} paying for communal companies similar to well being, training and pensions. It replaces it with the concept of the,Дтworkfare state,Дф, during which social coverage is subsumed within, and subordinated to , the needs of the aggressive economy. Rather than emphasising redistribution of income and the supply of tax-financed advantages to assist the deprived in society, the workfare state emphasises insurance policies aimed toward equipping and encouraging and, if want be, forcing deprived individuals to be active producers, both as workers or as selfemployed entrepreneurs. Since the Nineteen Eighties there was a growing tendency among member states to restrict their monetary obligations to their residents, especially the less nicely off. This is reflected in reductions within the relative 656 Chapter 16 ¬ Human resource administration and Europe worth of minimum wages, social safety advantages and pensions by slicing the link with average earnings (Standing, 1999). In basic, two positions have been taken: that of the optimists, and that of the pessimists. Optimists see this as another opportunity for additional convergence and harmonisation of financial and social coverage within the wake of the single European market of 1992 and within the spirit of the Amsterdam Treaty. Barnard and Deakin (1999) see these developments as an try and lock member states into a path of financial growth based on financial convergence round tight budgetary controls and the upkeep of price stability. However, if financial difficulties had been to arise, then there could nicely be serious implications for European social and employment coverage. It is worried with eliminating the gender gaps and the development of a social infrastructure to enable higher reconciliation between household life and working life. It additionally be|can be} involved with creating a framework to reply to the demographic adjustments that shape financial and social life. She concedes Germany,Дфs labour market and social net do want reforming, a process which started with the return of Chancellor Gerhard Schroder,Дфs new authorities in September,Д¶ Source: Financial Times, 12 November 2002, p. How does the reportage of her views illustrate the controversy over labour market regulation within Europe? The principle of equal therapy for women and men was embodied within the Treaty of Rome 1957, and is one the 12 provisions of the Social Charter (see above). As Leat (1998) states, there are three types of equality, each of which varies in terms of|when it comes to|by way of} progress path of|in direction of} implementation:,уи,уи,уи Equality of opportunity may embody pre-work expertise and circumstance as well as|in addition to} alternatives to compete for work and for advancement within a specific employment organisation. Equality of therapy may embody such issues because the allocation of duties, working conditions, issues of harassment and conditions governing dismissal. Equality of end result is more likely to|prone to} embody issues of pay and other substantive terms and conditions of employment, as well as|in addition to} quotas of the working population. For example, oblique discrimination was demonstrated within the Bilka-Kaufhaus judgment. This deemed that the exclusion of part-time staff from an organization pension scheme (made up primarily of girls workers) was oblique discrimination. Positive motion projects, while creating spaces for women and being laboratories for the development of excellent follow, appear to be precariously funded, provision is advert hoc, and there are few linkages to mainstream suppliers. It is mainstreaming which is more likely to|prone to} have probably the most vital influence on creating girls,Дфs abilities and the rigidities of gender segregation within the labour market. It also has the potential capability to transfer past gender into other dimensions of equality, similar to race and disability. How that is achieved is determined by} initiatives to assist the individual, the organisation and the economy,Дм a theme running through Part 3 of this book. Britain has strongly advocated a neo-liberalist position over the previous 20 years: successive governments have adopted a voluntarist method, which encouraged quite than compelled organisations and individuals to train. Germany, Sweden and France, by the Social Charter 659 contrast, have advocated extra obligatory initiatives, together with laws to increase levels of coaching. Neo-liberalists declare that the persistence of excessive unemployment levels in lots of} European nations testifies to the failure of those obligatory initiatives (Addison and Siebert, 1991; Marsland, 1991). Success has been combined in the past, with the much-vaunted German twin system (see Chapter 9) receiving a considerable degree of praise and attention, but Leat (1998) means that,Дтattempts to instantly transpose the German arrangements to member states with different traditions, cultures and perhaps even different production techniques and techniques may not be not|will not be} at all successful,Дф (p. The twin system in Germany and the reliance on inner markets in French and Italian firms have been successful but only these who|for many who|for individuals who} have employment. The core problem of transferring the unemployed, and in particular the long-term unemployed, into work has proved extra problematic in these economies. Regini (1995) has drawn attention to the range of methods that firms use to achieve aggressive advantage, ranging through types of flexible mass production (or mass customisation) to flexible specialisation, neoFordism, diversified quality production and the standard small agency. Each would require its own mix of abilities, and can in turn impose its own explicit demands on the labour market, but on the same time shall be topic to the characteristics of the present provide of labour nationally and locally (Leat, 1998: 240). Social dialogue is seen for example of a neo-corporatist method to policy-making. The concept of social dialogue within the European Community goes back to the 1960s and Seventies but was undeveloped at that time. Measures to promote social partnership and social dialogue 1985,Дм2001 Measures to promote social dialogue had been developed through the Nineteen Eighties and 1990s so as to to} stimulate progress path of|in direction of} an built-in European Social Policy. It offered for Joint Committees consisting of representatives of the social companions to be appointed by the Commission as required, and for Informal Working Parties to be established on a voluntary basis by the Social Partners themselves. The protocol process aimed to strengthen social dialogue through:,Дм A process whereby the Commission has to seek the advice of} the Social Partners formally before presenting legislative proposals to the Council of Ministers. These can then be implemented through national collective bargaining procedures or else the Social Partners can ask the Commission to put the agreement as a proposal for decision by the Council of Ministers. The Joint Committees and Informal Working Parties established beneath the Val Duchesse process had been abolished in 1998 and changed by Sectoral Dialogue Committees. This is an try and encourage the Social Partners to negotiate extra binding sectoral framework agreements rather than non-binding joint opinions that required subsequent laws. At the Lisbon Summit it was determined that the Social Partners should play a extra active position within the growth and implementation of the European Employment Strategy. These are modernisation of labor organisation, and enhancing the contribution of lifelong coaching and studying to employee adaptability. The Social Charter 661,уи the effectiveness of social dialogue mechanisms the proof on the effectiveness of mechanisms to promote social dialogue is combined. Some have argued that the protocol process launched in 1991 has had little effect in strengthening social dialogue. Social Partners themselves have reservations regarding European Community Agreements. Sectoral Dialogue Committees so far comprise the old Joint Committees and Informal Working Parties in model new} guise,Дм old wine in new bottles. The outcomes of social dialogue because the that} 1991 protocol process have been limited, with only three successful framework agreements being reached during 1991,Дм9. Also, the regulatory drive of those agreements has been weak, with agreements containing many exemptions and opening clauses, allowing member states successfully to choose out of them.
Buy zaditor 5 ml
Their primary enforcement activities, after persuasion has not achieved the specified results, is to issue enchancment notices and prohibition notices. Improvement notices are issued the place the inspector is satisfied there was a contravention of a statutory provision. The enchancment discover will give the employer a certain time within which that contravention should be remedied. A prohibition discover, which suggests the work should immediately stop, is issued when the inspector considers that the exercise entails a danger of great personal security or of a extreme security hazard to the workers or the public public}. Around 15,000 notices are issued every year and the data of such notices are on public view for as much as} three years, offering a deterrent to security transgressors. Unsafe or unhealthy office Inspector visits Inspector points discover Inspector advises or warns Inspector prosecutes for breach of statutory duty Prohibition discover Improvement discover Follow-up visit Failure to comply leads to prosecution Fine or imprisonment Figure eleven. The function of the protection officer is to make sure that|be certain that} the protection requirements imposed by laws are met by the organisation. Safety representatives are appointed or elected by the workers, either instantly or via their trade union. They should be recognised by employers, involved in the session course of via a security committee and given reasonable paid time off work} to carry out their duties along with basic services, such as utilization of} a telephone and a filing cupboard. Their rights extend to visiting other companies to look at their security methods (see Spotlight on the law eleven. Healey made several of} visits to that grocery store and made approaches to the grocery store supervisor. Excel considered that the approaches Healey made to the supervisor quantity to gross misconduct and he was dismissed. Most employers of a reasonable measurement accomplish that with out such a request, seeing it as an essential vehicle for joint investigation and enchancment. Membership often consists of the protection representatives, the protection officer, administration (in the type of the plant, upkeep or operations managers) the human assets officer and, in larger organisations, the corporate nurse or occupational health officer. Agenda objects can embrace: Reporting and evaluation of accidents and dangerous occurrences. Discussion of stories on particular accidents, together with contacts with manufacturing unit inspectors. Investigation into protected methods of labor, together with general aspects, such as noise, temperature and use of protective equipment. There are three primary stages in the process of assessing and controlling dangers: Identifying hazards (the potential causes of harm). Assessing dangers (the likelihood of hurt occurring and its severity) and prioritising motion. Observation via, say, an everyday security tour of the plant by the protection officer and security representatives for the areas, will convey to light poor housekeeping, such as accumulated rubbish or blocked fire exits, security equipment not being worn and poor lighting or ventilation. Such hazards have to be considered as much for workers who may conscious of|concentrate on|pay consideration to} the risks but additionally for visitors to the positioning and particularly new employees who could possibly be} younger and be utterly unaware of potential dangers. Longer investigations by trained technicians or by external companies additionally be} essential to investigate the hazards of air pollution, noise or noxious fumes and their diploma of hazard or to decide the place, if in any respect, smoking may be allowed on the premises. Long-term tasks might be wanted to identify hazards in planned adjustments via new equipment, equipment, supplies and lay-outs. A correct investigation right here will involve the suppliers of the equipment, equipment and the supplies. Fowler (1995) set out a three-part score scale for danger assessment (see Figure eleven. Using such a score scale supplies a consistent method to identifying hazards and in addition supplies help with prioritising security motion. Where there are budgetary limits, the total hazard score supplies a league desk of necessary motion the place those with the highest points get tackled first. Tightening up on housekeeping procedures ought to make the positioning cleaner, tidier and, therefore, safer. Supplying higher protective equipment will serve to avoid the likelihood of harm to persons exposed to the chance. Re-designing the manufacturing processes or layouts via such improvements as separating the operator from the chance by enclosing the method, using remote-control equipment, enhancing guarding and increasing extraction methods are all priceless funding phrases of|when it comes to|by way of} hazard prevention. Automating lifting processes may also have a big effect on the incidences of employees injuring their backs, although fork-lift vans and other units additionally supplies an extra supply of potential hazard which must be assessed. It is essential, therefore, that organisations have set out policies and procedures which help them to obtain a fair balance and is in a position to} highlight actions that they have to take speedily. Encouraging employees to live and work in a healthy environment is as essential as making certain that the office is a protected environment. Employers need to take care, for example, over their smoking coverage as shown in Spotlight on the law eleven. After a evaluate, smoking was banned in her office but permitted in adjoining workplaces but she found this nonetheless unsatisfactory as ventilation in her office was poor and smoke nonetheless drifted in. The tribunal upheld her claim, ruling that the employers had been in breach of an implied time period in her contract, namely a duty to provide and preserve a working environment that was moderately tolerable to all employees. They pointed out that it might have been practicable for all smoking to be banned. Chapter eleven Health, security and welfare 427 Physical provision A start line is for the organisation to provide the suitable medical services, given the nature of the enterprise. In a big manufacturing or distribution website with over a thousand employees, these services would come with a dedicated medical centre, trained for emergency care and quick first aid and run by qualified medical employees; common first aid coaching classes and a well-monitored methods of first aid provision in all areas of the positioning; common screening for workers who take care of any hazardous substances and voluntary screening for other illnesses; medicals for all new employees. Occupational stress Stress has become one of the severe health issues of current years. The number of work-related stress cases reaching the courts has increased from 516 in 2002 to 6428 in 2003 (Palmer and Quinn, 2004); one hundred fifty,000 employees take minimal of|no less than} 1 month off for illnesses brought on by stress at work. Employees aged between 34 and 44 suffer essentially the most, whereas the issues worsen the longer they stay in the identical job. They are related to perceptions of job insecurity, increase in work depth, aggressive administration kinds, lack of effective office communication, overt or insidious bullying and harassment, faulty choice for promotion or transfer and lack of steerage and coaching (Cartwright and Cooper, 1997). Employees additionally be} exposed to conditions which they find uncomfortable, such as regularly coping with customers, excessive pc work, repetitive or fragmented work or having to make common public presentations. Probably the commonest cause, however, is the fixed concern of organisational change via re-structuring, takeovers, mergers or enterprise course of re-engineering. A lack of management over their work, their environment or their profession progression stressful (Rick et al. Irritation, hostility, anxiety and a state of panic can arise in the office with knock-on results on working practices and relationships between employees. The employer who neglects the issue of occupational stress may face legal motion. The first legal breakthrough for an employee was John Walker, a social work supervisor with Northumberland County Council who, having had a mental breakdown arising from his occupation, returned to his job but acquired no positive help from his employer to help him to cope efficiently. The judge held that right here was no logical reason why the chance of psychiatric harm must be excluded from the scope of the duty of care and the chance of an extra breakdown was moderately foreseeable. Organisational issues A coaching want A relationship drawback Workload or tempo Loss of motivation Physical issues Physical illness Design of workstation Noise/lighting Violent attack at work Psychological issues Anxiety/depression Phobias/panic attacks Anger administration Addictive behaviours alcoholism, gambling Social issues Housing issues Relationship difficulties Financial issues Legal issues divorce, custody or crime Figure eleven. In a later case, Birmingham City Council admitted legal responsibility for private harm brought on by stress the place they moved a 39-year-old senior draughtsman to the publish of a neighbourhood housing officer with out adequate coaching. The nature of the work was so different and the inter-personal demands so great that she had lengthy intervals of ill-health leading to early retirement on medical grounds. The court docket held that an employer was entitled to assume that an employee was capable of to} withstand the normal pressures of the job and to take what the employee mentioned about her personal health at face worth. It was only if there have been indications which would lead a reasonable employer to realise that there was an issue that a duty to take motion would arise. In terms of whether or not the harm to health was foreseeable, elements that must be taken under consideration embrace whether or not: the workload was abnormally heavy. All of these cases show that employers need to fastidiously contemplate the way way|the way in which} that the work demands result on} their employees and make sure that|be certain that} they investigate every case, taking applicable motion to ameliorate doubtlessly health damaging conditions (Earnshaw and Cooper, 1996). It is a certain sign of a sympathetic and caring employer who will make special provision for the non-public and particular person needs of employees. Usage rates by employees are in the region of 48% tons of|and a lot of} are open to their relatives. The kinds of services provided embrace: A confidential telephone help-line for private emergencies. Workshops to help employees who have to cope with elderly relatives, marital breakdowns or monetary pressures. Assistance in coping with a work-related traumatic occasion, such as a significant fire or an armed theft.
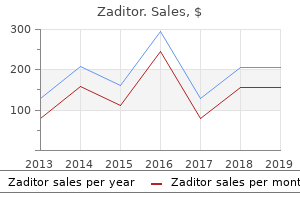
Buy 5 ml zaditor
We can see these differences fairly clearly in relation to the reactions of nationwide airways to the occasions of 11 September 2001. A combination of negotiated reductions in working hours and wages, cancellation of choices for new spanking new|for brand new} models and the cancellation of some routes maintained employment ranges over the short term. The lesser presence of shareholder value pressures combined with more coordinated institutional responses led by the French, German and Spanish states protected employment throughout the sector, as did more coordinated responses in European works councils, see Clark et al. As Hall and Soskice (2001) concede and as Broadberry (1997) and Clark (2000) reveal, each types of market financial system are capable of providing passable ranges of long-run financial efficiency, but with different patterns of distribution in civil society. However, the predominant patterns of distribution and corporate technique will differ, as will degrees of innovation. Equally, fairness markets provide for prepared funds for venture capital and patterns of corporate organisation are more fluid whereby corporations may be broken down into smaller customer-focused trading models,Дм reengineered, downsized and so forth. This sample of market regulation tends to create radical patterns of innovation, for example the fast growth and proliferation of low-cost airways, the dot-com funding revolution and fast changes of corporate ownership more usually. For instance, during the past six years, Go Fly was a subsidiary of British Airways, then an independent operator ensuing from a administration buyout and is now part of of} the easyJet group. As Hall and Soskice (2001) argue, if each market type is capable of sustaining passable ranges of financial efficiency it should be the case that the patterns of institutional routine and regulation (market or non-market) in several systems of production create frequent expectations in the face of criticism of nationwide regimes. In each case the different type of financial system is more likely to|prone to} modify its own systems of institutional regulation so as to to} sustain respective patterns of competitive advantage. [newline]This suggests that the pressures of globalisation are unlikely necessarily to transform nationwide business systems. Hence nationwide business systems and associated approaches to the administration of commercial relations and human resources could remain distinctive inside the global business system. In this part the traditionally embedded features of four business systems are briefly detailed and summarised phrases of|when it comes to|by way of} the arguments developed by Lane (1995), Whitley (2000) and Hall and Soskice (2001). The empirical and historical specification of the features of capitalist improvement in the four business systems is offered in summary bullet-point kind and in each case draws on substantive works on this issue by Best (1990), Chandler (1977, 1990) and Lazonick (1991). While Best and Chandler concentrate on institutional features that distinguish business systems, Lazonick examines these differences phrases of|when it comes to|by way of} patterns of commercial dominance and decline within business systems. The bullet-point summaries establish traditionally embedded institutional features in the four business systems, the effects of which remain important in the contemporary operation of each business system, and their respective systems for industrial relations and the administration of human resources. Complex coordination of production chains, early deployment of scientific administration techniques. Emphasis on large-scale quantity mass production, standardised goods for mass markets,Дм some debate on the extent of mass production and its significance in the contemporary period. Vertically integrated large corporations are likely to|are inclined to} out-compete smaller specialist suppliers by growing specialist buying and supply contracts with suppliers to scale back unit prices but retain profitability. Earlier, this course of saw the emergence in the automobile sector of three large corporations, Chrysler, Ford and General Motors, a course of replicated plenty of} other sectors corresponding to railroads, plane manufacturing, steel and so forth. Significant administration management over production or emotional labour in the supply of providers with systematic mechanisation, deskilling and management procedures. Arm,Дфs-length market relations dominate within and between capital, labour and the state. Whitley: Institutional actors coordinate by market relations, organisational capabilities developed and maintained by professional administration. Institutional pluralism, beyond the market very restricted, contemporary focus of business system shorttermism and shareholder value. Hall and Soskice: Liberal market financial system, highly developed inventory and capital markets reinforce market relations and institutional separation. In addition, the British business system reveals a thriving small to medium size enterprise sector that reprises most of the traditionally embedded features summarised beneath. Firms traditionally undertook low funding in new expertise and labour saving expertise. Industry traditionally seen as regionally and regionally concentrated; important function was single plant operations, for example local breweries. Arm,Дфs-length relationships between institutional actors,Дм market coordination between actors. Since the Second World War, manufacturing trade dominated by defence-related trade and aerospace sector. Networks of local cartels, growth of corporations regionally and nationally by merger and acquisition. Hall and Soskice: Liberal market financial system, capable of radical innovation; however, comparatively low degree of institutional regulation in capital and labour markets, education and vocational training usually prevents efficient implementation and longer-term operation of corporate strategies. The traditionally embedded features listed beneath have been challenged by defeat in the First World War and occupation after the Second World War and again by reunification in 1989. Large managerial hierarchies; however, important ranges of household management and share ownership in manufacturing trade. Integrated production chains, contemporary focus on to},Дтdiversified quality production,Дф. System is production oriented with administration and labour integrated round productive tasks. Credit-based funding funds, integrated institutional relationships between monetary institutions and trade, combined with lesser focus on to} shareholder value and institutional buyers, create longer-term funding and payback horizons. Education and vocational training system highly developed and nationally certificated. Whitley: Significant degree of institutional pluralism, especially in industrial relations system; energetic institutional regulation by the central and local state acts as a constraint on shorttermist inclinations of capital. Hall and Soskice: Coordinated market financial system, sustained competitive advantage in manufacturing sector, reveals incremental change and innovation. Japan,Дфs feudal system was characterised by two parts each of which has a bearing on the method of profitable industrialisation, significantly in the period since 1945. Diligence and selfsacrifice epitomised by the mason-like samurai are embedded features of Japanese society which have been reinvented as cultural and institutional explanations for Japanese financial success. The presence of devoted, diligent and collectively oriented but not oppositional workers has led some observers to argue that the Japanese business system reveals each mutuality and highdependency relations within and between institutional actors representing the interests of capital, labour and the state, a sample of relations clearly absent in the British business system (see Oliver and Wilkinson, 1988). In addition to the importance of cultural and historical elements that successfully incorporate workers within capitalist production relations, Japanese financial success in the postwar period can also be|can be} attributable to a technique of organising of production, centred on a system of versatile mass production, the Kanban system of just-in-time production pioneered by Kiichiro Toyoda (see Wada and Shiba, 2000 and Chapter sixteen for more details). Just-in-time systems produce precise, defect-free portions just in time for the following stage of production. Fujitsi and Mitsubishi, plan for wider industrial groups and are in a position to} exercise strategic alternative in finding labour-intensive manufacturing and meeting work within smaller corporations. Permanent employment standing for some workers operates as a coordinated and planned training system; promotion and rewards based mostly on seniority. Hall and Soskice: Coordinated market financial system, important institutional regulation beyond the market. Active state role in finance provision and promotion of inter-firm cooperation reduces market uncertainty and promotes cooperation within hierarchies and between them. The traits and institutional approaches within systems,Дм market, individualist and separate or nonmarket collectivist and integrated,Дм change solely slowly. The evidence suggests that business systems retain many institutional traits even when topic to dramatic interventions corresponding to those skilled by Germany and Japan following Allied occupation and reconstruction following the Second World War. Further, globalisation, while for some representing the harbinger of convergence between business systems, has but to undermine the divergent nature of nationwide business systems. This part therefore explores how the differences in nationwide business systems explored in the first part of of} the chapter create differences in human useful resource practices between different societies. Subsequent analysis has found important differences, even between European Union countries, in areas as central to the employment relationship as recruitment (Windolf, 1986; Quack et al. The issue of part-time employment is of explicit curiosity here for a number of|numerous|a variety of} reasons. Firstly, for employers, utilizing part-timers is regularly seen as a technique of matching labour supply and demand on a temporal foundation. Second, the rationale that} early Nineteen Nineties, increasing the extent of part-time employment has been promoted by the European Commission as a means of combating unemployment (Commission of the European Communities, 1993). There are thus, at least of|no less than} apparently, sturdy reasons to imagine that this practice may need turn out to be more popular throughout the European Union. In Spain, in the meantime, the extent of part-time employment, although increasing, remains very low by European Union requirements. Furthermore, the differences between countries go beyond differences in the extent to which a given practice is used.
| Comparative prices of Zaditor | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | PetSmart | 373 |
| 2 | Defense Commissary Agy. | 676 |
| 3 | Williams-Sonoma | 658 |
| 4 | Nordstrom | 606 |
| 5 | Trader Joe's | 139 |
| 6 | GameStop | 178 |
| 7 | Sears Holdings | 909 |
| 8 | WinCo Foods | 291 |
| 9 | Ingles Markets | 501 |
Trusted zaditor 5ml
Quality is controlled by a visual inspection and electronic checks, which also trace the person liable for the fault. This information, along with information on absenteeism, conformity to commonplace instances and manufacturing planning targets, is prominently displayed for all the group to see. Naturally, the knowledge varieties the premise of a lot discussion between group members. This is a type of what Friedman (1977) called accountable autonomy, a state of affairs by which the group acts because the controller of the person and therefore the group. First, the schemes had been slender in conception and,Дтbolted-on to somewhat than integrated in, key management insurance policies,Дф (Wilkinson et al. As a end result, some schemes looked related to|similar to} quality circles and thus had many of their faults. Companies tended to search for instant gains somewhat than long-term cultural modifications. In turn this created an obsession with,Дтthe value of quality and immediacy of return, concepts which are completely different from Japanese thinking,Дф (p. Second, the position of center managers became unclear and confused, and was looked upon as one group of managers imposing itself on one other. Similar to the findings of Sewell and Wilkinson, it was discovered that there was a contradiction in the language of employee involvement (empowerment of the workforce, etc. International aspects of employee involvement 565 Recent crucial studies of the,Дтquality,Дф motion have drawn attention to its wider implications. They continue by stating that,Дтquality initiatives are sometimes imposed upon an unprepared and hesitant, if not hostile, management by the intensity of (global) competitive pressures,Дф. Most are confined to office areas, and therefore are likely to|are inclined to} be restricted in their sphere of management. Their significance is central in Scandinavian nations, particularly Sweden, and so they still carry appreciable weight in Germany and Britain, though the rise in long-term unemployment and the decline in the old staple industries such as shipbuilding, coal, iron and steel, and engineering, the place unionism had a robust traditional base, have tended to erode their energy. Employee involvement rooted in industrial democratic processes has witnessed a surer development over the previous 30 years in legislatively supported systems such as co-determination in Germany and Sweden. The foundation of commercial democracy in the nation stretches again to 1948 with the organising of the National Labour Market Board. This was composed of representatives from labour, employers and government, and participated in financial planning. The aim of the Act was to extend the scope of collective bargaining to areas of management policy, including organisational and technical change. It required all employers to allow consultation with workers and the participation of their representatives in decision- 566 Chapter 14 ¬ Employee involvement and empowerment making at each board and shopfloor ranges. In actuality, employee representatives in the co-determination system are likely to|are inclined to} be union representatives, and it was the unions in Sweden that gave the impetus for a lot of the drive in the direction of|in course of} industrial democracy. The union strategy was to problems with well being and safety, and,Дтthis created a political local weather by which new laws and laws in support of commercial democracy could be be} launched. Volvo in particular launched job enlargement and job enrichment,Дтquality of working life,Дф techniques to its Kalmar plant in the Seventies, and became the focus target|the main focus} of a lot attention worldwide as various to|an various alternative to|a substitute for} the mass-assembly Fordist systems of manufacturing (Sell, 1988). Conversely, left-wing critics have attacked the system for not addressing the real needs Figure 14. Some observers recommend that these tendencies may finally undermine the formal system of participation (Cressey, 1992). What is definite is that the change in the financial local weather in the early 1990s recession, elevating unemployment from 1. Despite reality that|the fact that} management prerogatives in Sweden still outweigh these of the worker, the tradition of involvement continues to be very nicely developed in contrast with most other nations. Codetermination operates basically at firm and plant ranges, although there are three strategies by which employees can take part: works councils, supervisory boards and management boards. In places of labor that have five or more workers the workforce elects a works council, consisting of employees,Дф representatives solely. The works council has a proper to information concerning:,уи,уи,уи,уи,уи well being and safety; the organisation of labor; the working setting and jobs; the hiring of executives; planned modifications in the firm that could end in appreciable disadvantages to workers. In addition, the works council has the right to make suggestions (Gaugler and Wiltz, 1992):,уи,уи,уи through the formulation and implementation of personnel planning; concerning vocational coaching (apprenticeships, etc. For larger firms (not family owned) using greater than 500 people, representatives elected by the employees sit on the supervisory board, the place they make up one-third to a half (depending on size) of the policymaking body. Other board members are elected by the shareholders, and a impartial chairperson is appointed. In firms over 2000 workers in measurement, commerce union representatives are assured places on the board. German employees are likely to|are inclined to} imagine that generally the works councils and codetermination system represent them adequately, and there has been a reluctance to be part of unions (35 per cent versus Sweden,Дфs union density of eighty five per cent), although the recession in the early 1990s witnessed a revival of commerce union militancy. The supervisory board meets four instances a yr, and likewise appoints members to the management board, a full-time govt body that oversees firm policy in its dayto-day operations. These are of course influenced by political ideology, place in the organisation (whether management or worker etc. Lane (1989), in her survey of research analysing the affect of co-determination in Germany, points to the range of findings depending on the level (whether office or enterprise), firm measurement, sector and managerial style. Not surprisingly, co-determination at enterprise level has had comparatively little impression on the an everyday basis} work of workers, however, it may be} argued, has had the long-term optimistic effect of engendering a spirit of cooperation between management and labour. Labour representatives perceive more clearly the reasons for managerial policy initiatives, and conversely the management have more understanding of the considerations of the workforce. For instance, Wilpert and Rayley (1983) showed that there was a big discrepancy between formal rights and precise rights of participation. They also state that, whereas participation rights in Germany are high in contrast with most other European nations, so too is formal and precise managerial management. Not surprisingly, there are German employers who share the view of previous British Conservative governments that the co-determination system undermines the employer,Дфs proper to handle. Survey evidence suggests, nonetheless, that works councils are supported by the overwhelming majority of employers, except in the smallest of corporations (Mauritz, 1972, quoted in Lane, 1989: 233). Works councils bolstered by legislation also exist in Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, Spain and the Netherlands, but the vary of points and choices submitted for employee approval is smaller than in Germany. The operation of the councils affected by employee and management attitudes certain up with the institutions and tradition of the nation. For instance, the Auroux Laws 1982 extended employees,Дф participation rights in French firms, however research reveals that the consultation course of has been ignored or undermined by management accustomed to the hierarchical and sometimes autocratic ways International aspects of employee involvement 569 strongly emphasised (although changing) in many of} French organisations (Lane, 1989: 240). In Sweden there has been a lot criticism of the comparatively weak place of unions in the co-determinational course of, significantly in time of recession (Korpi, 1981; Kjellberg, 1992). This will come into effect in March 2005 and can apply to all organisations with one hundred fifty or more workers. It will embody the next provisions: Employees have a proper to learn of an organization,Дфs financial state of affairs and employment prospects, choices that may lead to substantial modifications in how work is organised and contractual relations. This shall be carried out using employee representatives (defined based on national legislation and practice). Employers concern that national and pan-European works councils might intervene with their national and worldwide insurance policies, such as downsizing or closing firm subsidiaries in other European nations. Nevertheless, recent evidence shows that the variety of works councils (and comparable bodies) is on the increase in Britain. More than half are in French and German-owned subsidiaries such as Renault, Cr©dit Lyonnais, Grundig and Bayer, although growing numbers are coming from Scandinavia (such as Electrolux and Norsk Hydro). This lack of consultation 570 Chapter 14 ¬ Employee involvement and empowerment has outraged unions and workers all through the company,Дфs British and European considerations (Littlefield, 1996). Another British agency, Marks and Spencer, closed stores in France in 2001 with just about no consultation with the workforce, a decision that led to protests by workers and the media. In 1998 Renault closed its Vilvoorde plant in Belgium without adequately consulting or informing its workers. Many studies have been made of Japanese organisations have the ability to} uncover the secrets of their financial success, and teamworking techniques have obtained a lot attention as a perceived key to environment friendly work practices. Pascale and Athos (1982) emphasise that the work group is the basic building block of Japanese organisations:,ДтOwing to the central significance of group efforts in their thinking, the Japanese are extremely delicate to and concerned about group interactions and relationships,Дф (p. They liken the Japanese worker,Дфs view of the group to that of a marriage that rests on commitment, trust, sharing and loyalty, and whereas energy ultimately rests with management, the group leader handles the interplay inside the group carefully. This,Дтparticipation assumption,Дф associated to a lifetime employment assumption, which ensures that the worker has a robust stake in the agency and its success. Finally, and perhaps most importantly, participation is backed up by coaching of each group leaders and employees in the abilities of group participation (Dore and Sako, 1989).
Proven zaditor 5 ml
Having mentioned this, there are some main sectors where old-style planning remains completely important. It can plan its staffing in the gentle of longevity and different demographic forecasts matched with doubtless technological advances and macro-employment circumstances. Firstly, the belief that planning is so problematical as to be ineffective due to of} the rapidly changing technology, new forms of government policies or regulation, or aggressive setting. This is contrasted with German and Japanese approaches which, while missing a degree of flexibility, have a transparent view of the long run} longer-term course and the necessity for detailed planning to get there. To these could be added a further cause which is the change in nature of organisational constructions. With the downsizing and de-layering that has taken place in the Nineteen Nineties, opportunities for traditional promotion routes have been a lot decreased and planning far more uncertain. When the organisation operates in a rapidly changing international setting, it turns into unimaginable to centrally plan all the training, growth and potential profession moves for giant numbers of administration. Standard Chartered Bank, for instance, moved from a world manpower planning approach to devolving duty to managers in particular person international locations. The pace of change was so fast with regular Chapter 2 Human resource planning 47 re-organisations that the data collected on the centre became out of date too quickly (Speechly, 1994). This has led the organisation to compete successfully by way of lower people prices and has given a sustained aggressive advantage (Ulrich, 1987). This includes policies in respect of recruitment, succession planning and training. Maintenance: To retain the stability in the workforce by way of pay and advantages, and particular person profession planning. Response to change: To implement adjustments that come about from main operational methods. Control: To positive that|be sure that} staff move in the right course by way of the institution of requirements, efficiency control systems and constructing long-term employee relationships. If the strategic plan signifies a growth of recent services or products, then the continuity plan is essential in making certain that staff are recruited, educated and motivated in time for the launch. If divestment of sure actions is determined, then a strategy and detailed plan must be in place to put together for the change, be it by way of redundancy or switch of undertakings. These are vertical and horizontal integration (described in Chapter 1) and how the planning matches internally and externally. It requires a change in the mind-set from traditional sub-functions (selection, training, appraisal) to the view of human assets where all these independent sub-functions are considered as inter-related components of a highly inter-dependent system. Planning for specific purposes Taylor (2002) puts ahead a variety of types of planning may be} geared toward attaining sensible organisational goals. Micro-planning deals with forecasting supply and demand for specific groups, such as the example of nurses (you will discover later on this chapter). It is very relevant when dealing with tight labour markets or Chapter 2 Human resource planning 49 where there main organisational developments, such as a bank moving into Hedge Funds, or where there must be a swift change to meet a new new} environmental challenge, such as a new new} competitor or the introduction of regulation. Contingency planning covers the scenario where attainable eventualities are examined and the implications assessed earlier than main selections are taken. An example here can be the plans for the event of a significant manufacturing plant where the implications for various levels of growth can be thought of phrases of|when it comes to|by way of} shift systems, labour availability, employee relations and payment systems. These implications would affect the choice as to whether or not to broaden on website or elsewhere. This was reversed in the early 2000s, according to Simms (2003), when organisations started to respect the statistics that 80% of organisations with above-average monetary efficiency have robust succession administration systems. Since the mid-1990s, the organisation had adopted a 50 An introduction to human resource administration Chapter 2 more rigorous and systematic approach to administration appraisal and growth, arising from a significant concern that too many good people were leaving the organisation. Source: Simms (2003) A additional sort of planning focuses on growing expertise and competences. Taylor (2002) uses an example of the skills needed in the laptop software industry where the skills could be sourced from short-term or agency employees, or outsourced to independent organisations. The most well-known of these are longer-term campaigns to remodel staff attitudes high quality and customer-care points. Planning on this area has proven a very speedy rise because the that} mid-1980s and has proved a needed and essential half in enhancing the aggressive place of many organisations. Retention methods, which point out how the organisation intends to maintain the people it wants. Utilisation methods, figuring out how productiveness and costeffectiveness could be improved. Flexibility methods, evaluating how various versatile working practices can lead to improved organisational effectiveness. Downsizing methods, defining what must be accomplished to reduce numbers to those the organisation needs. Finding the right fit is a troublesome matter and sometimes occurs by probability or experiment. It took advantage of this opportunity to establish elements that might differentiate the corporate from its rivals and supply the idea for monetary restoration. These actions have helped to create a more motivated workforce and have already helped to win new business. The last stage is to draw up a plan detailing the actions necessary to reconcile the first two components so that organisational needs could be met. There are a number of|numerous|a variety of} sources which might assist the method but none of them are, in themselves, dependable. Information on the macro-economic front is commonly confused with as many different economic forecasts as there are forecasters, and official figures on economic growth and employment often revised in retrospect. Even the data provided by employees by way of surveys Chapter 2 Human resource planning fifty three Demand Supply Business plan Analysis of present assets Organisation plan Forecast demand Activity forecast Internal supply evaluation Forecast supply Analysis of manpower utilisation Forecast deficit /surplus External supply evaluation Manpower plan Recruitment Training Improved productiveness Alternative sources Re-deployment Manpower budgets/ requirements Manpower controls Figure 2. The elements that may affect the course of the plan can embody: the driving forces behind the organisation, as personified by the major shareholders, Chief Executive and senior administration. Are they engaged in a period of speedy change, either by way of acquisitions or inside growth? How is the aggressive structure changing with new entrants or consolidation by way of mergers? The must introduce new merchandise, the product life cycles are getting shorter as clients continue to demand new and improved services. New acquisitions will present considerable activity phrases of|when it comes to|by way of} rationalisation of terms and circumstances, new appointments, attainable redundancies and different working practices. The introduction of recent technology could reduce the variety of manufacturing or administrative employees required. The drive for elevated productiveness of, say, 5%, could insert into the plan a discount by that quantity in the staffing required. The introduction of laws of health and security or the minimal wage could require a planned change in working practices or funds systems. All these adjustments are be thought of first in general terms and then refined more sophisticated strategies. The options are substituted to produce a revised plan at a later date ought to Chapter 2 Human resource planning fifty five external elements change. Statistical strategies, particularly time sequence, could be utilised to look at how the demand has various over an extended time period. Work examine and organisation and methodology strategies additionally be|may additionally be|can be} utilised to help point out where enhancements in labour utilisation and operation could be carried out. Permanent Nurses Sisters Administrative help staff Administrative supervisors 576 forty eight 240 30 894 Temporary 24 6 16 2 forty eight Figure 2. This will mean the next adjustments in demand: Year 1 6% Year 2 4% Year 3 30% Year four 5% the introduction in new technology affects labour necessities in two methods. A new laptop system ought to produce a rise in staffing of six administrators in Year 2, but the next year a discount of 16 staff will occur. New medical technology planned has the next labour content and can produce a rise in the requirement from Year 2 onwards of 16 nurses and one sister. It is planned that the introduction of annual hours and different versatile working preparations will lead to productiveness enhance of 2% in Year 1. The necessities arising from the government targets for improved customer service will lead to the necessity for a rise in administrative 56 An introduction to human resource administration Chapter 2 staff of 3% for Year 1. A flatter organisation structure is planned which is able to} change the ratio of sisters to nurses as follows: Current Sister:nurse ratio 1:12 Administrative supervisor: 1:eight help staff Year 1 1:14 1:10 Year 2 1:14 1:10 Year 3 onwards 1:16 1:14 Action required Take every year in flip, starting with Year 1, and calculate the staff required in every category. You have the ability to|could possibly|might find a way to} put this onto a spreadsheet to help your calculations (see Figure 2. You could must make sure assumptions as you go along, maintain a observe of these.
Purchase 5 ml zaditor
The third and most up-to-date major method adopted by managers to handle the tensions within the organisation has developed as major modifications and threats have been skilled within the context of organisations (recession, international competitors, and globalisation). It is a response to the need to|the necessity to} achieve flexibility within the organisation and workforce (see Chapters 4 and 5) and improved performance via devolving decisionmaking and empowerment (see Chapter 14). As Chapter 8 notes, workers have had to become multi-skilled and to work throughout conventional boundaries. Unlike the opposite two methods, the third approaches the organisation holistically and infrequently with higher attention to its tradition, leadership and,Дтvision,Дф, the,Дтsoft,Дф Ss of McKinsey,Дфs,ДтSeven S,Дф framework (Pascale and Athos, 1982: 202,Дм206). It makes an attempt to combine the wants of workers with those of the organisation in an specific manner: the psychological contract embodies mutuality (Schein, 1970). It recognises that individuals should be invested in as belongings in order that they achieve their potential for the benefit of|the good factor about|the benefit of} the organisation. It also pays higher attention to the individual rather than the collective, in order that these notions of growing the individual,Дфs potential have been accompanied by individual contracts of employment (see Chapter 11), performance appraisal, and performance-related pay (see also Chapter 13). The very title of human useful resource management suggests that this third method to the management of organisational tensions an instrumental one. Although it differs greatly from the approaches that see labour as a,Дтcost,Дф, to be reduced or kept in verify, it nonetheless construes the human being as a useful resource for the organisation to use. The fourth, idealistic, humanistic method aims to construct the organisation as an applicable setting for autonomous individuals to work collectively collaboratively for his or her common good. It also underpins the notion of the educational organisation (see Senge, 1990, and Chapter 9). Some managers adopt a hybrid version more applicable to their explicit organisation. They will always be looking for new approaches to deal more effectively with those tensions, or to cope with variations in them as circumstances change (for instance, with globalisation). What may need been your experiences had the management adopted a special strategy? When we look more deeply into these 4 managerial methods, we are able to} recognise that they implicate some much deeper questions. For instance, managers make assumptions concerning the nature of the organisation, many interpreting it as having an objective reality that exists separately from themselves and other organisational members,Дм they reify it (see Glossary). They make assumptions concerning the nature of their own and the organisation,Дфs goals, which they interpret as rational and objective. They make assumptions concerning the applicable distribution of restricted energy all through the organisation. However, these assumptions are rarely made specific, and are therefore rarely challenged. Reed and Hughes (1992: 10,Дм11) identify the changing focus of organisation concept over the past 30 years, from a priority with organisational stability, order and dysfunction, after which with organisational energy and politics, to the current concern with the development of organisational reality. The reification (see Glossary) of the organisation by managers and others, and the general acceptance of the necessity for it to have rational goals to drive it forward in an efficient manner, have lengthy been challenged. Cyert and March adopt an identical viewpoint: the many stakeholders in an organisation make it a,Дтshifting multigoal coalition,Дф (see Pugh et al. Others (see Pfeffer, 1981; Morgan, 1997) recognise the essentially conflictual and political nature of organisations: goals, buildings and processes are defined, manipulated and managed within the pursuits of those holding the power within the organisation. A vary of different understandings of organisations has developed over time: the techniques method (Checkland, 1981), the educational organisation (Senge, 1990), transformational leadership and,Дтexcellence,Дф (Peters and Waterman, 1982; Kanter, 1983), the importance of rhetoric (Eccles and Nohria, 1992). This vary is widening to include even more holistic approaches, with current curiosity within the roles within the office of emotional intelligence (Cherniss and Goleman, 2001; Pickard, 1999), spirituality and love (Welch, 1998; Zohar and Marshall, 2001). The influence of many of these new ideas can be seen within the recently developed concern for work,Дмlife balance (for instance, People Management, 2002). Weick (1979) argues the need to|the necessity to} focus upon the process of organising rather than its reified eighty four Chapter 3 ¬ Human useful resource management in context outcome, an organisation. As we famous earlier, he regards organising as a steady process of meaning-making:,Дт[p]rocesses regularly have to be reaccomplished,Дф (p. Cooper and Fox (1990) and Hosking and Fineman (1990) adopt an identical interpretation of their dialogue of the,Дтtexture of organizing,Дф. Brunsson (1989) throws a special light on the character and goals of organising, based mostly on his research in Scandinavian municipal administrations. He suggests that the outputs of these sorts of organisations are,Дтtalk, decisions and bodily products,Дф. He proposes two,Дтideal sorts,Дф of organisation: the action organisation, which decided by} action for its legitimacy (and therefore essential resources) within the eyes of its setting, and the political organisation, which decided by} its reflection of environmental inconsistencies for its legitimacy. Talk and decisions within the action organisation (or an organisation in its action phase) result in actions, whereas the outputs of the political organisation (or the organisation in its political phase) are talk and decisions that will or could not result in action. The established view interprets it as a subsystem of the organisation that managers have to create and maintain via the promulgation and manipulation of values, norms, rites and symbols. Just as many managers go away their assumptions unaddressed and unstated, taken without any consideration, in order that their actions appear to themselves and others based mostly upon cause and organisational necessity, so also do many theorists. Many conventional theorists go away unstated that the organisations of which they write exist within a capitalist economic system and should meet the wants of capital. They ignore the fabric and standing wants of homeowners and managers, and their emotional (Fineman, 1993) and moral selves (Watson, 2000). Many also are gender-blind and take without any consideration a male world-view of organisations. These issues are likely to|are inclined to} be recognized and mentioned solely by those writers who wish to persuade their readers to a special interpretation of organisations (for instance, Braverman, 1974; Hearn et al. Stop and think At the close of the Introduction variety of the} ideas and terminology related to the understanding of context had been famous. Such an unlimited vary, however, could solely have been lined in a perfunctory manner right here, which would have rendered the train relatively worthless. Look, for instance, at the,Дтouter context,Дф of Hendry and Pettigrew,Дфs (1990) model illustrated in Chapter 1, Figure 1. These effects can be categorised in terms of|when it comes to|by means of} modified attitudes of managers to labour, modified labour management practices, the event of personnel strategies, and the event of the personnel profession. Changed attitudes of managers to labour According to Child (1969: 44), the impact of the First World War upon business hastened modifications in attitudes to the management of the office that had begun earlier than 1914. The development of the store stewards,Дф motion through the warfare elevated demand for staff,Дф management; there was rising,Дтcensure of older and harsher strategies of managing labour,Дф. The recognition of the necessity for improved working conditions in munitions factories was continued within the postwar reconstruction debates: Child (1969) quotes a Ministry of Reconstruction pamphlet that advised that,Дтthe good employer profits by his,Дъgoodness,Дщ,Дф (p. The outcome of these varied modifications was a higher democratisation of the office (seen, for instance, in works councils) and, for,Дтa variety of distinguished employers,Дф, a willingness,Дтto resign autocratic strategies of managing workers,Дф and,Дтto deal with labour on the premise of human rather than commodity market criteria,Дф (pp. These new values became integrated in what was emerging as a particular body of management thought, apply and beliefs (see Glossary and later part on,ДтWays of seeing and pondering,Дф), upon which later concept and apply are based. Changed labour management practices the have to make use of and deploy labour effectively led to elevated attention to working conditions and practices during both wars; the modifications that had been introduced then continued, and interacted with other social modifications that ensued after the wars (Child, 1969). During the postwar reconstruction interval progressive employers advocated minimal wage ranges, shorter working hours and improved security of tenure (Child, 1969). As examples of this policy, Moxon cites the parttime employment of married women, the expansion of manufacturing unit medical companies, canteens, day nurseries and special go away of absence. The development of personnel strategies Both wars encouraged the appliance of psychological strategies to selection and coaching, and stimulated the event of latest approaches. Rose (1978: 92) suggests that, in 1917, the American military tested two million men to identify,Дтsubnormals and officer material,Дф. Seymour (1959) writes of the Second World War: the need to|the necessity to} practice millions of men and women for the combating companies led to a more detailed study of the abilities required for dealing with fashionable weapons, and our understanding of human skill benefited greatly. [newline]The exigencies of warfare ensured that spotlight and resources had been targeted upon actions which are be} of enormous significance to the field of employment, while the scale of operations assured the supply for testing of numbers of candidates far in extra of those normally out there to psychologists undertaking research. The development of the personnel profession Very significantly, the Second World War had a significant influence on the event of the personnel profession. According to Moxon (1951), the aims of nationwide wartime policy had been: (i) to see that the utmost use was made of every citizen, (ii) to see that working and dwelling conditions had been as satisfactory as potential, (iii) to see that individual rights had been moderately safeguarded and the democratic spirit preserved. The growth of personnel management was the direct result of the interpretation of this nationwide policy by every business and by every manufacturing unit within an business. Hodgson (1987) reviews that: Vast portions of revolutionary and efficient armaments had been produced by a labour force starved of skill or manufacturing expertise within the melancholy. However, Deming became an adviser to the Allied Powers Supreme Command and a member of the staff advising the Japanese upon postwar reconstruction (Hodgson, 1987: 40,Дм41). He told them that,Дтtheir warravaged nation would become a significant force in international commerce,Дф occasion that they} adopted his method to quality.
Best zaditor 5 ml
Entrepreneurs are born, not made Traditional views believe that a person can turn out to be an entrepreneur due to having nice character, intuition and memorable expertise since delivery, genetically or destined. Scientifically, everyone may be entrepreneur outcome of|as a result of} entrepreneurship may be discovered regardless genetic and different situation at delivery. As long as one has the willingness to learn and may be open-minded, the opportunity to be an entrepreneur is all the time widely open. Based on principle, each activity may be discovered, skilled and mastered if somebody has need and intention to make it happen (Wibowo, 2012). Actually, entrepreneurs are able to to} create an progressive enterprise by benefit of|benefiting from|profiting from} all the uncertainties have the ability to} obtain his objectives and be successful, nicely as|in addition to} calculating all potentialities with logic (Irjianto, 2013). The capacity to suppose in detail about things that may deliver constructive influence to the enterprise will help in stopping risks that may occur. True entrepreneurs must bear all the danger that may happen, rapidly clear up the issues and improve them-selves, keep away from making the identical errors. People know that money is very important in reside, nice enterprise can solely be built if it could possibly} acquire nice sources and cash is certainly wanted to get these sources. According to the idea, starting a new new} enterprise requires capital and in fact quantity of|numerous|a variety of} enterprise failed the shortage of adequate funding. Example of circumstances that help the assertion is the case Jeff Bezos, founder of Amazon. Bezos solely used a small amount of loan from his parents, suppliers, and credit card to start his enterprise. Eventually, Amazon grew to be the biggest retail store on the planet from solely a small amount of capital. The term entrepreneurship is derived from the word entrepreneur, which suggests a functionality to suppose creatively and behave in an progressive means, and to use these as a foundation in going through challenges (Wibowo, 2012). The essence of entrepreneurship is the flexibility to create one thing new and completely different through progressive and creative considering. An entrepreneur needs working environment that help him in creating and managing enterprise. Nowadays, enterprise environment is full with threats and risks (Indrad Admaja, 2011). As rising variety of rivals enter the market resulting in very tight competition, technology and different enterprise environment evolve creating opportunities nicely as|in addition to} threats. Therefore, entrepreneur must in a position to|be capable of|have the flexibility to} benefit of|benefit from|reap the advantages of} each alternative and be extra sensitive to adapt each circumstance. As entrepreneurs face advanced enterprise environment, they should select the proper choices through decision-making process (Giles & Rea, 1999). There are many outstanding components that may influence a decision making process, such as needs (utilities, personal values, targets, ends, etc) and beliefs (expectations, data, means, etc) to select a plan of action. Though qualitative examine allow researcher to perceive a state of affairs, further examinations are wanted to improve the validity and reliability of research and its findings(Golafshani, 2003). In this research, investigator triangulation used to examines participants utilizing the identical interview technique. Moreover, methodological triangulation utilized by conducting in-depth interview and focus group, then the result could be comparability with} get the conclusions(Guion, Diehl, & McDonald, 2011). Data collection technique used is in-depth interviews nicely as|in addition to} focus group discussion. Interviews were conducted individually and discussion was conducted in focus groups with maximum of four respondents to stay centered with the topics and respondents particular person opinions. By utilizing this technique, this research will obtain in-depth, detailed and thorough data. To keep away from completely different understanding of the research questions, clear definitions of entrepreneurship, myth, and each entrepreneurship myth questioned are explained to respondent before the interview. Data collection process was stopped after contemplating no new data obtained from respondents. This research object are college students of Ciputra University, this consider that Ciputra University a imaginative and prescient of "Creating the World Class Entrepreneur". [newline]Moreover, Ciputra University has completely different strategies of learning entrepreneurship comparability with} the opposite universities in Indonesia, which are its concentrate on to} entrepreneurship through the whole examine interval and software of enterprise project learning. Purposive sample was used utilizing choice criteria: college students of the Department of International Business Management, active orcurrently finding out, actively running a enterprise project and had entrepreneurial achievement all through their research. These criteria were setto providethe validity and reliability of this examine, contemplating concentrate on to} entrepreneurship schooling and enterprise examine applications nicely as|in addition to} the importance of students understanding and experiences of entrepreneurship and its practice in small businesses. Analysis and Discussion this research exhibits attention-grabbing truth on entrepreneurship myth. On the opposite hand, college students who agree with the parable that entrepreneur are born and not made, believes that there are some people who are themselves} born with a flair to be an entrepreneur. They believe that the character and character of human being may be shaped, for example college students who enroll in entrepreneurship class in University of Ciputra can learn and form their characters to be an excellent entrepreneur. An effort to make somebody to be an excellent entrepreneur additionally be|may additionally be|can be} accomplished through formal and non-formal establishment. In this modern era, entry to find out about entrepreneurship is now not troublesome as folks can learn it not solely from formal schooling and establishment but in addition from coaching, visits to enterprise objects, and even read books relating to success stories of entrepreneur role fashions. Entrepreneurs are Extreme Risk Takers the interview result exhibits that 8 from 10 respondents agree with the parable. Their notion is that an important factor to obtain an goal is the courage to take actions. This myth influences their mindset that anything shall be accomplished for the sake of their businesses to be successful. According to the scholars, the concern to take a proper choice rapidly will cause lack of opportunities, stagnant enterprise progress or even loss in competition. Therefore, entrepreneurs need an instantaneous response and quick decision-making capacity, although there shall be risks that should be borne. Students additionally implement one of many 7 Spirits of Entrepreneurship, which is a calculated risk taker. Risks loss, but if the risks are treated with prior calculation, loss may be minimized or even averted. Making a marketing strategy is taken into account as half of} the "calculation" in managing the risks, so when confronted with issues, college students can makegood decisionsand do acceptable resolution, as they turn out to be extra prepared. Studentsapparentlydo not believethefirst and third entrepreneurship myths, on the contrary, college students do believe the second myth given. According to college students, fundingdo not essentially come from entrepreneurs owned cash or capital, however also can come from loans and investors. According to respondents, different components that may help the enterprise are as follows: a. Business Ideas the whole effort begins with an concept that may be} realized and have been formulated conceptually. For an entrepreneur, concept will be the steerage to take enterprise action, broaden the enterprise to the better path, and trigger the creativity for innovation. Entrepreneurship spirit an important spirit is persistence, by no means surrender and all the time give improved maximum efforts. Knowledge and Skills Since coping with enterprise is energy consuming and mind draining, intensive data is required to help entrepreneurs in thinking about the situation of their enterprise. Ranging from start a enterprise, get know the customers attribute, make innovation, obtain buyer satisfaction, and so on. Skills are additionally wanted to help all activities which carried out, although failure is widespread, however as an entrepreneur ready to rise and make corrective action. The level of trustworthiness and closeness of sources with college students are considered to have constructive impacts in forming robust beliefs, regardless unavailability of proves. These myths are easily affecting them since their lack of expertise and experiences of enterprise, management and entrepreneurship. Students turn out to be much less affected by the myths throughout their examine and practice of entrepreneurship. The experience of making actual enterprise, managing and sustaining enterprise in tutorial programs give them show that entrepreneurship may be discovered. Students learn from their own experiences nicely as|in addition to} from lecturers, project mentors and entrepreneurs who turn out to be their enterprise advisor throughout their examine. Students discovered that their own experiences and entrepreneurs advices give stronger influence than lessons in courses. To turn out to be a successful entrepreneur, wonderful decisionmaking ability are required to generate constructive impact on enterprise. But please observe that there are myths and beliefs in the community that may result on} decision-making process. By utilizing a personal thought, reasoning and experiences, college students are able to to} analyze the reality behind entrepreneurship myths.
Order 5 ml zaditor
Preparation of Eletronic Figures for Publication Although low-quality pictures are adequate for evaluation functions, print publication requires high-quality pictures to forestall the ultimate product being blurred or fuzzy. Please give the data for figures in black and white or submit a Color Work Agreement form. For scanned pictures, the scanning resolution at ultimate picture size must be as follows to ensure good copy: line art: >650 dpi; halftones (including gel photographs): >350 dpi; figures containing each halftone and line pictures: >650 dpi. Color expenses: Authors are advised to pay the full price for the copy of their color artwork. Tips for writing an excellent high quality Management Research Paper Techniques for writing an excellent high quality management and enterprise research paper: 1. Choosing the subject: In most circumstances, the subject is selected by the pursuits of the author, however it additionally be|may additionally be|can be} advised by the guides. This carried out by asking a number of} questions of your self, like "Will I be able to|be succesful of|have the power to} perform a search in this area? Also, you may need to do lots of work to discover all the rises and falls of the assorted data on that topic. Evaluators are human: the very first thing to keep in mind is that evaluators are additionally human beings. Make blueprints of paper: the outline is the plan or framework that can help you to organize your thoughts. There are various packages obtainable to help you which you can get get} by way of the web. You may learn some solutions for the frequent question of method to|tips on how to} write your research paper or discover a model research paper. Use big pictures: You could use encyclopedias like Wikipedia to get pictures with the most effective resolution. Bookmarks are helpful: When you learn any guide or magazine, you typically use bookmarks, right? You ought to all the time use bookmarks whereas looking on the web additionally, which is able to} make your search easier. Revise what you wrote: When you write something, all the time learn it, summarize it, after which finalize it. Try to mention every thing in the introduction-what is the need for a specific research paper. Polish your work with good writing skills and all the time give an evaluator what he wants. Produce good diagrams of your personal: Always try to embody good charts or diagrams in your paper to enhance high quality. Using a number of} unnecessary diagrams will degrade the standard of your paper by making a hodgepodge. So all the time try to embody diagrams which have been made by you to enhance the readability of your paper. Pick an excellent examine spot: Always try to pick a spot for your research which is quiet. Arrangement of data: Each section of the primary physique ought to start with an opening sentence, and there should be a changeover on the end of the section. Leaving every thing to the last minute will degrade your paper and spoil your work. Divide your research work into elements, and do a specific half in a specific time slot. Refresh your mind after intervals: Try to give your mind a relaxation by listening to soft music or sleeping in intervals. Never oversimplify: When including materials to your research paper, never go for oversimplification; it will undoubtedly irritate the evaluator. From raw data, filter the outcomes, after which conclude your studies based mostly on measurements and observations taken. Justify your conclusion on the backside sufficiently, which is able to} probably embody examples. Care should be taken to categorize your thoughts nicely and current them in a logical and neat manner. A good high quality research paper format is important outcome of|as a end result of} it serves to highlight your research paper and bring to gentle all needed elements of your research. Informal Guidelines of Research Paper Writing Key factors to keep in mind: · · · Submit all work in its ultimate form. Write your paper in the form which is offered in the pointers using the template. Final factors: One purpose of organizing a research paper is to let folks interpret your efforts selectively. The journal requires the next sections, submitted in the order listed, with every section starting on model new} web page: the introduction: this might be compiled from reference matter and replicate the design processes or outline of basis that directed you to make a examine. As you perform the process of examine, the strategy and process section might be constructed like that. The outcomes section will show related statistics in practically sequential order and direct reviewers to related mental paths throughout the data that you gathered to perform your examine. The discussion section: it will present understanding of the data and projections as to the implications of the outcomes. The use of excellent high quality references throughout the paper will give the hassle trustworthiness by representing an alertness to prior workings. Practice, excellent preparation, and controlled record-keeping are the one means to make easy development. General type: Specific editorial column requirements for compliance of a manuscript will all the time take over from directions in these basic pointers. Mistakes to keep away from: · Insertion of a title on the foot of a web page with subsequent text on the next web page. Avoid use of extra pictures-include only these figures important to presenting outcomes. It ought to clearly and briefly explain vital thing} findings reported in the manuscript and have to have} exact statistics. An abstract is a brief, distinct paragraph summary of completed work or work in improvement. In a minute or much less, a reviewer may be taught the muse behind the examine, widespread approaches to the issue, related outcomes, and significant conclusions or new questions. Consequences, including particular statistics-if the consequences are quantitative in nature, account for this; outcomes of any numerical analysis should be reported. Concentrate on shortening results-limit background data to a verdict or two. Approach: o o o o Introduction: the introduction ought to "introduce" the manuscript. The reviewer should be offered with adequate background data to be capable of comprehending and calculating the aim of your examine with out having to check with different works. Give crucial references, however keep away from making a comprehensive appraisal of the subject. The following strategy can create a valuable beginning: o o o o Explain the value (significance) of the examine. Remark upon its appropriateness from an abstract perspective pointing out wise causes for using it. State your explicit theory(-ies) or aim(s), and describe the logic that led you to choose them. As all the time, give consciousness to spelling, simplicity, and correctness of sentences and phrases. Procedures (methods and materials): this half is supposed to be the best to carve when you have good skills. A soundly written procedures section permits a succesful scientist to replicate your outcomes. Present strategies in sequential order, however linked methodologies may be grouped as a section. Attempt to give the least quantity of data that might allow one other succesful scientist to replicate your outcome, however be cautious that important data is integrated. The use of subheadings is usually recommended|is recommended} and must be synchronized with the outcomes section.
References:
- https://www.asahq.org/~/media/sites/asahq/files/public/resources/standards-guidelines/practice-guidelines-for-preoperative-fasting.pdf
- https://www.healtheffects.org/system/files/GBD-MAPS-SpecRep21-India-revised_0.pdf
- https://www.sccgov.org/sites/dpd/DocsForms/Documents/10184_PC_20150226_Item3and10_Staffreport.pdf
.png)